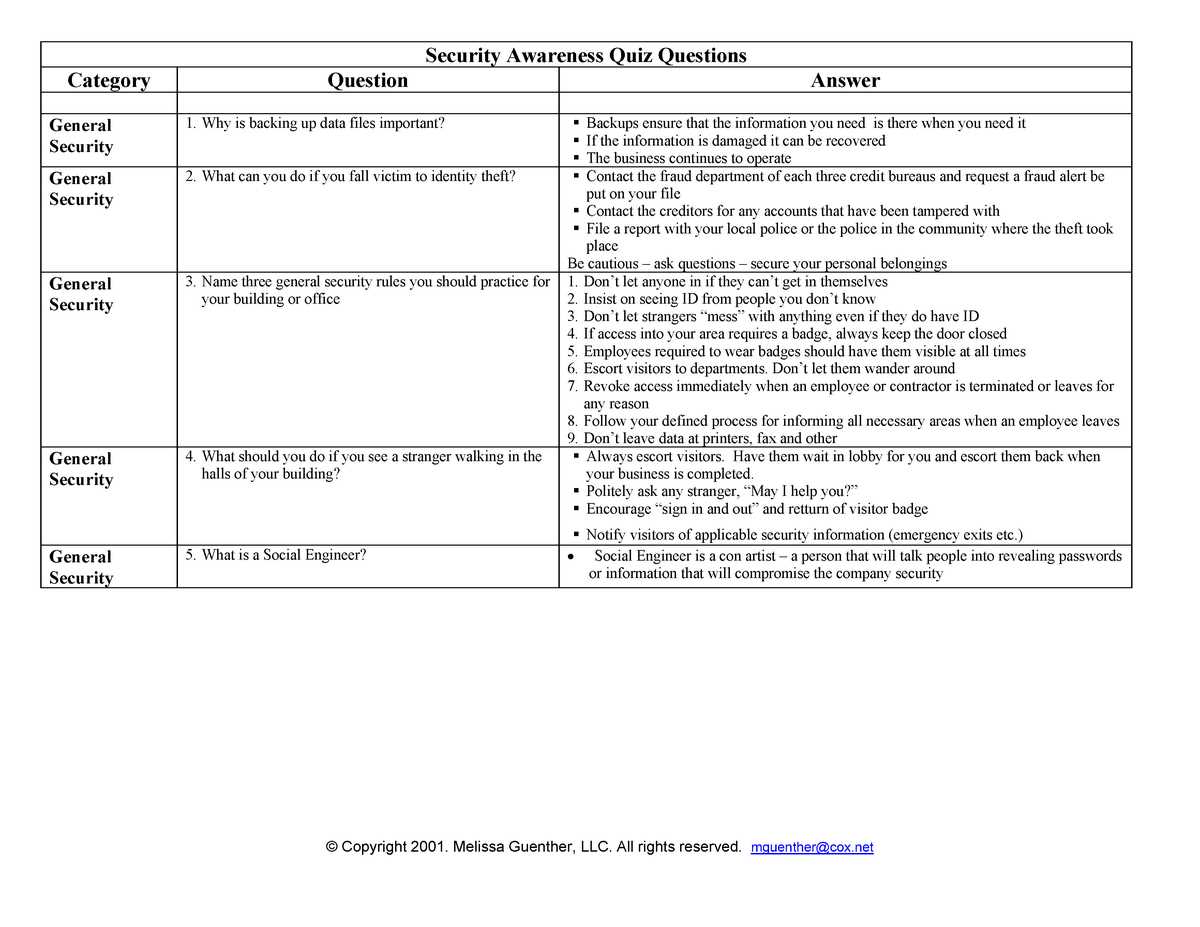
In today’s digital world, protecting sensitive data has never been more crucial. Understanding the fundamental principles of security and how to safeguard information is vital for anyone pursuing a career in cybersecurity. Whether you are preparing for a professional certification or simply looking to strengthen your security knowledge, grasping the core concepts is key to success.
Security practices encompass a wide range of techniques designed to keep data safe from unauthorized access, theft, and disruption. These practices involve various strategies, including risk management, encryption, and monitoring, which ensure that sensitive information remains confidential and intact. By mastering these concepts, individuals can significantly reduce vulnerabilities in their systems and networks.
Preparing for assessments related to this field requires a comprehensive understanding of the topics involved. Success hinges on the ability to recognize common threats, implement protective measures, and stay informed about emerging risks. In this guide, we will explore the essential knowledge areas needed to excel in certification tests focused on cybersecurity best practices, helping you feel confident in applying your expertise in real-world situations.
Understanding Information Assurance Principles

Protecting critical data is fundamental to maintaining the integrity of any organization. It involves a collection of practices and policies aimed at ensuring that systems remain secure from unauthorized access, alteration, or destruction. The goal is not only to defend against external threats but also to manage risks associated with the handling of sensitive material across various platforms and networks.
Core Concepts of Security Practices
At the heart of securing data lies the concept of confidentiality, which ensures that only authorized individuals have access to sensitive information. Alongside this, integrity focuses on maintaining the accuracy and completeness of data, ensuring that it is not tampered with or corrupted during transmission or storage. Lastly, availability ensures that information is accessible to authorized users when needed, preventing disruptions that could harm an organization’s operations.
Risk Management and Protection Strategies

Effective security strategies depend on identifying potential threats and evaluating the risks they pose. Risk management involves assessing vulnerabilities and implementing measures to minimize the likelihood of breaches. These measures include access controls, encryption techniques, and regular monitoring of systems for signs of unauthorized activity. By combining these elements, individuals can establish a robust defense against potential security incidents and ensure the continued safety of valuable data.
Key Concepts of Information Assurance
To effectively safeguard sensitive data and maintain secure systems, it is crucial to understand the underlying principles that guide security practices. These concepts serve as the foundation for building and maintaining secure networks, devices, and data management strategies. Mastering these core ideas allows professionals to better defend against threats and ensure the integrity of their digital assets.
Fundamental Security Pillars

The core elements of security focus on three primary pillars: confidentiality, integrity, and availability. These principles ensure that critical data remains protected, accurate, and accessible when needed.
- Confidentiality: Ensures that sensitive information is accessible only to authorized individuals or entities.
- Integrity: Maintains the accuracy and trustworthiness of data, preventing unauthorized modifications.
- Availability: Guarantees that authorized users can access data and resources when required, without disruptions.
Security Controls and Risk Mitigation
Implementing proper controls is essential to minimize vulnerabilities and mitigate potential risks. Security professionals employ various strategies to protect networks, including preventive, detective, and corrective measures.
- Preventive controls: Measures like firewalls and encryption to stop security breaches before they happen.
- Detective controls: Tools such as intrusion detection systems that monitor and identify suspicious activities.
- Corrective controls: Actions like restoring systems from backups to recover from security incidents.
By understanding these concepts and their role in cybersecurity, individuals can effectively contribute to creating secure environments, reducing the risk of breaches, and improving overall protection strategies.
Why Awareness Matters in Information Security

In the realm of cybersecurity, being informed and vigilant is essential for maintaining the safety of sensitive data and systems. Many security breaches occur due to human error, which can be prevented with proper knowledge and training. Recognizing potential risks, understanding security protocols, and knowing how to react to threats are crucial for minimizing vulnerabilities and defending against attacks.
Individuals within an organization play a key role in protecting against cyber threats. Their ability to identify phishing emails, recognize suspicious activity, and follow security best practices is often the first line of defense. The more aware employees and users are of potential risks, the more effectively they can contribute to a secure environment.
Additionally, as technology and cyber threats continue to evolve, staying up-to-date on the latest security trends and tools becomes even more important. An ongoing commitment to learning ensures that everyone involved can adapt to new challenges and prevent attacks before they happen. Cultivating a culture of security awareness helps reduce the likelihood of costly breaches and promotes a proactive security posture across the entire organization.
Preparing for the Information Assurance Exam
Proper preparation is key to succeeding in any security-related certification or assessment. Understanding the core principles, mastering relevant concepts, and practicing real-world scenarios will help you build confidence and improve your performance. By organizing your study approach and focusing on the most critical topics, you can effectively prepare for the challenges ahead.
Study Materials and Resources
Selecting the right study materials is essential. Focus on books, online courses, and resources that offer comprehensive coverage of the essential concepts. Using a variety of learning methods, such as video tutorials, practice tests, and group study sessions, can help reinforce your understanding and make complex topics easier to grasp.
| Resource Type | Purpose | Recommended Sources |
|---|---|---|
| Textbooks | Foundational knowledge and detailed explanations | Security textbooks, official certification guides |
| Online Courses | Interactive lessons and expert-led instruction | Udemy, Coursera, LinkedIn Learning |
| Practice Tests | Simulated exam conditions and question types | Quizlet, ExamSim, TestPrep |
Key Topics to Focus On
Familiarize yourself with the most important topics and areas that are typically covered in assessments. Understanding these key concepts will help you approach questions with confidence and improve your chances of success.
- Risk management and mitigation strategies
- Access controls and authentication methods
- Network security protocols and technologies
- Incident response and recovery procedures
- Legal and ethical considerations in cybersecurity
By focusing on these areas, you will be better equipped to tackle the material and perform well under exam conditions. Structured and targeted preparation is the most effective approach to mastering the concepts needed for certification success.
Common Questions in the Awareness Exam
When preparing for a security-related certification or assessment, it’s essential to understand the types of questions you are likely to encounter. These questions are designed to test your knowledge of key concepts, your ability to apply them in practical scenarios, and your understanding of best practices for safeguarding sensitive data and systems. Familiarizing yourself with common question formats can help you feel more confident and prepared when the time comes.
Most assessments focus on various security aspects, including risk management, network security, and threat detection. By practicing with questions that cover these areas, you can ensure that you are ready to address different types of challenges that may arise during the test.
| Question Type | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Multiple Choice | Test knowledge of key concepts and terminology | What is the primary goal of encryption? |
| Scenario-Based | Assess the ability to apply concepts to real-world situations | You are tasked with securing a company’s internal network. What is your first step? |
| True/False | Test understanding of basic facts and security principles | Firewalls are only useful for preventing external threats. (True/False) |
| Fill-in-the-Blank | Test detailed knowledge of specific terms and definitions | The process of verifying a user’s identity is called ________. |
By reviewing and practicing these types of questions, you can gain a better understanding of the key topics and improve your ability to recognize and answer similar questions when they appear. A well-rounded approach to preparation will help you tackle even the most challenging aspects of the assessment with confidence and accuracy.
Best Practices for Protecting Information
Securing valuable data and systems is a fundamental part of maintaining the integrity and trustworthiness of any organization. Employing the right protection measures helps to prevent unauthorized access, ensure data privacy, and mitigate potential risks. By following proven security practices, individuals and businesses can create a strong defense against evolving cyber threats.
Encryption is one of the most effective methods for safeguarding sensitive data, especially when stored or transmitted across networks. By converting information into unreadable formats, it ensures that even if data is intercepted, it cannot be accessed without the proper decryption key.
Another critical aspect is access control. Limiting access to critical systems and data only to those with a legitimate need reduces the risk of breaches. Role-based access ensures that employees only have the permissions necessary to perform their tasks, minimizing the potential for accidental or malicious actions.
Regular software updates are also essential. Keeping systems, applications, and antivirus software up-to-date ensures that known vulnerabilities are patched and that systems are protected against the latest threats. Regular audits and penetration tests help identify weaknesses before attackers can exploit them.
Finally, educating users and employees on security best practices, such as recognizing phishing attempts, using strong passwords, and avoiding suspicious links, is a key component of a comprehensive security strategy. Human error is often the weakest link in cybersecurity, but with proper training, the risk can be significantly reduced.
By integrating these best practices into daily operations, organizations can ensure that their data remains secure and that their systems are resilient in the face of growing security challenges.
Essential Security Policies to Know

Effective security policies form the backbone of any organization’s cybersecurity strategy. These guidelines set clear standards for how sensitive data and systems should be protected, who can access them, and what actions should be taken in the event of a breach. By establishing strong security policies, businesses can create a culture of protection and ensure they comply with legal and industry standards.
One of the most important policies is the Acceptable Use Policy (AUP), which outlines the appropriate use of company networks, devices, and resources. It helps employees understand what is permissible in terms of internet usage, data sharing, and accessing company systems, ensuring that all actions align with the organization’s security goals.
The Data Protection Policy is another critical guideline, detailing how personal and sensitive information must be handled, stored, and transmitted to prevent unauthorized access. This policy is particularly important for complying with privacy regulations such as GDPR or CCPA, which require businesses to safeguard customer data and inform them about how their information is used.
Incident Response Policy outlines the procedures to follow when a security breach or attack occurs. This policy ensures a swift and coordinated response, reducing the impact of the breach and aiding in a quicker recovery. It defines roles and responsibilities, communication strategies, and steps for containment, investigation, and reporting.
Additionally, the Access Control Policy sets rules for who can access various systems and data, based on their role within the organization. This ensures that only authorized individuals can view or modify sensitive information, reducing the risk of internal threats.
By familiarizing oneself with these essential policies, individuals and organizations can better protect their assets, maintain compliance with regulations, and enhance overall security posture. Effective implementation and enforcement of security policies are key to preventing potential breaches and safeguarding organizational integrity.
How to Tackle Difficult Exam Questions
Facing challenging questions during a test can be a stressful experience, but with the right strategies, you can approach them with confidence. It’s essential to remain calm and use systematic techniques to break down the question and find the best solution. Rather than getting overwhelmed, focusing on the structure of the question and applying your knowledge step-by-step can help you navigate through difficult sections more effectively.
Here are some practical tips for handling tough questions:
- Read Carefully: Make sure you fully understand what is being asked. Sometimes, difficult questions are tricky because the wording is complex. Read the question multiple times if necessary to grasp its meaning.
- Identify Keywords: Highlight or underline important terms that can guide you toward the right answer. Keywords can give clues about what the question is testing and help you focus on relevant concepts.
- Eliminate Obvious Mistakes: If the question has multiple-choice options, quickly rule out answers that are clearly incorrect. This will increase your chances of selecting the correct option.
- Break Down the Question: For more complex questions, divide them into smaller parts. Tackle each part separately and solve them one by one to make the problem more manageable.
- Use Process of Elimination: If you’re unsure of the answer, eliminate the least likely choices first. This can improve your odds if you need to make an educated guess.
- Stay Calm: Don’t let frustration build up. If a question is especially difficult, move on to other sections and return to it later with a fresh perspective.
By using these strategies, you can reduce the stress of difficult questions and increase your chances of answering correctly. Practice these techniques during preparation to enhance your confidence and performance when it matters most.
Common Misconceptions in Information Security
Many people have misconceptions about how to protect digital assets and secure systems. These misunderstandings can lead to gaps in protection, leaving networks and sensitive data vulnerable to attacks. It’s important to address these myths and clarify the most effective practices for keeping systems safe. A clear understanding of the core principles helps ensure that individuals and organizations follow appropriate security measures.
Myth 1: Only Large Companies Are Targeted
Many believe that cybercriminals only target large enterprises with valuable data, but this is far from true. Small businesses and individuals are often seen as easier targets because they may not have the robust security measures that bigger companies put in place. In fact, attacks on smaller entities are on the rise, making it essential for everyone to adopt security best practices.
Myth 2: Antivirus Software Is Enough to Stay Safe
While antivirus software is an important tool for detecting malicious software, it is not enough to protect against all types of cyber threats. Security involves a multi-layered approach that includes firewalls, encryption, secure passwords, and regular software updates. Relying solely on antivirus software leaves systems vulnerable to more sophisticated attacks like phishing or social engineering.
Myth 3: Strong Passwords Are All You Need
Although using strong passwords is crucial, it’s only one part of a broader security strategy. Passwords alone cannot prevent unauthorized access, especially if they are reused across multiple platforms or not stored securely. Implementing two-factor authentication (2FA) and using password managers are essential steps to enhance login security.
Myth 4: Cybersecurity Is a One-Time Task
Another misconception is that once systems are set up with security measures, they are safe for the long term. In reality, security is an ongoing process. As cyber threats evolve, so must the defense mechanisms. Regular audits, software updates, employee training, and staying informed about new vulnerabilities are essential to maintaining security.
Myth 5: Only External Threats Pose a Risk
Many believe that the biggest threats come from external sources, like hackers or malware. However, internal risks are just as dangerous. Employees, contractors, or anyone with authorized access can inadvertently or maliciously cause damage. It’s crucial to implement access controls, monitor activities, and train all users on the importance of maintaining a secure environment.
By addressing these common misconceptions and understanding the true nature of digital threats, individuals and businesses can improve their defense strategies and reduce the risk of security breaches. A comprehensive approach to protecting digital assets is key to staying safe in an increasingly connected world.
The Role of Risk Management in Security
Effective security strategies are built on the foundation of understanding and managing potential threats. Risk management plays a critical role in identifying, assessing, and prioritizing risks to ensure that resources are allocated to address the most pressing vulnerabilities. By systematically evaluating risks, organizations can mitigate potential damage and make informed decisions on how to protect valuable assets.
Identifying Risks is the first step in the process. This involves analyzing potential threats that could harm systems, data, or infrastructure. Threats can range from cyberattacks, natural disasters, to human error. Once identified, it becomes possible to assess their likelihood and potential impact, which helps in making informed decisions about where to focus security efforts.
Risk Assessment involves a deeper analysis of each identified threat, taking into account factors such as the probability of occurrence and the potential severity of its consequences. By assigning a risk level (low, medium, high), organizations can create a priority list for addressing the most dangerous threats first. This process helps streamline resources to areas that need the most attention and minimizes the chance of a security breach.
Risk Mitigation is the next stage, where strategies are developed to reduce or eliminate identified risks. Common mitigation strategies include implementing security protocols, conducting regular audits, and providing employee training. In some cases, it may involve transferring the risk through insurance or outsourcing certain functions to reduce exposure.
Finally, ongoing Risk Monitoring ensures that security measures continue to be effective over time. As new threats emerge and existing risks evolve, continuous monitoring and reevaluation are necessary to adapt security strategies accordingly. This proactive approach allows organizations to remain resilient against changing circumstances and emerging challenges.
In summary, risk management is integral to any security framework. By systematically identifying, assessing, and addressing risks, organizations can effectively protect their assets and ensure the long-term sustainability of their security measures.
Understanding Confidentiality, Integrity, and Availability
In any security strategy, ensuring the protection and accessibility of critical assets relies on three core principles: confidentiality, integrity, and availability. These three concepts form the foundation for designing systems that are resilient to attacks, data breaches, and errors. Together, they help safeguard sensitive data, maintain trust, and ensure uninterrupted services for users and organizations alike.
Confidentiality refers to the protection of sensitive information from unauthorized access. It ensures that only those with the proper credentials or permissions can view or use certain data. This principle is crucial in environments where data such as personal details, financial records, and intellectual property must remain secure from external and internal threats.
- Methods of ensuring confidentiality include encryption, secure access controls, and multi-factor authentication.
- Data masking and anonymization are also common practices to protect sensitive information from exposure.
Integrity focuses on maintaining the accuracy and trustworthiness of data. It ensures that information is not altered, corrupted, or tampered with, either by accidental errors or malicious actions. Integrity checks help verify that data remains unchanged throughout its lifecycle, from creation to storage and transmission.
- Techniques like hashing, digital signatures, and version control are commonly used to maintain integrity.
- Regular audits and validation processes also play a key role in preserving data accuracy.
Availability ensures that systems, data, and services are accessible and functional when needed. This principle is about ensuring uptime and minimizing downtime caused by system failures, attacks, or other disruptions. A secure system not only protects against unauthorized access but also ensures that legitimate users can reliably access the resources they need at all times.
- Redundancy, load balancing, and disaster recovery plans are essential components to maintaining availability.
- Backup strategies, such as periodic data backups, also help ensure continuity in case of an unexpected event.
When combined, these three principles–confidentiality, integrity, and availability–provide a robust framework for securing systems and protecting valuable assets. Understanding their importance and how to implement them effectively is essential for maintaining a secure and trustworthy environment in today’s digital landscape.
Effective Security Controls and Frameworks

In the realm of cybersecurity, implementing the right security measures and structures is essential to safeguard systems and data. Security controls and frameworks provide organizations with guidelines, protocols, and strategies to reduce vulnerabilities and protect against potential threats. A comprehensive approach ensures not only protection but also resilience, helping organizations respond effectively to new challenges and evolving risks.
Types of Security Controls
Security controls are the safeguards or countermeasures put in place to mitigate risks and protect critical assets. These controls can be categorized into three main types: preventive, detective, and corrective.
- Preventive Controls aim to stop security incidents before they happen. These include firewalls, encryption, and access management systems.
- Detective Controls focus on identifying and alerting organizations to potential security breaches. Examples include intrusion detection systems (IDS) and security monitoring tools.
- Corrective Controls help organizations recover from security incidents. This includes backup systems, patch management, and disaster recovery plans.
Popular Security Frameworks
Frameworks provide a structured approach to managing security practices within an organization. These guidelines not only help assess current security posture but also ensure continuous improvement in protecting valuable assets.
- NIST Cybersecurity Framework: A widely adopted framework that helps organizations identify, assess, and mitigate cybersecurity risks. It consists of five core functions: Identify, Protect, Detect, Respond, and Recover.
- ISO/IEC 27001: An international standard for managing information security. It outlines the establishment, implementation, and continual improvement of an information security management system (ISMS).
- CIS Controls: A set of 20 critical security controls that provide specific and actionable recommendations for securing IT systems. These controls focus on both technical and administrative measures.
- COBIT: A framework for managing and governing enterprise IT. It provides comprehensive guidance on how to manage risks and deliver value from IT investments.
By aligning with these frameworks and adopting a variety of security controls, organizations can create a robust defense against cyber threats. The continuous evaluation and refinement of these strategies ensure a proactive stance in managing security risks and maintaining resilience against future challenges.
Impact of Cyber Threats on Information Assurance
As organizations increasingly rely on digital systems and networks, they face a growing range of cyber threats that can severely impact the security of their data and infrastructure. These threats can undermine the integrity of sensitive assets, disrupt operations, and compromise the confidentiality of valuable information. Understanding the various types of cyber threats and their potential effects is crucial in building a resilient defense strategy and mitigating risks to critical systems.
Types of Cyber Threats
Cyber threats come in many forms, each with unique tactics aimed at exploiting vulnerabilities in systems and applications. Identifying and understanding these threats helps organizations prioritize resources and adopt appropriate security measures.
| Type of Threat | Description | Potential Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Malware | Malicious software designed to harm or exploit systems, such as viruses, worms, and ransomware. | Data loss, system downtime, and potential ransom demands. |
| Phishing | A social engineering attack where attackers impersonate legitimate entities to steal sensitive information. | Identity theft, financial fraud, and unauthorized system access. |
| Denial-of-Service (DoS) | An attack aimed at making a service or system unavailable by overwhelming it with traffic. | Service disruption, loss of business revenue, and reputation damage. |
| Insider Threats | Threats originating from within the organization, such as employees or contractors misusing their access. | Data breaches, theft of intellectual property, and sabotage. |
Consequences of Cyber Threats

The consequences of cyber threats can be far-reaching, affecting not only the organization’s immediate operations but also its long-term viability and reputation. The impact of a successful cyber attack can include:
- Financial Losses – The costs associated with a breach can include legal fees, fines, remediation efforts, and loss of business opportunities.
- Damage to Reputation – Trust is critical in business, and a data breach or security incident can severely damage a company’s public image and customer confidence.
- Regulatory Consequences – Organizations may face penalties for failing to comply with industry regulations and security standards, especially when sensitive data is involved.
- Operational Disruption – Cyber attacks can disrupt daily operations, causing delays, halting business processes, and affecting service delivery.
Given these potential impacts, it is essential for organizations to implement comprehensive security strategies that address these threats head-on. This includes investing in preventive measures, staying updated with the latest security trends, and training employees to recognize and respond to cyber threats effectively.
Exam Tips for Security Awareness Success
Preparing for a security-focused assessment requires both understanding key concepts and being familiar with the practical application of these principles. Success in such tests depends on a strategic approach to studying, managing time effectively, and tackling questions with confidence. Below are some useful tips to help you perform well and demonstrate your knowledge on critical security topics.
- Review Core Concepts Thoroughly – Ensure you have a solid grasp of the fundamental principles that underpin security practices, such as risk management, encryption, and access controls. Being clear on these topics will help you answer questions with precision.
- Practice with Mock Tests – Take practice tests to familiarize yourself with the format and types of questions you might encounter. This will help reduce test anxiety and improve your response time during the real assessment.
- Stay Updated with Current Trends – Cybersecurity is a rapidly evolving field, so make sure you’re aware of the latest developments, such as new types of threats, emerging technologies, and regulatory changes. Knowledge of current events will give you an edge.
- Understand Key Policies and Frameworks – Many questions will focus on established security frameworks and policies. Familiarize yourself with common standards such as ISO, NIST, and GDPR, as these are frequently tested in security assessments.
- Break Down Complex Questions – When faced with difficult questions, break them down into smaller parts. Identify the key components of the question and consider each one individually before selecting your answer.
- Stay Calm and Focused – During the test, maintain a calm and focused mindset. If you don’t know the answer to a question right away, move on to the next one and come back later. Don’t let a difficult question disrupt your progress.
By applying these tips, you’ll be well-prepared to approach the assessment with confidence, demonstrating both your theoretical knowledge and practical understanding of security practices. Remember, success is about consistency, focus, and preparation.
Legal and Regulatory Considerations in Security
When managing digital safety, it’s essential to recognize the complex web of laws and regulations that govern how data is protected, stored, and accessed. Organizations must not only follow industry best practices but also comply with a variety of legal requirements designed to safeguard sensitive data and ensure privacy. Understanding these legal frameworks is critical for minimizing risk and avoiding penalties. Below are key legal and regulatory considerations that impact security practices.
| Regulation | Description | Key Requirements |
|---|---|---|
| General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) | A European Union regulation focused on data protection and privacy for individuals. | Ensure data protection by design, obtain consent for processing, and implement data access rights for users. |
| Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) | A U.S. law that governs the privacy and security of healthcare data. | Ensure patient data confidentiality, secure electronic health information, and conduct regular audits. |
| California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) | A California state law that enhances privacy rights and consumer protection. | Give consumers the right to access, delete, and opt out of the sale of their personal data. |
| Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS) | A set of standards designed to protect card payment data. | Implement encryption, secure payment systems, and ensure proper authentication methods for payment transactions. |
Organizations must remain vigilant about their legal obligations to maintain data security. Compliance not only protects user privacy but also strengthens trust with customers and partners. Violations of these regulations can lead to significant legal consequences, including fines, legal actions, and reputational damage. Therefore, it is vital to stay informed about the evolving legal landscape and ensure that security practices are aligned with applicable laws.
Real-World Applications of Information Assurance
In today’s interconnected world, the need to protect sensitive data is more crucial than ever. Whether it’s securing personal information or corporate assets, the principles of safeguarding digital systems apply across a variety of industries. From finance to healthcare, the implementation of strong security practices is essential in preventing breaches and ensuring the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of critical information. This section explores how these concepts are applied in real-world scenarios and their importance in daily operations.
For example, in the banking sector, stringent measures are taken to prevent unauthorized access to customer accounts and financial transactions. Secure encryption, multi-factor authentication, and regular security audits are implemented to protect clients’ financial data from cybercriminals. Similarly, in the healthcare industry, electronic health records (EHRs) are protected through robust encryption methods and access controls, ensuring that patient data is only accessible to authorized personnel and maintaining patient privacy.
In the e-commerce industry, security is vital not just for protecting transaction data but also for building customer trust. Online retailers often utilize secure payment gateways and adopt the latest encryption technologies to protect sensitive payment information during online purchases. The success of these businesses relies heavily on the effectiveness of their cybersecurity measures, which guard against data breaches, fraud, and identity theft.
These examples highlight the need for a multi-layered approach to security, where technology, policies, and practices work in harmony to mitigate risks and safeguard vital assets. By applying these principles, organizations across various sectors can help ensure that their data remains secure, compliant, and resilient to evolving threats.
Key Takeaways for Information Assurance Exam
Understanding the fundamental concepts of cybersecurity is essential for anyone preparing for a related assessment. This section will summarize the most important points to remember, ensuring you’re well-prepared for any challenges you might face. A strong foundation in security principles, combined with knowledge of best practices, can greatly improve your chances of success. Here are some key points to focus on:
- Understanding Core Concepts: Grasp the basics of confidentiality, integrity, and availability, as these form the foundation of most security measures.
- Risk Management: Be prepared to explain how to assess, mitigate, and manage risks within different systems or environments.
- Security Frameworks: Familiarize yourself with well-established frameworks such as NIST, ISO/IEC, and COBIT, which guide the development of security policies and controls.
- Threat Identification: Learn how to recognize various types of threats (e.g., cyberattacks, malware, phishing) and the tactics used by attackers.
- Compliance and Legal Considerations: Understand the legal requirements and compliance standards relevant to data protection, such as GDPR or HIPAA.
- Security Technologies: Gain knowledge about security technologies such as firewalls, encryption, intrusion detection systems (IDS), and authentication protocols.
- Incident Response and Recovery: Know how to react to security breaches and understand the procedures for recovery and post-incident analysis.
By mastering these key areas, you’ll be in a strong position to not only perform well on the assessment but also apply your knowledge in real-world scenarios. Focusing on these critical elements will help ensure that you’re fully prepared for any challenges related to digital security and protection.