
Preparing for a major assessment in the field of physical and human environments can feel overwhelming. With numerous topics to cover, it’s essential to know which areas demand the most attention and how to approach the material effectively. A thorough understanding of key concepts and their real-world implications will be crucial for performing well.
Mastering core concepts will help you tackle any question, whether it involves understanding natural features, cultural influences, or global interconnections. Focus on the main principles that link various aspects of the planet’s structure, from the formation of landscapes to the distribution of populations.
By practicing with relevant material and refining your recall of essential facts, you’ll build confidence in addressing a range of questions. Concentrating on relationships between regions, climates, and human activities will also give you an edge. Make sure to go beyond memorization by understanding why certain patterns exist and how they affect the world today.
Comprehensive Review for Your Upcoming Assessment
Preparing for a comprehensive evaluation of the planet’s physical and cultural landscapes requires a methodical approach to ensure you grasp essential concepts. Focusing on key regions, environments, and human influences will help you respond to various questions effectively. Understanding the interconnectedness of these elements provides a foundation for success.
To succeed, it’s important to familiarize yourself with the critical factors that shape natural formations, climate patterns, and population distribution. A solid grasp of how different elements influence each other will allow you to apply knowledge to real-world situations. From identifying geographical landmarks to explaining the impact of human activities, each topic builds upon the last.
Prioritize the main areas that are most likely to appear on the assessment. This includes major continents, oceans, mountain ranges, rivers, and the diverse climates around the world. By revisiting essential definitions and strengthening your understanding of how different systems function together, you will be well-prepared for any question that comes your way.
Key Topics to Focus On
When preparing for an assessment covering the planet’s physical and cultural landscapes, it’s essential to target the most significant concepts and regions. Understanding core principles will help you connect the dots between various topics and apply them to a range of questions. Prioritizing the most relevant subjects allows for better retention and greater success on your test.
Start with the fundamental features of the Earth’s surface, including landforms like mountains, valleys, and plains. Understanding how natural forces shape these areas and their impact on human development will be crucial. Additionally, focus on major climate zones and the factors that influence weather patterns across different regions.
Another area to concentrate on is the distribution of populations and the factors that lead to migration. The study of political boundaries, capitals, and major countries is also vital, as is the recognition of key rivers, seas, and oceans. By ensuring familiarity with these topics, you’ll build a strong foundation for answering a variety of questions accurately.
Understanding Key Concepts in Physical and Human Systems
To excel in this subject, it’s crucial to grasp the fundamental ideas that shape our planet’s landscapes, climate, and human activities. These concepts form the foundation of your knowledge and will help you link different areas together. Understanding these core principles will not only aid in memorization but also in applying your knowledge to more complex questions.
Key concepts can be grouped into a few major categories:
- Physical Features: Learn how natural processes shape landforms and influence climate patterns.
- Human Interactions: Understand how humans adapt to and modify their environment through agriculture, urbanization, and technology.
- Cultural Regions: Study the distribution of languages, religions, and traditions across the globe.
- Political Boundaries: Get familiar with the formation and significance of borders and capitals.
Additionally, it’s important to consider how these concepts are interconnected. For example, how climate influences human settlement patterns or how physical barriers affect transportation and trade. A deep understanding of these relationships will help you navigate complex topics and provide a clearer perspective on various regions of the world.
Geographic Features You Need to Know
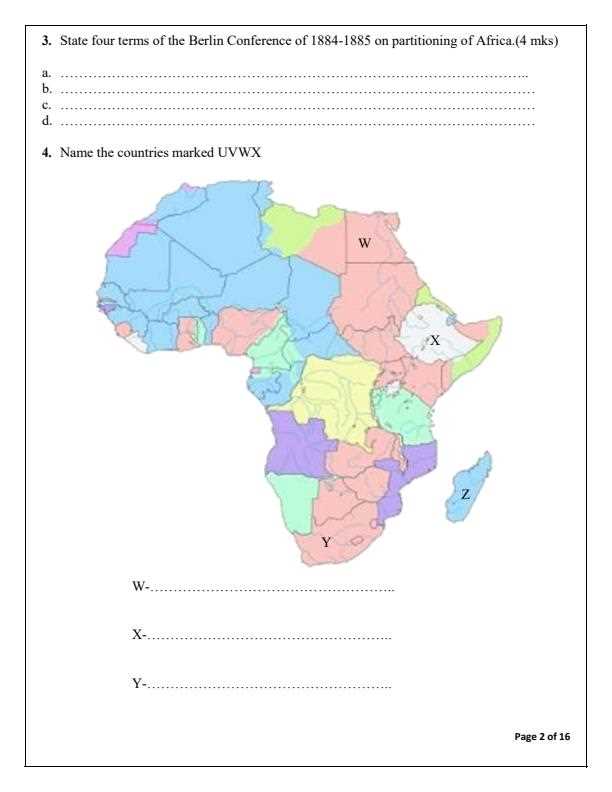
For a thorough understanding of the planet’s physical landscape, it’s essential to familiarize yourself with the most prominent natural features. These include landforms, bodies of water, and climate zones that have shaped the way humans live and interact with their environment. A strong grasp of these elements will allow you to answer questions about both natural formations and their significance in various regions.
The following features are key to your preparation:
- Mountains: Major ranges like the Himalayas, Andes, and Rockies play a critical role in influencing weather patterns, migration, and human settlement.
- Rivers: Know the significance of major rivers such as the Nile, Amazon, and Yangtze. These bodies of water have historically been centers of civilization.
- Oceans and Seas: Be familiar with the largest oceans (Atlantic, Pacific, Indian) and their impact on global trade and climate.
- Deserts: Understand the characteristics of vast arid regions like the Sahara and Arabian deserts, and how they affect human life and culture.
- Plateaus and Valleys: Recognize the importance of flat elevated areas and deep valleys in shaping local economies and ecosystems.
Understanding how these features interact with each other, such as the way mountains influence weather patterns or rivers provide water resources, is key to mastering the material. Focus on the geographic features that are most influential in different regions to ensure you’re prepared to tackle any related questions.
Tips for Effective Map Reading
Map reading is an essential skill for understanding the layout of regions, identifying key landmarks, and visualizing spatial relationships between different areas. Being able to interpret maps accurately will help you make sense of various locations and physical features. By following a few practical tips, you can improve your ability to read and analyze maps efficiently.
Here are some key strategies to enhance your map reading skills:
- Understand the Legend: Always start by reviewing the map’s legend or key to familiarize yourself with the symbols and color codes used. This will help you identify different features like mountains, rivers, and political boundaries.
- Pay Attention to Scale: The scale of a map shows the relationship between distances on the map and actual distances on the ground. Be sure to check the scale to avoid confusion when calculating distances.
- Identify the Compass Rose: The compass rose indicates directions on the map. Understanding cardinal directions (North, South, East, West) will help you orient yourself and navigate through the map.
- Look for Physical and Political Features: Maps often distinguish between physical features like mountains and bodies of water, and political features such as countries, cities, and borders. Knowing how to differentiate them will make it easier to understand the map’s purpose.
- Use Grid Coordinates: Many maps include a grid system that allows you to locate specific points more precisely. Familiarize yourself with how grid coordinates work to pinpoint locations quickly.
By mastering these tips, you’ll be able to read and interpret maps with confidence, helping you understand geographical layouts and relationships between different regions effectively.
Important Global Landmarks and Locations
Recognizing key landmarks and their locations is crucial for understanding the physical and cultural layout of the planet. These landmarks, whether natural or man-made, offer insight into historical, environmental, and societal developments. Familiarity with these locations will not only improve your understanding but also help in identifying their significance in various contexts.
Natural Landmarks
Some of the most iconic and influential natural landmarks have shaped both ecosystems and human settlements over the centuries. These include:
- Mount Everest: The highest peak in the world, located in the Himalayas, influencing both weather patterns and human exploration.
- The Grand Canyon: A vast geological formation in the United States, known for its stunning rock layers and rich geological history.
- The Amazon Rainforest: The largest tropical forest on Earth, critical for global biodiversity and carbon absorption.
- The Sahara Desert: The world’s largest hot desert, affecting climate and human migration patterns across northern Africa.
Man-Made Landmarks
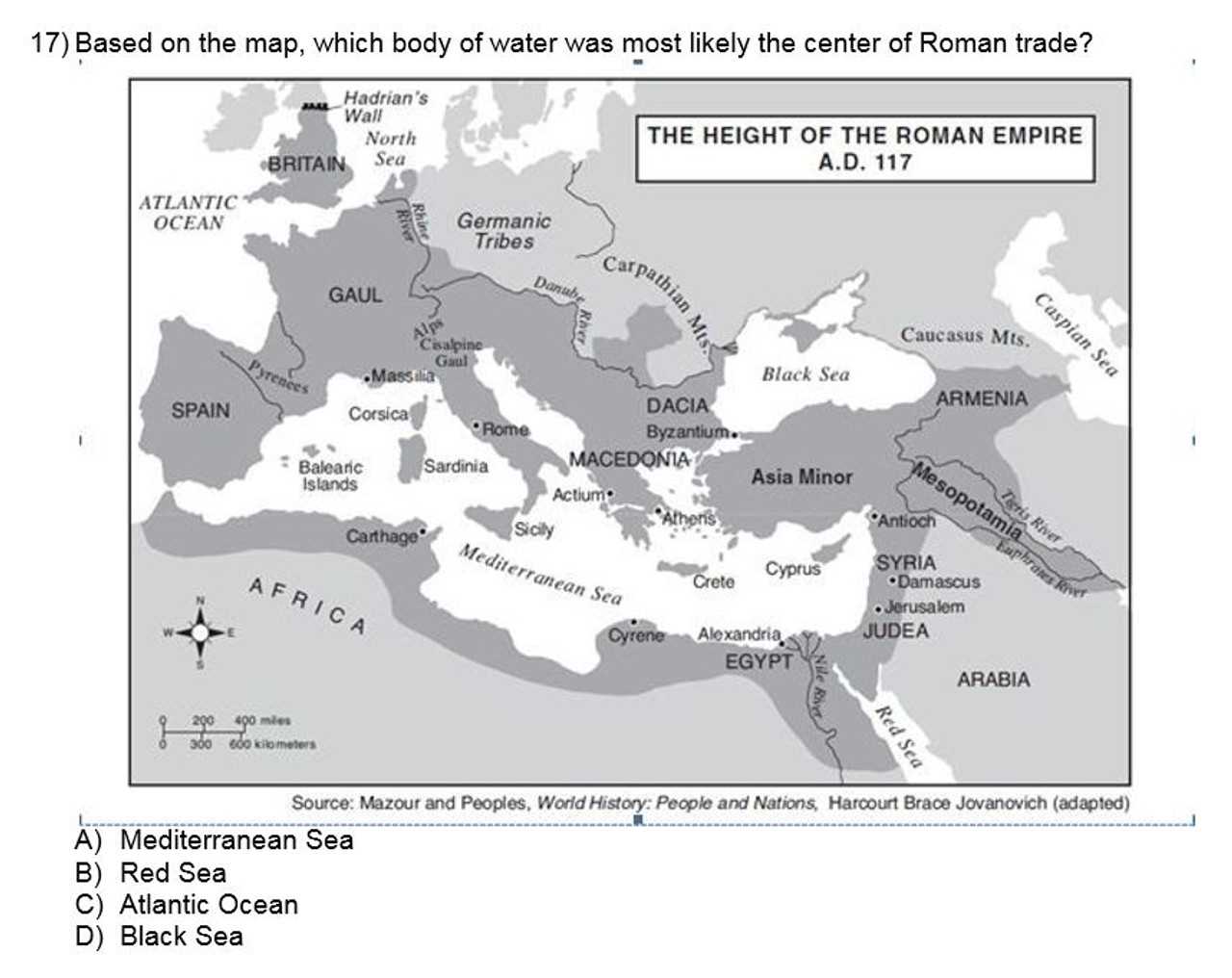
In addition to natural formations, many human-made structures hold immense cultural and historical value. These landmarks often represent the ingenuity and legacy of past civilizations:
- The Great Wall of China: An ancient defense structure stretching across northern China, symbolizing the country’s history and strength.
- The Pyramids of Giza: One of the Seven Wonders of the Ancient World, located in Egypt, highlighting the architectural brilliance of early civilizations.
- The Eiffel Tower: A world-famous symbol of France, located in Paris, representing innovation in architecture and engineering.
- The Taj Mahal: A stunning mausoleum in India, known for its beauty and cultural significance as a symbol of love.
Being familiar with these global landmarks will help in understanding the broader historical, environmental, and cultural contexts that define different regions across the globe.
How to Memorize Country Borders
Memorizing the boundaries between countries can be a challenging but rewarding task. Understanding where one nation ends and another begins is fundamental to mastering global regions. With the right techniques and tools, you can improve your recall and gain confidence in recognizing borders quickly and accurately.
Effective Techniques for Memorization
There are several strategies that can help you commit borders to memory:
- Use Visual Aids: Maps and interactive tools can enhance your ability to visualize borders. Regularly studying detailed maps will help solidify these mental images.
- Focus on Familiar Regions: Start with countries that share well-known borders, such as the United States and Canada, or France and Germany. Familiar areas are easier to recall and can serve as anchors for remembering others.
- Chunking Method: Break down the world into smaller regions, such as continents or groups of neighboring countries, and focus on memorizing each chunk separately before moving on to the next.
- Create Associations: Link countries that share borders with memorable characteristics, like cultural ties, historical events, or geographic features. Associating facts with borders will make them easier to remember.
Practice and Reinforcement
Repetition is key to reinforcing what you’ve learned. Consistent practice through quizzes or flashcards can help improve your recall. Try testing yourself with different maps and gradually increase the level of difficulty. Also, challenge yourself by focusing on lesser-known borders or those that are frequently confused.
- Timed Quizzes: Use online quizzes to test your knowledge and race against the clock. This will improve both speed and accuracy.
- Interactive Tools: Consider using apps or websites that offer interactive maps for memorizing borders, allowing you to practice with instant feedback.
By combining these strategies and practicing regularly, you’ll strengthen your ability to recall country borders and develop a deeper understanding of global boundaries.
Mastering Climate Zones and Regions
Understanding the diverse climate zones across the globe is essential for grasping how weather patterns affect ecosystems, human activities, and regional development. Different areas of the world experience distinct climates that influence everything from agriculture to urban planning. By mastering these climate regions, you will be able to recognize the major characteristics of each and their impact on life in those areas.
Climate zones can be categorized based on temperature, precipitation, and seasonal variations. To fully understand these distinctions, it’s helpful to break them down into key regions:
- Tropical Zones: These areas experience warm temperatures year-round with high humidity and frequent rainfall. Tropical rainforests and savannas are common in these zones, and they are typically found near the equator.
- Desert Regions: Characterized by very low precipitation, these areas can have extreme temperature variations between day and night. Deserts such as the Sahara and Arabian Desert are examples of regions with harsh conditions.
- Temperate Zones: These regions experience moderate temperatures and distinct seasonal changes. They include regions such as much of Europe, parts of North America, and East Asia, where winters are cold and summers are warm.
- Polar Regions: Found at the Earth’s poles, these areas are extremely cold with long winters and short summers. The Arctic and Antarctic are the most notable examples of polar climates.
Understanding how these climate zones overlap and transition is key to visualizing the Earth’s climate system. For instance, coastal areas may experience milder temperatures due to the influence of oceans, while inland regions may face more extreme conditions. Knowing the characteristics of each zone allows you to predict the types of vegetation, animals, and human activities that are possible in each area.
Political Divisions and Countries Explained

Understanding the political organization of the globe involves recognizing the structures that divide regions into separate entities with distinct boundaries, governments, and cultures. These divisions can range from countries and states to provinces and territories, each with its own level of sovereignty and control. In this section, we will explore how these divisions shape the way people live, interact, and govern themselves.
Types of Political Divisions

Political divisions can be organized at various levels, and each level of division plays a unique role in the governance of a region. Here are some common categories:
- Countries: The largest and most recognized political entities, countries are sovereign states with defined borders and centralized governments that manage national affairs.
- States and Provinces: These divisions occur within larger countries and usually have their own local governments to handle regional matters, such as education, transportation, and law enforcement.
- Territories: Some regions are considered territories, meaning they are governed by another nation or have limited self-governance, like Puerto Rico in relation to the United States.
- Capitals: Most countries have a capital city that serves as the administrative and political center of the government, such as Washington D.C. in the United States or Paris in France.
Understanding National Borders
National borders define the extent of a country’s territory and separate it from its neighboring countries. These boundaries are often influenced by a combination of historical, political, and natural factors. For example, rivers, mountain ranges, and oceans can naturally form borders, while historical events like wars and treaties often lead to the establishment of political boundaries.
- Natural Boundaries: Rivers, lakes, and mountain ranges often serve as natural borders between countries, as they are clear and difficult to cross.
- Artificial Boundaries: Many borders are created through human decisions, such as treaties, negotiations, or conflicts, and may not align with natural features.
- Disputed Areas: In some cases, borders are contested by two or more countries, leading to conflicts over land and resources.
Recognizing how political divisions operate allows for a clearer understanding of global interactions, conflicts, and the reasons behind the formation of countries and regions.
Significance of Historical Geography Events
Historical events that shape the physical and political landscape of the world have a profound influence on how regions develop and interact. Understanding the impact of these events helps to provide a context for modern geographical divisions, cultural identities, and global relations. Whether through wars, treaties, or the establishment of trade routes, these pivotal moments have left lasting marks on the map.
Key Events That Changed Borders
Throughout history, specific events have significantly altered territorial boundaries, creating new nations or dissolving old ones. These events often reflect the dynamic nature of human conflict, diplomacy, and migration.
| Event | Year | Impact on Borders |
|---|---|---|
| Treaty of Versailles | 1919 | Redrew the map of Europe after World War I, creating new countries and adjusting boundaries. |
| American Revolution | 1776-1783 | Established the United States and changed the territorial division in North America. |
| Fall of the Berlin Wall | 1989 | Led to the reunification of Germany and the collapse of Eastern European communist states. |
| Indian Independence | 1947 | Resulted in the partition of India and the creation of Pakistan, drastically changing the region’s borders. |
The Role of Exploration and Trade
Exploration, trade routes, and the movement of people have also played an essential role in shaping global geography. These activities facilitated the exchange of goods, culture, and ideas, but they also contributed to the shifting of territorial claims and the spread of influence.
- Colonial Expansion: European powers established colonies across the Americas, Africa, and Asia, significantly altering regional boundaries and cultures.
- Silk Road: The ancient trade route connected the East and West, fostering cultural exchange and influencing the development of cities and regions along the path.
- Age of Exploration: The voyages of explorers like Christopher Columbus and Vasco da Gama led to the discovery of new lands and the reshaping of global trade networks.
These historical events continue to influence modern political, economic, and social landscapes, offering insight into the ongoing evolution of regions and their borders.
Reviewing Economic Geography for Exams
When preparing for assessments in the field of physical regions and their economies, it is crucial to grasp the various concepts that influence the production, distribution, and consumption of goods and services. A solid understanding of how human activities interact with natural resources, trade networks, and industries can make a significant difference in your performance. In this section, we will highlight key aspects that you should focus on to enhance your comprehension and recall during evaluations.
Key Economic Concepts to Master
Familiarity with certain economic terms and principles is essential for understanding the functioning of economies at both global and local levels. Below are the main topics that you should review thoroughly:
- Resources: Understand the different types of resources (renewable, non-renewable, and human resources) and how their availability impacts economies.
- Trade and Markets: Review how international trade and market systems shape global economies, including the role of supply and demand, tariffs, and trade agreements.
- Industrialization: Be able to explain how industrial growth has transformed economies, particularly through the development of manufacturing and technological innovation.
- Globalization: Understand how the increasing interconnectedness of economies has led to both opportunities and challenges for nations.
- Economic Systems: Learn the differences between command, market, and mixed economies and how they operate in different parts of the world.
Geographical Factors Affecting Economic Growth

Geographical features often play a significant role in shaping the economic activities of a region. Being able to link natural landscapes to economic patterns is essential for a comprehensive understanding of economic processes.
- Climate: The local climate can determine what crops can be grown, which industries are viable, and how resources are utilized.
- Location: Strategic locations, such as access to waterways, coasts, and proximity to natural resources, greatly influence trade and economic development.
- Natural Resources: The availability of essential resources like water, fossil fuels, and minerals often dictates the economic power of a region.
By mastering these concepts and understanding the relationship between human activity and the environment, you will be well-prepared to tackle questions that require insight into how economies function and evolve.
Key Rivers and Mountains to Remember
When preparing for assessments related to the physical features of the Earth, it is essential to be familiar with the most significant natural landmarks, such as major rivers and mountain ranges. These geographical features play vital roles in shaping cultures, economies, and ecosystems. In this section, we will explore some of the most important rivers and mountains that you should focus on to ensure a solid understanding of their geographical significance.
Important Rivers Around the World
Rivers are crucial in terms of providing water, transportation routes, and supporting agriculture in many regions. Knowing the major rivers and their locations will help you connect their role in the development of civilizations and economies.
| River Name | Continent | Length | Significance |
|---|---|---|---|
| The Nile | Africa | 6,650 km | Supports agriculture and civilization development in Egypt and Sudan. |
| The Amazon | South America | 4,345 km | Home to the largest rainforest and vital for biodiversity. |
| The Yangtze | Asia | 6,300 km | Essential for trade, irrigation, and cultural development in China. |
| The Mississippi | North America | 3,780 km | Critical for trade and transportation in the United States. |
Notable Mountain Ranges
Mountain ranges are not only geological formations but also influential in determining climate patterns, ecosystems, and human settlements. Here are some of the most notable mountain ranges to be aware of:
| Mountain Range | Continent | Highest Peak | Importance |
|---|---|---|---|
| The Himalayas | Asia | Mount Everest (8,848 meters) | Highest mountains in the world, influencing climate and culture in South Asia. |
| The Andes | South America | Aconcagua (6,961 meters) | Longest mountain range in the world, impacting South America’s climate and agriculture. |
| The Alps | Europe | Mont Blanc (4,810 meters) | Key for tourism, agriculture, and historical significance in Europe. |
| The Rocky Mountains | North America | Mount Elbert (4,401 meters) | Important for ecosystems, resources, and tourism in Canada and the United States. |
These rivers and mountain ranges are fundamental to the natural world and human activities. Understanding their locations, characteristics, and significance will help you to connect their geographical importance with historical, cultural, and economic contexts. Be sure to review their key features for a comprehensive understanding of Earth’s physical environment.
Essential Geographical Terms to Study
To effectively navigate the complexities of the Earth’s physical and cultural features, it is crucial to understand key terms that describe these elements. A solid grasp of fundamental terminology helps in interpreting maps, understanding ecosystems, and identifying important locations. This section highlights essential concepts and definitions that will enhance your comprehension of various geographical aspects.
Basic Geographical Features
Familiarity with common terms related to landforms, bodies of water, and other physical elements is vital. These terms form the foundation of understanding the world’s landscapes and environments.
- Continent: A large continuous mass of land, typically divided into regions like Asia, Africa, and Europe.
- Island: A piece of land surrounded by water, smaller than a continent.
- Mountain: A large natural elevation of the Earth’s surface, usually with a peak.
- River: A large natural stream of water flowing toward an ocean, sea, or lake.
- Desert: A barren area of land where little precipitation occurs and living conditions are hostile for plant and animal life.
- Plateau: A flat elevated area that has been uplifted due to geological forces.
Human and Political Terminology
In addition to physical features, understanding human-made and political terms is essential when discussing the organization and distribution of human settlements and borders.
- Country: A distinct territorial body or political entity that is recognized as an independent state.
- Capital: The city where a government’s central offices and institutions are located.
- Border: A defined line separating two or more areas, usually marked by political boundaries.
- Region: An area that shares common characteristics, such as language, culture, or geography.
- Territory: An area of land under the jurisdiction or control of a government.
- Population Density: The number of people living per unit of area, often expressed as people per square kilometer.
Mastering these fundamental terms will provide a strong foundation for further study and help you understand complex geographical relationships and global patterns. By incorporating them into your learning process, you can improve your ability to analyze and interpret geographical data with accuracy and confidence.
Analyzing Population Distribution Patterns
Understanding how populations are spread across the planet is key to examining human settlement patterns, resource allocation, and regional development. Population distribution refers to the arrangement or spread of people within a given area, and this can vary significantly based on environmental, social, and economic factors. By analyzing these patterns, we can gain insight into the factors influencing population growth, migration, and urbanization.
Several factors influence where and why people settle in particular regions. These factors include climate, availability of resources, and proximity to trade routes or economic centers. Natural features such as rivers, coastlines, and fertile land are often key drivers of settlement, while economic opportunities, political stability, and infrastructure development also play crucial roles.
Key Factors Influencing Population Distribution
The following table summarizes the primary factors that influence how and where populations are distributed:
| Factor | Influence on Population |
|---|---|
| Climate | Extreme climates such as deserts or polar regions have low population densities due to harsh living conditions, while temperate climates attract higher populations. |
| Resources | Areas with abundant natural resources, such as water, arable land, and minerals, tend to support larger populations. |
| Accessibility | Regions with easy access to transportation networks, including rivers, roads, and ports, are more likely to experience higher population densities. |
| Economic Opportunities | Populations tend to concentrate in areas with thriving economies, job opportunities, and industrial development, leading to urbanization. |
| Political Stability | Regions with stable governments and political peace often attract larger populations, as people seek safety and security. |
Global Population Trends

Population distribution is not static; it evolves over time due to various trends such as urbanization, migration, and demographic shifts. Major cities, particularly in developed nations, tend to experience rapid population growth, while rural areas may see a decline as people move to urban centers for better job prospects and living conditions. Additionally, some regions experience population decline due to factors such as aging populations, emigration, and low birth rates.
By understanding the patterns of population distribution and the factors that drive them, we can make informed decisions about urban planning, resource management, and future development. Recognizing these trends helps policymakers address issues related to overcrowding, poverty, and environmental sustainability.
Resources for Geography Practice Tests
When preparing for assessments related to spatial knowledge, it is crucial to have access to reliable practice materials. These resources help reinforce learning by providing opportunities to test your understanding of various topics. Engaging with practice tests allows you to become familiar with the format, identify knowledge gaps, and improve time management under exam conditions. Below are several valuable resources to assist in your preparation for assessments focused on physical and cultural spaces.
There are numerous platforms that offer practice questions and tests, ranging from online quizzes to printed workbooks. These tools cover a wide array of topics, including map reading, physical features, political boundaries, and demographic trends. Many educational websites and apps provide interactive features such as feedback on answers, progress tracking, and personalized learning paths, making it easier to focus on areas where improvement is needed.
Top Websites and Tools for Practice
| Resource | Description | Access Link |
|---|---|---|
| Khan Academy | Offers free practice exercises and instructional videos on a variety of topics, including human and physical features. | Visit Website |
| Quizlet | Provides user-generated flashcards and practice tests on different subjects, including geography-related topics. | Visit Website |
| National Geographic | Offers quizzes, interactive maps, and articles focused on the environment, physical spaces, and human activity. | Visit Website |
| Sporcle | Features a wide range of quizzes on locations, capitals, landmarks, and more, with a fun and competitive edge. | Visit Website |
Books and Printed Resources

In addition to online tools, printed resources such as workbooks and printed flashcards are also excellent ways to test your knowledge. These books often include detailed explanations for each answer, helping you understand where you may have made mistakes and how to improve. Many popular educational publishers offer specialized books designed specifically for those preparing for tests in this field.
| Resource | Description |
|---|---|
| Scholastic Study Guides | Provides comprehensive practice exercises and mock tests with answers explained in detail. |
| McGraw-Hill’s Practice Tests | Offers a series of tests focusing on different aspects, from world landmarks to cultural patterns. |
By utilizing a mix of digital and printed resources, learners can enhance their knowledge retention and boost their confidence ahead of any assessment. Consistent practice with these tools will not only improve your test-taking abilities but also deepen your overall understanding of the subject matter.
Common Mistakes to Avoid in Geography
When studying spatial knowledge, it’s easy to make mistakes that could hinder your understanding and performance. Many learners overlook certain details or misinterpret information, which can lead to confusion during assessments or real-world applications. By being aware of the most common errors, you can improve your accuracy and strengthen your comprehension of key concepts. Below are some frequent pitfalls to watch out for when engaging with the subject.
Confusing Location and Direction
A common mistake is mixing up the names and directions of places. For instance, confusing the Northern and Southern Hemispheres or misidentifying continents and countries can be detrimental. The key to overcoming this is to regularly review maps and atlases and practice locating regions using both physical and political features. Additionally, understanding cardinal directions and how they relate to the position of different places is essential for a more accurate mental map.
Overlooking Scale and Distance
Another frequent error is not paying attention to scale and distance when reading maps. A map’s scale is essential for understanding the actual size and distance between locations. Ignoring scale can lead to incorrect assumptions about the proximity of places, making it difficult to estimate travel times or plan routes accurately. It’s important to consistently reference the scale and practice converting distances to real-world measurements to ensure precision in your understanding.
Relying Too Heavily on Memory

While memorization is important, it should not be the sole strategy for learning. Over-reliance on rote memorization without understanding the context behind the information can result in mistakes. Instead, focus on understanding how places are interconnected and the reasons behind their characteristics. For example, learning why certain climates are found in specific regions or understanding historical factors that influenced the development of cities can help create a deeper understanding.
Misinterpreting Data
Interpreting data, such as population statistics or climate patterns, can be tricky if you are not careful. It’s easy to misread graphs, tables, or charts, especially when they include complex numbers or trends. To avoid this mistake, practice analyzing different types of data and learn how to interpret various visualizations accurately. Understanding the context of data is just as important as knowing how to read it, so always ask questions about what the numbers or trends represent.
By avoiding these common mistakes, you can sharpen your skills and gain a more comprehensive understanding of spatial topics. Regular practice, a clear understanding of concepts, and careful attention to details will significantly improve your performance and ability to think critically about the subject matter.
Final Review Strategies for Success
As the time for final assessments approaches, it is essential to implement effective strategies for reviewing the material. A solid review process involves more than just cramming information; it requires focused, organized, and strategic preparation. By refining your approach, you can boost your confidence, enhance your recall, and perform at your best. Below are several proven techniques to help you succeed in the final stages of preparation.
1. Prioritize Key Topics
Begin your final review by identifying the most important concepts that are likely to appear. Focus on the following:
- High-priority areas covered in class and materials provided by instructors.
- Areas that you found challenging during previous lessons or assignments.
- Commonly tested topics based on past reviews or sample questions.
By concentrating on the most significant content, you ensure that you maximize your time and energy where it’s most needed.
2. Use Active Recall and Practice
Passive reading is often not enough for thorough comprehension. Instead, practice active recall by testing yourself on key concepts. Here are some helpful strategies:
- Write down what you know from memory, then check for accuracy.
- Create flashcards with questions on one side and answers on the other for quick self-quizzing.
- Work through practice questions or mock tests to simulate the actual conditions of the assessment.
Active recall engages your brain more effectively and strengthens long-term memory retention.
3. Break Down the Material into Manageable Chunks

Breaking your review into smaller, more manageable sections can make a large amount of information less overwhelming. Instead of trying to cover everything at once, break the content into categories such as:
- Regions and their physical features.
- Historical events and their impact on development.
- Key data points, such as population statistics or climate patterns.
By reviewing in chunks, you can concentrate on one section at a time, making it easier to digest and retain the material.
4. Focus on Understanding, Not Just Memorizing
While memorization is necessary, focusing on understanding the material at a deeper level will help you make connections between different concepts. This strategy can make it easier to recall information in context during assessments. Aim to:
- Explain concepts in your own words to test your understanding.
- Relate new knowledge to things you already know to build connections.
- Look for patterns or trends across different topics to improve conceptual clarity.
5. Get Adequate Rest and Manage Stress
Effective preparation isn’t just about what you do with your study time; it’s also about taking care of yourself. Make sure to:
- Take breaks during study sessions to avoid burnout.
- Get enough sleep, as rest is crucial for memory consolidation.
- Practice relaxation techniques to manage anxiety and stay calm during the review period.
Balancing study with self-care is key to staying sharp and focused during your final review.
By following these strategies, you can approach your review sessions with confidence and effectiveness. Remember, consistent preparation and smart study habits will set you up for success when it matters most.