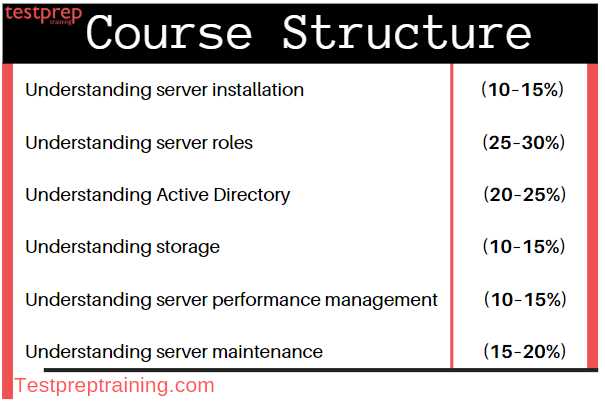
Preparing for a certification that covers the essential concepts of IT infrastructure can seem overwhelming at first. However, understanding the core principles and acquiring practical knowledge is crucial to success. This guide will help clarify the main topics, providing a structured approach to mastering the required skills.
While navigating the intricacies of network management, security protocols, and system maintenance, it is important to focus on hands-on experience alongside theoretical knowledge. By engaging with the right tools and techniques, candidates can confidently move towards certification and demonstrate their proficiency in managing modern IT environments.
Effective preparation involves understanding the various roles and responsibilities within IT systems, from managing users and data storage to ensuring security and troubleshooting issues. Each of these areas is interrelated, and knowing how to optimize them can be the key to excelling in the certification process. Focused study and practical application of the concepts are vital in achieving success and standing out as a skilled professional in the field.
Understanding Core IT Certification Concepts
Achieving proficiency in key IT areas requires a clear understanding of essential concepts related to network management, system security, and maintenance. The certification process is designed to assess your knowledge of the critical elements necessary for managing complex IT environments. To pass, candidates need to demonstrate their capability in handling real-world challenges while mastering the fundamental skills required for the role.
Key Areas of Focus
- Network Infrastructure: Understanding how different devices communicate within a network, including configuring and managing connections.
- System Maintenance: Regular updates, monitoring, and managing the health of IT systems to ensure smooth operation.
- Security Principles: Implementing measures to protect sensitive information and prevent unauthorized access.
- User and Group Management: Assigning appropriate access levels, ensuring users have the correct permissions.
Preparation Tips
- Practice using virtual environments to simulate real-world scenarios and deepen your understanding of system management.
- Focus on the key tools and protocols that are commonly used in managing IT infrastructures.
- Study troubleshooting methods to identify and resolve issues quickly.
By focusing on these areas, candidates can build a solid foundation, making them well-prepared for the challenges of managing and optimizing IT systems in any organization. Success in this certification reflects both theoretical knowledge and practical experience, showcasing readiness for the demands of the industry.
Overview of Exam 98-365 Requirements
The certification assessment for IT professionals focuses on evaluating essential skills related to the management and support of modern technological environments. To succeed, candidates must demonstrate competence in core areas such as system configuration, network management, and security protocols. The assessment covers a wide range of topics, each testing your ability to handle real-world situations and make informed decisions in complex environments.
Core Topics Covered
- Networking Fundamentals: Understanding how different devices and systems communicate within a network and ensuring their optimal performance.
- System Setup and Configuration: Installing and configuring operating systems, hardware components, and managing key resources.
- Security Measures: Implementing access control, data protection, and maintaining the overall security of IT environments.
- Data Management and Backup: Managing files, storage systems, and ensuring that appropriate backup procedures are in place.
Preparation Requirements
- Familiarity with the tools and technologies commonly used in modern IT environments is essential for success.
- Hands-on experience through practical scenarios will help deepen understanding and solidify theoretical knowledge.
- Reviewing troubleshooting techniques and learning how to resolve issues efficiently will be beneficial during the assessment.
Thorough preparation is key to achieving a passing score. By gaining expertise in these critical areas and applying your knowledge in practice, you will be well-equipped to meet the requirements of the certification.
Key Topics Covered in Exam 98-365
The assessment evaluates your understanding of various critical aspects necessary for effectively managing IT infrastructures. These core areas form the foundation of the knowledge required to support and maintain complex systems. A comprehensive grasp of these topics ensures that professionals can handle the demands of modern technology environments.
Network Configuration and Management
- Networking Protocols: Understanding how different communication protocols function within an IT environment.
- Device Management: Configuring and maintaining devices that communicate across a network.
- IP Addressing: Assigning and managing IP addresses, as well as ensuring network connectivity.
System Setup and Maintenance
- Operating System Installation: Installing and configuring essential software to support IT infrastructure.
- Hardware Configuration: Managing physical devices and components required for system operation.
- System Monitoring: Utilizing monitoring tools to track system health and performance.
Security and Access Control
- Access Control Policies: Defining and enforcing user permissions to secure data and system resources.
- Security Protocols: Implementing measures to safeguard sensitive information from unauthorized access.
- Data Protection: Ensuring data integrity and security through encryption and other techniques.
Backup and Recovery
- Data Backup: Implementing reliable backup strategies to prevent data loss.
- Disaster Recovery: Preparing and executing plans for restoring data and services after a failure.
Mastering these key topics will not only prepare you for the certification but also provide the essential skills needed for effective IT management and troubleshooting in real-world environments.
How to Prepare for the 98-365 Exam
Effective preparation for the certification assessment involves more than just memorizing facts. It requires developing a deep understanding of core concepts, honing practical skills, and learning to apply them in real-world scenarios. A structured approach to studying can help build confidence and ensure readiness for the challenges you will face during the evaluation.
Build a Strong Foundation
- Understand Core Concepts: Focus on mastering the key principles behind network management, system configuration, and security measures.
- Hands-On Practice: Set up virtual environments or use labs to gain practical experience with the tools and techniques discussed in your study material.
- Focus on Weak Areas: Identify areas where you feel less confident and dedicate extra time to reviewing and practicing them.
Use Effective Study Resources
- Official Study Guides: Invest in reputable guides and textbooks that cover all the topics in detail.
- Online Courses and Tutorials: Enroll in online learning programs that offer structured courses and hands-on labs.
- Practice Tests: Take practice exams to familiarize yourself with the question format and assess your knowledge.
By following these preparation strategies, you can ensure that you are well-prepared to succeed in the certification. The combination of theoretical study and practical application will help you achieve a solid understanding of the material and build the skills necessary to pass the assessment confidently.
Common Mistakes to Avoid in Exam Preparation
When preparing for a certification assessment, it’s easy to fall into certain traps that can hinder progress. Avoiding these common mistakes can make a significant difference in how effectively you grasp the material and ultimately perform on the test. Understanding what to watch out for ensures that your study efforts are both efficient and productive.
One major mistake is relying too heavily on passive learning methods, such as simply reading through study guides without engaging with the material in a hands-on way. It’s important to apply the concepts learned by practicing with tools, simulations, or virtual environments. Without practical experience, it’s easy to forget key details when faced with real-world scenarios.
Another common error is neglecting areas of weakness. It’s tempting to focus only on topics you already understand, but skipping over harder subjects can lead to gaps in your knowledge. A balanced study plan that allocates time to both strengths and weaknesses will ensure a more thorough understanding of the material.
Lastly, failing to simulate actual testing conditions can leave you unprepared for the time pressure and structure of the assessment. Practice tests are crucial to familiarize yourself with the question format and develop strategies for managing time during the evaluation. Without this, you might find yourself overwhelmed during the actual test.
By being mindful of these mistakes and actively working to avoid them, you can enhance your preparation and increase your chances of success. A focused and strategic approach will help ensure that you are fully prepared for the challenges ahead.
Understanding Active Directory for Exam Success
Mastering directory services is essential for managing user access, security, and resources within an IT environment. Understanding how directory services function will significantly enhance your ability to configure and manage resources efficiently. This knowledge is crucial for handling user authentication, policy enforcement, and maintaining a secure network infrastructure.
Core Concepts of Directory Services
- User and Group Management: Learn how to create, modify, and organize users and groups to ensure secure access to network resources.
- Domain Structure: Understand the hierarchical structure of domains, forests, and organizational units (OUs) for effective management.
- Authentication and Permissions: Gain knowledge about how user credentials are validated and how permissions are assigned to ensure proper access control.
Best Practices for Managing Directories
- Effective Group Policies: Learn how to implement group policies for managing user settings and enforcing security across the network.
- Security Protocols: Understand how to use security groups, password policies, and other measures to safeguard sensitive information.
- Backup and Recovery: Familiarize yourself with best practices for backing up and restoring directory data in case of system failure.
By mastering these key concepts and best practices, you will have the knowledge needed to work effectively with directory services, ensuring the efficient management of users and resources. A strong understanding of directory services will not only prepare you for the certification but also provide you with practical skills for real-world IT management tasks.
Role of Networking in Server Administration
Networking plays a crucial role in the effective operation and management of IT environments. It enables communication between devices, ensures seamless access to resources, and supports essential services like file sharing, internet access, and security protocols. Understanding networking principles is vital for maintaining a reliable, efficient, and secure infrastructure.
Effective management of network connectivity allows administrators to monitor data flow, troubleshoot issues, and optimize performance. Networking also underpins security measures, such as firewalls and access control, to protect sensitive data from unauthorized access.
Key Networking Concepts for IT Management
| Networking Concept | Description |
|---|---|
| IP Addressing | Assigning unique addresses to devices for identification and communication over a network. |
| DNS and DHCP | DNS resolves domain names into IP addresses, while DHCP automatically assigns IP addresses to devices. |
| Routing and Switching | Routing determines the best path for data to travel, and switching ensures data reaches the correct destination within a local network. |
| Network Security | Measures like firewalls and VPNs protect data integrity and restrict unauthorized access. |
| Bandwidth Management | Allocating bandwidth effectively to ensure optimal data flow and minimize congestion. |
Understanding these core concepts enables administrators to optimize network performance, enhance security, and ensure seamless communication across systems. Networking knowledge is integral to ensuring smooth operations and addressing challenges efficiently within an IT environment.
Exam 98-365: Key Tools and Technologies
To excel in certification assessments, it’s essential to familiarize yourself with the key tools and technologies that form the backbone of IT management. These tools help manage and secure resources, optimize performance, and ensure that the network infrastructure operates efficiently. By mastering these technologies, you’ll be able to effectively troubleshoot, configure, and monitor systems as required in the assessment.
Essential Tools for IT Infrastructure Management
- Task Scheduler: Automates routine tasks and operations, saving time and reducing the need for manual intervention.
- Control Panel: Provides a centralized interface for managing system settings, user accounts, and network configurations.
- Event Viewer: Monitors system logs, helping administrators identify and resolve issues in real time.
- Remote Desktop: Facilitates remote management and troubleshooting of systems from a different location.
- File Sharing Tools: Enable the sharing of files and resources across different machines within the network.
Technologies for Enhancing Security and Connectivity
- Firewall Configuration: Helps prevent unauthorized access and ensures that only approved traffic passes through the network.
- Virtual Private Networks (VPNs): Secure remote connections to a network over the internet, enhancing privacy and protecting data transmission.
- DNS Services: Essential for resolving domain names into IP addresses, ensuring that devices can communicate across the network.
- DHCP Servers: Automates the assignment of IP addresses to devices, streamlining network management.
Mastering these tools and technologies is fundamental to not only succeeding in the certification but also excelling in real-world IT management roles. Understanding how to utilize these resources effectively will ensure smooth system performance, robust security, and streamlined operations.
Working with Storage and File Systems
Efficient management of storage and file systems is fundamental to maintaining an organized and secure IT infrastructure. It involves ensuring that data is stored, accessed, and protected properly across the network. Understanding how to work with storage devices, file systems, and related tools enables administrators to handle large volumes of data, optimize performance, and troubleshoot issues effectively.
Types of Storage Solutions
| Storage Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Local Storage | Directly attached storage devices, such as hard drives or SSDs, used for system and user data storage. |
| Network Attached Storage (NAS) | A centralized storage device that connects to a network and allows file sharing across multiple devices. |
| Storage Area Network (SAN) | A high-performance network of storage devices, offering block-level access to data and typically used for larger enterprise environments. |
File Systems Overview
File systems manage how data is stored and retrieved on storage devices. Each system has unique characteristics, designed for different use cases and performance requirements. Understanding the various file systems allows for efficient data organization, fast retrieval, and secure management of files.
| File System | Features |
|---|---|
| NTFS | Offers advanced features like security permissions, encryption, and large file support, widely used in enterprise environments. |
| FAT32 | Legacy file system with wide compatibility but limitations on file size and partition size. |
| ReFS | A newer file system designed for resilience and large-scale storage, with automatic error correction and better data integrity. |
By understanding the different types of storage and file systems, administrators can choose the best options for performance, security, and scalability. Efficient data management ensures seamless operations, especially in large IT infrastructures where data availability and integrity are critical.
Securing Servers for the 98-365 Exam
In the field of IT infrastructure management, ensuring the security of systems is a critical aspect of daily operations. Securing devices and networks from unauthorized access, cyber threats, and data breaches is paramount for maintaining system integrity and reliability. Proper configuration of security tools, access controls, and monitoring mechanisms are all essential in protecting assets and achieving a stable IT environment.
When preparing for certification assessments, understanding the best practices for securing systems is crucial. This includes mastering techniques for hardening systems, applying security patches, and ensuring proper network security configurations. These practices not only improve performance but also mitigate risks associated with cyber threats.
Key Security Measures to Implement
- Firewall Configuration: Deploying firewalls to filter incoming and outgoing network traffic is essential in preventing unauthorized access to your network.
- Encryption: Using encryption protocols to protect sensitive data both at rest and in transit ensures data privacy and prevents unauthorized interception.
- User Authentication and Access Control: Implementing strong authentication methods, such as multi-factor authentication (MFA), along with role-based access control (RBAC), ensures only authorized users can access critical systems.
- Security Patches and Updates: Regularly applying security patches and updates to your systems helps mitigate vulnerabilities and protect against known exploits.
Monitoring and Response Strategies
- Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS): Monitoring systems for signs of unauthorized access and activity through IDS helps quickly identify potential threats.
- Event Logging: Enabling event logs for system and network activity provides a trail that can be reviewed for abnormal or suspicious actions.
- Backup and Disaster Recovery: Ensuring that regular backups are performed and recovery processes are in place can minimize downtime in case of data loss or system failure.
By mastering these security practices and tools, you will be well-prepared not only for certification assessments but also for the challenges of real-world IT security management. Strong security measures safeguard data, prevent breaches, and enhance the overall stability of an organization’s infrastructure.
Understanding Server Virtualization Concepts
Virtualization is a technology that enables the creation of multiple virtual instances of systems, enabling resources to be shared efficiently across a single physical platform. By abstracting hardware resources, this technology allows for better utilization, cost savings, and more flexible management of computing environments. Understanding the key concepts and benefits of virtualization is essential for modern IT operations and infrastructure management.
One of the core advantages of virtualization is the ability to run multiple operating environments simultaneously on a single physical machine. This increases efficiency and scalability, and reduces the need for additional hardware. Virtualization also simplifies deployment, testing, and recovery of systems.
Key Components of Virtualization
- Hypervisor: The software layer that enables virtualization by managing virtual machines (VMs) and controlling the allocation of physical resources.
- Virtual Machines (VMs): Virtualized instances of physical machines, each with its own operating system, storage, and resources, running on top of a hypervisor.
- Virtual Disk: A storage medium that exists in the form of a file and is used by virtual machines, simulating a physical hard disk.
- Guest Operating Systems: The operating systems running inside virtual machines, independent of the host system.
Types of Virtualization
- Hardware Virtualization: Involves abstracting the physical hardware to create virtual machines that operate independently of the host system.
- Operating System Virtualization: Allows multiple isolated user environments or containers to share a single operating system instance.
- Storage Virtualization: Combines multiple physical storage devices into a single virtualized resource, simplifying storage management and improving scalability.
- Network Virtualization: The process of combining physical network hardware into virtual resources, providing flexibility in network management.
Virtualization plays a crucial role in simplifying infrastructure management, improving resource efficiency, and enabling faster deployment of new services. By understanding these concepts, IT professionals can leverage virtualization to optimize performance, reduce operational costs, and maintain a highly flexible and scalable environment.
Effective Troubleshooting Techniques for Exam Success
In IT management, the ability to diagnose and resolve issues efficiently is essential for maintaining smooth operations. Effective troubleshooting involves systematically identifying the root cause of problems, testing potential solutions, and implementing fixes while minimizing downtime. Mastering troubleshooting techniques is vital for professionals aiming to excel in assessments and real-world challenges alike.
To effectively approach issues, it’s important to follow a structured process that ensures no detail is overlooked and that solutions are implemented in a timely manner. Below are several key techniques to apply when troubleshooting complex situations.
Key Troubleshooting Steps
- Identify the Problem: Begin by gathering information on the symptoms and error messages. Speak with users or stakeholders to understand the issue from their perspective.
- Establish a Theory of Cause: Use available data to form hypotheses about what might be causing the issue. Consider possible recent changes, configuration errors, or hardware failures.
- Test the Theory: Test your hypothesis with controlled experiments. Try simple solutions first, such as rebooting devices or checking basic settings, to narrow down the cause.
- Implement a Solution: Once the root cause is identified, apply the most appropriate fix. This could be a software update, configuration change, or hardware replacement.
- Verify System Functionality: After implementing a solution, verify that the issue is resolved and that the system is functioning as expected.
- Document the Process: Keep detailed records of the troubleshooting process, including steps taken, tests performed, and final outcomes, to assist with future troubleshooting efforts.
Common Tools for Troubleshooting

- Event Logs: Check system logs for error messages and warnings that provide insights into the cause of the issue.
- Diagnostic Software: Use tools such as system performance monitors, network analyzers, and hardware diagnostics to gather more information.
- Ping and Traceroute: These basic networking tools help identify connectivity issues by testing the flow of data between devices.
- Command Line Tools: Command line utilities such as ipconfig, netstat, and chkdsk can provide detailed information about network and system health.
By mastering these troubleshooting methods and utilizing the appropriate tools, you will be prepared to handle a wide range of technical issues. This structured approach not only enhances your problem-solving skills but also boosts your confidence when facing challenges in assessments and practical work environments.
Managing Users and Groups in Windows Server
Efficiently managing user accounts and groups is crucial for ensuring that access control and security measures are maintained in any IT infrastructure. By organizing users into specific groups and assigning the right permissions, administrators can ensure proper resource access and safeguard sensitive data. Proper user and group management not only streamlines operations but also enhances overall system security by limiting unauthorized access.
At the heart of user and group management is understanding the relationship between users, permissions, and the roles they play within an organization. Creating and maintaining user profiles, managing passwords, and assigning roles based on job functions are all essential practices that contribute to the smooth running of any network environment.
The process typically involves several key tasks:
- Creating User Accounts: Each individual who needs access to the system must have a dedicated account, which stores their personal settings and security credentials.
- Assigning Permissions: Users are granted permissions based on their roles and the resources they need to access. This step is critical for maintaining security and privacy across the network.
- Organizing Users into Groups: Grouping users based on similar roles or access needs simplifies the management of permissions. For example, a group of employees working in the finance department might have access to different resources than those in marketing.
- Managing Group Policies: Group policies allow administrators to enforce rules for all users within a specific group, ensuring uniform access controls and security settings.
- Maintaining User Information: User details, such as email addresses, contact information, and job roles, should be regularly updated to ensure that system access is accurate and up-to-date.
By regularly reviewing and auditing user access and group membership, organizations can reduce the risk of security breaches and ensure compliance with internal policies and regulatory standards. This ongoing process ensures that users only have the level of access they need to perform their roles, and no more.
Key Concepts in System Monitoring
System monitoring is an essential practice for ensuring the reliability, performance, and security of an IT infrastructure. By continuously tracking the health of various components, administrators can identify potential issues before they escalate into critical problems. Monitoring involves observing key metrics, analyzing system behaviors, and responding to anomalies to maintain smooth operations and safeguard data integrity.
Several fundamental concepts play a crucial role in effective system monitoring, helping to ensure that resources are being used efficiently and that any issues are detected early. These include understanding system resources, establishing performance baselines, and utilizing appropriate monitoring tools. Additionally, timely alerting and proactive troubleshooting are key components of a comprehensive monitoring strategy.
Some of the core aspects of system monitoring include:
- Resource Usage Tracking: Monitoring CPU usage, memory consumption, disk space, and network bandwidth helps detect any potential bottlenecks or overutilization that could impair system performance.
- Performance Baselines: Establishing baseline performance levels allows administrators to compare real-time data with historical values, making it easier to identify unusual patterns that may indicate underlying issues.
- Real-Time Alerts: Configuring alerts for abnormal system behavior ensures that administrators are notified of potential problems immediately, allowing for quicker intervention and resolution.
- Log Analysis: Reviewing system logs and event records is a crucial part of diagnosing issues and tracking any changes or errors that could impact system stability.
- Automation and Scripting: Automation tools and scripts can streamline repetitive monitoring tasks, such as generating reports or restarting services, improving overall efficiency and response times.
By focusing on these critical aspects, administrators can improve the resilience and performance of their systems, ensuring that any issues are addressed promptly and effectively. Comprehensive system monitoring not only helps prevent downtime but also provides valuable insights that can be used to optimize the IT environment continuously.
Backup and Recovery Strategies
Effective data backup and recovery strategies are essential for minimizing the risk of data loss in any IT environment. By implementing a solid backup plan, administrators can ensure that critical information is securely stored and can be restored quickly in the event of a system failure, accidental deletion, or any other form of data corruption. Recovery procedures must also be thoroughly planned to ensure that data is restored quickly and efficiently, minimizing downtime and impact on business operations.
There are several strategies to consider when developing a backup and recovery plan. These include regular backups, the use of both on-site and off-site storage, and understanding the importance of different backup types. It’s also crucial to establish recovery point objectives (RPO) and recovery time objectives (RTO) to guide the recovery process. Below is an overview of these key strategies:
Key Backup Types
| Backup Type | Description | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| Full Backup | A complete copy of all data on a system. | Fastest recovery time, full copy of data. | Time-consuming, requires significant storage space. |
| Incremental Backup | Backs up only the data that has changed since the last backup. | Faster than full backups, saves storage space. | Slower recovery time, as multiple backups need to be restored. |
| Differential Backup | Backs up all changes made since the last full backup. | Faster recovery than incremental, less storage than full backups. | Requires more storage than incremental backups. |
Key Recovery Strategies
When developing a recovery plan, administrators must also consider the following strategies to ensure quick restoration of services:
- Test Restores: Regularly test backup files to ensure that they can be restored successfully in the event of a disaster.
- Off-site Backups: Store backups in a remote location to protect against local disasters such as fires or floods.
- Cloud-Based Backups: Use cloud services for off-site backups, offering scalable storage and quick recovery options.
- Disaster Recovery Plans: Develop comprehensive plans for dealing with catastrophic failures, including detailed procedures for data recovery.
Backup and recovery strategies should be designed with the specific needs of the organization in mind, balancing cost, time, and data protection requirements. By selecting the right types of backups and recovery methods, organizations can ensure that their critical data remains safe and can be quickly restored when necessary.
Practice Tests and Study Resources
To effectively prepare for any certification, using a combination of practice tests and study materials is crucial. These resources help reinforce knowledge, identify areas of weakness, and familiarize candidates with the format of questions they will encounter. By integrating mock assessments and comprehensive study guides, individuals can gauge their readiness and improve their confidence before taking the real test. It’s important to utilize a variety of learning methods, such as hands-on labs, video tutorials, and textbooks, to ensure thorough preparation.
Here are some valuable tools and resources to enhance your preparation:
Practice Tests
Mock tests simulate the actual certification assessment, offering a realistic experience and allowing candidates to practice under timed conditions. They also help identify which areas of the material need more focus.
- Official Practice Tests: These are the most accurate reflection of the real test, often offered by the certifying body.
- Third-Party Test Providers: Many online platforms offer practice questions and timed exams, which can help familiarize candidates with the structure of the real assessment.
- Self-Assessment Tools: Some study platforms offer interactive quizzes and flashcards, helping users assess their knowledge in smaller chunks.
Study Resources
Study guides, books, and online tutorials provide in-depth coverage of all the required topics and concepts. These materials allow for a more structured learning approach and can supplement practical testing methods.
- Official Study Guides: Typically created by the certifying organization, these guides cover the full range of topics needed for success.
- Books and Ebooks: Numerous textbooks and digital resources are available, often including step-by-step walkthroughs, explanations, and practice exercises.
- Online Video Courses: Video tutorials are particularly helpful for visual learners and can offer a deeper understanding of complex topics through demonstrations.
- Forums and Study Groups: Engaging with peers in forums and discussion groups provides an opportunity to ask questions, share insights, and learn from others’ experiences.
By consistently practicing and engaging with these materials, candidates can effectively build their knowledge base and refine their problem-solving skills. This approach will not only improve their chances of passing but will also ensure they are well-prepared for the challenges of the certification process.
Time Management Tips During the Assessment
Effectively managing time during an assessment is crucial to ensure that all questions are answered without rushing. By setting a clear strategy for how to approach the test, you can maintain a steady pace, reduce stress, and maximize performance. A well-structured plan helps to avoid spending too much time on any single question, allowing you to allocate time wisely across the entire test.
Strategies for Managing Time
Here are some proven strategies to help you use your time efficiently during the assessment:
- Read Through the Entire Test First: Take a few minutes at the start to glance through all the questions. This gives you a sense of the topics covered and helps you plan your approach.
- Prioritize Easy Questions: Tackle questions you find easier or more familiar first. This will build your confidence and save time for the more difficult ones later.
- Set Time Limits for Each Section: Break the test into manageable sections and set a target for how long to spend on each one. This helps prevent lingering too long on one part of the test.
- Don’t Overthink: If you’re unsure of an answer, make your best guess and move on. Spending too much time on difficult questions may cause you to miss easier ones later.
Time Allocation Tips
How you allocate your time can make a big difference in how effectively you complete the test. Here’s a suggested breakdown for managing time during a typical assessment:
| Task | Recommended Time |
|---|---|
| Review entire test | 5 minutes |
| Answer easy questions | 50% of total time |
| Answer moderate questions | 30% of total time |
| Review and finalize | 15% of total time |
By following these strategies and time allocation tips, you can ensure that you remain calm and focused throughout the assessment. Efficient time management allows you to maximize the potential of your knowledge and gives you the best chance for success.
What to Expect on the Assessment Day

The day of an assessment can be both exciting and nerve-wracking, but knowing what to expect can help you feel more prepared and confident. It’s important to arrive at the test center with a clear mind and the necessary materials, ready to approach the challenge strategically. The assessment environment is designed to allow you to focus solely on answering questions, without distractions, so understanding the structure of the day can ease any nerves and set you up for success.
Before the Assessment
Before entering the testing area, you’ll need to check in and verify your identity. Here are some common steps you can expect:
- Arrive Early: Plan to arrive at least 30 minutes before the scheduled start time to allow for check-in and any necessary preparations.
- Identity Verification: You will need to show identification to confirm your registration. This could include a government-issued ID or other forms of proof as required by the test center.
- Materials Required: Bring any necessary materials such as a valid ID, test confirmation, and any other documents specified by the test provider.
During the Assessment
Once you begin, the assessment will typically consist of multiple sections, each with specific types of questions. It is important to pace yourself and stay focused.
- Timed Sections: Each section will have a time limit, so be mindful of the clock. Avoid spending too much time on any one question and keep track of your progress.
- Question Formats: You will encounter multiple-choice questions, possibly including simulations or other types of interactive formats. Read each question carefully and ensure you understand the requirements before answering.
- Breaks: Depending on the test provider, there may be scheduled breaks. Use this time to relax, hydrate, and refocus.
By familiarizing yourself with the process ahead of time, you can reduce stress and approach the assessment with confidence. Stay calm, pace yourself, and focus on applying what you’ve learned throughout your preparation.