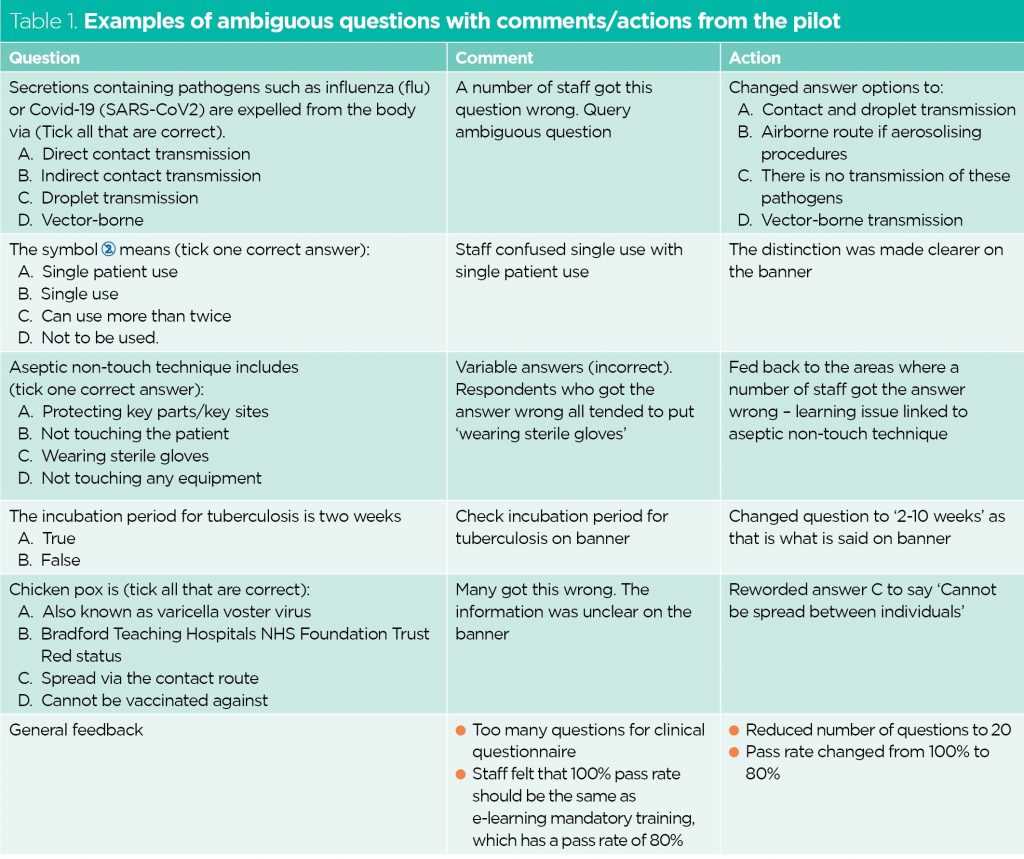
Maintaining a healthy environment, especially in healthcare settings, requires a thorough understanding of best practices aimed at minimizing the spread of harmful microorganisms. These practices involve specific techniques, protocols, and precautions designed to safeguard both patients and medical professionals from various risks.
Effective prevention measures involve a combination of sanitation, personal protective gear, and proper handling of contaminated materials. Whether you are working in a hospital, clinic, or any other setting, understanding these strategies is essential for reducing the likelihood of diseases being transmitted.
Educating healthcare workers and the general public about these practices ensures better outcomes and a safer environment. As new threats emerge, adapting to these challenges with the right knowledge is key to effective protection. In this section, we will explore common concerns and expert guidance on maintaining a safe and hygienic space for everyone.
Infection Control Questions and Answers
Understanding the best practices to reduce the spread of harmful pathogens is essential for ensuring a safe environment in healthcare settings. It is important to address common concerns and clarify effective methods for minimizing risks to patients, healthcare workers, and visitors. In this section, we will explore key topics related to safety procedures and offer practical solutions to frequently asked inquiries.
Common Concerns About Health Safety Protocols
- What are the most effective sanitation methods?
- How often should medical equipment be disinfected?
- What protective gear is essential for healthcare workers?
- When is hand hygiene most critical?
- What steps can be taken to prevent cross-contamination in patient care areas?
Expert Tips for Preventing Disease Spread
- Ensure proper use of personal protective equipment, including gloves, masks, and gowns.
- Implement regular handwashing routines for all staff members and visitors.
- Clean and sanitize all high-touch surfaces frequently to prevent microbial buildup.
- Educate all personnel on the proper disposal of contaminated materials.
- Monitor and improve ventilation systems to reduce airborne pathogens.
What is Infection Control?
Maintaining a safe environment within healthcare facilities requires strict measures to prevent the transmission of harmful microorganisms. These procedures aim to protect both patients and staff from various diseases. By implementing specific guidelines, it is possible to minimize the risk of contamination and ensure that safety standards are met across all levels of care.
Key Practices for Safe Environments
Effective practices include personal protective equipment, sterilization of medical instruments, and proper hygiene protocols. In addition, there are several important measures to ensure that harmful agents do not spread between individuals or surfaces. Here are some of the key aspects:
| Practice | Purpose | Frequency |
|---|---|---|
| Hand Hygiene | Reduces the spread of pathogens | Before and after patient care |
| Sanitizing Surfaces | Prevents contamination of workspaces | Hourly or as needed |
| Disposal of Contaminated Materials | Minimizes the risk of exposure to harmful agents | Immediately after use |
| Protective Equipment | Protects healthcare workers from harmful exposures | As required by procedures |
Ensuring a Safe Environment
By adhering to these guidelines, healthcare facilities can reduce the risk of cross-contamination, creating a safer space for patients and medical staff alike. Continuous education and monitoring help ensure that practices are followed consistently and correctly.
Why Infection Control is Crucial
Ensuring a healthy environment within healthcare settings is essential for protecting both patients and staff. The spread of harmful pathogens can lead to severe consequences, including outbreaks of disease, longer recovery times, and even death. Effective measures are needed to prevent contamination and mitigate the risks associated with cross-contamination, particularly in high-risk areas like hospitals and clinics.
Impact on Patient Health
Minimizing the spread of harmful agents directly contributes to better patient outcomes. When proper precautions are not in place, patients, especially those with weakened immune systems, become highly vulnerable to acquiring additional illnesses. These secondary infections can complicate recovery and extend hospitalization.
Protecting Healthcare Workers

Healthcare workers are on the front lines, interacting with patients who may be carrying pathogens. Without rigorous safety protocols, medical staff risk exposure to dangerous microorganisms, which can lead to illness, burnout, and increased healthcare costs. Implementing strict procedures reduces this risk and ensures staff are well-protected while delivering care.
Common Methods of Preventing Infections
To ensure a safe environment, it is crucial to implement a range of practices aimed at reducing the transmission of harmful microorganisms. These methods play a significant role in safeguarding both patients and healthcare providers. By following these steps, the spread of diseases can be minimized, and overall health can be better protected in high-risk settings.
Proper Hygiene and Sanitation
One of the most effective ways to prevent the spread of pathogens is through regular cleaning and proper hygiene practices. Ensuring that hands are washed frequently, especially after direct contact with patients or contaminated surfaces, is essential. Disinfecting equipment and high-touch surfaces regularly helps to limit microbial growth and prevents cross-contamination between individuals.
Use of Protective Equipment
Personal protective equipment (PPE) serves as a barrier between healthcare workers and potential contaminants. Items such as gloves, masks, face shields, and gowns help prevent the direct transmission of harmful agents. PPE must be used correctly and consistently, especially when dealing with high-risk procedures or patients known to carry infectious agents.
How to Properly Disinfect Surfaces
Maintaining a hygienic environment requires effective cleaning practices, especially in areas that are frequently touched or exposed to contaminants. Proper surface disinfection reduces the risk of harmful microorganisms being transferred to people or objects, contributing to a safer space. The right methods ensure that pathogens are eliminated effectively, preventing potential health risks.
The process begins by selecting the appropriate cleaning agents that are proven to kill a wide range of harmful agents. Once the right product is chosen, surfaces must be thoroughly wiped down, ensuring that all areas are covered. Special attention should be given to high-touch surfaces, such as door handles, light switches, and countertops, as these are more likely to harbor pathogens.
Additionally, it’s important to allow sufficient contact time for disinfectants to work. Following the manufacturer’s instructions regarding application time ensures the maximum effectiveness of the cleaning solution. For environments with high contamination risks, regular disinfection routines should be established, particularly in healthcare or communal spaces.
Personal Protective Equipment Guidelines
Proper use of personal protective gear is essential for maintaining a safe environment, especially when interacting with potentially harmful substances or individuals. These protective items create a barrier between the wearer and various hazards, significantly reducing the risk of exposure to dangerous pathogens or chemicals. Following clear guidelines ensures that the equipment is used correctly and effectively.
Gloves, masks, face shields, and gowns are some of the most common types of protective gear. Each type serves a specific purpose, and selecting the right one for the task is crucial. For example, gloves protect hands from direct contact with contaminants, while masks prevent the inhalation of airborne particles. Face shields provide additional protection for the eyes and face, while gowns cover clothing and skin from potential splashes or contact with harmful agents.
Proper fit is equally important to ensure that protective gear functions as intended. Ill-fitting gloves or masks can compromise safety, allowing contaminants to enter. Additionally, it is essential to follow correct procedures when donning and removing protective items to avoid accidental exposure. Regularly inspecting and replacing worn-out equipment also contributes to maintaining a safe environment.
Hand Hygiene Best Practices
Maintaining proper hand hygiene is one of the most effective methods to prevent the spread of harmful microorganisms. This simple yet crucial practice helps to safeguard both individuals and the environment by reducing the likelihood of contamination. Regularly cleaning hands ensures that pathogens are removed before they can be transferred to surfaces or others.
When washing hands, it is essential to use soap and clean water, scrubbing all areas, including the palms, backs of hands, between the fingers, and under the nails. The process should last for at least 20 seconds to ensure thorough cleaning. In situations where water is unavailable, alcohol-based hand sanitizers with at least 60% alcohol can be an effective alternative.
It is also important to wash hands at key moments, such as before and after eating, using the restroom, caring for a patient, or touching potentially contaminated surfaces. Additionally, when using hand sanitizers, apply enough product to cover the entire surface of the hands and rub together until dry. Regular practice of these guidelines significantly reduces the risk of transmitting harmful pathogens.
Role of Vaccines in Infection Prevention
Vaccination plays a crucial role in reducing the spread of harmful diseases by stimulating the body’s immune system to recognize and fight specific pathogens. This proactive approach helps protect individuals and communities by preventing serious illness and reducing the overall burden of disease. By providing immunity against certain harmful agents, vaccines are a cornerstone of public health efforts.
How Vaccines Work
Vaccines introduce a weakened or inactivated form of a pathogen into the body, prompting the immune system to produce antibodies without causing illness. This process trains the immune system to recognize the pathogen if it is encountered again in the future. Some key benefits include:
- Prevention of severe diseases and complications
- Reduction in the spread of disease within communities
- Protection for vulnerable groups, such as the elderly and immunocompromised
Types of Vaccines
There are various types of vaccines, each designed to target different diseases. Some of the most common types include:
- Inactivated vaccines: Contain killed versions of pathogens.
- Live attenuated vaccines: Contain weakened forms of the pathogen.
- Subunit, recombinant, or conjugate vaccines: Contain pieces of the pathogen, such as proteins or sugars.
By utilizing these vaccines, individuals can significantly reduce their risk of contracting and spreading infectious diseases, contributing to the overall health and well-being of the population.
Managing Antibiotic Resistance in Healthcare
Antibiotic resistance is a growing challenge in healthcare settings, where the overuse and misuse of antimicrobial drugs contribute to the development of resistant strains of bacteria. As these pathogens become more difficult to treat, the effectiveness of standard treatments diminishes, leading to longer hospital stays, increased medical costs, and higher mortality rates. Managing this issue requires a coordinated approach involving healthcare professionals, patients, and policymakers to ensure the responsible use of antibiotics.
Strategies for tackling antibiotic resistance include implementing stricter prescribing guidelines, promoting stewardship programs, and educating both healthcare providers and the public on the proper use of antibiotics. Additionally, monitoring and tracking resistance patterns within healthcare facilities is critical to adapting treatment protocols and minimizing the spread of resistant strains.
| Strategy | Description |
|---|---|
| Antibiotic Stewardship | Programs focused on optimizing the use of antibiotics, ensuring they are prescribed only when necessary and appropriate. |
| Surveillance and Monitoring | Regular tracking of resistance patterns to identify emerging threats and adapt treatment strategies accordingly. |
| Education | Raising awareness among healthcare providers and the public about the risks of overuse and misuse of antibiotics. |
By integrating these practices into daily healthcare operations, the spread of resistant pathogens can be minimized, improving patient outcomes and ensuring the continued effectiveness of antimicrobial treatments.
Cleaning Procedures in Healthcare Settings

Maintaining a clean environment in healthcare facilities is vital for ensuring the safety and well-being of patients, staff, and visitors. Proper cleaning practices help reduce the risk of harmful agents being transmitted through surfaces or air. In healthcare settings, where the risk of contamination is high, effective cleaning protocols must be followed rigorously to minimize the spread of pathogens.
The cleaning process typically involves several steps, including the removal of visible dirt, the use of appropriate cleaning agents, and thorough disinfection of surfaces. High-touch areas such as door handles, bedrails, and medical equipment should be cleaned frequently throughout the day to prevent the buildup of harmful microorganisms. Additionally, ensuring that cleaning materials such as cloths and mops are regularly changed or disinfected helps avoid cross-contamination.
Key Areas for Regular Cleaning:
- Patient Rooms: All surfaces, including furniture, bed linens, and medical devices, should be cleaned and disinfected after each patient’s discharge.
- Bathrooms and Restrooms: These areas require frequent attention to prevent the spread of contaminants, particularly in shared spaces.
- Common Areas: Hallways, waiting rooms, and lounges should be cleaned thoroughly to maintain a hygienic environment for visitors and staff.
Effective Cleaning Tools:
- Microfiber Cloths: These are effective at trapping dirt and reducing the spread of pathogens, making them a preferred choice in healthcare cleaning.
- Disinfectants: Use EPA-approved disinfectants that are proven to eliminate harmful bacteria, viruses, and fungi.
- Disposable Wipes: For quick and efficient cleaning of high-touch surfaces, disposable wipes are ideal for preventing cross-contamination.
By following these procedures, healthcare facilities can maintain a clean, safe environment, ensuring the protection of all those who rely on the facility’s services.
Dealing with Healthcare-Associated Infections
Healthcare-associated illnesses pose a significant challenge in medical environments, affecting patients who are already vulnerable due to pre-existing conditions or treatments. These complications are often caused by harmful microorganisms that spread within hospitals or clinics. Effectively managing such risks requires a multi-layered approach that focuses on prevention, early detection, and swift treatment to minimize harm and improve patient outcomes.
Prevention Strategies
Preventing the spread of these conditions within healthcare settings is paramount. The most effective strategies include:
- Strict hand hygiene protocols for healthcare workers.
- Use of personal protective equipment (PPE) in areas of high risk.
- Regular cleaning and disinfection of medical equipment and patient rooms.
- Educating patients and staff about recognizing early signs of potential complications.
Early Detection and Management

Detecting these illnesses early is crucial for preventing their spread. Routine screenings, monitoring patient symptoms, and isolating affected individuals are essential steps in minimizing transmission. When necessary, targeted treatments are administered to control the spread of resistant pathogens.
| Action | Description |
|---|---|
| Hand Hygiene | Regular washing and sanitizing to reduce microorganism spread. |
| Use of PPE | Protective gear like gloves and masks to prevent contact with contaminated surfaces or fluids. |
| Surveillance | Ongoing monitoring of patient health and staff interactions to identify potential outbreaks. |
By focusing on these key areas, healthcare facilities can better manage and reduce the incidence of illnesses acquired within medical settings, ensuring a safer environment for patients and staff alike.
Infection Control in Surgical Environments

In surgical settings, maintaining a sterile environment is essential to minimize the risk of harmful microorganisms affecting patients undergoing procedures. The high-stakes nature of these environments, combined with the complexity of surgical procedures, makes it crucial to implement rigorous hygiene practices, safety measures, and infection prevention strategies to ensure the best possible outcomes for patients.
Several key factors contribute to the prevention of contamination during surgical procedures. These include proper preparation of the operating room, the use of sterile instruments, and the strict adherence to personal protective equipment guidelines. Surgeons, nurses, and support staff must all follow standardized procedures to reduce the risk of introducing pathogens into the surgical site.
Key Practices in Surgical Environments:
- Pre-Surgical Preparation: Ensuring the operating room is thoroughly cleaned and disinfected before any procedure, and verifying the sterility of surgical instruments.
- Use of Sterile Equipment: All tools, including scalpels, forceps, and needles, must be sterilized before use to prevent cross-contamination.
- Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): Surgeons and other medical staff must wear appropriate PPE such as gloves, masks, gowns, and face shields to minimize the risk of contamination during procedures.
Post-Surgical Considerations:
- Wound Care: Proper dressing and care of the surgical site to ensure healing without complications, using sterile materials.
- Patient Monitoring: Close monitoring of patients for signs of complications or post-operative risks, with prompt intervention when necessary.
By adhering to these critical protocols, surgical teams can significantly reduce the risk of complications and ensure a safer, more effective experience for patients undergoing surgery.
Importance of Isolation Precautions
In healthcare settings, taking steps to limit the spread of harmful microorganisms is crucial, especially when dealing with patients who are more vulnerable to complications. Isolation measures are designed to prevent the transmission of pathogens between patients, healthcare workers, and the environment. These practices help protect both the patient and the broader community from potential harm.
Preventing the Spread of Harmful Pathogens
Isolation precautions are essential in limiting the transmission of infectious agents that can spread through direct or indirect contact. By separating individuals who may be carrying contagious microorganisms, healthcare facilities can mitigate the risk of an outbreak and ensure that other patients, staff, and visitors are not exposed.
Key Types of Isolation Precautions:
- Contact Precautions: Used when harmful organisms can be spread by touching surfaces or people. This involves the use of gloves, gowns, and disinfecting surfaces regularly.
- Airborne Precautions: Required for diseases that can be transmitted through the air. This includes using specialized ventilation systems and masks, like N95 respirators.
- Droplet Precautions: Applied for illnesses spread through droplets in the air, such as during coughing or sneezing. Masks and distance are essential in these cases.
Reducing Risks in Healthcare Settings
Implementing proper isolation strategies is not only crucial for the safety of patients but also for the protection of medical personnel. These precautions help limit cross-contamination, reduce the burden of healthcare-associated complications, and contribute to a safer treatment environment. In addition, these measures support public health by preventing the spread of resistant organisms and other contagious diseases.
By adhering to the correct isolation protocols, healthcare facilities can minimize the risk of transmission, ensuring a safer and more controlled environment for both patients and healthcare workers.
Training Healthcare Workers on Infection Control

Educating healthcare professionals on proper practices to prevent the spread of harmful microorganisms is essential in maintaining a safe environment for both patients and staff. Comprehensive training programs equip medical teams with the knowledge and skills to implement protocols effectively, ensuring that all individuals in a healthcare facility are protected from potential risks. Continuous learning and practice are key to minimizing hazards in clinical settings.
Key Areas of Focus in Healthcare Training
Healthcare workers need to be well-versed in several core areas to properly prevent the spread of diseases. These training modules typically cover:
- Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) Usage: Ensuring staff know how to properly wear, use, and dispose of protective gear such as gloves, masks, gowns, and eye protection.
- Hand Hygiene Techniques: Emphasizing the importance of regular hand washing and the use of sanitizers to reduce the risk of cross-contamination.
- Safe Handling of Equipment: Educating workers on how to sterilize and manage medical tools and devices to avoid contamination.
- Environmental Cleaning Practices: Training on how to clean and disinfect patient care areas, medical devices, and frequently touched surfaces.
Methods for Effective Training
To ensure that healthcare workers are properly trained and up-to-date on the latest best practices, various methods can be used:
- Hands-on Practice: Interactive sessions and practical exercises allow staff to practice correct techniques in real-life scenarios.
- Simulation Drills: Simulating emergencies or outbreaks helps workers learn how to act efficiently under pressure while maintaining proper protocols.
- Ongoing Education: Regular workshops, refresher courses, and access to updated materials keep healthcare professionals informed about evolving standards and regulations.
Proper training not only improves the safety of patients but also reduces the burden on healthcare systems by decreasing the likelihood of outbreaks and complications. By investing in continuous education, healthcare institutions ensure that their workforce is always prepared to manage risks effectively.
Impact of Infection Control on Public Health

Proper measures to prevent the spread of harmful microorganisms have a significant influence on the overall well-being of the population. When healthcare facilities, communities, and individuals follow effective practices, they contribute to the broader effort of safeguarding public health. These measures reduce the risk of outbreaks, improve health outcomes, and ensure that resources are used efficiently to protect society at large.
The role of preventive strategies extends beyond individual care and directly influences the collective health of a society. With the rise of new diseases and emerging threats, it has become increasingly clear that systematic approaches to managing health risks are vital. A robust framework helps mitigate the spread of illnesses, especially in vulnerable populations, such as the elderly, children, and those with compromised immune systems.
Key Benefits to Public Health

Implementing comprehensive precautions has numerous advantages for the community:
- Reduced Transmission of Diseases: Preventive practices reduce the likelihood of pathogens spreading from one individual to another, decreasing the overall burden of disease in communities.
- Lower Healthcare Costs: By reducing the incidence of preventable illnesses, hospitals and clinics can allocate resources more effectively, minimizing the need for costly treatments and hospitalizations.
- Improved Health Equity: Ensuring that all individuals have access to the same preventive measures creates a more equitable healthcare system, where risks are mitigated for all, regardless of socio-economic background.
Public Health Strategies to Support Infection Prevention
Beyond healthcare facilities, several public health strategies are key to supporting preventive measures:
- Community Awareness Campaigns: Public education about hygiene practices, vaccination, and safe behaviors can empower individuals to take proactive steps in safeguarding their health.
- Collaboration Between Organizations: Partnerships between governmental agencies, non-profits, and healthcare systems create a unified approach to tackling health risks at local, regional, and national levels.
- Surveillance and Monitoring: Ongoing tracking of disease outbreaks and trends helps public health authorities respond quickly to emerging threats and implement containment measures effectively.
By prioritizing these efforts, society can ensure a healthier future, reduce the spread of harmful pathogens, and increase resilience against potential public health crises.
Key Infection Control Policies to Follow
Adhering to well-established guidelines for safeguarding health within healthcare settings and communities is crucial for minimizing the spread of harmful pathogens. A structured approach, supported by clear policies, ensures a consistent, effective response to potential health risks. These policies cover a wide range of practices that help protect both patients and healthcare providers, creating a safer environment for all.
Implementing these measures is not only about preventing individual cases but also about ensuring a holistic approach that benefits public health overall. Every healthcare facility and community should have a set of rules in place that are regularly reviewed and updated based on the latest evidence and expert recommendations.
Essential Policies to Implement
To maintain a healthy environment, the following guidelines should be followed:
- Hand Hygiene: Ensure regular handwashing with soap and water or using alcohol-based hand sanitizers, especially before and after patient care, to reduce the transmission of harmful microorganisms.
- Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): Mandate the use of appropriate PPE, such as gloves, masks, gowns, and eye protection, when interacting with patients or handling contaminated materials.
- Cleaning and Disinfection: Establish a routine for cleaning and disinfecting surfaces, equipment, and other frequently touched areas to prevent cross-contamination.
- Isolation Protocols: Set up clear guidelines for isolating patients with contagious diseases to prevent the spread of illnesses to others in healthcare settings.
- Vaccination Policies: Ensure that healthcare workers and patients are vaccinated according to current guidelines to reduce the risk of outbreaks within the facility.
Training and Awareness
To ensure the effectiveness of these policies, continuous training and awareness programs should be implemented. These initiatives should focus on:
- Staff Education: Regular training on hygiene, PPE use, and emergency procedures to ensure everyone is well-prepared to handle any situation.
- Patient Education: Informing patients about their role in maintaining a safe environment, including practicing good hygiene and following isolation protocols when necessary.
- Auditing and Feedback: Conducting regular audits of practices to identify areas for improvement and providing feedback to staff to reinforce compliance.
By following these essential policies, healthcare facilities can create a safer environment for both patients and workers, significantly reducing the risk of harm and ensuring the well-being of all involved.