
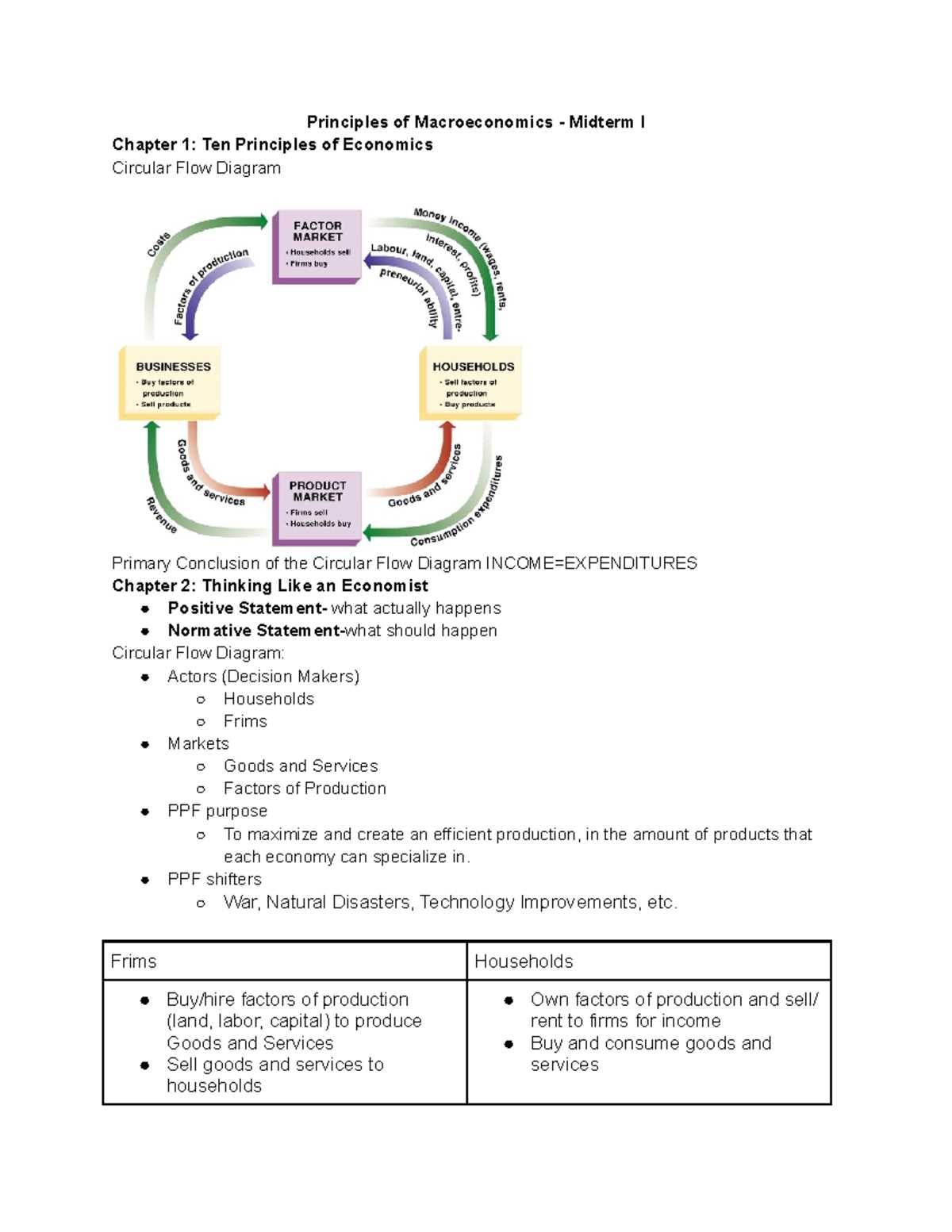
Preparing for a major assessment in economics requires a thorough understanding of key concepts and the ability to apply them under pressure. Success depends on mastering various theories, calculations, and analytical skills. Whether you’re revising core principles or tackling practice questions, strategic preparation is essential to navigate the complexities of the subject efficiently.
Focus on recognizing patterns within economic trends, understanding how different factors interact, and being able to explain these relationships clearly. The ability to evaluate and interpret real-world data is just as important as memorizing formulas and definitions. Effective study techniques, along with a clear approach to problem-solving, will help you perform confidently and accurately.
Macroeconomics Midterm Exam Overview
Understanding the structure and content of a major economics test is crucial for effective preparation. These assessments typically cover a wide range of topics, from theoretical concepts to practical applications, and require students to demonstrate both their knowledge and problem-solving abilities. The format may include various question types, such as multiple-choice, short answer, and numerical calculations, all designed to test different aspects of your understanding.
Familiarity with the main areas of focus can significantly enhance your study strategy. Key topics often include economic models, fiscal and monetary policies, market behavior, and national economic indicators. Knowing how to approach each type of question and where to allocate your study time will give you a structured path to follow and increase your chances of success.
Key Topics to Review for Success
Focusing your efforts on the most important concepts is essential for achieving a strong performance in any major assessment. Identifying and mastering core areas not only improves understanding but also boosts confidence during the test. A strategic review of these key subjects can help ensure you are prepared for the range of questions likely to appear.
Critical areas to cover include national economic indicators, market equilibrium, and the effects of government policies on the economy. Understanding how supply and demand interact, the role of central banks, and how fiscal tools like taxation and spending influence economic activity is also essential. Familiarity with these topics will provide a solid foundation to tackle various question formats and scenarios effectively.
Understanding Economic Theories for Exams
Grasping fundamental economic theories is essential for success in assessments that test your understanding of how economies function. These theories form the backbone of many questions, requiring not just memorization but also the ability to apply concepts to real-world scenarios. To excel, it’s important to familiarize yourself with both classical and contemporary economic models and the assumptions they rest on.
Key Economic Theories to Master
- Classical Theory: Focuses on the idea that free markets operate efficiently when left alone, with minimal government intervention.
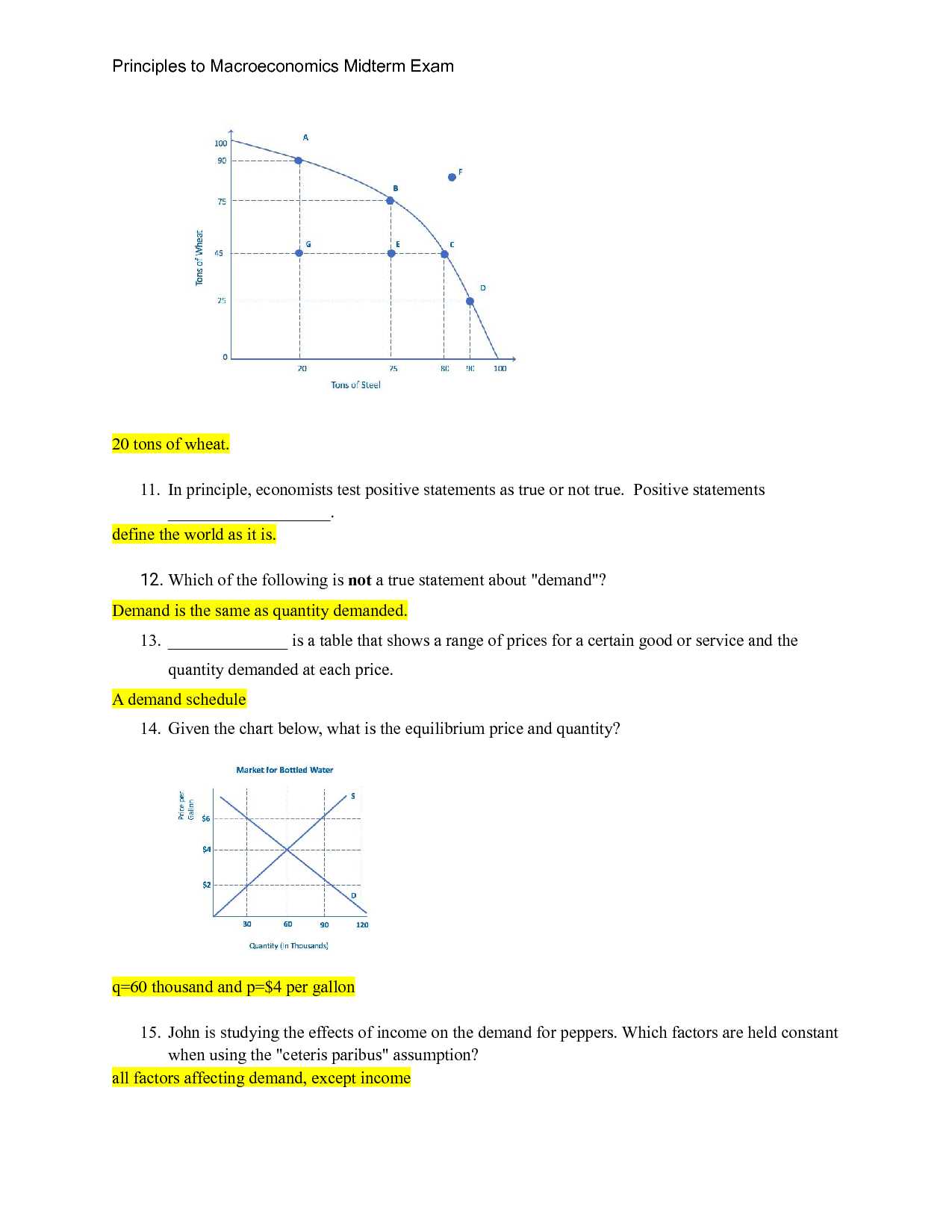
- Keynesian Theory: Emphasizes the role of government spending and fiscal policy in managing demand during economic downturns.
- Supply-Side Economics: Centers on policies aimed at increasing the supply of goods and services by cutting taxes and reducing regulations.
- Monetarism: Highlights the control of money supply as the key to managing inflation and stabilizing the economy.
How to Apply Economic Theories
- Understand the basic assumptions behind each theory and how they influence economic behavior.
- Be prepared to explain how different theories address key issues like inflation, unemployment, and economic growth.
- Practice applying these theories to various case studies, as they may require you to suggest solutions to hypothetical scenarios.
Top Formulas You Must Memorize
In any economics assessment, mastering key formulas is crucial for solving quantitative problems efficiently. These formulas serve as essential tools for analyzing relationships between different economic variables. Having a solid grasp of the core equations allows you to quickly apply them when needed, ensuring accuracy and saving valuable time during your test.
Essential Economic Formulas

- GDP (Gross Domestic Product): GDP = C + I + G + (X – M)
- C = Consumer spending
- I = Investment spending
- G = Government spending
- X – M = Net exports (exports – imports)
- Unemployment Rate: Unemployment Rate = (Number of unemployed / Labor force) x 100
- Inflation Rate: Inflation Rate = ((CPI in current year – CPI in base year) / CPI in base year) x 100
- Elasticity of Demand: Elasticity = % change in quantity demanded / % change in price
Additional Key Formulas

- Money Multiplier: Money Multiplier = 1 / Reserve Requirement Ratio
- Aggregate Demand: AD = C + I + G + (X – M) (same as GDP, used in different contexts)
- Budget Deficit: Budget Deficit = Government Spending – Tax Revenues
- Interest Rate (Fisher Equation): Nominal Interest Rate = Real Interest Rate + Inflation Rate
How to Analyze Economic Graphs
Interpreting economic graphs is a critical skill for understanding complex relationships between different variables. These visual representations simplify intricate data, making it easier to analyze trends, shifts, and movements. Being able to quickly interpret graphs helps not only in answering theoretical questions but also in applying concepts to real-world scenarios.
When analyzing economic graphs, focus on identifying the axes and what each represents. Understand the curves or lines plotted, as they usually reflect key economic variables like supply, demand, price, and output. Pay close attention to any shifts in curves, as these indicate changes in the underlying factors affecting the economy. The ability to draw conclusions from graph data is essential for providing accurate and well-supported answers in any assessment.
Steps to Effectively Analyze Graphs
- Examine the Axes: Identify what each axis represents–typically one axis shows the price, while the other shows quantity or output.
- Identify Key Curves: For example, supply and demand curves or aggregate demand and supply curves, depending on the graph.
- Look for Shifts: Determine if there are any shifts in the curves and understand the causes, such as changes in consumer preferences or government policies.
- Interpret the Equilibrium: Recognize where the curves intersect, as this point often represents market equilibrium.
Common Types of Economic Graphs
- Supply and Demand Curves: Shows the relationship between the price of a good and the quantity supplied or demanded.
- Phillips Curve: Illustrates the inverse relationship between inflation and unemployment in the short run.
- Production Possibility Frontier (PPF): Depicts the maximum possible output combinations of two goods that an economy can achieve, given its resources.
- Aggregate Demand and Supply Graph: Shows the total demand and supply in an economy and how they interact at different price levels.
Exam Strategies for Time Management
Effective time management during any important assessment is essential to ensure that you can complete all sections thoroughly without feeling rushed. Prioritizing tasks, pacing yourself, and allocating sufficient time to each question or section will help you stay focused and maximize your performance. Developing a solid strategy for managing time allows you to avoid panic and use your available time efficiently.
Start by familiarizing yourself with the total time allocated for the assessment and the number of questions or tasks you must complete. This will give you a clear idea of how much time you can devote to each section and prevent you from spending too long on any single part. Break down the test into manageable segments, ensuring you leave enough time for review at the end.
Key Time Management Tips
- Read Instructions Carefully: Spend a few minutes understanding the directions to avoid wasting time on incorrect assumptions.
- Prioritize Easier Questions: Begin with questions you find easier to build confidence and secure quick points.
- Set Time Limits for Each Section: Allocate a specific amount of time for each part of the assessment and stick to it to avoid spending too much time on one task.
- Skip and Return: If you get stuck on a difficult question, move on and return to it later to ensure you don’t lose valuable time.
Maximizing Review Time

- Leave Time for Revisions: Always aim to finish at least 5–10 minutes before the deadline to review your work and catch any errors.
- Quickly Check for Mistakes: During your review, focus on simple mistakes like miscalculations or missed points in your responses.
- Don’t Rush the Final Review: Use the final minutes wisely to check answers that carry more weight or are more difficult.
Common Mistakes to Avoid in Macroeconomics
When preparing for any major assessment in economics, certain mistakes can hinder your ability to achieve the best results. These errors often stem from misunderstandings of key concepts, misapplication of theories, or failing to fully answer questions. By being aware of these common pitfalls, you can refine your approach and increase your chances of success.
One frequent mistake is misinterpreting the question. It’s important to read carefully and ensure you understand what is being asked before jumping into an answer. Another common error is overlooking important assumptions that underpin economic models. Ignoring these details can lead to incomplete or inaccurate responses. Finally, failing to manage time effectively can result in rushed or unfinished answers, leaving valuable points untapped.
Key Mistakes to Avoid
- Misunderstanding the Question: Always take a moment to fully comprehend what is being asked before answering, especially in complex scenarios.
- Overlooking Assumptions: Many economic models rely on certain assumptions–neglecting these can lead to incorrect conclusions.
- Relying Too Much on Memorization: Focus on understanding concepts rather than rote memorization, which can limit your ability to apply knowledge flexibly.
- Failing to Show Work: In problems requiring calculations, make sure to show all steps and logic behind your solution, as partial credit may be awarded for the process.
- Time Mismanagement: Spending too much time on difficult questions can lead to missing easier ones–practice pacing to avoid this.
How to Avoid These Mistakes
- Practice Active Reading: When reading questions, underline key terms and instructions to ensure complete comprehension.
- Review Core Concepts: Consistently revisit fundamental economic principles and theories to understand their real-world application.
- Prioritize Time Management: Create a plan to allocate your time wisely across the entire assessment, leaving room for review.
Reviewing Aggregate Demand and Supply

Understanding the relationship between total demand and total supply in an economy is central to grasping how markets function and how various economic policies impact the broader economy. These two key concepts help explain fluctuations in price levels, output, and employment. A solid understanding of aggregate demand and supply is essential for analyzing shifts in the economy and their effects on economic activity.
Aggregate demand represents the total quantity of goods and services that consumers, businesses, the government, and foreign buyers are willing to purchase at different price levels. On the other hand, aggregate supply reflects the total output that producers are willing and able to provide at various price levels. The intersection of these two curves determines the equilibrium price and output in the economy.
Key Factors Affecting Aggregate Demand
- Consumer Confidence: When consumers feel optimistic about the economy, they are more likely to spend, increasing demand for goods and services.
- Government Policies: Changes in fiscal policy, such as taxation and government spending, can directly impact aggregate demand by influencing the purchasing power of households and firms.
- Interest Rates: Lower interest rates encourage borrowing and spending, which increases aggregate demand, while higher rates tend to reduce demand.
- Exchange Rates: A weaker currency can increase demand for a country’s exports, shifting the aggregate demand curve outward.
Factors Influencing Aggregate Supply

- Input Costs: A rise in the cost of labor, raw materials, or energy can reduce the quantity of goods and services firms are willing to supply at a given price level.
- Technology and Productivity: Improvements in technology or productivity can increase aggregate supply by making production more efficient and cost-effective.
- Government Regulations: Stricter regulations or taxes on businesses can increase costs and reduce the economy’s overall supply potential.
- Resource Availability: The availability of labor, capital, and natural resources affects the economy’s capacity to produce goods and services.
Important Economic Indicators to Know
When analyzing the health and performance of an economy, certain key metrics provide valuable insights into its overall direction and stability. These indicators are essential for understanding economic growth, inflation, unemployment, and other vital factors that influence both policy decisions and market trends. Familiarity with these indicators allows individuals to assess economic conditions and make informed predictions about future developments.
Some of the most widely followed metrics include the national income, the unemployment rate, inflation levels, and interest rates. Each of these measures provides a different perspective on how the economy is functioning, helping policymakers, businesses, and individuals make strategic decisions.
Key Economic Indicators
- Gross Domestic Product (GDP): This is a comprehensive measure of a country’s economic activity, representing the total value of all goods and services produced within a nation’s borders. A rising GDP indicates economic growth, while a decline may signal contraction.
- Unemployment Rate: This indicator shows the percentage of the workforce that is actively seeking work but is unable to find employment. High unemployment often signals economic distress, while low unemployment can indicate a healthy economy.
- Inflation Rate: Inflation measures the rate at which the general level of prices for goods and services rises, eroding purchasing power. A moderate level of inflation is typical of a growing economy, but excessive inflation can be harmful.
- Interest Rates: Set by central banks, interest rates influence borrowing costs for businesses and consumers. Higher interest rates can slow down economic activity, while lower rates encourage spending and investment.
Other Relevant Indicators

- Consumer Price Index (CPI): The CPI tracks changes in the price of a basket of common goods and services, providing a snapshot of the cost of living and inflation trends.
- Trade Balance: The trade balance measures the difference between a country’s exports and imports. A surplus indicates that a nation exports more than it imports, which can be a sign of economic strength.
- Productivity: Productivity measures how efficiently goods and services are produced. An increase in productivity generally leads to higher economic output and improved living standards.
Fiscal Policy Concepts You Should Understand

Understanding how governments manage their finances is essential for interpreting economic policies and their impact on the broader economy. Fiscal policy involves the use of government spending and taxation to influence economic conditions, such as inflation, unemployment, and overall growth. The tools of fiscal policy can be used to stabilize the economy during periods of recession or boom, making it a critical area of focus for both policymakers and analysts.
Governments may adopt either an expansionary or contractionary fiscal policy depending on the economic situation. Expansionary policies are typically used to stimulate economic activity by increasing government spending or cutting taxes, while contractionary policies aim to reduce inflationary pressures by decreasing spending or raising taxes. Understanding these approaches and their consequences is key to grasping the role of fiscal policy in shaping economic outcomes.
Types of Fiscal Policy

| Policy Type | Purpose | Typical Actions |
|---|---|---|
| Expansionary | Stimulate economic growth during a recession | Increase government spending, reduce taxes |
| Contractionary | Control inflation during periods of high growth | Decrease government spending, increase taxes |
Key Tools of Fiscal Policy

- Government Spending: Increasing or decreasing government expenditure directly affects aggregate demand, influencing economic activity.
- Taxation: Altering tax rates affects disposable income, consumer spending, and business investment, which in turn impacts overall economic demand.
- Public Debt: The government may borrow money to finance deficits, but excessive borrowing can lead to long-term economic challenges such as inflation and debt servicing costs.
Monetary Policy and Its Impact
Monetary policy plays a crucial role in regulating the economy by controlling the money supply and interest rates. It is primarily managed by a nation’s central bank and is aimed at achieving key economic objectives, such as maintaining price stability, fostering economic growth, and reducing unemployment. By adjusting the availability of money and the cost of borrowing, monetary policy can either stimulate or slow down economic activity, depending on the current needs of the economy.
There are two main types of monetary policy: expansionary and contractionary. Expansionary policy seeks to increase the money supply and lower interest rates to encourage borrowing and investment, especially during periods of economic downturn. Conversely, contractionary policy aims to reduce the money supply and raise interest rates to curb inflation when the economy is growing too quickly. Both types of policy have far-reaching consequences for consumers, businesses, and the overall economy.
Key Instruments of Monetary Policy
| Instrument | Purpose | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Open Market Operations | Buy or sell government securities to influence the money supply | Increasing money supply by purchasing securities, or reducing it by selling them |
| Discount Rate | Set the interest rate for loans to commercial banks | Lowering the rate encourages borrowing, while raising it discourages borrowing |
| Reserve Requirements | Set the minimum reserves that banks must hold against deposits | Reducing reserve requirements increases the money supply, while increasing them reduces it |
Economic Effects of Monetary Policy
- Inflation Control: By adjusting interest rates, central banks can either stimulate or reduce demand in the economy, helping to control inflationary pressures.
- Consumer Spending: Lower interest rates can reduce borrowing costs for consumers, encouraging spending and investment in the economy.
- Employment: Through stimulating economic activity, expansionary monetary policy can lower unemployment by encouraging businesses to hire more workers.
- Currency Value: Changes in interest rates can also influence the value of the national currency, affecting imports, exports, and the overall trade balance.
How to Interpret Economic Data
Interpreting economic data is essential for understanding the broader trends and dynamics that shape an economy. This data comes from a variety of sources, such as government reports, private sector studies, and central banks, providing insights into factors like inflation, growth, employment, and trade. The ability to analyze and interpret this data helps individuals, businesses, and policymakers make informed decisions about future actions and strategies.
To make sense of economic data, it is important to understand the context in which it is presented. Raw figures often need to be compared with historical trends, economic forecasts, and other related indicators to provide meaningful insights. Additionally, recognizing the limitations and assumptions behind the data helps avoid misinterpretations and supports more accurate conclusions.
Key Economic Indicators to Analyze
- Gross Domestic Product (GDP): Represents the total value of goods and services produced by a country, often used as an indicator of economic health.
- Unemployment Rate: Measures the percentage of the labor force that is actively seeking work, helping assess the health of the job market.
- Inflation Rate: Reflects the rate at which prices for goods and services rise, indicating the purchasing power of currency and cost of living changes.
- Interest Rates: Set by central banks, these rates influence borrowing costs, consumer spending, and overall economic activity.
Steps for Analyzing Economic Data
- Identify the Source: Ensure the data comes from a reliable and reputable source, such as government reports or trusted financial institutions.
- Compare with Historical Data: Look at past trends to understand if current data is part of a pattern or indicates a shift in economic conditions.
- Contextualize the Data: Consider external factors, such as global events or policy changes, which might be influencing the figures.
- Examine Relationships: Analyze how different data points, like GDP and inflation, interact to get a clearer picture of economic health.
- Draw Conclusions: Use the data to make informed decisions or predictions about economic trends and the potential impact on businesses and individuals.
Tips for Answering Multiple-Choice Questions

Multiple-choice questions are a common way to assess knowledge and understanding, and they require a strategic approach to answer effectively. With a variety of answer options, it’s important to carefully evaluate each question and option before making your selection. Taking the right steps can significantly improve accuracy and efficiency in responding to these types of questions.
Before diving into the options, it’s essential to read the question thoroughly. Often, subtle wording can give you hints about the correct answer. Pay attention to keywords such as “always,” “never,” “most likely,” and “except,” as these can help guide you in choosing the most accurate response. Additionally, eliminate answers that are obviously incorrect to increase your chances of selecting the right one.
Effective Strategies
- Understand the Question: Read each question carefully to make sure you understand what is being asked. Sometimes, questions can be tricky and require careful interpretation.
- Eliminate Incorrect Options: Cross out the answers that you know are wrong. This helps narrow down your choices and boosts your odds of selecting the right answer.
- Look for Clues in the Question: Frequently, questions contain hints that can help you identify the correct response. Pay close attention to the wording.
- Don’t Overthink: Trust your initial instinct. If you are unsure between two choices, think about your first impression and choose the answer that feels most familiar or logical.
What to Do When You’re Stuck

- Skip and Return: If a question is too difficult, move on and come back to it later. Sometimes, later questions can trigger ideas that help you solve the earlier ones.
- Make Educated Guesses: If you must guess, base your decision on any relevant knowledge or patterns you’ve identified in the test. Don’t leave a question blank.
How to Approach Short Answer Questions
Short answer questions often require you to provide a concise, focused response that directly addresses the topic at hand. Unlike multiple-choice questions, where you are given a set of options, short answer questions demand clarity, precision, and the ability to articulate your thoughts effectively in a few sentences. Approaching these questions with a clear strategy can help ensure that your responses are both accurate and well-organized.
The first step in tackling short answer questions is to carefully read the prompt. Pay attention to any keywords or specific instructions that indicate what is being asked. Sometimes, these questions will ask you to explain a concept, provide an example, or make a comparison, and identifying this will guide the structure of your response.
Effective Techniques
- Be Direct: Focus on answering the question directly. Avoid unnecessary information or long-winded explanations. Stick to the main point.
- Use Clear Examples: When possible, support your response with specific examples or relevant evidence to strengthen your argument.
- Stay Focused: Keep your response concise and to the point. If the question asks for a definition, provide a clear and precise explanation without going off-topic.
- Organize Your Thoughts: Structure your response logically, even in short answers. A clear and coherent flow of ideas will make your answer more understandable and convincing.
What to Avoid
- Avoid Over-Explaining: Short answer questions should be brief. Don’t waste time explaining unrelated concepts or providing excessive detail that doesn’t directly answer the question.
- Don’t Ramble: Stick to the essentials. Long, rambling answers can muddy the clarity of your response and lose the focus required to score well.
Utilizing Practice Exams for Preparation
Using practice assessments is one of the most effective strategies for preparing for any type of evaluation. These practice materials simulate real test conditions, allowing you to familiarize yourself with the format, types of questions, and pacing required. By incorporating these exercises into your study routine, you can identify areas where you need further review and build confidence in your ability to answer under time constraints.
One of the key benefits of working through practice exams is the opportunity to assess your knowledge and skills in a controlled environment. These exercises provide a clear picture of which topics you’ve mastered and which require more attention. Moreover, repeated practice can help reduce test anxiety by improving your familiarity with the testing process.
How to Effectively Use Practice Tests

- Simulate Real Conditions: Take practice tests in a quiet space with a timer. This helps replicate the time pressure you will face during the actual assessment and improves your time management skills.
- Review Mistakes Thoroughly: After completing each practice test, go over your wrong answers and understand why you made mistakes. This will help you avoid similar errors in the future.
- Track Your Progress: Keep a record of your practice test scores and note any patterns in the areas where you struggle. This will help you focus your future study sessions on the most challenging topics.
Maximizing Your Practice Test Experience
- Take Multiple Tests: Do not rely on just one practice test. The more you practice, the more comfortable and prepared you will become.
- Mix Up Question Types: Ensure your practice materials include a variety of question types, such as multiple-choice, short answer, and problem-solving. This will help you build skills for all aspects of the assessment.
- Time Yourself: Practice under timed conditions to improve your speed and efficiency. This will help you become more accustomed to managing your time during the actual assessment.
Key Economic Models to Study
Understanding core economic models is essential for grasping the principles that drive national and global economies. These models represent theoretical frameworks that explain how different economic forces interact and influence outcomes such as inflation, unemployment, and economic growth. By familiarizing yourself with these concepts, you can better interpret economic trends and make informed decisions when analyzing real-world situations.
Each model offers a unique perspective on economic behavior, helping to explain the relationships between various factors like government policy, consumer behavior, and market dynamics. Studying these models not only helps you understand past trends but also equips you with tools to predict future economic shifts.
The Aggregate Demand and Supply Model
The aggregate demand and supply model is a fundamental concept used to explain the total demand for and total supply of goods and services within an economy. It is used to analyze how changes in factors like consumer spending, business investment, and government policies can impact overall economic output. The model helps illustrate the relationship between inflation and unemployment, offering insights into business cycles and government intervention.
The IS-LM Model
The IS-LM (Investment Saving – Liquidity Preference Money Supply) model is another crucial framework in macroeconomics. It explores the relationship between the real economy (goods and services) and the money market. By examining the intersection of the IS curve (which represents equilibrium in the goods market) and the LM curve (which represents equilibrium in the money market), this model helps explain how monetary and fiscal policies can influence interest rates, output, and investment levels.
Both of these models are essential for understanding how various factors within an economy interact and how they can be managed to achieve desired economic outcomes such as stability, growth, and low inflation.
Managing Stress During Your Test
Test anxiety is a common challenge faced by many individuals, and managing this stress is crucial for performing well under pressure. Learning how to stay calm and focused can make a significant difference in your ability to recall information and think critically during your assessment. By implementing a few simple strategies, you can reduce stress and improve your overall performance when it matters most.
Effective stress management not only helps in staying composed but also aids in maintaining a clear mindset throughout the duration of the test. The key is to manage your emotions and reactions so that they do not interfere with your ability to focus on the questions at hand.
Preparation Is Key
One of the best ways to manage test-related stress is through adequate preparation. Knowing that you have covered all the necessary material will give you confidence going into the assessment. Additionally, breaking down your study sessions into smaller, manageable chunks can prevent feelings of being overwhelmed. Make a study plan and stick to it, ensuring that you allocate time for review and practice.
Breathing and Relaxation Techniques
During the test, if you feel overwhelmed, take a moment to practice deep breathing or relaxation techniques. Close your eyes for a few seconds, inhale deeply, hold for a moment, and exhale slowly. These simple exercises can help calm your nerves and allow you to focus on the task at hand. Taking short breaks when necessary can also prevent mental fatigue and improve concentration.
By incorporating these techniques, you can manage stress effectively and perform to the best of your abilities during your test.
Post-Test Review and Reflection
After completing your assessment, it’s important to take time for reflection. This process allows you to understand what worked well and where there is room for improvement. Reviewing your performance can help identify areas of strength, pinpoint weaknesses, and refine your preparation strategies for the future. It also provides an opportunity to reinforce your learning and better understand the material.
Reflecting on the experience not only improves your academic approach but also helps reduce any lingering stress or anxiety. Whether you performed well or encountered difficulties, taking a constructive approach to the post-test period can enhance your skills and mindset for upcoming challenges.
Steps to Effective Post-Test Reflection
Here are some practical steps to guide your review process:
- Analyze your performance: Look at the questions you found easy versus those you struggled with. This will help you identify which topics need more focus in your future studies.
- Review your mistakes: Understand why you made certain errors, whether due to misunderstanding the question, rushing, or missing details. Learning from these mistakes is crucial for improvement.
- Seek feedback: If available, review the test with your instructor or peers. Discussing your answers and the reasoning behind them can provide valuable insights.
- Adjust your study techniques: Based on your reflections, modify your approach for next time. This may include changing how you organize your study materials or how you approach practicing similar content.
Reflection Table
| Area | What Went Well | Areas for Improvement |
|---|---|---|
| Time Management | Completed most questions within the time limit | Improve speed on lengthy questions |
| Content Knowledge | Strong understanding of core concepts | Need more practice with specific theories |
| Question Understanding | Well understood direct questions | Misinterpreted a few multi-part questions |
By taking the time to review and reflect on your performance, you can build a stronger foundation for future challenges and continuously improve your study habits. This constructive process ensures that you are always growing and developing, making each assessment a valuable learning experience.