
The study of the planet’s dynamic processes is essential for gaining a deeper understanding of its structure, systems, and changes over time. In this section, we explore crucial principles related to the Earth’s composition and natural phenomena. These foundational topics help to form a comprehensive view of how various elements interact within the environment.
As you navigate through these ideas, you’ll encounter a range of challenging yet insightful exercises designed to test your grasp of the material. Mastery of these concepts is vital for anyone looking to expand their knowledge of the forces shaping our world. By focusing on problem-solving techniques and recognizing key patterns, you’ll enhance your understanding of the subject and improve your ability to apply this knowledge effectively.
Earth Science Chapter 24 Overview
This section explores the fundamental concepts related to the planet’s physical structure and its ever-changing processes. The focus is on understanding the interactions between various elements within the environment and how they contribute to the planet’s dynamic nature. By examining key topics, this part of the curriculum provides essential insights into the forces that shape the natural world.
Throughout this section, learners are introduced to a range of topics that cover critical processes such as tectonic movements, atmospheric dynamics, and the water cycle. Each concept is designed to build a comprehensive understanding of the interconnected systems that drive environmental changes. Mastering these principles is crucial for anyone seeking to deepen their knowledge of how the planet functions and evolves over time.
Key Concepts of Chapter 24

This section introduces crucial ideas that explain the planet’s structure and the forces that influence its various systems. Understanding these concepts is vital for grasping how natural phenomena occur and interact over time. The focus is on the foundational elements that shape the environment and how they work together to maintain balance within the system.
The key principles include the movement of tectonic plates, the role of the atmosphere in supporting life, and the continuous cycle of water that sustains ecosystems. These processes are interconnected and essential for understanding how the planet functions as a whole. Mastering these concepts provides a clearer view of the natural forces at play and their impact on the world we live in.
Important Definitions to Remember
In order to fully grasp the material, it’s essential to familiarize yourself with key terms that form the foundation of this subject. These terms are not only critical for understanding the processes discussed but also serve as the building blocks for solving related problems. Mastery of these definitions allows for a deeper comprehension of how the various systems and forces interact.
Plate Tectonics refers to the theory explaining the movement of the Earth’s lithosphere. It helps to understand seismic activity, mountain formation, and other geophysical events. Convection Currents describe the flow of heat within the mantle, driving tectonic movements. Hydrological Cycle outlines the continuous movement of water between the atmosphere, surface, and underground reservoirs, essential for sustaining ecosystems.
Understanding Earth’s Processes
Grasping the fundamental processes that drive the planet’s activities is crucial for understanding how various natural systems interact and evolve. These processes are interdependent and constantly shape the world in profound ways. By examining these dynamic forces, we can gain a better understanding of how different environmental systems contribute to the planet’s overall functioning.
Internal and External Forces

The internal forces, such as tectonic movements, play a key role in shaping the planet’s structure. External forces, including atmospheric and oceanic systems, are equally significant in influencing weather patterns and climate. Together, these forces form the complex web of interactions that govern the Earth’s behavior.
Key Processes to Consider
| Process | Description |
|---|---|
| Tectonic Activity | The movement and interaction of tectonic plates lead to the formation of mountains, earthquakes, and volcanic activity. |
| Weather Systems | The dynamic atmosphere, driven by solar energy, generates patterns such as storms, winds, and temperature variations. |
| Water Cycle | The continuous movement of water through evaporation, precipitation, and runoff sustains ecosystems and shapes landscapes. |
Common Mistakes in Chapter 24 Assessments

When tackling exercises related to the subject, it’s easy to make certain errors that can affect your understanding of the material. These common mistakes often arise from overlooking key details or misinterpreting concepts. Identifying these pitfalls early can help you avoid confusion and ensure a clearer grasp of the subject matter.
One frequent mistake is rushing through questions without fully reading the instructions. Skipping steps or misinterpreting specific terms can lead to incorrect answers. Additionally, failing to properly understand the relationships between different processes or concepts can cause errors in explanations or solutions. It’s also important to review your work for any small oversights that might change the outcome of your response.
Step-by-Step Problem Solving Tips
When approaching complex problems, breaking them down into manageable steps is essential for finding accurate solutions. By following a systematic approach, you can ensure that no important details are overlooked and that your reasoning remains clear throughout the process. This method not only helps in solving individual problems but also enhances your overall understanding of the material.
Understanding the Problem
Before jumping into calculations or explanations, take a moment to fully comprehend the problem at hand. Identify the key elements and understand the relationships between them. This will guide your approach and ensure you focus on the most relevant information.
Organizing Your Work

Once you have a clear understanding of the problem, begin to organize your solution. Break it into logical steps, and tackle each part individually. This structured approach prevents errors and ensures you stay focused on the task at hand.
How to Approach Multiple-Choice Questions

Multiple-choice questions can sometimes be tricky, but with the right approach, they become much easier to handle. The key is to carefully analyze each option and use your understanding of the material to eliminate incorrect answers. By focusing on the structure of the question and your knowledge of the topic, you can improve your chances of selecting the correct answer.
Steps to Effectively Tackle Multiple-Choice Questions

- Read the Question Thoroughly: Always read the question carefully before looking at the answer choices. Make sure you understand exactly what is being asked.
- Analyze All Options: Review each answer option before making your choice. Sometimes, options may seem similar, but small differences can reveal the correct answer.
- Eliminate Clearly Incorrect Answers: Remove options that are clearly wrong. This increases the probability of choosing the correct answer from the remaining choices.
- Use Contextual Clues: If you’re unsure, use clues from the question or your prior knowledge to guide your decision.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
- Rushing Through Questions: Don’t rush. Carefully consider each answer to avoid mistakes.
- Overthinking: Don’t second-guess yourself too much. Trust your initial instincts unless you find a clear mistake.
- Leaving Questions Blank: If unsure, attempt to answer using the process of elimination or educated guesses rather than leaving the question unanswered.
Strategies for Answering Short-Answer Questions
Short-answer questions require you to provide concise and clear responses, focusing on key points and essential details. Unlike multiple-choice questions, these require a more thorough understanding of the material and the ability to express your knowledge effectively. By following some straightforward strategies, you can ensure your responses are well-organized and relevant to the question.
Key Tips for Writing Effective Responses

When answering short-answer questions, it’s important to be direct and to the point. Here are some strategies to help you craft clear and focused answers:
- Be Concise: Stick to the core idea and avoid unnecessary elaboration. Aim for clarity and precision.
- Use Specific Examples: Whenever possible, include relevant examples to support your response, demonstrating a deeper understanding of the topic.
- Address All Parts of the Question: Ensure that your answer covers all aspects of the question. If it has multiple parts, respond to each one in turn.
- Organize Your Thoughts: Write your response in a logical sequence, starting with the main point followed by explanations or supporting details.
Structure of a Strong Short-Answer
| Element | Description |
|---|---|
| Introduction | Start with a brief overview or a direct answer to the question. |
| Body | Provide details, explanations, and examples that support your main idea. |
| Conclusion | Finish with a clear closing sentence that reinforces the main point or summarizes your response. |
Review of Major Topics
This section provides a comprehensive review of the key concepts that underpin the subject. Understanding these fundamental topics is crucial for gaining insight into the natural world and the processes that shape it. From the forces beneath the surface to the interactions within the atmosphere, mastering these areas of study enables a deeper understanding of the complex systems at work.
Key Areas of Focus

- Tectonic Activity: The movement of the planet’s outer layers, leading to earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, and mountain formations.
- Atmospheric Interactions: The relationship between air currents, weather patterns, and climate systems that regulate temperature and precipitation.
- Hydrological Cycle: The movement of water through various stages, including evaporation, condensation, and precipitation, essential for sustaining ecosystems.
- Natural Resources: Understanding the Earth’s materials, such as minerals, fossils, and water, and their role in supporting life and industries.
Important Concepts to Remember
- Plate Boundaries: The different types of plate boundaries–divergent, convergent, and transform–have distinct geological features and effects on the environment.
- Climate Change: The ongoing shifts in global weather patterns, driven by both natural processes and human activities, with significant ecological and social impacts.
- Volcanism: The processes that lead to the eruption of magma from beneath the surface, contributing to landscape formation and influencing the atmosphere.
- Soil Formation: The creation of soil through weathering of rocks and the accumulation of organic matter, vital for agriculture and ecosystems.
Examining the Earth’s Layers and Structure
The structure beneath our feet is far more complex than it may initially appear. The planet consists of several distinct layers, each with its own unique properties and functions. By studying these layers, we can better understand natural phenomena such as earthquakes, volcanic activity, and even the movement of tectonic plates. Each layer plays a crucial role in shaping the environment and supporting life as we know it.
Layers of the Planet
At the core of the planet lies the innermost layer, surrounded by the mantle, and then the outer crust. These layers interact with each other in dynamic ways, resulting in various geological processes. Below is a brief overview of each of the main layers:
- Inner Core: Composed mainly of iron and nickel, it is solid and extremely hot, reaching temperatures higher than the surface of the sun.
- Outer Core: This layer is liquid and generates the magnetic field through the movement of molten metals.
- Mantle: Thick and semi-solid, the mantle is responsible for the convection currents that drive tectonic plate movement.
- Crust: The outermost layer, which is thin and brittle compared to the other layers, and supports all life on the planet.
Understanding the Interactions Between Layers
The interactions between these layers can lead to both gradual and catastrophic changes. For instance, the movement within the mantle can cause the crust to crack, leading to earthquakes or the formation of mountain ranges. Similarly, the transfer of heat between layers plays a significant role in volcanic eruptions and the cycling of materials through the planet’s systems.
Insights on Plate Tectonics and Movement
The dynamic movement of the planet’s outer layers has profound effects on the surface, leading to the formation of mountains, earthquakes, and volcanic activity. This movement occurs through a process known as plate tectonics, where large slabs of solid rock, called tectonic plates, shift and interact with one another. Understanding how these plates move and interact is key to explaining many of the geological events that shape our world.
Types of Plate Movements
There are different types of interactions between tectonic plates, each contributing to distinct geological features and events. These interactions can be categorized into three primary types:
| Type of Movement | Explanation | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Divergent Boundaries | Plates move apart, creating new crust and often leading to the formation of mid-ocean ridges. | Mid-Atlantic Ridge |
| Convergent Boundaries | Plates collide, resulting in mountain building, subduction zones, and volcanic activity. | Himalayas, Pacific Ring of Fire |
| Transform Boundaries | Plates slide past each other, causing friction and frequent earthquakes along fault lines. | San Andreas Fault |
The Impact of Plate Movement

The movement of tectonic plates is responsible for some of the most dramatic events in the planet’s history. Earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, and the gradual drift of continents all result from the shifting of these plates. As plates move, they can cause shifts in the land, creating new landforms, altering ocean currents, and even affecting global climate over long periods of time.
Understanding the Atmosphere in Detail
The atmosphere is a crucial layer surrounding the planet, playing an essential role in sustaining life. It is composed of various gases that interact with each other and the environment, creating weather patterns, protecting from harmful radiation, and maintaining temperatures suitable for living organisms. Understanding the structure, composition, and functions of this gaseous envelope is fundamental to studying the dynamics of the planet’s climate and weather systems.
The atmosphere is made up of several distinct layers, each with unique characteristics. These layers vary in temperature, pressure, and composition, influencing everything from cloud formation to the movement of air currents. The interaction between these layers drives weather systems and climatic changes, making it a critical component of the planet’s overall environmental system.
One of the most important functions of the atmosphere is its role in regulating temperature. It acts as a protective shield, absorbing and redistributing solar energy, helping to maintain conditions conducive to life. Additionally, it provides the necessary gases, such as oxygen and nitrogen, that are essential for respiration and other biological processes.
Impact of Natural Disasters on the Planet
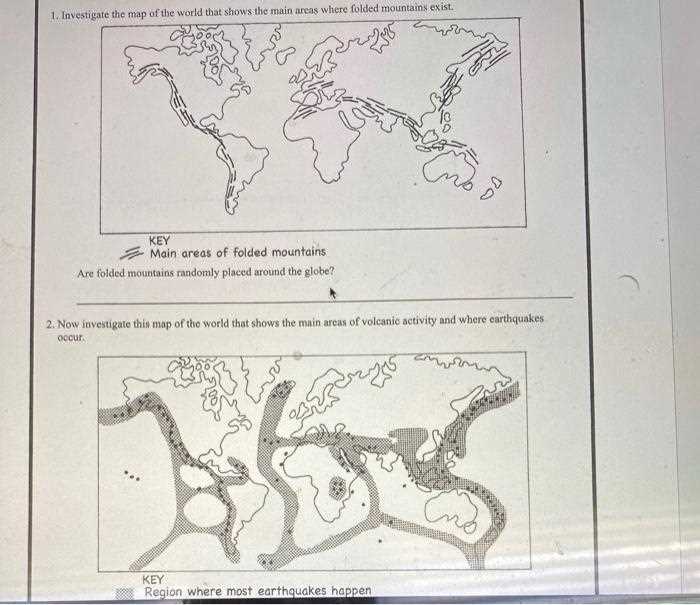
Natural disasters, such as earthquakes, floods, and volcanic eruptions, can have profound and lasting effects on the planet’s surface and ecosystems. These events disrupt the environment, cause widespread destruction, and alter the natural balance of regions affected. The aftermath of such occurrences can reshape landscapes, change habitats, and affect human societies both immediately and in the long term.
Effects on Geographical Features
One of the most immediate impacts of natural disasters is the alteration of the landscape. Earthquakes can cause shifts in landforms, creating faults or even new land features. Volcanic eruptions can reshape mountains, while floods may dramatically alter river paths and coastal areas. These changes can have lasting effects on local ecosystems and human settlements.
Long-Term Environmental Consequences
Beyond immediate damage, natural disasters can have long-term environmental consequences. Floods may lead to soil erosion and the destruction of agricultural lands, while wildfires can drastically alter local flora and fauna. Additionally, the pollutants and debris from such events can affect air and water quality, leading to health risks for both humans and wildlife. Restoration efforts can take years, and in some cases, ecosystems may never fully recover.
Reviewing the Water Cycle Processes
The movement of water through various stages in the environment is a continuous and vital process for sustaining life. This cycle involves multiple stages that are interconnected, allowing water to move between the atmosphere, land, and bodies of water. Understanding these processes is crucial for grasping how water is distributed, purified, and reused in nature.
The water cycle is driven by energy from the sun, which heats the surface and causes water to evaporate into the air. This vapor then rises, cools, and condenses to form clouds. Eventually, water returns to the ground through precipitation, replenishing lakes, rivers, and groundwater supplies. Below is a review of the main stages involved:
- Evaporation: The process by which water turns into vapor and rises into the atmosphere from oceans, lakes, and rivers.
- Condensation: The cooling of water vapor in the atmosphere, which forms clouds and water droplets.
- Precipitation: The release of water from clouds back to the surface in the form of rain, snow, sleet, or hail.
- Infiltration: The process by which water soaks into the soil and replenishes groundwater supplies.
- Runoff: Water that flows over the ground and eventually returns to bodies of water such as rivers, lakes, or oceans.
These stages, though distinct, are part of a continuous cycle that ensures water availability for ecosystems and human use. Understanding each of these steps helps in managing water resources and addressing challenges related to water scarcity and environmental conservation.
How to Effectively Use Study Guides
Study guides are invaluable tools for mastering complex material and preparing for exams. They help break down large topics into manageable sections, making it easier to focus on key concepts and important details. By using study guides effectively, you can maximize retention and improve your understanding of the material.
Organize and Prioritize Information
Start by reviewing the study guide to identify the most crucial concepts. Break down each section, focusing on areas where you need the most improvement. Highlight or underline terms and ideas that are essential to your understanding. Organize your notes and create a prioritized list of what needs further review, ensuring that you spend more time on difficult topics while reinforcing the basics.
Practice Active Recall and Application

Rather than passively reading through the study guide, engage with the material actively. Test your knowledge by answering questions from the guide without looking at your notes. This method of active recall helps solidify the information in your memory. Additionally, try to apply what you’ve learned to real-world examples or scenarios, as this will deepen your comprehension and make the material more meaningful.
Practical Tips for Test Preparation
Preparing for a test requires more than just reading through notes; it involves a strategic approach to ensure you’re retaining the information and applying it effectively. By using a few practical techniques, you can boost your efficiency and confidence, making your study sessions more productive and less stressful.
Set a Consistent Study Schedule

One of the most effective ways to prepare for any exam is to establish a consistent study routine. Allocate specific time slots each day to review different topics, breaking down the material into smaller, more manageable sections. By studying regularly, you avoid cramming and give your brain time to absorb and consolidate information.
Practice with Sample Questions
Make use of practice tests or sample questions that resemble the format of the actual exam. These exercises help familiarize you with the types of questions you might encounter and allow you to gauge your understanding of key concepts. Practicing regularly will also help you manage time more effectively during the real test.
Resources for Further Study and Learning
When preparing for an exam or aiming to deepen your understanding of specific topics, additional resources can play a crucial role. These materials can provide alternative explanations, exercises, and examples that enhance your comprehension and help reinforce the concepts you have studied. Whether you prefer books, online courses, or interactive platforms, there are numerous options available to support your learning journey.
Books and Textbooks
Traditional textbooks often serve as the foundation for your studies. However, there are additional books available that explain the same concepts from different perspectives, providing deeper insights. Consider exploring:
- Study Guides: Comprehensive guides designed to break down complex topics and offer practice questions.
- Reference Books: Specialized texts that dive into specific areas you want to explore in greater depth.
Online Resources and Platforms
The internet offers a vast array of resources that can complement your studies. Here are some helpful options:
- Interactive Websites: Websites with quizzes, videos, and visual aids to help solidify your knowledge.
- Online Courses: Structured learning paths offered by various platforms, often including tests and certificates.
- YouTube Channels: Educational channels with detailed video lessons and explanations on key topics.
By leveraging these additional resources, you can reinforce your knowledge, fill in any gaps, and increase your confidence in tackling related questions during the exam.