
In the world of financial analysis, mastering valuation methods is essential for making informed investment decisions. One of the most fundamental approaches involves assessing the value of an asset based on its future potential, taking into account various economic factors and projections. This process requires a clear understanding of key concepts and the ability to apply them accurately in different scenarios.
Financial modeling plays a critical role in this, allowing analysts to estimate future performance and calculate present values based on a series of assumptions. These models are essential tools for professionals in corporate finance, investment banking, and asset management. To truly excel, it’s important to grasp the methodology behind the numbers and refine your skills through practice and real-world applications.
Throughout this section, we will explore the core principles behind advanced valuation models, focusing on their practical application and common pitfalls. By enhancing your understanding, you’ll be equipped to navigate complex financial challenges and improve your analytical capabilities.
Mastering Financial Valuation Techniques
Successfully navigating complex financial assessments requires a strong grasp of essential valuation strategies. To effectively determine the worth of an asset, professionals rely on various analytical methods that incorporate assumptions about future performance, risks, and market conditions. Developing proficiency in these techniques is crucial for making sound investment decisions and performing accurate valuations in real-world scenarios.
One of the core skills in financial analysis involves creating detailed models that predict an asset’s potential cash flows and the rate at which these should be discounted. While mastering this skill takes time, understanding the key components of these models can greatly improve one’s accuracy and efficiency.
The following steps are crucial to achieving mastery in financial analysis:
- Understand the fundamentals: Before diving into complex calculations, ensure you have a solid understanding of core concepts like cash flow forecasting and discounting rates.
- Work with real-life examples: Practical experience with financial models is essential. Practice by applying methods to real or hypothetical data.
- Avoid common mistakes: Identifying and understanding the typical errors made in valuation calculations can help you improve accuracy and avoid costly mistakes.
- Refine your assumptions: Accurate assumptions about growth rates, risk factors, and market conditions are vital for producing reliable outcomes.
- Use advanced tools: Familiarity with financial modeling software and spreadsheet tools is necessary for implementing complex valuation models effectively.
By focusing on these areas, financial analysts can enhance their ability to evaluate investment opportunities and provide well-informed recommendations. Ultimately, it’s about developing a keen understanding of the variables that impact asset value and how to apply these insights through effective modeling techniques.
Understanding the Valuation Methodology
Accurately assessing the value of an asset requires a structured approach that accounts for future financial performance and the time value of money. This methodology involves projecting the expected cash flows over a specified period and then determining their present value by applying an appropriate discount rate. The goal is to estimate the intrinsic value of an asset based on its ability to generate future income, adjusted for risk and market conditions.
Core Concepts of Financial Valuation
At the heart of this valuation method are two fundamental concepts: the estimation of future cash flows and the calculation of the discount rate. Future cash flows represent the expected revenues or savings generated by an asset, while the discount rate reflects the risk and time value associated with those cash flows. Together, these elements provide a comprehensive framework for determining an asset’s present worth.
Importance of Accurate Assumptions
The reliability of the valuation depends heavily on the assumptions made about future performance. Factors such as projected growth rates, inflation, and risk premiums can significantly influence the outcome of the valuation. It’s essential to ensure these assumptions are based on realistic data and a thorough analysis of market trends, industry conditions, and historical performance.
Key Concepts in Financial Modeling
Financial modeling is an essential skill for anyone involved in analyzing investment opportunities, corporate finance, or asset management. It involves creating a representation of a company or investment’s financial performance over time, allowing analysts to forecast future outcomes and make informed decisions. A well-built model provides a comprehensive picture of the asset’s financial health and potential for growth.
At its core, financial modeling relies on a set of key concepts that must be understood and applied effectively to produce accurate results. These include the estimation of revenues, expenses, and future cash flows, as well as the calculation of important financial metrics and ratios. Below are some of the most critical components to consider when building a financial model:
- Revenue Projections: Estimating future revenue is a fundamental aspect of any financial model. This typically involves analyzing historical performance and considering market trends and growth potential.
- Cost Structure: Identifying fixed and variable costs is crucial to determining profitability. A detailed understanding of cost behavior allows for more accurate forecasting.
- Capital Expenditures (CapEx): These are investments in long-term assets, such as property or equipment. Understanding CapEx is necessary for forecasting the future capital needs of a company.
- Discount Rate: The discount rate is used to calculate the present value of future cash flows. It reflects the time value of money and the risk associated with the investment.
- Working Capital: Analyzing a company’s working capital–current assets minus current liabilities–helps gauge its short-term financial health and operational efficiency.
Each of these concepts plays a vital role in building a robust financial model. When used in conjunction, they allow for a more accurate representation of an asset’s potential and risks, ensuring that analysts can provide valuable insights for decision-making.
Common Mistakes in Financial Valuation Calculations
In financial modeling, small errors in the calculation process can lead to significant inaccuracies in the final valuation. These mistakes often stem from incorrect assumptions, misapplication of formulas, or a failure to account for key variables. Recognizing and avoiding these common pitfalls is essential for producing reliable and accurate models that reflect the true value of an asset or investment.
Overlooking the Importance of Assumptions
One of the most frequent mistakes in financial valuation is relying on overly simplistic or unrealistic assumptions. Projections about growth rates, discount rates, and future market conditions must be based on thorough analysis, rather than guesswork. Incorrect assumptions about these variables can lead to a distorted view of an asset’s potential, causing analysts to either overestimate or underestimate its true value.
Incorrect Calculation of Terminal Value
The terminal value plays a critical role in many financial models, as it represents the value of an asset beyond the forecast period. However, it is often miscalculated or misunderstood. A common mistake is using an overly high or low growth rate for the terminal period, which can skew the entire valuation. Ensuring that the terminal value is calculated with careful consideration of long-term economic conditions is crucial for accuracy.
How to Approach Financial Valuation Assessments
Successfully tackling a financial valuation test requires both a strategic mindset and a structured approach. Rather than rushing through the process, it is essential to break down the problem into manageable steps and focus on each element individually. By following a systematic approach, you can ensure that every aspect of the valuation is considered, reducing the risk of overlooking critical details.
One of the best ways to approach these assessments is by following a clear sequence of actions. The table below outlines the key steps to take when working through a financial valuation task:
| Step | Action | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Understand the key assumptions | Clarify growth rates, risk factors, and market conditions. |
| 2 | Gather and organize financial data | Ensure you have accurate historical figures and projections. |
| 3 | Build the model structure | Create sections for revenue forecasts, costs, and cash flows. |
| 4 | Calculate key metrics | Determine the discount rate, terminal value, and cash flow projections. |
| 5 | Review and check for errors | Double-check calculations and assumptions to ensure accuracy. |
By following these steps, you can approach a financial valuation task with confidence. Prioritizing accuracy and clarity in your calculations and assumptions will help you build a strong, reliable model that reflects the true value of the asset being analyzed.
Discount Rate Calculation Explained
The discount rate is a crucial element in financial valuation as it adjusts future cash flows to reflect their present value. This rate is essential for determining the time value of money, as it accounts for the fact that money received in the future is worth less than money today. In other words, the further in the future cash flows occur, the less they are worth in today’s terms.
Calculating the discount rate involves several factors, with the most common being the cost of capital and the risk associated with the asset being evaluated. It is typically derived from the weighted average cost of capital (WACC), which combines the costs of debt and equity financing in proportion to their respective contributions to the overall capital structure.
Key factors influencing the discount rate include:
- Risk-Free Rate: This is the return on a risk-free asset, such as government bonds, and serves as the baseline for the discount rate.
- Equity Risk Premium: The additional return required by investors to compensate for the risk of investing in equities over risk-free assets.
- Beta: A measure of the asset’s volatility in relation to the market as a whole. A higher beta indicates greater risk and, therefore, a higher discount rate.
- Debt Risk Premium: This reflects the cost of debt financing, considering the company’s credit risk.
By carefully considering these components, analysts can derive a discount rate that appropriately reflects the risk and expected returns of the asset being valued. A well-calculated discount rate ensures that the present value of future cash flows is accurate and reliable, leading to a more informed valuation decision.
Interpreting Terminal Value in Financial Valuation
The terminal value is a key component in many financial models, representing the value of an asset or company at the end of the explicit forecast period. It accounts for the portion of value that is expected to continue beyond the initial forecast horizon, capturing long-term growth potential. Understanding how to interpret and calculate terminal value is critical for accurately assessing the full value of an investment or business.
Importance of Terminal Value
The terminal value is particularly important because it often represents a large portion of the total valuation. Since it extends beyond the forecast period, it reflects assumptions about the asset’s future performance, including its ability to generate cash flows indefinitely. This makes it a crucial factor in determining the overall worth of a company, as it encapsulates the long-term outlook and stability of the asset.
Methods of Calculating Terminal Value
There are two common methods used to calculate terminal value: the perpetuity growth model and the exit multiple method. Each approach has its strengths and is suited to different situations.
- Perpetuity Growth Model: This method assumes that the company will continue to grow at a constant rate indefinitely. The terminal value is calculated by applying a constant growth rate to the final year’s projected cash flow and then dividing by the difference between the discount rate and the growth rate.
- Exit Multiple Method: In this approach, the terminal value is derived by applying an industry-specific multiple (e.g., EBITDA or revenue) to the company’s financial metrics in the final forecast year. This method is often used in mergers and acquisitions to reflect market conditions.
Both methods require careful consideration of future assumptions, such as growth rates and market conditions. The choice of method can significantly affect the final valuation, making it important to select the one that best aligns with the asset’s characteristics and market environment.
Preparing for the Financial Valuation Assessment
Preparing for a financial modeling and valuation assessment requires a strategic approach and focused preparation. Understanding the core concepts, mastering the technical skills, and being comfortable with the tools and techniques used are essential to succeeding. Whether you are preparing for an interview, certification, or personal development, taking the time to review key topics and practice calculations can make a significant difference in your performance.
A well-structured preparation plan involves focusing on the fundamental principles, practicing real-world scenarios, and refining your ability to make quick, accurate decisions. Below is a table outlining the essential steps for preparation:
| Step | Action | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Review core financial concepts | Understand financial statements, ratios, and valuation techniques. |
| 2 | Practice calculations | Work on key metrics like free cash flow, terminal value, and discount rates. |
| 3 | Study real-world case studies | Apply theoretical knowledge to practical business scenarios. |
| 4 | Use financial modeling software | Become familiar with tools and templates commonly used in the industry. |
| 5 | Simulate timed practice sessions | Prepare for the pressure of completing tasks under time constraints. |
By following these steps, you can ensure that you are well-prepared for any financial valuation assessment. Consistency in practice, attention to detail, and understanding the underlying principles are the key elements for mastering these challenging assessments.
Understanding Free Cash Flow Projections
Free cash flow projections are essential for estimating the financial health and future performance of a business. These projections reflect the amount of cash that a company generates after accounting for capital expenditures necessary to maintain or expand its asset base. By evaluating future free cash flow, analysts can gain valuable insights into the company’s ability to generate value for its investors, pay down debt, or reinvest in the business.
Free cash flow is considered one of the most important metrics in financial analysis because it provides a clearer picture of the company’s true profitability, excluding non-cash items and accounting for necessary reinvestments. Projecting future free cash flow requires forecasting revenue growth, operating costs, taxes, and capital expenditures, all of which are key components in determining how much cash will be available for distribution or reinvestment over time.
There are several factors that influence the accuracy of free cash flow projections:
- Revenue Growth: Estimating future sales is a primary driver, as it impacts operating income and, consequently, cash flow.
- Capital Expenditures: Understanding future investments in assets is crucial since these expenditures reduce the cash available for other uses.
- Operating Expenses: Predicting future costs associated with running the business helps refine cash flow expectations.
- Tax Rate: Changes in taxation policies or rates can significantly impact the amount of free cash flow available.
Accurate free cash flow projections provide a foundation for making informed investment decisions, evaluating a company’s valuation, and assessing its ability to meet financial obligations. Understanding and carefully projecting these cash flows is crucial for anyone involved in financial analysis or investment planning.
Importance of Assumptions in Financial Valuation

Assumptions play a critical role in financial models as they form the basis for projecting future performance and determining the value of a business or asset. These assumptions guide the inputs that drive the calculations for future cash flows, discount rates, and terminal values. Even small changes in the assumptions can have a significant impact on the outcome of a valuation, which makes it essential to carefully consider and justify each assumption used in the model.
The accuracy and reliability of a financial model depend on the reasonableness of the assumptions made. When assumptions are overly optimistic or unrealistic, they can lead to inflated valuations, which may mislead investors or decision-makers. Conversely, overly conservative assumptions can undervalue the business, potentially causing missed opportunities. Therefore, it is crucial to ensure that the assumptions used reflect the most likely future scenarios based on available data and sound judgment.
Some of the key assumptions that influence a financial model include:
- Revenue Growth: Estimates of how much a company’s sales will increase over time.
- Cost Structure: Assumptions about future operating expenses, including fixed and variable costs.
- Capital Expenditures: Expectations regarding the investments a company will make in assets and infrastructure.
- Discount Rate: The rate used to discount future cash flows, which reflects the risk and return expectations of the business.
- Terminal Growth Rate: The expected long-term growth rate beyond the forecast period, influencing the terminal value calculation.
Given their impact on the final valuation, it is important to critically assess the assumptions made, cross-check them with industry standards, and adjust them when necessary. Regularly updating assumptions to reflect changing market conditions, economic trends, and company performance is essential for maintaining the accuracy and relevance of the financial model.
Challenges with Financial Valuation Models
Valuation models, particularly those relying on future cash flow projections, can present significant challenges. The process involves forecasting uncertain variables such as revenue growth, capital expenditures, and discount rates. The inherent complexity of predicting future financial performance, coupled with external market factors, makes the accuracy of these models highly sensitive to assumptions. Understanding and addressing these challenges is crucial for anyone relying on valuation models for investment decisions or business strategy.
Uncertainty in Forecasting
One of the primary challenges in financial valuation is accurately predicting future cash flows. While historical data and trends can provide insights, the future remains unpredictable. A small error in forecasting can dramatically affect the calculated value of a business. This uncertainty can be amplified in volatile industries or during periods of economic instability. As a result, creating a reliable forecast requires extensive research, careful judgment, and a deep understanding of market dynamics.
Choosing the Right Discount Rate
Another significant challenge is determining the appropriate discount rate. This rate is crucial for adjusting future cash flows to their present value and reflects the risk of the investment. However, choosing the right discount rate can be difficult, as it requires factoring in both company-specific risks and broader economic conditions. Different methods and models for calculating the discount rate can lead to varying results, making it essential to select an approach that accurately reflects the risks involved.
Overall, financial valuation models, while valuable tools, require careful consideration of assumptions and methods. It is important to remain aware of the limitations and potential inaccuracies of these models. Regularly updating assumptions, testing different scenarios, and using multiple valuation methods can help mitigate some of these challenges and lead to more informed decision-making.
Step-by-Step Financial Analysis Guide
Performing a comprehensive financial analysis involves several key steps that help determine the value of a business or asset based on projected cash flows and other relevant factors. This step-by-step guide outlines the essential components of such an analysis, breaking down each phase from initial data gathering to final calculations. Understanding and executing these steps correctly ensures a thorough and accurate valuation process, providing insights into the financial health and potential of an investment.
Step 1: Gather Historical Data
The first step in any financial valuation process is to collect historical financial data. This includes reviewing financial statements such as income statements, balance sheets, and cash flow statements. Accurate historical data is crucial as it forms the foundation for future projections. In this stage, focus on understanding key financial metrics like revenue, expenses, capital expenditures, and profit margins.
Step 2: Project Future Cash Flows
Once historical data is gathered, the next step is to forecast future cash flows. This involves estimating the company’s revenue growth, operational expenses, and investments for the upcoming years. Forecasts should be realistic, reflecting both industry trends and company-specific factors. It is also important to account for any potential market changes or economic shifts that could influence these projections.
Step 3: Determine the Discount Rate

The discount rate is used to adjust future cash flows to their present value. It accounts for the time value of money and reflects the risk associated with the business or asset being valued. Selecting the appropriate discount rate is critical, as it impacts the final valuation. The rate can be derived using various methods, such as the weighted average cost of capital (WACC), which considers both the cost of equity and debt financing.
Step 4: Calculate the Terminal Value
The terminal value represents the estimated value of a business beyond the forecast period. It captures the long-term growth potential and provides a more accurate picture of the company’s value at the end of the projection period. There are two common methods for calculating terminal value: the perpetuity growth method and the exit multiple method. Each method requires careful consideration of assumptions such as long-term growth rates and industry multiples.
Step 5: Perform the Final Calculation
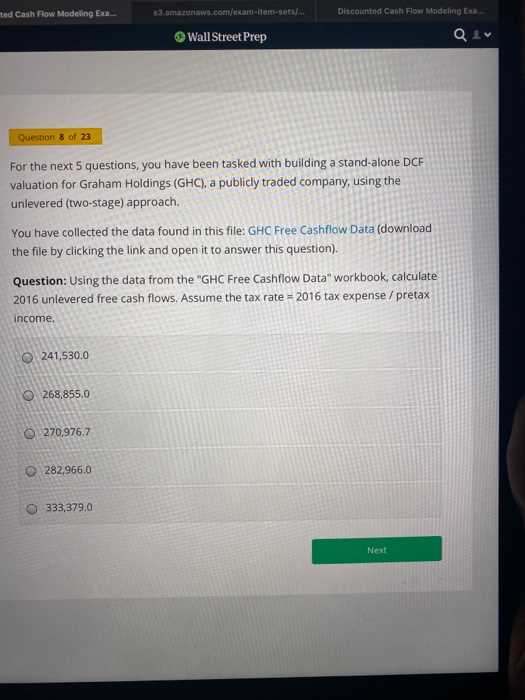
Once all the components–forecasted cash flows, discount rate, and terminal value–are determined, the final calculation can be made. The present value of future cash flows is then summed up, providing the total enterprise value. This calculation is the foundation of the financial model, offering a snapshot of the business’s current worth based on projected performance.
| Step | Action | Key Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Gather Historical Data | Review financial statements, analyze revenue, expenses, and margins |
| 2 | Project Future Cash Flows | Estimate future revenue, costs, and capital expenditures |
| 3 | Determine the Discount Rate | Calculate WACC or choose an appropriate rate based on risk |
| 4 | Calculate the Terminal Value | Choose between perpetuity growth or exit multiple methods |
| 5 | Perform the Final Calculation | Sum present values of future cash flows and terminal value |
By following these steps systematically, you can perform a detailed financial analysis that accurately reflects the value of a business or asset, taking into account both present and future considerations. Each stage of the process requires attention to detail and careful judgment to ensure the final valuation is as reliable and meaningful as possible.
How to Use Sensitivity Analysis
Sensitivity analysis is a powerful tool used to assess how the different variables in a financial model can impact the overall outcome. By adjusting key assumptions and observing the changes in results, sensitivity analysis helps to identify which factors are most influential and how changes in these inputs can affect the projected outcomes. This technique is essential for understanding the potential risks and rewards associated with any financial decision.
To effectively use sensitivity analysis, the first step is identifying the key variables in the model. These could include factors such as revenue growth rates, operating costs, capital expenditures, and discount rates. Once these variables are determined, different scenarios can be created by altering each assumption within a reasonable range. The results of these scenarios allow you to gauge the range of potential outcomes and assess the robustness of your financial model.
Steps to Implement Sensitivity Analysis
To carry out a successful sensitivity analysis, follow these general steps:
- Step 1: Identify critical variables that impact the model’s output.
- Step 2: Set reasonable ranges for these variables based on historical data or industry benchmarks.
- Step 3: Alter one variable at a time while keeping others constant, and observe the effect on the overall result.
- Step 4: Repeat the process for other variables to evaluate the combined impact.
- Step 5: Analyze the results to determine which variables have the most significant impact on the model’s conclusions.
Example of Sensitivity Analysis

For example, if you are valuing a business, you might want to test how sensitive the enterprise value is to changes in the revenue growth rate and the discount rate. If small changes in the revenue growth assumption result in significant shifts in the value, this indicates that revenue is a critical factor to monitor. Similarly, adjusting the discount rate can show how sensitive the valuation is to changes in the cost of capital.
Sensitivity analysis does not provide a single answer; instead, it helps in making more informed decisions by highlighting potential risks and offering a range of possible outcomes. This is especially valuable in uncertain environments, where variables are likely to fluctuate over time.
Mastering Excel for DCF Modeling

Mastering Excel is essential for creating robust financial models, especially when performing valuation analysis. Excel provides the flexibility and powerful tools necessary for structuring and calculating complex financial models. By leveraging formulas, functions, and data visualization techniques, you can efficiently conduct sensitivity analysis, assess different scenarios, and produce accurate results. The ability to use Excel proficiently not only streamlines the modeling process but also ensures that the conclusions drawn from the analysis are reliable and well-supported.
To effectively use Excel for financial modeling, it’s important to understand the key features and techniques that will optimize your workflow. Here are the core aspects to focus on when building your models:
Essential Excel Skills for Financial Modeling
- Formulas and Functions: Master basic financial functions such as NPV (Net Present Value), IRR (Internal Rate of Return), PMT (Payment), and other related calculations.
- Data Validation: Use data validation tools to ensure accurate and consistent data entry. This is particularly useful when working with large datasets or creating interactive models.
- Conditional Formatting: Conditional formatting can help highlight key data points or assumptions that need attention, making it easier to spot critical issues in the model.
- Pivot Tables: Pivot tables are great for summarizing data and conducting quick analysis, especially when working with large financial statements or historical data.
- Charting and Visualization: Use charts and graphs to visually represent the results of your financial analysis. Visualization helps stakeholders quickly grasp insights and trends.
- Cell Referencing: Understanding the difference between absolute, relative, and mixed cell references is key to building flexible and dynamic models.
Steps to Build an Effective Financial Model in Excel
- Step 1: Set up a structured framework, organizing your model into separate tabs (Assumptions, Income Statement, Balance Sheet, Cash Flow, Valuation, etc.).
- Step 2: Input historical data and assumptions. Use consistent formatting and clear labels for ease of reference.
- Step 3: Link all sections of the model logically, ensuring that inputs drive the outputs correctly.
- Step 4: Incorporate advanced Excel functions like IF statements, INDEX/MATCH, and array formulas to automate calculations.
- Step 5: Double-check your formulas and test the model by adjusting key assumptions to ensure the calculations update correctly.
- Step 6: Use scenario analysis and sensitivity tables to evaluate different outcomes and understand the sensitivity of your model to changes in key assumptions.
As you continue to build your expertise in Excel, remember that practice and attention to detail are key. A well-constructed Excel model should not only provide accurate results but also be clear, transparent, and easy to audit. By mastering these skills, you can ensure that your financial models are both efficient and insightful, enabling you to make better-informed decisions in any financial analysis or valuation project.
Tips for Effective DCF Exam Preparation
Preparing for a financial valuation test requires a combination of thorough understanding, practice, and strategic planning. Successful preparation goes beyond simply memorizing formulas; it involves gaining a deep comprehension of how different components of a financial model work together. Being well-prepared will not only help you perform better under pressure but also enable you to apply the knowledge to real-world scenarios. In this section, we’ll explore key strategies to improve your approach and boost your confidence when tackling these types of assessments.
Master the Fundamentals
Start by revisiting the core concepts that underpin financial valuation models. A solid grasp of accounting, financial statements, and how cash flows are projected is crucial. Understanding the fundamental building blocks allows you to approach complex problems with clarity. Focus on:
- Understanding the core components: Be familiar with concepts like cost of capital, future projections, and terminal value calculations.
- Grasping key formulas: Ensure you can easily apply common formulas and understand their meaning, such as NPV (Net Present Value) and IRR (Internal Rate of Return).
- Reviewing financial modeling structure: Know how different sections of the model are interconnected and how changes in one part can affect the rest of the model.
Practice with Realistic Scenarios
Once you have a solid understanding of the theory, practice is essential. Work through realistic practice scenarios that simulate the structure and challenges of the actual assessment. This will help you get comfortable with time constraints and identify areas where you need improvement. Key tips include:
- Use previous tests or mock exams: Practice with real past assessments or mock exams to become familiar with the format and typical question types.
- Simulate exam conditions: Time yourself and work in a quiet environment to replicate the actual test conditions. This will help you manage your time effectively during the real test.
- Analyze your mistakes: After practicing, review your answers carefully and identify areas where you struggled. Understand why you made those errors and correct them for future attempts.
By focusing on both theory and practical application, you’ll be able to approach your test with confidence, knowing you have the tools to succeed. Don’t forget to maintain a balance between studying and taking breaks to avoid burnout, ensuring you stay sharp throughout the preparation process.
Real-Life Applications of DCF Models
Discounted cash flow (DCF) models are a crucial tool used in finance to assess the value of an investment or company by estimating its future cash flows and discounting them to the present value. While this method is often associated with theoretical exercises, it is widely used in practical scenarios by professionals in various sectors. Understanding how these models are applied in real-world situations can provide valuable insights into their importance and versatility in decision-making processes.
Investment Valuation
One of the primary applications of discounted cash flow models is in the valuation of companies or investments. By projecting future earnings and applying an appropriate discount rate, analysts can determine the present value of a business or project. This method is commonly used in:
- Mergers and Acquisitions: DCF models help buyers assess the fair value of a target company, ensuring that the price paid aligns with the expected future cash flows.
- Equity Valuation: Investors use DCF models to determine the intrinsic value of a stock by estimating future cash flows and comparing them to the current market price.
- Private Equity and Venture Capital: Firms often rely on DCF analysis to evaluate the potential return on investments in start-ups or private companies, helping to guide funding decisions.
Project and Asset Valuation
DCF models are not only limited to corporate valuation but also play a critical role in assessing specific projects or assets. This application is particularly relevant in industries such as infrastructure, real estate, and natural resources. Here’s how DCF can be applied:
- Real Estate Investment: Investors in commercial or residential properties use DCF to evaluate the potential return on investment by factoring in projected rental income and future resale values.
- Infrastructure Projects: Governments and private companies use DCF models to evaluate large-scale infrastructure projects, such as highways or energy plants, by analyzing long-term cash flow generation.
- Natural Resources: In industries like mining and oil, DCF models are used to estimate the value of reserves or exploration projects, considering factors such as extraction costs and commodity price fluctuations.
By incorporating DCF models into these real-life applications, businesses and investors can make informed decisions that align with their financial goals and risk tolerance. The ability to accurately project future cash flows and adjust for time value is an essential skill in evaluating the potential of any financial venture.
Improving Accuracy in DCF Estimates
Accurate financial forecasting is a critical element in assessing the value of a company or investment. To ensure the reliability of these forecasts, it’s essential to refine the assumptions and methodologies used in valuation models. Enhancing the precision of future cash flow projections, discount rates, and terminal value assumptions can significantly improve the overall accuracy of financial estimates.
Refining Assumptions is one of the most important aspects of improving the accuracy of valuation models. The assumptions made regarding revenue growth, profit margins, and capital expenditures should be based on realistic, data-driven insights. It’s crucial to base these assumptions on historical performance, industry benchmarks, and macroeconomic trends. Regularly revisiting these assumptions ensures they remain aligned with current market conditions.
Sensitivity Analysis plays a vital role in increasing confidence in estimates. By testing how small changes in key inputs–such as growth rates or discount rates–affect the final valuation, analysts can better understand the range of possible outcomes. This process helps identify the most sensitive variables and highlights the areas that need careful consideration.
Utilizing Historical Data
Historical data provides valuable insights into past performance and can serve as a foundation for making future projections. By analyzing long-term trends in a company’s revenue, operating expenses, and capital structure, more accurate assumptions can be made for future periods. Additionally, incorporating historical volatility into projections can help mitigate over-optimism or overly conservative estimates.
Choosing the Right Discount Rate
The discount rate is a key component that significantly impacts the present value of future cash flows. A slight misjudgment in selecting an appropriate rate can distort the overall valuation. When choosing a discount rate, it’s essential to consider the risk profile of the business, the cost of capital, and prevailing market conditions. Using an industry-specific weighted average cost of capital (WACC) can improve precision by tailoring the rate to the unique risks of the investment or company.
By focusing on refining assumptions, applying sensitivity analysis, and using historical data effectively, financial analysts can enhance the accuracy and reliability of their valuation models. These practices are essential for making well-informed investment decisions and providing accurate financial insights to stakeholders.
Key Takeaways from Financial Modeling Courses
Mastering financial modeling is a critical skill for anyone involved in investment analysis, valuation, or corporate finance. Various resources offer structured learning to help individuals enhance their skills and improve their understanding of complex valuation techniques. Below are some key lessons and takeaways from these structured financial modeling courses, designed to equip learners with the tools and knowledge they need to succeed in financial analysis.
Understanding Core Valuation Methods
One of the main takeaways from these courses is the importance of understanding the core methodologies used in valuation. These include:
- Discounted Cash Flow (DCF): This method involves estimating future cash flows and discounting them to present value using an appropriate rate. It’s crucial to understand how to accurately project cash flows and select the right discount rate.
- Comparable Company Analysis: By comparing the target company with similar publicly traded companies, learners gain insights into how relative market multiples can help assess value.
- Precedent Transactions: This approach focuses on analyzing past transactions within the same industry to gauge appropriate valuation benchmarks.
Practical Application and Excel Skills
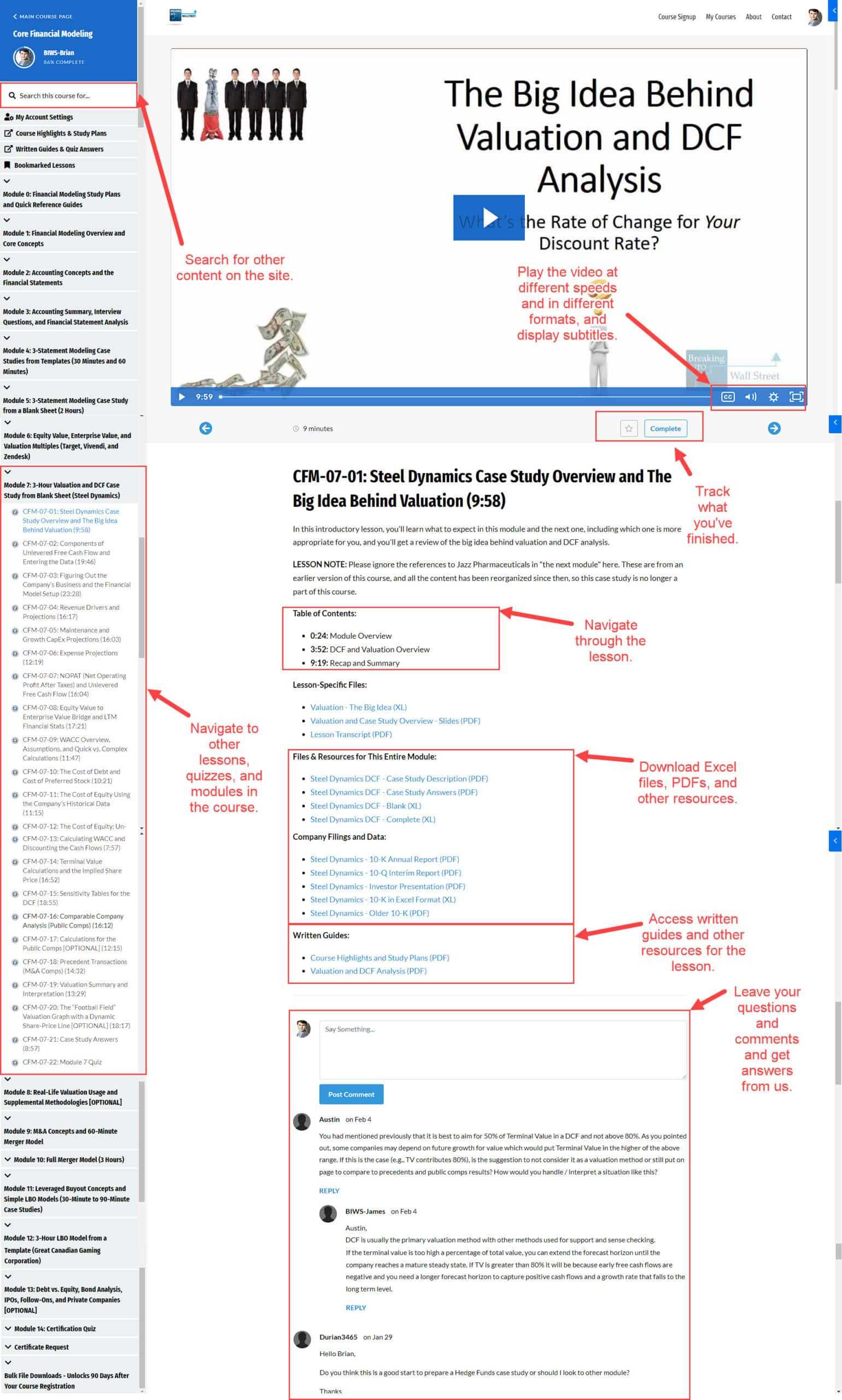
Another key takeaway is the emphasis on applying theoretical knowledge in real-world scenarios. Most courses place a strong focus on Excel proficiency, as financial modeling requires effective use of spreadsheet tools for building complex models. Key Excel skills include:
- Building Dynamic Financial Models: Learn to construct flexible models that can adjust to changing inputs and assumptions, such as incorporating different revenue growth rates or cost assumptions.
- Mastering Excel Functions: Utilize advanced functions such as VLOOKUP, INDEX/MATCH, and data validation tools to create more accurate and efficient models.
- Scenario and Sensitivity Analysis: Understand how to run sensitivity analysis by creating different scenarios to analyze the impact of changing assumptions on the final results.
Importance of Accurate Assumptions
Accurate assumptions are fundamental to the success of any financial model. Courses emphasize the need to carefully assess market trends, historical performance, and industry dynamics when making projections. An understanding of the following is crucial:
- Revenue Projections: Estimating future sales growth based on historical data, market trends, and company-specific factors.
- Operating Costs and Capital Expenditures: Understanding the cost structure and investment requirements of the business helps ensure that financial forecasts remain realistic and reliable.
- Discount Rate Selection: Choosing an appropriate discount rate based on the company’s risk profile and industry benchmarks is key to ensuring a valid valuation.
These courses not only cover the theory behind financial modeling but also teach students how to apply it practically in real-life scenarios. By mastering these skills, learners are better equipped to analyze investments, assess corporate performance, and make informed financial decisions in any industry.