
In the world of networking, practical exercises are essential for mastering key concepts and troubleshooting techniques. These tasks simulate real-world scenarios, allowing individuals to hone their skills and gain confidence in their abilities. For learners and professionals alike, completing these simulations accurately is critical for both exam preparation and everyday work.
Many network training modules involve configuring devices, resolving connectivity issues, and ensuring that systems operate seamlessly. These labs test your understanding of routing, switching, and overall network management. However, completing them can often present challenges, as small errors in configuration or logic can lead to significant issues down the line.
In this guide, we will explore effective strategies for approaching these exercises, highlight common pitfalls to avoid, and provide solutions for overcoming frequent obstacles. Whether you’re new to network configuration or preparing for certification, this information will serve as a valuable resource in mastering key skills for your career or studies.
Networking Lab Solutions Overview
Effective completion of network configuration exercises requires not only theoretical knowledge but also practical application of various protocols, devices, and settings. These labs challenge participants to configure and troubleshoot virtual networks, ensuring all devices communicate as intended and meet specific operational criteria. Understanding the structure and requirements of these tasks is crucial for successful completion.
The purpose of this section is to provide a clear overview of the solutions for common exercises found in network simulation tasks. By reviewing these strategies and answers, you can enhance your problem-solving skills and improve your performance in both lab environments and real-world network management.
Common Configuration Steps
When tackling network configuration challenges, it’s important to follow a systematic approach. Begin by reviewing the network layout, identifying the devices and their roles within the simulation. Configuring routers, switches, and end devices should be done step by step, ensuring that each device’s settings are correct and compatible with others. Troubleshooting begins once the initial setup is complete, requiring keen attention to detail and a methodical process to isolate and resolve issues.
Addressing Network Connectivity Issues
One of the most common hurdles in these exercises is connectivity failure. Whether it’s a misconfigured routing table, incorrect IP address assignment, or issues with physical connections, identifying the root cause is key to finding an appropriate solution. In many cases, using diagnostic tools like ping and traceroute, along with checking the configurations of routers and switches, can help pinpoint and correct errors effectively.
Understanding Networking Lab Exercises
In networking labs, participants are tasked with setting up and troubleshooting virtual networks, simulating real-world scenarios to test their technical abilities. These exercises are designed to challenge your understanding of networking protocols, configurations, and troubleshooting techniques. They require a combination of theoretical knowledge and practical skills to ensure that the network operates correctly and efficiently.
Each task typically involves configuring multiple devices such as routers, switches, and end-user systems. The goal is to ensure proper communication between these devices, whether through routing protocols, static IP assignments, or security settings. Mastery of these exercises not only prepares you for exams but also provides invaluable experience for real-world network management.
Key Challenges in Networking Lab Exercises
Network simulation labs are designed to test a range of skills, from basic configuration to advanced troubleshooting. While these exercises offer valuable learning opportunities, they also come with their own set of challenges that require both problem-solving and technical proficiency. Addressing these challenges effectively is essential for mastering network administration tasks.
One of the primary difficulties often encountered is the configuration of multiple devices to work together seamlessly. Ensuring that routers, switches, and connected devices are correctly set up to communicate requires careful attention to detail, as even small misconfigurations can lead to larger network failures. In addition, managing IP addressing, routing protocols, and access control lists (ACLs) can be complex and confusing for beginners.
Another significant challenge is troubleshooting. When something goes wrong in a network setup, pinpointing the exact cause of the issue can be time-consuming. Issues may arise from incorrect cabling, faulty configurations, or incompatible settings. Mastery of diagnostic tools and systematic problem-solving approaches is essential to resolve these problems efficiently.
Finally, the integration of security measures poses a challenge. Ensuring that the network is not only functional but secure requires configuring firewalls, encryption, and other protective measures, all while maintaining network performance. Balancing these factors is often tricky, especially in complex network environments.
Steps to Complete Networking Lab Exercises
Successfully completing network configuration tasks requires following a structured process that ensures all components are correctly set up and functioning. These exercises typically involve multiple stages, from initial setup to troubleshooting, and each step must be carefully executed to avoid errors. Below are the key stages to follow when working through these labs.
Initial Setup and Configuration
The first step in any networking lab is to set up and configure the devices according to the given instructions. This includes connecting routers, switches, and end devices, and assigning IP addresses as required. Make sure to verify each device’s basic configuration before proceeding.
- Connect routers and switches as per the network diagram.
- Assign IP addresses and subnet masks to devices.
- Ensure each device has the correct hostname and credentials.
Testing and Troubleshooting
Once the network devices are configured, it’s time to test the connectivity between them. This will help you identify any misconfigurations or errors in the setup. If issues arise, use diagnostic tools to help pinpoint and resolve the problem.
- Use the ping command to test connectivity between devices.
- Check routing tables and ensure proper path configuration.
- Verify IP addressing and ensure no conflicts exist.
- If there are issues, systematically troubleshoot by isolating and addressing each device or link.
By following these steps, you can ensure that your network configuration is both functional and optimized, allowing you to complete the lab successfully.
Common Errors in Networking Lab Exercises
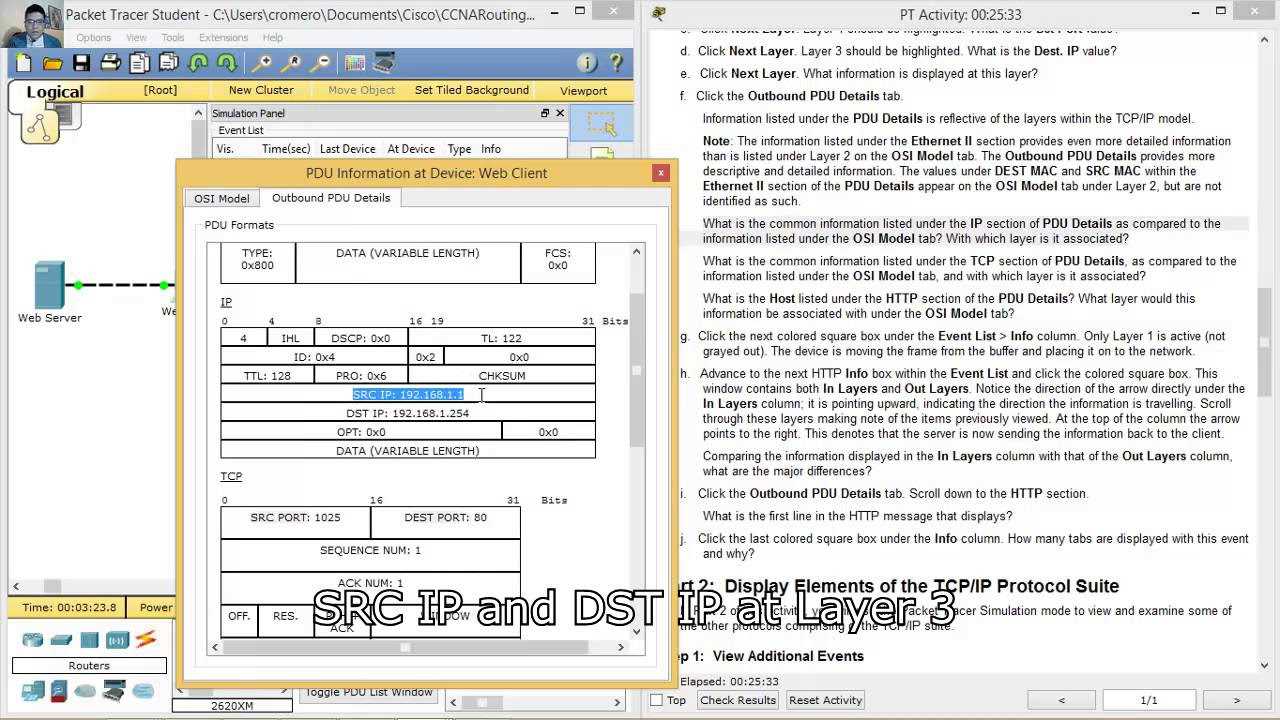
While working through network simulation tasks, it’s common to encounter a variety of errors, ranging from simple misconfigurations to more complex issues. Identifying and resolving these problems is an essential skill for network administrators and technicians. Below are some of the most frequent errors that users face when completing network exercises.
Configuration Mistakes
Incorrect device configuration is one of the most common errors in these tasks. This can include assigning wrong IP addresses, incorrect subnet masks, or misconfigured routing protocols. These mistakes often prevent devices from communicating with each other, making the network ineffective.
| Error | Cause | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Wrong IP Addressing | Devices have conflicting or incorrect IP settings. | Verify IP addresses and subnet masks; ensure no conflicts exist. |
| Misconfigured Routing Protocol | Routing tables are incorrectly set, causing failed communication. | Check routing protocol configurations and ensure proper network paths. |
| Improper VLAN Configuration | Switch ports not properly assigned to the correct VLAN. | Ensure each port is assigned to the correct VLAN and configured correctly. |
Connectivity Issues
Even after the initial setup is correct, connectivity issues can still arise due to faulty physical connections or problems with network devices. These errors can be difficult to diagnose without the right tools and systematic troubleshooting approaches.
| Error | Cause | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Disconnected Cables | Physical connections are not properly established between devices. | Check all cables and ensure they are securely connected. |
| Incorrect Switch Configuration | Switch ports might not be properly configured for the required functionality. | Review the switch settings and ensure the right ports are active and configured. |
| Access Control Issues | Access control lists (ACLs) may be blocking traffic. | Review and modify ACLs to allow necessary traffic. |
By recognizing and addressing these common errors, you can ensure a more successful completion of your network exercises, improving both your troubleshooting skills and your overall understanding of network management.
Networking Lab Solution Tips
Successfully completing network simulation tasks requires a strategic approach and careful attention to detail. These exercises test both your technical skills and your ability to troubleshoot issues. By following specific tips, you can streamline the process, avoid common mistakes, and ensure that you arrive at the correct solution in a more efficient manner.
Begin with a thorough review of the instructions and network diagram before configuring any devices. Understanding the structure of the network and the specific tasks required is crucial to avoid making unnecessary mistakes. Carefully follow each step to ensure that no configuration detail is overlooked.
Double-check your settings at each stage of the configuration. It’s easy to overlook small details like IP addresses, subnet masks, and routing protocol settings, which can lead to connectivity issues. Before proceeding to the next step, confirm that all devices are set up according to the given specifications.
Use diagnostic tools effectively when troubleshooting. Tools like ping, traceroute, and show commands can help you identify where the issue lies. These tools allow you to test connectivity between devices, check the routing tables, and verify that all configurations are correct.
Stay systematic when resolving issues. If you encounter problems, don’t jump to conclusions. Instead, methodically test each part of the network to isolate the issue. Start by verifying physical connections, then move on to checking IP configurations, and finally, review routing settings and protocols.
By following these tips and maintaining a focused approach, you can complete network simulations more efficiently, gaining confidence and improving your network management skills.
How to Analyze Networking Lab Exercises
Analyzing network simulation tasks requires a structured approach to ensure that all configurations are accurate and the network functions as expected. The goal is to identify both successful and unsuccessful configurations, troubleshoot any issues, and ensure optimal performance. Below are the steps to help you effectively analyze a networking task.
Step-by-Step Analysis Process
To thoroughly analyze a network simulation, follow a systematic process that breaks down the task into manageable steps. This will help you identify and address any issues while ensuring that the network setup is both functional and optimized.
- Review the Requirements: Begin by thoroughly reading the instructions and understanding the desired outcome of the task. Familiarize yourself with the network topology, devices involved, and specific configurations needed.
- Check Device Configuration: Ensure each device is configured correctly, including IP addresses, subnet masks, and routing protocols. Verify that devices are set up according to the specified parameters.
- Test Connectivity: Once the network is configured, test the connectivity between devices using ping or other diagnostic tools. This will help identify if there are any network communication issues.
- Analyze Routing: Check the routing tables and verify the correct routes are in place. Ensure that the routing protocols are functioning properly and that routes are being advertised correctly.
- Troubleshoot Problems: If you encounter connectivity or performance issues, use diagnostic tools like traceroute, show commands, and packet sniffers to identify the root cause of the problem. Isolate the issue by systematically testing each component of the network.
Common Issues to Look For
While analyzing, it’s important to be aware of common issues that can disrupt the network setup. Pay close attention to the following:
- IP Address Conflicts: Ensure there are no duplicate IP addresses assigned within the network, as this can cause devices to lose connectivity.
- Misconfigured Subnet Masks: Incorrect subnet masks can prevent devices from communicating properly. Verify that the subnet masks match the network’s requirements.
- Routing Loops: Ensure that routing loops are not created due to improper route configurations. These can lead to network traffic being endlessly redirected.
- Firewall and ACL Issues: Check for any access control lists (ACLs) or firewall settings that might be blocking legitimate traffic.
By following these steps and identifying potential issues early, you can ensure a smoother analysis process and more effective network configurations.
Network Setup for Simulation Tasks
Setting up a network in a simulation environment involves a series of steps to ensure that all devices are correctly connected and configured. The goal is to create a functional network where devices can communicate effectively. By following the right procedures, you can set up a network that mimics real-world configurations and test various scenarios with ease.
Initial Configuration and Topology
The first step in setting up a network is to design the network topology. This involves placing the necessary devices such as routers, switches, and computers on the simulation canvas. Once the devices are in place, you need to establish the physical connections between them using the correct cables. Ensure that all devices are properly linked according to the desired network design.
After the physical connections are established, the next task is to configure the basic settings for each device. This typically includes assigning IP addresses, subnet masks, and default gateways for the routers and computers. Additionally, configuring routing protocols and VLANs might be necessary, depending on the specific requirements of the simulation task.
Verifying Connectivity and Troubleshooting
Once the network devices are configured, it’s essential to verify connectivity between all devices. This can be done by using tools like ping and traceroute to check if devices are reachable across the network. If issues arise, troubleshooting steps should be followed to identify and resolve common issues such as misconfigured IP settings, faulty cables, or incorrect routing protocols.
By following a structured approach to network setup, you can create an efficient simulation that allows you to test different networking scenarios, troubleshoot problems, and better understand network behavior in a controlled environment.
Configuring Devices in Network Simulations
Configuring network devices correctly is essential to ensure proper functionality and communication within a simulated network environment. Each device, whether it’s a router, switch, or computer, must be set up according to the specific network requirements. Proper configuration allows devices to communicate, route traffic, and implement security measures such as access control lists (ACLs) and firewalls.
Step-by-Step Device Configuration
Below is a general guide for configuring different types of devices in a network simulation. It covers the basic settings for routers, switches, and computers.
| Device | Basic Configuration Steps |
|---|---|
| Router |
|
| Switch |
|
| Computer |
|
Each device’s configuration must be tailored to fit the specific requirements of the network and the tasks at hand. Whether setting up a simple LAN or simulating a complex enterprise network, following these steps will help ensure that all devices are correctly configured and ready for testing and troubleshooting.
Troubleshooting Guide for Network Simulations
When working with simulated network environments, issues may arise that prevent devices from functioning as expected. Troubleshooting these problems requires a systematic approach to identify and resolve network connectivity or configuration errors. This guide covers common troubleshooting steps to help diagnose and fix issues in the simulated network setup.
Common Issues and Solutions
Below are some frequent problems encountered during network simulations and their respective solutions:
- Connectivity Issues
- Ensure that devices are properly connected with the correct cables (copper straight-through or crossover cables).
- Verify that the IP configuration (IP address, subnet mask, default gateway) is correct on all devices.
- Check for any active firewalls or ACLs that may block communication between devices.
- Routing Problems
- Ensure that routing protocols are correctly configured on routers (e.g., OSPF, RIP, EIGRP).
- Check if the correct interfaces are enabled and assigned to the proper IP subnets.
- Verify that there are no routing loops or misconfigured routes in the routing tables.
- Device Configuration Errors
- Ensure all devices have the correct settings for VLANs, IP addresses, and subnet masks.
- Check for mismatches in device configurations, such as mismatched VLAN IDs or wrong port settings on switches.
- Confirm that any necessary services (e.g., DHCP or NAT) are properly configured and enabled.
Using Diagnostic Tools
To effectively troubleshoot, network simulations provide several diagnostic tools that can help identify issues:
- Ping: This tool can be used to test the reachability of devices across the network. If the ping fails, it indicates a connectivity issue between devices.
- Traceroute: This tool helps trace the path that data takes between devices, showing where delays or packet loss occur.
- Show Commands: On routers and switches, the show commands (e.g., show ip route, show interfaces) provide detailed information about device configurations and status.
- Simulation Mode: In simulation mode, you can view how data flows through the network and examine any errors or dropped packets at each stage.
By using these tools and following the steps outlined above, you can quickly identify the root cause of most issues in the network and apply appropriate solutions to restore functionality.
Key Concepts in Network Simulations
Understanding the fundamental principles behind network configurations and troubleshooting is essential for successfully completing any simulated network exercise. These concepts form the foundation for designing, managing, and analyzing network environments. In this section, we will explore some of the key ideas that are vital to mastering network simulations and ensuring effective solutions.
Network Topology and Configuration
Network topology refers to the physical and logical layout of devices and their interconnections. It defines how devices such as routers, switches, and computers are linked and communicate with each other. When setting up a network, it is crucial to select the correct topology that suits the needs of the network, whether it’s a bus, star, or mesh topology. Proper configuration ensures devices can communicate effectively, with the correct IP addressing, routing protocols, and network interfaces in place.
Routing and Switching Fundamentals
At the core of network communication are routing and switching. Routers direct data packets between different networks based on IP addresses, while switches handle communication within the same network by forwarding data to specific devices. A clear understanding of these processes is critical for troubleshooting connectivity issues and optimizing network performance. Effective routing protocols, such as OSPF or RIP, and correct VLAN configurations for switches, ensure smooth data flow across the network.
Network Security and Troubleshooting is another essential concept. Ensuring network security involves configuring access control lists (ACLs), firewalls, and encryption protocols to protect data from unauthorized access. Troubleshooting skills, on the other hand, are vital for identifying and resolving issues that arise within the network, whether they be related to connectivity, performance, or configuration errors.
Best Practices for Network Simulation Labs
When working on network simulation labs, adhering to best practices ensures a smoother experience and more accurate results. Whether you are designing a network topology, troubleshooting an issue, or configuring devices, following proven strategies helps streamline the process and improves learning outcomes. This section outlines key practices that will help you optimize your simulations and get the most out of your network exercises.
Planning and Organizing Your Network
Before diving into device configuration and network setup, it’s important to plan your network design carefully. A clear plan minimizes errors and optimizes the network’s efficiency. Here are some essential steps to take when preparing for a lab:
- Define Objectives: Understand the goals of the lab before starting. This could be configuring routers, implementing security measures, or testing communication protocols.
- Design the Network Topology: Choose the appropriate topology that best suits the lab’s objectives. Make sure to plan for the right number of devices, connections, and network layers.
- Document the Configuration: Write down the configuration settings you intend to use. This includes IP addresses, subnet masks, and routing protocols to be implemented. Documentation can help you troubleshoot later if issues arise.
Efficient Troubleshooting and Testing
During network simulation, troubleshooting is inevitable. However, knowing how to efficiently identify and solve issues can save you time and effort. Follow these practices for effective problem resolution:
- Use Simulation Mode: The simulation mode helps visualize the data flow across the network, allowing you to identify where issues occur and isolate problems effectively.
- Check Configuration Settings: Double-check configurations on each device to ensure that routing protocols, IP addresses, and other settings are correctly applied.
- Perform Incremental Testing: Test each part of the network incrementally as you build it. Start by verifying basic connectivity before moving on to more complex configurations like routing or security.
- Document Troubleshooting Steps: Keep track of the steps you’ve taken to resolve issues. This will help you avoid repeating the same mistakes and improve your problem-solving skills.
By following these best practices, you can create efficient, functional simulations that provide a realistic and effective learning environment. Careful planning, testing, and troubleshooting will make your experience more valuable and help you better understand real-world network management challenges.
Optimizing Network Settings in Network Simulation
To ensure efficient performance in network simulations, it is essential to optimize various configuration settings. Properly tuned settings can help minimize issues like latency, packet loss, and connectivity problems, ultimately providing a more accurate and responsive environment for testing and learning. This section will explore key strategies to enhance the performance of your network setup, from fine-tuning device parameters to optimizing communication protocols.
Adjusting Device Settings
One of the first steps in optimizing a network simulation is to configure the devices appropriately. Each device in the network should be set up to meet the specific requirements of the simulation. Here are some areas to focus on:
- IP Addressing: Ensure that IP addresses and subnet masks are correctly assigned to each device. Proper addressing ensures smooth communication and avoids address conflicts that can disrupt network traffic.
- Routing Protocol Configuration: For networks that require routing between subnets, choose the right routing protocols and configure them correctly. Using dynamic routing protocols like OSPF or EIGRP can significantly improve network performance by automating routing decisions.
- Device Performance: Check the device performance settings in the simulation software. Sometimes, simulation tools allow you to limit the processing power or resources available to devices, which can impact overall performance if not properly adjusted.
Optimizing Network Topology
The network topology plays a crucial role in the efficiency and scalability of the simulated network. A well-structured topology helps reduce bottlenecks and ensures optimal data flow between devices. Consider the following:
- Minimize Network Hops: The fewer the hops between devices, the faster the communication. Avoid unnecessary intermediate devices or overly complex configurations unless necessary for the simulation’s objectives.
- Utilize VLANs: Virtual LANs (VLANs) can be used to segment traffic, reducing broadcast domains and enhancing overall network performance. This is particularly useful in larger network setups.
- Effective Use of Links: Ensure that the links between devices are not overloaded. High-capacity links, like gigabit connections, can help prevent congestion and improve data transfer speeds.
Monitoring and Performance Tuning
Regular monitoring and performance tuning are vital for identifying areas of improvement in a network simulation. By observing traffic patterns and adjusting settings accordingly, you can ensure optimal performance throughout the simulation. Some tips include:
- Traffic Analysis: Use simulation tools to analyze the flow of traffic between devices. This can help identify slow links or areas where bottlenecks occur.
- Adjusting Latency: Modify latency settings where necessary to simulate real-world conditions. Too high or too low latency can distort test results, so it is important to strike a balance.
- Check for Packet Loss: Excessive packet loss can indicate issues with device configurations or network congestion. Regularly test your setup for packet loss to identify areas for improvement.
Optimizing network settings in a simulation is key to achieving accurate and reliable results. By carefully configuring devices, refining your topology, and monitoring network performance, you can ensure that your simulation environment is efficient and effective for both learning and testing purposes.
Using Simulation Tools for Networking Exams
Simulation software plays a crucial role in preparing for networking exams, offering a practical environment for hands-on learning and testing theoretical knowledge. By simulating real-world network configurations, candidates can gain valuable experience without needing physical hardware. This section explores how to effectively use network simulation tools to study for certification exams and improve problem-solving skills in networking scenarios.
Advantages of Using Simulation Software
Simulation tools provide an array of benefits that make them ideal for exam preparation. Here are some of the key advantages:
- Hands-On Experience: Simulation environments allow users to configure devices, set up networks, and troubleshoot issues in a virtual setting. This practical experience is invaluable, especially for visual learners.
- Cost-Effective: Using virtual labs eliminates the need for expensive physical networking equipment. Candidates can experiment with various configurations without worrying about hardware costs.
- Flexibility and Convenience: Simulation software can be used anytime, anywhere, providing flexibility for exam preparation. Candidates can practice at their own pace and focus on specific areas they find challenging.
How to Maximize Learning with Simulation Tools
To get the most out of a simulation tool, it is essential to approach your studies strategically. Here are some tips to enhance your learning experience:
- Follow a Structured Approach: Start with basic configurations and gradually work your way up to more complex scenarios. Understanding fundamental concepts is essential before tackling advanced network setups.
- Practice Real-World Scenarios: Try to simulate real-life network configurations and troubleshoot common issues. This will help you familiarize yourself with typical exam questions and real-world network challenges.
- Utilize Diagnostic Tools: Most simulation tools come with diagnostic utilities that allow you to test network connectivity, check routing tables, and troubleshoot problems. Make sure to practice using these tools to refine your troubleshooting skills.
By integrating simulation software into your exam preparation, you can build both the confidence and the skills needed to succeed in networking certification exams. Practicing network configurations and troubleshooting techniques in a virtual setting will help you develop a deep understanding of networking principles and ensure you’re ready for any challenge that comes your way in the exam environment.
Common Mistakes to Avoid in Network Simulation Tools
When working with network simulation tools, it’s easy to make mistakes, especially if you’re new to the environment. These tools provide an excellent way to practice and refine your networking skills, but certain common errors can hinder progress and lead to incorrect configurations. Understanding these pitfalls can help you avoid them and maximize the learning experience.
1. Incorrect Device Configuration
One of the most frequent mistakes is misconfiguring devices, whether it’s incorrect IP addressing, wrong subnet masks, or improper routing configurations. These errors can cause network failures that are difficult to troubleshoot. To avoid this:
- Always double-check your device configurations before proceeding with other tasks.
- Ensure that IP addresses are correctly assigned, and all devices are in the same network or properly routed.
- Familiarize yourself with subnetting and make sure all subnet masks are accurately applied.
2. Ignoring Basic Troubleshooting Tools
Simulation tools often come with built-in diagnostic tools that can help identify network issues. A common mistake is overlooking or not utilizing these tools, which can lead to wasting time on manual troubleshooting. To optimize your workflow:
- Use ping tests to check connectivity between devices.
- Utilize tracert or traceroute tools to identify routing issues.
- Leverage the command line interface to check routing tables, ARP tables, and other critical information.
By paying attention to these common mistakes and making sure to verify your configurations and tools regularly, you can avoid frustration and ensure more effective learning when working in simulation environments. With time and practice, these errors will become easier to spot and resolve.
Network Simulation Exam Preparation
Preparing for networking exams involves a combination of hands-on practice and theoretical knowledge. Simulation tools offer an invaluable way to familiarize yourself with real-world scenarios and test your skills in configuring and troubleshooting various network setups. This section will guide you through the key strategies to effectively prepare for exams using simulation platforms, ensuring you are well-equipped to handle the challenges you may face.
To excel in networking exams, it is important to understand the fundamentals of network devices, IP addressing, routing, and switching. In addition to theoretical study, practical experience in configuring and troubleshooting network devices in simulation environments is crucial. By using these tools, you can practice real-world tasks such as setting up routers, switches, and end devices, configuring IP addresses, and testing connectivity between devices.
Key preparation strategies include:
- Familiarizing yourself with the simulation tool interface and features to ensure smooth navigation during the exam.
- Practicing various network configurations and troubleshooting scenarios to build confidence in solving issues quickly.
- Reviewing common network protocols and their configurations, including IP addressing schemes, subnetting, and routing protocols.
- Working on time management by practicing completing tasks within the exam’s time constraints.
By consistently applying these strategies and reinforcing both your practical and theoretical understanding, you will be better prepared for the networking exam and equipped to successfully complete the required tasks under exam conditions.