
Preparing for a major academic assessment can feel overwhelming, especially when it covers a wide range of material. Success requires more than just memorization; it demands a clear understanding of key events, individuals, and themes that have shaped the past. With effective strategies, you can confidently approach this important task and perform at your best.
In this section, we’ll explore the essential topics and skills needed to excel. From key figures and defining moments to the influences that shaped different societies, understanding these concepts will not only help you succeed but also deepen your appreciation of the material. The journey of review will be more manageable and less stressful with the right approach and mindset.
Stay organized and focus on the core ideas that are most likely to appear. Use practice materials to reinforce your knowledge, and break down complex topics into manageable sections. With consistent effort and smart preparation, you can ensure that you’re fully equipped to tackle the challenges ahead.
Comprehensive Assessment Preparation
This evaluation covers a wide spectrum of material from different periods, requiring students to demonstrate a deep understanding of key events, figures, and movements. Mastering this content involves not only recalling facts but also connecting ideas and recognizing the broader implications of historical developments. A strong grasp of these topics will ensure you approach the test with confidence and clarity.
To succeed, it’s essential to focus on the most significant themes and the cause-and-effect relationships that shaped past civilizations. Examining how political, social, and economic factors interacted across various time periods will provide valuable context. Studying past documents and sources will also help you better understand how historical narratives are constructed and interpreted.
Preparation should be systematic. Begin by reviewing the major milestones and influential leaders that had a profound impact on the course of events. Using study guides and practice tests will help you reinforce what you’ve learned and identify areas that require additional focus. Through structured review and consistent effort, you can tackle this challenge effectively.
Key Topics to Study for the Assessment
To perform well in this comprehensive review, it’s crucial to focus on the most impactful themes and events that shaped past civilizations. Understanding how these developments influenced societies, economies, and politics will help you answer questions with depth and insight. Make sure to highlight the moments and figures that have had lasting effects on global trends.
Key areas to prioritize include significant political revolutions, the rise and fall of empires, major social movements, and the evolution of economic systems. Additionally, be sure to review critical wars and conflicts that altered the course of nations. Emphasizing these topics will give you a clear foundation for success.
By organizing your study sessions around these core subjects, you can ensure that you’re well-prepared to tackle various questions and demonstrate a strong grasp of the material. Practice by reviewing summaries and timelines to reinforce your understanding of these key concepts.
Understanding Major Historical Events

Key moments in the past have had a profound impact on shaping societies and cultures. Understanding these pivotal events is essential for grasping the broader context in which civilizations developed. These events not only changed the course of individual nations but also influenced the global landscape in ways that still resonate today.
To fully comprehend these moments, it’s important to break them down into their causes, main events, and long-term consequences. Focusing on the following will help you gain a deeper understanding:
- Revolutions and uprisings that led to significant political shifts.
- Wars that altered borders, economies, and power dynamics.
- Technological advancements that reshaped societies.
- Social movements that sparked changes in rights and freedoms.
- Colonization and its lasting effects on the world’s geography and cultures.
Each of these events played a crucial role in the development of modern nations. By examining the interconnectedness of these moments, you can better understand how the past informs the present. Focusing on the causes and consequences of each event will prepare you to approach questions with a clear and well-rounded perspective.
Reviewing Important Figures in History
Throughout time, certain individuals have played pivotal roles in shaping the course of events. Understanding the contributions and impact of these key figures is essential for a comprehensive grasp of historical developments. These leaders, thinkers, and innovators were often at the forefront of change, influencing not only their immediate surroundings but the world at large.
Key Leaders and Their Contributions
Some figures are known for their leadership during critical moments in history. Their decisions and actions often determined the fate of nations and civilizations. Below is a table of influential leaders and their lasting legacies:
| Name | Period | Contribution |
|---|---|---|
| Alexander the Great | 4th Century BCE | Conquered much of the known world, spreading Greek culture and influence. |
| Napoleon Bonaparte | 18th-19th Century | Reformed European politics and law through his military conquests and leadership. |
| Queen Elizabeth I | 16th Century | Led England through a period of cultural flourishing and military success. |
| Winston Churchill | 20th Century | Guided Britain through World War II with resilience and strategic vision. |
Revolutionaries and Visionaries
In addition to leaders, revolutionaries and visionaries have also shaped societies by challenging the status quo. Their ideas and actions sparked widespread change, often influencing future generations and entire civilizations.
Examining Cultural and Social Movements
Cultural and social movements have long been catalysts for change, shaping societies and challenging existing norms. These movements often arise in response to injustices or inequalities, aiming to transform political, economic, and cultural systems. By understanding the dynamics of such movements, we can better appreciate their profound impact on societal development and modern life.
Key movements throughout history have been driven by the desire for greater equality, freedom, and justice. From the fight for civil rights to the push for women’s suffrage, these movements often lay the foundation for lasting change. The leaders, ideas, and actions of these groups have reshaped the social fabric of many nations, influencing laws, attitudes, and the course of future events.
Understanding these movements requires exploring their origins, goals, key figures, and ultimate outcomes. By doing so, you can gain a clearer perspective on how cultural and social shifts have affected not only individual nations but also global trends.
Political Systems Through History
Political systems have evolved throughout time, adapting to the needs of societies and influencing the course of nations. From monarchies and empires to democratic governments and authoritarian regimes, the ways in which power is structured and exercised have varied significantly across different cultures and time periods. Understanding these systems is crucial for analyzing how societies functioned and how political power shaped major events and developments.
Evolution of Governance Structures
Over the centuries, different forms of governance emerged, each with its own strengths, weaknesses, and challenges. Some systems were built on the concentration of power in the hands of a few, while others allowed for broader participation by the people. The rise and fall of various political structures have had lasting effects on how nations operate today.
| Political System | Period | Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| Monarchy | Ancient to Early Modern | Power concentrated in the hands of a single ruler, often hereditary. |
| Republic | Ancient to Modern | Governance by elected officials and representatives, typically with laws safeguarding individual freedoms. |
| Feudalism | Medieval | Decentralized system with local lords holding power over lands and vassals. |
| Communism | 20th Century | System where the state controls all aspects of the economy and society, with a focus on equality. |
| Democracy | Modern | Power rests with the people, typically through voting and representative governance. |
Impact of Political Structures
The political systems that arose throughout time have had profound effects on the course of events. They shaped social hierarchies, influenced economic development, and determined the relationships between nations. Studying these systems provides valuable insights into how societies organize power and address the needs of their people.
Impact of Geography on Civilizations

The physical environment has played a critical role in the development of civilizations throughout history. The availability of natural resources, the proximity to bodies of water, and the geography of the land influenced how societies were formed, how they interacted with each other, and how they adapted to their surroundings. Geography shaped the economy, culture, and even the military strategies of different civilizations.
Geographical Factors That Shaped Early Societies
Various aspects of geography have had a profound influence on the rise of civilizations. These factors determined where people settled, how they farmed, and what trade routes they used. Key geographical elements include:
- Rivers: Major rivers provided fertile soil for agriculture and transportation routes. Civilizations such as those in Egypt, Mesopotamia, and China flourished along riverbanks.
- Mountains: Natural barriers like mountains helped protect civilizations from invasions but also isolated them, creating distinct cultures.
- Climate: The climate of a region determined what crops could be grown and how people could live. Harsh climates led to technological innovations, while temperate climates supported larger populations.
- Access to Seas and Oceans: Proximity to water bodies facilitated trade, exploration, and cultural exchange between distant civilizations.
Geography and Conflict
Geography not only influenced peaceful development but also played a significant role in conflict and conquest. Natural barriers often protected societies from invasions, while other geographical features, such as plains or river valleys, became hotspots for military campaigns. The strategic value of geography has been a deciding factor in many historical battles and territorial expansions.
- Fertile Crescent: The fertile land of the Mesopotamian region became a contested area for various empires.
- Mountain Passes: Certain mountain passes, like the Khyber Pass, became key entry points for invaders throughout history.
- Coastal Regions: Control over coastlines allowed civilizations to control trade routes and engage in maritime warfare.
In summary, the environment in which civilizations developed was not just a backdrop but an active factor in shaping their cultural, economic, and political trajectories. Geography influenced the very fabric of ancient societies and continues to impact modern nations today.
Analyzing Economic Systems and Changes

Economic systems play a fundamental role in the organization and functioning of societies. They define how resources are distributed, goods and services are produced, and wealth is shared among individuals and groups. Over time, these systems have undergone significant transformations, driven by shifts in technology, ideology, and the needs of growing populations. Analyzing the development and changes within these systems provides a deeper understanding of how societies evolve and adapt to both internal and external pressures.
Historically, economic systems have ranged from agrarian economies based on manual labor and barter to highly complex market economies characterized by currency, trade, and global interactions. The way resources are allocated–whether through centralized control or free-market mechanisms–has shaped civilizations, influencing everything from the rise of powerful empires to the establishment of democratic nations.
The transition between different economic models, such as the shift from feudalism to capitalism, reveals the impact of technological advancements, colonialism, and the changing demands of labor. Each transformation has left a lasting mark on social structures, wealth distribution, and the global balance of power.
Significance of Revolutions in History

Revolutions have played a pivotal role in shaping societies and altering the course of human events. These movements, often driven by a desire for change, challenge the established order and bring about radical transformations in political, economic, and social structures. While each revolution is unique in its causes and outcomes, their collective impact on global progress is undeniable.
Key Elements of Revolutions
Revolutions are typically fueled by various factors, such as social inequality, economic hardship, and political oppression. They often involve mass mobilization, the overthrow of existing authorities, and the establishment of new ideologies. Understanding these key elements helps to grasp why revolutions have such profound and lasting effects on the nations involved.
- Social Unrest: Widespread dissatisfaction with the status quo, often due to inequality and exploitation, is a common catalyst for revolutionary movements.
- Economic Discontent: Economic hardship, such as high taxes or inflation, can push people to demand change and challenge the existing system.
- Political Oppression: Authoritarian regimes or corrupt governments often face revolt when they fail to represent the will of the people.
- Ideological Shifts: New ideas, often inspired by philosophies of liberty, justice, and equality, can fuel movements that aim to overthrow established power structures.
Impact of Major Revolutions
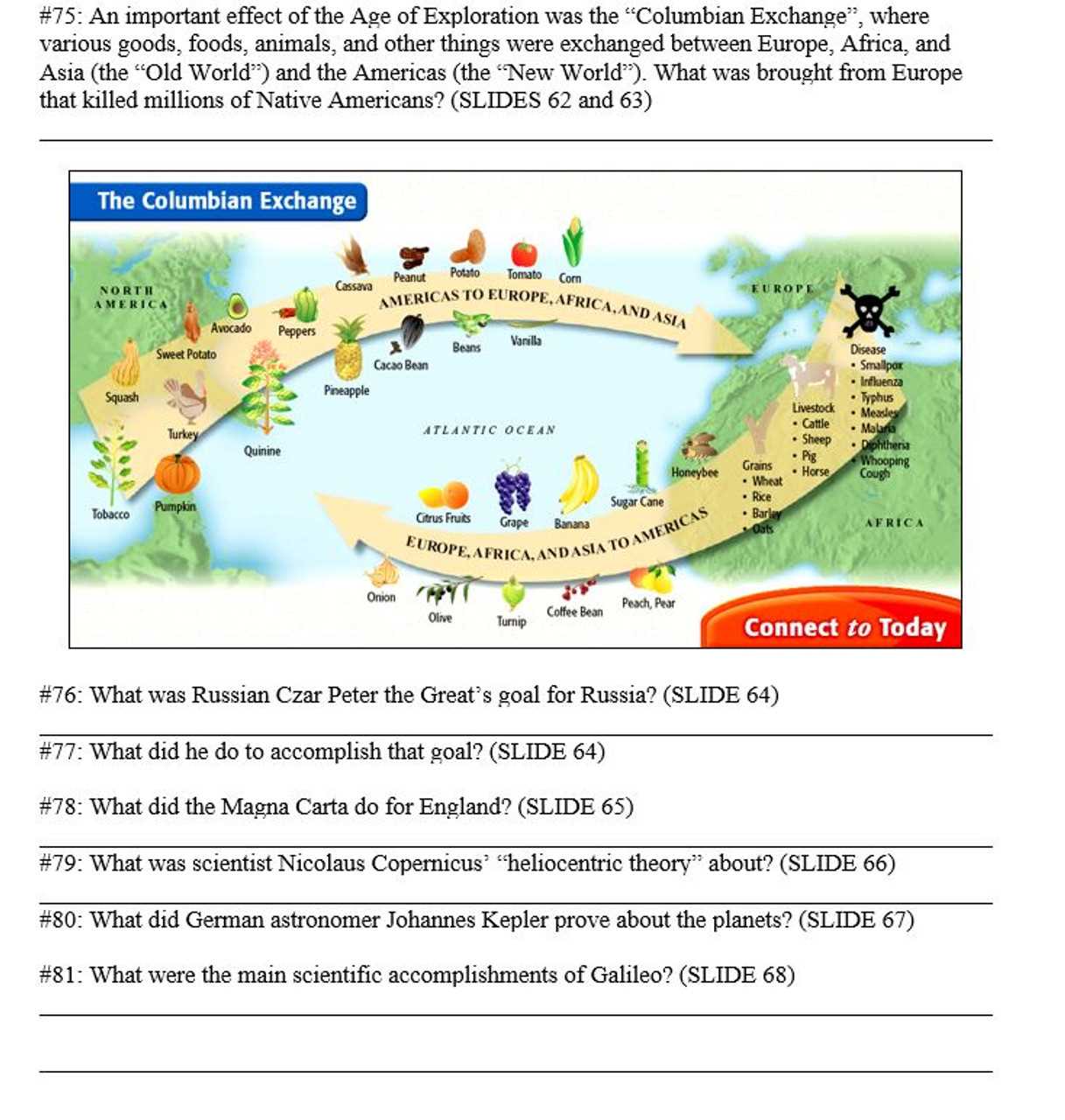
The influence of revolutions extends beyond the borders of the nations where they occur. Often, they serve as catalysts for broader global change, inspiring similar movements in other parts of the world. Some revolutions lead to the formation of new governments, while others spark the development of new social systems, ideologies, or economic models.
- The French Revolution: Aimed at overthrowing the monarchy and establishing a republic, it profoundly impacted ideas about citizenship, human rights, and governance.
- The Industrial Revolution: Not a political revolution but a transformative period that reshaped economies, urbanized societies, and set the stage for modern capitalism.
- The Russian Revolution: The overthrow of the Tsarist autocracy led to the rise of communist rule, influencing global politics for much of the 20th century.
- The American Revolution: Marked the birth of a new nation and the spread of democratic ideals across the world.
In summary, revolutions are a defining feature of human history, often altering the balance of power and transforming societies. By understanding their causes, processes, and impacts, we can better appreciate the forces that shape the world around us.
Global Conflicts and Their Effects
Major conflicts between nations or groups often leave deep and lasting impacts on both the involved countries and the broader international community. These struggles, whether they take the form of wars, ideological clashes, or territorial disputes, shape political landscapes, influence economies, and affect millions of lives. Understanding the outcomes of these global confrontations helps us learn from the past and better navigate the complexities of modern international relations.
Throughout history, significant conflicts have led to widespread destruction, the loss of life, shifts in power dynamics, and the creation of new alliances. The consequences of these events often extend far beyond the immediate aftermath, influencing cultural, economic, and geopolitical conditions for decades or even centuries.
Key Effects of Global Conflicts

While the specific outcomes of each conflict vary, certain patterns emerge when analyzing the broader effects. These include changes in political systems, shifts in global power, and long-term social and economic consequences. Below are some key areas affected by such events:
| Effect | Description |
|---|---|
| Political Reorganization | Conflicts often lead to the redrawing of borders, the rise and fall of empires, and the reshaping of governmental structures. |
| Economic Devastation | Wars and large-scale conflicts result in widespread economic disruption, including resource depletion, destruction of infrastructure, and trade disruptions. |
| Social and Cultural Impact | Global conflicts influence societies by causing displacement, loss of life, and the breakdown of social norms, often leading to long-term trauma. |
| Technological Advancements | Conflict-driven innovation often accelerates technological progress, particularly in areas like military technology, medicine, and communications. |
| Formation of New Alliances | The aftermath of conflicts often results in new diplomatic relationships, the creation of international organizations, and the establishment of alliances aimed at preventing future wars. |
In conclusion, global conflicts have far-reaching effects that extend well beyond their immediate causes. By studying the outcomes of past confrontations, we gain valuable insights into the consequences of war and violence, as well as the potential for diplomacy and cooperation in preventing future crises.
Pre-Colonial Civilizations and Empires
Before the era of exploration and colonization, numerous powerful civilizations and empires thrived across the globe, each contributing to the development of human culture, knowledge, and governance. These societies were marked by advanced technologies, rich traditions, and complex political systems. Their influence can still be felt in modern times through their legacies in architecture, art, philosophy, and governance.
In this section, we will explore the foundations and achievements of several pre-colonial civilizations, examining how they shaped the world before the arrival of foreign powers. These societies were diverse in their geography, culture, and accomplishments, yet shared a common drive for growth, innovation, and stability.
Notable Civilizations and Their Achievements
Throughout history, several key civilizations left their mark on global development. These cultures laid the groundwork for future empires and nations, with their contributions in various fields such as agriculture, engineering, and governance. Below are some of the most influential pre-colonial civilizations:
- The Ancient Egyptians: Known for their monumental architecture, including the pyramids, as well as advances in mathematics, medicine, and writing.
- The Mayans: Renowned for their achievements in astronomy, calendar systems, and the development of a written language.
- The Roman Empire: A vast empire that revolutionized law, governance, and military strategy, influencing Western civilization for centuries.
- The Gupta Empire: A golden age in India, noted for advancements in mathematics, science, art, and literature.
- The Mali Empire: A West African empire famous for its wealth, particularly in gold, and its support of education and culture, especially through the city of Timbuktu.
Impact on Modern Society

The legacies of these ancient civilizations have shaped modern societies in many ways. From the mathematical principles of the Mayans to the legal systems inherited from the Romans, the innovations of these pre-colonial empires continue to influence contemporary culture and thought. Their stories remind us of the rich history that existed long before the onset of colonization, offering a deeper understanding of the world’s diverse past.
Ancient Civilizations You Must Know
Throughout human history, several early civilizations laid the foundations for modern societies, contributing immensely to culture, technology, and governance. These ancient peoples established systems that influenced the development of agriculture, urbanization, law, and trade, shaping the course of future generations. Understanding the key characteristics of these civilizations provides valuable insight into the roots of contemporary civilizations.
This section highlights some of the most significant ancient civilizations, each with its unique contributions to the world. From the rise of monumental architecture to the birth of writing systems, these civilizations played a crucial role in shaping the world as we know it today.
- The Egyptians: Famous for their monumental pyramids, complex religion, and advances in mathematics, medicine, and writing.
- The Mesopotamians: Known for the invention of the wheel, the creation of the first writing system (cuneiform), and the establishment of the first cities in Sumer.
- The Indus Valley Civilization: Renowned for its advanced urban planning, sophisticated drainage systems, and a script that remains undeciphered.
- The Greeks: Revered for their contributions to philosophy, democracy, mathematics, and art, and for laying the foundation for Western civilization.
- The Romans: Masters of engineering and governance, with an extensive legal system and vast empire that shaped much of modern Europe.
These civilizations not only thrived in their own times but also left legacies that continue to shape the modern world. By studying their achievements, we gain a deeper appreciation for the complex societies that came before us and the lasting impact they have had on our current systems and cultures.
Understanding Historical Sources and Evidence
To grasp the past, it is essential to understand the various forms of evidence that historians rely on. These sources provide insights into the lives, cultures, and events of earlier times, offering valuable context and perspective. From written documents to physical artifacts, every piece of evidence tells a story about how societies functioned and evolved.
Historical sources can be divided into two primary categories: primary and secondary sources. Primary sources are created during the time period being studied and offer firsthand accounts of events. Secondary sources, on the other hand, are interpretations or analyses based on primary materials, written after the fact. Both types of sources play a critical role in constructing an accurate view of the past.
Types of Primary Sources
Primary sources include any original material that has survived from a past era. These sources offer direct insight into the thoughts, actions, and experiences of individuals or groups. Some common examples include:
- Written documents: Letters, diaries, government records, and official reports.
- Artifacts: Tools, pottery, artwork, and other objects that reflect daily life and cultural practices.
- Oral histories: Personal accounts passed down through generations or recorded interviews.
- Architectural remains: Buildings, ruins, and monuments that tell stories of ancient civilizations and their structures.
Evaluating Secondary Sources
Secondary sources are essential for understanding the broader implications of historical events. These sources are often written by historians or scholars who analyze primary materials and draw conclusions. They may take the form of books, journal articles, documentaries, or essays. While secondary sources can offer valuable interpretations, it’s important to remember they are influenced by the author’s perspective and the time in which they were created.
When examining both primary and secondary sources, it’s crucial to consider their reliability, context, and potential biases. By carefully analyzing the evidence available, historians can reconstruct a more accurate and nuanced understanding of the past.
How to Organize Your Study Sessions
Effective preparation for any major assessment requires a structured approach to studying. By organizing your study time wisely, you can maximize productivity, reduce stress, and retain more information. Planning ahead and breaking down your study tasks into manageable sections can ensure that you cover all the necessary material without feeling overwhelmed.
The key to a successful study session is setting clear goals, maintaining a consistent routine, and creating an environment that supports focus. This strategy not only helps you stay on track but also builds confidence as you progress through the material. Below are some important tips to help you organize your study sessions effectively:
Tips for Organizing Your Study Time
| Tip | Description |
|---|---|
| Set Clear Goals | Define what you need to accomplish in each study session. Break larger topics into smaller, more manageable chunks to avoid feeling overwhelmed. |
| Prioritize Topics | Focus on the most challenging or important areas first. Spend extra time on topics that you find difficult or unfamiliar. |
| Create a Study Schedule | Plan your study sessions in advance. Designate specific times each day to study and stick to that schedule for consistency. |
| Take Regular Breaks | Taking short breaks every 25-30 minutes helps maintain focus and prevents burnout. Use these breaks to relax or stretch. |
| Stay Organized | Keep your study materials, notes, and resources neatly organized. This reduces distractions and makes it easier to find what you need. |
| Use Active Learning Techniques | Engage with the material by summarizing information, asking questions, or teaching concepts to someone else. This reinforces learning. |
By following these strategies, you will be able to approach your study sessions with a clear plan, making it easier to manage your time and material effectively. The more organized your approach, the better prepared you will be for any assessment.
Effective Time Management Tips for Studying
Time management plays a crucial role in preparing for any academic assessment. Organizing your study schedule wisely ensures that you cover all necessary material without last-minute stress. By prioritizing tasks and using time efficiently, you can increase productivity and improve your understanding of the content. The following tips will help you make the most of your study time and boost your performance.
Essential Time Management Strategies
- Set Specific Goals: Break your study material into smaller, manageable tasks. Set clear objectives for each session, so you know exactly what you need to achieve.
- Use a Study Calendar: Plan your study schedule ahead of time. Allocate specific days and hours for each subject to ensure balanced coverage.
- Prioritize Difficult Topics: Tackle the most challenging subjects first when your energy is at its peak. This will give you more time to focus on areas that need the most attention.
- Use the Pomodoro Technique: Study in focused intervals of 25-30 minutes, followed by a 5-minute break. This method helps maintain concentration and reduces mental fatigue.
- Avoid Multitasking: Stick to one task at a time to ensure quality study time. Switching between tasks can lead to distraction and decreased efficiency.
- Stay Consistent: Make studying a daily habit. Consistency helps you retain information better and reduces the pressure of cramming later on.
Tools to Help You Stay on Track
- Timers and Alarms: Set timers for each study session to help you stay focused and remind you when it’s time for a break.
- Study Apps: Use apps that track your study progress, block distracting websites, and help you stick to your schedule.
- Study Groups: If possible, work with classmates to review material. Discussing topics together can enhance understanding and reinforce memory.
By implementing these time management tips, you will be able to study smarter, not harder. A structured approach to studying leads to better retention, reduced anxiety, and overall academic success.
Common Mistakes to Avoid on the Exam

When preparing for an academic assessment, avoiding common pitfalls can make a significant difference in your performance. Many students fall into certain traps that can impact their overall score, from misreading questions to wasting time on less important tasks. Recognizing these potential mistakes beforehand will help you approach the test with more confidence and clarity. Here are some of the most frequent errors and how to avoid them.
- Misunderstanding the Question: It’s crucial to carefully read and comprehend each question. Skipping over key details or rushing through can result in answering incorrectly. Always take a moment to ensure you understand what is being asked before writing your response.
- Overthinking Simple Questions: Sometimes, the simplest questions can be the trickiest. Don’t overcomplicate your answers. Trust your first instinct and avoid second-guessing yourself, unless you are certain there’s a mistake.
- Spending Too Much Time on One Question: While it’s important to give thoughtful answers, don’t spend an excessive amount of time on a single question. If you find yourself stuck, move on and return to it later, once the easier questions have been tackled.
- Leaving Questions Blank: Always attempt to answer every question, even if you’re unsure. A blank answer earns you no points, but a well-educated guess might get you partial credit.
- Failing to Manage Time: Poor time management can lead to rushed answers and missed questions. Allocate time to each section and keep an eye on the clock to ensure you can finish the test comfortably.
- Not Reviewing Your Answers: If time permits, always review your answers before submitting the test. Look for any careless mistakes, incomplete answers, or questions you may have skipped.
- Not Following Instructions: Exam instructions may seem repetitive or obvious, but failing to follow them can lead to unnecessary errors. Pay attention to word counts, required formats, and specific directions for each section.
By being aware of these common mistakes, you can improve your chances of performing at your best and avoid unnecessary setbacks. Stay calm, stay focused, and approach each question with care and clarity.
Strategies for Answering Multiple Choice Questions

Multiple choice questions can be challenging, but with the right strategies, you can improve your accuracy and speed. These types of questions often contain distractors designed to confuse, but understanding how to approach them can help you identify the correct answer. Below are some effective techniques for tackling multiple choice questions with confidence.
- Read the Question Carefully: Before looking at the options, make sure you fully understand the question. Pay attention to key phrases such as “except,” “always,” or “never,” which can change the meaning of the question significantly.
- Eliminate Clearly Wrong Answers: Start by crossing out the answers that are obviously incorrect. This will narrow down your choices and increase your chances of selecting the correct option, even if you need to make an educated guess.
- Look for Clues in the Question: Sometimes the question itself can contain hints or keywords that align with one of the options. Look for any familiar terms or concepts that can help you identify the correct answer.
- Beware of Absolute Statements: Be cautious when an answer choice contains words like “always” or “never.” These absolutes are often incorrect because they leave little room for exceptions. Choose answers that offer more flexibility, unless you are certain the statement is universally true.
- Consider the Context: Think about the broader context of the subject when choosing an answer. If you are unsure, reflect on what you have learned in class and try to recall related information that may help you make the best decision.
- Watch Out for Similar Answers: If two or more options seem very similar, one of them is usually correct. Compare the subtle differences between them, paying attention to small details that might indicate which one is the right choice.
- Don’t Overthink: Trust your first instinct when you have a strong initial idea. Overthinking can lead to second-guessing, which may result in choosing the wrong answer. If you’re unsure, mark the question and move on, returning to it later if time allows.
- Use All Available Time: If you finish early, go back and double-check your answers. Make sure that you didn’t misread any questions and confirm that you’ve chosen the most accurate option.
By applying these strategies, you can enhance your ability to correctly answer multiple choice questions and boost your overall performance. Staying calm and systematic in your approach will help you navigate through these questions with ease.
Reviewing Past Exam Papers and Practice Tests
One of the most effective ways to prepare for any assessment is to review previous test papers and practice exercises. This method helps you familiarize yourself with the format and types of questions that may appear, as well as identify areas where you might need additional focus. By working through past materials, you can assess your strengths and weaknesses, boosting both your confidence and performance.
Why Reviewing Past Papers is Beneficial
Looking over past assessments provides a unique opportunity to understand the testing style and identify recurring themes or topics. These practice exercises often reflect the core subjects that are repeatedly tested, giving you a clear idea of where to direct your attention. Regularly engaging with this material helps reinforce knowledge, improving recall during the actual test.
- Familiarize with Question Formats: Different assessments may ask questions in various formats, such as multiple choice, short answer, or essay-based. Reviewing old papers allows you to become comfortable with these structures, reducing test anxiety.
- Identify Common Topics: Many exams focus on specific key areas. By reviewing old tests, you can identify these recurring topics and prioritize them in your study sessions.
- Improve Time Management: Practicing under timed conditions can help you manage the clock during the actual test. Simulating the exam environment allows you to gauge how much time to spend on each question.
How to Make the Most of Practice Tests
Practice tests are not only helpful for improving knowledge, but they also enhance your ability to apply concepts under pressure. Here’s how you can use them effectively:
- Take Tests Under Real Conditions: Try to replicate the actual testing environment as much as possible. This includes timing yourself, minimizing distractions, and simulating the actual test day.
- Review Your Mistakes: After completing a practice test, thoroughly review your mistakes and understand why you got an answer wrong. This analysis helps prevent repeating the same errors.
- Use Feedback for Improvement: Use feedback from teachers, tutors, or online resources to address areas of weakness. This targeted approach can make a significant difference in your overall preparation.
By consistently reviewing past materials and practicing under test-like conditions, you will be able to fine-tune your skills and increase your chances of success. The more you engage with the content, the more prepared you will be when the actual assessment arrives.