Preparing for an important assessment in the field of life sciences requires focused review and deep understanding of key biological systems. This guide offers a thorough approach to help reinforce knowledge, sharpen recall, and build confidence before facing the challenge of your upcoming evaluation. With targeted preparation, mastering complex topics becomes more manageable.
Covering essential aspects of human biology, this section is designed to highlight core concepts and provide useful strategies for reviewing important material. By exploring critical body functions, systems, and structures, students will be well-equipped to answer questions and apply their understanding in real-world scenarios.
While revising, it’s important to focus not only on memorization but also on connecting ideas and recognizing how different systems work together. Strong preparation will help you approach the assessment with clarity and confidence, making it easier to navigate even the toughest questions.
Essential Topics for Anatomy Exam
When preparing for an evaluation in the life sciences, certain subjects form the foundation for a comprehensive understanding of human biology. Focusing on the fundamental systems of the body and their interactions will provide a strong base for answering complex questions and applying theoretical knowledge in practical scenarios. It is essential to cover a range of concepts that connect the structure and function of each body part.
Understanding Body Systems
A detailed grasp of the major systems within the human body, such as the circulatory, respiratory, and muscular systems, is crucial. These systems are interdependent, and understanding how they work together to maintain homeostasis is key. Studying the organs involved, their functions, and how they support overall health will help reinforce your knowledge for practical applications.
Mastering the Skeletal Structure
The skeletal system plays a vital role in providing support, protecting vital organs, and enabling movement. Knowing the different types of bones, their structure, and their functions is fundamental for understanding the body’s overall functionality. Key areas of focus should include the major bone groups, joints, and the processes involved in bone growth and repair.
Key Muscular System Concepts to Review
The muscular system is essential for movement, stability, and maintaining posture. A thorough understanding of muscle structure, function, and the way muscles interact with other systems is vital. Focus should be placed on the types of muscles, their roles in bodily movements, and the mechanisms involved in muscle contraction.
Understanding the differences between skeletal, smooth, and cardiac muscles is crucial, as each type has unique characteristics and functions within the body. Additionally, knowing the key processes involved in muscle contraction and relaxation will help clarify how muscles work together to produce coordinated movement.
| Muscle Type | Location | Function |
|---|---|---|
| Skeletal | Attached to bones | Facilitates voluntary movements |
| Smooth | Walls of organs and blood vessels | Controls involuntary movements |
| Cardiac | Heart | Responsible for heartbeats and pumping blood |
To master this system, students should also focus on key terms such as the sliding filament theory, motor units, and the role of calcium in muscle contraction. A solid understanding of these concepts will provide the foundation for tackling related questions and applying knowledge to real-world scenarios.
Understanding the Human Skeletal Structure

The skeletal system provides the framework that supports the body, protects vital organs, and enables movement. Comprising a complex network of bones and joints, it plays an essential role in overall health and function. Mastery of the skeletal structure involves not only recognizing the individual bones but also understanding how they work together to facilitate movement and maintain stability.
The human skeleton consists of 206 bones, which are divided into two main parts: the axial skeleton, which includes the skull, spine, and rib cage, and the appendicular skeleton, which includes the limbs and girdles. Each bone type has a specific structure and function that contribute to the body’s overall mobility and strength.
Focusing on the major bones, their landmarks, and their relationships to muscles and ligaments is key to mastering the skeletal system. In addition, understanding the various joint types and their range of motion will aid in comprehending how movement is achieved and regulated in the body.
Understanding the Human Skeletal Structure
The skeletal system provides the framework that supports the body, protects vital organs, and enables movement. Comprising a complex network of bones and joints, it plays an essential role in overall health and function. Mastery of the skeletal structure involves not only recognizing the individual bones but also understanding how they work together to facilitate movement and maintain stability.
The human skeleton consists of 206 bones, which are divided into two main parts: the axial skeleton, which includes the skull, spine, and rib cage, and the appendicular skeleton, which includes the limbs and girdles. Each bone type has a specific structure and function that contribute to the body’s overall mobility and strength.
Focusing on the major bones, their landmarks, and their relationships to muscles and ligaments is key to mastering the skeletal system. In addition, understanding the various joint types and their range of motion will aid in comprehending how movement is achieved and regulated in the body.
Digestive System Overview for Success
The digestive system is crucial for converting food into energy and nutrients that the body can use. Understanding how different organs contribute to this process is essential for grasping how the body sustains itself. This system involves a series of stages that break down complex food into simpler molecules, which can then be absorbed and transported throughout the body.
Key Organs Involved in Digestion
The digestive process is complex, involving several organs that perform specialized tasks. Below are the main organs responsible for processing food:
- Mouth: Initiates the breakdown of food through chewing and the action of saliva.
- Esophagus: Transports food from the mouth to the stomach.
- Stomach: Mixes food with digestive juices to continue the breakdown process.
- Small Intestine: The primary site for nutrient absorption into the bloodstream.
- Large Intestine: Absorbs water and forms waste for elimination.
Digestive Enzymes and Their Functions
Enzymes play a pivotal role in speeding up the breakdown of food. Each enzyme targets specific types of nutrients, allowing them to be processed and absorbed efficiently:
- Amylase: Breaks down carbohydrates into simple sugars.
- Protease: Breaks down proteins into amino acids.
- Lipase: Breaks down fats into fatty acids and glycerol.
Mastering the functions of each organ and enzyme will give you a comprehensive understanding of how the body processes food and absorbs essential nutrients.
Reviewing Respiratory System Functions
The respiratory system plays a vital role in supplying the body with oxygen and removing carbon dioxide, crucial for sustaining life. Understanding how air flows into the lungs, how oxygen is exchanged for carbon dioxide, and how the body regulates breathing is key to mastering this system. The process involves several organs working together to ensure that the body maintains homeostasis by managing gas exchange efficiently.
Key Organs Involved in Breathing
The respiratory system consists of multiple organs that each serve a specific function in facilitating the intake of oxygen and expulsion of carbon dioxide:
- Nose: The entry point for air, filtering out dust and debris.
- Trachea: The windpipe that directs air to the lungs.
- Bronchi: The two large airways branching from the trachea into each lung.
- Lungs: The primary site for gas exchange between the air and the bloodstream.
- Alveoli: Small air sacs where oxygen is absorbed, and carbon dioxide is released.
The Mechanics of Breathing
Breathing involves the movement of air into and out of the lungs, a process regulated by the diaphragm and other muscles. When the diaphragm contracts, the chest cavity expands, allowing air to flow into the lungs. When it relaxes, air is expelled. This cycle helps maintain a continuous supply of oxygen and facilitates the removal of carbon dioxide.
Understanding the mechanics and functions of each component will provide a solid foundation for answering questions related to respiratory health and processes.
Exploring the Nervous System Basics

The nervous system is the body’s communication network, coordinating and regulating functions across all organs and systems. It enables responses to stimuli, processes sensory information, and maintains homeostasis. Understanding the structure and function of the central and peripheral components is essential for grasping how the body reacts to the environment and manages internal processes.
Key Components of the Nervous System
The nervous system consists of two main parts, each with specific roles in transmitting signals and processing information:
- Central Nervous System (CNS): Comprising the brain and spinal cord, this system processes information and sends out signals to control body functions.
- Peripheral Nervous System (PNS): This system includes all the nerves outside the CNS, connecting the central system to the limbs and organs.
Basic Functions of Neurons

Neurons are the functional units of the nervous system. These specialized cells transmit electrical signals throughout the body. They play a critical role in communication between the brain, spinal cord, and the rest of the body:
- Motor Neurons: Transmit signals from the CNS to muscles, causing movement.
- Sensory Neurons: Relay information from sensory receptors to the brain.
- Interneurons: Connect neurons within the CNS, integrating sensory and motor information.
A solid understanding of how these components work together to process signals and control body functions is essential for mastering the basics of the nervous system.
Exploring the Nervous System Basics
The nervous system is the body’s communication network, coordinating and regulating functions across all organs and systems. It enables responses to stimuli, processes sensory information, and maintains homeostasis. Understanding the structure and function of the central and peripheral components is essential for grasping how the body reacts to the environment and manages internal processes.
Key Components of the Nervous System
The nervous system consists of two main parts, each with specific roles in transmitting signals and processing information:
- Central Nervous System (CNS): Comprising the brain and spinal cord, this system processes information and sends out signals to control body functions.
- Peripheral Nervous System (PNS): This system includes all the nerves outside the CNS, connecting the central system to the limbs and organs.
Basic Functions of Neurons
Neurons are the functional units of the nervous system. These specialized cells transmit electrical signals throughout the body. They play a critical role in communication between the brain, spinal cord, and the rest of the body:
- Motor Neurons: Transmit signals from the CNS to muscles, causing movement.
- Sensory Neurons: Relay information from sensory receptors to the brain.
- Interneurons: Connect neurons within the CNS, integrating sensory and motor information.
A solid understanding of how these components work together to process signals and control body functions is essential for mastering the basics of the nervous system.
Key Principles of Human Reproduction
Human reproduction involves complex biological processes that ensure the continuation of the species. It is characterized by the fusion of genetic material from two individuals, resulting in the development of offspring. This process is regulated by various systems, each playing a distinct role in the creation of life. Understanding the fundamental mechanisms of reproduction is essential for a deeper insight into how human life begins and is sustained.
Primary Stages of Reproductive Process
The reproductive process consists of several stages, each critical for the successful creation of new life. These stages include the production of gametes, fertilization, and the development of the embryo. The following table outlines these key stages:
| Stage | Description |
|---|---|
| Gametogenesis | The formation of sperm in males and eggs in females. |
| Fertilization | The union of sperm and egg to form a zygote. |
| Embryonic Development | The process where the fertilized egg develops into an embryo, leading to implantation in the uterus. |
| Gestation | The period of development in the womb, culminating in childbirth. |
Hormonal Regulation of Reproduction
Reproduction is also controlled by a variety of hormones that regulate the function of the reproductive organs. These hormones ensure that the reproductive process occurs in a coordinated and timely manner. Key hormones involved include:
- Estrogen: Promotes the development of female reproductive traits and regulates the menstrual cycle.
- Testosterone: Stimulates the development of male reproductive traits and sperm production.
- Progesterone: Prepares the uterus for pregnancy and supports the early stages of fetal development.
By understanding these key principles, one can better grasp the intricacies of human reproduction and the physiological processes involved in the creation of life.
Understanding the Lymphatic System
The lymphatic system plays a crucial role in the body’s defense mechanisms, helping to protect against infections and maintaining fluid balance. This network of vessels, tissues, and organs works tirelessly to filter out harmful substances and return excess fluid to the bloodstream. A solid understanding of how this system functions is essential for recognizing its importance in overall health and immune function.
Key Components of the Lymphatic System
The lymphatic system consists of several vital components that work together to transport lymph and support immune responses:
- Lymph: A clear fluid that circulates throughout the system, carrying white blood cells and waste products.
- Lymph Vessels: A network of vessels that transport lymph from tissues to lymph nodes and back to the bloodstream.
- Lymph Nodes: Small, bean-shaped organs that filter lymph and trap harmful substances like bacteria and viruses.
- Spleen: An organ that filters blood, removes old red blood cells, and helps fight infection.
- Tonsils: Lymphoid tissues located in the throat that help protect against pathogens entering through the mouth and nose.
- Thymus: A gland where T-cells mature, playing a key role in the immune response.
Functions of the Lymphatic System
This system is essential not only for immune defense but also for maintaining fluid homeostasis in the body:
- Immune Function: Lymph nodes and other lymphatic organs filter out pathogens and produce immune cells to defend against infections.
- Fluid Balance: The system helps to drain excess fluid from tissues, preventing swelling and maintaining proper fluid distribution.
- Absorption of Fat: The lymphatic system helps absorb fats and fat-soluble vitamins from the digestive tract.
Understanding the lymphatic system’s role in immunity and fluid balance can help individuals appreciate its importance in health and disease prevention.
Importance of Cellular Biology in Anatomy
Cellular biology provides a foundational understanding of how the body is structured and how its various systems function. Every part of the body, from organs to tissues, is made up of cells, and their properties govern overall function. Understanding cellular processes is essential for comprehending how the body develops, maintains its health, and responds to diseases or injuries. The study of cells offers key insights into the basic units that make up all living organisms.
Key Cellular Processes in the Body

Cells are involved in a variety of processes that support the function and structure of organs and tissues. These fundamental activities include:
| Process | Description |
|---|---|
| Cell Division | The process by which cells replicate, allowing growth and tissue repair. |
| Protein Synthesis | The creation of proteins from amino acids, essential for cell function and tissue structure. |
| Metabolism | Cellular processes that convert nutrients into energy, supporting bodily functions. |
| Signal Transduction | How cells communicate with each other to coordinate actions and respond to stimuli. |
The Role of Cellular Biology in Understanding Health
A deep knowledge of cellular biology aids in understanding how cells interact within larger structures and systems. It enables medical professionals to pinpoint the underlying causes of various conditions, ranging from genetic disorders to infections. By focusing on how cells behave in different environments, scientists can develop targeted therapies that address specific cellular dysfunctions, improving treatment outcomes.
In summary, cellular biology serves as the cornerstone of understanding how the body functions, making it crucial for anyone studying the body’s structure and responses to various conditions.
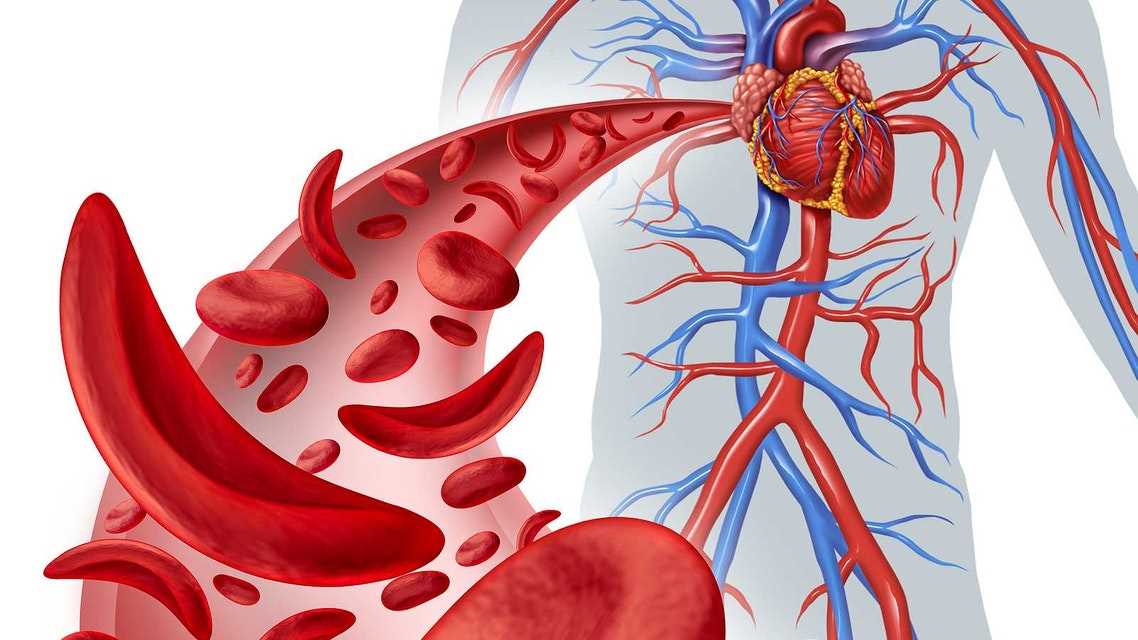
In-Depth Look at Cardiovascular Health
Cardiovascular health is vital for the overall functioning of the body, as it directly impacts the delivery of oxygen and nutrients to various tissues and organs. A strong, well-functioning circulatory system ensures that blood flows efficiently, supporting both metabolic processes and immune function. In this section, we explore the key components and factors that contribute to maintaining heart and vascular health, as well as the importance of monitoring it for early detection of potential issues.
The cardiovascular system consists of the heart, blood vessels, and blood. Together, these elements work to circulate oxygenated blood throughout the body, while also returning deoxygenated blood back to the heart and lungs for reoxygenation. Maintaining a balance in this system is crucial, as imbalances can lead to various health concerns, including hypertension, heart disease, and stroke.
One of the most important factors in maintaining cardiovascular health is understanding the risk factors and lifestyle choices that can positively or negatively influence heart function. Regular exercise, a balanced diet, and avoiding smoking can help reduce the risk of heart-related issues. Additionally, staying informed about blood pressure and cholesterol levels is key for early intervention and long-term health management.
Monitoring cardiovascular health requires a combination of clinical tests and self-awareness. Regular check-ups, including blood pressure and cholesterol screenings, as well as keeping an eye on lifestyle habits, are essential for preventing chronic conditions and improving long-term heart health.
In-Depth Look at Cardiovascular Health
Cardiovascular health is vital for the overall functioning of the body, as it directly impacts the delivery of oxygen and nutrients to various tissues and organs. A strong, well-functioning circulatory system ensures that blood flows efficiently, supporting both metabolic processes and immune function. In this section, we explore the key components and factors that contribute to maintaining heart and vascular health, as well as the importance of monitoring it for early detection of potential issues.
The cardiovascular system consists of the heart, blood vessels, and blood. Together, these elements work to circulate oxygenated blood throughout the body, while also returning deoxygenated blood back to the heart and lungs for reoxygenation. Maintaining a balance in this system is crucial, as imbalances can lead to various health concerns, including hypertension, heart disease, and stroke.
One of the most important factors in maintaining cardiovascular health is understanding the risk factors and lifestyle choices that can positively or negatively influence heart function. Regular exercise, a balanced diet, and avoiding smoking can help reduce the risk of heart-related issues. Additionally, staying informed about blood pressure and cholesterol levels is key for early intervention and long-term health management.
Monitoring cardiovascular health requires a combination of clinical tests and self-awareness. Regular check-ups, including blood pressure and cholesterol screenings, as well as keeping an eye on lifestyle habits, are essential for preventing chronic conditions and improving long-term heart health.
Techniques for Studying Anatomy Efficiently
Mastering the complexities of the human body requires effective strategies to retain vast amounts of detailed information. To efficiently absorb and understand the material, students need a variety of approaches that enhance learning and make the process more manageable. The following techniques are proven to help break down complex concepts into digestible pieces, improving both comprehension and retention.
- Active Recall: Test yourself regularly on key concepts instead of simply reviewing notes. This forces the brain to retrieve information, strengthening memory.
- Spaced Repetition: Review material at increasing intervals to reinforce long-term retention. Spacing out study sessions helps combat forgetting and keeps the material fresh.
- Visual Aids: Diagrams, charts, and models are powerful tools for understanding relationships between different structures. Visualizing processes and structures can deepen comprehension.
- Study Groups: Collaborating with peers provides a chance to discuss complex ideas, clarify doubts, and share perspectives. Teaching others is also a powerful way to reinforce your own understanding.
- Mnemonics: Create memory aids to remember complex terms or processes. Associating concepts with simple words, phrases, or stories makes them easier to recall.
- Focused Sessions: Study in short, intense bursts with breaks in between. Focused sessions prevent burnout and improve concentration.
These methods can be customized to fit individual learning styles. Consistency, self-discipline, and effective time management are crucial for mastering the material and ensuring academic success. Make use of these strategies regularly, and you’ll improve your ability to recall and apply knowledge when it matters most.
Common Mistakes in Anatomy and Physiology
Studying the human body can be challenging due to its complexity, and many students make similar mistakes that hinder their understanding. These errors often stem from misinterpreting concepts, failing to connect different systems, or not paying attention to key details. Recognizing and avoiding these common mistakes can improve learning outcomes and help solidify important concepts.
One of the most frequent mistakes is overlooking the relationships between different bodily systems. While it’s important to learn each system individually, understanding how they interact with one another is crucial for a holistic grasp of how the body functions. For example, knowing how the circulatory and respiratory systems work together to transport oxygen is fundamental to understanding human physiology.
Another common mistake is memorizing information without truly understanding it. While rote memorization may seem effective in the short term, it doesn’t foster deep comprehension. Instead, focus on understanding the “why” and “how” behind each process. This helps in applying knowledge to various scenarios and solving complex problems.
Additionally, many students fail to review material consistently. Cramming information the night before a test is ineffective and often leads to poor retention. It’s better to adopt a study plan that includes regular reviews and breaks down the material into smaller, manageable sections. This method allows for long-term retention and better understanding over time.
Lastly, not using diverse study methods can limit the depth of learning. Relying on only one form of study–such as reading the textbook–can be less effective than combining different techniques like diagrams, practice questions, group discussions, and hands-on models. Integrating visual aids and active learning strategies ensures that concepts are retained more effectively.
Effective Time Management for Exams
Time management is a crucial skill that can make a significant difference in the outcome of any assessment. Proper planning and organization allow students to balance their study schedule, review material effectively, and avoid last-minute stress. When managing time efficiently, students can ensure they are fully prepared without feeling overwhelmed.
One of the first steps in effective time management is creating a realistic study plan. Break down your study sessions into focused blocks of time, setting specific goals for each period. For example, designate one session to reviewing a specific chapter or topic and another to practicing problems or questions. This prevents feeling like you’re tackling everything at once and helps ensure you cover all necessary material.
Another important strategy is prioritizing tasks based on their difficulty or importance. Some topics may require more time or attention, so allocate extra time to those areas. Additionally, identify any weaker areas where you may need more practice or clarification and schedule time for review accordingly. This targeted approach helps make the most of your study time.
Additionally, it’s important to include breaks in your study schedule. While it might seem productive to study non-stop, taking regular short breaks can actually improve focus and retention. Use techniques like the Pomodoro method, where you work for 25 minutes, followed by a 5-minute break. After a few sessions, take a longer break. This method keeps the mind fresh and maintains productivity over longer study periods.
Finally, avoid procrastination by setting specific deadlines for when you want to complete each section of your study plan. Sticking to these deadlines helps you stay on track and prevents last-minute cramming. Starting your preparation early and staying consistent with your study schedule will ensure you’re well-prepared, reducing stress as the time for assessment approaches.
Tips for Retaining Complex Information
Effectively retaining challenging material requires more than just reading through it once. Successful memorization and understanding are built on strategies that enhance focus, organization, and active engagement. By using proven methods, students can increase retention, reduce stress, and boost their confidence when recalling difficult concepts.
Here are some strategies to improve retention of complex information:
- Chunking: Break down large amounts of information into smaller, more manageable units. For example, instead of memorizing a long list, divide it into categories or related groups to make the content easier to remember.
- Visualization: Create mental images to link abstract concepts to something more tangible. Drawing diagrams or picturing processes can help solidify complex ideas in your mind.
- Spaced Repetition: Review material at increasing intervals over time. This technique takes advantage of the brain’s ability to retain information more effectively through repeated exposure.
- Active Recall: Test yourself frequently on the material without looking at your notes. Active recall forces your brain to retrieve information, strengthening memory pathways and enhancing recall ability.
- Mnemonics: Use memory aids like acronyms or rhymes to make remembering complex terms or sequences easier. These mental shortcuts help trigger memory and make abstract ideas more accessible.
By applying these techniques consistently, the process of retaining challenging material becomes more efficient, helping you stay on track during your studies and perform at your best when it counts.