
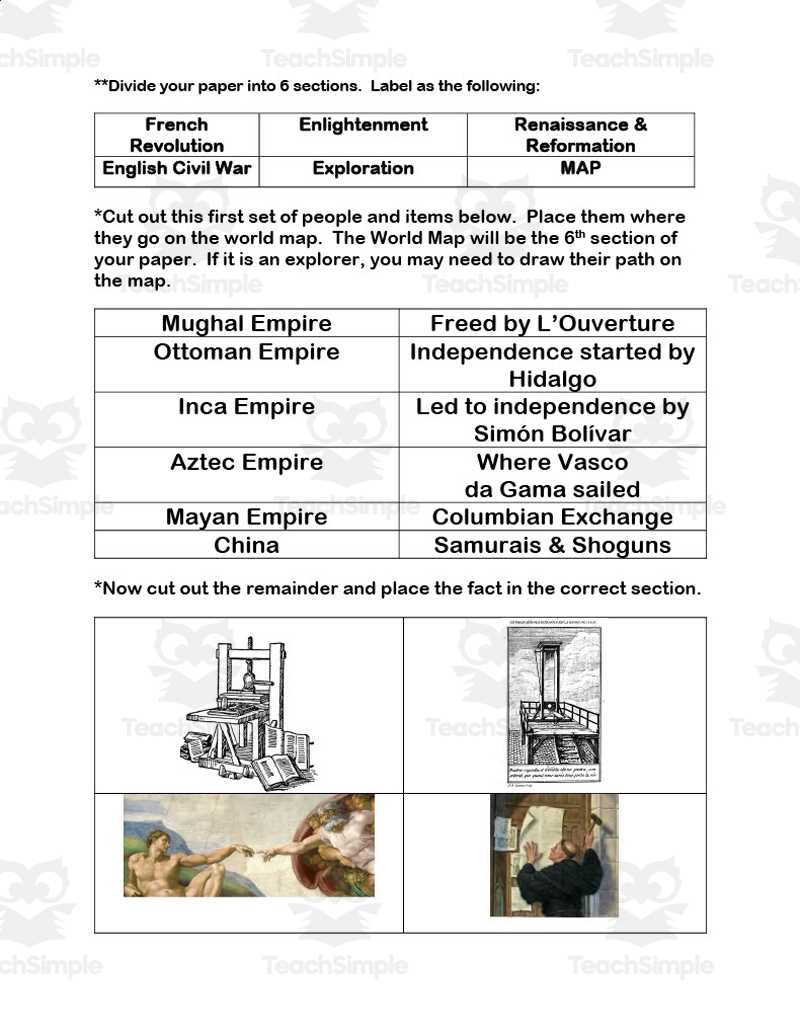
As you prepare for your upcoming assessment, it’s essential to focus on the most significant themes and events that have shaped the course of human development. Understanding the key turning points, influential figures, and impactful movements will help you connect the dots across different periods and regions. This approach will allow you to grasp the broader context and provide deeper insights into the material.
Critical moments of change are often the focal point in many assessments, and reviewing these milestones will help you recall major developments. Whether it’s the rise of empires, the spread of new ideologies, or shifts in power dynamics, it’s important to recognize how each of these elements played a pivotal role in shaping our modern world.
Additionally, focusing on essential concepts such as political, social, and economic structures will ensure a well-rounded preparation. By the end of your review, you’ll have a clearer understanding of the connections between historical events and their lasting impact on contemporary society.
Comprehensive Review for Key Historical Concepts
This section will focus on essential topics and crucial information that you should grasp in order to excel in your assessment. Understanding the most impactful events and movements will help you build a strong foundation for success. By focusing on pivotal developments and key figures, you’ll be able to draw connections across various periods and regions.
Key Themes and Important Figures
The following table highlights some of the most influential themes and historical personalities that are critical for your preparation. Recognizing their roles will help you understand how each has contributed to the global narrative.
| Key Themes | Important Figures |
|---|---|
| Rise and Fall of Empires | Alexander the Great, Napoleon Bonaparte |
| Industrial Revolution | James Watt, Henry Ford |
| Major Wars and Conflicts | Winston Churchill, Adolf Hitler |
| Political Movements | Abraham Lincoln, Vladimir Lenin |
Key Events to Review
In addition to understanding important figures and themes, be sure to review major events that have shaped the course of civilization. Familiarity with these significant moments will provide valuable context for the connections between different periods.
| Key Events | Impact |
|---|---|
| French Revolution | Overthrew monarchy, established Republic |
| American Civil War | End of slavery, preservation of the Union |
| World War I | Shift in global power structures |
| Cold War | Ideological divide between superpowers |
Key Topics for the Assessment
Focusing on the essential themes and significant events will give you a clear understanding of what to prioritize for your preparation. By identifying the most impactful moments, movements, and figures, you can organize your review to cover the most relevant material. This approach ensures that you’re ready to tackle the most common and critical questions.
Critical Historical Events
Make sure to review the major turning points that have shaped global development. These events have had far-reaching consequences and are key to understanding the shifts in political, economic, and social landscapes. Below are some of the most important events to focus on:
- The rise and collapse of powerful empires
- Key military conflicts and their outcomes
- Social movements that changed societies
- Technological and industrial revolutions
Influential Figures and Leaders
Understanding the contributions of key figures will provide valuable context for the major changes in the world. Leaders, thinkers, and revolutionaries have left a lasting legacy that continues to shape our world today. Pay attention to:
- Political leaders and their influence on governance
- Military figures who changed the course of battles
- Intellectuals who introduced new philosophies
- Reformers who challenged existing systems
Important Historical Events to Review
To ensure a comprehensive understanding, it’s crucial to focus on the most significant milestones that have shaped global development. These moments often represent crucial turning points that have altered the course of nations and civilizations. By reviewing these events, you’ll gain a deeper perspective on how the past influences the present.
Major Wars and Conflicts

Conflicts throughout time have had profound impacts on borders, political structures, and the global balance of power. Below are some key wars and conflicts that played pivotal roles:
- World War I: A devastating conflict that redrew national boundaries and established new global powers.
- World War II: The largest and most destructive war in history, leading to significant changes in governance and international relations.
- The Cold War: A prolonged period of tension between the United States and the Soviet Union, shaping modern geopolitics.
Revolutions and Social Movements
Revolutions have often signaled shifts in social order, governance, and economic systems. Understanding these movements is essential for grasping how societies evolve:
- The French Revolution: A defining event in the struggle for democracy and the end of monarchies in Europe.
- The Industrial Revolution: This period transformed economies, introduced mass production, and drastically altered social structures.
- The Civil Rights Movement: A crucial turning point in the fight for equality and justice, particularly in the United States.
Key Figures and Their Contributions
Throughout the course of time, numerous individuals have had a profound impact on the development of societies and civilizations. These figures, through their leadership, innovation, or ideas, have altered the course of events, shaping the world in significant ways. By understanding their contributions, you can better appreciate how different forces have molded the present.
Leaders Who Changed the Course of Nations

Political figures and rulers have had lasting effects on governance and territorial control. Their decisions often influenced not only their nations but the global landscape as well. Consider these key leaders:
- Napoleon Bonaparte: A military genius whose conquests across Europe led to the reshaping of national borders and the introduction of new legal systems.
- Winston Churchill: The British Prime Minister who led the United Kingdom through the dark days of World War II, helping to secure victory against the Axis powers.
- Abraham Lincoln: Known for his leadership during the American Civil War, Lincoln’s Emancipation Proclamation ended slavery in the United States.
Innovators and Thinkers Who Shaped Ideas
Intellectuals, scientists, and philosophers have introduced groundbreaking ideas that revolutionized various fields of study. Their work paved the way for advancements in politics, science, and human rights:
- Isaac Newton: A physicist whose laws of motion and universal gravitation laid the foundation for modern physics.
- Charles Darwin: The naturalist who introduced the theory of evolution, forever altering our understanding of biology and human development.
- Karl Marx: The philosopher and economist whose theories on socialism and class struggle inspired political movements around the globe.
Understanding Major Wars and Conflicts
Conflicts between nations and groups have shaped the political, social, and economic landscape of the world. These wars have often determined the balance of power, influenced technological advancements, and prompted significant changes in cultural and social structures. A deeper understanding of these key conflicts will reveal how they have driven major shifts throughout time.
Key Wars and Their Impact
Throughout history, several wars have had profound effects on the course of nations and empires. Below is a table that outlines some of the most significant conflicts, their causes, and the outcomes that changed the world:
| Conflict | Causes | Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Napoleonic Wars | Expansionist ambitions of Napoleon, competition for power in Europe | Defeat of Napoleon, redrawing of European borders |
| American Civil War | Slavery, states’ rights, political power struggle | End of slavery, preservation of the Union, economic changes |
| World War I | Nationalism, militarism, alliances, assassination of Archduke Ferdinand | Collapse of empires, redrawn borders, emergence of new nations |
| World War II | Fascism, expansionist policies, economic instability | Defeat of Axis powers, United Nations established, Cold War division |
Long-term Effects of Conflict
The aftermath of major wars extends beyond the immediate consequences, often reshaping societies in ways that can last for generations. Changes in political alliances, economic systems, and social structures frequently result from these battles. Understanding these long-term impacts is crucial for grasping how conflicts have influenced the modern world.
Political Movements You Should Know
Political movements have often been the driving force behind societal change, challenging existing systems and promoting new ideas. These movements have shaped the political and social frameworks of many nations, influencing the course of events for centuries. By understanding the core principles and goals of key movements, you can gain insight into the evolution of global governance and society.
Many of these movements arose in response to injustice, inequality, or political oppression, and their impact continues to resonate today. From the fight for civil rights to the struggle for independence, each of these movements has contributed to the transformation of political systems around the world.
- The Enlightenment: A philosophical movement that emphasized reason, individual rights, and the separation of powers, influencing the development of modern democracies.
- Socialism and Communism: Ideologies advocating for the redistribution of wealth and the establishment of a classless society, championed by thinkers like Karl Marx and Vladimir Lenin.
- The Women’s Suffrage Movement: A global effort aimed at securing voting rights for women, which played a critical role in shaping gender equality in modern societies.
- Nationalism: A movement that emphasizes the importance of national identity, sovereignty, and self-determination, which has led to the creation of new nations and independence movements.
- The Civil Rights Movement: A campaign to end racial discrimination and secure equal rights for African Americans, most notably in the United States during the 1960s.
Revolutions That Shaped the World

Revolutions have played a crucial role in transforming societies, overthrowing outdated systems, and introducing new ideologies. These movements have often been sparked by a desire for greater freedom, equality, and justice. By challenging existing power structures, revolutions have not only changed governments but have also reshaped the very fabric of social, political, and economic life.
From the rise of democracy to the birth of new nations, revolutionary movements have led to the establishment of modern political systems and the spread of key ideas. Below are some of the most significant revolutions that altered the course of history:
- The American Revolution: A pivotal moment in the establishment of democratic principles, this revolution led to the independence of the United States and the creation of a new political system based on liberty and justice.
- The French Revolution: A radical transformation that ended centuries of monarchical rule in France, inspiring movements for liberty, equality, and fraternity around the globe.
- The Industrial Revolution: A sweeping change that revolutionized economies and societies, introducing new technologies, shifting labor systems, and creating urban centers of production.
- The Russian Revolution: A series of events that led to the fall of the Russian Empire and the rise of the Soviet Union, influencing the spread of communism worldwide.
- The Chinese Revolution: A critical movement that resulted in the overthrow of imperial rule and the establishment of the People’s Republic of China, shifting the balance of power in Asia.
- The Haitian Revolution: The first successful slave revolt, leading to the independence of Haiti and the abolition of slavery in the Americas.
Influential Empires and Civilizations
Throughout the ages, various empires and civilizations have left a lasting impact on the development of cultures, economies, and political systems across the globe. These powerful entities often shaped the course of events through their advances in science, philosophy, art, and governance. Understanding the legacy of these societies helps in grasping how modern nations have evolved and how global interactions have been influenced by these past powers.
The achievements and contributions of these civilizations were far-reaching, affecting everything from military strategies to social structures. They built monumental cities, created lasting innovations, and fostered rich cultural exchanges. Below are some of the most influential empires and their enduring legacies:
The Roman Empire

The Roman Empire, at its peak, spanned vast regions and was known for its advancements in law, engineering, and governance. The Roman legal system and architectural achievements, such as aqueducts and roads, have had a lasting influence on Western civilizations.
The Mongol Empire
The Mongol Empire, under the leadership of Genghis Khan, created the largest contiguous land empire in history. Its impact was felt in terms of trade, military tactics, and cultural diffusion across Eurasia.
The Ottoman Empire
Stretching across Southeast Europe, Western Asia, and North Africa, the Ottoman Empire was a major force in world politics for centuries. Its legacy includes architectural masterpieces, such as the Hagia Sophia, and significant contributions to art, science, and cuisine.
The Ancient Egyptian Civilization
One of the earliest and most influential civilizations, Ancient Egypt made advancements in architecture, mathematics, and medicine. The construction of the pyramids and the development of hieroglyphics remain enduring symbols of their achievements.
The Byzantine Empire
As the eastern continuation of the Roman Empire, the Byzantine Empire preserved Roman culture and law while influencing the development of Christianity, art, and the spread of Greek knowledge throughout Europe and Asia.
The Indus Valley Civilization

One of the oldest urban cultures, the Indus Valley Civilization introduced innovations in city planning, drainage systems, and trade that influenced later societies in South Asia and beyond.
Social Changes and Cultural Shifts
Throughout time, societies have experienced profound transformations that reshaped the way individuals interact, perceive the world, and organize their communities. These changes often stem from shifts in values, technological innovations, or responses to political and economic challenges. Social and cultural evolution is the result of both internal and external forces that push boundaries and redefine norms.
The movements and events that lead to social change have influenced art, literature, religion, and everyday life. From the rise of new ideologies to the challenges of modernization, these shifts have had lasting effects on how cultures develop and how people relate to one another across generations. Key moments in these transformations include the rise of human rights movements, advancements in gender equality, and the global spread of new technological advancements.
Some of the most significant social and cultural shifts include:
- Renaissance and Enlightenment: A period that rekindled interest in science, philosophy, and humanism, shaping modern Western thought and encouraging individual rights and freedoms.
- Industrialization: The widespread shift from agrarian economies to industrialized urban centers, leading to changes in labor, family structures, and social classes.
- Feminist Movements: A long-standing cultural shift that pushed for gender equality and women’s rights, challenging traditional gender roles and improving social and political opportunities for women.
- Urbanization: The movement of populations from rural areas to cities, which sparked new cultural dynamics, including diverse communities, new forms of entertainment, and changing social roles.
- Globalization: The interconnectedness of the world through trade, communication, and travel, leading to a blending of cultures, ideas, and economic systems.
Economic Theories and Their Impact
Over the centuries, various economic theories have emerged, each shaping the way societies manage resources, wealth, and trade. These ideas have not only influenced national policies but have also had a profound effect on global markets, class structures, and the distribution of power. Economic theories often provide the framework for understanding how different systems operate, ranging from capitalism to socialism, and they continue to guide policymakers today.
The evolution of economic thought has led to significant changes in the way societies function, impacting everything from the role of government in the economy to the way businesses operate. Understanding these theories is key to grasping how economies grow, stabilize, or falter. Below are some of the most influential economic theories and their lasting effects on the world:
- Classical Economics: Developed by thinkers such as Adam Smith, this theory emphasizes the importance of free markets and the “invisible hand” that guides supply and demand. It laid the foundation for modern capitalist economies and advocates minimal government intervention.
- Keynesian Economics: Proposed by John Maynard Keynes, this theory advocates for government intervention in times of economic downturns to stimulate demand and reduce unemployment. It shaped policies of welfare states and became central to post-World War II economic strategies in many countries.
- Marxist Economics: Based on the works of Karl Marx, this theory critiques capitalist economies by highlighting class struggles and the exploitation of labor. It has influenced socialist and communist movements worldwide, promoting the idea of classless societies and collective ownership of resources.
- Monetarism: Popularized by Milton Friedman, monetarism stresses the importance of controlling the money supply to manage inflation. It advocates for limiting government intervention and is associated with the economic policies of the 1980s in countries like the United States and the United Kingdom.
- Supply-Side Economics: Focuses on boosting economic growth by increasing the supply of goods and services, often through tax cuts and deregulation. Proponents argue that this approach leads to more investment, job creation, and overall economic expansion.
Each of these economic theories has shaped the policies and practices of nations in unique ways. From the rise of industrial economies to the push for social welfare, the impact of these ideas continues to influence both national and global economic landscapes.
Religions and Philosophies to Study

Throughout human civilization, different belief systems and philosophical frameworks have emerged, influencing the way individuals view the world, ethics, and existence. These systems often serve as guides for moral behavior, social organization, and spiritual practices. Understanding these belief systems is essential not only for appreciating the diversity of human thought but also for grasping their impact on cultures, politics, and global relations.
The various religious and philosophical ideas that have shaped societies across time and space can be categorized into distinct traditions. Some emphasize the importance of spirituality and divine worship, while others focus on human reason, ethics, and the search for truth. Below are key religions and philosophies that have played significant roles in shaping civilizations:
- Christianity: Centered on the life and teachings of Jesus Christ, Christianity has shaped the moral and cultural landscape of Western societies. It emphasizes love, forgiveness, and the belief in salvation through faith.
- Islam: Based on the teachings of the Prophet Muhammad and the Qur’an, Islam has significantly influenced the social and political fabric of many countries. It teaches submission to the will of God (Allah) and emphasizes the importance of charity, prayer, and community.
- Hinduism: One of the oldest belief systems, Hinduism offers a diverse range of practices and philosophies, including the belief in karma, reincarnation, and moksha (liberation from the cycle of rebirth). It also emphasizes the importance of dharma (duty) and devotion to deities.
- Buddhism: Founded by Siddhartha Gautama (Buddha), this philosophy emphasizes the pursuit of enlightenment through meditation, mindfulness, and ethical living. It teaches the Four Noble Truths and the Eightfold Path as a means to overcome suffering.
- Confucianism: Rooted in the teachings of Confucius, this philosophy focuses on the importance of relationships, social harmony, and moral conduct. It stresses respect for authority, filial piety, and the cultivation of virtuous behavior in both personal and political life.
- Existentialism: A modern philosophy that emphasizes individual freedom, choice, and the search for meaning in an often indifferent or absurd world. Key figures such as Jean-Paul Sartre and Albert Camus challenged traditional views on religion and ethics.
These belief systems and philosophies offer diverse perspectives on existence, ethics, and the universe, providing frameworks that have influenced individuals and societies across the globe. Studying these traditions allows for a deeper understanding of human culture and the ways in which different societies have approached fundamental questions about life, purpose, and morality.
Understanding Global Exploration and Trade
The period of global exploration and commerce saw a dramatic expansion of cross-cultural interaction and the exchange of goods, ideas, and technologies. This era, often marked by bold voyages and the establishment of international trading networks, reshaped economies and societies across continents. The desire for wealth, territorial expansion, and the spread of knowledge drove individuals and nations to seek new trade routes, often leading to the discovery of distant lands and the establishment of powerful global networks.
Exploration was not only about geographical discovery but also about the flow of resources, culture, and knowledge between different parts of the world. As new territories were explored, global trade routes were established, facilitating the exchange of goods such as spices, silk, precious metals, and other valuable commodities. This, in turn, encouraged the rise of powerful empires, driven by the wealth generated from international commerce.
Key elements that shaped the age of exploration and trade include:
- Technological Advancements: The development of navigational tools, such as the compass, astrolabe, and more advanced ship designs, played a critical role in enabling long-distance sea voyages. These innovations made it possible to explore new routes and establish global trading systems.
- European Expansion: European nations, particularly Spain, Portugal, and later England and France, sought new trade routes to the East, driving the exploration of Africa, the Americas, and Asia. The quest for spices, silk, and other luxuries became a significant motivation for exploration.
- Colonization: The establishment of colonies in newly discovered lands allowed for the extraction of valuable resources, such as gold, silver, and agricultural products. Colonization also led to the exchange of crops, animals, and technologies between the Old and New Worlds in what became known as the Columbian Exchange.
- Trade Networks: The creation of vast trade networks connected distant regions, with major trading hubs emerging in Europe, Africa, the Middle East, and Asia. Cities like Venice, Lisbon, and Malacca became central points for the exchange of goods, while the Silk Road and transatlantic routes facilitated the flow of merchandise across continents.
- Impact on Indigenous Populations: While exploration brought wealth and new opportunities to European nations, it had devastating effects on indigenous peoples. Many were forced into slavery, displaced, or decimated by disease brought by the explorers. The effects of colonization continue to shape the world today.
The era of global exploration and trade left a lasting legacy, influencing global economics, culture, and geopolitics for centuries. The establishment of interconnected trade routes, the exchange of goods and ideas, and the interactions between diverse cultures significantly impacted the course of global development.
Analyzing World Geography and Borders
The geography of a region plays a critical role in shaping the political, economic, and cultural landscape of its societies. Boundaries, both natural and man-made, have historically determined the distribution of resources, the rise and fall of civilizations, and the movement of peoples. By examining geographical features and the creation of borders, we can gain a deeper understanding of how civilizations interacted with their environment and with each other. The division of land into distinct territories has always been influenced by factors such as geography, climate, and the strategic interests of those in power.
The physical features of land, such as mountains, rivers, and coastlines, often serve as natural barriers that have influenced the establishment of borders. On the other hand, artificial borders, created through treaties or conquests, have sometimes led to conflict and shifted the balance of power. The exploration of geography and borders also highlights how societies have adapted to their surroundings and how these regions have evolved over time. Understanding the complex relationship between geography and territorial boundaries offers valuable insight into global interactions, from trade routes to military conflicts.
Geographical Features Shaping Boundaries
Geography significantly impacts the establishment and maintenance of borders. Natural barriers such as mountains, rivers, and oceans often determine the limits of territories, providing both protection and division. For instance, the Himalayas in Asia and the Andes in South America have acted as borders between different civilizations for centuries. Similarly, oceans and seas have historically separated continents, influencing the spread of cultures and trade.
Human-Created Boundaries
Man-made borders, defined through treaties, wars, and negotiations, have dramatically altered the geopolitical landscape. The creation of artificial boundaries has often led to political and social challenges, especially in regions where different cultural groups were divided. The division of Africa during the colonial period and the redrawing of borders after major wars, such as World War I and World War II, are prime examples of human-made boundaries that continue to shape current international relations.
| Geographical Feature | Impact on Borders |
|---|---|
| Mountains | Form natural boundaries that separate civilizations and limit movement. |
| Rivers | Act as natural borders and facilitate trade, but can also cause disputes over territory. |
| Oceans | Provide natural separation between continents, influencing maritime trade and exploration. |
| Deserts | Create harsh, uninhabitable zones that limit human settlement and interaction. |
In summary, geography and the creation of borders are intertwined with the development of human societies. From ancient civilizations to modern nation-states, the interaction between people and their environment has been a driving force in shaping the world as we know it today. By analyzing both natural and artificial borders, we can better understand the forces that have influenced global dynamics throughout history.
Technological Advancements in History
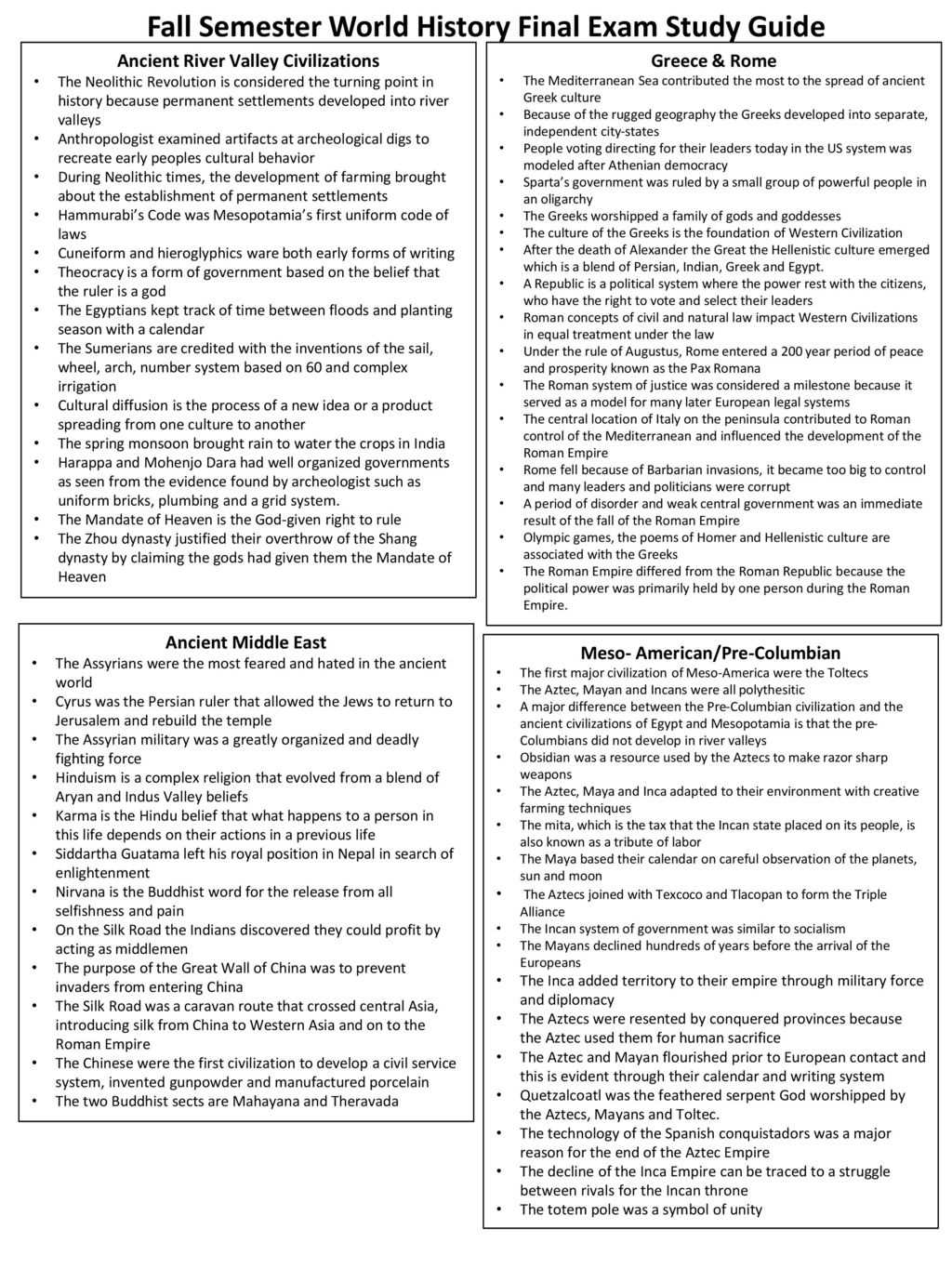
Throughout human existence, the development of new technologies has been a driving force behind societal transformation. From the creation of simple tools to the advent of complex machinery, these innovations have shaped the way civilizations function and evolve. Technological progress has not only changed how people work and live but also influenced communication, transportation, and even the structure of economies and governments. Understanding key moments of advancement highlights the profound impact these inventions had on the global stage, often altering the course of entire nations or cultures.
The earliest breakthroughs in human technology were often simple solutions to immediate needs, such as the creation of fire-starting tools or the invention of the wheel. Over time, as knowledge accumulated and societies grew more complex, technological advancements became more sophisticated. From the printing press to the internet, each new development created new opportunities for progress, but also posed challenges and risks. The interplay between innovation, its applications, and its consequences continues to shape the world today.
Key Technological Milestones
The following list highlights some of the most pivotal inventions and discoveries in shaping the modern world:
- The Wheel: One of the earliest innovations, revolutionizing transportation and the movement of goods.
- The Printing Press: Invented by Johannes Gutenberg, this technology enabled the mass production of books, leading to the spread of knowledge and the beginning of the Renaissance.
- The Steam Engine: This breakthrough in energy production revolutionized industry and transportation during the Industrial Revolution.
- The Telegraph: A communication device that allowed for long-distance transmission of messages, paving the way for modern communication systems.
- Electricity: The harnessing of electrical power facilitated the development of countless technologies, from lighting to machinery.
- The Internet: A transformative development that has reshaped communication, commerce, education, and social interaction globally.
Impact of Technology on Societies
Technological advancements have had profound effects on human societies, often creating significant shifts in the way people live and interact. These changes can be categorized into several key areas:
- Economic Transformation: New technologies often led to the creation of industries, the expansion of markets, and shifts in the workforce.
- Social Change: Advances in communication and transportation have reshaped social structures, enabling greater mobility and connectivity.
- Cultural Impact: Innovations like the printing press and the internet have enabled the spread of cultural ideas and artistic movements across borders.
- Political Influence: Technological developments have often influenced political structures, from the use of the printing press in revolutionizing governance to the role of the internet in modern political movements.
In conclusion, the continuous development of technology has been one of the most significant factors in shaping the course of human progress. Each major advancement has brought both opportunities and challenges, influencing not just individuals but entire civilizations. Understanding these breakthroughs provides insight into how societies have adapted and transformed over time, as well as the ways in which innovation continues to influence our present and future.
Legacy of Colonialism and Imperialism
The long-lasting effects of colonization and imperial expansion have left deep marks on societies across the globe. These periods of domination reshaped the political, economic, and social landscapes of both the colonizers and the colonized. While colonial powers often claimed to bring civilization and development, the reality was far more complex, with enduring consequences that continue to influence global relations today. The legacy of this era includes the reshaping of national boundaries, the exploitation of resources, and the imposition of foreign governance systems, all of which have left lasting impacts on the countries involved.
Colonial and imperial endeavors were often driven by the desire for wealth, power, and control over strategic territories. In many cases, the benefits of these empires were primarily enjoyed by the colonial powers, while local populations faced oppression, displacement, and cultural erasure. Despite the eventual end of formal colonial rule, the ramifications of these actions have persisted, shaping modern geopolitical struggles, economic inequalities, and social divisions.
Key Effects of Colonialism
The effects of colonial rule can still be seen in several critical areas:
- Artificial Borders: Many national boundaries were drawn without regard to local cultures or ethnic groups, leading to ongoing conflicts and struggles for autonomy in post-colonial states.
- Economic Dependency: Colonies were often economically exploited, their resources extracted for the benefit of the colonizing countries, leading to a legacy of economic dependency in many regions.
- Cultural Displacement: Indigenous cultures were often suppressed or replaced by foreign languages, religions, and customs, leaving lasting scars on local identities.
- Political Instability: Many newly independent nations faced challenges in establishing stable governments, as colonial powers often left behind weak political structures that were ill-equipped to manage diverse populations.
Ongoing Impact on Global Relations
The consequences of colonialism continue to affect global relations, particularly in areas like trade, diplomacy, and international aid. Former colonial powers often maintain economic and political ties with their former colonies, sometimes leading to unequal partnerships. Additionally, the exploitation of resources during the colonial era has left some regions with underdeveloped economies that continue to struggle in the face of global competition.
Furthermore, the cultural exchange that occurred during the imperial era, although sometimes harmful, also led to a blending of traditions, languages, and ideas that has shaped the modern world. Despite the negative aspects of colonization, some of the cultural interactions fostered during this period have contributed to global trade, technology, and the spread of knowledge.
In conclusion, the legacy of colonialism and imperialism is far-reaching and complex. While it has caused significant harm, it has also shaped the development of nations and global systems in profound ways. Acknowledging and understanding these legacies is crucial for addressing current inequalities and fostering more equitable international relations.
Preparing for Multiple Choice Questions
When approaching objective-style questions, it’s important to develop strategies that help you identify the correct answers quickly and accurately. These types of questions are designed to test your knowledge of key facts, concepts, and ideas, so it’s crucial to review and understand the material thoroughly. Effective preparation for multiple-choice assessments involves practicing specific techniques that improve your ability to analyze each option critically, manage time efficiently, and avoid common pitfalls that could lead to incorrect answers.
Strategies to Improve Accuracy

To maximize your chances of selecting the correct response, consider the following approaches:
- Read Carefully: Pay attention to the wording of both the question and all answer choices. Often, slight differences in wording can make one option stand out as the correct answer.
- Eliminate Clearly Wrong Answers: If you can identify one or more options that are clearly incorrect, eliminate them right away. This increases your chances of choosing the correct answer by narrowing down your choices.
- Look for Keywords: Keywords or phrases in both the question and the options often provide clues that point to the right answer. Focus on these elements to guide your decision-making process.
- Consider Context: Think about the context of the material you’ve studied. Does the answer choice align with what you know about the topic? Use your understanding of the subject to test each option logically.
Time Management and Test-Taking Tips

Efficient time management is essential when taking objective tests, as you must allocate enough time to review each question thoroughly. Here are a few tips to help you navigate the test effectively:
- Don’t Rush: Take your time to read each question carefully and think about the options before making a choice. If you’re unsure, it’s better to skip and return later than to rush and make an error.
- Review Your Answers: If time permits, go back and double-check your answers. Revisit questions you were uncertain about and ensure your responses align with your understanding of the material.
- Use the Process of Elimination: If you’re stuck on a question, eliminate the least likely options first. This strategy can significantly improve your odds of guessing correctly when you’re unsure of the answer.
By mastering these strategies, you can approach multiple-choice questions with greater confidence, improve accuracy, and enhance your overall performance. Practicing regularly and staying focused during the test will help you feel prepared and ready to tackle any challenge presented in the format.