
Achieving a certification in occupational health and safety requires a deep understanding of risk management, safety standards, and organizational procedures. The certification process tests knowledge of industry-specific regulations and the ability to assess a company’s adherence to these practices. This section will explore the key elements required to succeed in this evaluation and provide valuable insights for candidates preparing for the assessment.
To successfully navigate this challenge, individuals must be well-versed in the core principles of safety management systems and their application within various organizational contexts. The process involves not only theoretical knowledge but also practical problem-solving skills that can be demonstrated in real-world situations. Understanding the structure and expectations of the certification procedure is critical for anyone aiming to pass the assessment with confidence.
Preparation is essential, and this guide will highlight the most important aspects of the test, offering strategies to improve your readiness. Focus areas will include common topics and the best approaches for tackling practical scenarios. With a structured study plan and a clear grasp of the requirements, candidates can boost their chances of success and advance their careers in the field of safety management.
ISO 45001 Lead Auditor Exam Overview
The certification process for occupational health and safety management involves a rigorous assessment of your ability to evaluate organizational compliance with safety regulations. The purpose of this assessment is to ensure that candidates have the required knowledge and skills to evaluate the effectiveness of safety systems in various workplace environments. A successful outcome will not only demonstrate a thorough understanding of safety protocols but also the ability to apply them in real-world scenarios.
Structure of the Assessment
The certification procedure is typically divided into theoretical and practical components. The theoretical part focuses on your understanding of relevant safety standards, risk assessments, and audit techniques. The practical section requires you to demonstrate your ability to assess the implementation of safety management systems in actual organizational settings. Both parts are designed to evaluate your depth of knowledge, critical thinking, and problem-solving capabilities.
Key Areas of Focus
During the certification procedure, you will be expected to cover a variety of core subjects, such as risk management, legal and regulatory requirements, and the evaluation of workplace safety performance. Understanding how to conduct a thorough review of a company’s safety practices is essential. Preparing for this assessment requires familiarizing yourself with the industry standards and common pitfalls in safety practices, as well as honing your ability to identify potential risks and gaps in safety protocols.
Key Concepts in Occupational Safety Management Auditing
Effective evaluation of workplace safety systems involves understanding several fundamental principles that guide how risks are identified, controlled, and managed. These core concepts form the backbone of any safety management review, and mastering them is essential for anyone involved in assessing an organization’s compliance with safety regulations. A comprehensive understanding of these concepts ensures that the audit process is both thorough and effective in identifying potential hazards and improving overall safety performance.
Risk Assessment and Control
One of the primary aspects of safety management is the ability to assess and mitigate risks. This involves identifying potential hazards within the workplace, evaluating the likelihood of these risks occurring, and implementing controls to minimize their impact. A deep understanding of risk assessment techniques, including hazard identification, risk analysis, and the application of preventive measures, is essential. The goal is to ensure that the work environment is as safe as possible for all employees.
Compliance with Legal and Regulatory Standards
Another crucial concept in safety system evaluations is ensuring compliance with both local and international safety regulations. Organizations must adhere to legal requirements to maintain a safe working environment. Understanding these laws and regulations is vital for conducting an effective review. This includes familiarity with industry-specific standards, best practices, and any updates to legislation that may impact safety protocols.
Common Questions in Occupational Safety Certification
When preparing for a certification in workplace safety management, it’s important to anticipate the types of scenarios and concepts that may be tested. These assessments are designed to evaluate your ability to apply safety principles to real-world situations, ensuring that candidates are fully capable of identifying risks and implementing effective safety measures. Familiarizing yourself with the types of challenges that may appear will help you approach the test with confidence and clarity.
Understanding Safety Management Systems
One common area of focus involves assessing your knowledge of safety management systems and their components. Expect questions about how to evaluate the effectiveness of a system, including its ability to identify hazards, control risks, and promote continuous improvement. You may be asked to analyze case studies and explain how you would assess the adequacy of an organization’s safety protocols and policies.
Risk Identification and Control Measures
Another frequent topic is risk management. Questions may challenge you to demonstrate your understanding of hazard identification, risk evaluation, and the development of appropriate control measures. This could involve determining how to prioritize risks based on their potential impact and likelihood, as well as how to implement strategies to minimize those risks. The ability to think critically about safety challenges and propose practical solutions is essential for this part of the certification.
Understanding the Audit Process
The evaluation of safety systems within an organization follows a structured process that helps identify potential risks, assess compliance, and ensure continuous improvement. This process involves several stages, each designed to gather the necessary information to make an accurate assessment. A clear understanding of these stages is essential for anyone involved in the review process, as it ensures a thorough and effective evaluation.
Stages of the Review Process
The process of assessing workplace safety typically unfolds in multiple phases. Each stage serves a distinct purpose, from initial planning to final reporting. Below are the key stages of a typical safety system evaluation:
- Preparation: Prior to conducting any review, it is essential to gather relevant documentation, understand the scope of the assessment, and plan the audit approach.
- On-Site Evaluation: This phase involves direct observation of the workplace, interviews with employees, and reviewing procedures in practice to ensure they align with documented standards.
- Data Collection: During this stage, auditors collect information through various means, such as questionnaires, checklists, and direct inspections, to assess compliance and identify gaps.
- Analysis: Once data is collected, it is analyzed to determine whether the safety practices in place are effective in managing risks and adhering to regulations.
- Reporting: The findings are compiled into a report that highlights strengths, weaknesses, and recommendations for improvement.
Critical Skills for Effective Auditing
Successfully navigating the review process requires a mix of technical knowledge and practical skills. Among the most important skills are:
- Attention to Detail: Being able to spot potential hazards and inconsistencies is crucial for accurate assessments.
- Analytical Thinking: The ability to analyze complex data and determine the root causes of safety issues is essential.
- Communication Skills: Clear communication, both in interviews and in reporting, is vital for conveying findings and recommendations effectively.
Essential Skills for Lead Auditors
Conducting an effective evaluation of workplace safety systems requires a unique set of skills that go beyond basic knowledge of regulations and procedures. The role involves analyzing complex data, identifying risks, and ensuring that safety practices are aligned with industry standards. To succeed in this demanding role, professionals must possess a combination of technical expertise, communication abilities, and critical thinking skills. Mastering these key skills is essential for ensuring the success of any safety management review.
Key Competencies for Effective Evaluation
Lead evaluators must be equipped with several core competencies to perform their duties efficiently. Below are some of the most important skills:
- Attention to Detail: Being able to notice even the smallest inconsistencies or potential hazards is critical for conducting a thorough evaluation. Missing small details could lead to larger issues being overlooked.
- Analytical Thinking: The ability to analyze collected data, identify patterns, and interpret findings is essential for determining the root causes of safety issues and proposing actionable solutions.
- Problem-Solving: Effective evaluators must be able to think critically and propose practical solutions to identified safety challenges, considering both short-term fixes and long-term improvements.
Communication and Interpersonal Skills
In addition to technical proficiency, the role requires excellent communication and interpersonal abilities. These are vital for gathering information, interviewing staff, and conveying findings to stakeholders. Key skills include:
- Clear Reporting: Being able to present findings in a clear, concise, and constructive manner is essential for ensuring that recommendations are understood and acted upon.
- Active Listening: Listening carefully to employees and management allows evaluators to understand concerns and gain insights that may not be immediately obvious.
- Leadership and Diplomacy: Leading teams and handling potentially sensitive situations with professionalism and diplomacy ensures a smooth and effective evaluation process.
How to Prepare for the Assessment
Successfully completing a certification in safety management requires thorough preparation, as the process tests both your theoretical knowledge and practical skills. To approach this challenge effectively, it’s crucial to create a structured study plan and focus on key areas that are likely to be assessed. Understanding the core concepts, mastering the necessary techniques, and practicing real-world scenarios will help build confidence and ensure you are ready for the evaluation.
Develop a Study Plan
Start by identifying the main topics and areas of focus for the certification. Create a timeline that allows you to cover each subject systematically, ensuring that you spend adequate time on each aspect. Break down complex topics into manageable sections and focus on understanding the principles behind each concept rather than memorizing facts. A well-organized study plan will help you stay on track and reduce stress as the assessment approaches.
Use Practical Resources
Alongside theoretical study, it’s important to familiarize yourself with practical tools and resources. These may include sample case studies, templates for safety management reviews, and guides on conducting risk assessments. Hands-on experience is essential for applying your knowledge in real-life situations, so seek opportunities to practice through mock assessments or role-playing exercises. Additionally, reviewing past reports or safety audits can provide valuable insights into the evaluation process.
Review Key Concepts
- Risk Management: Understand how to assess, identify, and mitigate risks within an organization.
- Regulatory Compliance: Familiarize yourself with the legal requirements related to workplace safety and how they apply to various industries.
- System Evaluation: Learn how to evaluate the effectiveness of safety management systems and identify areas for improvement.
Incorporating both theoretical knowledge and practical experience into your study routine will ensure that you are well-prepared for the assessment. Focus on understanding the methodology behind the review process and how to apply it effectively in any workplace setting.
Tips for Answering Exam Questions
Approaching any evaluation requires careful strategy and focus. When responding to the challenges presented, it’s important to structure your answers effectively, ensuring clarity and precision. By following a few key strategies, you can enhance your performance and demonstrate your understanding of the subject matter. Below are some practical tips to guide you through answering the questions during the assessment.
Key Strategies for Success
| Tip | Description |
|---|---|
| Understand the Question | Before jumping into your response, take a moment to carefully read and analyze the question. Identify what is being asked and break it down into smaller components. This will help ensure that your answer addresses all parts of the question directly. |
| Provide Clear Examples | Whenever possible, illustrate your answers with real-world examples or hypothetical scenarios. This demonstrates your ability to apply theoretical knowledge in practical situations, which is essential for success in the assessment. |
| Structure Your Response | Organize your thoughts before writing. Use bullet points or numbered lists for clarity, and ensure that each part of your answer is clearly separated. Start with a brief introduction, followed by a detailed explanation, and end with a conclusion or recommendation. |
| Stay Concise | While it’s important to be thorough, avoid unnecessary details that do not directly answer the question. Focus on delivering clear, concise responses that stay on topic and address the key points. |
| Review Your Answer | After completing your response, take a few moments to review your answer for clarity, accuracy, and completeness. Ensure that you’ve answered every part of the question and that your response flows logically. |
By following these strategies, you will improve the clarity and quality of your answers, allowing you to effectively showcase your knowledge and reasoning skills. Preparation is key, and with the right approach, you can navigate the evaluation process with confidence.
Structure of Occupational Safety Certification
The process of obtaining certification in workplace safety involves a systematic framework that is designed to ensure organizations adhere to essential safety standards. This framework is divided into several key components, each addressing different aspects of safety management. Understanding this structure is crucial for organizations seeking certification, as well as for individuals aiming to assess or review these systems. The following sections break down the structure into its primary components, offering insight into the process and criteria involved.
Core Elements of the Certification Process
The certification process is organized into a series of steps, each contributing to a comprehensive evaluation of an organization’s safety management system. These steps include:
- Initial Assessment: The first step involves a thorough review of the organization’s existing safety policies, procedures, and practices. This helps determine the scope of the evaluation and areas that may need improvement.
- System Documentation: Organizations must document their safety management systems in a clear and structured manner. This includes outlining policies, risk management procedures, and safety objectives.
- Internal Review: Before applying for certification, organizations must conduct an internal review to ensure that all safety measures are being implemented correctly and effectively. This step ensures the organization is ready for the official evaluation.
Standards and Requirements for Certification
The certification process is based on a set of predefined standards and criteria, which organizations must meet to achieve official recognition. Key requirements include:
- Risk Management: Organizations must demonstrate effective identification, assessment, and control of workplace risks to protect employees’ health and safety.
- Compliance with Legal Requirements: It is essential that organizations comply with all relevant local, national, and international safety regulations.
- Continuous Improvement: The certification process emphasizes the need for ongoing evaluation and improvement of safety practices to adapt to emerging risks and changing regulations.
By following this structured process, organizations can achieve certification that verifies their commitment to creating a safe and compliant work environment. Each stage plays an integral role in ensuring that all safety measures are appropriately implemented and maintained.
Study Materials for Lead Auditor Certification
Preparing for a safety management certification requires access to reliable and comprehensive study materials that cover all aspects of the assessment process. These resources will help candidates build a deep understanding of safety standards, regulatory requirements, and effective evaluation techniques. Whether through books, online courses, or practice exercises, the right study materials will ensure that individuals are fully equipped to succeed in the certification process.
Recommended Books and Guides
Books and manuals remain one of the most effective ways to prepare for any certification. They offer detailed explanations, practical examples, and exercises that help reinforce key concepts. Here are some useful study materials:
- Official Standards Documentation: Always begin with the official standards documents that define safety management system requirements. These documents outline the exact expectations for safety practices and provide a foundation for understanding the certification criteria.
- Comprehensive Textbooks: Many textbooks are written specifically for those preparing for certification in safety management. These guides cover topics like risk assessment, regulatory compliance, and system audits in detail, offering structured learning.
- Practice Guides: Guides that include practice tests and sample assessments are invaluable for familiarizing yourself with the format and types of questions you may encounter during the certification process.
Online Resources and Courses
In addition to traditional books, many individuals turn to online platforms that offer interactive courses, webinars, and other digital resources. These options provide flexible learning and can be particularly useful for busy professionals.
- Online Training Courses: Many accredited organizations offer online courses tailored to the certification process. These courses often include video lessons, quizzes, and real-life case studies that help cement understanding.
- Webinars and Workshops: Participating in live webinars or workshops allows candidates to ask questions and engage with instructors. These are excellent opportunities to clarify difficult concepts and gain practical insights from experienced professionals.
- Interactive Practice Exams: Some online platforms provide simulated assessments that mimic the real certification process. These interactive exams help candidates gauge their readiness and identify areas for improvement.
Using a combination of books, online materials, and practical exercises will provide a well-rounded approach to preparing for the certification, ensuring that candidates are confident and well-prepared on the day of evaluation.
Common Mistakes to Avoid During the Assessment
When preparing for a safety management certification, it’s easy to overlook certain details or fall into common traps that can impact performance. Understanding these pitfalls ahead of time will help you approach the evaluation process with greater confidence and avoid unnecessary errors. Below are some of the most frequent mistakes candidates make and tips on how to avoid them.
Typical Pitfalls to Watch Out For
- Rushing Through Questions: One of the biggest mistakes is rushing through questions without carefully reading and analyzing them. Skimming the question can lead to missing important details, which may affect the accuracy of your response. Always take the time to read each question thoroughly before answering.
- Overlooking Key Concepts: It’s easy to focus on familiar topics, but neglecting less familiar areas can be detrimental. Ensure that you give equal attention to all topics, especially those that you may find more challenging. Don’t assume certain sections won’t be covered.
- Misunderstanding the Format: Many candidates struggle because they are unfamiliar with the assessment format. Before starting, make sure you understand how the questions are structured. Some assessments may ask for brief responses, while others require detailed explanations or case studies.
- Failing to Manage Time: Poor time management can lead to incomplete answers or rushing through the last questions. Practice pacing yourself by taking timed practice tests before the actual evaluation. This will help you allocate enough time to each section.
- Ignoring the Instructions: Not following the instructions provided at the beginning of the assessment can result in confusion or even disqualification. Pay close attention to guidelines such as word limits, required formats, or the type of responses expected.
How to Overcome These Mistakes
- Practice Active Reading: Make sure to focus on the details of each question. Break down complex questions into smaller parts to better understand what’s being asked.
- Review All Topics: Don’t just focus on your strongest areas. Spend time studying all sections of the certification material to ensure you’re fully prepared.
- Simulate Real Conditions: Taking practice exams under real conditions will help you become familiar with the format and timing, reducing stress and improving your ability to manage time effectively.
- Understand the Assessment Criteria: Knowing the type of responses expected for each question will help you structure your answers in a way that aligns with the evaluation process.
Avoiding these common mistakes will significantly improve your chances of success. Preparation, attention to detail, and managing your time effectively are key strategies to help you navigate the assessment confidently and accurately.
Assessment Scoring and Passing Criteria
Understanding the scoring system and the criteria required to pass is essential for candidates preparing for a safety management certification. The evaluation process is designed to assess both theoretical knowledge and practical application of safety standards. It is important to know how the points are allocated, what percentage is required to pass, and the different methods used to assess overall performance.
How Scoring Works
The scoring system is typically based on a point allocation for each section of the assessment. This may include multiple-choice questions, case studies, and practical assessments. Here’s how the scoring generally works:
- Weight of Sections: Different sections of the assessment may have different point values, depending on their complexity and importance. For example, theoretical sections might be worth fewer points than practical, scenario-based questions.
- Scoring for Multiple Choice: In multiple-choice sections, each correct answer typically earns a set number of points. There are no penalties for incorrect answers, but wrong responses do not contribute to the overall score.
- Case Study Evaluation: When evaluating case studies or situational responses, the assessor looks for a demonstration of problem-solving skills and application of safety management principles. These responses are often graded on a scale, considering clarity, depth, and relevance.
Passing Criteria
The passing score is determined by the certification body and usually reflects the candidate’s understanding of the essential topics covered in the assessment. Here’s an overview of what typically determines whether a candidate has passed:
- Minimum Percentage: Most certification assessments require candidates to score a minimum percentage–typically between 70-80%–to pass. This ensures that candidates have a solid understanding of the material.
- Overall Performance: Some certifications also require candidates to perform well across different sections, meaning that even if you do well in one area, failing another may result in not passing overall.
- Practical Competency: For certifications that include practical elements, demonstrating the ability to apply knowledge in real-world situations is as important as theoretical understanding. Passing this component is essential for obtaining certification.
By understanding the scoring system and passing criteria, candidates can better tailor their preparation to meet the necessary requirements. Focusing on both theoretical knowledge and practical skills ensures a well-rounded approach to passing the assessment.
Practical Applications of ISO 45001
Safety management systems are designed to ensure that workplaces provide a safe and healthy environment for employees. Implementing these systems effectively requires an understanding of how to apply principles in real-world scenarios. By integrating the relevant standards into daily operations, organizations can reduce workplace hazards, enhance productivity, and create a culture of safety. Below are key practical applications of safety management principles in various industries.
Key Areas of Application

- Risk Assessment and Control: Identifying, assessing, and managing risks is a cornerstone of safety management. Organizations use specific frameworks to conduct thorough risk assessments, focusing on preventing accidents before they occur. This includes evaluating workplace hazards, creating risk profiles, and implementing controls to mitigate risks.
- Employee Involvement: Successful safety management relies on active employee participation. Involving employees in the identification of risks, safety programs, and training initiatives helps build awareness and promotes a proactive approach to safety. Employees are encouraged to report hazards and contribute to safety discussions regularly.
- Continuous Monitoring: Regular monitoring and reviews of safety procedures ensure that safety management systems remain effective. This includes conducting internal audits, monitoring key safety metrics, and reviewing accident reports to identify areas for improvement. This ongoing evaluation helps in refining and updating safety protocols.
- Training and Awareness Programs: Training is a vital component for ensuring all employees understand their roles in maintaining a safe workplace. Effective safety programs provide clear guidance on best practices, emergency procedures, and the proper use of equipment. Continuous education keeps safety standards fresh and top of mind for all personnel.
- Emergency Preparedness: Having a clear, well-communicated emergency plan is essential for every organization. This involves preparing for potential incidents by creating evacuation plans, providing first aid training, and regularly conducting drills. A proactive approach to emergency preparedness helps minimize the impact of unforeseen events.
Sector-Specific Applications
- Manufacturing: In manufacturing environments, applying safety management principles means identifying equipment hazards, ensuring proper maintenance, and ensuring compliance with regulations regarding chemicals and machine safety. Risk assessments are critical in mitigating common manufacturing risks like machinery accidents and exposure to hazardous substances.
- Construction: The construction industry faces specific safety challenges such as working at heights, using heavy machinery, and dealing with potentially hazardous materials. Safety management systems help mitigate risks through detailed safety plans, equipment checks, and training on safe work practices.
- Healthcare: In healthcare settings, safety systems help protect employees from workplace hazards like infections, needle injuries, and physical strain. Regular training, use of protective equipment, and incident reporting systems are essential to maintaining a safe working environment for healthcare workers.
- Transportation: Safety management in the transportation sector focuses on minimizing risks related to vehicle operation, cargo handling, and logistics. Driver safety programs, vehicle inspections, and load management protocols help reduce accidents and ensure the safe delivery of goods and passengers.
By embedding safety management principles into everyday business operations, organizations can ensure the well-being of their workforce and comply with the relevant standards. Effective application of these principles not only helps in legal compliance but also fosters a culture of continuous improvement and accountability, driving long-term success.
Assessment Format and Time Management
Understanding the structure and timing of a certification assessment is crucial for effective preparation. This section outlines the common format of the assessment, how questions are typically presented, and tips for managing time efficiently during the process. Proper time management ensures that candidates can answer all questions thoroughly and accurately without feeling rushed.
Assessment Structure
The assessment is generally divided into multiple sections, each designed to test specific areas of knowledge. Here’s an overview of what you can expect:
- Multiple Choice Questions: This section consists of questions that test theoretical knowledge. Candidates must choose the correct answer from a set of options. It is important to read each question carefully and identify key terms that might indicate the right answer.
- Case Studies: These are scenario-based questions where candidates are required to apply their knowledge to real-world situations. These types of questions often require detailed responses, demonstrating both understanding and practical application of principles.
- Practical Assessment: Depending on the certification, some exams include practical assessments that evaluate how well candidates can apply their knowledge in simulated situations. This could involve analyzing documents, conducting audits, or developing safety plans based on given scenarios.
- Essay-Type Questions: These questions assess in-depth knowledge and the ability to explain complex concepts clearly. Answers should be structured logically, focusing on providing comprehensive explanations.
Time Management Tips

Efficient time management is a key factor in performing well during the assessment. Here are some strategies to help manage time effectively:
- Allocate Time for Each Section: Before starting the assessment, quickly review the number of sections and questions, then estimate how much time you should spend on each section. For example, if there are 50 multiple-choice questions and 30 minutes for that section, plan to spend about 30 seconds per question.
- Prioritize Questions: Start by answering questions that are easiest for you or those that you are most confident about. This will give you a sense of accomplishment and ensure that you tackle the most straightforward questions first.
- Don’t Overthink: Avoid spending too much time on any one question. If you’re stuck, move on and return to it later if time permits. It’s better to answer all questions partially than to leave some unanswered.
- Use the Breaks Wisely: If the assessment includes breaks, use them to relax, stretch, and refocus. This will help you maintain mental clarity and energy for the remaining sections.
- Practice Time-Management Techniques: Before taking the assessment, practice with timed mock tests. This will help you get accustomed to managing time effectively and develop a strategy for completing each section within the allotted time.
By understanding the format and utilizing effective time-management techniques, candidates can approach the assessment with confidence. The key is to stay organized, focus on the task at hand, and allocate sufficient time for each part of the test.
Importance of Risk Assessment in Auditing
Risk assessment plays a critical role in the auditing process by identifying potential hazards and evaluating their impact on the overall system. By assessing risks early, professionals can focus on areas that require attention, ensuring a more efficient and effective audit. This approach helps in identifying gaps, preventing potential issues, and ensuring that safety and compliance standards are met.
Why Risk Assessment is Crucial
Risk assessment is essential for a thorough audit because it guides the auditor in prioritizing areas that need closer examination. Here’s why it matters:
- Identifying Critical Areas: Risk assessment allows auditors to identify high-risk areas that could have significant consequences if not addressed properly. By focusing on these areas, auditors ensure that their efforts are spent where they are most needed.
- Improved Decision-Making: A solid risk assessment provides valuable information that enhances decision-making during the audit. It enables auditors to choose the most effective audit techniques and allocate resources efficiently.
- Preventing Potential Loss: Through the identification of potential risks, auditors can recommend measures to mitigate or eliminate hazards, ultimately preventing potential financial, operational, or reputational losses.
- Compliance Assurance: Regular risk assessments help ensure that an organization is compliant with relevant safety regulations and standards, safeguarding its reputation and avoiding legal issues.
Types of Risks Assessed in Auditing
Different types of risks need to be considered during an audit. Understanding these risks allows auditors to focus on the areas that could have the most significant impact. Below are some of the key risks assessed during an audit:
| Risk Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Operational Risk | Risk of failure in internal processes, systems, or procedures that could affect performance or safety. |
| Compliance Risk | Risk of not adhering to laws, regulations, or standards that govern the organization’s activities. |
| Financial Risk | Risk of financial loss due to inefficiencies, fraud, or mismanagement. |
| Reputational Risk | Risk of damage to the organization’s reputation, which could result in loss of trust from stakeholders. |
| Strategic Risk | Risk related to the organization’s long-term strategy and its ability to achieve objectives. |
Incorporating a risk assessment into the audit process ensures that auditors can focus on potential threats and make recommendations that improve the overall effectiveness of the system. This proactive approach not only ensures that risks are identified but also mitigates the potential for future complications.
Critical Areas to Focus on for Success

Achieving success in any certification or assessment process requires a focused approach to key areas that determine the overall performance. These critical factors shape the outcome and ensure that every aspect of the process meets the required standards. By dedicating attention to these essential components, you can increase your chances of a successful outcome and demonstrate a comprehensive understanding of the subject matter.
1. Understanding the Standards
A deep understanding of the standards and requirements is the foundation of success. It is essential to thoroughly review the criteria and guidelines to ensure that all aspects of the system or process are covered. A strong grasp of these standards will help you identify what to focus on during the process and how to meet the expectations effectively. The key areas to understand include:
- Frameworks and Principles: Familiarize yourself with the core frameworks that guide the entire process.
- Regulatory Requirements: Be well-versed in the legal and regulatory obligations that need to be adhered to.
- Best Practices: Learn the best practices within the industry to ensure effective implementation and continuous improvement.
2. Risk Management and Mitigation
Risk management is an essential part of any successful audit or evaluation process. Identifying potential risks early on helps in crafting strategies to mitigate them. This proactive approach ensures that challenges are addressed before they escalate, keeping the process on track. The following aspects of risk management should be prioritized:
- Identifying Potential Risks: Assess potential risks that could affect the outcome of the process, including operational, financial, and reputational risks.
- Mitigation Strategies: Develop actionable plans to address identified risks, ensuring the least possible disruption to the process.
- Continuous Monitoring: Implement systems for ongoing risk assessment and make adjustments as needed during the process.
Focusing on these critical areas will ensure that you are well-prepared, confident, and capable of succeeding in the assessment process. Attention to detail, knowledge of standards, and effective risk management are essential steps toward achieving your goals.
Reviewing Sample Questions and Answers
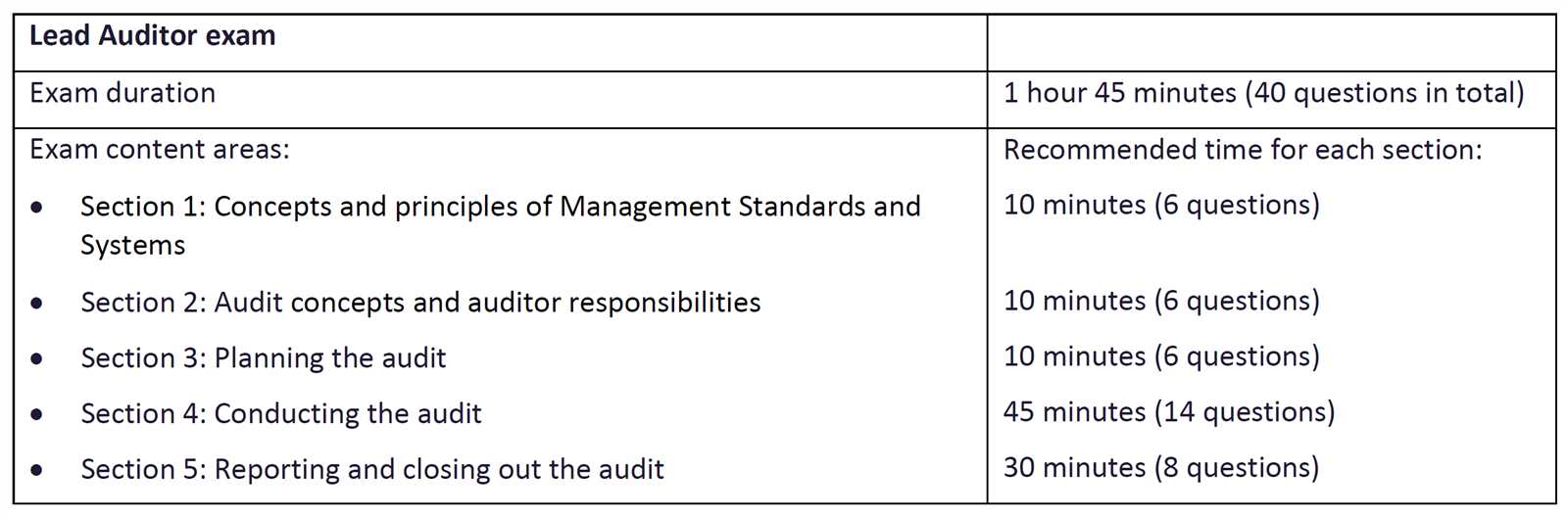
To better prepare for any assessment or certification process, reviewing examples of common scenarios can significantly enhance your understanding and performance. By analyzing sample inquiries and responses, you can gain insight into the types of challenges you may face, the level of detail expected in your responses, and the areas to prioritize. This practice not only builds confidence but also helps in refining your approach to complex topics.
1. Importance of Practice Questions
Practicing with sample scenarios is a valuable strategy in preparing for any assessment. By familiarizing yourself with the format and structure of potential inquiries, you can identify patterns in how questions are posed and develop effective strategies for responding. Focus on understanding the key concepts behind each sample, rather than memorizing responses, as this ensures you are able to think critically when faced with similar challenges during the actual process.
| Sample Question | Key Focus Area | Sample Response Tip |
|---|---|---|
| What are the primary elements of a risk management system? | Risk Identification, Risk Evaluation, Risk Mitigation | Highlight the steps in the risk management process and provide examples of practical applications. |
| How would you approach a non-compliance issue within a company? | Root Cause Analysis, Corrective Actions, Preventative Measures | Focus on systematic identification of the problem and suggest clear corrective steps, with a focus on sustainability. |
2. Key Aspects to Focus On
When reviewing sample inquiries, ensure you focus on the following elements to sharpen your preparation:
- Understanding Core Concepts: Prioritize mastering the fundamental principles that guide the system.
- Providing Clear Responses: When crafting responses, ensure they are concise yet thorough, demonstrating both knowledge and the ability to apply it.
- Identifying Pitfalls: Be aware of common mistakes, such as misinterpretation of standards or incomplete responses, and work to avoid them in your answers.
Reviewing sample questions is an excellent way to solidify your understanding, spot potential weak spots, and prepare yourself for success. By practicing regularly, you will refine both your technical knowledge and your approach to answering inquiries effectively.
ISO 45001 Lead Auditor Certification Benefits
Obtaining a certification in the field of occupational health and safety management systems offers numerous advantages. Professionals who undergo this rigorous training gain a deep understanding of key concepts, frameworks, and practical skills needed to implement and assess safety protocols. These certifications not only enhance one’s credentials but also open up opportunities for career growth, better job security, and increased marketability in the field of safety and risk management.
Here are some key benefits of obtaining a certification in this area:
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Enhanced Career Opportunities | Having a certification demonstrates your expertise and opens up opportunities for higher-level positions in safety management and auditing roles. |
| Increased Earning Potential | Professionals with certifications in this area often command higher salaries due to their specialized knowledge and skills. |
| Credibility and Recognition | Achieving certification enhances your credibility within the industry, making you a trusted expert in occupational safety. |
| Improved Knowledge and Skills | Certification programs provide a comprehensive understanding of safety management, risk assessment, and compliance, ensuring you are well-equipped to handle challenges effectively. |
| Global Recognition | This qualification is recognized internationally, enabling professionals to work in various countries and industries. |
With these benefits, the certification not only provides a competitive edge in the job market but also helps to ensure that professionals are fully prepared to make a positive impact in their organizations by fostering safer work environments and reducing risks.