In the journey of medical education, students face various challenges that test their understanding and skills. Among these, the hands-on evaluation plays a crucial role in assessing one’s ability to apply theoretical knowledge in real-world scenarios. This type of assessment requires not only memorization but also precision, attention to detail, and the ability to think critically under pressure.
Success in this evaluation depends on a variety of factors, such as familiarity with human structures, the ability to identify key elements accurately, and effective problem-solving techniques. Adequate preparation involves a blend of active study, practical experience, and strategic planning to approach the test with confidence.
In this guide, we will explore essential strategies to excel in such assessments, offering practical advice on preparation, common pitfalls to avoid, and tips to perform with clarity and focus when faced with physical demonstrations of your knowledge.
Comprehensive Guide to Medical Hands-On Evaluation
In medical training, demonstrating practical competence is just as vital as theoretical knowledge. A hands-on assessment requires students to show proficiency in identifying, analyzing, and interacting with physical specimens, often under time pressure. Mastery in this area is essential for becoming a successful healthcare professional, as it bridges the gap between theoretical study and real-world application.
Key Areas of Focus
Preparation for this type of evaluation demands a solid grasp of key body systems and the ability to recognize various structures with accuracy. Students should focus on developing observational skills, manual dexterity, and the capacity to apply anatomical knowledge in practical scenarios. The following table outlines common areas covered in these assessments:
| Body System | Common Structures | Assessment Focus |
|---|---|---|
| Musculoskeletal | Bones, joints, muscles | Identification and function |
| Nervous | Brain, spinal cord, nerves | Localization and functions |
| Circulatory | Heart, arteries, veins | Pathways and functionality |
| Respiratory | Lungs, trachea, bronchi | Identification and function |
| Digestive | Stomach, intestines, liver | Structures and digestion process |
Effective Preparation Tips
Building confidence in this type of evaluation begins with a comprehensive study routine. Regular practice with models, cadavers, or virtual simulations helps improve both speed and accuracy. Additionally, understanding the relationships between structures and their functions will enhance overall performance. Group study sessions can also be beneficial, as discussing and explaining concepts to peers reinforces individual learning.
Understanding the Structure of the Evaluation
In medical education, evaluations that assess hands-on knowledge are typically structured in a way that requires students to apply what they have learned in a practical setting. These evaluations usually consist of several components that test various skills, from identifying structures to demonstrating procedures. The structure is designed to reflect real-world scenarios and challenges that a medical professional will face in their daily practice.
Types of Assessment Tasks
During the evaluation, students may encounter a variety of tasks that assess their understanding and manual dexterity. The main types of tasks are:
- Identification – Students are asked to recognize and label specific structures from physical specimens or models.
- Demonstration – Students are required to perform certain procedures or manipulations, such as measurements or dissection techniques.
- Analysis – Involves answering questions or explaining the function and relationship of structures within a system.
- Problem-solving – Situational tasks where students must apply their knowledge to solve clinical-like problems based on real-life scenarios.
Typical Evaluation Format
The format of the hands-on assessment can vary between institutions, but most commonly, it consists of:
- Stations – The evaluation is often divided into multiple stations, each focusing on a different aspect of medical knowledge or skill.
- Time Limits – Each task or station has a time limit to assess how well students perform under pressure.
- Scoring Criteria – Each task is scored based on accuracy, technique, and the ability to explain or apply knowledge in context.
Key Skills Tested in Medical Hands-On Evaluation
In hands-on assessments, several critical skills are evaluated to ensure students can effectively apply theoretical knowledge in a practical context. These skills go beyond simple memorization and require a combination of precision, critical thinking, and technical ability. Mastery of these areas is essential for success in the healthcare field, as they mirror the tasks professionals regularly perform in clinical environments.
The main abilities tested during these assessments include:
- Identification – Recognizing and labeling key structures accurately from models, cadavers, or images.
- Manual Dexterity – Demonstrating skillful handling of tools and specimens, such as during dissections or when preparing samples for examination.
- Knowledge Application – Understanding the function and interrelationship of structures, and applying that knowledge to solve clinical scenarios.
- Attention to Detail – Carefully observing and noting key features, which is crucial in diagnosing or performing medical procedures.
- Problem Solving – Applying theoretical knowledge to real-world problems, requiring students to demonstrate both technical and critical thinking abilities.
- Time Management – Performing tasks within set time limits, simulating real-life scenarios where quick yet accurate decision-making is vital.
Each of these skills plays an integral role in preparing students for clinical practice, ensuring that they can perform tasks with accuracy, efficiency, and confidence when interacting with patients or specimens in a medical setting.
Common Mistakes to Avoid During the Evaluation
During a hands-on assessment, students often encounter situations where small mistakes can lead to significant consequences. These errors typically arise from a lack of preparation, poor time management, or overlooking key details. By recognizing and avoiding these common pitfalls, students can increase their chances of performing well and demonstrate their competency with greater confidence.
Here are some common mistakes to avoid:
- Rushing Through Tasks – Trying to finish quickly can result in missing important details or making errors in identification and technique. It’s essential to stay focused and complete each task carefully.
- Not Following Instructions – Ignoring the specific instructions given for each task can lead to incorrect answers or incomplete procedures. Always read and listen to instructions carefully before proceeding.
- Overlooking Key Structures – Failing to identify or describe important features can impact your score. Take the time to observe thoroughly and ensure you have noted all relevant aspects.
- Panic or Stress – Anxiety can cloud judgment and hinder performance. Practice relaxation techniques and maintain composure throughout the assessment.
- Neglecting Hygiene and Safety – In medical evaluations, safety protocols are critical. Always adhere to proper handling and sanitation procedures when interacting with specimens or equipment.
- Ignoring Time Constraints – Losing track of time can result in incomplete tasks. Use a watch or timer to stay aware of your progress and avoid rushing at the end.
Being mindful of these mistakes and preparing adequately can ensure a smoother and more successful evaluation experience. By focusing on precision, organization, and calmness, students can confidently navigate the challenges posed by these assessments.
How to Improve Your Dissection Skills

Mastering dissection is a crucial skill for anyone studying medical sciences, as it allows students to explore and understand the structures of the body in detail. The ability to perform a dissection effectively requires not only knowledge but also technique, patience, and precision. By honing these skills, students can gain a deeper understanding of the subject matter and prepare themselves for real-world clinical tasks.
Developing Technique and Precision
One of the key elements of a successful dissection is learning how to handle instruments and specimens with care and accuracy. The following tips can help improve your dissection technique:
- Practice Proper Handling – Learn to use scalpels, scissors, and forceps with control. Focus on making precise cuts and avoiding unnecessary damage to the tissue.
- Work Slowly – Take your time to ensure each step is performed correctly. Rushing can lead to mistakes and missed structures.
- Follow a Structured Approach – Develop a systematic method for each dissection. Plan each step, from the initial incision to identifying and labeling structures.
Enhancing Observation Skills
Dissection is not only about cutting and manipulating the specimen; it’s equally important to observe and identify structures accurately. To improve your observation skills:
- Focus on Detail – Pay attention to the smallest features and relationships between structures. Every detail counts in understanding function and location.
- Use Multiple Resources – Refer to anatomical atlases, online tools, and 3D models to gain a better visual understanding of the structures you are working with.
- Ask for Feedback – Regularly seek guidance from instructors or peers to ensure you are identifying structures correctly and efficiently.
By practicing these techniques and improving your observational skills, you’ll gain greater confidence and competence in performing dissections. This will not only enhance your practical abilities but also deepen your understanding of the body’s intricacies.
Study Resources for Medical Hands-On Assessments
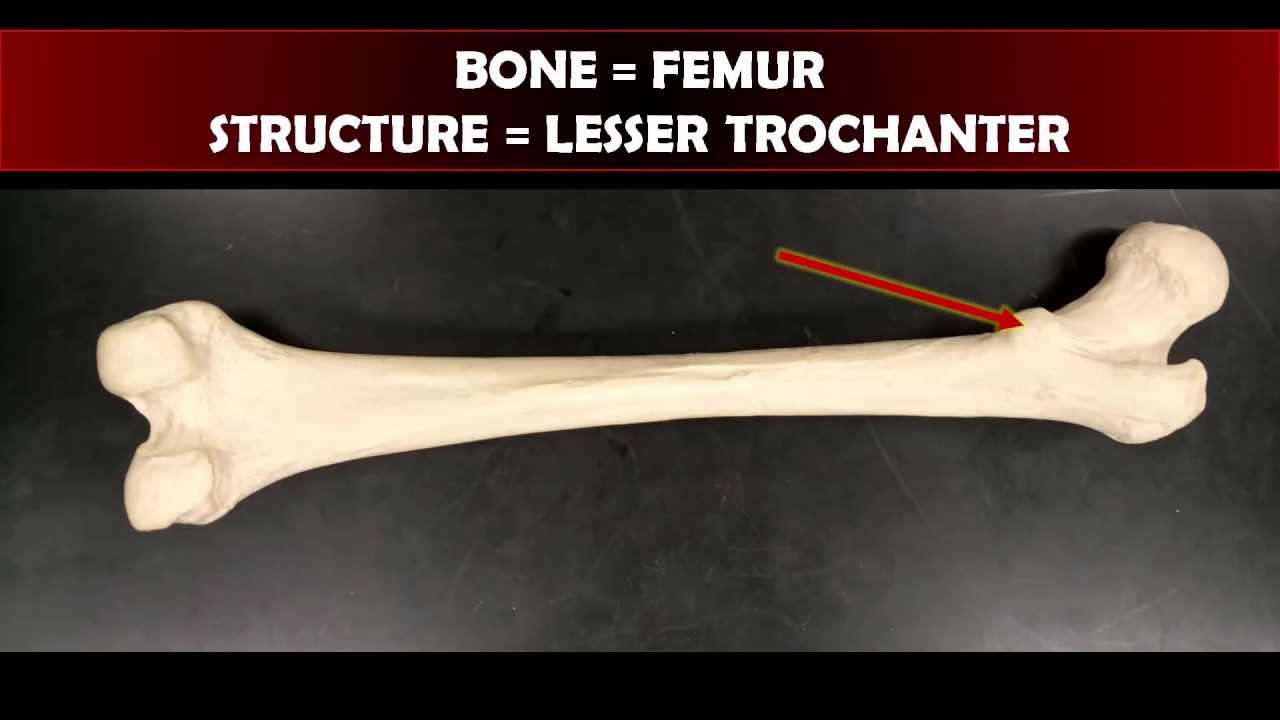
Effective preparation for hands-on assessments requires a blend of resources that cater to both theoretical knowledge and practical application. By utilizing a range of study materials, students can strengthen their understanding of structures, functions, and techniques, enhancing their overall performance. The right resources can provide both foundational knowledge and advanced insights into the complexities of human systems.
Key Resources for Hands-On Learning
Below are some of the most useful study tools for preparing for hands-on evaluations:
- Anatomical Atlases – Detailed books and online references, such as Netter’s Atlas of Human Anatomy, provide high-quality illustrations that are crucial for understanding body structures.
- 3D Models and Virtual Simulations – Interactive software and apps like Visible Body offer virtual dissections and anatomical exploration, allowing for an immersive study experience.
- Dissection Guides – Comprehensive manuals that provide step-by-step instructions for dissections are essential for mastering technique and procedure.
- Flashcards – Flashcard sets, whether physical or digital, help reinforce key terms and structures by testing recall in a rapid, focused manner.
- Practice Labs – If available, working in a dedicated lab space with real specimens allows for hands-on practice, which is critical to building muscle memory and dexterity.
Online Learning Platforms
In addition to traditional books and physical resources, online platforms offer convenient and effective tools for students:
- Online Courses – Platforms like Khan Academy and Coursera offer courses that cover essential topics and provide quizzes and interactive elements to reinforce learning.
- YouTube Tutorials – Channels focused on medical studies can be a valuable resource for visual learners, providing demonstrations and tips on identifying structures and performing techniques.
- Peer Study Groups – Collaborative study sessions with fellow students allow for discussion, clarification of concepts, and mutual support in mastering difficult areas.
By integrating these diverse resources into your study routine, you can gain a well-rounded understanding and improve both theoretical knowledge and hands-on skills for any assessment.
Preparing for the Evaluation Day
The day of a hands-on assessment can be both exciting and nerve-wracking. Proper preparation in the days leading up to the event and a clear strategy for the morning of the assessment can make a significant difference in your performance. It’s not just about studying the material; it’s also about managing your time, maintaining your composure, and ensuring you have everything you need to succeed.
Here are some essential steps to take in the final hours before the evaluation:
- Review Key Concepts – In the days before the assessment, focus on reviewing important structures and their functions. Use study aids like flashcards or interactive models to reinforce your knowledge.
- Organize Your Materials – Make sure all the tools and materials you will need are ready and in good condition. This includes things like dissection instruments, gloves, and any required notes or diagrams.
- Get a Good Night’s Sleep – Ensure you’re well-rested the night before. A clear mind and a rested body will help you perform better under pressure.
- Eat a Balanced Breakfast – Have a nutritious breakfast that will fuel you for the day. Avoid heavy or sugary foods that might lead to an energy crash during the assessment.
- Arrive Early – Aim to arrive at the assessment venue with plenty of time to spare. This gives you time to relax, get organized, and mentally prepare before the session begins.
By following these steps, you’ll approach the assessment day with confidence and a focused mindset, setting yourself up for success.
Effective Time Management Strategies
Proper time management is crucial for performing well in any hands-on assessment. When faced with time constraints, knowing how to prioritize tasks, allocate time wisely, and stay organized can greatly improve your efficiency. The goal is to balance thoroughness with speed, ensuring that you complete all tasks accurately without feeling rushed.
Here are some key strategies to help manage your time effectively during the assessment:
- Plan Ahead – Before starting, quickly scan all the tasks or objectives and plan how much time to allocate for each. Break the overall assessment into smaller, manageable parts to stay organized.
- Set Time Limits – Set a reasonable time limit for each task and try to stick to it. This will help prevent spending too much time on any one part and ensure that you have enough time to complete everything.
- Prioritize Tasks – Focus on the most important or challenging tasks first. This ensures you give them the attention they require while you’re still fresh and focused.
- Use a Timer – If permitted, use a timer or watch to keep track of the time. Regularly check your progress to stay on schedule.
- Stay Focused – Avoid distractions and stay focused on the task at hand. If you find yourself getting off track, gently refocus and move on to the next part of the assessment.
By incorporating these time management techniques, you can improve both your efficiency and the quality of your performance, reducing stress and increasing your chances of success.
Tips for Identifying Anatomical Structures
Accurately identifying body structures during hands-on assessments is essential for success. Whether you’re working with models, specimens, or diagrams, developing a sharp eye for detail and understanding the relationships between different parts can significantly enhance your performance. Here are some effective strategies to help you identify key structures with confidence.
Consider the following tips when approaching the task of recognizing and labeling body parts:
- Study Spatial Relationships – Understand how different structures are positioned relative to one another. Knowing their orientation and proximity helps you visualize and recognize them more easily during practical sessions.
- Focus on Key Landmarks – Identify prominent landmarks that can serve as reference points. For example, in a dissection, knowing the location of major blood vessels or bones can help you pinpoint surrounding structures.
- Use Mnemonics and Visual Aids – Create memory aids or use diagrams to reinforce your understanding of complex systems. Visual tools such as 3D models and flashcards are great for repeated exposure to structures.
- Take Your Time to Observe – Carefully examine each specimen or model from multiple angles. A methodical approach ensures that no key feature is overlooked.
- Label as You Go – During your study sessions, practice labeling structures as you review them. This active recall method helps reinforce your memory and boosts recognition during assessments.
With consistent practice and attention to detail, identifying body structures will become second nature, giving you the clarity and confidence needed during assessments.
Importance of Hands-On Practice
Hands-on practice is a crucial component of mastering any skill, especially when it comes to tasks that require precision and attention to detail. Engaging directly with materials, models, and specimens allows you to gain a deeper understanding of the concepts you study in theory. It helps solidify your knowledge and refine your technique, turning theoretical learning into practical expertise.
Building Confidence and Skill
One of the key benefits of hands-on practice is the opportunity to build both confidence and skill. The more you engage with physical specimens or interactive models, the more comfortable you become with identifying structures and performing tasks accurately. Repetition is vital, as it ingrains the processes in your muscle memory, making them more automatic and efficient.
Enhancing Problem-Solving Abilities
Practical sessions often present challenges that are difficult to anticipate in a theoretical setting. By working directly with the material, you develop critical problem-solving abilities. You learn to adapt to different situations, think on your feet, and apply your knowledge in real-time, which is essential for success in assessments and beyond.
Incorporating regular hands-on practice into your study routine not only prepares you for evaluations but also strengthens your overall competency, making it an indispensable part of the learning process.
How to Stay Calm and Focused
Maintaining composure during a hands-on assessment is essential for performing at your best. Stress and anxiety can impair focus and decision-making, which can impact your ability to complete tasks efficiently. The key to success is learning how to stay calm, manage stress, and concentrate on the task at hand. Here are some techniques that can help you stay focused and maintain a clear mind during the assessment.
Below are some effective strategies to help you stay calm and perform at your best:
| Technique | How It Helps |
|---|---|
| Deep Breathing | Calms the nervous system, reduces stress, and helps you regain focus quickly. |
| Visualization | Mentally rehearsing the steps of the assessment helps you feel more confident and prepared. |
| Time Management | Allows you to allocate time effectively, reducing the pressure of rushing and increasing productivity. |
| Stay Positive | A positive mindset helps you maintain clarity, overcome challenges, and approach each task with confidence. |
| Breaks When Needed | A short break can help you clear your mind and refocus, especially after intense periods of concentration. |
By incorporating these strategies into your preparation and approach, you can remain calm and focused during the assessment, ensuring optimal performance under pressure.
Using Models and Visual Aids
Incorporating models and visual aids into your study routine can significantly enhance your understanding and recall of complex structures. These resources provide a tangible and interactive way to engage with material, allowing you to better grasp spatial relationships and identify key features. Whether working with 3D models, diagrams, or interactive tools, these aids offer valuable support during study sessions and assessments.
Here are some effective ways to use these resources:
- 3D Models – Physical or digital 3D models provide a detailed, three-dimensional view of structures. Manipulating them in space helps solidify your understanding of their shape and orientation, making recognition easier during assessments.
- Interactive Software – Digital platforms that allow you to explore and label structures interactively offer a dynamic learning experience. These tools often include quizzes and challenges to test your knowledge in real-time.
- Detailed Diagrams – High-quality, labeled diagrams help reinforce memory and provide a visual representation of different body systems. Practice identifying structures on these diagrams to improve speed and accuracy.
- Flashcards – Flashcards are a great way to test your recall. They provide a simple method for reviewing key structures and their functions, improving retention and boosting confidence.
By integrating models and visual aids into your study habits, you gain a deeper understanding of the material and develop better recognition skills. This hands-on approach makes complex subjects more approachable and enhances overall learning effectiveness.
Role of Memorization in Practical Assessments
Memorization plays a crucial role in hands-on evaluations where quick recall and accurate identification of structures are essential. While understanding concepts is key, the ability to recall information rapidly under pressure can greatly influence performance. Developing strong memorization skills allows you to navigate complex tasks with confidence and precision, helping you make accurate decisions in a limited amount of time.
How Memorization Affects Performance
Strong memorization skills enable you to quickly recognize patterns, identify key components, and recall vital details when interacting with specimens or models. The process of memorizing information also strengthens neural pathways, enhancing retention and recall during critical moments.
Techniques to Improve Memorization
- Chunking – Breaking down large amounts of information into smaller, manageable units can make it easier to remember complex data.
- Association – Linking new information with familiar concepts or creating visual associations helps improve recall. For instance, associating the shape of a structure with its function can aid in identification.
- Repetition – Regular repetition, whether through flashcards, quizzes, or self-testing, helps reinforce memory over time.
- Visualization – Mentally visualizing structures or processes allows you to better internalize information and strengthen recall during an evaluation.
By incorporating these memorization techniques into your study routine, you can enhance your ability to recall critical details during assessments, improving your overall performance and reducing stress.
Collaborating with Study Groups
Working with study groups can provide a collaborative and supportive environment, making the learning process more efficient and enjoyable. When preparing for hands-on evaluations, group study sessions offer the opportunity to share knowledge, clarify difficult concepts, and test each other’s understanding. Collaborative learning can also improve retention, as discussing and teaching others helps reinforce the material.
Benefits of Group Study
- Diverse Perspectives – Each group member may have different strengths and knowledge, which can help fill in gaps and provide a more comprehensive understanding of complex topics.
- Active Learning – Group discussions and quizzes encourage active participation, making it easier to engage with the material and enhance retention.
- Accountability – Studying in a group setting can help keep everyone motivated and accountable, ensuring consistent progress and focus.
- Immediate Feedback – Group study allows for quick feedback, enabling members to correct mistakes or misunderstandings early in the learning process.
Tips for Effective Group Study
- Set Clear Goals – Before each session, establish specific topics or tasks to focus on, ensuring that everyone is aligned on the learning objectives.
- Teach Each Other – One of the best ways to solidify knowledge is to explain concepts to others. Teaching your peers reinforces your own understanding.
- Use Practice Materials – Collaboratively work through practice questions, diagrams, or models to simulate real-world tasks and improve practical skills.
- Stay Focused – Keep discussions on track and minimize distractions to ensure that each session is productive and beneficial to everyone involved.
By collaborating with others, you can leverage the collective knowledge of your peers, gain new insights, and enhance your preparation for the task at hand.
What to Expect During the Exam
When you enter a hands-on assessment, you can expect to be tested on your ability to identify and interact with various structures or components. The environment will likely be structured, with stations or tasks that require practical application of what you’ve studied. Each section may involve a different challenge, from identifying specific features to demonstrating procedures or techniques.
Throughout the process, you will be observed by assessors who will evaluate both your knowledge and the precision with which you execute the tasks. You may be asked to explain your reasoning or demonstrate certain steps as part of the evaluation. The time constraints will encourage you to work efficiently, but also maintain accuracy and focus under pressure.
It is important to remain calm and stay organized. Although you may encounter unexpected challenges or questions, the goal is to show your competence through methodical thinking and clear communication. Be prepared to demonstrate your understanding of key concepts and apply them practically, ensuring that you can showcase both your theoretical knowledge and hands-on skills.
How to Tackle Written and Practical Sections
Approaching assessments that combine both theoretical and hands-on components requires a balanced strategy. For written sections, it’s important to focus on clarity and precision. Review the key concepts and terminology beforehand so you can confidently answer questions. If you’re given a choice of questions, choose those you’re most comfortable with, ensuring that you can provide detailed and accurate responses.
For the hands-on part, preparation is key. Before you enter the assessment, familiarize yourself with the procedures, tools, and techniques you’ll be tested on. When it comes to performing tasks, work methodically and carefully. Pay close attention to instructions, and if you’re unsure about something, don’t hesitate to ask for clarification. Time management is crucial, so allocate enough time to each task and avoid spending too long on any one activity.
Strategies for the Written Section

- Review key concepts and terminology in advance.
- Read questions carefully to ensure you understand what’s being asked.
- Write clear, concise, and well-structured responses.
- Use examples to support your answers when appropriate.
Strategies for the Hands-On Section
- Familiarize yourself with all required tools and equipment.
- Take your time to assess the situation before acting.
- Stay organized and methodical in your approach.
- Prioritize tasks and keep track of time during the assessment.
Post-Assessment Review and Improvement
After completing an assessment, it’s essential to reflect on your performance to identify areas for growth. Reviewing your work allows you to analyze both strengths and weaknesses, helping you focus on where improvement is needed. This post-assessment period is an opportunity to enhance your skills for future tasks and to refine your approach to various techniques and concepts.
Start by carefully reviewing any feedback you receive, whether it’s from instructors or peers. Take note of the areas where you struggled and create a plan to address those weaknesses. Consider revisiting specific techniques, revising your study strategies, or practicing more with tools and materials. Regularly revisiting these concepts will help reinforce your learning and boost your confidence for the next challenge.
Analyzing Mistakes and Successes
- Identify the areas where you made mistakes and understand why they occurred.
- Recognize the aspects of the task that you performed well to reinforce good practices.
- Reflect on how you can handle similar situations more effectively in the future.
Creating a Plan for Improvement
- Set specific goals for practice based on areas of weakness.
- Incorporate regular review sessions into your study routine to reinforce learned concepts.
- Seek additional resources or guidance if certain topics remain unclear.
Preparing for Future Assessments
Looking ahead to upcoming assessments requires a focused approach to ensure long-term success. The preparation process involves not only reinforcing knowledge but also refining techniques and strategies for dealing with new challenges. Developing a comprehensive study plan, setting clear goals, and reviewing past experiences can significantly improve your readiness for future tasks.
In order to optimize your preparation, it’s essential to break down complex topics into manageable segments. This allows for steady progress while reducing the feeling of being overwhelmed. Time management and consistency play key roles in maintaining a balance between theoretical knowledge and hands-on practice.
Key Areas to Focus On

| Area of Focus | Action Plan |
|---|---|
| Understanding Core Concepts | Review foundational material regularly and make connections between concepts. |
| Hands-on Experience | Practice with real materials and models to build muscle memory. |
| Time Management | Create a study schedule and adhere to deadlines to avoid last-minute cramming. |
| Review and Feedback | Solicit feedback from instructors or peers and apply it to future studies. |
By consistently working on these areas, you’ll build a solid foundation that not only prepares you for the next challenge but also enhances your confidence and competence. Each assessment provides an opportunity for growth and improvement, and maintaining a proactive, focused mindset will contribute to your overall success.