
In this section, we will explore the essential topics that form the foundation of network configuration and management. Whether you’re looking to advance your skills or validate your knowledge, mastering these concepts is key to passing the relevant assessments in the field of networking.
Focusing on core principles such as network protocols, addressing schemes, and routing techniques will equip you with the knowledge needed to tackle practical scenarios. It is crucial to have a clear understanding of how networks are structured and how various devices communicate across them.
By concentrating on the key concepts in this area, you will be prepared to handle both theoretical questions and hands-on simulations. Building confidence with the material will improve your ability to solve problems efficiently and accurately during the assessment.
CCNA 3 Chapter 2 Exam Overview
This section covers the fundamental concepts required for understanding network configurations and addressing schemes. The focus is on grasping the critical elements needed to work with various network topologies and routing protocols. A solid comprehension of these topics ensures you can effectively manage and troubleshoot networks.
Key areas to concentrate on include:
- Network design and topology fundamentals
- IP addressing and subnetting techniques
- Routing protocols and their configurations
- Basic network security principles
Understanding the core principles behind each of these topics is essential for success in practical applications and real-world network management. By mastering these subjects, you’ll be better prepared to configure and troubleshoot different types of networks with ease.
As you study, focus on building your problem-solving skills and becoming comfortable with different network devices, such as routers and switches. This hands-on experience will be invaluable when tackling real-world scenarios.
Key Concepts to Focus On
To succeed in networking assessments, it is important to concentrate on the core concepts that form the backbone of network management and configuration. Mastery of these topics will not only help in theoretical tests but also prepare you for real-world network troubleshooting and optimization.
The most crucial areas to focus on include:
- IP Addressing: Understand the structure of both IPv4 and IPv6 addresses, including subnetting and the significance of address classes.
- Routing Protocols: Familiarize yourself with how dynamic and static routing works, especially the configuration of protocols like RIP, OSPF, and EIGRP.
- Subnetting: Practice subnetting techniques and the ability to divide networks into smaller, more manageable segments.
- Network Topology: Learn how various network devices (routers, switches, firewalls) interact within different topologies, such as star, mesh, and hybrid networks.
- VLANs and Switch Configurations: Be comfortable configuring virtual LANs to segment network traffic for security and performance improvements.
- Basic Security Measures: Focus on access control, firewalls, and other security protocols essential for protecting network infrastructure.
Having a strong grasp of these topics will ensure you’re equipped to handle any network configuration challenges and perform well in practical and theoretical assessments. Practicing real-world scenarios will further strengthen your skills and understanding.
Important Topics in Networking
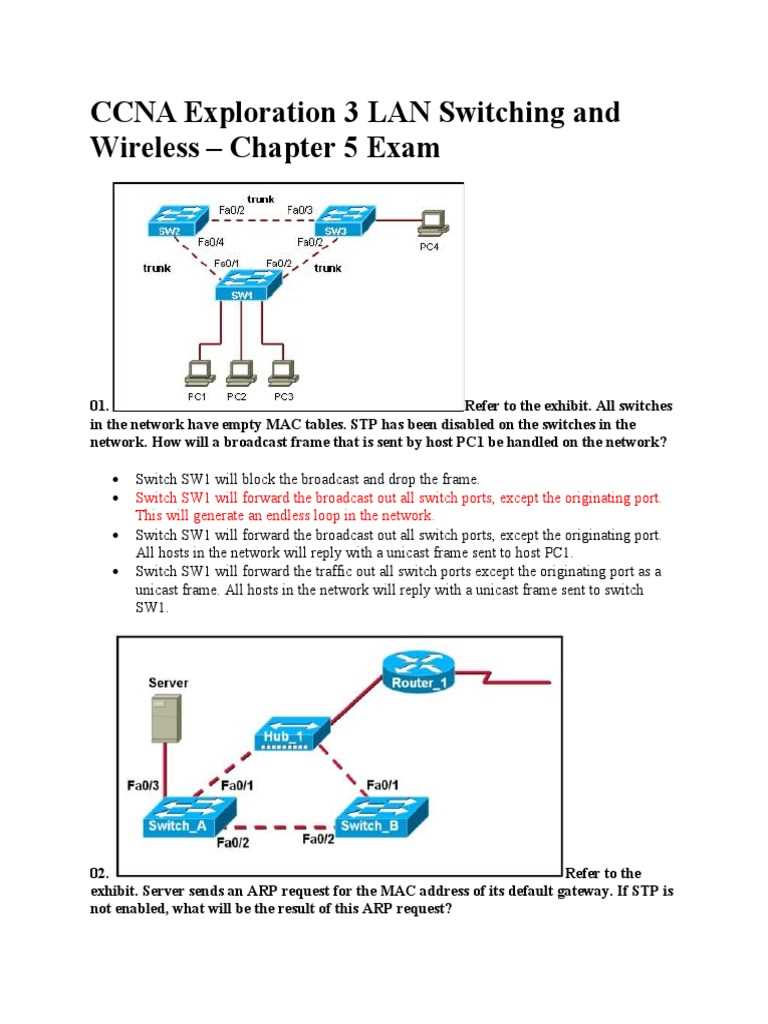
Networking is a complex field that involves various layers of technology, each playing a critical role in how devices communicate and share resources. Understanding the core topics within this domain is essential for both theoretical knowledge and practical application. By focusing on key areas, you can ensure efficient management and troubleshooting of network systems.
Network Protocols and Communication

One of the foundational aspects of networking is understanding how data is transmitted between devices. Key protocols like TCP/IP, HTTP, and DNS form the backbone of internet communication. Learning how these protocols function will help in configuring, managing, and securing networks.
Routing and Switching Fundamentals
Routing and switching are critical for directing network traffic to the correct destination. Familiarize yourself with routing protocols such as OSPF and RIP, as well as the mechanics of switching, including VLANs and trunking. These concepts allow efficient traffic flow and segmentation within networks, making them essential for both small and large-scale networks.
Mastering these key areas will provide a strong foundation for more advanced topics, enabling you to design, manage, and secure networks effectively.
Understanding IP Addressing
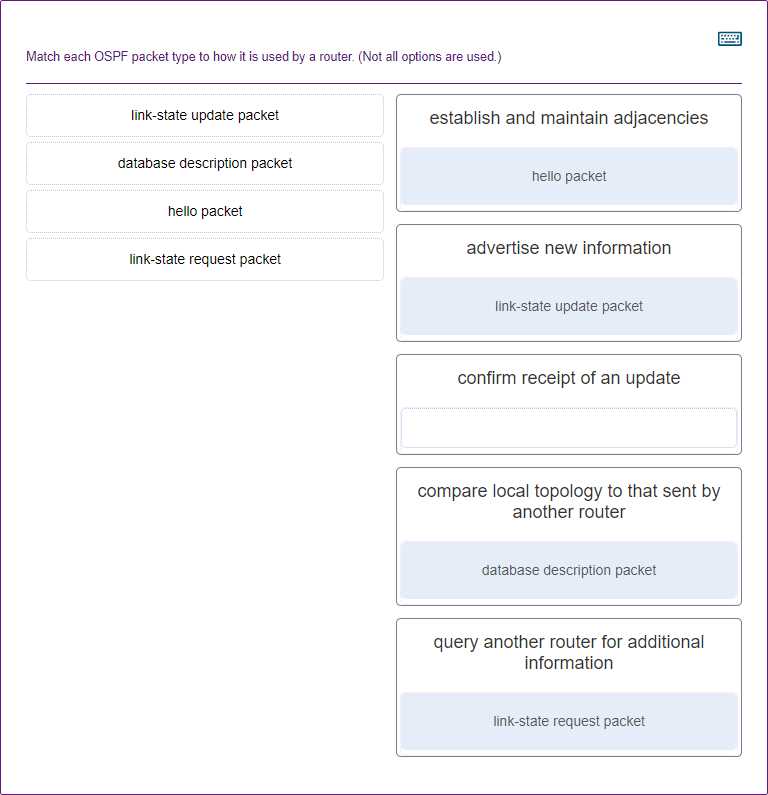
IP addressing is a fundamental concept in networking that enables devices to identify and communicate with each other across networks. Properly understanding how addresses are structured and assigned is crucial for network design, troubleshooting, and optimization. This topic covers both the theory behind IP addressing and the practical aspects of assigning and managing IP addresses.
There are two main types of IP addresses that you will encounter:
- IPv4: The most commonly used address format, which uses a 32-bit address structure represented by four octets (e.g., 192.168.1.1).
- IPv6: A newer format designed to accommodate the increasing demand for IP addresses, using a 128-bit structure (e.g., 2001:0db8:85a3:0000:0000:8a2e:0370:7334).
Key concepts to understand in IP addressing include:
- Subnetting: Dividing a network into smaller subnets for efficient address management and improved security.
- Private vs. Public Addresses: Differentiating between private IP addresses used within local networks and public addresses that are routable on the internet.
- Subnet Masks: Used in conjunction with IP addresses to define the range of addresses within a network.
- CIDR Notation: A more flexible method of specifying network prefixes, which helps conserve IP address space.
Mastering IP addressing involves understanding how these concepts work together to ensure that devices can communicate effectively within a network and across different networks. Proper address assignment and management are essential for ensuring smooth network performance and security.
Routing Protocols You Should Know
Routing protocols are essential for managing how data packets traverse a network. These protocols determine the best path for data to travel based on various metrics and criteria. Understanding how each protocol operates and when to use them is crucial for network efficiency and reliability.
Distance-Vector Protocols
One common type of routing protocol is the distance-vector protocol. These protocols work by calculating the distance to each destination based on the number of hops, or intermediate devices, the data must pass through. The most widely known protocol in this category is RIP (Routing Information Protocol), which uses hop count as its metric.
Link-State Protocols
In contrast, link-state protocols maintain a complete map of the network topology, allowing routers to make more informed decisions about routing. One of the most commonly used link-state protocols is OSPF (Open Shortest Path First), which uses a more sophisticated algorithm to calculate the best route based on various factors like link cost and bandwidth.
Other important routing protocols to familiarize yourself with include:
- EIGRP (Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol): A hybrid protocol that combines elements of both distance-vector and link-state protocols, offering faster convergence and better scalability.
- BGP (Border Gateway Protocol): The protocol used to route traffic between different autonomous systems on the internet. It’s critical for large-scale networks and global internet routing.
Mastering these protocols will allow you to configure and troubleshoot routers more effectively, ensuring optimal network performance and reliability.
IPv4 vs IPv6 Differences
The transition from IPv4 to IPv6 represents a significant shift in the way network addresses are structured. While both protocols are designed to allow devices to communicate over a network, they differ greatly in terms of address length, capabilities, and scalability. Understanding these differences is essential for network configuration, management, and future-proofing your infrastructure.
Address Length and Format

The most noticeable difference between IPv4 and IPv6 is the address length. IPv4 uses a 32-bit address format, which allows for around 4.3 billion unique addresses. In contrast, IPv6 uses a 128-bit address format, providing an almost limitless number of unique addresses. This expansion is essential as the number of internet-connected devices continues to grow.
- IPv4: 32-bit address, typically represented in decimal format (e.g., 192.168.1.1).
- IPv6: 128-bit address, represented in hexadecimal format (e.g., 2001:0db8:85a3:0000:0000:8a2e:0370:7334).
Scalability and Efficiency
IPv6 was designed to address the limitations of IPv4, particularly the shortage of available IP addresses. Additionally, IPv6 improves network efficiency by simplifying address allocation and routing. IPv6’s large address space enables more efficient routing protocols and eliminates the need for techniques like NAT (Network Address Translation), which is common in IPv4 networks.
- IPv4: Limited address space, requiring the use of NAT for many devices.
- IPv6: Vast address space, eliminating the need for NAT and simplifying network management.
While IPv4 remains the dominant protocol, IPv6 adoption is essential for ensuring that networks can scale and accommodate the growing number of internet-connected devices worldwide.
Subnets and Subnetting Techniques
Subnetting is a critical process in network design that allows network administrators to divide a larger network into smaller, more manageable segments. This technique not only optimizes the use of IP addresses but also enhances network security, performance, and ease of management. Understanding the concepts of subnets and how to efficiently allocate addresses within them is fundamental for configuring and maintaining scalable networks.
Subnetting involves creating sub-networks within a larger network by adjusting the subnet mask. This practice allows each subnet to communicate independently while still being part of the overall network. The key to successful subnetting is understanding how to divide and calculate address ranges, which can vary depending on the number of devices and the specific network requirements.
Here is an example of how a network might be divided into subnets using IPv4:
| Network | Subnet Mask | Usable IP Range | Subnet Size |
|---|---|---|---|
| 192.168.1.0 | 255.255.255.0 | 192.168.1.1 – 192.168.1.254 | 254 hosts |
| 192.168.1.0 | 255.255.255.128 | 192.168.1.1 – 192.168.1.126 | 126 hosts |
| 192.168.1.0 | 255.255.255.192 | 192.168.1.1 – 192.168.1.62 | 62 hosts |
By understanding subnet masks and applying them correctly, network engineers can efficiently manage IP space, minimize broadcast traffic, and improve network security. Proper subnetting also reduces the likelihood of address conflicts and ensures that each subnet has sufficient capacity to meet the needs of the devices within it.
OSI Model in Networking
The OSI model is a conceptual framework used to understand and describe how different networking protocols interact within a network. It divides the communication process into seven distinct layers, each responsible for specific tasks that enable data transmission across diverse systems. This model provides a systematic approach to troubleshooting and designing networks, ensuring that each layer performs its function efficiently and independently.
Each layer in the OSI model communicates with the layers directly above and below it, allowing for a structured and organized flow of information. The model helps in isolating problems within a specific layer, facilitating faster diagnosis and resolution of network issues.
The seven layers of the OSI model are as follows:
- Physical Layer: Handles the transmission of raw data bits over a physical medium such as cables or wireless signals.
- Data Link Layer: Responsible for the reliable transmission of data across a physical link, including error detection and correction.
- Network Layer: Manages routing and addressing of data packets, ensuring they reach their correct destination.
- Transport Layer: Ensures reliable data transfer, including flow control, error recovery, and segmentation.
- Session Layer: Manages sessions or connections between applications, handling the opening, closing, and maintenance of communication sessions.
- Presentation Layer: Translates data into a format that can be understood by the receiving system, including encryption and data compression.
- Application Layer: Provides services and interfaces directly to end-users, enabling communication between applications and the network.
Understanding the OSI model is essential for anyone working in networking, as it simplifies the process of designing, managing, and troubleshooting complex network systems. By breaking down communication into manageable layers, the OSI model provides clarity and a standardized approach to network operations.
How to Configure Network Devices
Configuring network devices is a critical task that ensures seamless communication between systems within a network. From routers and switches to firewalls and access points, proper setup allows devices to efficiently forward data, manage traffic, and secure communication. The process involves setting up device parameters, such as IP addresses, routing protocols, and security settings, to create a reliable and secure network environment.
The configuration of network devices generally follows a series of steps, starting with connecting to the device, entering the necessary configuration mode, and then applying the appropriate settings. Understanding each device’s role in the network is essential to determine the correct configuration for optimal performance.
Basic Configuration Steps
Regardless of the device type, there are common steps involved in configuring most network devices. These include assigning IP addresses, configuring routing protocols, and adjusting security settings to protect the network. Here is a simple overview of the configuration process:
| Step | Action | Device Example |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Connect to the device through console or SSH | Router, Switch |
| 2 | Enter configuration mode | Router, Switch |
| 3 | Assign IP address and subnet mask | Router, Switch |
| 4 | Set up routing protocols (if needed) | Router |
| 5 | Configure security settings (e.g., passwords, access control lists) | Router, Switch, Firewall |
| 6 | Save the configuration | Router, Switch |
Advanced Configuration Considerations
For more complex networks, additional configuration options are often necessary to ensure optimal performance. This can include setting up VLANs, configuring Quality of Service (QoS), and implementing network redundancy protocols. These configurations help manage traffic flow, improve performance during high-demand periods, and ensure that the network remains operational in case of device failure.
By understanding the specific configuration requirements for different network devices, administrators can ensure that each component operates as expected within the larger network. Regular updates and maintenance are also crucial to address emerging security threats and evolving technology standards.
Access Control Lists in Networking
Access Control Lists (ACLs) are essential tools in networking that help manage and filter network traffic based on specified security rules. By defining permissions and restrictions for data packets, ACLs control the flow of traffic into or out of network devices, such as routers and firewalls. This functionality is crucial for maintaining network security, ensuring that only authorized users and devices can access sensitive information or network resources.
ACLs are used to permit or deny traffic based on criteria such as IP addresses, subnets, and transport layer protocols. These lists are an effective way to restrict network access, prevent malicious attacks, and manage bandwidth usage by filtering unwanted traffic. Understanding how to configure and implement ACLs is vital for network administrators, as these lists are one of the primary means of enforcing security policies in both small and large-scale networks.
Types of Access Control Lists
There are two primary types of Access Control Lists: standard and extended. Each type serves a different purpose and offers varying levels of control over network traffic.
| ACL Type | Description | Use Cases |
|---|---|---|
| Standard ACL | Filters traffic based only on the source IP address. | Used for basic filtering and controlling access to specific parts of the network. |
| Extended ACL | Filters traffic based on source and destination IP addresses, as well as protocols and ports. | Provides more granular control and is often used to secure specific services or applications. |
Configuring Access Control Lists

When configuring ACLs, network administrators define the rules based on specific network requirements. The rules are processed in a top-down manner, meaning that the first match in the list determines the action taken. If no match is found, the default action is to deny traffic.
Typically, administrators will use command-line interfaces (CLI) to configure ACLs on routers and switches. The configuration involves specifying the type of ACL, the rule criteria, and applying the ACL to the correct interfaces. Below is a simplified example of how an extended ACL might be configured:
ip access-list extended BLOCK_WEB deny tcp 192.168.1.0 0.0.0.255 any eq 80 permit ip any any
In this example, the ACL blocks HTTP traffic (port 80) from the 192.168.1.0 subnet while allowing all other traffic.
By carefully planning and configuring ACLs, network administrators can ensure better security, enhance network performance, and safeguard network resources against unauthorized access.
Common Mistakes to Avoid in Certification Tests
When preparing for certification tests, candidates often make certain mistakes that can hinder their performance. These errors can arise from lack of preparation, misunderstanding instructions, or simply rushing through the test. Recognizing and addressing these common pitfalls can make a significant difference in your results. It is essential to approach each section methodically, ensuring that you are not just memorizing content, but truly understanding the underlying concepts.
Avoiding mistakes during the test not only helps you perform better but also boosts your confidence. By being aware of these common errors, you can develop strategies to overcome them and increase your chances of success.
1. Misunderstanding the Question
One of the most frequent mistakes is misinterpreting the question or the task. This can lead to providing incorrect answers or skipping over important details. To avoid this:
- Read each question carefully, and underline key phrases.
- Take a moment to ensure you fully understand what is being asked.
- Look for qualifiers such as “always,” “never,” or “only,” as they are important in shaping the answer.
2. Rushing Through the Test
Many candidates rush through the test in an attempt to finish quickly, but this often leads to mistakes. Take your time to consider each question thoroughly before answering. If unsure about a particular answer, flag it and move on, coming back to it later with a fresh perspective.
3. Failing to Manage Time Effectively
Time management is crucial in any test. Failing to pace yourself can leave you with incomplete sections. Ensure that you allocate sufficient time for each section and that you leave room for reviewing your answers before submitting. Using a timer can help you keep track of how much time you have left.
4. Ignoring Review Opportunities
Many candidates skip reviewing their answers, thinking they’ve completed the test. However, revisiting your responses allows you to spot any mistakes you might have overlooked initially. Before submitting, check for errors in spelling, calculation, or logic that could cost valuable points.
5. Not Understanding the Format
Each test format comes with its own set of rules and question types, such as multiple choice, drag-and-drop, or simulations. Failing to understand these formats can lead to confusion during the test. Familiarize yourself with the test structure beforehand, so you know what to expect.
By avoiding these common mistakes and adopting a focused, strategic approach to your study and test-taking, you can significantly improve your chances of success in any certification test.
Using Simulation Questions Effectively
Simulation questions are designed to assess your practical skills and problem-solving abilities in real-world scenarios. These questions often mimic actual network configurations, providing you with a hands-on experience to demonstrate your understanding. Unlike multiple-choice questions, simulations require you to actively configure, troubleshoot, or analyze a network environment, making them an essential component of your preparation.
To use simulation questions effectively, it’s important to approach them with a structured mindset. Understanding how to navigate through these simulations and apply your knowledge in a virtual environment can greatly improve your confidence and overall performance. Here are a few strategies to maximize your success when working with simulation-based questions.
1. Familiarize Yourself with Common Scenarios
Most simulations are based on common networking tasks such as IP addressing, routing configurations, and subnetting. By practicing these tasks repeatedly, you can familiarize yourself with the tools and interfaces you’ll encounter. Some common areas to focus on include:
- Configuring routers and switches
- Setting up VLANs and subnets
- Troubleshooting network connectivity issues
By becoming comfortable with these typical scenarios, you can reduce the amount of time spent figuring out the basics during the test, allowing you to focus on solving the problem efficiently.
2. Practice Hands-On in a Lab Environment
While theoretical knowledge is important, hands-on practice in a simulated lab environment is essential for success. Setting up your own home lab or using online platforms that offer practice simulations can help reinforce the concepts you’ve studied. The more you practice, the more you will improve your speed and accuracy during the real test. Make sure to:
- Practice different configurations to understand how to troubleshoot effectively.
- Test your knowledge by using simulators or virtual environments like Packet Tracer or GNS3.
- Time yourself to simulate the pressure of the actual test environment.
Remember, the goal is not only to get the right answers but also to understand the steps involved in solving the problem. The more familiar you are with simulation-based tasks, the more confident you’ll feel when tackling them during the test.
Time Management During the Exam
Effective time management is crucial when taking any certification test, especially when it involves a combination of theoretical questions and practical simulations. With a limited amount of time to complete the entire test, managing each section wisely can make the difference between success and failure. Being able to pace yourself ensures that you have enough time to address all parts of the assessment without rushing through critical tasks.
One of the key strategies for managing time effectively is to allocate a set amount of time for each question or section. The trick is to not get stuck on one difficult problem for too long, as this can leave you with insufficient time to complete the rest of the test. Instead, focus on answering questions efficiently and return to any challenging ones later, if time allows. Below are some essential tips to optimize your time management during the test:
- Prioritize Easier Questions First: Start with the questions you are most confident about. Answering these quickly will give you a sense of progress and confidence, leaving more time for tougher sections.
- Set Time Limits: For each section, allocate a fixed amount of time. For example, if there are 60 minutes for the test, divide this into smaller time blocks (e.g., 40 minutes for multiple-choice questions and 20 minutes for simulations).
- Avoid Perfectionism: Aim for accuracy, but don’t get bogged down by small details. If a question or simulation seems too complex, make your best effort and move on. You can always return to it later.
- Practice Time-Based Mock Tests: Before the actual assessment, simulate test conditions by timing yourself during practice sessions. This will help you build familiarity with the time constraints and improve your pacing.
By staying mindful of your time and following a strategic approach, you can ensure that you complete the test with confidence and efficiency, maximizing your potential for success.
Preparing for Practical Labs

Hands-on labs are an essential part of network training, as they allow you to apply theoretical knowledge in real-world scenarios. These practical exercises are designed to test your ability to configure and troubleshoot network devices, so proper preparation is key to performing well. Understanding the tools and processes involved, along with gaining experience in simulating network setups, will ensure you are ready for the challenges that these labs present.
When preparing for practical labs, the focus should be on developing familiarity with the configurations, protocols, and troubleshooting methods commonly used in network environments. Here are several strategies to help you succeed:
- Understand the Lab Objectives: Before starting any practical exercise, take the time to read through the objectives and requirements. This will give you a clear idea of what tasks need to be accomplished and how to approach them.
- Practice Configurations: Spend time working with networking devices, such as routers and switches, in virtual environments or using real equipment. Practice configuring various protocols, IP addressing, and routing methods until you can do them without hesitation.
- Familiarize Yourself with Network Topologies: Knowing the different network setups–such as point-to-point, star, and mesh topologies–will help you visualize how the devices are interconnected and how data flows across the network.
- Utilize Simulation Software: Use simulation tools like Packet Tracer or GNS3 to create virtual networks and simulate configurations. These platforms provide a safe environment to experiment without the risk of causing real network issues.
- Learn Troubleshooting Techniques: Troubleshooting is a critical skill for any networking professional. Focus on mastering common troubleshooting commands and techniques, such as using ping, traceroute, and the show commands, to quickly diagnose and resolve issues in a simulated network.
- Review Previous Labs: Revisiting past labs and reviewing your performance can help reinforce learning. Identify areas where you struggled and spend extra time practicing those skills.
By preparing thoroughly for practical labs, you’ll gain confidence in your ability to configure and troubleshoot network devices, making you more proficient in applying your knowledge in real-world situations. Regular practice, along with an organized study plan, is key to mastering the hands-on aspects of networking tasks.
Reviewing Questions and Answers
Thoroughly reviewing questions and answers is a crucial step in preparing for any certification. This process allows you to assess your understanding of the material, identify areas that require further study, and gain confidence in answering similar questions in a real assessment. By reviewing both the questions and the corresponding answers, you can reinforce your knowledge and develop strategies to approach different types of inquiries more effectively.
How to Approach Reviewing
When revisiting the questions and answers, it is important to focus on the following aspects:
- Understand the Rationale Behind Answers: Don’t just memorize the correct answers–make sure you understand why a particular answer is correct. This will help you apply similar logic when facing different questions.
- Identify Patterns: Look for recurring topics and question types. Certain themes, such as subnetting, routing, or security configurations, often appear in various forms. Recognizing these patterns will allow you to prioritize your study time effectively.
- Review Incorrect Answers: Pay extra attention to questions you answered incorrectly. Analyze why you chose the wrong answer and understand the correct reasoning. This will help you avoid making the same mistake in the future.
- Test Your Knowledge with Simulated Scenarios: After reviewing the answers, try to apply what you’ve learned to new, similar questions. This will simulate the real-world scenario where you need to solve problems under time constraints.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
While reviewing, be mindful of these common mistakes:
- Skipping Difficult Questions: Avoid the temptation to skip questions you find difficult. These are often the areas that need the most attention and will have a significant impact on your overall understanding.
- Relying Only on Memorization: Memorization can help in the short term, but a deeper understanding of concepts is key to answering complex questions correctly.
- Not Reviewing All Answer Options: In multiple-choice questions, it’s important to consider all possible answers before making a decision. Sometimes, the best answer is not immediately obvious, and other options may provide insights into the correct choice.
By reviewing questions and answers in this systematic manner, you will be better prepared to tackle challenges and demonstrate a deeper comprehension of networking concepts when faced with practical or theoretical assessments.
Study Resources for Networking Certification
Finding the right study materials is key to success when preparing for networking certifications. A variety of resources, ranging from books to interactive labs, can help you grasp essential concepts and improve your practical skills. It’s important to utilize multiple sources to ensure a well-rounded understanding of networking principles and technologies.
Recommended Books
Books remain one of the most effective tools for structured learning. The following books are widely recommended for understanding core networking topics:
- Networking Fundamentals: A comprehensive guide that explains foundational networking concepts, ideal for building a solid understanding.
- Routing and Switching Concepts: Focuses on routing protocols, switching techniques, and network management, essential for mastering network configurations.
- Network Security: Learn the principles of securing networks, a crucial aspect of modern network infrastructure.
Online Learning Platforms

Interactive courses and video tutorials provide a hands-on approach to learning. Here are some popular platforms to enhance your study sessions:
- Udemy: Offers in-depth courses with video lessons, quizzes, and practical examples that allow you to progress at your own pace.
- Pluralsight: A platform with detailed networking paths, offering expert-led tutorials and labs.
- LinkedIn Learning: Provides a variety of courses on networking topics, perfect for quick tutorials and concept reinforcement.
Practice Labs and Simulators
Practical experience is vital when mastering networking concepts. Using network simulators and virtual labs allows you to practice configurations and troubleshoot real-world scenarios:
- Packet Tracer: Cisco’s own simulation tool, allowing you to create and test network configurations without needing physical devices.
- GNS3: An advanced simulator for building complex network setups, perfect for those looking to take their skills further.
- Boson NetSim: A professional network simulation tool designed for certification preparation, providing various network scenarios and practice exams.
By using a combination of these resources, you can build a strong foundation in networking and be well-prepared for any related assessments or certifications.
Tips for Exam Day Success
When the day of your assessment arrives, it’s important to approach it with a calm and focused mindset. Proper preparation leading up to the day is just as crucial as how you manage yourself during the test. By implementing a few strategies, you can increase your chances of success and make the most of your time during the assessment.
Prior to the Exam
Setting yourself up for success starts before the exam day. Consider these tips in the days and hours leading up to the test:
- Review Key Concepts: In the final days before your assessment, focus on reviewing key topics rather than trying to cram everything. A quick recap of the main points can help reinforce your understanding.
- Get Enough Rest: Ensure that you get plenty of sleep the night before. A well-rested mind will help you stay alert and think more clearly during the test.
- Prepare Your Materials: Double-check that you have everything you need for the assessment, whether it’s your ID, a calculator, or any other required materials.
During the Assessment
Once you’re in the test environment, how you manage your time and approach the questions is critical. Keep these strategies in mind during the assessment:
- Read Questions Carefully: Take your time to understand each question fully before answering. Pay attention to the details and make sure you aren’t overlooking any important clues.
- Manage Your Time: Keep an eye on the clock to ensure you’re not spending too much time on any one question. Allocate time based on the complexity of the question and move on if you’re unsure.
- Stay Calm and Confident: If you encounter a challenging question, don’t panic. Take a deep breath and tackle the problem step by step. Confidence in your preparation will help you overcome difficult moments.
By following these tips and maintaining a calm, organized approach, you’ll be in a better position to demonstrate your knowledge and skills effectively. Success on the assessment often comes down to a combination of good preparation and smart test-taking strategies.