
In business management, understanding how different variables impact financial outcomes is essential for making informed decisions. By mastering fundamental concepts related to how costs, sales, and production volume interact, individuals can effectively determine strategies for growth and sustainability. This section provides an in-depth look into the core principles that drive financial performance in any organization.
Grasping these principles is crucial for tackling various challenges in the field. Whether you’re planning for the future or optimizing current operations, understanding how changes in one area can influence the overall business environment is fundamental. This knowledge helps both managers and students navigate complex scenarios with confidence.
Preparing for assessments in this subject requires more than memorizing formulas. It involves a deep understanding of how to apply theoretical knowledge to real-world situations. Through practice, you can enhance your ability to approach problems systematically and deliver solutions that are both efficient and practical.
Cost Volume Profit Analysis Exam Guide
Understanding the key factors that affect financial outcomes in business is essential for tackling complex problems in various scenarios. The ability to evaluate how different elements interact allows for better decision-making and strategic planning. This section will provide an overview of the most important topics to focus on when preparing for assessments in this field, offering useful insights into the underlying concepts.
To succeed in this area, it is important to be comfortable with mathematical models and how they reflect real-world situations. Recognizing patterns and applying appropriate formulas enables you to solve problems quickly and accurately. Being able to break down complex challenges into manageable parts is crucial for both theoretical understanding and practical application.
Focus on key concepts such as the relationship between fixed and variable components, as well as how fluctuations in production levels can impact overall performance. These principles serve as the foundation for many problems you may encounter. By mastering these core ideas, you’ll be well-equipped to approach a variety of scenarios with confidence.
Understanding Cost Volume Profit Concepts
Grasping the relationship between different business factors is fundamental to managing financial performance. It involves understanding how specific elements like expenses, output, and revenue interact to affect the overall economic health of an organization. This section will explore key concepts that help to predict how changes in one area can impact others, providing a foundation for informed decision-making.
The following table outlines the key components that are central to these concepts:
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Fixed Expenses | Costs that remain constant regardless of production or sales levels. |
| Variable Expenses | Costs that fluctuate depending on the level of output or sales. |
| Break-even Point | The point at which total revenues equal total costs, resulting in no gain or loss. |
| Contribution Margin | The amount remaining from sales after covering variable costs, contributing to fixed costs and profits. |
| Margin of Safety | The difference between actual sales and break-even sales, indicating risk level. |
Mastering these core elements allows for better forecasting and a deeper understanding of how different factors affect business sustainability. Recognizing how each of these variables operates within a broader framework will enhance your ability to make strategic choices that drive success.
Key Formulas for CVP Analysis
To make well-informed decisions, it is crucial to apply the right mathematical formulas that reflect the relationship between various business variables. These formulas allow for quick calculations that help predict outcomes based on different scenarios. Below are the key formulas essential for understanding how changes in certain factors can affect financial results.
The table below highlights the main formulas used to evaluate the impact of different elements on an organization’s financial performance:
| Formula | Description |
|---|---|
| Break-even Point = Fixed Expenses / Contribution Margin per Unit | Calculates the level of output needed to cover all fixed expenses, resulting in no profit or loss. |
| Contribution Margin = Sales – Variable Expenses | Measures how much each unit sold contributes to covering fixed expenses. |
| Contribution Margin Ratio = Contribution Margin / Sales | Shows the percentage of sales that contributes to covering fixed expenses. |
| Margin of Safety = Actual Sales – Break-even Sales | Represents the difference between current sales and the break-even point, indicating the buffer before losses begin. |
| Target Profit Sales = (Fixed Expenses + Target Profit) / Contribution Margin per Unit | Determines the level of output required to achieve a desired target profit. |
Mastering these formulas is vital for solving real-world problems quickly and accurately. With a clear understanding of how to apply these equations, you can assess potential scenarios and make strategic decisions based on expected outcomes.
Common Cost Structures in CVP
Understanding different financial frameworks is essential for making informed decisions in any business. The structure of expenditures plays a critical role in determining the overall financial health and scalability of a company. By classifying expenses into specific categories, businesses can better forecast and plan their operations, especially when assessing the impact of changes in production or sales.
Types of Expense Structures
There are several common types of financial frameworks that businesses typically encounter. These structures allow for more accurate predictions and help in strategic planning. Below are the main categories:
- Fixed Expenses: These remain constant regardless of the level of production or sales. Examples include rent, salaries, and insurance premiums.
- Variable Expenses: These fluctuate based on the level of production or sales. Common examples include raw materials, direct labor, and shipping costs.
- Mixed Expenses: These contain both fixed and variable components, such as utilities that include a fixed monthly fee and a variable charge based on usage.
Analyzing Financial Frameworks
Once the different types of financial structures are understood, it becomes easier to assess how each component affects overall operations. The ability to distinguish between fixed and variable components is crucial when calculating key metrics and evaluating different business scenarios.
- Break-even Point: Understanding how different expenses impact the threshold at which a business neither makes a profit nor incurs a loss.
- Contribution Margin: Identifying how each unit sold contributes to covering fixed costs and eventually generating profit.
By recognizing these distinct structures, you can better manage resources and optimize financial strategies to achieve sustainable success.
Break-Even Point Calculation Techniques
Determining the level of output at which a business neither incurs losses nor generates a surplus is a key financial skill. It helps assess the minimum performance needed to cover all required expenses. Several methods exist to calculate this threshold, each offering a unique approach based on the business’s financial structure and the available data.
Basic Formula for Break-Even Calculation
The most straightforward way to calculate the break-even point involves using the basic formula. This technique requires identifying two key components: fixed expenses and contribution per unit. The formula is simple:
- Break-even Point = Fixed Expenses / Contribution Margin per Unit
By dividing the fixed expenses by the contribution margin, you can determine how many units need to be sold to cover all expenditures. This method is effective for businesses with consistent costs and sales prices.
Alternative Methods for Calculating Break-Even

For more complex financial structures, additional methods might be necessary. These approaches help address different scenarios where the basic formula might not fully capture the business dynamics:
- Break-even in Sales Dollars: This method calculates the sales needed to cover all expenses in terms of revenue rather than units sold. The formula is:
- Break-even Point in Dollars = Fixed Expenses / Contribution Margin Ratio
Another method is used when variable costs are not directly tied to the output level but fluctuate with various factors such as market conditions or pricing changes. These methods allow for a more refined estimate of the break-even point under changing circumstances.
Mastering these techniques equips businesses with a solid understanding of their financial boundaries, enabling more precise strategic planning and better decision-making.
Contribution Margin and Its Importance
The contribution margin is a vital metric that helps businesses determine how much revenue from each unit sold is available to cover fixed expenses and generate surplus. It represents the difference between sales revenue and variable costs, providing insight into how individual sales impact the financial health of a company. Understanding this figure allows businesses to evaluate the profitability of products and make informed decisions about pricing, product mix, and operational efficiency.
By calculating the contribution margin, companies can assess which products or services are contributing most to covering the fixed expenses. It serves as a key indicator when considering pricing strategies, cost-cutting measures, or expanding the product line. A higher contribution margin typically indicates a stronger ability to cover fixed costs and produce a surplus, making it an essential tool for strategic planning.
Furthermore, this metric is critical for decision-making processes. Whether a business is assessing the feasibility of new ventures, evaluating the impact of pricing changes, or analyzing product performance, the contribution margin provides valuable insights that drive smarter, more effective business strategies.
Analyzing Profitability Using CVP
Understanding how different factors impact the financial performance of a business is essential for making informed decisions. By examining various components like pricing, sales mix, and fixed expenditures, businesses can gain clarity on how these elements influence overall earnings. This approach helps determine the necessary conditions to reach a desired financial outcome, enabling organizations to focus on strategies that will maximize their success.
Identifying Key Factors That Affect Financial Outcomes
Several elements play a crucial role in determining whether a company reaches its financial goals. By evaluating the interplay of these variables, businesses can focus on the most impactful areas for improvement. Some of the key factors include:
- Pricing strategies
- Market demand and sales trends
- Fixed and variable expenses
By adjusting these variables, a company can understand the effect on its financial results and make adjustments to ensure profitability.
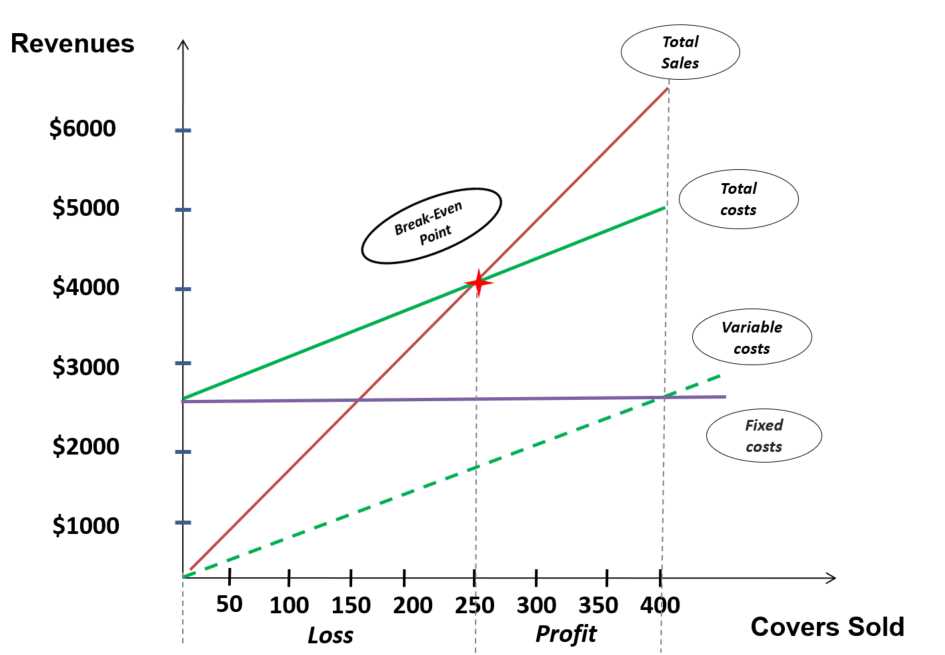
Using Graphs to Visualize Break-even Points
Graphs can provide a visual representation of how changes in different factors influence the overall financial picture. Below is an example of a basic graph depicting the relationship between sales and expenses, illustrating where the business reaches its balance point:
| Sales | Expenses | Break-even Point |
|---|---|---|
| 100,000 | 50,000 | 50,000 |
| 200,000 | 100,000 | 100,000 |
| 300,000 | 150,000 | 150,000 |
This table demonstrates how sales figures correspond to expenses, with the break-even point highlighted at various levels. By calculating these points, businesses can make adjustments to increase their margins and ensure consistent growth.
Interpreting CVP Graphs and Charts
Visual representations, such as graphs and charts, are powerful tools for understanding the relationship between different financial variables. They allow businesses to clearly see how changes in factors like pricing, sales, and fixed costs affect overall financial performance. By analyzing these visual aids, decision-makers can gain insights into key aspects of their operations, helping them adjust strategies for better results.
Understanding the Key Elements in Graphs
When interpreting these visual tools, it’s important to recognize the key components that impact the financial outcomes. The main elements typically include:
- Revenue line: Shows how income increases with sales.
- Expense line: Depicts the relationship between fixed and variable costs over time.
- Break-even point: The point where the revenue and expenses lines intersect, indicating no net gain or loss.
These elements allow businesses to pinpoint when they move from a loss to a gain, offering a clear target for decision-making.
Using the Graphs to Make Strategic Decisions
By examining the trends shown in the charts, companies can easily identify patterns in their operations. For example, a rising revenue line with an increasing expense line might indicate that while sales are growing, costs are also climbing, potentially affecting profitability. Conversely, if the revenue line starts to steeply rise while the expenses level off, it can signal an increase in efficiency.
Graphs and charts provide an intuitive way to evaluate the financial health of a business, enabling leaders to make informed decisions about pricing, production, and investment strategies.
Calculating Margin of Safety
Understanding the margin of safety is crucial for evaluating how much a business can endure in terms of a decline in sales before it begins to incur losses. This metric helps companies determine how resilient they are to adverse financial situations. By calculating this buffer, businesses can make informed decisions regarding risk management and operational adjustments to ensure continued profitability even in less favorable circumstances.
Formula for Margin of Safety

The margin of safety can be calculated using a simple formula. It measures the difference between actual sales and the break-even sales level. The formula is as follows:
Margin of Safety = Actual Sales – Break-even Sales
Once calculated, this value can be used to assess the financial stability of a business, giving it a cushion to absorb fluctuations without immediately impacting the bottom line.
Interpreting the Margin of Safety
A higher margin of safety indicates a greater buffer, meaning the company is in a stronger position to weather downturns in sales. Conversely, a lower margin of safety suggests that the business is more vulnerable to market changes. Companies can use this information to plan their strategies and make adjustments that mitigate potential risks.
By monitoring this metric regularly, businesses can better understand their financial position and make proactive decisions to avoid financial distress.
Role of Fixed and Variable Costs
Understanding the different types of expenses in a business is essential for effective financial planning and decision-making. Two primary categories of expenses are those that remain constant regardless of production levels and those that fluctuate depending on the output. Each type plays a unique role in determining the financial health and operational efficiency of a company.
Fixed Expenses

Fixed expenses are those that do not change with the level of goods or services produced. They remain constant over time, regardless of the business’s performance. These expenses are typically long-term obligations and are essential for maintaining business operations. Common examples include:
- Rent for facilities or office spaces
- Insurance premiums
- Loan repayments
- Depreciation on equipment
Managing fixed expenses effectively is crucial, as they represent ongoing financial commitments that must be met regardless of sales or production volumes.
Variable Expenses
Variable expenses, on the other hand, change in direct proportion to the level of output. As production increases, these expenses rise; conversely, when production decreases, they fall. Understanding these expenses helps businesses adapt quickly to changing market conditions. Some examples include:
- Raw materials
- Labor costs (wages for hourly workers)
- Utilities used in production
- Packaging and shipping costs
By monitoring variable expenses closely, businesses can make informed decisions about scaling production and optimizing resource use, which directly impacts overall financial outcomes.
In conclusion, both fixed and variable expenses are critical to understanding the operational dynamics of a company. Managing these costs effectively helps ensure financial stability and supports strategic planning for growth and profitability.
Examining Operating Leverage in CVP
Operating leverage refers to the relationship between fixed expenses and the changes in earnings resulting from fluctuations in sales. Companies with high operating leverage can experience significant variations in their earnings as a result of even small changes in revenue. This concept plays a crucial role in understanding how a company’s structure impacts its overall financial performance and risk level.
When a business has a higher proportion of fixed expenses, small increases in sales can lead to disproportionately larger gains in earnings. Conversely, during periods of declining sales, these companies may face more significant reductions in their earnings. The ability to manage this leverage effectively is essential for ensuring profitability during both favorable and challenging market conditions.
In summary, understanding operating leverage helps businesses assess their sensitivity to changes in sales and the potential risks involved. Properly managing this balance allows companies to maximize their returns while minimizing financial instability, particularly in dynamic market environments.
Real-World Applications of CVP Analysis
In business decision-making, understanding the relationship between fixed expenses, sales, and earnings is essential for determining the financial stability and profitability of a company. Real-world applications of this concept are diverse, as it helps companies identify the most effective pricing strategies, determine break-even points, and assess the impact of potential changes in their operations.
For instance, retailers often use this method to establish product pricing. By knowing how changes in sales volumes will affect their returns, they can adjust prices to maintain a competitive edge while ensuring profitability. In the manufacturing industry, companies can optimize their production processes by understanding how variations in fixed and variable expenses impact their bottom line. This information is especially useful when making decisions about scaling operations, launching new products, or entering new markets.
Moreover, companies in the service sector utilize this approach to evaluate the impact of changes in service delivery models, customer acquisition costs, and labor expenses. By modeling different scenarios, they can develop strategies to maximize revenue and minimize financial risks.
In summary, the application of this approach in various industries allows companies to make informed decisions that align their operational strategy with their financial goals, providing a roadmap for sustained success and growth.
Impact of Sales Price Changes on CVP
Adjusting the price at which products or services are offered can significantly influence the financial performance of a business. Understanding how these adjustments affect overall outcomes is crucial for strategic decision-making. Price modifications can alter several key factors, including the overall contribution to covering fixed expenses and achieving profitability. It is essential to evaluate how these changes impact both the required sales levels and the overall financial health of the company.
Effects of Price Increases

Raising the price of a product or service can lead to a range of outcomes, depending on the market dynamics and customer response. The following points highlight the potential effects:
- Higher Margins: Increasing prices typically leads to higher margins per unit sold, contributing more towards covering fixed expenses.
- Reduced Sales Volume: A price hike may lead to a decrease in the number of units sold if customers are sensitive to price changes.
- Impact on Break-Even Point: A higher price can reduce the number of units that need to be sold to cover fixed expenses, potentially lowering the break-even threshold.
Effects of Price Reductions
Lowering the price of goods or services can have the opposite impact. Key considerations include:
- Increased Sales Volume: A price reduction may stimulate higher demand, leading to an increase in the number of units sold.
- Lower Margins: While volume increases, the reduced price per unit may decrease the overall contribution towards fixed expenses, requiring higher sales to break even.
- Profitability Concerns: Without an increase in volume, reduced prices can diminish profitability, potentially leading to financial strain if not managed carefully.
In conclusion, price changes directly influence the financial structure of a business, and understanding these effects is essential for making informed pricing decisions that align with overall business goals. By strategically adjusting prices, companies can optimize their financial outcomes while balancing the need for competitive pricing and profitability.
Determining Profit at Various Sales Volumes

Understanding how varying levels of sales impact a company’s financial outcomes is crucial for effective decision-making. By calculating the financial return at different sales numbers, businesses can evaluate how performance changes as units sold increase or decrease. This helps in setting realistic targets, managing expenses, and ensuring that the organization remains financially healthy across different market conditions.
Key Factors Affecting Financial Results
The following factors must be considered when determining financial outcomes at different sales levels:
- Sales Price per Unit: The amount received from customers for each unit sold plays a direct role in the financial outcome. A higher price per unit can result in better returns, even with fewer units sold.
- Fixed Expenses: These expenses do not change regardless of the number of units sold. They must be covered before any financial returns are realized.
- Variable Expenses per Unit: These expenses change with each unit sold. As sales increase, so do these expenses, which directly impact overall financial returns.
Evaluating Profit at Different Sales Levels
To evaluate the financial results at varying sales numbers, follow these steps:
- Calculate the Contribution per Unit: Subtract variable expenses from the sales price to determine the amount each unit contributes toward covering fixed expenses.
- Determine Break-Even Sales: Calculate the number of units required to cover fixed expenses by dividing the total fixed expenses by the contribution per unit.
- Analyze Profit at Different Levels: To estimate profit at various sales numbers, multiply the contribution per unit by the actual number of units sold and subtract fixed expenses.
In summary, determining financial returns at different sales numbers helps businesses understand their break-even points and identify sales targets needed to achieve desired outcomes. By continuously monitoring sales performance, companies can make informed decisions to drive growth and maintain financial stability.
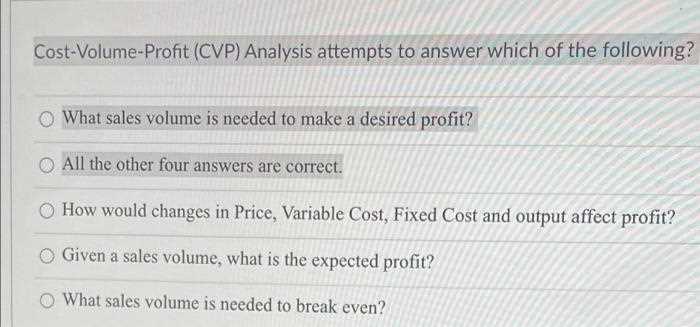
Exam Questions on CVP Formulas
Understanding the key formulas used to evaluate financial performance is essential for mastering related concepts. These formulas provide the necessary tools for determining important metrics such as the break-even point, the contribution margin, and the required sales to reach specific financial goals. By practicing with questions based on these formulas, individuals can sharpen their skills and apply the knowledge to real-world scenarios.
Important Formulas to Know
The following formulas are fundamental in calculating essential business metrics:
- Contribution Margin per Unit: The difference between the selling price per unit and the variable expenses per unit.
- Break-Even Point: The point where total revenue equals total expenses. It can be calculated by dividing fixed expenses by the contribution margin per unit.
- Required Sales for Desired Profit: To find the sales needed to achieve a specific profit, use the formula: (Fixed Expenses + Desired Profit) ÷ Contribution Margin per Unit.
Sample Problems and Solutions
Here are a few examples of how to apply the formulas in practice:
- Example 1: If the selling price of a product is $50, the variable cost is $30, and fixed expenses are $10,000, what is the break-even point?
- Solution: Contribution margin per unit = $50 – $30 = $20. Break-even point = $10,000 ÷ $20 = 500 units.
rubyCopy code
- Solution: Required sales = ($12,000 + $5,000) ÷ $15 = 1,133 units.
Practicing with such problems will strengthen the understanding of how these formulas work and how they can be applied to assess the financial health and performance of a business.
Typical CVP Case Study Scenarios
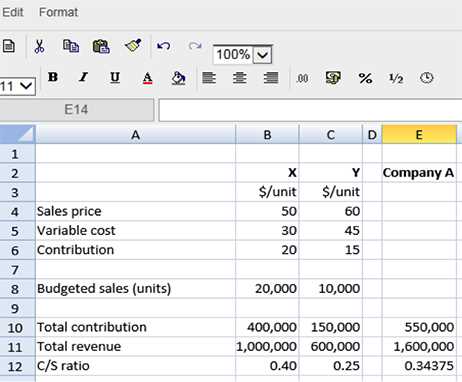
Case studies provide valuable opportunities to apply key concepts in realistic situations. They often involve analyzing a company’s financial setup and determining how different variables impact its overall financial health. Through such scenarios, individuals can better understand how adjustments in factors like price, production, or expenses affect outcomes like break-even points and the required sales to reach goals. By working through various cases, one can build practical skills to tackle similar challenges in the real world.
Scenario 1: New Product Launch
A company plans to introduce a new product to the market. The management wants to determine the number of units that need to be sold to cover the initial expenses and achieve a specific financial target. In this scenario, it is essential to calculate the break-even point, evaluate the impact of fixed and variable expenditures, and assess the effect of changes in the selling price on the overall outcome.
- Key Variables: Fixed expenses for production, price per unit, variable expenses per unit.
- Objective: Calculate the break-even point and the required sales for a desired financial goal.
Scenario 2: Expansion of Operations
Another case study involves a company considering an expansion of its operations. The expansion would involve increasing production capacity and introducing a larger product range. The company needs to evaluate how this move will affect its financial stability. Key aspects of this case include understanding how additional fixed and variable factors influence the number of units required to break even and how changes in fixed expenses might alter the company’s ability to meet financial goals.
- Key Variables: New fixed expenses due to expanded operations, potential increase in production efficiency, expected changes in selling price and variable expenses.
- Objective: Assess the impact of the expansion on financial performance and determine the necessary adjustments to maintain profitability.
By working through these scenarios, individuals can gain insight into how different aspects of business operations impact financial performance and how to make data-driven decisions in uncertain environments.
How to Answer CVP Exam Questions Effectively
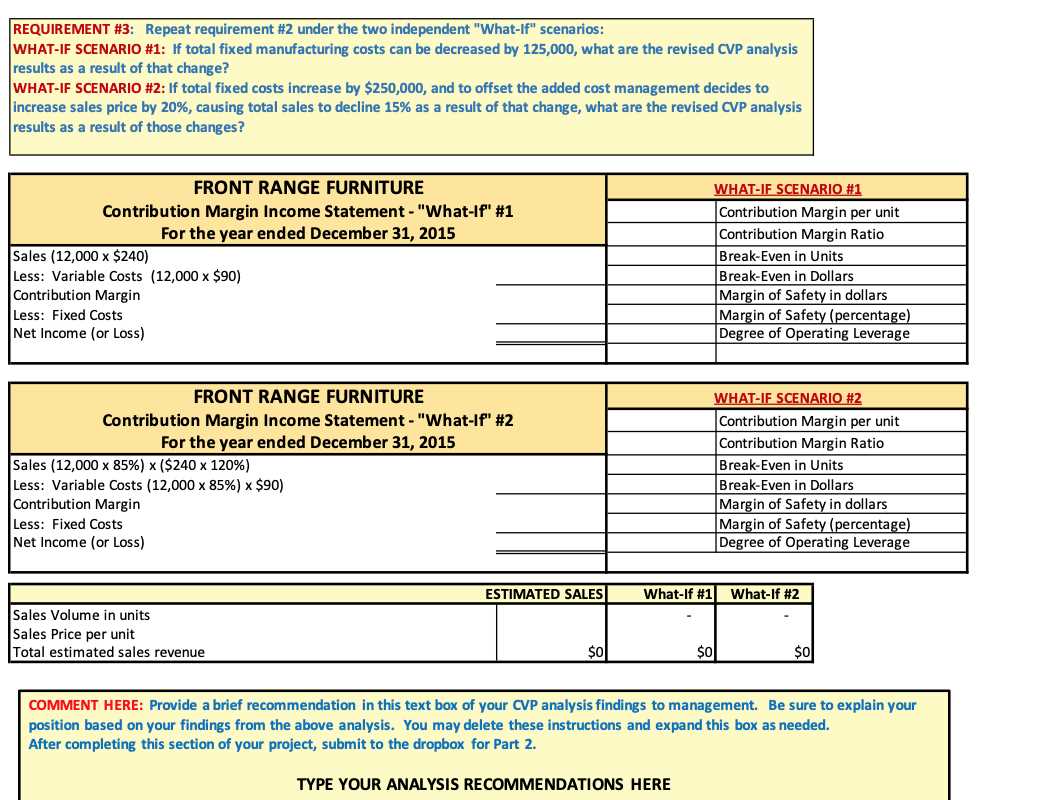
To approach these types of assessments with confidence, it’s essential to break down the problem into manageable steps. Understanding the fundamentals of how different financial factors interact will help you approach the scenario logically. Additionally, knowing the key formulas and how to apply them in different contexts will guide you in providing accurate and well-structured responses.
Follow these steps to improve your approach:
- Understand the Key Concepts: Familiarize yourself with the basic principles, such as fixed expenses, variable expenses, contribution margin, and break-even analysis.
- Identify the Variables: Carefully read the question to determine which financial elements are provided and which need to be calculated. This might include identifying changes in selling price, production levels, or fixed expenses.
- Apply the Formulas: Use the appropriate formulas to compute key values such as break-even points, required sales, or margin of safety. Always remember to adjust your calculations according to the specific details provided in the scenario.
- Double-Check Your Work: Verify your calculations and check that your answer aligns with the question’s requirements. Ensure that you are interpreting the data correctly and that your final response addresses the question fully.
Here’s an example of a breakdown for a typical problem:
| Step | Action | Formula/Method |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Identify fixed and variable expenses | Use the provided values from the problem |
| 2 | Calculate contribution margin | Contribution margin = Sales – Variable expenses |
| 3 | Determine break-even point | Break-even point = Fixed expenses / Contribution margin |
| 4 | Check required sales to reach a target | Required sales = (Fixed expenses + Target) / Contribution margin |
By following these steps and ensuring a systematic approach to each scenario, you will be able to answer these types of questions with clarity and precision.