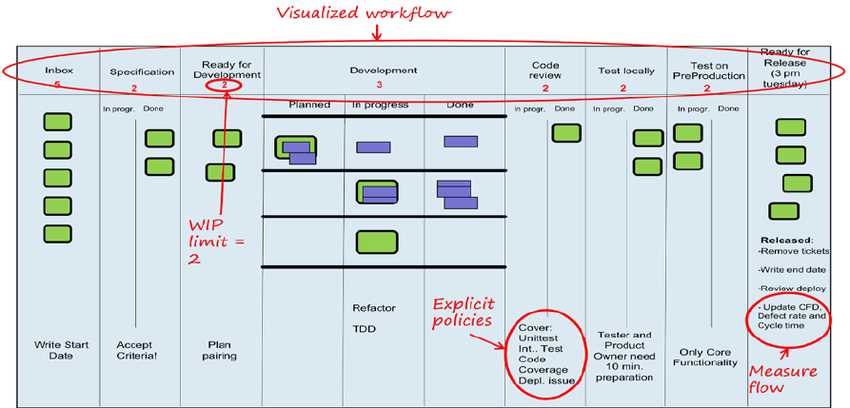
In today’s fast-paced business environment, managing projects efficiently requires a strong grasp of dynamic frameworks that prioritize flexibility and responsiveness. Understanding the core principles behind these methodologies is essential for successfully navigating the complexities of modern initiatives. Whether you are involved in product development or team coordination, mastering these practices will help you deliver results faster and with higher quality.
One of the most sought-after skills in the field of project management is the ability to work within frameworks that allow for continuous improvement and rapid adaptation. Professionals must be familiar with the techniques used to collect, document, and refine project goals while ensuring all stakeholders are aligned. The approach emphasizes iterative progress and regular feedback loops, helping teams stay on track even when requirements evolve.
Preparing for any assessment related to these practices requires a solid understanding of their principles and how they can be applied in real-world scenarios. Through dedicated study and practice, individuals can enhance their competency in applying these concepts effectively across various industries. The ability to demonstrate proficiency in these methods will set you apart as a capable and knowledgeable project leader.
Agile Requirements Foundations LinkedIn Learning Exam Guide
Preparing for an assessment in modern project management techniques involves gaining a clear understanding of key concepts and how they influence the flow of work. This guide is designed to help individuals navigate the core principles that enable teams to stay adaptive and responsive to changing needs. By mastering these concepts, you can ensure that your skills align with industry standards and demonstrate proficiency in handling real-world challenges effectively.
In this section, we focus on the essential elements needed to excel in an assessment that tests your knowledge of flexible project frameworks. It’s important to familiarize yourself with the specific practices and strategies that make these methodologies successful. Understanding the various stages of planning, execution, and feedback will provide you with the insights necessary to answer questions confidently and accurately.
To succeed, it’s crucial to grasp not only the theoretical aspects but also the practical applications that drive successful outcomes. By reviewing real-life examples and engaging with relevant practice materials, you can sharpen your understanding and improve your problem-solving abilities. With the right preparation, you will be equipped to handle any challenge that comes your way in this field.
Understanding Methodology Basics
The key to successful project management lies in adopting approaches that prioritize adaptability, collaboration, and iterative progress. These frameworks are designed to help teams respond swiftly to change and continuously improve their work. By breaking down tasks into smaller, manageable units, teams can deliver results faster and more efficiently, allowing for flexibility throughout the entire project lifecycle.
At the core of this approach is a focus on delivering value incrementally. The emphasis is on regular feedback, collaboration with stakeholders, and the ability to make adjustments as new information emerges. This enables teams to stay on track and maintain alignment with the project’s objectives, even as priorities shift or new challenges arise.
Understanding the basics of this methodology is essential for anyone looking to succeed in managing complex projects. Whether you are coordinating a small team or overseeing a large-scale initiative, mastering these principles will ensure that you can effectively meet your goals while remaining adaptable to change.
Key Concepts in Agile Requirements
To successfully manage projects in dynamic environments, it’s important to understand the central ideas that guide how goals and objectives are identified, refined, and implemented. These concepts emphasize continuous collaboration, adaptability, and a focus on delivering value in short cycles. By embracing these principles, teams can better align with changing needs and ensure that outcomes are consistently aligned with stakeholder expectations.
Iterative Development and Flexibility
One of the most fundamental aspects is the iterative approach to development. Instead of following a rigid, linear path, work is broken down into smaller, manageable stages. Each stage delivers a usable product increment, which allows for constant feedback and adjustments. This flexibility ensures that the team can pivot when necessary, responding quickly to new requirements or shifting priorities.
Collaboration and Stakeholder Engagement
Active involvement from all stakeholders is critical in this process. Continuous communication with customers, team members, and other key parties ensures that everyone is aligned on expectations and progress. This collaborative approach not only helps in gathering valuable insights but also in making informed decisions that reflect the project’s goals.
How Agile Practices Benefit Project Management
Implementing modern methodologies in project management brings numerous advantages that contribute to more efficient and effective execution. These approaches focus on flexibility, collaboration, and iterative progress, all of which enhance a team’s ability to deliver high-quality results while adapting to ever-changing conditions. By breaking large tasks into smaller, manageable units, teams can track progress more easily and make necessary adjustments along the way.
Increased Flexibility and Responsiveness
One of the key benefits is the ability to adapt quickly to changing circumstances. As projects progress, new challenges or opportunities may arise. The use of short cycles allows teams to reassess their priorities regularly and pivot when necessary. This responsiveness ensures that teams are always working towards the most valuable goals, even as external factors evolve.
Enhanced Collaboration and Communication
Another significant advantage is the emphasis on open and continuous communication. Frequent check-ins and feedback loops ensure that all team members and stakeholders stay aligned, reducing misunderstandings and improving overall transparency. This collaboration fosters a sense of shared ownership and commitment to the project’s success, leading to better results and stronger teamwork.
Preparing for the Certification Test
Effective preparation is key to succeeding in any professional assessment. To perform well in this certification, it’s important to understand the core concepts, processes, and best practices covered in the material. By focusing on the main principles and their practical applications, you can build a strong foundation for the test and confidently demonstrate your skills.
Study the Key Concepts Thoroughly

Start by revisiting the fundamental principles that are central to the framework. Take the time to review key terms, techniques, and strategies that drive project success. Understanding how these concepts are applied in real-world scenarios will help you answer questions accurately. Focusing on practical applications rather than just theoretical knowledge will ensure that you are prepared for any scenario presented in the test.
Practice with Sample Scenarios
Another essential step in preparing is to practice with sample questions or case studies. These practice tests simulate the types of challenges you might face and help you refine your decision-making process. By familiarizing yourself with the test structure and timing, you can improve your confidence and performance. Make sure to review both correct and incorrect answers to understand why a particular approach is preferable in certain situations.
Common Challenges in Agile Requirements

While modern project management practices offer flexibility and efficiency, they also come with their own set of challenges. One of the key difficulties teams face is maintaining clarity and alignment throughout the project’s lifecycle. As goals evolve and new information emerges, it can be challenging to keep all stakeholders on the same page, ensuring that priorities remain consistent and the team stays focused on delivering the most valuable outcomes.
Scope Creep and Changing Priorities

One of the most common obstacles is the tendency for project scope to expand beyond initial expectations. As requirements are continually refined, new ideas or demands can lead to an increase in the amount of work to be done. This can create confusion and make it harder to maintain a clear direction. To address this, it’s important to set clear boundaries and prioritize work based on value and feasibility.
Stakeholder Communication and Engagement
Another challenge is keeping all stakeholders engaged and informed throughout the project. Regular communication is crucial to ensure that feedback is integrated and decisions are made collaboratively. However, balancing input from multiple stakeholders can be difficult, especially when their expectations differ. It’s essential to establish effective communication channels and ensure that all voices are heard, while also managing expectations to avoid conflicts.
Tools for Agile Requirement Gathering
Effective gathering of project goals and objectives is a critical component of success in dynamic workflows. The right tools enable teams to capture, refine, and prioritize needs efficiently, ensuring that everyone involved stays aligned. These tools facilitate collaboration, streamline communication, and provide a framework for organizing and tracking progress as the project evolves.
Collaboration and Communication Tools
Tools designed for collaboration and communication play a key role in gathering input from stakeholders, team members, and clients. They help ensure that feedback is continuous and can be integrated into the project process. Some popular tools include:
- Jira: A powerful platform for tracking tasks and managing workflows in real-time.
- Confluence: Used for documenting project goals, decisions, and discussions to maintain transparency.
- Trello: A simple, visual tool for managing tasks and priorities, perfect for smaller teams.
- Slack: Facilitates real-time communication and sharing of ideas among team members.
Requirement Elicitation Tools
In addition to collaboration platforms, there are specialized tools that assist with capturing detailed project needs and converting them into actionable items. These tools help teams clarify scope, define objectives, and gather essential information from various stakeholders:
- User Stories: A method for capturing project needs from the user’s perspective, often documented in simple formats for easy prioritization.
- Surveys and Questionnaires: Used to gather feedback and opinions from stakeholders quickly and systematically.
- Mind Mapping Software: Tools like MindMeister help visualize ideas and connections between different project elements.
- Workshops and Focus Groups: Facilitated discussions to gather in-depth insights and ensure alignment among all parties.
Test Your Knowledge on Project Management Principles

Understanding the key concepts and methodologies behind successful project execution is essential for anyone aiming to lead or contribute to a team. Testing your grasp of core practices ensures that you are well-prepared to tackle challenges and make informed decisions during any project lifecycle. This section helps assess your understanding of the foundational principles and provides opportunities to reinforce your learning through practical scenarios.
Key Principles Overview
The following table outlines several core principles that guide successful projects. Review each concept to test your familiarity with how these ideas translate into effective project management practices.
| Principle | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Iterative Progress | Breaking work into smaller cycles to deliver value incrementally. | Delivering a product prototype after each cycle for feedback. |
| Collaboration | Continuous communication between stakeholders and team members. | Regular meetings with clients to discuss changes in priorities. |
| Adaptability | Quickly adjusting to new requirements or challenges. | Revising the project scope based on new market conditions. |
| Customer Focus | Ensuring the product meets the needs of the end users. | Gathering user feedback after each iteration to refine the product. |
Self-Assessment
Now that you’ve reviewed the key principles, challenge yourself by reflecting on how these concepts apply to your past projects or potential future scenarios. How would you implement these ideas in your own work environment? By testing your understanding and applying these principles, you can enhance both your practical knowledge and strategic thinking.
Top Study Tips for the Test
Successfully preparing for a certification or assessment requires a strategic approach to studying. By focusing on key concepts, practicing with relevant materials, and managing your time efficiently, you can increase your chances of performing well. Whether you’re tackling complex principles or refining your skills, these tips will help you stay organized and confident throughout the preparation process.
First, prioritize understanding the core concepts and how they apply in real-world scenarios. This will ensure you not only memorize facts but also know how to use them effectively when faced with practical situations. Additionally, regularly review and test your knowledge to reinforce what you’ve learned.
Another helpful strategy is to break your study sessions into manageable chunks. Use techniques like spaced repetition to reinforce information over time. By reviewing smaller portions of material consistently, you’ll be able to retain information more effectively and avoid cramming.
Lastly, practice time management by simulating test conditions. Practice with mock tests or timed exercises to get comfortable with the format and pacing. This will also help you identify areas where you may need more focus, ensuring you’re well-prepared when it’s time to take the assessment.
Understanding the Manifesto for Efficient Project Practices
The Manifesto for Efficient Project Practices is a guiding framework designed to prioritize flexibility, collaboration, and customer satisfaction in project management. It emphasizes adapting to change rather than rigidly following predefined plans. By focusing on value delivery, it seeks to create a work environment where continuous improvement and responsiveness to feedback lead to better outcomes. Understanding its core principles is essential for anyone involved in modern project management practices.
The Manifesto is built on four key values:
- Individuals and Interactions over Processes and Tools: Emphasizes the importance of communication and collaboration between team members, rather than relying solely on tools and processes.
- Working Solutions over Comprehensive Documentation: Prioritizes delivering functional outcomes that meet user needs over extensive documentation that might delay progress.
- Customer Collaboration over Contract Negotiation: Focuses on working closely with the customer, allowing for flexibility and adjustments, rather than adhering strictly to contract terms.
- Responding to Change over Following a Plan: Encourages adapting to evolving requirements and circumstances, rather than rigidly sticking to an initial plan.
In addition to these values, the Manifesto outlines twelve principles that guide decision-making and actions within a project. These principles emphasize continuous delivery, close communication with stakeholders, and maintaining a sustainable pace for teams.
By following the Manifesto’s values and principles, teams are better equipped to adapt to changes, deliver high-quality results, and meet customer expectations more effectively.
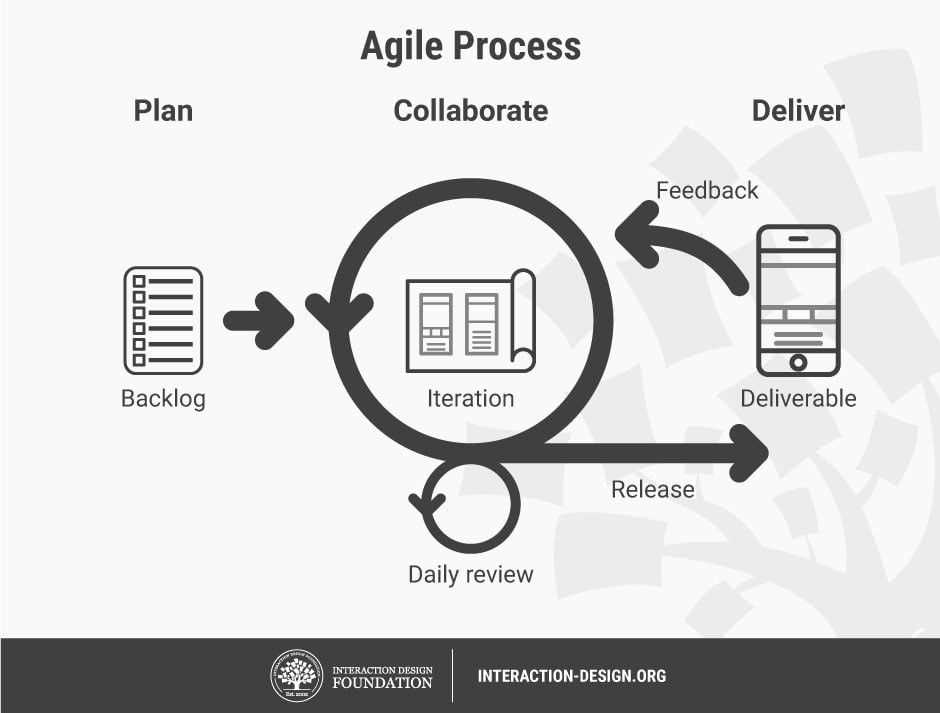
How Iterative Approaches Impact Product Development
Adopting a flexible and iterative approach to product development can significantly transform how teams design, test, and deliver products. By focusing on small, manageable iterations rather than long, drawn-out processes, development teams are able to quickly adjust to changes, gather feedback, and deliver high-value features at a steady pace. This approach encourages collaboration, enhances responsiveness to customer needs, and ultimately leads to products that are more aligned with market demands.
Benefits of Iterative Development
With iterative methods, product development becomes more dynamic, allowing teams to continuously refine and improve a product throughout its lifecycle. Key benefits include:
- Faster Time to Market: Delivering working versions of the product in shorter cycles allows for quicker releases and early user feedback.
- Increased Flexibility: Teams can make adjustments to features or direction based on ongoing testing and market feedback.
- Improved Quality: Regular testing within each iteration helps identify issues early, leading to higher-quality products.
- Customer-Centric Focus: By incorporating feedback from stakeholders and users during each cycle, the final product is more likely to meet their needs.
Comparison: Traditional vs. Iterative Development
The following table highlights key differences between traditional development methods and more flexible, iterative approaches:
| Aspect | Traditional Development | Iterative Development |
|---|---|---|
| Project Scope | Defined upfront, with little flexibility | Adjustable as new information and feedback emerge |
| Customer Feedback | Received at the end of the development cycle | Incorporated continuously throughout the project |
| Risk Management | Risks are harder to address until later in the process | Frequent iterations help identify and mitigate risks early |
| Delivery | Final product delivered after a long development cycle | Working versions delivered regularly in increments |
By embracing these iterative techniques, teams can better respond to the evolving needs of the market, improve collaboration, and ensure that the final product is refined and aligned with user expectations.
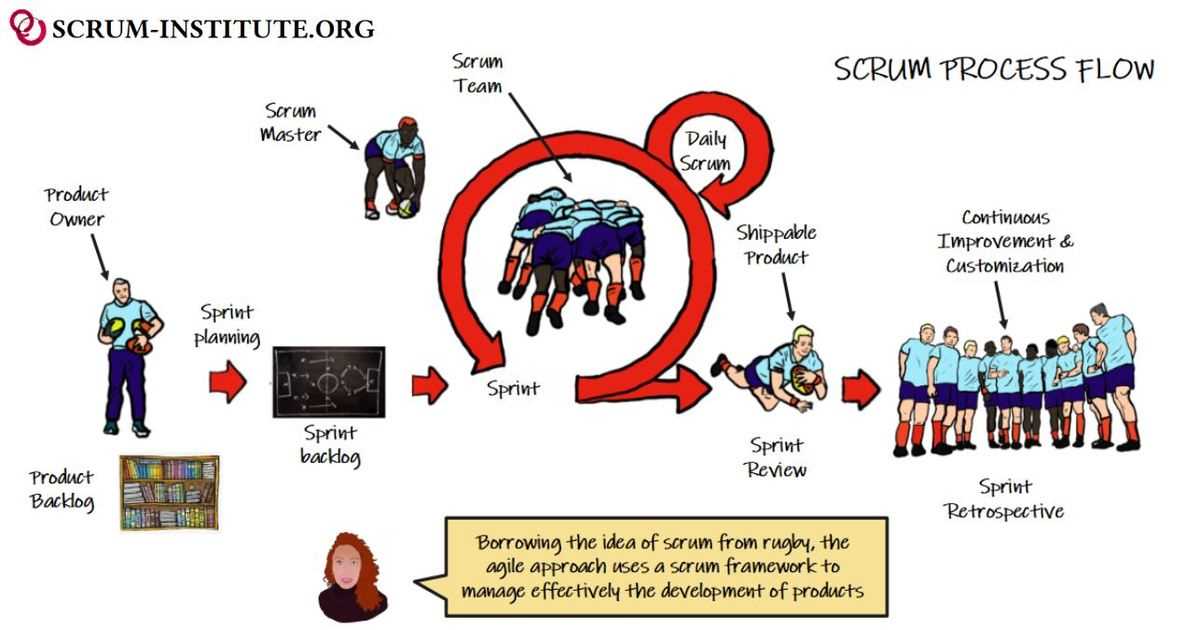
Scrum vs Kanban in Project Management
When managing projects that require adaptability and responsiveness, two popular approaches often come into play: Scrum and Kanban. Both aim to improve efficiency and provide better results, but they differ in their structure and execution. While Scrum is a framework that emphasizes iterative progress through time-boxed sprints, Kanban focuses on continuous flow and the management of work in progress. Understanding the differences between these two methods is key to selecting the right one for a given project or team.
Key Differences Between Scrum and Kanban
Each approach has its unique strengths and is suited to different types of projects or work environments. Scrum is ideal for teams that work in short cycles with a defined goal for each cycle, while Kanban is better suited for environments that need ongoing, flexible work management. Below are the primary distinctions between the two:
| Aspect | Scrum | Kanban |
|---|---|---|
| Structure | Time-boxed iterations (Sprints) | Continuous flow of tasks |
| Focus | Deliverables after each sprint | Ongoing task management and delivery |
| Work Limits | Set number of tasks per sprint | Limited number of tasks in progress at any time |
| Role of Team | Defined roles (Scrum Master, Product Owner, etc.) | Flexible roles, no specific titles |
| Iterations | Fixed duration sprints (e.g., 2 weeks) | No predefined time periods |
Choosing Between Scrum and Kanban
The choice between Scrum and Kanban largely depends on the project’s nature and the team’s needs. Scrum is most effective in environments that benefit from structured planning, defined roles, and a focus on completing set objectives in a set timeframe. On the other hand, Kanban is ideal for teams that work with continuously evolving tasks and need more flexibility in managing workflows.
For teams looking for a more predictable and systematic approach, Scrum may be the better option. However, for teams that require adaptability and ongoing adjustments based on real-time needs, Kanban provides an excellent framework for ensuring continuous delivery without rigid constraints.
Documentation and Requirement Techniques in Project Management
Effective documentation and proper techniques for gathering and managing project goals are critical components of any project. These processes ensure clear communication, transparency, and alignment across teams and stakeholders. Different methodologies emphasize various approaches to documentation, focusing on flexibility, collaboration, and responsiveness. Understanding the key techniques can help teams effectively manage expectations while maintaining adaptability throughout the project lifecycle.
Common Documentation Techniques
There are several popular techniques used to manage project details and expectations. These techniques help teams focus on delivering value while avoiding unnecessary complexity in documentation:
- User Stories: Short, simple descriptions of features or functionality from the perspective of the end user. These allow teams to prioritize work based on user value.
- Use Cases: Scenarios that describe how a system will interact with users or other systems. Use cases outline functional requirements in a structured format.
- Flowcharts: Visual diagrams that illustrate the flow of tasks or processes. They help in mapping out the steps in a workflow, making it easier to understand dependencies.
- Product Backlogs: A prioritized list of tasks, features, or goals that need to be completed in the project. This is continuously updated based on changing requirements.
- Roadmaps: High-level visual plans outlining the key milestones or phases of a project. They provide a broad view of the project’s goals and timelines.
Techniques for Gathering Information
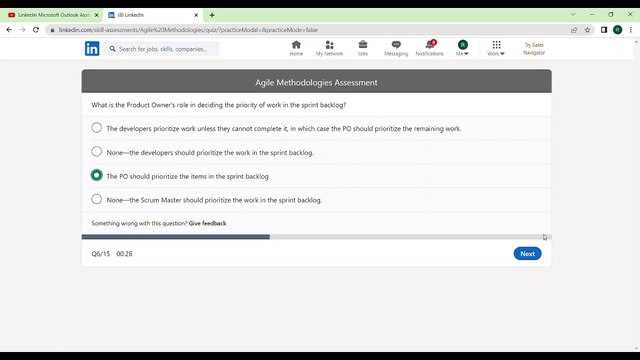
Successful project management requires effective methods for gathering and documenting requirements. The right techniques can improve the quality of the deliverables while fostering better collaboration:
- Interviews: One-on-one meetings with stakeholders to gather detailed information about their needs and expectations.
- Workshops: Collaborative sessions with key stakeholders where ideas and requirements are discussed in real-time.
- Surveys: Questionnaires designed to gather broad feedback from a large audience. This method is effective for collecting general input from multiple stakeholders.
- Prototyping: Creating a preliminary version of a product or feature that stakeholders can interact with to refine requirements and expectations.
- Observations: Studying the way users interact with existing systems to understand pain points and areas for improvement.
These documentation and gathering techniques ensure that project teams can effectively manage changing goals while remaining aligned with the broader vision and objectives. By using the right combination of methods, teams can deliver value incrementally and efficiently while maintaining clarity throughout the project lifecycle.
Effective Communication in Teams
Clear and transparent communication is the cornerstone of any successful project. In a collaborative environment, where team members come from diverse backgrounds and areas of expertise, ensuring that everyone is on the same page is vital for achieving goals efficiently. Strong communication practices not only enhance the flow of information but also foster trust and accountability among team members. Understanding the best approaches for sharing ideas, updates, and feedback can make a significant difference in the success of the project.
Key Elements of Communication
There are several crucial components that ensure communication remains effective in a team environment:
- Clarity: Messages must be concise and to the point, avoiding ambiguity and ensuring that everyone understands the key points being communicated.
- Active Listening: Team members should actively listen to one another, which includes fully focusing on the speaker, asking clarifying questions, and providing feedback.
- Timeliness: Sharing information as it becomes available is essential to avoid delays and ensure that all team members are working with the most up-to-date data.
- Openness: Encouraging open and honest discussions helps to address potential challenges early and builds trust among the team.
- Feedback: Constructive feedback allows team members to learn from their mistakes and continuously improve their performance and collaboration.
Effective Communication Channels
Choosing the right tools and channels for communication can streamline information flow and improve team collaboration:
- Daily Standups: Short, focused meetings where team members share their progress, challenges, and next steps. This format keeps everyone aligned on priorities.
- Collaboration Platforms: Tools like instant messaging and project management software facilitate quick communication and easy sharing of documents, updates, and tasks.
- Documentation: Written records ensure that key decisions, plans, and requirements are documented and accessible to all team members for future reference.
- Workshops and Brainstorming Sessions: Interactive sessions that allow for idea sharing and problem-solving in a collaborative manner, promoting team cohesion and creativity.
- One-on-One Conversations: Regular one-on-one meetings between team members and managers help build personal connections and ensure that individual concerns are addressed.
By fostering clear and open communication, teams can overcome challenges more efficiently, build stronger relationships, and deliver better outcomes. The ability to communicate effectively is a critical skill that drives success in team-based projects.
Best Practices for Writing User Stories
Effective user stories are essential for driving clear communication between stakeholders and development teams. These stories should accurately represent the needs of users and be detailed enough to guide the team toward creating valuable features. Writing strong user stories requires understanding the end user’s perspective and focusing on delivering small, manageable chunks of value. By following best practices, teams can ensure that the user stories are clear, actionable, and contribute to successful project outcomes.
Key Principles for Crafting Strong User Stories
When writing user stories, consider the following essential guidelines to ensure clarity and effectiveness:
- Focus on the User: Always frame the story from the user’s point of view. This ensures that the team understands the feature’s purpose and how it benefits the end user.
- Be Specific but Concise: While user stories should be short and clear, they must also provide enough detail for the development team to understand what needs to be done.
- Use the “As a… I want… So that…” Format: This format helps structure the story around who the user is, what they want, and the value or outcome they expect.
- Ensure Testability: Each story should include clear acceptance criteria that make it easy to test the feature once it’s implemented.
- Prioritize Stories: Rank user stories based on their importance and business value. This helps the team focus on delivering the most impactful features first.
Additional Tips for Effective User Stories
To further enhance the quality of user stories, consider the following practices:
- Collaborate with Stakeholders: Involve relevant stakeholders, such as customers, product owners, or end users, in the process of writing and reviewing stories.
- Keep Stories Small: Break down large features into smaller stories that can be completed within a sprint. This ensures that the team can make consistent progress and delivers incremental value.
- Review and Refine Regularly: Continuously revisit and refine user stories based on feedback and new insights. This helps ensure they remain aligned with the project goals.
- Avoid Technical Jargon: Focus on the user’s needs and outcomes rather than the technical aspects. This keeps stories user-centric and easier for non-technical team members to understand.
- Include Clear Acceptance Criteria: Acceptance criteria define the conditions for success, helping the team understand what “done” looks like for each story.
By following these best practices, teams can write user stories that guide the development process, align the team on goals, and ultimately ensure the delivery of high-value features. The quality of the user stories directly impacts the success of a project, making it essential to invest time and attention to detail in their creation.
Strategies for Project Success
To achieve successful outcomes in any project, effective planning, collaboration, and continuous improvement are essential. Teams that adopt flexible methods are better equipped to handle change, align with client needs, and meet deadlines. By employing specific strategies, project teams can ensure they remain focused, deliver high-quality results, and adapt efficiently to new challenges. These strategies help streamline processes, improve communication, and ultimately drive project success.
Key Approaches for Effective Project Management
Implementing proven techniques can greatly increase the likelihood of project success. Below are some key approaches that contribute to effective project management:
- Clear Goal Setting: Start with a well-defined vision and set specific, measurable, attainable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) goals. This clarity keeps the team focused and aligned with project objectives.
- Regular Feedback and Reviews: Continuously gather feedback from stakeholders and team members to evaluate progress and make necessary adjustments. This ensures that the project stays on track and meets expectations.
- Collaboration and Communication: Foster open communication between all team members, clients, and stakeholders. Transparency helps address issues early, preventing misunderstandings and ensuring everyone is aligned with the project vision.
- Flexibility and Adaptability: Being able to respond to changes in scope or requirements is crucial for long-term success. A flexible mindset allows teams to pivot when necessary without derailing the entire project.
- Effective Risk Management: Identify potential risks early and develop mitigation strategies. Proactively addressing risks can prevent disruptions and allow teams to maintain momentum.
Optimizing Team Performance
Maximizing the performance of the team is another critical factor in achieving project success. These strategies help create an environment conducive to high performance:
- Empower Teams: Provide teams with the autonomy to make decisions and manage their work. Empowered teams are more engaged and motivated, leading to increased productivity and creativity.
- Ensure Continuous Learning: Encourage team members to continuously improve their skills and knowledge. This not only enhances individual performance but also contributes to the overall success of the project.
- Build Trust and Accountability: Trust within the team is essential for fostering collaboration and high morale. Establishing clear roles and responsibilities ensures accountability and drives progress.
- Celebrate Milestones: Recognize and celebrate achievements, both big and small. This boosts morale, reinforces progress, and motivates the team to keep moving forward.
By incorporating these strategies into project management practices, teams are more likely to experience success and overcome challenges. Strong planning, open communication, and continuous adaptation are the foundation of any project’s long-term success, enabling teams to stay on course and deliver valuable results.
Assessing Your Knowledge in Iterative Project Management
Evaluating your understanding of iterative project management is crucial for identifying strengths and areas that need improvement. This process allows you to measure your grasp of key concepts, practices, and methodologies that drive successful project delivery. By engaging in assessments, you can ensure that you are equipped to handle dynamic project requirements and contribute effectively to team goals.
Effective Ways to Measure Understanding
There are various methods to assess your comprehension of essential principles in iterative project management. Here are some effective strategies:
- Self-Reflection: Regularly review the concepts you’ve learned and assess how well they align with real-world scenarios. Reflect on your ability to adapt these concepts to different challenges.
- Quizzes and Practice Tests: Engage in quizzes or mock tests that challenge your understanding of key principles. These exercises help reinforce knowledge and identify gaps that may require further study.
- Peer Feedback: Seek feedback from colleagues or mentors who are experienced in project management. Their insights can provide valuable perspectives on areas where you excel and where improvement is needed.
- Real-World Application: Apply the principles to actual projects or case studies. This hands-on approach allows you to evaluate your problem-solving skills and ability to implement learned concepts in a practical context.
Strengthening Your Knowledge
Once you’ve assessed your knowledge, it’s essential to take steps to strengthen your understanding. Consider these strategies to deepen your expertise:
- Continuous Learning: Stay up to date with the latest trends, methodologies, and tools in the field. Participating in workshops, reading books, and engaging with industry resources can broaden your knowledge.
- Join Communities: Engage with online forums or communities that focus on project management. Networking with others in the field will help you stay informed about new practices and challenges others are facing.
- Real-Life Application: The more you apply your knowledge in practical settings, the better you’ll understand how to use it effectively. Consider volunteering for projects or taking on roles that allow you to practice what you’ve learned.
By actively assessing and refining your understanding, you can continuously improve your abilities in iterative project management. Regular evaluations help you stay prepared for the demands of the profession and enhance your overall effectiveness in leading successful projects.
Test Results and Key Insights
Understanding your performance after taking assessments is crucial to identifying areas for improvement and reinforcing the knowledge you’ve gained. By reviewing the results, you can pinpoint the concepts you have mastered and those that may need further attention. This reflection is an essential part of refining your skills and becoming more proficient in managing iterative projects effectively.
Breaking Down Common Mistakes
After completing assessments, it’s important to analyze the questions or areas where you struggled. Common mistakes can provide valuable insights into your understanding and highlight where further learning is needed. Here are a few things to consider:
- Conceptual Gaps: If you answered questions incorrectly, it may be due to a misunderstanding of key concepts. Going back to review foundational ideas can help clarify these areas.
- Application vs. Theory: Sometimes, knowing the theory isn’t enough. The real challenge lies in applying that knowledge to practical scenarios. Make sure you practice with case studies or real-world examples to bridge this gap.
- Misinterpretation of Questions: Some mistakes may occur simply due to misreading or misinterpreting the wording of the question. Pay close attention to the specifics of each question during future assessments.
Key Takeaways for Improvement

Here are some strategies to enhance your knowledge and increase your performance in future assessments:
- Focus on Key Concepts: Make sure you have a solid understanding of the core principles. Revisit the materials that outline these foundational ideas, and ensure you can apply them in different situations.
- Practice Regularly: The more you engage with real-world examples, the better prepared you’ll be. Take the time to practice answering questions, simulating real scenarios, and testing your comprehension in a variety of contexts.
- Seek Feedback: Getting input from peers, mentors, or instructors can help clarify any doubts and provide different perspectives. Use their feedback to refine your approach and enhance your overall performance.
By reflecting on your results and incorporating these insights into your study habits, you can continue to improve and strengthen your expertise in the field, ultimately becoming more effective in project management and problem-solving.