
Before undergoing certain health assessments, it is often recommended to avoid consuming food or beverages for a set period of time. This practice helps ensure the accuracy of test results by eliminating potential influences from digestion or nutrient absorption. By following specific guidelines, you can optimize your chances of receiving reliable outcomes during your visit to the healthcare provider.
Understanding the importance of adhering to these recommendations is essential. While it might seem inconvenient, skipping meals or restricting certain substances can provide clearer insights into your overall health. It’s crucial to know the right approach, including how long to refrain from eating and what exceptions, if any, exist.
By learning about the specifics of how pre-assessment preparation works, you can approach your appointment confidently, knowing that you’re taking the necessary steps to ensure precise results. Whether it’s for routine checkups or more detailed diagnostic tests, proper preparation is key to achieving the most accurate health data possible.
Fasting Guidelines for Health Screenings
When preparing for certain medical assessments, it’s essential to follow specific instructions to ensure that test results are as accurate as possible. This often involves refraining from eating or drinking for a period of time before the procedure. Understanding the exact requirements and why they are necessary can help you navigate the preparation process with ease.
Key Preparation Steps
- Follow your healthcare provider’s recommendations on how long to abstain from food and drinks.
- Pay attention to any specific instructions about medications, as some may need to be taken with water.
- Avoid consuming alcohol or excessive amounts of caffeine before the assessment.
- Stick to clear liquids such as water or tea, if allowed, to stay hydrated.
- In certain cases, you may be instructed to skip meals the night before.
What to Expect During the Process
Adhering to these guidelines helps eliminate any interference from food or beverages, which could affect the accuracy of certain health indicators like blood sugar or cholesterol levels. If you’re unsure about any restrictions, don’t hesitate to ask your healthcare provider for clarification.
By following these simple yet important steps, you ensure that the healthcare provider can obtain the clearest and most reliable results, which is crucial for your health assessment.
Why Fasting Matters for Tests
When preparing for certain health assessments, it’s important to follow guidelines that help ensure accurate results. By limiting the intake of food and drinks beforehand, you eliminate potential factors that could skew measurements, such as blood sugar levels or cholesterol. This practice enables your healthcare provider to get a true reading of your baseline health.
How Eating Affects Results
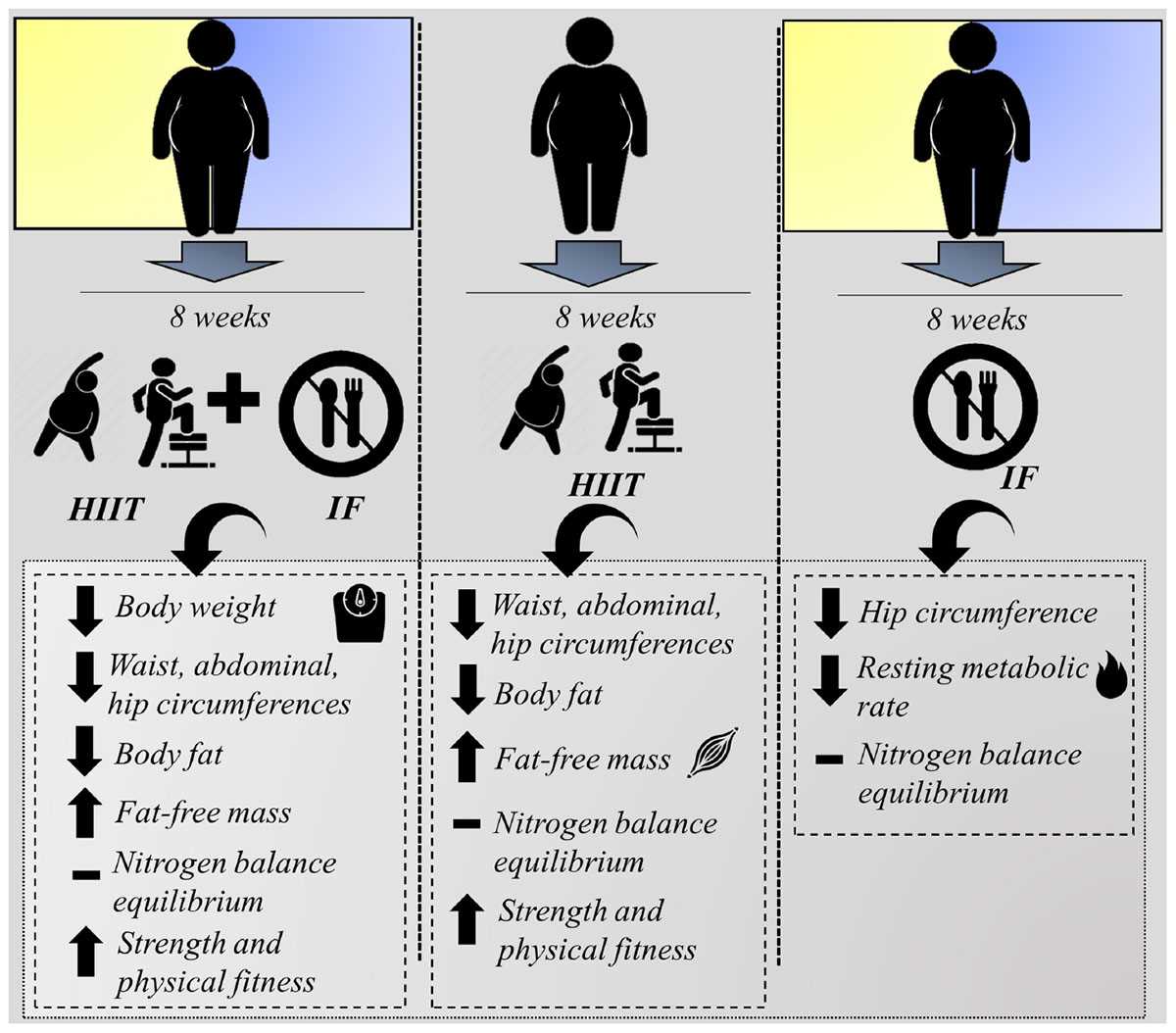
Consuming food or beverages before a test can alter several physiological factors, making it difficult to obtain precise data. The body processes nutrients differently, which may influence readings like glucose, lipid profiles, and liver function. This is why avoiding food intake is often essential to getting accurate results.
Impact on Common Health Tests
| Test Type | Effect of Eating |
|---|---|
| Blood Glucose Test | Eating can increase blood sugar levels, affecting the accuracy of the results. |
| Lipid Panel | Fat intake can influence cholesterol levels, leading to skewed readings. |
| Liver Function Test | Food can alter enzymes and proteins in the blood, impacting liver health indicators. |
By following pre-assessment preparation instructions, you give your healthcare provider the clearest picture of your current health status, making it easier to make informed decisions about your care.
How Long to Fast Before a Checkup
The length of time you should refrain from eating or drinking before a medical assessment depends on the type of test being performed. Generally, a period of 8 to 12 hours is recommended to ensure the most accurate results. However, the exact duration can vary based on your healthcare provider’s instructions and the specific tests being conducted.
For routine tests like blood work, 8 to 12 hours of abstaining from food is typically sufficient. If more specialized tests are required, such as glucose or cholesterol screenings, longer periods of preparation may be necessary. Always check with your healthcare provider to confirm the specific requirements for your appointment.
Preparing for Blood Work and Fasting
Before undergoing a blood test, it is crucial to follow certain guidelines to ensure that the results are accurate and reliable. Avoiding food and beverages for a specific time helps prevent substances from interfering with the measurements, such as blood sugar or cholesterol levels. The preparation process varies depending on the type of test, so it’s important to know what to expect and how to prepare effectively.
General Guidelines
- Typically, a 12-hour period without eating or drinking is recommended before blood tests that measure cholesterol, glucose, or lipid levels.
- Clear liquids, such as water, may be permitted during this time, but other beverages like coffee, tea, or juice should be avoided.
- Ensure you are well-hydrated by drinking plenty of water, which helps with blood collection and improves the accuracy of certain tests.
- Follow any specific instructions provided by your healthcare provider, as some tests may have different requirements.
What to Avoid
- Avoid eating solid foods, especially fatty or sugary items, as they can alter test outcomes.
- Steer clear of alcohol consumption, which can interfere with liver function and other health indicators.
- Refrain from consuming beverages with caffeine, as it may affect certain metabolic processes that are measured during tests.
By adhering to these guidelines, you help ensure the most accurate and reliable results during your blood test, providing a clearer picture of your overall health.
Understanding the Impact of Fasting
Refraining from eating or drinking before certain health assessments has a significant effect on your body’s processes, allowing for a clearer and more accurate understanding of your overall health. When you avoid food intake, your body enters a state where it can provide a baseline measurement for key indicators, free from the interference of recently consumed nutrients. This process ensures that the results reflect your natural health status.
By temporarily halting the digestive process, you allow medical tests to measure things like glucose levels, cholesterol, and liver function without the immediate impact of digestion. This helps healthcare professionals evaluate your health more precisely, as the absence of food-related changes in your system leads to more reliable readings. Understanding this impact is essential for proper preparation and ensuring accurate outcomes during your medical visit.
Common Tests Requiring Fasting
Certain health assessments require individuals to avoid food and drink for a period of time to ensure accurate results. These tests measure vital indicators such as glucose levels, cholesterol, and liver function. By abstaining from eating, the body is in a more controlled state, allowing medical professionals to gather precise data on various health factors without interference from digestion.
Key Tests Requiring Preparation
| Test Type | Purpose | Preparation Details |
|---|---|---|
| Blood Glucose Test | Measures the body’s blood sugar levels | Avoid food and beverages for 8-12 hours before the test |
| Lipid Profile | Assesses cholesterol and fat levels in the blood | Abstain from eating for 12 hours to ensure accurate readings |
| Complete Blood Count (CBC) | Helps evaluate overall health and detect disorders | No food or drink for 8-12 hours before the procedure |
| Liver Function Test | Monitors liver enzymes and health markers | 12-hour fast is typically recommended to avoid skewed results |
Why Preparation is Crucial
Accurate readings are essential for proper diagnosis and treatment. By following the required guidelines for each test, you ensure that the results reflect your natural health state, free from any temporary changes caused by digestion or food intake. Always consult with your healthcare provider to understand specific instructions and avoid potential complications in your results.
Foods and Drinks to Avoid
When preparing for medical tests, it’s important to avoid certain foods and beverages that could interfere with the accuracy of your results. Some items can cause temporary changes in your body, affecting factors like blood sugar, cholesterol, and other critical health markers. By steering clear of these substances, you help ensure that the results reflect your true health status.
What to Avoid
- Sugary Foods: Items like candy, pastries, and sugary snacks can spike blood sugar levels and alter glucose test results.
- Fatty Foods: Fried foods or meals high in fats can influence cholesterol and lipid readings.
- Caffeinated Beverages: Coffee, tea, and energy drinks can affect metabolism and hydration, skewing certain health tests.
- Alcohol: Alcohol consumption can impact liver function and disrupt metabolic processes, leading to inaccurate results.
- Dairy Products: High-fat dairy may influence lipid profile readings and other markers in the blood.
Why Avoid These Foods?
Consuming these foods or drinks before your test can lead to inaccurate measurements of vital health indicators. They can raise blood sugar, alter enzyme levels, or affect your body’s ability to process nutrients, making it difficult to get a clear picture of your health. To achieve the best results, it’s crucial to follow the preparation guidelines provided by your healthcare provider.
Hydration Tips During Fasting
Staying hydrated is essential, even when avoiding food and drinks before certain health tests. Proper hydration ensures that your body functions optimally, supporting processes like blood circulation and maintaining energy levels. It’s important to know which fluids are appropriate during this period to avoid interference with test results while still keeping hydrated.
What to Drink
- Water: The best option to stay hydrated without affecting test outcomes. It’s important to drink plenty of water before and during the preparation phase.
- Herbal Teas: Unsweetened herbal teas can be a good alternative if you need something warm, but make sure they are caffeine-free.
- Clear Broth: A simple, clear broth can provide hydration without the added nutrients from solid foods.
What to Avoid
- Caffeinated Beverages: Coffee, tea, and energy drinks can alter hydration levels and impact your body’s systems.
- Juices: Fruit juices contain sugars that could skew test results, particularly for glucose and lipid assessments.
- Alcohol: Alcohol dehydrates the body and can interfere with several health measurements, including liver function and blood pressure.
By sticking to water and other permitted fluids, you maintain optimal hydration without compromising the integrity of your health tests. Always follow specific instructions provided by your healthcare provider to ensure the best possible results.
Can You Take Medications While Fasting?
When preparing for health assessments, it’s important to understand whether you can continue taking your regular medications. Some prescriptions may need to be adjusted, while others can be taken as usual. The key is to make sure that the medications do not interfere with the accuracy of the test results or cause any adverse effects during the preparation period.
General Guidelines
- Prescription Medications: Most prescription medications, especially those for chronic conditions like hypertension or diabetes, can generally be taken with a small sip of water. However, consult your doctor for specific instructions regarding your medication.
- Over-the-Counter Medications: OTC drugs, including pain relievers and supplements, should be avoided unless explicitly directed by your healthcare provider, as they may alter test results.
- Medications with Food Requirements: Some medications require food to be absorbed properly, and it’s essential to ask your doctor whether to adjust the timing of these medications around the assessment.
Consult Your Healthcare Provider
Always inform your healthcare provider about all the medications you’re currently taking. They will advise you on whether any adjustments are needed before your appointment. In some cases, it may be necessary to pause certain medications temporarily or alter the timing to avoid interference with test results.
What Happens if You Break the Fast?
Breaking the preparation period can have significant consequences on the accuracy of the health tests. Consuming food or drinks before the designated time can alter various bodily functions, leading to misleading results. The effects can range from mild to severe, depending on the type of test and the substance consumed.
| Effect | Test Impact | Potential Consequences |
|---|---|---|
| Blood Sugar Elevation | Glucose and Diabetes Tests | Higher readings could result in misdiagnosis of diabetes or poor glucose control. |
| Increased Cholesterol | Lipid Profile | May show inaccurate cholesterol levels, leading to incorrect heart disease risk assessment. |
| Dehydration | Kidney Function and Electrolyte Tests | Increased risk of skewed results due to dehydration affecting kidney and electrolyte readings. |
| Altered Metabolism | Thyroid and Hormone Tests | Can lead to inaccurate hormone levels, making it difficult to diagnose thyroid issues. |
If you accidentally break the preparation guidelines, inform your healthcare provider before the test. They will determine whether to reschedule the assessment or proceed with caution, understanding that the results may not be entirely reliable. It’s crucial to follow all guidelines to ensure the best possible outcomes and avoid unnecessary retesting or delays.
How Fasting Affects Your Energy Levels
When you refrain from eating or drinking for a set period before health assessments, your body undergoes various changes that can affect your energy levels. These effects are often temporary and depend on factors like the duration of abstinence and individual health conditions. Understanding these changes can help you better prepare for the process and manage any discomfort that might arise.
Short-Term Effects
- Initial Drop in Energy: During the first few hours without food, you may feel fatigued or sluggish as your body adjusts to the lack of immediate fuel.
- Increased Focus: After an initial dip, some people experience heightened mental clarity and focus due to lower insulin levels, which can help in certain health tests.
- Mild Headaches: Dehydration or blood sugar fluctuations can cause headaches or dizziness, especially if fluids are also restricted.
Long-Term Effects
- Energy Conservation Mode: After an extended period of not eating, your body switches to a mode where it conserves energy, possibly leading to feelings of tiredness.
- Metabolic Shift: Prolonged lack of food leads your body to burn stored fat for energy, which may impact overall energy levels but also helps prepare for some tests.
- Rebound Fatigue: Once food is reintroduced, you might experience temporary fatigue as your body shifts back to normal metabolism.
It’s important to listen to your body and stay hydrated during this time to minimize discomfort. Always follow the preparation guidelines provided by your healthcare provider to ensure accurate results while maintaining your well-being.
Fasting and Medical History Considerations
When preparing for health assessments, it’s essential to consider your medical history. Certain pre-existing conditions can influence how your body responds during the period of abstaining from food and drink. Understanding these factors can help ensure both accurate test results and your safety during the preparation process.
Key Factors to Consider
| Condition | Potential Impact | Recommendations |
|---|---|---|
| Diabetes | Risk of low blood sugar, dizziness, or fainting. | Monitor blood sugar levels and consult your healthcare provider for advice on adjusting medication. |
| Heart Disease | Increased strain on the heart, especially in cases of dehydration. | Ensure proper hydration and discuss with your doctor if any adjustments to the preparation period are needed. |
| Kidney Issues | Dehydration may cause stress on kidney function. | Consult your doctor about proper hydration and whether to alter preparation guidelines. |
| Pregnancy | Increased risk of dehydration or nutrient deficiency. | Seek advice from your healthcare provider to ensure safety for both mother and baby. |
Discussing with Your Healthcare Provider
Before beginning the preparation process, it’s important to communicate openly with your healthcare provider about any chronic conditions, medications, or health concerns. They can help tailor the guidelines to suit your individual needs and ensure that the procedure will not compromise your health or affect the test outcomes.
Special Considerations for Pregnant Women
When preparing for medical assessments during pregnancy, extra precautions are necessary to ensure the well-being of both the mother and the developing baby. Certain practices, especially those that involve withholding food or liquids, may have different effects on pregnant women compared to the general population. It’s essential to understand these differences and follow tailored advice from healthcare professionals.
Potential Risks
- Dehydration: Pregnant women are more susceptible to dehydration, which can lead to complications such as dizziness, fainting, and reduced amniotic fluid levels.
- Low Blood Sugar: Going without food for extended periods can cause blood sugar levels to drop, increasing the risk of hypoglycemia, which could affect both mother and baby.
- Stress on the Body: The body of a pregnant woman requires additional nutrients and energy to support the growing fetus. Restricting intake may cause unnecessary strain and discomfort.
Guidelines for Safe Preparation
- Consult Your Healthcare Provider: Always discuss any preparatory requirements with your doctor, who may adjust the procedure to suit your pregnancy stage and individual health needs.
- Avoid Prolonged Restrictions: If fasting is necessary, keep it short, and focus on hydration to prevent dehydration and maintain energy levels.
- Consider Alternative Preparations: In some cases, your healthcare provider might recommend modified procedures or allow for flexibility in the preparation period to prioritize your health and comfort.
Pregnant women should prioritize their health and the health of their baby during any medical assessment. Clear communication with healthcare providers is essential to ensure that all procedures are safe and tailored to individual needs.
Fasting for Children and Older Adults
When it comes to medical preparations involving food and drink restrictions, special care must be taken with children and older adults. Both groups have distinct nutritional needs and may be more vulnerable to the effects of not eating or drinking. Understanding the unique considerations for these age groups ensures their health and well-being during medical procedures.
Children
Children’s bodies are still developing, which means they have higher energy demands and may be more susceptible to the negative effects of prolonged periods without food or liquids. This can lead to irritability, fatigue, and dehydration, which could disrupt their overall health. When preparing a child for a medical assessment, it is important to minimize fasting periods and ensure they are hydrated. In some cases, modified instructions can be given to reduce discomfort.
Older Adults
Older adults often face a range of health challenges that can make food or fluid restrictions more risky. Issues such as chronic conditions, medication interactions, and reduced metabolic rates can make it harder for older individuals to tolerate fasting. Special attention should be given to their hydration levels and nutrient needs. It is essential to consult with healthcare providers to ensure that any fasting requirements are adapted to suit the individual’s health status.
For both children and older adults, it is crucial to work closely with healthcare professionals to customize any preparatory instructions, ensuring that they remain safe and comfortable throughout the process.
How to Manage Hunger During Fasting
Going without food for an extended period can lead to feelings of hunger, which can be challenging for many individuals. Understanding how to manage these sensations is key to making the experience more comfortable and effective. With the right strategies, it’s possible to alleviate discomfort and stay focused on the goal at hand.
Stay Hydrated
One of the best ways to manage hunger is by ensuring you are well-hydrated. Sometimes, what feels like hunger is actually dehydration. Drinking water or herbal teas can help curb hunger pangs and keep your body functioning properly during the period of restriction. It’s important to stay mindful of your fluid intake, as this can play a significant role in reducing hunger.
Keep Busy
Distractions can be a helpful tool when trying to ignore feelings of hunger. Engaging in activities that require focus, such as work, reading, or light exercise, can take your mind off food. When you’re mentally engaged, you’re less likely to fixate on food cravings.
Eat Balanced Meals Beforehand
What you consume before a period of food restriction plays a significant role in how well you manage hunger. Eating balanced meals with a mix of protein, healthy fats, and fiber will help keep you feeling full longer. Avoiding sugary or highly processed foods can prevent energy crashes and feelings of extreme hunger.
Practice Deep Breathing
Managing stress and anxiety during this time can also help reduce hunger. Deep breathing exercises or mindfulness techniques can help you stay calm and focused, preventing emotional or stress-related eating triggers.
By incorporating these strategies, you can reduce discomfort and make the experience more manageable, all while ensuring you stay on track with your health goals.
Fasting Myths and Facts
There are many misconceptions surrounding the practice of going without food for a period of time. Understanding the truth behind these beliefs can help clarify any confusion and guide individuals toward making informed decisions regarding their health. Let’s separate fact from fiction to gain a clearer perspective on this process.
Myth 1: Skipping Meals Slows Down Your Metabolism
One common myth is that skipping meals can slow down your metabolism significantly. In reality, while your body may adjust to periods without food, it does not drastically affect your metabolism in the long term. Many studies have shown that the body remains efficient in processing energy even during times of restriction, and in some cases, the process of reducing food intake can actually help improve metabolic function.
Myth 2: Going Without Food Will Cause Muscle Loss
Another widespread belief is that restricting food intake leads to muscle loss. While prolonged periods of malnutrition can indeed lead to muscle degradation, short-term food restriction, especially when done under medical supervision, does not significantly impact muscle mass. In fact, your body will primarily burn stored fat for energy, preserving muscle tissue.
Myth 3: You Can’t Stay Hydrated During This Time
A third myth is the idea that you cannot consume any liquids while refraining from food. In reality, staying hydrated is encouraged, and drinking water or herbal teas can actually help ease hunger and maintain bodily functions. Hydration is essential and does not interfere with the process.
Fact: Short-Term Food Restriction Can Improve Health
Studies have shown that reducing food intake for a short time may offer several health benefits. It can help lower blood sugar levels, improve cholesterol, and potentially reduce inflammation. When done properly, this practice can have a positive impact on overall health, including improved metabolic markers and enhanced cellular repair.
Understanding these myths and facts helps ensure that individuals approach this practice with a clearer understanding of its effects. It’s essential to rely on scientific evidence rather than hearsay when making decisions about health-related practices.
Alternatives to Fasting for Certain Tests
While skipping meals is a common preparation method for various medical procedures, it is not always necessary. There are alternative approaches that can be just as effective, depending on the type of test being conducted. Understanding these alternatives can provide more flexibility and reduce the stress that some individuals may experience when asked to refrain from eating.
1. Timed Eating
Instead of avoiding food entirely, a timed eating approach can be an option. For some tests, eating a light meal several hours before the procedure may still provide reliable results. This method allows the body to process the meal without compromising the accuracy of certain tests.
2. Hydration Focus

Maintaining proper hydration is critical when preparing for tests that traditionally require no food intake. In many cases, water or herbal tea can be consumed without affecting the results. Staying hydrated helps maintain bodily functions and can alleviate discomfort during the waiting period.
3. Specific Supplementation
Some tests may allow or even encourage the intake of specific nutrients, like electrolytes, before the procedure. This option ensures that the body remains balanced without the need for prolonged food abstention.
4. Reduced Caloric Intake
For those who have trouble completely avoiding food, a reduced caloric intake option may be suggested. Instead of going without food, individuals may be advised to consume very small amounts of food, such as clear broth or low-calorie liquids, to still provide minimal nourishment while avoiding heavy meals.
5. Alternative Test Methods
In some cases, newer testing methods may not require food restrictions at all. Advancements in medical technology and testing protocols may offer more flexibility, eliminating the need to prepare by skipping meals altogether. Discussing alternative test methods with a healthcare provider can help determine if these newer approaches are viable.
Choosing the right preparation method depends on the type of test being performed, your individual health needs, and the guidance of your healthcare provider. There are many ways to achieve accurate test results without having to go without food for long periods.
When to Seek Medical Advice for Fasting
While temporarily abstaining from food and drink is often a part of medical preparation, there are certain situations where it’s important to consult with a healthcare professional. Some individuals may experience difficulties or underlying conditions that make it unsafe or uncomfortable to follow these instructions. Understanding when to seek medical guidance can help ensure your safety and improve the accuracy of the results you’re preparing for.
1. Persistent Hunger or Discomfort
If you experience persistent discomfort, dizziness, or weakness that doesn’t subside, it’s essential to consult a healthcare provider. These symptoms may indicate that your body is not responding well to the restriction, and adjustments to the preparation plan might be necessary. Severe fatigue, nausea, or headaches that interfere with your daily life should also prompt a visit to your doctor.
2. Chronic Health Conditions
Individuals with chronic conditions like diabetes, heart disease, or gastrointestinal disorders may face additional risks when following these guidelines. For those managing such conditions, it’s crucial to speak with a healthcare provider before proceeding with any type of restriction. Medical advice ensures that your treatment regimen and test results are not adversely affected by temporary dietary changes.
3. Special Populations
Pregnant women, children, and older adults are particularly vulnerable to complications during periods of restricted intake. In these cases, seeking medical advice beforehand ensures that any potential risks to health are minimized. Adapting the approach to meet specific needs helps maintain well-being without compromising the accuracy of the test.
Always prioritize your health by consulting with a professional if you’re unsure about the safety or impact of dietary restrictions. Timely medical advice can prevent complications and ensure you’re adequately prepared for the test while safeguarding your health.