Assessments play a key role in evaluating an individual’s potential and abilities. These evaluations are designed to measure various cognitive, logical, and personal traits that can provide valuable insights into how a person might perform in different environments. A solid understanding of how to approach such evaluations can significantly improve results and increase confidence.
Preparation is essential for achieving a strong performance, and familiarizing yourself with the different types of tasks that may appear is an important part of the process. By practicing specific problem-solving strategies and becoming comfortable with the format, you can gain a competitive edge.
Learning how to effectively tackle these challenges requires not just knowledge, but also the ability to remain calm under pressure. Knowing what to expect, understanding the types of tasks involved, and improving your ability to analyze and solve problems will ensure you’re fully prepared for success.
Understanding Assessment Formats
Different types of evaluations are designed to assess specific abilities, ranging from cognitive skills to behavioral traits. These formats can vary greatly, but they generally aim to test your capacity to solve problems, analyze situations, and apply knowledge effectively. Becoming familiar with the structure of such tests allows you to better prepare for them and respond with confidence.
Types of Evaluation Formats

Commonly, these assessments can be divided into sections that evaluate reasoning abilities, problem-solving skills, and personality traits. Some may involve numerical puzzles, while others assess verbal reasoning or abstract thinking. Additionally, situational judgment tests are frequently included to evaluate how an individual might respond to real-life scenarios.
Time Constraints and Pressure
One common feature across many assessments is the time constraint. Time-limited challenges are designed to assess how efficiently a person can perform under pressure. Being aware of the time limits in advance helps you develop strategies for managing the clock, ensuring that you focus on the most important tasks without rushing or missing critical steps.
Types of Assessment Tasks
Evaluations designed to assess cognitive abilities and personal traits often consist of various task types. Each format serves a distinct purpose, providing insight into specific skills, from logical reasoning to interpersonal behavior. Understanding the different categories of tasks is crucial for effective preparation, as each requires a unique approach.
Reasoning and Problem-Solving Tasks
These tasks often involve numerical or verbal puzzles that challenge your ability to identify patterns, solve complex problems, and make decisions based on limited information. Common examples include sequences of numbers or words, where you must deduce the next in the series. These tasks test your analytical thinking and attention to detail.
Behavioral and Situational Tasks
These tasks focus on how you would react in hypothetical, real-world situations. They assess emotional intelligence, decision-making, and interpersonal skills by presenting scenarios that require you to choose the best course of action. This category helps to understand how individuals approach challenges, work in teams, and handle stress.
How to Prepare for Assessments
Successful performance in these evaluations requires a focused approach and a clear understanding of what to expect. Preparation is key to building confidence and ensuring you can navigate different task types efficiently. By practicing relevant skills, managing time effectively, and familiarizing yourself with test formats, you can enhance your chances of success.
Practice Regularly
Consistent practice is one of the most effective ways to improve your performance. By engaging with similar challenges beforehand, you can build familiarity with the types of tasks and improve your problem-solving speed. This also allows you to identify areas where you may need to focus more effort.
Develop Effective Time Management
Many evaluations are time-sensitive, requiring quick thinking and efficient decision-making. Developing strategies to manage your time during these tasks is crucial. Set aside time to practice under timed conditions to simulate the pressure of a real assessment, helping you become more comfortable with working against the clock.
Common Mistakes in Assessments
When participating in these evaluations, it’s easy to fall into certain traps that can negatively impact your performance. Many individuals make simple errors due to lack of preparation, stress, or misunderstanding the task requirements. Recognizing and avoiding these common pitfalls can help improve your results and ensure a smoother experience.
Rushing Through the Tasks

One of the most frequent mistakes is rushing to complete tasks without carefully reading the instructions or fully considering each option. This can lead to avoidable errors, especially in tasks that require detailed analysis or logical thinking. Taking a moment to double-check your answers can significantly reduce mistakes.
Neglecting to Manage Time
Underestimating the time needed for certain sections is another common issue. Without proper time management, it’s easy to spend too much time on difficult tasks and leave others incomplete. Practicing time management techniques beforehand will help you allocate time wisely during the actual evaluation.
Time Management Strategies for Success
Effective time management is essential when facing time-sensitive assessments. Being able to allocate sufficient time to each task, avoid distractions, and stay focused can make a significant difference in your overall performance. Proper planning and strategic thinking will help ensure that you complete the tasks efficiently and accurately.
Prioritize the Most Challenging Tasks
Start by identifying the more difficult tasks that may require extra time and effort. Tackle these first, when your focus and energy are at their peak. By addressing the harder challenges early on, you’ll avoid rushing through them under pressure, ensuring that you give them the attention they need.
Set Time Limits for Each Section
Divide your available time across the different sections of the assessment. Setting specific time limits for each section allows you to keep track of your progress and ensures you don’t spend too much time on any one task. Stick to these limits as much as possible, and move on to the next section even if you haven’t completed the current one entirely.
How to Interpret Assessment Results
Understanding the outcomes of these evaluations can be a crucial step in determining strengths, areas for improvement, and how well you align with specific roles or tasks. Results typically offer valuable insights into cognitive abilities, problem-solving skills, and personality traits. However, interpreting them correctly requires a clear understanding of the scoring system and what each metric represents.
| Score Range | Interpretation |
|---|---|
| 90-100 | Exceptional performance, demonstrating strong analytical and problem-solving abilities. |
| 70-89 | Above average, indicating good understanding and capability in key areas. |
| 50-69 | Average, shows potential but may require improvement in certain areas. |
| Below 50 | Needs significant improvement; consider further development of specific skills. |
Interpreting results is not just about the scores; it’s also about understanding how each section of the assessment reflects your skills. Pay attention to feedback and specific areas that might require additional focus or practice to enhance your overall performance in future tasks.
Sample Questions to Practice Assessments
Practicing with sample tasks is one of the best ways to prepare for evaluations. By working through a variety of exercises, you can become familiar with the types of challenges you may encounter. This practice helps to build confidence, improve speed, and refine your problem-solving techniques. Below are some examples of tasks to test your abilities and prepare effectively.
Numerical Reasoning:
If 3x + 5 = 20, what is the value of x?
Solution: x = 5
Verbal Reasoning:
Which word is most similar in meaning to “benevolent”?
A) Kind
B) Cruel
C) Neutral
D) Indifferent
Solution: A) Kind
Abstract Reasoning:
What comes next in the sequence: 2, 4, 8, 16, ___?
Solution: 32 (each number doubles the previous one)
Working through a variety of tasks like these will help you get accustomed to the different areas of assessment. Continue practicing to sharpen your skills and improve your performance in future evaluations.
What Employers Look for in Assessments
Employers use these evaluations to gain a deeper understanding of a candidate’s abilities, personality traits, and overall fit for a role. Rather than focusing solely on academic qualifications or experience, they are interested in how individuals approach challenges, solve problems, and interact with others in various situations. Understanding what employers look for can help you better prepare and align your strengths with their expectations.
- Problem-solving skills: Employers often look for candidates who can think critically and tackle complex challenges efficiently.
- Attention to detail: The ability to spot patterns, notice inconsistencies, and focus on the finer details is highly valued in many roles.
- Time management: Efficiently managing time and prioritizing tasks under pressure is an essential skill that employers seek in candidates.
- Emotional intelligence: Understanding and managing emotions, as well as interacting well with others, is key in team-oriented environments.
- Adaptability: Employers value individuals who can adapt to new environments and challenges quickly and effectively.
These assessments provide insights into how well you can handle both structured tasks and unpredictable situations. By focusing on these key attributes during preparation, you can demonstrate your suitability for the role and make a strong impression during the hiring process.
Improving Your Cognitive Abilities

Enhancing your cognitive abilities is essential for excelling in various assessments and real-life tasks. It involves strengthening the mind’s ability to process information, reason logically, solve problems, and retain knowledge efficiently. By dedicating time to mental exercises and adopting healthy habits, you can improve your overall brain function and increase your success in challenges that require mental agility.
Effective Strategies for Improvement
- Practice regularly: Engage in activities that challenge your thinking, such as puzzles, games, and brainteasers.
- Read extensively: Reading stimulates the brain and helps expand your vocabulary, comprehension, and analytical thinking skills.
- Stay curious: Cultivate a habit of asking questions and seeking out new knowledge in different fields.
- Engage in memory exercises: Work on activities that improve memory retention, such as repeating information or using mnemonic devices.
- Exercise regularly: Physical activity boosts brain function by increasing blood flow to the brain and reducing stress.
Maintaining a Healthy Mindset

- Manage stress: Practice relaxation techniques such as meditation or deep breathing to reduce mental fatigue.
- Get enough sleep: Quality sleep is essential for cognitive function and memory consolidation.
- Stay social: Engaging in social activities and discussions stimulates your brain and improves communication skills.
By incorporating these practices into your daily routine, you can enhance your cognitive abilities, which will ultimately help you perform better in assessments and problem-solving tasks.
Different Approaches to Logical Reasoning
Logical reasoning is a critical skill that involves drawing conclusions based on evidence, patterns, and structured thinking. There are various methods to approach logical problems, each focusing on different aspects of reasoning and analysis. Understanding these approaches allows individuals to choose the most effective strategy for solving complex problems, especially when facing time-sensitive challenges.
Deductive Reasoning

Deductive reasoning starts with a general premise or statement and applies it to specific cases to reach a conclusion. This approach is often used in situations where the rules are clear and the information is reliable. By applying broad principles to particular scenarios, individuals can derive conclusions that are logically sound, assuming the premises are accurate.
- Example: All humans are mortal. John is a human. Therefore, John is mortal.
Inductive Reasoning
In contrast, inductive reasoning involves making generalizations based on specific observations or patterns. This approach is more flexible but less certain, as conclusions are based on probabilities rather than certainties. Inductive reasoning is useful when making predictions or identifying trends based on available data.
- Example: Every time I’ve seen a swan, it has been white. Therefore, all swans are likely white.
Both deductive and inductive reasoning play important roles in logical thinking. Depending on the situation, one may be more applicable than the other, but developing proficiency in both approaches allows individuals to approach problems from multiple angles and arrive at more accurate conclusions.
Verbal and Numerical Reasoning Skills
Effective reasoning abilities are key to solving complex tasks that require logical thinking. These skills can be divided into two primary categories: verbal and numerical reasoning. Both areas test an individual’s capacity to process information and make decisions, but each focuses on different aspects of cognition. Mastering both types of reasoning can significantly improve performance in a variety of assessments and real-world challenges.
Verbal Reasoning
Verbal reasoning involves the ability to understand, analyze, and interpret written information. This skill is important for tasks that require comprehension, deduction, and critical thinking. It helps individuals draw conclusions from written material, recognize relationships between words, and solve problems related to language. Developing strong verbal reasoning skills enhances communication, decision-making, and overall cognitive agility.
- Example: Analyzing a passage of text to identify underlying assumptions or conclusions.
- Example: Recognizing relationships between words or phrases based on context.
Numerical Reasoning
Numerical reasoning focuses on the ability to work with numbers, interpret data, and solve problems that require mathematical logic. This skill involves using quantitative information to make decisions, identify patterns, and calculate solutions. Strong numerical reasoning abilities are essential in various fields, from finance to engineering, and help individuals approach problems systematically and accurately.
- Example: Solving word problems that involve calculations or percentages.
- Example: Interpreting data presented in charts, graphs, or tables.
Both verbal and numerical reasoning skills complement each other and are crucial for tackling diverse tasks. By improving both areas, individuals can enhance their ability to analyze situations, draw conclusions, and make informed decisions quickly and effectively.
Tips for Passing Personality Assessments
Personality assessments are designed to evaluate an individual’s characteristics, preferences, and behavioral patterns. These evaluations are often used to determine how well a person might fit into a particular role or environment. Success in these tests comes not from “answering correctly,” but from presenting an authentic reflection of your traits while understanding the traits that are valued by employers. With some preparation and awareness, you can navigate these assessments with confidence.
Understand the Purpose of the Test
Before you take any assessment, it’s important to understand its purpose. Personality evaluations are meant to measure your behavioral tendencies, not to test your intelligence or knowledge. Keep in mind that there are no right or wrong answers. These assessments aim to match your traits to those that best fit the job or team environment. Understanding this can help alleviate stress and allow you to respond more naturally.
Be Honest, Yet Strategic
While it’s important to answer questions truthfully, there’s also an element of strategy. You should reflect on your natural tendencies but also consider how your strengths align with the role you are aiming for. Avoid giving answers you think might be what the employer wants to hear–this can lead to inconsistencies in your results. At the same time, think about the traits that are typically valued in the position and highlight those through your responses.
- Example: If the role requires strong teamwork skills, highlight your ability to collaborate and your positive approach to group work.
- Example: For a leadership role, emphasize traits such as decision-making ability and responsibility.
Manage Your Time and Focus
Many personality assessments are timed, so it’s crucial to manage your time efficiently. Don’t rush through the questions, but avoid overthinking your answers either. Trust your instincts and try to maintain a steady pace throughout the test. If you feel stuck on a particular question, move on and come back to it later, if necessary.
Incorporating these tips will help you approach personality assessments with a clearer mindset and improve your chances of presenting your traits in a way that aligns with the role you are seeking.
Why Psychometric Tests Are Used
These assessments are increasingly used by organizations to evaluate a candidate’s mental capabilities and behavioral traits. Their primary purpose is to provide a structured and standardized method of understanding how individuals may perform in various roles. These tools offer valuable insights that go beyond resumes and interviews, helping employers make more informed decisions. By assessing key attributes such as cognitive abilities, personality traits, and problem-solving skills, these evaluations help in identifying the best fit for a position.
Advantages for Employers
Employers use these assessments for several reasons, such as ensuring a fair evaluation process and reducing bias in hiring decisions. By using a standardized format, organizations can compare candidates on a consistent basis, leading to more objective decision-making. These tests also help employers understand how candidates approach tasks, manage stress, and fit within team dynamics, providing deeper insights than traditional methods alone.
Key Benefits
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Consistency | Tests provide a uniform way to assess all candidates, ensuring fairness. |
| Efficiency | Quickly identifies key strengths and areas for development in candidates. |
| Better Fit | Helps match candidates’ attributes to the specific demands of the job. |
| Reduced Bias | Minimizes subjective judgment, leading to more equitable selection processes. |
Overall, these assessments are an essential tool for companies seeking to make smarter, data-driven hiring decisions that are not only based on past experience but also on future potential and compatibility with organizational goals.
Overcoming Test Anxiety and Stress
For many individuals, facing assessments can be a source of significant stress and anxiety. This feeling can hinder performance and create a cycle of fear that impacts both preparation and execution. However, there are effective strategies to manage these emotions and approach evaluations with greater calmness and confidence. By understanding the causes of anxiety and learning techniques to counteract it, candidates can improve both their mindset and overall performance.
Techniques for Reducing Anxiety
One of the most effective ways to alleviate stress is through proper preparation. Familiarizing yourself with the structure and format of the evaluation can help reduce uncertainty and boost confidence. Additionally, practicing regularly under timed conditions can simulate the actual environment, making the process feel less overwhelming. It’s also important to prioritize self-care in the lead-up to an assessment, including sufficient rest, exercise, and relaxation techniques.
Mindfulness and Relaxation Techniques
Incorporating mindfulness and relaxation practices can significantly help reduce anxiety. Simple breathing exercises, such as deep diaphragmatic breathing, can calm the mind and lower stress levels. Visualization techniques, where you imagine yourself succeeding in the assessment, can also create a positive mindset. Taking breaks and ensuring regular mental rest during preparation periods can prevent burnout and maintain focus.
By adopting these strategies, individuals can approach their assessments with a clearer, more focused mindset, ultimately leading to better outcomes and reduced stress levels.
How to Analyze Your Performance
After completing any type of assessment, it’s essential to assess how well you performed. Understanding your results allows you to identify strengths and areas for improvement. By thoroughly analyzing your performance, you can refine your strategies for future challenges and work on the specific skills that may need more attention. This process not only helps you become more aware of your capabilities but also enables you to better prepare for similar evaluations in the future.
Key Steps in Analyzing Your Results
Follow these steps to effectively evaluate your performance:
- Review Your Scores: Start by examining your scores in detail. Look at how you performed in various sections or categories. This gives insight into where you excel and where there may be room for improvement.
- Identify Patterns: Look for patterns in the types of tasks that caused difficulties. Were they related to logic, numerical reasoning, or verbal comprehension? Recognizing these patterns can help you target specific areas to work on.
- Evaluate Time Management: Consider how well you managed your time during the evaluation. Did you spend too much time on one section, or did you struggle to finish on time? Effective time management is crucial for success, and reviewing this aspect can be enlightening.
Improvement Strategies
Once you’ve analyzed your results, it’s time to focus on areas that need improvement:
- Practice Regularly: Repetition is key to improving performance. Regular practice helps build confidence and improves speed and accuracy in tackling similar tasks.
- Seek Feedback: If possible, seek feedback from others who have taken the same assessment or from experts in the field. Understanding their strategies can offer valuable insights and tips for improvement.
- Focus on Weak Areas: Devote extra time to areas where you scored lower. Whether it’s logical reasoning, pattern recognition, or speed, targeted practice can make a significant difference.
By following these steps, you can gain a deeper understanding of your performance, build on your strengths, and improve your overall effectiveness in future evaluations.
Practical Examples of Assessment Tasks
To fully prepare for any type of evaluative task, it’s helpful to explore real-world examples of the challenges you may encounter. These examples can provide insight into the types of skills tested, such as logical thinking, pattern recognition, and problem-solving abilities. By familiarizing yourself with different types of problems, you can sharpen your approach and increase your chances of success during the actual process.
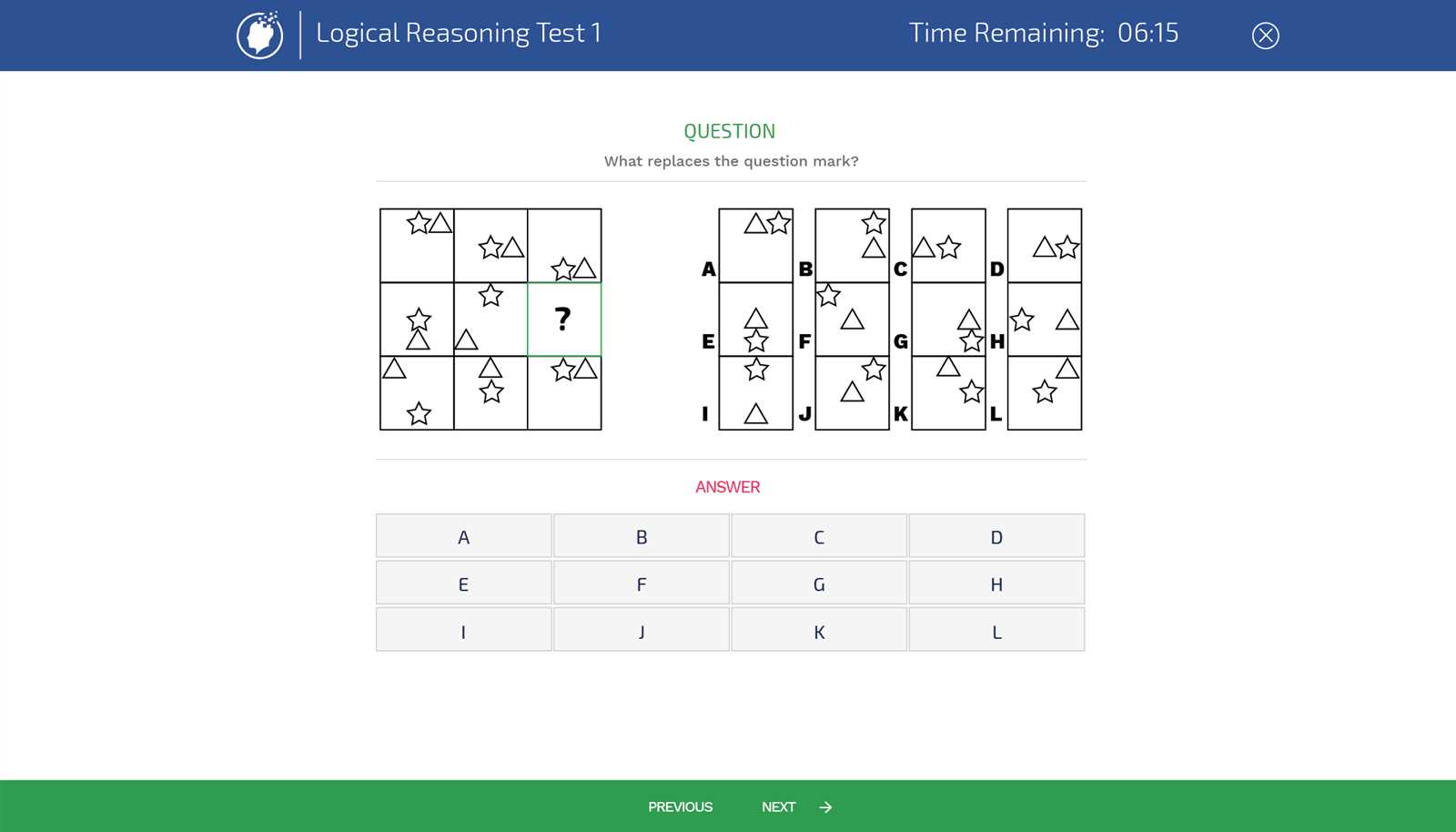
Example 1: Logical Reasoning
This task typically involves solving puzzles or identifying patterns in sequences. The goal is to test your ability to think critically and logically under pressure. Here’s an example:
- Example: What comes next in the series? 2, 4, 8, 16, __
- Answer: 32 (The series doubles with each step.)
Example 2: Verbal Reasoning
These tasks assess your ability to understand, analyze, and interpret written information. Here’s an example:
- Example: “The company reported a significant increase in profits, driven by new product launches.” What does this statement suggest?
- Answer: The company’s growth is attributed to the successful introduction of new products.
Example 3: Numerical Reasoning
In numerical reasoning tasks, you will be asked to solve problems that involve numbers, data interpretation, or simple arithmetic calculations. Here’s an example:
- Example: If a car travels 50 miles in one hour, how long will it take to travel 150 miles?
- Answer: 3 hours (150 ÷ 50 = 3)
Example 4: Abstract Reasoning
These tasks focus on your ability to recognize patterns in abstract shapes or sequences. Here’s an example:
- Example: Which shape logically follows in the sequence? △, ○, △, ○, __
- Answer: △ (The sequence alternates between triangles and circles.)
Practicing these types of examples can help you become more comfortable with the format and improve your problem-solving efficiency during real assessments. Whether it’s logic puzzles, interpreting data, or understanding written material, these exercises will prepare you for success.