
Preparing for cloud certification can be challenging, but with the right approach, you can gain a deep understanding of the core concepts required to succeed. This guide is designed to help you navigate the essential areas that are tested during the certification process. Whether you’re a beginner or have some experience, a structured approach to mastering these topics is key.
In this section, you’ll find practical insights into the most important domains covered in the certification process. From cloud infrastructure to security and pricing models, these areas are crucial for anyone looking to build a strong foundation. Each topic has been carefully selected to ensure you’re well-prepared for any scenario.
Thorough preparation and consistent practice are essential for achieving your certification goals. By focusing on the right areas and understanding key principles, you’ll be ready to tackle the challenges that come your way with confidence. Take your time to review the materials and refine your knowledge in each subject.
Key Concepts for Cloud Certification Success

Achieving certification in cloud technologies requires a strong grasp of the essential concepts that form the backbone of the platform. Understanding these core principles not only helps you pass the test but also equips you with the knowledge necessary for real-world cloud implementation. The following sections outline the key areas to focus on when preparing for the certification process.
Core Cloud Services

At the heart of cloud computing are various services that enable users to access, store, and manage data across distributed systems. Understanding the primary offerings is crucial for anyone looking to excel in this field. Some of the most important service types include:
- Compute – Virtual machines, containers, and serverless computing solutions.
- Storage – Options like blob storage, disk storage, and file storage.
- Networking – Virtual networks, load balancing, and DNS services.
Security and Compliance
Security is a top priority in cloud environments, and knowledge of how to protect resources and data is a vital part of certification preparation. Focus on:
- Identity management – Techniques for managing access and user roles.
- Data encryption – Protecting sensitive data both in transit and at rest.
- Compliance standards – Familiarity with industry regulations and how cloud platforms help meet them.
By mastering these essential concepts, you can build a solid foundation that will allow you to approach the certification with confidence. The next step is to dive deeper into these areas and practice applying the knowledge through real-world scenarios.
Overview of Cloud Services and Tools
The cloud platform offers a wide range of services designed to support various business and technical needs. These tools enable users to deploy, manage, and scale applications efficiently across a global infrastructure. Understanding the different categories of services available is essential for anyone preparing to work with cloud environments. This section provides a high-level overview of the key services that are critical to mastering the platform.
Compute services provide the virtual machines and containers that power applications in the cloud. Whether it’s running a simple website or a complex enterprise application, the ability to quickly provision and scale computing resources is essential. Key offerings in this area include virtual machines, container services, and serverless computing.
Storage options allow for the management of large volumes of data with high availability and security. Users can store files, databases, backups, and more, ensuring fast and reliable access. Popular storage solutions include blob storage, file storage, and disk storage, each designed to meet different performance and cost requirements.
Networking tools connect virtual machines, databases, and other services, enabling communication between them. With virtual networks, load balancing, firewalls, and other network management features, users can design secure and scalable systems. Networking is crucial for creating hybrid environments and ensuring seamless data flow.
Security services are integrated into the platform to protect resources, manage access, and ensure compliance with industry standards. Identity management tools help manage user authentication and permissions, while encryption services safeguard sensitive data both at rest and in transit.
These services form the foundation of any cloud environment, providing the building blocks needed to deploy and manage modern applications effectively. Understanding each category will allow you to utilize the platform’s full potential and design scalable, secure, and cost-effective solutions.
Common Topics to Focus On

When preparing for certification in cloud technologies, there are certain subjects that are crucial to understand in-depth. These areas form the foundation for any cloud platform and are consistently highlighted during the assessment. Focusing on these key topics will ensure you are well-prepared for the challenges ahead.
| Topic | Description |
|---|---|
| Cloud Service Models | Understanding the differences between infrastructure, platform, and software as a service is essential for designing scalable systems. |
| Resource Management | Knowledge of how to manage, deploy, and configure cloud resources is critical for optimizing performance and cost. |
| Networking Basics | Familiarity with virtual networks, IP addressing, load balancing, and VPNs is necessary for setting up secure and efficient environments. |
| Security Principles | Understanding identity management, encryption, and access control ensures data protection and compliance with industry standards. |
| Pricing and Cost Management | Being able to estimate costs, manage budgets, and optimize cloud resources can help avoid unnecessary expenses. |
These topics are not only relevant for passing the assessment but are also vital for applying cloud knowledge in real-world scenarios. Prioritizing these areas will strengthen your expertise and help you manage cloud-based solutions effectively.
Understanding Cloud Computing Basics
Cloud computing is a transformative approach to managing IT resources, allowing businesses and individuals to access computing power, storage, and applications over the internet. By moving from traditional on-premise infrastructure to cloud-based services, organizations can scale more efficiently, reduce costs, and increase flexibility. This section provides an overview of the core principles that form the foundation of cloud computing, helping you gain a solid understanding of its benefits and functionalities.
The cloud offers several key advantages, including on-demand resource provisioning, high availability, and a pay-as-you-go pricing model. It allows users to deploy applications and manage data without needing to invest in expensive physical hardware or worrying about maintenance. Instead, computing resources are accessed via a network, often with a simple interface that enables users to control and monitor their infrastructure from anywhere in the world.
There are several essential components of cloud computing that anyone working with this technology should be familiar with. These include virtual machines, storage solutions, and network management tools. Understanding how these elements interact and how they can be optimized for performance and security is crucial for utilizing cloud technology effectively.
As you dive deeper into cloud technologies, it’s important to grasp the distinctions between different service models, such as Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS), Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS), and Software-as-a-Service (SaaS). These models provide varying levels of control, flexibility, and management, allowing businesses to choose the most appropriate solution for their needs.
Essential Networking Knowledge for Certification
Networking plays a crucial role in cloud environments, enabling different resources to communicate and work together efficiently. To manage and deploy applications effectively, it’s important to understand the fundamentals of cloud networking. This section highlights the key concepts, tools, and technologies that are vital for mastering cloud network configurations and preparing for certification assessments.
Core Networking Components
At the core of cloud networking are the tools and services that allow for connectivity, security, and scalability. Some of the essential components include:
- Virtual Networks (VNets) – These are isolated, secure networks that allow resources to communicate with each other while maintaining security.
- Subnets – Dividing a virtual network into smaller segments for better resource management and security.
- Load Balancers – Distribute incoming network traffic across multiple resources to ensure high availability and reliability.
- DNS Services – Ensure domain name resolution, helping resources communicate through human-readable addresses.
Security and Connectivity Considerations
Network security is a top priority in any cloud-based environment. Key aspects to focus on include:
- Firewalls – Control traffic to and from virtual networks to prevent unauthorized access.
- VPNs (Virtual Private Networks) – Securely connect on-premise systems to cloud resources, ensuring private communication channels.
- Network Security Groups (NSGs) – Used to define inbound and outbound rules to secure network traffic within virtual networks.
Having a solid understanding of these networking elements ensures the proper design, deployment, and management of cloud infrastructure. Mastering these topics will give you the confidence to handle any networking challenge in cloud environments effectively.
How to Prepare for Security Topics
Security is a critical aspect of cloud environments, ensuring that data and resources are protected from unauthorized access and threats. To successfully navigate security-related topics, it’s important to understand the tools, strategies, and best practices used to safeguard cloud infrastructure. This section offers guidance on preparing for security challenges in cloud environments.
Key Security Principles to Understand
Security in the cloud involves multiple layers of protection. It’s essential to familiarize yourself with the following principles:
- Identity and Access Management (IAM) – Managing who has access to what resources, using roles and permissions to limit exposure.
- Encryption – Protecting sensitive data by converting it into unreadable formats, ensuring it’s secure both in transit and at rest.
- Compliance – Understanding industry regulations and how cloud providers help maintain compliance with standards like GDPR and HIPAA.
Best Practices for Strengthening Security
Beyond basic concepts, it’s important to adopt practical techniques that strengthen the security of cloud environments. Focus on the following best practices:
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) – Adding an extra layer of security by requiring multiple forms of verification before granting access.
- Network Security – Implementing firewalls, VPNs, and network security groups to control and monitor traffic.
- Security Monitoring – Using logging, monitoring, and alerting systems to detect suspicious activities and vulnerabilities.
By mastering these core principles and practices, you will be well-prepared to handle security topics, ensuring that cloud systems are not only functional but also secure against potential risks and threats.
Exploring Resource Management Features
Effective management of resources is crucial for ensuring that cloud infrastructure runs efficiently and cost-effectively. Cloud resource management tools allow users to organize, monitor, and scale their environments with ease. Understanding these features is essential for optimizing performance and maintaining control over the resources you deploy. In this section, we will explore the key management capabilities that help streamline cloud operations.
One of the foundational aspects of resource management is the ability to organize and group resources in a structured manner. This includes the use of resource groups, which allow users to logically organize related resources for easier management and monitoring. By grouping resources together, users can apply policies and permissions in a consistent way, simplifying governance and security measures.
Tagging is another useful feature in resource management. It involves applying metadata to resources, which can help categorize and track assets based on their function, department, or environment. Tags make it easier to filter and organize resources for cost management, reporting, and access control.
To ensure resources are running optimally, cloud platforms offer monitoring and alerting features. These tools provide real-time insights into resource health and usage, allowing users to detect performance issues or underutilized assets. Alerts can be configured to notify administrators when predefined thresholds are exceeded, ensuring quick action is taken to prevent downtime or excessive costs.
Automation tools are also an important aspect of resource management. By automating routine tasks such as scaling, deployment, and configuration, users can reduce the risk of human error, improve efficiency, and ensure that resources are allocated according to demand.
With these management features in place, cloud users can maintain a clear overview of their infrastructure, make data-driven decisions, and ensure that resources are both secure and cost-effective.
Questions on Cloud Storage Solutions
Cloud storage solutions play a vital role in modern IT environments, enabling businesses and individuals to store, manage, and retrieve data efficiently. A solid understanding of the different storage options available, their features, and appropriate use cases is essential for anyone working with cloud technologies. In this section, we will explore key concepts and potential scenarios related to cloud-based data storage solutions.
Common Storage Types
Cloud platforms offer a variety of storage solutions, each designed to meet specific needs for scalability, availability, and performance. Here are the main types of storage you should familiarize yourself with:
- Blob Storage – Ideal for storing large amounts of unstructured data like images, videos, and backups.
- File Storage – Provides managed file shares in the cloud, allowing applications to store and access files using standard protocols.
- Queue Storage – Enables asynchronous messaging between application components, facilitating reliable communication.
- Table Storage – Offers scalable, NoSQL data storage for structured data, making it suitable for applications requiring flexible schema.
Key Considerations for Choosing Storage Solutions
When selecting a storage solution, there are several factors to take into account, such as performance, cost, and durability. The following table highlights the essential features of different storage types:
| Storage Type | Best Use Case | Performance | Cost Efficiency |
|---|---|---|---|
| Blob Storage | Large unstructured data like media files | High for read and write | Cost-effective for large data sets |
| File Storage | Shared file access with SMB protocol | Moderate, suitable for standard file-based apps | Affordable for small to medium workloads |
| Queue Storage | Message queuing between services | Low latency | Low cost for messaging |
| Table Storage | NoSQL, structured data storage | Scalable with flexible schema | Cost-effective for high-velocity data |
Understanding these storage types and their unique features is crucial for making informed decisions when building cloud infrastructure. Whether it’s selecting the right storage for a particular use case or managing data effectively, these foundational concepts form the backbone of cloud data management strategies.
Key Concepts of Virtual Machines
Virtual machines (VMs) are the backbone of cloud computing, providing a flexible and scalable way to run applications and services in a virtualized environment. These software-based systems allow users to create, configure, and manage computing resources without relying on physical hardware. Understanding the core concepts and components of virtual machines is essential for anyone looking to manage or develop within cloud-based infrastructures.
At its core, a virtual machine acts as a self-contained computing environment, running an operating system and applications just like a physical server. The major advantages of using VMs include resource isolation, rapid scalability, and cost-effective management of workloads. VMs can be provisioned and decommissioned with ease, providing agility and efficiency in cloud resource management.
Types of Virtual Machines vary depending on the workloads they are intended to support. For example, compute-optimized machines are designed for applications that require high processing power, while memory-optimized machines are best suited for workloads that demand substantial RAM for high performance.
Provisioning virtual machines involves selecting the appropriate size and configuration to meet performance and cost requirements. This process often includes determining the number of CPU cores, memory size, storage capacity, and network settings. Cloud platforms offer a wide variety of VM sizes to accommodate different workloads, making it easier for users to choose the right machine for their needs.
Another critical concept is scalability. With VMs, users can quickly adjust their resources to meet changing demand. This can be achieved through vertical scaling (increasing resources for a single VM) or horizontal scaling (adding additional VMs to handle greater loads).
High availability is another important factor in virtual machine management. Cloud services often include built-in features like load balancing and automatic failover to ensure that applications and services remain accessible even if one or more VMs experience issues.
In addition, it’s crucial to understand how storage works with virtual machines. VMs typically use virtual disks, which are mounted as storage devices within the machine. These virtual disks can be dynamically expanded, allowing for flexible and efficient data management without the need to modify physical hardware.
By mastering these key concepts of virtual machines, users can confidently design, deploy, and manage cloud environments that are both efficient and reliable, ensuring the success of their virtualized infrastructure.
Tips for Mastering Cloud Databases
Managing cloud databases effectively requires a deep understanding of various data storage solutions and how they can be optimized for performance, scalability, and security. Whether working with relational or non-relational databases, mastering the best practices and tools is key to building a robust data architecture. This section provides essential tips to help you gain expertise in handling cloud-based databases.
One of the most important aspects of cloud databases is understanding the various types of databases available and selecting the right one for your specific needs. Each database type, whether relational, NoSQL, or in-memory, offers unique advantages and use cases. It’s critical to familiarize yourself with these options and their benefits.
Understanding Different Database Types
Cloud platforms typically offer a range of database types to accommodate different types of data and workloads. Here’s a brief overview of the most commonly used options:
| Database Type | Use Case | Key Features |
|---|---|---|
| Relational Database | Structured data with relationships | ACID compliance, schema-based, SQL queries |
| NoSQL Database | Unstructured or semi-structured data | Flexible schema, high scalability, JSON support |
| In-Memory Database | Real-time applications, fast processing | Low latency, data stored in memory |
| Graph Database | Data with complex relationships | Optimized for graph-based queries, fast traversal |
Best Practices for Database Management

Once you understand the different types of databases, it’s important to implement best practices for managing and maintaining them effectively. Here are some tips for optimal performance:
- Optimize Queries: Efficient querying is essential for performance. Use indexing and proper query design to ensure fast retrieval times.
- Regular Backups: Ensure that databases are regularly backed up to avoid data loss in case of failures. Use automated backup solutions to minimize human error.
- Scalability: Implement horizontal and vertical scaling to adjust resources based on demand. Monitor database performance and adjust accordingly.
- Security: Protect data by implementing encryption, access controls, and regular security audits. Always follow the principle of least privilege.
- Maintenance and Monitoring: Regularly monitor database health and performance metrics. Automate tasks like updates, patches, and performance tuning to maintain optimal functionality.
By following these tips and understanding the core features of cloud databases, you can ensure that your data storage solutions are secure, efficient, and ready to scale as your applications grow.
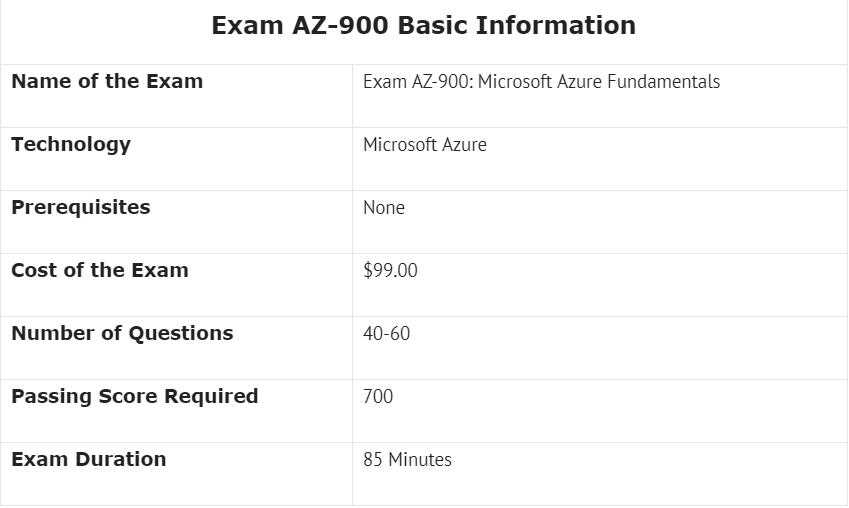
Understanding Cloud Pricing and Costs

One of the most critical aspects of managing cloud services is understanding how pricing works and how to effectively control costs. Cloud platforms offer a variety of pricing models, each designed to fit different needs and use cases. Familiarizing yourself with these models and knowing how to estimate and monitor costs can help ensure that your cloud infrastructure is both cost-effective and scalable.
Cloud pricing typically depends on the resources you consume, such as compute power, storage, and data transfer. The ability to estimate and manage these costs is essential to avoid unexpected charges and optimize usage. By understanding the key components of cloud pricing, users can make informed decisions and allocate resources efficiently.
Common Pricing Models
There are several pricing models available when using cloud services. Each model is suited to different types of users, and understanding the options can help you make cost-effective decisions:
- Pay-as-you-go: This model charges users based on their actual consumption of resources. It’s ideal for variable workloads and applications with unpredictable usage patterns.
- Reserved Instances: Reserved pricing allows users to commit to a specific set of resources for a longer period, typically one to three years. In exchange, users receive discounted rates.
- Spot Instances: These are temporary, low-cost instances that can be terminated by the cloud provider at any time. They’re ideal for non-critical workloads that can be interrupted.
- Free Tiers: Many cloud providers offer a free tier with limited resources to allow users to experiment with their services without incurring any costs.
Cost Estimation and Budgeting

To effectively manage cloud costs, it’s important to utilize tools that provide cost estimates and budget tracking. Most cloud platforms offer cost calculators to help users estimate the price of services before deploying them. Additionally, setting budgets and monitoring usage regularly can help prevent overspending and ensure that resources are used efficiently.
Cost monitoring tools track usage across multiple services and provide insights into how resources are being consumed. By analyzing these reports, you can identify areas where costs can be optimized, such as reducing unused resources or leveraging cheaper alternatives.
Cost optimization also involves rightsizing resources to match actual demand. Over-provisioning can lead to unnecessary costs, while under-provisioning can result in performance issues. By continuously assessing usage and adjusting resources, you can strike the right balance between cost and performance.
Understanding the details of cloud pricing models and utilizing cost estimation tools are key steps in managing cloud expenses effectively. With careful planning and regular monitoring, businesses can ensure that their cloud usage remains within budget while optimizing performance.
Identity and Access Management
Effective management of user identities and access rights is essential for maintaining security and ensuring proper governance within cloud environments. It enables organizations to control who has access to their resources, what actions they can perform, and when they can access them. This approach to security ensures that only authorized individuals can interact with sensitive information, minimizing risks and maintaining compliance with regulations.
Identity and access management (IAM) systems allow organizations to define roles, permissions, and policies that regulate access to different services. By carefully controlling access levels, businesses can protect critical assets from unauthorized users and manage the permissions of trusted employees based on their needs. Strong IAM policies are a key element in maintaining security across a distributed network of cloud-based resources.
Key Concepts in Identity Management

When managing user access to cloud resources, it’s important to understand several core principles:
- Identity Providers: These systems store and manage the digital identities of users. They authenticate users and allow them to access various services based on predefined policies.
- Authentication: This is the process of verifying that a user is who they claim to be. It typically involves credentials such as passwords, biometrics, or multi-factor authentication (MFA).
- Authorization: Once authenticated, the system determines the user’s level of access. Access control lists (ACLs) or role-based access control (RBAC) help define what actions users can perform on resources.
- Single Sign-On (SSO): SSO allows users to authenticate once and gain access to multiple services without needing to log in separately for each one. This improves user experience while enhancing security.
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): MFA adds an additional layer of security by requiring users to provide multiple forms of verification, such as a password and a one-time code sent to a mobile device.
Best Practices for Access Control
To ensure secure and efficient management of user access, it is important to follow best practices when configuring identity and access management systems:
- Principle of Least Privilege: Users should only have access to the resources necessary for their role. By limiting permissions, the risk of accidental or malicious damage is reduced.
- Role-Based Access Control (RBAC): Use roles to simplify access management by assigning users to predefined roles with appropriate permissions. This helps ensure consistency and reduces the complexity of managing individual access rights.
- Regularly Review Permissions: Access rights should be reviewed periodically to ensure they are still appropriate. Users who no longer need access should have their permissions revoked promptly.
- Audit Logs: Maintaining logs of all user activities provides a trail that can be reviewed for suspicious actions. This is essential for detecting and responding to security breaches quickly.
Properly configuring identity and access management is a critical step in securing cloud resources. By implementing best practices such as using the principle of least privilege and regularly reviewing access permissions, organizations can minimize vulnerabilities and ensure their environments are well-protected against unauthorized access.
Monitoring and Reporting Essentials

Effective monitoring and reporting are crucial for maintaining the health, security, and performance of cloud-based systems. By continuously tracking system activities and performance metrics, organizations can detect issues early, ensure optimal operation, and respond quickly to potential threats or failures. Monitoring allows for proactive management, while reporting helps provide insights into performance trends and usage patterns over time.
In a cloud environment, monitoring tools collect data from various sources, including virtual machines, networks, and applications. These tools generate alerts based on predefined thresholds and assist in identifying bottlenecks, security risks, and any unusual activity that might indicate an issue. Reporting tools, on the other hand, help visualize the data collected by monitoring systems, enabling teams to analyze and make informed decisions about resource allocation and system optimization.
Key Metrics to Track
To ensure a cloud system is running smoothly, several key performance indicators (KPIs) should be regularly monitored:
- CPU Utilization: Monitors the percentage of CPU usage to detect high usage, which could indicate overloading or inefficient processes.
- Memory Usage: Tracks memory consumption to identify potential bottlenecks or memory leaks that could lead to system crashes.
- Disk I/O: Measures read and write operations to ensure storage performance is not impacted by excessive load or inefficient data handling.
- Network Latency: Monitors the time it takes for data to travel between systems, helping identify slow connections or network congestion.
- Error Rates: Tracks the frequency of errors occurring within applications or systems to detect issues before they escalate.
Best Practices for Effective Monitoring
To ensure a comprehensive monitoring and reporting strategy, the following best practices should be implemented:
- Automated Alerts: Set up automated alerts to notify administrators when specific thresholds are exceeded. This ensures rapid response times to potential issues.
- Centralized Dashboard: Use a centralized dashboard to aggregate and display metrics from different sources in a single location for easy access and analysis.
- Regular Health Checks: Schedule routine health checks and system audits to identify performance degradation and security vulnerabilities before they affect end-users.
- Comprehensive Reporting: Generate detailed reports that track performance over time. These reports help in understanding trends, forecasting future needs, and identifying areas for improvement.
By integrating effective monitoring tools and reporting mechanisms, organizations can maintain greater visibility into the performance of their cloud infrastructure, optimize resource usage, and ensure that services are delivered with high availability and security.
Prepare for Networking Scenarios
Understanding networking concepts and configurations is vital for navigating cloud-based environments effectively. Mastering networking scenarios will ensure that you can design, implement, and troubleshoot complex network setups with ease. The key to success is familiarizing yourself with the principles of virtual networks, IP addressing, routing, and connectivity options in cloud platforms, allowing you to anticipate challenges and optimize performance.
In a cloud setting, networking involves establishing secure communication channels between resources, ensuring reliable data flow, and maintaining robust security measures. By preparing for various scenarios, you will be able to design scalable, efficient, and secure network architectures that meet the demands of modern businesses.
Key Networking Concepts to Master
To excel in networking scenarios, focus on understanding the following core concepts:
- Virtual Networks: Virtual networks provide isolated environments for resources to communicate securely. Understanding how to create, configure, and manage these networks is crucial.
- Subnets: Dividing a virtual network into subnets allows for better organization and traffic management. Each subnet can have its own routing rules and security configurations.
- IP Addressing: Grasping the structure of public and private IP addresses, including static and dynamic assignments, is essential for ensuring seamless communication.
- Routing: Understanding routing protocols and how to configure routes between different networks is key to ensuring traffic reaches the correct destination.
- Network Security: Implementing network security measures such as network security groups (NSGs), firewalls, and VPNs ensures that the network remains protected from unauthorized access.
Best Practices for Networking Scenarios
When preparing for cloud networking challenges, adhere to the following best practices:
- Design for Scalability: Ensure your network architecture can scale as the organization grows, accommodating additional users and resources without sacrificing performance.
- Prioritize Security: Apply security measures throughout your network, including encryption, secure access points, and regular audits to prevent unauthorized access.
- Optimize for Performance: Use load balancing, optimize routing paths, and reduce bottlenecks to maintain high-speed connectivity and low latency.
- Test Connectivity: Regularly test network connections and configurations to identify potential issues before they impact operations.
By focusing on these key concepts and best practices, you’ll be well-prepared to handle any networking scenario, ensuring that your cloud infrastructure is both efficient and secure.
Solution Design Principles for Exams
Designing efficient, scalable, and secure solutions is crucial for ensuring that cloud infrastructure meets the needs of businesses and users. Understanding key principles for solution design helps you address the most common challenges, such as performance, reliability, and security. A well-designed system takes into account the technical and operational requirements, enabling seamless integration with existing processes and systems.
As you prepare for cloud-related assessments, it’s essential to grasp the foundational principles of solution architecture. These principles guide how to structure and deploy resources effectively, ensuring that solutions can scale, adapt, and meet specific business needs. Additionally, a deep understanding of best practices for resilience and cost efficiency will enhance your ability to create optimal solutions.
Core Design Principles
Below are some of the fundamental design principles that every solution architect should be familiar with:
- Scalability: The system must be able to grow and handle increased demand without significant performance degradation. It’s important to design with flexibility in mind, allowing for resource scaling based on needs.
- Availability: High availability ensures that the system remains operational and accessible even during failures or disruptions. Redundant configurations and automatic failover mechanisms help achieve this.
- Security: A secure design protects sensitive data and resources from unauthorized access or malicious attacks. Implementing proper encryption, identity management, and access controls are key components of secure design.
- Performance: Optimizing performance involves reducing latency, ensuring fast response times, and efficiently managing system resources. It’s essential to balance speed with resource utilization.
- Cost Efficiency: The solution should be designed with cost considerations in mind, ensuring that resources are used efficiently to avoid unnecessary expenditure while maintaining performance standards.
Best Practices for Solution Design

In addition to understanding the core principles, applying best practices will ensure that the solution is both functional and sustainable over time. Here are several practices to follow:
- Use of Managed Services: Leverage cloud providers’ managed services to offload operational complexity and reduce the need for manual maintenance.
- Automation: Implement automated workflows to reduce human error, speed up deployment, and improve consistency across the environment.
- Modular Architecture: Break down solutions into smaller, reusable components. This makes it easier to modify, scale, or troubleshoot individual parts of the system without disrupting the entire solution.
- Continuous Monitoring: Establish continuous monitoring and logging to track performance, detect issues early, and respond proactively to any system anomalies.
- Disaster Recovery Planning: Design systems with disaster recovery in mind to minimize downtime and data loss in the event of a failure.
By focusing on these design principles and best practices, you will be well-equipped to create cloud solutions that are robust, scalable, secure, and cost-effective, meeting the needs of businesses and users alike.
Best Study Materials for Success
Preparing for cloud certification assessments requires a solid foundation of knowledge, practical skills, and the right study resources. Choosing the most effective study materials can make a significant difference in understanding key concepts, as well as building confidence to succeed in these evaluations. A mix of official documentation, online courses, hands-on labs, and practice tests ensures comprehensive preparation.
It’s important to approach the learning process with a strategy that aligns with your strengths, whether that involves visual, auditory, or kinesthetic learning styles. A variety of study tools will help reinforce concepts and allow you to practice the application of knowledge in real-world scenarios. Below are the top resources to guide your preparation for cloud-related assessments.
Official Documentation and Resources
One of the most authoritative sources for cloud certifications is the official documentation provided by cloud service providers. These materials offer in-depth explanations, detailed use cases, and tutorials.
- Product Documentation: Comprehensive manuals and guides available on the official website provide the latest updates and best practices for cloud technologies.
- Whitepapers: Official whitepapers focus on security, architecture, and governance best practices for cloud systems.
- Learning Paths: Many cloud providers offer structured learning paths tailored for beginners or advanced users, which include video lessons and reading materials.
Online Courses and Video Tutorials

Enrolling in structured online courses can offer a step-by-step approach to mastering the topics required for certification. Many platforms provide interactive lessons that walk you through key concepts and include practice exercises.
- Platform-Specific Courses: Websites like Pluralsight, LinkedIn Learning, and Udemy offer cloud-focused courses, often developed by experienced instructors and cloud professionals.
- Video Tutorials: Free video tutorials on YouTube or cloud provider channels help you gain hands-on insights into real-world scenarios, often demonstrating practical usage of various tools.
- Instructor-Led Training: Live, instructor-led sessions can provide a more personalized learning experience, with the opportunity to ask questions and get clarification on complex topics.
Hands-On Practice and Labs
Applying theory to practical scenarios is one of the best ways to retain knowledge. Cloud environments allow users to create and manage virtual machines, storage, networking, and security configurations. Hands-on labs simulate real-world tasks and help you develop practical expertise.
- Cloud Sandboxes: Cloud platforms often provide free or trial access to resources, allowing you to experiment and gain hands-on experience.
- Lab Environments: Platforms like A Cloud Guru and Microsoft Learn offer guided exercises where you can practice configuring, managing, and troubleshooting cloud infrastructure.
- Simulated Environments: Some online tools offer simulated environments for practicing cloud deployment and management scenarios, which is especially useful for honing your skills in cloud management tasks.
Practice Tests and Quizzes
Testing your knowledge regularly is key to identifying areas for improvement and reinforcing your understanding. Practice tests mirror the real testing experience, allowing you to get accustomed to the format, time constraints, and type of content you may encounter.
- Official Practice Tests: Many cloud providers offer practice tests that mimic the actual certification assessment in terms of difficulty and content.
- Third-Party Practice Exams: Websites such as Whizlabs and ExamTopics provide a wide range of practice exams with answers and detailed explanations, helping you refine your skills.
- Quizzes: Regularly taking quizzes on specific topics can help you gauge your knowledge retention and focus on areas where you’re still unsure.
By using a combination of official resources, online courses, hands-on labs, and practice tests, you’ll be well-prepared to master the necessary skills and pass your cloud-related certifications with confidence.