
Understanding the core principles of population patterns, urban growth, and agricultural trends is essential for mastering this segment of your AP course. It explores how societies organize themselves and the challenges they face in maintaining sustainability. Whether you’re looking to improve your grasp on complex concepts or need a strategy to tackle difficult questions, a solid foundation is the key to success.
Throughout this section, you’ll encounter models and theories that explain how various factors shape human settlement and development. From examining demographic changes to the evolution of cities, it’s crucial to recognize the interconnectedness of these themes. Grasping these ideas will help you apply them effectively during assessments and demonstrate a deeper understanding of the material.
Preparation is crucial when approaching questions related to these topics. Knowing the fundamental concepts, terms, and their real-world applications will provide you with the confidence to navigate challenging inquiries. This guide will provide the necessary insights and strategies to help you succeed in your studies.
AP Human Geography Chapter 9 Test Answers
Mastering the material in this section requires an in-depth understanding of how populations grow, cities develop, and agricultural systems evolve. These concepts explore the way societies organize resources and space, and the challenges that arise from these processes. To perform well in this unit, it’s crucial to understand both the theoretical models and their practical implications in the real world.
When studying this section, focus on key themes such as demographic transitions, urbanization, and the economic forces that shape development. Be sure to familiarize yourself with the different types of population distributions and how they impact various regions. In addition, understanding the forces that drive rural to urban migration and the effects of these movements will be important for tackling questions in this area.
By reviewing essential vocabulary, such as terms related to spatial organization and development patterns, you can build a strong foundation for successfully answering questions. The ability to apply concepts to hypothetical situations or case studies is equally important. Preparing for this part of your exam will require both memorization and the ability to think critically about how these concepts fit together.
Key Concepts to Understand for Chapter 9
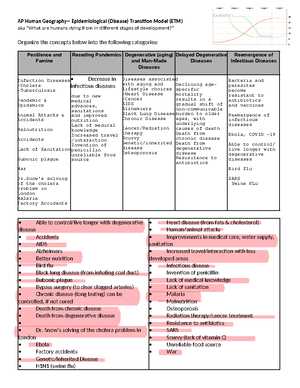
In this section, it’s essential to grasp the fundamental ideas that shape how societies evolve, how populations distribute themselves, and how cities grow. Understanding these core concepts will help you make sense of patterns that influence everything from economic development to migration. Focus on the relationships between these key areas to see the broader picture and how they are interconnected.
Population Distribution and Demographic Changes
Understanding the movement of populations, whether it’s rural-to-urban migration or shifts due to environmental factors, is central to this section. Demographic changes directly affect resource allocation and urban planning. Grasping these shifts is crucial for interpreting the real-world impacts of population dynamics.
Urbanization and Economic Development
The growth of cities and their role in economic systems is a major focus. Urbanization often goes hand in hand with industrial development, and understanding this relationship will help you better answer questions about global trends. Be sure to explore how urbanization affects infrastructure, employment, and social structure.
| Key Concept | Definition | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Demographic Transition | A model explaining the shift from high birth and death rates to low birth and death rates as societies industrialize. | Countries like the U.S. and Japan |
| Urban Sprawl | The uncontrolled expansion of urban areas into surrounding rural land. | Los Angeles, Mexico City |
| Economic Sectors | The categorization of economic activities into primary, secondary, and tertiary sectors. | Agriculture (Primary), Manufacturing (Secondary), Services (Tertiary) |
By understanding these concepts, you can develop a comprehensive understanding of how societies function and change over time. This knowledge will be vital for answering questions effectively and making connections between different elements of the course material.
Important Topics in AP Human Geography
To excel in this area of study, it’s important to focus on the key concepts that shape the way populations and cities develop, as well as the factors that drive social and economic progress. Understanding the interconnections between these topics will help in both conceptualizing complex ideas and applying them effectively during assessments.
Several major topics will appear frequently throughout this unit. By mastering these areas, you’ll be able to understand the broader trends that influence global development. Below are some of the most essential concepts to focus on:
- Population Dynamics: The study of how populations change over time, including birth rates, death rates, and migration patterns.
- Urbanization: The process through which more people move into cities, impacting both infrastructure and society.
- Agricultural Systems: How agricultural practices vary across different regions and the effects they have on economic structures.
- Economic Development: Understanding the stages of development from pre-industrial to post-industrial economies.
- Social Structure: How societies organize themselves based on factors such as class, ethnicity, and economic standing.
These topics are central to understanding the forces that shape societies around the world. By paying close attention to these areas, you will gain valuable insights into global trends and regional variations.
Key Areas to Focus On
- Impact of industrialization on urban growth and societal shifts.
- The relationship between economic growth and environmental sustainability.
- The role of government policies in shaping demographic trends.
- Understanding global inequality and its implications for development.
Mastering these concepts will prepare you for any questions related to population, urbanization, and economic progress, ensuring you are well-equipped to tackle more advanced discussions in the subject.
How to Approach Chapter 9 Questions
When preparing for assessments on this topic, it’s essential to develop an effective strategy for answering questions. The material covers various aspects of societal development, population dynamics, and urban growth. A clear approach to each question type will help you focus on key concepts and apply your knowledge confidently.
Here are some useful tips for tackling questions related to this section:
- Understand Key Concepts: Make sure you have a strong grasp of core ideas like population distribution, economic structures, and urbanization trends. These concepts will be foundational in answering most questions.
- Read Questions Carefully: Pay attention to what each question is specifically asking. Focus on identifying keywords and phrases that indicate whether the question requires a definition, explanation, or application of a concept.
- Practice with Case Studies: Many questions will involve applying concepts to real-world examples. Review case studies and be prepared to analyze them from different perspectives.
- Use Process of Elimination: If you are unsure about an answer, eliminate the choices that are obviously incorrect. This strategy can increase your chances of selecting the right response.
Effective Study Habits for Success
- Review practice questions to get familiar with common formats.
- Make sure you can explain key terms and theories in your own words.
- Group related topics together for easier recall during exams.
- Simulate exam conditions to practice time management and accuracy.
By following these strategies, you can approach the questions in a more organized and confident manner, ensuring you perform at your best. The key is to stay focused on the material while applying your knowledge to specific scenarios.
Common Mistakes on the Chapter 9 Test
When preparing for assessments in this unit, there are several common errors that students tend to make. These mistakes often stem from a lack of attention to detail, misunderstanding key concepts, or not properly applying the material. Being aware of these pitfalls can help you avoid them and improve your performance.
One common mistake is failing to fully understand the context of questions, especially those related to demographic shifts and urban development. Another issue arises when students confuse similar concepts or overlook important details in case study questions. Additionally, not applying the correct terminology or failing to address all parts of a question can result in lost points.
| Error | Explanation | How to Avoid |
|---|---|---|
| Misunderstanding Key Terms | Students often confuse terms like “urbanization” and “suburbanization” or misinterpret demographic terms. | Review definitions and ensure you can differentiate similar concepts. |
| Overlooking Data in Case Studies | Some students neglect important data points in case studies, which can lead to incorrect conclusions. | Always read and analyze all the data provided in case study questions. |
| Answering Partially | Failing to address all aspects of a question leads to incomplete responses. | Ensure you answer every part of the question thoroughly before moving on. |
| Ignoring Regional Variations | Many overlook how the material applies to different regions or fail to consider variations in development. | Keep in mind how concepts vary across regions and apply them in your answers. |
By being mindful of these common mistakes, you can approach questions more effectively and avoid missteps that may hinder your performance. Remember to take your time, carefully read each question, and apply your knowledge with precision.
Essential Vocabulary for Chapter 9
In order to fully understand the material covered in this section, it’s crucial to familiarize yourself with the key terms that define the concepts. A strong grasp of these terms will help you better interpret questions and apply your knowledge during assessments. These words are central to discussions about population, urban growth, and development patterns, so make sure to integrate them into your study routine.
Below are some of the most important terms to know:
- Urbanization: The process by which an increasing percentage of a population moves to cities and towns, often leading to the growth of metropolitan areas.
- Demographic Transition: A model that explains the transition from high birth and death rates to low birth and death rates as a country develops.
- Population Density: A measurement of the number of people living in a given area, typically expressed as people per square kilometer or mile.
- Infrastructure: The basic physical and organizational structures needed for the operation of a society, including transportation systems, communication networks, and energy supply.
- Suburbanization: The movement of people from urban areas to the outskirts of cities, often leading to the expansion of suburban neighborhoods.
- Industrialization: The process through which an economy transforms from primarily agricultural to one based on the manufacturing of goods.
- Migration: The movement of people from one place to another, often driven by economic, political, or environmental factors.
- Globalization: The increasing interconnectedness of the world through the exchange of goods, services, information, and culture.
Understanding these terms will not only help you during exams but also provide a solid foundation for analyzing the complex relationships between society, economy, and the environment. Be sure to regularly review and practice using these words in context to reinforce your understanding.
Reviewing Human Geography Theories
When studying societal development and spatial patterns, it’s important to understand the key theories that explain how populations, economies, and cities evolve. These frameworks help to interpret complex patterns of settlement, migration, and growth, providing insights into both historical and modern trends. Reviewing these theories will deepen your understanding and improve your ability to analyze related topics effectively.
Below are some of the most influential theories in this field that you should focus on:
- Central Place Theory: This theory explains the size and distribution of cities and towns, suggesting that settlements are organized in a hierarchical pattern based on their function and the goods or services they provide.
- Concentric Zone Model: Developed by sociologist Ernest Burgess, this model describes urban areas as a series of rings, each representing different land uses and socio-economic groups.
- Sector Model: This model, proposed by Homer Hoyt, suggests that cities develop in wedge-shaped sectors rather than concentric rings, with different areas influenced by transportation routes and social factors.
- Multiple Nuclei Model: This theory, developed by Chauncy Harris and Edward Ullman, argues that cities do not grow from a single center but rather from multiple nodes or centers of activity.
- World-System Theory: Immanuel Wallerstein’s theory focuses on the global economic system, emphasizing the division between core, semi-periphery, and periphery nations, and how these regions interact within the global economy.
- Rostow’s Stages of Economic Growth: This model outlines the stages through which societies move as they develop economically, from traditional society to high mass consumption.
These theories offer essential perspectives on the spatial organization of societies and can be used to understand patterns of development, migration, and economic activity. Familiarizing yourself with these concepts will provide a solid foundation for analyzing real-world issues and trends.
Examining Population Distribution Patterns
Understanding where and why populations are distributed in specific areas is essential to studying the development and dynamics of societies. The patterns of settlement are influenced by a variety of factors such as climate, resources, economic opportunities, and historical events. By examining these patterns, we can better understand the factors that shape regions and their growth over time.
Population distribution is rarely uniform, and various regions exhibit distinct clustering or dispersal based on environmental, social, and economic conditions. For instance, areas with fertile land, access to water, and favorable climates tend to support higher population densities, while harsh environments like deserts and mountains see lower concentrations of people.
Several key factors influence these patterns:
- Climate: Mild climates with regular rainfall and moderate temperatures are often more conducive to settlement.
- Resources: The availability of natural resources like water, fertile soil, and minerals plays a significant role in attracting populations.
- Economic Opportunities: Areas with strong job markets, industrial activity, or agricultural potential tend to attract larger populations.
- Transportation: The development of roads, railways, and ports allows people to settle in previously inaccessible areas.
- Historical Factors: Historical events such as colonization, trade routes, or migration patterns can shape the distribution of people over time.
These patterns are not static and can change over time due to shifts in economic conditions, technological advancements, or environmental changes. Understanding how populations are distributed provides valuable insights into the challenges and opportunities faced by different regions and communities.
Urbanization and Its Effects Explained
As populations increasingly move from rural to urban areas, the transformation of societies becomes evident. The shift towards cities and towns, driven by factors such as employment opportunities, better living standards, and infrastructure development, reshapes the physical, social, and economic landscapes. This process of urban growth leads to significant changes in the way people live, work, and interact with their environment.
Urbanization often brings about both positive and negative consequences. While cities offer better access to services, technology, and education, they also introduce challenges such as overcrowding, pollution, and strain on resources. Understanding these effects is crucial for planning sustainable urban development and ensuring a balanced approach to growth.
Key effects of urbanization include:
- Economic Growth: Urban areas often become economic hubs, attracting businesses, industries, and workers, which can lead to increased job opportunities and a higher standard of living.
- Improved Infrastructure: Cities tend to develop better transportation systems, healthcare facilities, and educational institutions, improving overall quality of life for residents.
- Environmental Impact: The expansion of urban areas can result in the depletion of natural resources, increased pollution, and loss of green spaces.
- Social Stratification: As urban areas grow, social inequalities may become more pronounced, with wealthier residents living in well-maintained areas while poorer populations may be relegated to informal settlements.
- Overcrowding: The rapid influx of people can lead to overcrowded living conditions, inadequate housing, and overburdened public services.
- Cultural Shifts: Urban environments often bring diverse populations together, resulting in cultural exchange and, in some cases, the blending of traditions and lifestyles.
Urbanization is a complex phenomenon that requires careful consideration of both its benefits and challenges. To manage its effects, city planners and governments must implement policies that promote sustainable development, ensuring that urban areas can continue to grow while maintaining livability and environmental health.
Understanding Agricultural Practices in Geography

Agricultural practices play a fundamental role in shaping the way societies interact with their environment. The methods used for growing crops, raising livestock, and utilizing natural resources are deeply intertwined with cultural, economic, and environmental factors. Understanding how these practices evolve and differ across regions is essential for grasping the broader dynamics of population distribution, food production, and sustainability.
These practices vary significantly depending on local conditions such as climate, soil type, and technological advancements. While some areas rely on intensive farming techniques and modern machinery, others may focus on more traditional or subsistence methods. The choice of practice is often influenced by the availability of resources, market demand, and governmental policies.
Key agricultural practices include:
- Subsistence Farming: This practice involves growing crops and raising livestock primarily for local consumption rather than for sale in markets. It is common in regions with limited access to resources or markets.
- Commercial Farming: Commercial agriculture focuses on the large-scale production of crops and livestock for sale in national and global markets. It relies heavily on modern technologies and advanced machinery.
- Shifting Cultivation: This involves clearing land for farming by cutting down and burning vegetation, then moving on to a new area once the soil becomes less fertile. It is often practiced in tropical regions with abundant land.
- Pastoral Nomadism: A form of subsistence agriculture where herders move their livestock between grazing grounds. This practice is common in arid regions where resources are scarce.
- Intensive Farming: Intensive farming practices focus on maximizing the yield from small plots of land. It often involves the use of fertilizers, pesticides, and irrigation to increase productivity.
- Agroforestry: This method integrates trees and shrubs into agricultural landscapes, improving biodiversity, reducing erosion, and enhancing food security.
As the global population continues to grow and urbanize, the demand for food and agricultural products will rise, placing greater pressure on these practices. Sustainable farming techniques and innovations in agricultural technology are crucial to meet the challenges of providing food for a growing world population while minimizing environmental degradation.
Geographic Models in Human Development
The study of societal growth and evolution often involves understanding patterns and trends across different regions. Geographic models help explain how various factors, such as location, resources, and infrastructure, influence the development of societies. These models allow researchers to predict the trajectory of urbanization, economic growth, and population dynamics in various areas. By examining these frameworks, one can gain deeper insights into how regions evolve over time and how they interact with each other on a global scale.
Geographic models serve as tools to analyze and understand how spatial and environmental factors shape human development. They focus on the relationships between people and their surroundings, illustrating the patterns of settlement, migration, and resource use. These models are essential for understanding the factors that influence everything from city planning to global trade networks.
Some of the prominent models used in studying societal development include:
| Model | Description |
|---|---|
| Rostow’s Stages of Growth | Rostow’s model describes five stages of development that nations go through, from traditional societies to high mass consumption, with a focus on economic factors. |
| Central Place Theory | This model explains the distribution of cities and towns, proposing that settlements are spaced out in a hierarchical structure based on their market and service functions. |
| World-Systems Theory | World-Systems Theory categorizes countries into core, semi-periphery, and periphery, suggesting that global inequality is structured through economic relationships. |
| Bid-Rent Theory | This model examines how land value decreases with distance from the city center, affecting where businesses and individuals choose to settle. |
| Concentric Zone Model | The concentric zone model shows the spatial structure of cities, where different land uses are distributed in rings around a central business district. |
These models offer valuable frameworks for understanding the dynamics of societal growth, urban planning, and resource distribution. They help in addressing issues such as inequality, environmental sustainability, and global economic disparities. As cities and societies continue to evolve, geographic models remain essential tools in analyzing and guiding development strategies across the world.
Testing Your Knowledge of Demographics
Understanding the patterns and trends in population distribution is essential for analyzing various social, economic, and political phenomena. Demographics offer valuable insights into how populations grow, age, and migrate over time. Testing your knowledge in this field involves exploring key concepts such as population growth rates, migration patterns, and the impact of age structures on society.
By examining these factors, you can gain a deeper understanding of how demographic changes affect everything from urbanization to healthcare systems and workforce development. Below are some key areas to test your knowledge:
Population Growth and Decline
Population growth rates play a critical role in shaping a nation’s future. Understanding how birth rates, death rates, and migration influence overall population size is key to analyzing social and economic development. Factors such as fertility rates, mortality rates, and life expectancy provide essential data to assess population dynamics.
Migration and Population Distribution
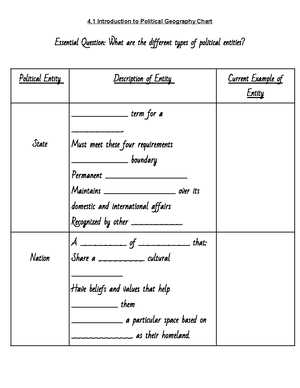
Migration patterns are another important aspect of demographics. Understanding the reasons behind migration, whether voluntary or forced, and the impact it has on population density in various regions can reveal much about global trends. Internal migration, urbanization, and international relocation all contribute to the shifting distribution of people across the globe.
To deepen your understanding, consider testing yourself with questions related to these areas. For example:
- What are the primary factors that influence population growth in different regions?
- How do migration patterns differ between developed and developing countries?
- What impact does an aging population have on economic development?
By continually challenging yourself with these types of questions, you can enhance your comprehension of demographic concepts and their real-world applications. Testing your knowledge of these topics is an excellent way to stay informed and prepared for further study in population dynamics and related fields.
How to Study for Chapter 9 Effectively

Preparing for assessments on complex topics requires a strategic approach. A well-organized study plan can help you retain key concepts, understand intricate theories, and apply knowledge effectively. Whether you’re studying for a quiz, a major exam, or simply reviewing the material, focusing on the right areas and using the most effective methods will help you succeed.
To study efficiently, break down the material into manageable sections, review key terminology, and understand the underlying principles that connect various ideas. Testing your knowledge with practice questions and revisiting challenging topics will strengthen your understanding. Here are some effective study strategies:
| Study Strategy | Description |
|---|---|
| Active Recall | Test yourself regularly on the material you’ve just learned to reinforce your memory and retention. |
| Spaced Repetition | Review material periodically at increasing intervals to help commit it to long-term memory. |
| Mind Mapping | Create visual diagrams to organize and connect concepts, helping to visualize relationships between ideas. |
| Group Study | Collaborate with peers to discuss difficult concepts and share different perspectives to improve understanding. |
| Practice Quizzes | Use sample quizzes or create your own questions to simulate the exam experience and identify areas of weakness. |
By incorporating these techniques into your study routine, you can maximize your learning potential. Focus on one section at a time, actively engage with the material, and ensure you understand both the details and broader themes. Review consistently and give yourself time to absorb the information rather than cramming at the last minute. This approach will not only prepare you for assessments but also provide you with a deeper understanding of the subject matter.
Preparing for Multiple-Choice Questions

When preparing for assessments with multiple-choice questions, it is essential to develop a strategic approach to ensure accuracy and efficiency. Unlike open-ended questions, multiple-choice formats require quick decision-making, a solid understanding of the material, and the ability to eliminate incorrect answers. By mastering these techniques, you can improve both your speed and accuracy when tackling this question style.
Key Strategies for Multiple-Choice Success
- Read Each Question Carefully – Take the time to fully understand the question before looking at the options. This ensures that you are focused on what is being asked.
- Eliminate Obvious Wrong Answers – Narrow down your choices by discarding the options that are clearly incorrect. This increases your chances of selecting the right answer.
- Use Contextual Clues – Pay attention to any details within the question or the other options that may provide hints about the correct answer.
- Don’t Overthink – After eliminating incorrect options, trust your instincts and select the answer that feels most accurate. Often, your first choice is the right one.
Effective Study Techniques for Multiple-Choice Questions
- Practice with Past Questions – Reviewing old practice questions or quizzes helps familiarize you with the types of questions asked and how they are worded.
- Understand Key Concepts – Focus on understanding the core ideas and how they relate to one another. Strong conceptual knowledge will help you quickly identify the correct answer.
- Work on Time Management – Practice answering questions under timed conditions to simulate exam scenarios and improve your speed.
- Review Incorrect Answers – When practicing, carefully review any questions you got wrong to understand why a particular answer was correct or incorrect.
By applying these strategies, you will be better prepared to confidently approach multiple-choice questions. Mastering these skills can significantly improve your performance and ensure that you approach each question with a clearer focus and improved judgment.
Breaking Down Chapter 9 Case Studies
Case studies are powerful tools for understanding complex concepts and real-world applications of theoretical ideas. By examining specific examples, you can better grasp how abstract principles are applied in various contexts. In this section, we will explore some of the key case studies from the chapter, breaking them down to highlight the critical insights they offer. This approach not only helps in mastering the material but also improves your ability to analyze and interpret similar cases in the future.
Understanding Key Case Studies
Each case study offers a unique perspective on the topics discussed in the section. Whether focusing on specific regions, historical events, or contemporary issues, these examples serve as practical demonstrations of theoretical concepts. Key areas of focus include:
- Urbanization Patterns – Case studies in urban development highlight the challenges and opportunities that cities face as they grow and evolve. Understanding these patterns is crucial for analyzing current trends.
- Agricultural Shifts – Examining changes in farming practices across regions helps to contextualize the impact of technological advancements, climate change, and global trade.
- Economic Development – Case studies focused on regions experiencing different levels of economic progress provide insight into the factors driving growth or hindering development.
Analyzing and Applying Insights from Case Studies
To fully benefit from case studies, it’s important to analyze them critically. Here are a few tips to effectively approach these examples:
- Identify Key Trends – Look for repeating patterns or common factors that may explain the outcomes in each case. Recognizing these trends helps you understand broader concepts.
- Consider Contextual Influences – Each case study is shaped by a range of social, political, and economic factors. Understanding these influences is key to interpreting the results accurately.
- Apply Theory to Practice – Reflect on how theoretical knowledge applies to real-world situations by using the case studies as evidence. This approach strengthens both conceptual understanding and practical application.
Breaking down case studies allows for a deeper understanding of the material, providing practical insights that extend beyond memorization. By engaging with these examples critically, you can build a more comprehensive knowledge base that prepares you for exams and practical challenges alike.
Mastering AP Test Strategies

Achieving success in any exam requires a combination of knowledge, skill, and strategic approach. To excel in your exam, it’s essential to understand not only the material but also how to navigate the exam effectively. By mastering key strategies, you can improve your ability to recall information, manage time efficiently, and reduce stress during the exam. In this section, we will explore various techniques that can help you perform at your best.
Effective Time Management
One of the most important aspects of exam preparation is time management. The ability to pace yourself allows you to allocate sufficient time to each section, ensuring that you don’t rush through important questions. Here are a few tips to manage your time efficiently:
- Set time limits for each section – Before starting, determine how much time you’ll allocate to each part of the exam. Stick to this plan to avoid spending too much time on any one section.
- Prioritize difficult questions – If you encounter a question you find challenging, don’t spend too much time on it. Move on and return to it later if time allows.
- Practice timed mock exams – Simulate exam conditions by taking practice tests under timed conditions. This will help you develop a sense of how to pace yourself during the real exam.
Improving Accuracy and Confidence
Answering questions accurately and confidently is key to achieving a high score. Below are strategies to help you improve both your accuracy and your confidence during the exam:
- Read questions carefully – Ensure you understand what each question is asking before selecting your answer. Avoid rushing through questions, as misreading can lead to simple mistakes.
- Eliminate obvious wrong answers – If unsure, use the process of elimination to remove clearly incorrect choices, increasing your odds of selecting the correct one.
- Trust your instincts – If you’re uncertain about an answer but have a strong feeling about one option, trust your initial instinct. Overthinking can lead to second-guessing and mistakes.
Staying Calm and Focused

Staying calm and focused during the exam is critical for maintaining clarity of thought and making sound decisions. Here are strategies to help you stay composed:
- Practice relaxation techniques – Before the exam, practice deep breathing or visualization exercises to help you relax and clear your mind.
- Stay positive – Keep a positive attitude and avoid negative self-talk. Confidence can greatly influence your performance.
- Take breaks if needed – If the exam format allows, take brief pauses to stretch or clear your mind. This can help you stay focused and avoid burnout.
By incorporating these strategies into your exam routine, you can enhance your performance and approach the test with a greater sense of confidence. A well-prepared mind, combined with effective techniques, will set you up for success.