
Preparing for a challenging assessment in the field of infectious agents requires a deep understanding of essential concepts and processes. Focusing on the mechanisms by which these pathogens affect living organisms, their methods of transmission, and the body’s defense systems is crucial for success. Whether you’re reviewing structural components or understanding diagnostic methods, each topic plays a vital role in ensuring you’re well-equipped for your upcoming evaluation.
Comprehensive study is key when facing complex subject matter. By addressing a wide range of topics, from pathogen classification to immune responses, you can gain a more nuanced perspective. Furthermore, practicing with real-life scenarios and sample items will strengthen your grasp on important details and improve your ability to recall information under pressure.
Focused preparation involves knowing not only the theory behind infectious agents but also how they interact with human systems. This approach helps to bridge gaps between textbook knowledge and practical application, which is essential for answering more advanced or scenario-based challenges. Mastery of these areas will set a solid foundation for any upcoming test.
Virology Exam Questions and Answers
In this section, we focus on key topics that frequently appear in assessments related to infectious agents. Understanding core concepts and their practical applications is essential for effectively tackling complex scenarios. By reviewing typical scenarios, terminology, and fundamental processes, you can prepare thoroughly for any challenges you might encounter.
Below, we have compiled a table summarizing common topics along with sample items that test your comprehension. These examples will give you insight into the types of questions that may arise and the appropriate ways to approach them during the evaluation.
| Topic | Sample Item | Suggested Response |
|---|---|---|
| Pathogen Classification | Describe the difference between RNA and DNA viruses. | RNA viruses have single-stranded or double-stranded RNA as their genetic material, while DNA viruses contain DNA as their genome. Their replication methods also vary due to the different nucleic acid structures. |
| Immune Response | How does the body react to viral infections? | The immune system activates both innate and adaptive responses, including the release of interferons, activation of T cells, and production of antibodies to fight the infection. |
| Transmission Routes | Explain how respiratory viruses are spread. | Respiratory viruses are primarily transmitted through airborne droplets produced when an infected individual coughs, sneezes, or talks, as well as through contact with contaminated surfaces. |
| Diagnostic Methods | What is PCR used for in detecting viral infections? | Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) is a technique used to amplify and detect specific viral genetic material, allowing for precise identification of the pathogen. |
Understanding Virology for Exam Success
Achieving success in assessments related to infectious organisms requires more than just memorizing facts. A deep understanding of how these pathogens interact with hosts, their structure, and the immune responses they trigger is essential. A strategic approach to studying these topics will ensure a solid foundation and boost confidence when facing any related challenge.
Key Areas to Focus On
To master the material, it’s important to prioritize the following concepts:
- Pathogen Behavior: How these agents enter, spread, and infect hosts.
- Immune Defense: How the body’s defenses respond to infections.
- Diagnostic Methods: Techniques used to identify specific pathogens.
- Prevention and Treatment: Strategies to manage and reduce the impact of infections.
Effective Study Strategies
To ensure comprehensive preparation, consider using the following approaches:
- Active Learning: Engage with the material through practice tests and case studies.
- Review Core Concepts: Focus on understanding processes rather than memorizing terms.
- Study in Groups: Collaborative study sessions can offer different perspectives and reinforce learning.
- Utilize Visual Aids: Diagrams, charts, and videos can make complex processes easier to understand.
Common Virology Topics to Review
When preparing for assessments in the field of infectious agents, it is essential to review a variety of foundational subjects. These topics cover the mechanisms, classification, and effects of pathogens, as well as the ways the human body responds to infections. A well-rounded understanding of these areas will help you perform confidently in any related challenges.
Key Concepts in Pathogen Biology
Understanding the biology of pathogens is fundamental. Focus on the following areas:
- Pathogen Structure: Differences between viral, bacterial, and fungal organisms.
- Life Cycle: The processes by which these agents replicate and spread.
- Genetic Material: How DNA and RNA influence the behavior of microorganisms.
Human Defense Mechanisms
The body’s response to infection is a critical area to review. Pay particular attention to:
- Immune System Activation: How the body identifies and combats harmful invaders.
- Inflammation: The role of inflammation in defending against infection.
- Adaptive Immunity: How the body develops immunity after exposure to pathogens.
Key Concepts in Viral Replication
Understanding the process by which infectious agents reproduce within a host cell is crucial for mastering the fundamental principles of pathogenesis. This process involves several intricate steps that allow these organisms to multiply and spread. Grasping the mechanisms of replication will provide deeper insights into how infections progress and how they can be managed.
Attachment and Entry: The first step in replication involves the pathogen attaching to a specific receptor on the host cell surface. This is followed by the pathogen entering the cell, either by fusion with the cell membrane or through endocytosis.
Genome Uncoating: Once inside the cell, the pathogen’s genetic material is released from its protective coat. This step is essential for the next phases of replication, where the genetic instructions will be read by the host machinery.
Replication and Transcription: The pathogen’s genome is copied, and the genetic material is transcribed into RNA or proteins that are necessary for creating new pathogen particles. This step is highly dependent on the host’s cellular machinery.
Assembly and Release: New viral particles are assembled inside the host cell, utilizing components produced during the replication process. Once fully formed, these particles exit the cell, often destroying it in the process, and begin the cycle again by infecting nearby cells.
Understanding these phases is essential for exploring antiviral treatments and the mechanisms that allow these pathogens to evade the immune system and persist in the host.
Important Viruses in Human Disease
Certain pathogens have had a profound impact on human health, leading to widespread infections and long-lasting health issues. These viral agents are responsible for some of the most common and serious illnesses. Understanding the nature of these viruses, their transmission, and the diseases they cause is essential for both prevention and treatment efforts worldwide.
Key Pathogens and Their Diseases
The table below highlights several prominent viruses, the diseases they cause, and the methods by which they are transmitted:
| Virus | Associated Disease | Transmission |
|---|---|---|
| Influenza | Seasonal Flu | Airborne droplets, direct contact |
| HIV | AIDS | Blood, sexual contact, mother-to-child |
| Hepatitis B | Liver Disease | Blood, sexual contact, mother-to-child |
| Herpes Simplex | Cold sores, genital herpes | Direct contact with infected skin or mucous membranes |
| SARS-CoV-2 | COVID-19 | Airborne droplets, surface contact |
Global Health Impact
Each of the viruses mentioned above has significant consequences for public health. From causing seasonal epidemics to contributing to chronic, life-threatening conditions, these pathogens present ongoing challenges for healthcare professionals. As research advances, understanding the mechanisms of viral spread and infection is crucial for mitigating their global impact and improving patient care.
Overview of Viral Structure and Function

The study of viral particles involves understanding their basic composition and how they interact with host cells to facilitate replication. Viruses are unique in their simplicity, consisting of essential components that allow them to infect and reproduce within living organisms. Their structure plays a key role in determining how they invade host cells and propagate their genetic material.
At their core, viral particles typically consist of a protein coat known as a capsid, which encases their genetic material. This genetic material can either be DNA or RNA, depending on the type of virus. The outer structure may also be enveloped by a lipid membrane, which aids in the virus’s ability to enter host cells. The interaction between the viral surface proteins and host cell receptors is crucial for infection, as it dictates the virus’s specificity for particular cell types.
Once inside the host cell, viruses hijack the cell’s machinery to replicate and assemble new viral particles. This process is highly efficient and often leads to the destruction of the host cell. The viral replication cycle is tightly regulated, and understanding each stage provides insight into how viruses cause disease and how they might be targeted for therapeutic interventions.
Viral Transmission Methods Explained
The spread of viruses is a complex process that can occur through various routes. Understanding how these pathogens transfer from one host to another is crucial in controlling their spread and preventing infection. Viruses are equipped with different mechanisms that allow them to navigate through environmental barriers and infect susceptible individuals.
Common Transmission Routes
There are several key pathways through which viruses can be transmitted. These include:
- Airborne Transmission: Viruses can spread through droplets released when an infected person coughs, sneezes, or talks. These droplets can be inhaled by people in close proximity.
- Direct Contact: Physical contact with an infected individual or contaminated surfaces can transfer viral particles to new hosts, often through mucous membranes or broken skin.
- Vector-borne Transmission: Certain viruses are carried by insects or animals, which transfer the virus when they bite or come into contact with humans.
- Fecal-oral Route: Some viruses are spread through contaminated food or water, entering the body via the digestive tract.
Impact of Transmission Methods on Control
Understanding how a virus spreads is essential for developing effective prevention strategies. In some cases, transmission can be minimized by isolating infected individuals or improving hygiene practices. In other cases, vaccines or antiviral treatments are necessary to reduce the risk of infection and limit outbreaks.
Immune Response to Viral Infections
The body’s defense against viral pathogens involves a sophisticated network of cells, proteins, and molecules designed to detect and eliminate invading viruses. When a virus enters the body, the immune system quickly responds through both innate and adaptive mechanisms to recognize, attack, and neutralize the threat. The efficiency of this response can determine the outcome of the infection, from complete recovery to chronic disease.
Initial defenses are carried out by the innate immune system, which includes barriers like the skin, mucosal membranes, and immune cells such as macrophages and dendritic cells. These cells are responsible for identifying foreign invaders and triggering inflammatory responses that help contain the virus. In parallel, specialized proteins called interferons are released to limit viral replication and signal neighboring cells to heighten their defense mechanisms.
The adaptive immune system takes over if the infection persists, utilizing specific immune cells like T cells and B cells. T cells directly attack infected cells, while B cells produce antibodies that bind to viral particles, preventing them from entering new host cells. This coordinated response helps clear the infection and also establishes immune memory, which allows the body to mount a faster, stronger response if the virus is encountered again.
Diagnostic Techniques for Viruses
Accurately identifying viral infections is essential for effective treatment and control. Various diagnostic methods are used to detect viral presence, quantify viral load, and determine the type of virus involved. These techniques range from direct detection of viral particles to indirect methods that assess the immune response or genetic material of the virus.
One common method for diagnosing viral infections is through molecular techniques such as polymerase chain reaction (PCR). PCR allows for the amplification of viral DNA or RNA, making it possible to detect even small amounts of the virus in the sample. This method is highly sensitive and specific, enabling the detection of a wide range of viruses.
In addition to molecular diagnostics, serological tests play an important role in identifying viral infections. These tests detect antibodies in the blood, which are produced by the immune system in response to the virus. The presence and concentration of these antibodies can indicate whether an individual has been exposed to a virus, is currently infected, or has developed immunity.
Viral Evolution and Mutation Mechanisms
Viruses are known for their rapid ability to evolve, which allows them to adapt to changing environments and evade host defenses. This constant change occurs through various mechanisms of genetic variation, enabling viruses to develop new characteristics that may increase their survival or infectivity. Understanding how these mutations occur is crucial for developing effective treatments and vaccines.
The primary mechanism behind viral evolution is mutation. When viruses replicate, their genetic material may undergo changes, either spontaneously or due to external factors. These mutations can be beneficial, neutral, or detrimental to the virus’s ability to infect its host. Some of the most common mutation processes include:
- Point Mutations: Single changes in the genetic code, often leading to the alteration of one protein or enzyme, which can affect viral function or drug resistance.
- Recombination: The exchange of genetic material between different viral strains or types, leading to the creation of hybrid viruses with new properties.
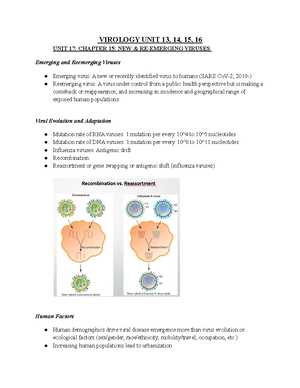
- Reassortment: The mixing of genetic material from two or more viruses, often seen in RNA viruses, which can result in new viral strains with different pathogenic potential.
These evolutionary processes are driven by selective pressures such as immune responses, antiviral medications, or changes in the environment. As a result, viral populations are highly dynamic, with new variants emerging regularly. This constant evolution poses challenges for long-term disease management and vaccine development, highlighting the need for ongoing surveillance and adaptation in medical strategies.
Role of Vaccines in Virology
Vaccines play a critical role in preventing viral infections and controlling the spread of diseases. They work by stimulating the immune system to recognize and fight specific viruses without causing illness. By introducing a harmless part of the virus, such as a protein or inactivated form, vaccines prepare the immune system for future exposure to the actual virus, reducing the severity of infection or preventing it entirely.
How Vaccines Strengthen Immunity
When a vaccine is administered, the body’s immune system recognizes the viral component introduced and produces specific antibodies. These antibodies remain in the bloodstream and can quickly respond if the body encounters the same virus later. This process helps the body fight off infections before they cause significant harm.
Impact on Public Health
Vaccination not only protects individuals but also contributes to broader public health goals. Widespread vaccination can lead to herd immunity, where enough of the population is immune to prevent the virus from spreading widely. This is especially important for protecting vulnerable groups, such as those with weakened immune systems or newborns who cannot receive certain vaccines.
Common Virology Exam Questions
Preparing for assessments related to the study of viruses often involves understanding the core concepts and mechanisms that govern viral infections. This section outlines some of the most frequent types of inquiries encountered during evaluations. It is important to focus on a variety of topics, such as viral replication, transmission, and the immune response, to be well-equipped for the challenge.
Typical Topics Covered in Assessments
During assessments, certain themes are explored more frequently. Below is a table showcasing key areas of interest that commonly appear in tests related to viral studies:
| Topic | Description |
|---|---|
| Viral Structure | Understanding the components that make up viruses, including their genetic material and protective capsid. |
| Viral Replication | Key processes involved in how viruses reproduce inside host cells. |
| Immune Response | How the human immune system recognizes and fights off viral infections. |
| Transmission Methods | Different ways viruses spread between hosts, including direct contact, airborne particles, and vectors. |
| Prevention Strategies | Methods used to reduce the spread of viral infections, such as vaccines and hygiene practices. |
Strategies for Success
Familiarity with these topics can improve understanding and preparation for evaluations. A deep knowledge of each concept, supported by real-life examples and case studies, is essential for performing well in assessments. Focus on mastering each key area, and practice with sample scenarios to increase proficiency and confidence.
Tips for Answering Virology Questions
Successfully addressing inquiries related to the study of viruses requires a strategic approach that emphasizes clarity, detail, and accurate information. It’s not only about knowing the correct answers but also about presenting them in a logical, concise, and well-supported manner. Here are some essential tips for tackling questions in this field.
1. Understand the Key Concepts
Before answering, ensure that you fully grasp the fundamental principles of viral biology. A strong understanding of topics like viral structure, replication cycles, and immune responses will help you address a variety of topics confidently. Focus on:
- Viral life cycles and replication steps
- Different modes of transmission
- How the immune system responds to viral infections
- Strategies for prevention and control
2. Read the Question Carefully
Pay close attention to the wording of the question to ensure that you are addressing what is being asked. Avoid rushing through the question; understanding its core requirements is crucial for providing a relevant response. Key points to consider include:
- What is being specifically asked–definition, process, or comparison?
- Any specific examples or case studies mentioned?
- Are there any limitations or exceptions that need to be considered?
3. Organize Your Thoughts
Structure your response in a logical sequence. Start with an introduction or overview of the topic, followed by the main body of your explanation, and conclude with a summary or final thought. Organizing your points ensures that your answer flows naturally and covers all the relevant aspects. Try these techniques:
- Provide a brief introduction to the topic.
- Break down complex ideas into simpler, digestible parts.
- Use bullet points or numbered lists for clarity when appropriate.
- Conclude by highlighting the main takeaway or implications.
4. Provide Specific Examples
Where possible, incorporate specific examples to back up your explanation. Examples can help demonstrate your understanding and make your response more concrete. For instance, if asked about transmission methods, mention real-world examples like airborne transmission of influenza or vector-borne transmission of Zika virus.
5. Stay Concise
Avoid long-winded responses that stray from the main topic. Stick to relevant details and explain them clearly. When answering, be sure to:
- Keep explanations to the point
- Avoid unnecessary jargon or overly complex language
- Use clear and simple terminology where possible
6. Practice with Sample Scenarios
One of the most effective ways to prepare is by practicing with sample scenarios. These allow you to apply your knowledge to real-world situations, helping you think critically and efficiently when answering similar inquiries during assessments.
Practice Questions for Virology Exams
Preparing for assessments in this field involves testing your knowledge with various inquiries that challenge your understanding of fundamental principles, processes, and real-world applications. Practicing with a diverse range of topics can help solidify your grasp on the subject and improve your ability to respond confidently under pressure. Below are some examples of scenarios that can be used for self-testing or group study sessions.
1. Basic Concepts and Definitions
Start by testing your knowledge of key concepts. These types of inquiries often require concise definitions or brief explanations of fundamental terms.
- Define the structure of a typical virus and explain its components.
- Describe the main stages of a viral life cycle.
- Explain how a virus can be transmitted between hosts.
- Identify the role of the host cell in the replication of viral genetic material.
2. Mechanisms of Infection
Next, consider questions that focus on the mechanisms through which viruses infect hosts and replicate. These scenarios often require you to explain processes or compare different methods of infection.
- Compare and contrast lytic and lysogenic cycles.
- Explain how viruses enter host cells and the role of receptors in this process.
- What are the primary differences between RNA and DNA virus replication?
- Describe how viral mutations can affect host cell infection and replication.
3. Immune Response and Defense Mechanisms
Questions in this category test your understanding of how the body defends itself against viral infections. They may ask you to describe processes or assess how different systems work together to provide immunity.
- Explain the role of antibodies in defending against viral pathogens.
- Describe how the innate immune system responds to viral infections.
- What is the difference between cellular and humoral immunity in response to viruses?
- How do vaccines work to prevent viral infections?
4. Real-World Applications and Case Studies

These types of questions ask you to apply your knowledge to specific scenarios or current global events. They help develop your ability to analyze situations and consider practical solutions.
- Discuss how the rapid spread of the flu virus is managed in a healthcare setting.
- Explain how vector-borne viruses are transmitted and the methods used to control outbreaks.
- Describe the global efforts to eradicate smallpox and the role of vaccination in this process.
- Analyze the potential impact of emerging viruses on public health systems.
5. Advanced Topics
For more advanced inquiries, questions may delve into specific viral families or cutting-edge research. These often require a deeper understanding of molecular biology or current scientific developments.
- What are the main characteristics of retroviruses, and how do they integrate into the host genome?
- Explain the mechanisms of antiviral resistance and how it develops in populations of viral pathogens.
- Describe the challenges of designing antiviral drugs that target viral enzymes.
- Discuss the ethical considerations surrounding gene therapy for viral infections.
6. Practice Application
To further solidify your understanding, try answering some of these inquiries on your own or as part of a group discussion. Reviewing each question thoroughly and explaining your reasoning behind the answers will deepen your comprehension and prepare you for any future assessments.
Understanding Virology Exam Formats
Familiarizing yourself with the structure of assessments in this field is crucial for effective preparation. Different types of evaluations may be used to assess your knowledge, ranging from multiple-choice to essay-style formats. Understanding these various approaches can help you tailor your study strategy to the specific requirements of each format. Below is an overview of the common structures used to evaluate your comprehension and application of key concepts.
1. Multiple-Choice Questions

These types of questions assess your ability to recall and apply information quickly. You are typically presented with a prompt and several possible answers, and your task is to select the most accurate or relevant option. This format tests both factual knowledge and critical thinking, as some options may seem similar but only one will be correct.
- Focus on understanding the key concepts, definitions, and functions related to the topic.
- Practice answering questions under timed conditions to improve your speed and accuracy.
- Learn to identify distractors–incorrect answers that are designed to confuse or mislead.
2. Short-Answer Questions
These questions require you to provide brief, concise responses to specific prompts. You will need to demonstrate your understanding of the material without the option to elaborate in lengthy paragraphs. This format evaluates your ability to recall key points and explain them clearly and succinctly.
- Review important terms, mechanisms, and definitions to ensure you can explain them concisely.
- Practice writing short responses to various prompts to get comfortable with the format.
3. Long-Answer or Essay Questions
Essay-style inquiries are often used to assess your deeper understanding of complex topics. These questions require you to provide a thorough explanation, integrating various concepts and offering a well-rounded perspective. The goal is to demonstrate both your breadth and depth of knowledge in relation to the subject matter.
- Focus on organizing your thoughts before writing–outline key points to ensure a structured answer.
- Support your arguments with evidence and examples from the material you have studied.
- Ensure your writing is clear, logical, and well-structured, with an introduction, body, and conclusion.
4. Case Studies and Problem-Solving

Case studies or problem-solving prompts often present a real-world scenario and ask you to apply theoretical knowledge to practical situations. These questions assess your ability to analyze complex situations, recognize patterns, and propose solutions based on your understanding of the material.
- Practice analyzing case studies and identifying relevant concepts that can be applied to the scenario.
- Develop a logical approach to problem-solving and decision-making based on your knowledge.
5. Practical or Lab-Based Questions
In some assessments, you may be asked to apply what you have learned in a laboratory or hands-on setting. These types of questions often require you to demonstrate your technical skills and understanding of experimental procedures, as well as interpret data or results.
- Review the key experimental techniques and their purposes to be able to interpret results accurately.
- Ensure you are familiar with common laboratory equipment and protocols related to the field.
6. Oral Presentations
Oral presentations may also be part of the evaluation process, where you are required to present a topic or discuss a case in front of an audience or examiner. This format assesses your communication skills, clarity of thought, and ability to articulate complex concepts verbally.
- Prepare by practicing your presentation skills, focusing on clarity, organization, and engagement with the audience.
- Anticipate possible follow-up questions and prepare answers to demonstrate a deep understanding of the topic.
Conclusion
Each assessment format presents unique challenges, but by understanding the structure and expectations for each type, you can better prepare and approach your evaluations with confidence. Practicing with different question types and refining your test-taking strategies will ultimately help you succeed in demonstrating your knowledge and skills effectively.
How to Prepare for Virology Tests
Effective preparation for assessments in this field requires a strategic approach that balances knowledge acquisition with practical application. Success comes from understanding key concepts, mastering essential skills, and practicing problem-solving techniques. Below are some valuable tips to help guide your study efforts and ensure you are well-prepared for upcoming challenges.
1. Review Core Concepts
Understanding the fundamental principles is crucial. Focus on key ideas that frequently appear in assessments, such as transmission methods, immune responses, and diagnostic tools. This knowledge will serve as the foundation for more advanced topics and practical applications.
- Study essential terms, definitions, and classifications.
- Understand the mechanisms of viral replication and host interactions.
- Familiarize yourself with common diseases caused by viruses and their symptoms.
2. Practice with Previous Assessments
One of the best ways to prepare is by reviewing past materials. This helps familiarize you with the structure of the prompts, the level of detail expected, and the types of questions commonly asked. By practicing, you can identify areas that need further attention and adjust your study plan accordingly.
- Work through sample scenarios and problem-solving exercises.
- Time yourself to improve your speed and efficiency.
- Review any feedback received from previous evaluations to pinpoint areas of improvement.
3. Focus on Application of Knowledge
It’s not enough to memorize facts; you must also be able to apply them. Understanding how to use your knowledge in different contexts is essential. Practice explaining concepts in your own words and solving problems that require you to integrate various ideas.
- Analyze case studies to identify the most relevant information and apply your understanding.
- Work with practice problems that require logical thinking and the application of learned material.
4. Join Study Groups
Collaborating with others can be incredibly beneficial. Study groups allow for different perspectives on complex topics, help reinforce difficult concepts, and provide opportunities for discussion and clarification.
- Discuss challenging topics with peers to gain new insights.
- Teach each other key concepts–explaining something to others reinforces your own understanding.
5. Stay Organized
Effective preparation requires careful organization. Break down your study sessions into manageable chunks and focus on specific topics at a time. Use study guides, outlines, or mind maps to help organize information in a logical flow.
- Create a detailed study schedule with specific goals for each session.
- Organize notes, diagrams, and resources for quick reference during revision.
6. Use Visual Aids
Visual aids can be incredibly helpful for understanding complex concepts, such as viral structures, replication cycles, or the immune response. Diagrams, charts, and tables make it easier to visualize relationships between different components.
- Review diagrams and labeling exercises to familiarize yourself with key structures.
- Use flashcards with visuals to reinforce key concepts and their associations.
7. Take Care of Your Well-Being

Good physical and mental health is crucial for effective study and performance. Ensure you are getting enough sleep, eating well, and taking breaks to avoid burnout. A well-rested mind is more efficient at retaining and recalling information.
- Set aside time for regular breaks to prevent fatigue.
- Maintain a healthy sleep schedule to enhance focus and memory retention.
Conclusion
Preparation is a key factor in performing well during assessments. By mastering core principles, practicing application, and staying organized, you can approach your studies with confidence. Take a balanced approach by integrating all the tips mentioned above to ensure you are fully prepared for the challenges ahead.
Resources for Studying Virology Effectively
To master this subject, it is essential to utilize a variety of tools that provide comprehensive coverage of the material. A well-rounded approach includes textbooks, online platforms, peer-reviewed journals, and interactive materials. Below are some key resources to support your studies and enhance your understanding of the topic.
1. Textbooks and Reference Materials
Textbooks are foundational in providing a structured overview of core principles. Choose resources that are clear, concise, and up-to-date. Some textbooks may also include practice questions and real-world case studies to help apply what you’ve learned.
- “Molecular Biology of the Cell” by Alberts et al. – A comprehensive resource for understanding the molecular underpinnings of disease.
- “Fields Virology” by David M. Knipe & Peter M. Howley – A thorough guide, often considered a standard reference for this field.
- “Medical Microbiology” by Murray et al. – Covers a wide array of pathogens, with detailed chapters on viral agents and their mechanisms.
2. Online Learning Platforms
In addition to textbooks, online platforms offer interactive tutorials and lectures that break down complex topics into digestible segments. These platforms are great for visual learners and those who prefer more flexible, self-paced learning environments.
- Coursera: Offers specialized courses from top universities, including topics related to infectious diseases and virus transmission.
- edX: Provides in-depth courses that range from basic biology to advanced viral pathogenesis.
- Khan Academy: A free resource with video lectures on microbiology and infectious diseases, perfect for reinforcing foundational knowledge.
3. Scientific Journals and Research Articles
For those looking to dive deeper into the latest developments, reading peer-reviewed journals and research papers is invaluable. These resources provide up-to-date information on ongoing studies and breakthroughs in the field.
- The Journal of Clinical Investigation – Covers a broad spectrum of research related to human diseases, including viral infections.
- Virology Journal – Focuses on the molecular mechanisms of viral replication, pathogenesis, and immune response.
- Journal of Infectious Diseases – Includes studies on the clinical aspects of viral diseases and the development of new treatment methods.
4. Interactive Learning Tools
Interactive tools like simulations, quizzes, and apps can help reinforce learning. These resources offer engaging ways to test your knowledge and visualize complex processes, such as viral replication and host immune responses.
- Quizlet: Offers flashcards and study sets created by other users, great for memorization.
- Visible Body: A 3D human anatomy app that provides detailed views of viruses and their interaction with cells.
- BioMan Biology: Provides fun and educational games related to microbiology and pathogens.
5. Study Groups and Peer Collaboration
Collaborating with peers can enhance learning by providing different perspectives and fostering a deeper understanding of the material. Forming study groups allows for active discussion, clarifying concepts, and sharing useful resources.
- Join a study group on platforms like Discord or Facebook, where you can discuss key topics and share resources.
- Participate in online forums such as Reddit’s Science and Biology sections, where experts and students exchange knowledge.
- Collaborate with classmates to work through practice problems and case studies together.
6. Practice and Review
Constant practice and review are key to mastering the subject. Regularly test yourself using sample questions, review notes, and revisit difficult concepts. This method strengthens recall and solidifies your knowledge base.
| Resource Type | Example | Usefulness |
|---|---|---|
| Textbooks | “Molecular Biology of the Cell” | Provides detailed foundational knowledge on molecular mechanisms |
| Online Learning | Coursera, Khan Academy | Accessible and interactive learning platforms for foundational concepts |
| Journals | Virology Journal, The Journal of Clinical Investigation | Provides up-to-date research and deeper insights |
| Interactive Tools | Quizlet, Visible Body | Engaging ways to reinforce knowledge and test your understanding |
Conclusion
Effective studying requires a combination of structured resources, interactive tools, and collaboration. By utilizing these materials, you can deepen your understanding, enhance your retention, and apply what you’ve learned more effectively. Take advantage of the variety of available resources to support your learning journey and ensure academic success.