
Preparing for a challenging assessment in the field of human biology requires a deep understanding of essential concepts and systems. This section provides the necessary tools to tackle the first major evaluation, offering insight into the critical topics that will be tested. Whether you’re reviewing key processes or refining your knowledge of specific functions, this guide will ensure you’re well-equipped for success.
Effective preparation involves more than memorizing definitions. It requires the ability to connect different biological functions and systems, as well as applying that knowledge to solve complex problems. Focusing on both theoretical and practical aspects of the subject will help you gain a comprehensive understanding and improve your performance in the test.
Throughout this article, you’ll find valuable information on the core areas, study strategies, and tips that can enhance your learning experience. With the right approach, you will not only perform well on the assessment but also build a solid foundation for future studies in this field.
Comprehensive Review for Exam 1
To excel in this critical assessment, it’s important to have a thorough grasp of the major topics that will be covered. This section serves as an all-encompassing review of the foundational material, ensuring that key concepts are fully understood and can be effectively applied during the test. The aim is to help you connect various biological systems and their functions, so you can approach the evaluation with confidence.
Key Concepts to Focus On
Mastering the fundamental concepts is essential for achieving a high score. Topics such as human body structure, cellular functions, and system interrelationships form the backbone of the subject. Familiarity with these areas allows you to understand how different systems work together to maintain health and balance in the body. It’s critical to not only memorize facts but also to comprehend their practical implications.
Effective Study Tips
Active recall and regular practice are key to reinforcing what you’ve learned. Consider reviewing each concept multiple times and testing yourself using flashcards or practice questions. Additionally, breaking down complex processes into smaller, manageable steps can help in retaining information. Create diagrams or charts to visualize connections between systems, as this will strengthen your understanding and make studying more effective.
Key Concepts in Human Anatomy
Understanding the structure and function of the human body is fundamental to mastering the subject. This section highlights essential topics that form the core knowledge needed to excel in the assessment. These concepts include the organization of the body, how systems work together, and the specific roles of tissues, organs, and cells.
The complexity of the body’s design can be seen in the intricate relationships between various systems. From the skeletal framework that provides support, to the circulatory network that transports vital nutrients, each element plays a critical role in maintaining overall health. A deep comprehension of these components is necessary for both theoretical understanding and practical application in assessments.
Physiological Systems Overview
Understanding the body’s functional networks is crucial for mastering the subject. This section provides a detailed exploration of the major systems that work in concert to maintain balance and health. Each system performs specialized tasks, yet they are all interconnected, supporting the body’s overall functioning.
The Role of Organ Systems
The body consists of several key organ systems, each responsible for specific functions. For instance, the respiratory system enables gas exchange, while the digestive network breaks down food to provide nutrients. These systems rely on coordination to ensure that the body’s internal environment remains stable.
Interdependence of Systems
These systems are not isolated; they interact and influence one another. For example, the cardiovascular system circulates blood, which carries oxygen and nutrients to cells, supporting the functions of other systems. Understanding these interactions is essential for seeing the bigger picture of how the body operates as a whole.
Important Study Strategies for Success
Effective preparation is the key to mastering complex material and performing well in any assessment. This section offers valuable techniques for organizing study sessions, improving retention, and boosting confidence. A strategic approach to learning not only helps retain critical information but also ensures that you’re able to apply it successfully when needed.
One of the most efficient methods for retaining information is active recall, which involves testing yourself regularly on the material. Another helpful strategy is spaced repetition, where you review topics at increasing intervals to strengthen long-term memory. Combining these techniques will enhance your grasp of the subject and prepare you to tackle any challenge during the assessment.
Understanding the Nervous System

The nervous system plays a crucial role in coordinating and controlling the body’s functions. It allows the body to respond to stimuli, process information, and maintain homeostasis. This section explores the structure and function of this complex network, focusing on how its components work together to regulate behavior and bodily processes.
Key Components of the Nervous System
The nervous system is made up of two primary components:
- Central Nervous System (CNS): Includes the brain and spinal cord, responsible for processing information and sending commands to the rest of the body.
- Peripheral Nervous System (PNS): Consists of nerves outside the CNS, which transmit signals to and from the central system.
How the Nervous System Works
Communication within the nervous system occurs through electrical signals transmitted by neurons. The process follows these steps:
- Stimulus detection: Sensory receptors detect changes in the environment.
- Signal transmission: Neurons carry electrical impulses to the CNS.
- Processing and response: The brain interprets the signals and sends appropriate commands to effect a response.
Circulatory System Functions Explained
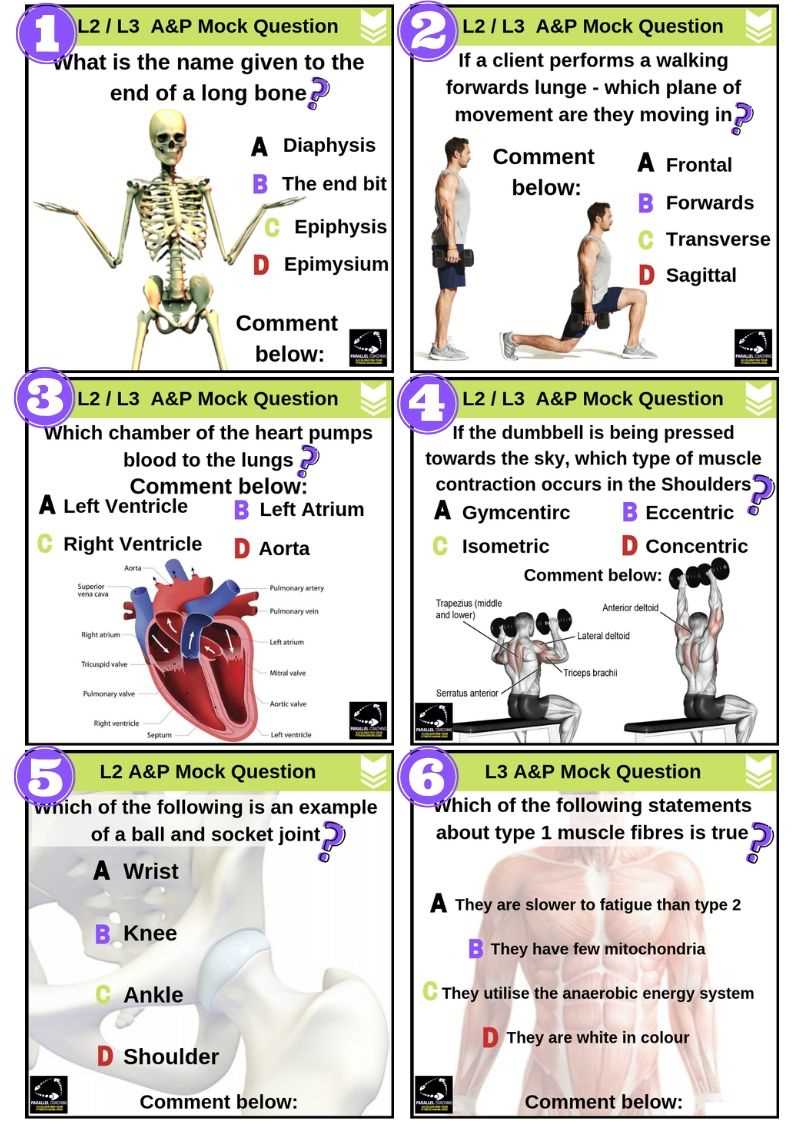
The circulatory network is essential for maintaining life, as it is responsible for the movement of substances throughout the body. It delivers oxygen and nutrients to cells, removes waste products, and helps regulate body temperature. Understanding how this system functions is crucial for grasping its role in sustaining overall health and homeostasis.
The system is composed of the heart, blood vessels, and blood. The heart acts as a pump, circulating blood through arteries, veins, and capillaries, which together form an intricate network. This continuous flow ensures that cells receive the necessary resources to function and thrive, while also carrying away metabolic byproducts.
Muscular System and Its Role
The muscular network is fundamental to movement, stability, and overall functionality of the body. It enables a wide range of activities, from simple tasks like walking to complex actions such as speaking or lifting. The system works by contracting and relaxing, which allows the body to perform both voluntary and involuntary functions that are vital for survival.
This system is composed of three primary types of muscles, each with distinct functions. Below is a summary of these muscle types:
| Muscle Type | Location | Function |
|---|---|---|
| skeletal | Attached to bones | Enables voluntary movement |
| cardiac | Heart | Pumps blood involuntarily |
| smooth | Walls of organs and blood vessels | Regulates involuntary functions, like digestion |
Each muscle type plays a unique role, contributing to the overall efficiency and adaptability of the body’s movement. Whether for conscious actions or automatic processes, the muscular system is key to maintaining homeostasis and supporting various bodily functions.
Digestive Processes You Should Know
The breakdown of food into nutrients is essential for maintaining energy levels and supporting various bodily functions. This section explains the key stages involved in the processing of food, from ingestion to absorption, highlighting the mechanisms that ensure nutrients are efficiently extracted and waste is eliminated.
Stages of Digestion
The digestive system follows a complex sequence of stages, each designed to break down food and absorb the necessary nutrients. Here’s a quick look at the key phases:
| Stage | Description |
|---|---|
| Ingestion | Food is taken into the mouth, where mechanical and chemical digestion begin. |
| Mechanical Digestion | Food is physically broken down into smaller particles, primarily through chewing. |
| Chemical Digestion | Enzymes and acids break down food into smaller molecules, such as carbohydrates and proteins. |
| Absorption | Small nutrients are absorbed through the walls of the intestines into the bloodstream. |
| Elimination | Waste products that cannot be digested are removed from the body. |
Enzymes Involved in Digestion

Digestive enzymes play a crucial role in breaking down food into simpler molecules. These proteins facilitate the conversion of large food particles into nutrients that the body can use. Enzymes are secreted by different organs such as the salivary glands, stomach, and pancreas, each specializing in the breakdown of specific nutrients.
Respiratory System Essentials
The respiratory network is vital for delivering oxygen to the bloodstream while removing carbon dioxide from the body. This system enables cellular functions by ensuring that the body’s tissues receive the necessary oxygen to perform metabolic activities. In addition, it helps maintain proper acid-base balance and regulate the body’s overall fluid levels.
The process of breathing involves several key structures and mechanisms, which work together to facilitate gas exchange. Below are the essential components of this system:
- Nose and Mouth: Primary entry points for air, filtering and warming it before it reaches the lungs.
- Trachea: A tube that directs air into the bronchi, leading to the lungs.
- Lungs: The main organs where gas exchange occurs through tiny air sacs called alveoli.
- Diaphragm: A muscle that contracts and relaxes to control the intake and expulsion of air.
Effective lung function depends on the proper coordination of these structures. The oxygen we inhale travels to the alveoli, where it diffuses into the blood, while carbon dioxide is removed from the bloodstream and exhaled. This continuous cycle is essential for sustaining life.
Endocrine System in Focus
The network of glands that release hormones plays a critical role in regulating various body functions, from growth and metabolism to mood and immune response. These chemical messengers travel through the bloodstream to target organs, helping the body respond to changes in the environment and maintain balance. Understanding the key elements of this system is essential for recognizing how the body adapts and functions optimally.
At the core of this system are several major glands, each responsible for producing specific hormones. Here’s a breakdown of the key glands involved:
- Hypothalamus: Controls the release of hormones from the pituitary and regulates hunger, thirst, and body temperature.
- Pituitary Gland: Often referred to as the “master gland,” it regulates other glands and influences growth, metabolism, and reproduction.
- Thyroid Gland: Produces hormones that control metabolism, energy production, and temperature regulation.
- Adrenal Glands: Release hormones such as adrenaline and cortisol that are involved in stress response, metabolism, and immune function.
- Pancreas: Produces insulin and glucagon, regulating blood sugar levels.
The precise balance of these hormones is crucial for maintaining normal bodily functions. Even small disruptions in hormone levels can lead to a variety of health issues, emphasizing the importance of this system in overall health and wellness.
Immune System Insights

The body’s defense mechanisms are essential for protecting against harmful invaders such as bacteria, viruses, and other pathogens. The immune network works tirelessly to detect, neutralize, and remove these threats, ensuring the body stays healthy and resilient. It consists of a complex system of cells, proteins, and organs that collaborate to identify and eliminate foreign substances.
At the heart of this defense system are specialized cells that play crucial roles in identifying and attacking invaders. Some key components include:
- White Blood Cells: These cells patrol the body for harmful pathogens and are essential for the immune response.
- Lymphatic System: A network of vessels and nodes that helps transport immune cells throughout the body and filters harmful substances.
- Antibodies: Proteins produced by the immune system to recognize and neutralize specific pathogens.
- Spleen: An organ that filters the blood and stores immune cells to help fight infections.
The body’s ability to recognize foreign invaders and develop a targeted response is crucial for long-term health. Immunity is enhanced through exposure, vaccines, and proper nutrition, which all support the immune system’s function. Understanding how these processes work together helps us appreciate the complexity and importance of this protective network.
Effective Time Management Tips
Managing time efficiently is a crucial skill that enhances productivity and reduces stress. By organizing tasks, prioritizing responsibilities, and setting clear goals, you can maximize your available time and achieve better results. This approach not only improves performance but also helps create a balanced lifestyle, allowing you to focus on both personal and academic or professional commitments.
Here are some practical strategies for better time management:
- Set Clear Goals: Break down large projects into manageable tasks with specific, measurable objectives.
- Prioritize Tasks: Focus on high-priority items first, and tackle less important tasks later.
- Create a Schedule: Plan your day or week ahead of time, allocating time blocks for each task or activity.
- Avoid Multitasking: Focus on one task at a time to improve efficiency and reduce mistakes.
- Use Time Tracking Tools: Utilize apps or planners to track how you spend your time and identify areas for improvement.
- Set Boundaries: Limit distractions by setting clear boundaries for work, study, or relaxation periods.
By incorporating these tips into your daily routine, you can gain better control over your schedule, leading to greater success and a more productive lifestyle.
Exam Question Types and Tips
Understanding the different formats of questions commonly encountered in assessments can help improve performance. By recognizing the structure of questions, you can develop strategies to approach them effectively. Whether it’s multiple choice, short answer, or essay-based questions, each type requires different methods of preparation and critical thinking.
Here are some common question types and tips for tackling them:
| Question Type | Tips |
|---|---|
| Multiple Choice | Carefully read all options before selecting. Eliminate clearly wrong answers to increase your chances of choosing the correct one. |
| True/False | Look for keywords in the statement that can clarify its accuracy. Pay attention to words like “always,” “never,” or “only” which may indicate extremes. |
| Short Answer | Be concise but thorough. Focus on answering the specific question and avoid including unnecessary details. |
| Essay | Structure your response with a clear introduction, body, and conclusion. Ensure you address all parts of the question in a logical sequence. |
By preparing for these question types, you can better manage your time during assessments and respond with more confidence. Practice and familiarity with the question formats will enhance your ability to recall information and apply knowledge efficiently.
Common Mistakes and How to Avoid Them

During assessments, certain errors can hinder performance, even when the material is well understood. Identifying these common pitfalls ahead of time allows for better preparation and ultimately improves outcomes. Many of these mistakes are preventable with a few simple strategies.
Here are some frequent mistakes and how to avoid them:
- Overlooking Key Instructions: Always read the instructions carefully before answering any question. Missing a small detail can change the entire direction of your response. Take a moment to fully understand what is being asked.
- Rushing Through Questions: Speeding through the test may lead to careless mistakes. Pace yourself and review each answer before moving on. It’s better to take a bit more time than to make avoidable errors.
- Not Reviewing Your Work: Many students fail to revisit their responses before submitting. Double-check your answers, especially for true/false or multiple-choice questions, where small errors can easily go unnoticed.
- Misinterpreting the Question: Read questions multiple times if necessary. If unsure, underline keywords to help focus on the core topic. This ensures your response directly addresses the main point of the question.
- Neglecting Time Management: Failing to allocate time appropriately can result in rushed or unfinished answers. Set aside time for each section of the test, ensuring a balance between speed and quality.
By being aware of these potential mistakes, you can implement strategies to avoid them and approach your tasks with more confidence and precision. Preparation isn’t just about studying the material–it’s about developing effective test-taking habits as well.
Reviewing Lab Work and Practical Exams
Hands-on assessments are an essential component of understanding complex concepts. Whether it’s conducting experiments, analyzing data, or performing techniques, these tasks require both theoretical knowledge and practical application. Properly reviewing your lab work and preparing for practical assessments is crucial to mastering the material and excelling in these types of evaluations.
Key Steps for Effective Review
To ensure a solid understanding and avoid common mistakes during practical tasks, consider the following steps:
- Revisit Procedures: Go over the step-by-step processes involved in your previous lab work. Pay special attention to any areas where you encountered difficulties or felt uncertain about your techniques.
- Understand the Purpose: Reflect on the objective of each experiment. Knowing why you perform each task helps connect theoretical concepts to practical applications.
- Review Data Interpretation: Ensure you understand how to analyze the data you collected, how to identify patterns, and how to draw meaningful conclusions from your findings.
Strategies for Success in Practical Assessments
To perform well in hands-on evaluations, practice the following strategies:
- Repetition and Practice: The more you practice, the more confident and accurate you’ll be during practical tasks. Repeating procedures in a controlled setting will help reinforce skills.
- Prepare Equipment Familiarity: Know your tools and equipment well. Familiarity with the instruments used in the lab ensures you can quickly set up and complete the task efficiently.
- Plan for Time Management: Hands-on evaluations often have time constraints. Develop a plan to manage your time effectively, ensuring you can complete all necessary steps without rushing.
Mastering these elements can transform lab work and practical assessments from challenging tasks into opportunities for success. The goal is to make practical knowledge as second nature as theoretical understanding.
Test-Taking Techniques for Anatomy Exams
Approaching a challenging evaluation requires more than just knowledge of the subject matter; it demands strategic preparation and effective techniques during the test. By adopting the right approach, you can maximize your performance and reduce test anxiety. This section focuses on practical strategies to excel during assessments that involve detailed memorization and complex concepts.
Preparation Techniques
Effective preparation begins long before the actual test. Consider incorporating these strategies into your study routine:
- Active Recall: Instead of passively reading through your notes, test yourself regularly on key concepts. This strengthens memory retention and reinforces your understanding of important material.
- Organize Material: Break down the content into manageable sections and study in focused intervals. This helps prevent information overload and ensures better absorption.
- Group Study Sessions: Collaborating with classmates can clarify complex topics. Discussing material with others allows you to see different perspectives and fill in any gaps in understanding.
Effective Strategies During the Test
When it’s time to sit for the assessment, employing the right test-taking strategies can make a significant difference:
- Read Questions Carefully: Ensure you understand each question before answering. Look for keywords that specify exactly what’s being asked.
- Eliminate Obvious Incorrect Answers: In multiple-choice questions, rule out options that are clearly wrong to improve your chances of selecting the correct one.
- Manage Your Time: Keep track of time and pace yourself. Don’t spend too long on any single question. If you’re stuck, move on and return to it later.
- Answer What You Know First: Quickly answer questions you’re confident about, then tackle more difficult ones. This builds momentum and prevents unnecessary stress.
By applying these techniques, you not only enhance your ability to recall important material but also improve your overall performance under exam conditions. Mastering these strategies will help you approach assessments with confidence and composure.
Final Review and Study Resources
As the assessment day approaches, it’s important to consolidate all your knowledge and ensure you are well-prepared. A final review is essential for reinforcing key concepts, filling in any gaps, and boosting your confidence. This section will guide you on how to effectively organize your last-minute study sessions and highlight resources that can aid in your revision process.
Effective Final Review Techniques
To make the most of your final review, consider the following approaches:
- Prioritize Weak Areas: Focus your attention on topics you find most challenging. Revisiting difficult concepts will help solidify your understanding and boost your confidence.
- Practice Under Test Conditions: Simulate real exam conditions by timing yourself while practicing questions. This will help you manage time effectively during the actual assessment.
- Review Past Assessments: Look over previous tests, quizzes, or assignments. They can provide insights into the types of questions that may appear and the format you can expect.
Study Resources
There are numerous resources available that can help you reinforce your learning and clarify complex material. Below are some valuable tools:
- Textbooks and Class Notes: Your class materials should be your primary reference. Ensure you have reviewed key chapters and highlighted important points.
- Online Platforms: Websites like Quizlet, Khan Academy, or Coursera offer practice questions, video tutorials, and summaries of key concepts.
- Study Groups: Join or form study groups with classmates to review material together. Group discussions allow you to test each other’s knowledge and gain new insights.
- Flashcards: Create flashcards for important terms and processes. This is an excellent way to test your recall and reinforce important concepts.
By combining a structured review plan with these resources, you will ensure that you are thoroughly prepared. This final push can make a significant difference in your performance and help you approach the assessment with confidence.