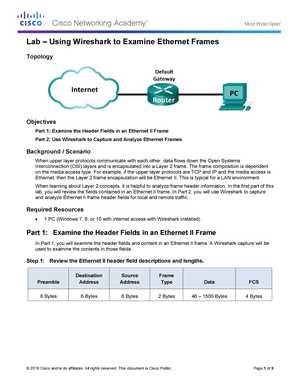
Learning the fundamentals of computer networks often requires hands-on experience with simulations that closely mirror real-world scenarios. These interactive exercises allow students and professionals to practice configuring network devices, troubleshooting issues, and applying theoretical knowledge in practical contexts. Successful completion of such tasks helps reinforce understanding and develop problem-solving skills in networking.
For those tackling complex network configurations, it is essential to have clear guidance on the best approaches and strategies. By breaking down each exercise step-by-step, users can build confidence in their abilities to manage various network components, from routers to switches. Gaining proficiency in these practical activities enhances both academic performance and real-world expertise.
In this guide, we’ll explore helpful tips and solutions for overcoming common challenges faced during network simulations. From basic configurations to more advanced troubleshooting, understanding key concepts and their application in virtual environments will set the foundation for mastering networking scenarios.
How to Approach Packet Tracer Tasks
When working on network simulation exercises, it’s essential to have a clear strategy for approaching the challenges presented. Whether you’re setting up devices, configuring protocols, or troubleshooting issues, a methodical approach can significantly improve efficiency and success. Understanding the structure and requirements of the task is the first step toward completing it effectively.
1. Analyze the Requirements
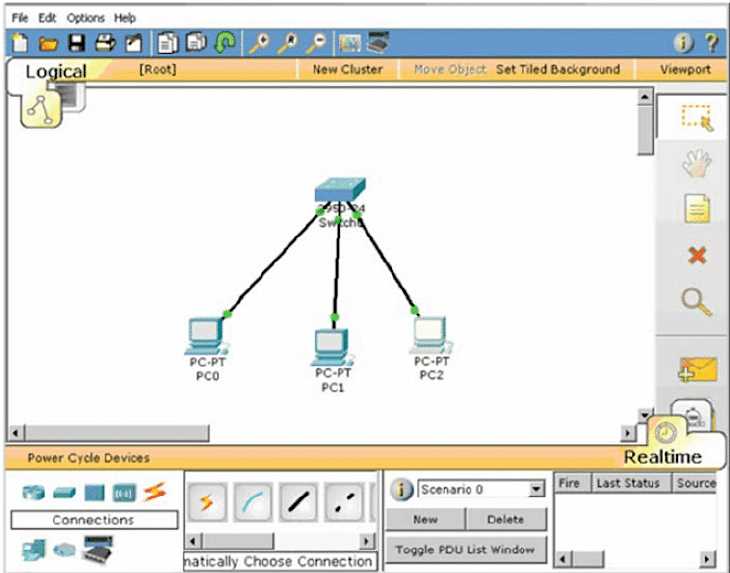
Before diving into the configuration process, take the time to carefully review the problem statement. Identify the devices involved, their connections, and the protocols or services that need to be configured. This overview will help you understand the broader context and set priorities for your actions.
2. Break the Task into Steps
Divide the task into smaller, manageable segments. Start with basic device configuration and then move on to more complex settings like routing or security measures. Completing each step systematically ensures that you won’t overlook critical details and makes troubleshooting easier if things don’t go as planned.
Common Challenges in Network Configuration Tasks
While working on network design and troubleshooting exercises, certain issues tend to arise frequently. These challenges can range from misconfigured settings to connection problems, each requiring a methodical approach to identify and resolve. Understanding common pitfalls can help you navigate through tasks more effectively and avoid potential setbacks.
1. Incorrect Device Configuration
One of the most common issues in network exercises is improper configuration of devices. This can include incorrect IP addressing, mismatched routing protocols, or improperly set up interfaces. These small errors can disrupt the entire network and make it difficult to troubleshoot. It’s essential to review every configuration step to ensure accuracy.
2. Connectivity Issues Between Devices
Connectivity problems often occur due to incorrect physical connections or software configurations. Ensuring that cables are correctly plugged in and that interfaces are enabled can help resolve these issues. Furthermore, verifying the correct routing or switching paths is crucial for smooth communication between network devices.
| Issue | Possible Cause | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Device not reachable | Wrong IP address or subnet mask | Double-check network settings on each device |
| Failed pings | Incorrect routing configuration | Verify and correct routing tables |
| Unresponsive interface | Interface shutdown or cable issue | Ensure the interface is up and check physical connections |
Step-by-Step Guide for Success
To achieve success in network configuration exercises, a structured approach is essential. Following a systematic process helps ensure that every task is addressed thoroughly, minimizing errors and enhancing efficiency. By breaking down the steps and focusing on each stage, you can tackle even the most complex scenarios with confidence.
1. Understand the Objectives
Before starting, make sure to carefully read through the requirements and identify the core objectives. Understanding the overall goal will help you prioritize your actions and avoid unnecessary distractions. Whether you are setting up a network, configuring security, or troubleshooting, a clear grasp of the task will guide your decisions.
2. Execute Configuration in Phases
Start small by configuring the basic settings on each device first. This includes assigning IP addresses, enabling interfaces, and ensuring devices can communicate. Once the fundamentals are in place, move on to more advanced configurations, such as setting routing protocols or security settings. Take it one step at a time and verify each part as you go along to ensure there are no overlooked issues.
Key Concepts in Network Configuration Tasks
Understanding the essential principles behind network configuration exercises is crucial for success. Mastering these fundamental concepts enables a smooth setup, troubleshooting, and optimization of network systems. This section covers the core elements that will help guide you through complex tasks and ensure accurate configurations.
1. Device Configuration
Configuring devices properly is the backbone of any network task. Each device has specific settings that need to be accurately applied to ensure they function within the network. Key aspects to consider include:
- Assigning unique IP addresses and subnet masks
- Enabling interfaces for communication
- Setting up routing protocols for inter-device connectivity
2. Connectivity and Communication
Devices must be properly connected to communicate effectively. Ensuring that each connection is correctly established and that cables and interfaces are properly configured is essential for seamless data transfer. The following are important factors to consider:
- Correct cable types for device connections (e.g., Ethernet, fiber)
- Verifying interface status (up or down)
- Ensuring proper routing paths between devices
Examining Networking Protocols Used
In any network configuration task, understanding the protocols that govern communication between devices is essential. These protocols define the rules and conventions that allow data to be transferred across a network efficiently and securely. Familiarity with key protocols helps in configuring devices, ensuring connectivity, and troubleshooting communication issues.
1. Routing Protocols
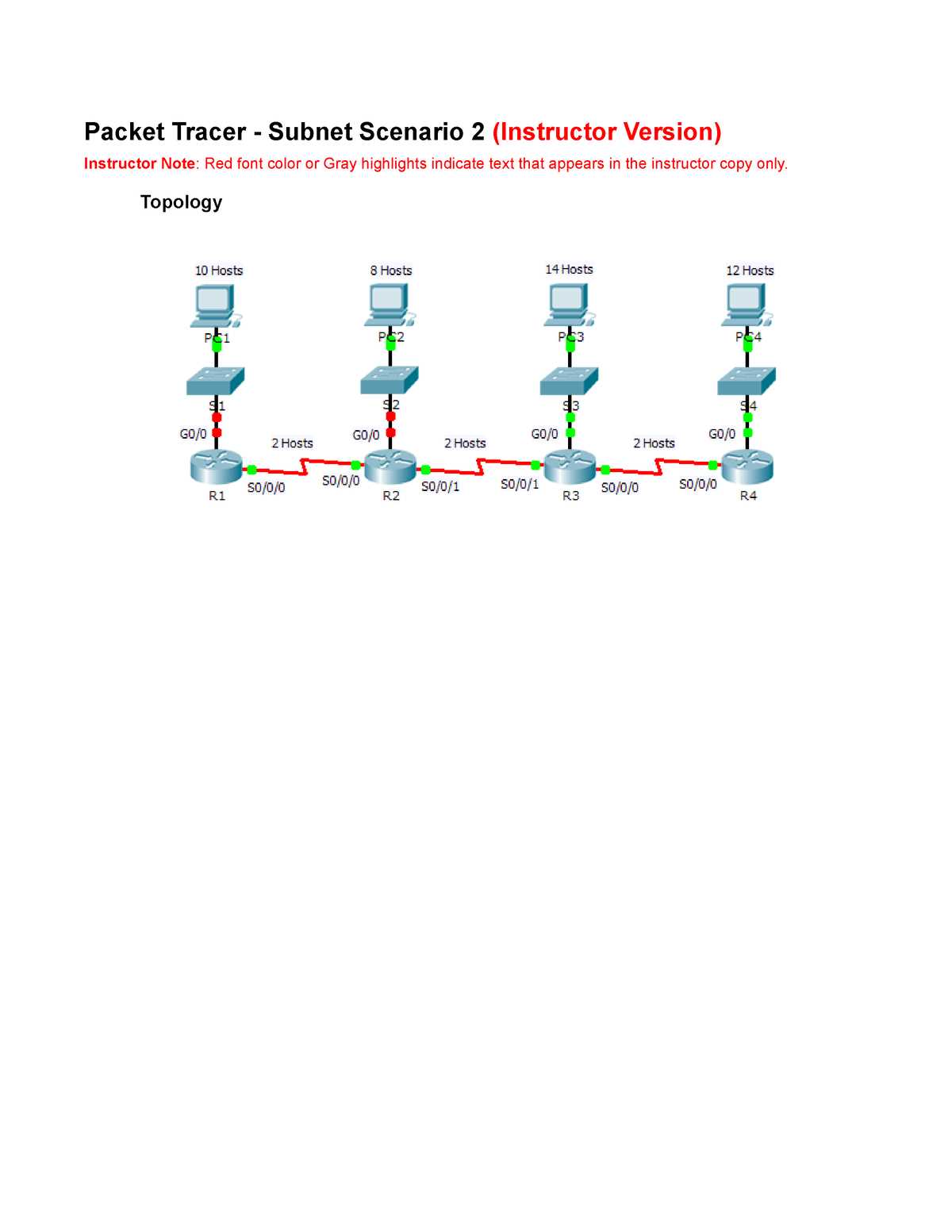
Routing protocols are responsible for determining the best paths for data to travel across a network. They allow devices to share information about the network topology, ensuring that data packets reach their correct destination. Some commonly used routing protocols include:
- RIP (Routing Information Protocol): A distance-vector protocol used for simpler network configurations.
- OSPF (Open Shortest Path First): A link-state protocol that is more scalable and efficient for larger networks.
- EIGRP (Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol): A hybrid protocol that combines features of both distance-vector and link-state protocols.
2. Data Link and Transport Layer Protocols
At the data link and transport layers, several protocols ensure that data is reliably delivered between devices. These protocols handle error detection, flow control, and the actual transmission of data. Some important ones to know are:
- Ethernet: A widely used protocol for local area networks (LANs) that governs the physical and data link layers.
- TCP (Transmission Control Protocol): A connection-oriented protocol that ensures reliable data transmission by establishing a connection before sending data.
- UDP (User Datagram Protocol): A connectionless protocol that sends data without establishing a connection, often used for time-sensitive applications.
Configuring Devices in Network Simulations
Proper configuration of network devices is a critical step in ensuring a functional and efficient network setup. Each device in the network has specific roles and settings that must be adjusted to meet the requirements of the simulation. By correctly configuring routers, switches, and other devices, you can ensure smooth communication and optimal performance across the network.
1. Configuring Routers
Routers are essential for directing data between different networks. When configuring a router, the most important tasks include assigning IP addresses to interfaces, enabling routing protocols, and setting up access control lists (ACLs) to secure the network. Additionally, make sure to verify that routing tables are correctly populated to allow for proper data forwarding.
2. Setting Up Switches
Switches operate at the data link layer and are responsible for managing communication within a local network. When configuring switches, focus on VLANs (Virtual Local Area Networks), port security settings, and Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) to prevent loops. Also, ensure that switch ports are assigned to the correct VLAN and are operating in the correct mode (access or trunk).
Tips for Completing Network Configuration Activities
Successfully completing network configuration exercises requires both a solid understanding of networking concepts and a strategic approach. By following a structured process and keeping certain best practices in mind, you can avoid common mistakes and enhance your ability to troubleshoot and optimize network setups.
1. Start with a Clear Plan
Before diving into configuration tasks, take a moment to review the objectives and create a plan of action. Identify the key devices involved, the necessary settings, and the protocols you will need to configure. Having a clear roadmap helps you stay focused and ensures you don’t miss any critical steps.
2. Check Connections and Interfaces
One of the most common issues in network simulations is incorrect or overlooked connections between devices. Make sure that all physical and virtual connections are properly established and that interfaces are enabled. A quick verification of your device connections can often save time and prevent frustration later on.
3. Use Simulation Mode for Troubleshooting
Many network simulation tools offer a “simulation mode” that allows you to visualize packet flows and identify where issues may be occurring. If things aren’t working as expected, this mode can help you track down configuration mistakes or network disruptions, allowing you to fix problems more efficiently.
Identifying Errors in Network Simulation
During network configuration simulations, errors can often arise due to misconfigurations or overlooked details. Identifying and resolving these errors is a crucial skill for any network administrator or student. By systematically troubleshooting and understanding common sources of issues, you can efficiently pinpoint the root causes of connectivity problems or misbehaving devices.
1. Check Device Configurations
Improper device configurations are a frequent source of errors. Key areas to review include:
- Incorrect IP addressing or subnet masks
- Misconfigured routing protocols
- Disabled interfaces or incorrect VLAN assignments
- Incorrect access control lists (ACLs) or firewall settings
2. Verify Physical and Logical Connections
Issues may arise if devices are not properly connected, whether physically or logically. To identify errors in connections, verify the following:
- Check that all cables are securely attached and correctly chosen (e.g., straight-through vs. crossover cables)
- Ensure that network interfaces are enabled and correctly assigned to the appropriate devices
- Confirm that all routers and switches are properly interconnected
3. Use Simulation Tools for Troubleshooting
Many network simulation platforms include built-in tools that help visualize traffic flow and diagnose errors. Common tools include:
- Ping and traceroute to test connectivity between devices
- Simulation mode to observe packet flow and identify where data gets lost
- Console logs to check for any error messages or misconfigurations
Understanding IP Addressing in Network Simulations
IP addressing is a fundamental concept in networking that allows devices to communicate with each other over a network. Correctly assigning IP addresses is essential for ensuring that data reaches the right destination. In simulation environments, managing IP addresses properly is key to setting up functional and scalable network systems.
1. Key Concepts of IP Addressing
Each device in a network requires a unique IP address to be identified and to send and receive data. IP addresses are typically divided into classes and ranges, depending on the network size and requirements. The two most important components of an IP address are:
- Network ID: Identifies the specific network the device belongs to.
- Host ID: Uniquely identifies the device within the network.
In addition to understanding the structure of IP addresses, it’s also crucial to be aware of subnetting, which helps divide networks into smaller, more manageable segments.
2. Using IP Addressing in Network Configurations
When configuring devices in a network, proper IP addressing ensures communication between them. A typical process includes:
- Assigning static or dynamic IP addresses to devices.
- Ensuring that devices are within the correct subnet to communicate directly.
- Configuring gateway addresses for devices to reach external networks.
| IP Address | Network Class | Default Subnet Mask |
|---|---|---|
| 192.168.1.1 | Class C | 255.255.255.0 |
| 10.0.0.1 | Class A | 255.0.0.0 |
| 172.16.0.1 | Class B | 255.255.0.0 |
Setting Up Routing and Switching
Configuring routing and switching is a crucial aspect of building a functional network. These two processes enable devices to communicate across different segments, manage traffic efficiently, and ensure data reaches its correct destination. Proper setup of routers and switches is essential for creating a reliable, secure, and scalable network infrastructure.
1. Configuring Routing
Routing refers to the process of directing data packets between different networks. When setting up a router, the main tasks involve:
- Assigning IP addresses to interfaces to ensure proper communication between devices.
- Enabling routing protocols such as RIP, OSPF, or EIGRP to allow routers to exchange information and determine the best path for data.
- Verifying routing tables to ensure all routes are properly configured and reachable.
Routing protocols automatically adjust to changes in the network, ensuring that devices can always find the best path to their destination.
2. Configuring Switching
Switching is responsible for directing data within a single network, ensuring that devices can communicate within a local area network (LAN). Key tasks for configuring a switch include:
- Creating VLANs (Virtual Local Area Networks) to segment the network and improve performance and security.
- Configuring port security to prevent unauthorized access and enhance network security.
- Enabling Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) to prevent network loops and ensure that there is always a backup path in case of a failure.
Switches operate at the data link layer, using MAC addresses to forward data within the same network, and must be properly set up to ensure smooth communication between connected devices.
Verification Techniques for Network Simulations
When configuring a network, it’s essential to verify that all devices are correctly set up and that the network functions as intended. Verification helps identify configuration errors, connectivity issues, and misconfigurations that may affect the overall performance. Employing effective verification techniques ensures that each step of the network setup is correctly implemented and working optimally.
1. Testing Connectivity with Ping and Traceroute
One of the most straightforward methods of verifying network functionality is using basic network diagnostic tools like ping and traceroute. These tools allow you to test connectivity between devices and trace the path that data packets take to reach their destination.
- Ping: Sends a test message to a destination IP address and checks if a reply is received. It verifies that devices can communicate across the network.
- Traceroute: Tracks the route packets take across the network, providing valuable information about the devices along the path and highlighting any issues or delays.
2. Verifying Device Configurations
Another important verification step involves checking device configurations. Ensure that each device has the correct settings, such as:
- IP address configurations (static or dynamic)
- Correct VLAN assignments and interface statuses
- Routing protocol configurations and updates
- Access control lists (ACLs) to verify security settings
Use commands like show running-config or show ip interface brief to review the settings and ensure everything is correctly configured. If any settings are incorrect, address the issues before moving forward.
Common Mistakes and How to Fix Them
When working with network configurations, it’s easy to overlook small details or make errors that can disrupt the flow of data or prevent devices from communicating properly. Recognizing these common mistakes and knowing how to fix them is crucial for ensuring a smooth and efficient network setup. Below are some of the most frequent issues encountered and their solutions.
1. Incorrect IP Addressing
One of the most common mistakes is assigning the wrong IP address or subnet mask to a device. This can lead to connectivity issues, as devices may not be able to communicate within the same network or with other devices.
- Solution: Double-check the IP addressing scheme. Ensure that devices are using the correct subnet mask and that IP addresses are within the correct range for their network. Use tools like ping to verify connectivity.
2. Misconfigured Routing Protocols
Another frequent issue is misconfiguring routing protocols, such as forgetting to enable them on routers or using incorrect network statements. This can prevent the routers from exchanging routing information, leading to communication failures between networks.
- Solution: Review routing protocol configurations and ensure that the correct network ranges are included in the routing table. Also, make sure that the routers are properly configured to use the appropriate protocol (e.g., RIP, OSPF, or EIGRP).
3. VLAN Misconfigurations
Incorrect VLAN assignments on switches can cause devices to be placed in the wrong broadcast domain, preventing them from communicating as intended. This mistake often happens when configuring multiple VLANs or trunking links.
- Solution: Verify that each switch port is assigned to the correct VLAN. Use the show vlan brief command to check VLAN assignments and ensure that trunking is properly configured on links between switches.
4. Access Control List (ACL) Errors
Improperly configured ACLs can block legitimate traffic, preventing devices from communicating with each other or accessing external networks. This often happens when the wrong rules are applied or if an ACL is mistakenly set to deny instead of allow.
- Solution: Review ACL configurations to ensure that only the necessary traffic is filtered. Use the show access-lists command to verify the applied rules and make sure that the ACL allows the required traffic to pass.
By carefully reviewing these areas and addressing any configuration issues, network setup errors can be minimized, ensuring a smoother operation and better network performance.
Simulation Tools Explained
Network simulation software provides a set of powerful tools that allow users to model, configure, and test network environments without the need for physical hardware. These tools are essential for troubleshooting, learning, and experimenting with network topologies. Understanding how to use these tools effectively can greatly enhance your ability to design and debug networks.
1. Real-Time vs. Simulation Mode
One of the most important features of simulation software is the ability to switch between real-time and simulation mode. Each mode serves a distinct purpose:
- Real-Time Mode: In this mode, the network functions as it would in a real-world environment. Devices communicate in real time, and events unfold instantly, just as they would on physical equipment.
- Simulation Mode: This mode allows users to visualize the flow of data packets across the network. It provides a step-by-step view of packet transmission, making it easier to identify issues and analyze the behavior of the network. This mode is especially helpful for educational purposes and troubleshooting.
2. Key Tools for Network Analysis
Several tools within the simulation environment are designed to help users troubleshoot and optimize network setups. Some of the most useful include:
- Packet Tracer: Tracks the movement of data packets through the network, showing how they are routed from one device to another. This tool helps identify issues like misconfigurations or network loops.
- Device Console: Provides a command-line interface for configuring devices. It mimics the behavior of physical routers, switches, and other devices, enabling users to enter commands as they would in a real-world scenario.
- Ping Tool: Used to test network connectivity between devices. The tool sends a request to a destination device and waits for a reply, helping diagnose network reachability issues.
By utilizing these tools, users can gain a deeper understanding of how networks operate and address problems more efficiently. Mastery of these tools is key to becoming proficient in network design and troubleshooting.
Maximizing Learning from Simulation Tools
To get the most out of network simulation software, it’s essential to approach the learning process with the right mindset and strategy. Rather than just following pre-designed scenarios, actively engaging with the tool can enhance your understanding and skills in network configuration, troubleshooting, and problem-solving. Here are several methods to maximize your learning experience.
1. Experiment with Custom Scenarios
While predefined exercises are useful for structured learning, creating your own network configurations can offer a deeper insight into how different elements interact. Try building custom topologies from scratch, experimenting with different devices, protocols, and configurations. This hands-on approach allows you to learn through trial and error, helping you to better understand how networks behave in real-world situations.
2. Troubleshoot Simulated Issues
One of the most valuable ways to learn is by facing challenges and figuring out how to overcome them. Use the simulation tools to create intentional network problems, such as incorrect IP addressing, faulty routing, or misconfigured VLANs. Then, use the available troubleshooting tools, like the packet analyzer or ping tool, to identify and fix the issues. This process will build your problem-solving skills and help you develop the ability to diagnose real-world network problems efficiently.
3. Document Your Work
As you progress through different exercises or simulations, it’s helpful to document the steps you took to achieve a working network. This not only reinforces your learning but also provides a useful reference for future troubleshooting. By writing down key configurations, commands, and solutions to problems, you create a personalized resource that you can revisit whenever needed.
4. Leverage the Built-in Help Features
Simulation platforms often include built-in help features, such as tutorials or troubleshooting guides. Don’t hesitate to use these resources, especially when you encounter difficulties. They can offer quick solutions or provide explanations for more complex concepts. However, always challenge yourself to explore and understand the material rather than relying solely on the help feature.
By adopting these practices, you can enhance your learning experience, gain a deeper understanding of network design and troubleshooting, and build a strong foundation for working with real-world networks.
Advanced Configuration for Network Scenarios
When working with network simulations, advancing beyond basic configurations is crucial for mastering complex scenarios. Advanced setups involve configuring routing protocols, implementing security measures, optimizing traffic, and troubleshooting intricate network issues. By diving into these more sophisticated configurations, you can gain deeper insights into real-world networking challenges and improve your ability to design, implement, and maintain robust networks.
1. Configuring Routing Protocols
One of the key elements in advanced network setups is understanding how to configure and manage routing protocols. Routing protocols determine how data is directed across the network, and correctly implementing them ensures efficient communication between devices. Below are common routing protocols to consider:
- RIP (Routing Information Protocol): A distance-vector protocol that helps routers exchange information about the reachability of network destinations.
- OSPF (Open Shortest Path First): A link-state protocol that offers faster convergence and is scalable for large networks.
- BGP (Border Gateway Protocol): Used for routing data across the internet, BGP is crucial for managing routing between different autonomous systems.
When configuring these protocols, it’s important to understand the key concepts, such as network masks, cost metrics, and routing tables, to ensure efficient data transmission across your network.
2. Implementing Security Features
In advanced scenarios, securing the network from unauthorized access and threats is a top priority. The following steps are crucial for securing devices and ensuring network integrity:
- Access Control Lists (ACLs): ACLs define which traffic can enter or leave the network based on specific criteria, such as IP addresses or ports. Properly configuring ACLs helps control network traffic and prevent unauthorized access.
- VPNs (Virtual Private Networks): VPNs encrypt data sent over the network, providing a secure communication channel between remote devices or locations.
- Port Security: This feature limits the number of devices that can connect to a switch port, preventing unauthorized devices from gaining access to the network.
3. Optimizing Network Traffic
Network optimization is critical in ensuring that the network operates efficiently, particularly in large or complex environments. Key techniques include:
- Quality of Service (QoS): QoS prioritizes certain types of traffic (e.g., VoIP, video streaming) to prevent congestion and ensure high performance for critical services.
- VLANs (Virtual Local Area Networks): By segmenting networks into different VLANs, you can reduce congestion, improve security, and streamline management.
- Load Balancing: This technique distributes traffic evenly across multiple network paths to avoid bottlenecks and improve overall performance.
Mastering these advanced configurations is essential for building scalable, secure, and efficient networks. By understanding and applying these concepts, you will be prepared to tackle complex network challenges and optimize the performance of any given network environment.
How 5.2.1.7 Prepares for Networking Exams
Preparing for networking exams requires hands-on experience with network configurations, troubleshooting, and understanding key concepts. Practicing in a simulated environment allows you to build the skills necessary to tackle complex real-world scenarios. The structured exercises found in various simulations offer a step-by-step approach to help reinforce theoretical knowledge and enhance practical application, making them an essential tool for exam preparation.
1. Understanding Key Networking Concepts
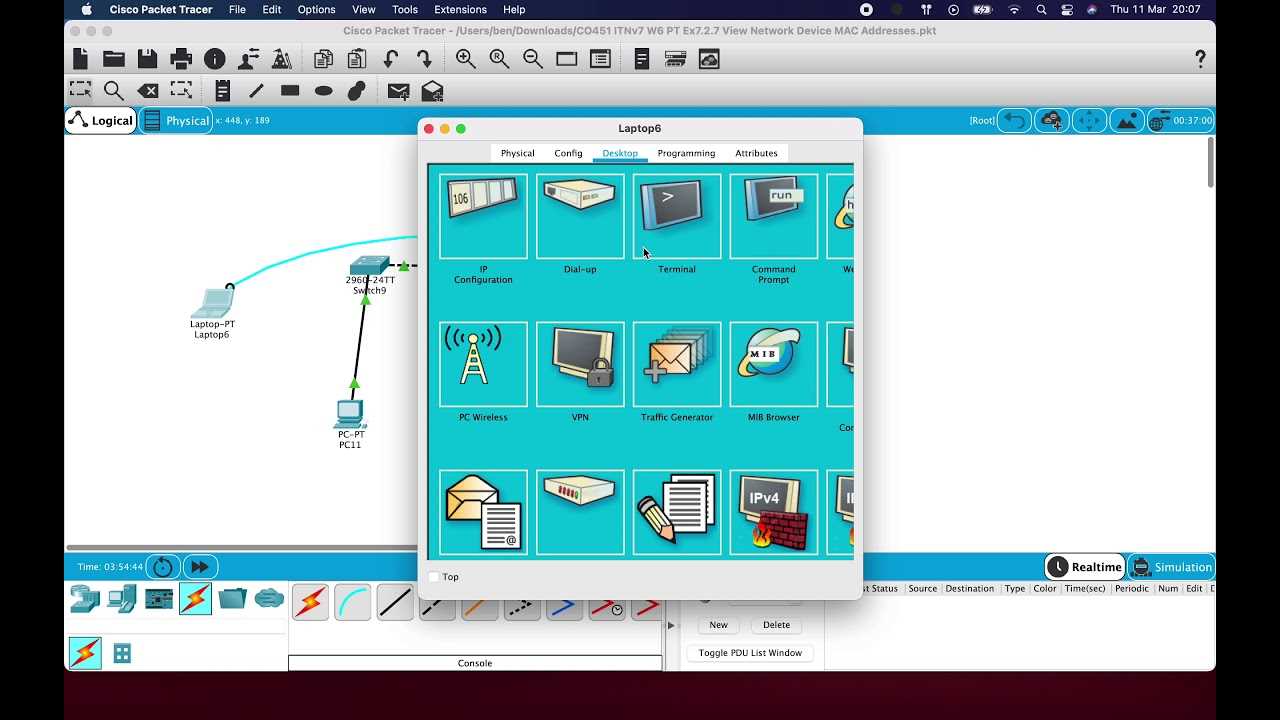
Networking exams often test your knowledge of various protocols, devices, and configurations. The simulations focus on the fundamentals, helping you understand and apply key concepts such as:
- IP Addressing: Understanding subnetting, network masks, and IP assignment is critical for configuring devices and troubleshooting network issues.
- Routing Protocols: Learning how to configure and troubleshoot common routing protocols like RIP, OSPF, and BGP is essential for exam success.
- Network Security: Examining and configuring security features such as ACLs, VPNs, and firewalls to protect network infrastructure.
Through practice, you can gain confidence in applying these concepts under exam conditions, ensuring you’re ready for practical tasks and theoretical questions.
2. Hands-On Practice with Configurations
To perform well in networking exams, you need to be proficient in configuring devices, setting up networks, and troubleshooting problems. Simulated exercises allow you to practice these tasks in a controlled, risk-free environment. Key tasks include:
- Device Configuration: Practicing the configuration of routers, switches, and other network devices, ensuring that you can navigate command-line interfaces and graphical interfaces with ease.
- Creating Network Topologies: Designing and implementing network layouts that meet specific criteria and troubleshooting issues that may arise during configuration.
- Testing and Troubleshooting: Running diagnostics to identify and resolve network faults, such as misconfigured IP addresses, routing loops, and connectivity problems.
These exercises help you develop the practical skills that are vital for both exams and real-world network management.
3. Building Confidence with Realistic Scenarios
Exam simulations recreate realistic network environments that mirror the challenges you might face on actual certification tests. This preparation method enhances your problem-solving skills, as you are required to:
- Identify Network Issues: Troubleshoot common problems, such as connectivity issues, slow network performance, or misconfigured devices.
- Apply Best Practices: Configure networks using industry best practices, ensuring security, scalability, and reliability.
- Optimize Network Performance: Implement techniques for improving network traffic flow, such as Quality of Service (QoS) and load balancing.
By experiencing these scenarios, you will be better equipped to manage network challenges and pass the exam with confidence.
Ultimately, engaging in hands-on practice with these simulated environments provides the skills, knowledge, and confidence needed to excel in networking exams, ensuring that you’re well-prepared for both the theoretical and practical components of your certification. By mastering these exercises, you can build a solid foundation for a successful networking career.
Additional Resources for Practice
To enhance your networking skills and deepen your understanding, utilizing additional resources can complement your practice. Beyond simulation environments, several platforms, books, and communities can help broaden your knowledge and refine your abilities. These resources provide opportunities to tackle various networking scenarios, engage with experts, and stay up-to-date with the latest industry practices.
1. Online Learning Platforms
Online platforms offer a wealth of interactive content, including video tutorials, practice exams, and community discussions. These platforms are excellent for self-paced learning and provide hands-on exercises to reinforce concepts. Some popular platforms include:
- Udemy: Courses tailored to networking professionals, ranging from beginner to advanced topics.
- LinkedIn Learning: Access to courses designed by industry experts, with a focus on practical application and certifications.
- Pluralsight: Offers deep dives into networking topics, with guided learning paths for various certifications.
These platforms often include practical labs, where you can simulate different networking setups and configurations, further enhancing your skills.
2. Networking Communities and Forums
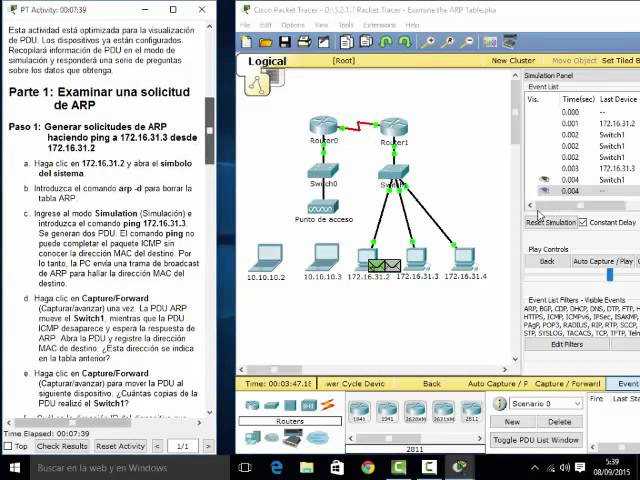
Engaging with online communities allows you to connect with fellow learners and experienced professionals. These communities provide valuable insights into troubleshooting, configuration tips, and common industry challenges. Key resources include:
- Reddit: Subreddits like r/networking and r/ccna provide discussions, solutions, and learning materials.
- Cisco Learning Network: Cisco’s own community hub, offering forums, study materials, and direct interaction with experts.
- Network Engineering Stack Exchange: A question-and-answer community where users can seek help on a variety of networking topics.
These forums foster a collaborative learning environment, where you can ask questions, share experiences, and get feedback from peers and professionals.
3. Books and Textbooks
Books remain an essential resource for in-depth knowledge. Several textbooks are ideal for learners preparing for networking certifications and provide theoretical foundations alongside practical exercises. Popular titles include:
- “Routing and Switching Essentials” by Cisco Press: A comprehensive guide that covers essential networking concepts and configurations.
- “TCP/IP Illustrated” by W. Richard Stevens: An in-depth resource for understanding networking protocols.
- “Network Warrior” by Gary A. Donahue: Offers practical advice and real-world scenarios for network engineers.
These books not only cover theoretical knowledge but also provide valuable exercises that help cement concepts through real-world application.
By leveraging these additional resources, learners can gain a more holistic understanding of networking concepts and further enhance their practical skills. This diverse approach ensures a well-rounded preparation, making it easier to tackle any challenge in both exams and real-world networking environments.