
Preparing for a comprehensive assessment in the field of medicine can be daunting, especially when it involves a wide range of complex topics. Success in this type of test requires a deep understanding of key concepts, attention to detail, and the ability to recall critical information under time pressure.
Effective study techniques play a crucial role in achieving high scores. Focusing on core principles, recognizing patterns, and practicing application through sample questions will make a significant difference. By focusing on the most relevant material and using smart review methods, candidates can approach the assessment with confidence and preparedness.
Strategic preparation is the key to mastering the material, and familiarizing yourself with the structure of the questions will help eliminate uncertainty. This guide will provide you with valuable insights and tips to tackle the most challenging areas of study, ensuring you perform at your best when it counts the most.
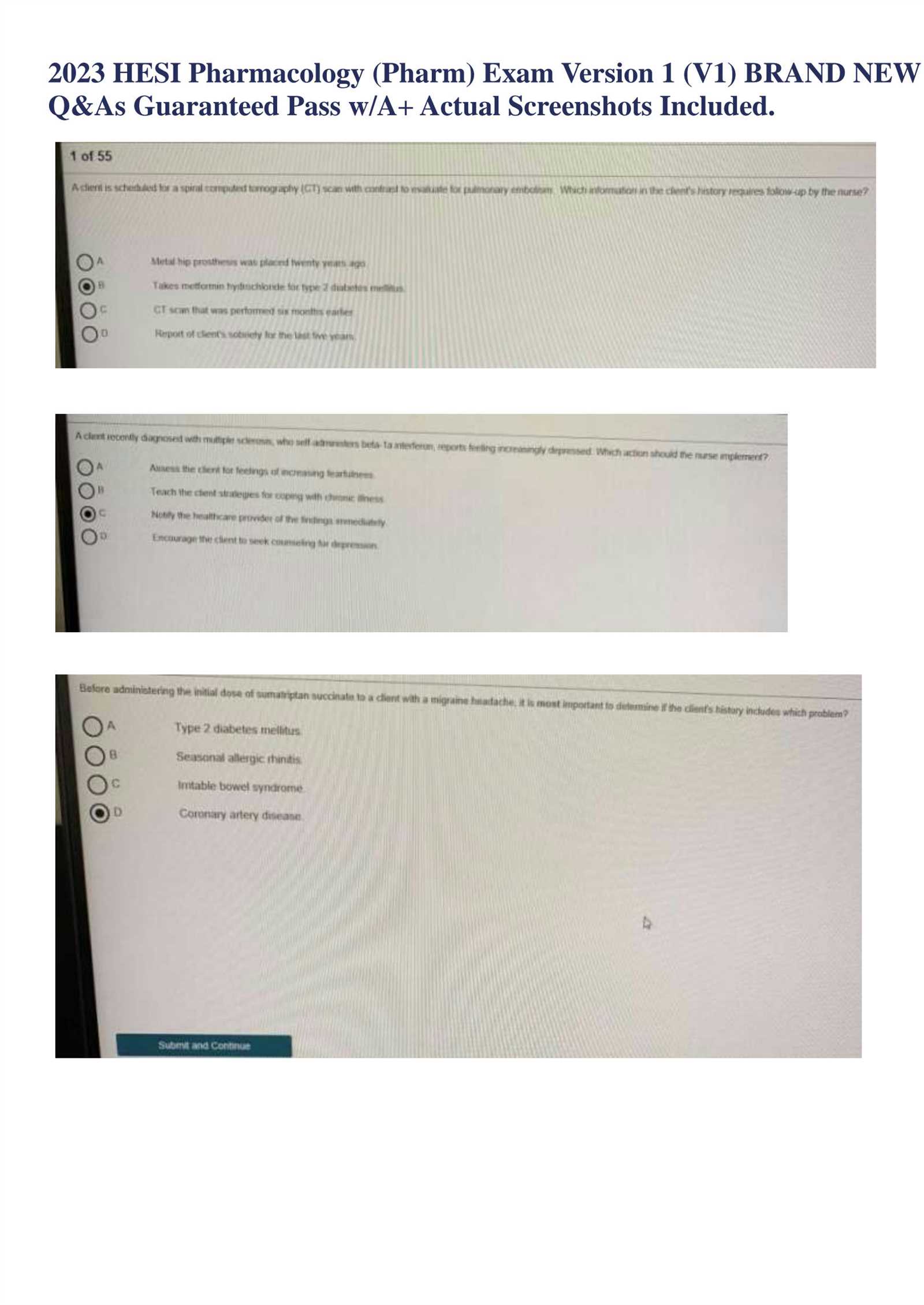
Pharmacology HESI Final Exam Overview
Assessments in the medical field require a thorough understanding of various topics, including drug interactions, therapeutic effects, and patient safety. These evaluations are designed to test not only your theoretical knowledge but also your practical ability to apply what you’ve learned in real-life scenarios.
The structure of this evaluation is meant to challenge your ability to think critically, recall essential facts, and make sound decisions under pressure. It covers a broad spectrum of material, from drug classifications and mechanisms of action to adverse reactions and therapeutic uses. Understanding the scope of this test is vital for effective preparation.
Comprehensive preparation involves mastering the core areas that will be tested. Reviewing the most important concepts, familiarizing yourself with common question formats, and practicing under timed conditions are all key strategies to ensure success. This section will provide a detailed breakdown of what to expect, helping you approach the evaluation with clarity and confidence.
Key Concepts to Focus On
When preparing for a rigorous assessment in the healthcare field, it’s essential to prioritize the most critical topics. Understanding the core areas will help you focus your efforts and increase your chances of success. Here are some key concepts to concentrate on during your studies:
- Drug Classifications: Know the different categories of medications, their uses, and common examples. Understanding these will help with questions about therapeutic effects and adverse reactions.
- Mechanisms of Action: Familiarize yourself with how medications work in the body, including their interaction with receptors and enzymes.
- Pharmacokinetics: Focus on how drugs are absorbed, distributed, metabolized, and excreted from the body. This concept is crucial for understanding drug efficacy and safety.
- Adverse Effects and Contraindications: Be aware of common side effects, potential drug interactions, and when certain medications should not be used due to patient conditions.
- Dosage Calculations: Review how to calculate the correct dosage for various forms of medication, including converting units and understanding safe ranges.
Mastering these areas will ensure you have a solid foundation to tackle any challenging questions and demonstrate a well-rounded understanding of essential topics. Make sure to allocate enough time to study each concept thoroughly, as they form the backbone of the assessment.
Study Strategies for Success
Achieving success in a challenging assessment requires more than just memorization–it involves mastering effective study techniques that enhance comprehension and retention. By implementing the right strategies, you can ensure that your preparation is both efficient and effective. Below are some proven methods to guide you through your study sessions.
Active Learning Techniques
Engaging with the material actively will help you retain information better than passive reading. Here are some strategies to incorporate into your study routine:
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
| Self-Quizzing | Regularly test your knowledge with flashcards or practice questions to identify gaps in your understanding. |
| Teaching Others | Explain complex concepts to a peer to reinforce your own understanding. |
| Mind Mapping | Create visual diagrams to link related concepts, helping you see connections between different topics. |
| Summarization | Write summaries of what you’ve learned in your own words to improve recall and clarity. |
Time Management Tips
Properly managing your study time is just as important as the content itself. Effective time management ensures that you stay on track without feeling overwhelmed. Consider these tips:
- Create a Study Schedule: Plan your study sessions in advance to allocate enough time to each topic without rushing.
- Use Breaks Wisely: Follow the Pomodoro technique by studying for 25-30 minutes and then taking a 5-minute break.
- Prioritize Challenging Areas: Focus more time on topics that you find difficult and require more attention.
Implementing these strategies will not only help you manage your study time more effectively but also deepen your understanding and retention of the material.
Top Pharmacology Topics to Review
When preparing for a comprehensive medical evaluation, it’s essential to focus on the most relevant topics that will appear throughout the assessment. Some areas are particularly important because they form the foundation of understanding how different substances interact within the body. Reviewing these key topics will help you feel more confident and well-prepared.
Drug Classifications and Categories
One of the most crucial aspects to review is the classification of various substances used in healthcare. Understanding how medications are grouped and their specific roles can help you answer many of the questions related to their therapeutic use. Be sure to focus on:
- Antibiotics: Different types, their mechanisms of action, and spectrum of activity.
- Analgesics: The differences between non-opioid and opioid pain relievers, as well as their potential side effects.
- Antihypertensives: Classes of drugs used to manage blood pressure, such as ACE inhibitors, beta-blockers, and calcium channel blockers.
Drug Interactions and Side Effects
Understanding potential drug interactions and their effects on the body is critical for patient safety. Review common combinations of medications that may lead to adverse reactions or alter therapeutic outcomes. Focus on:
- Synergistic Effects: When two or more drugs work together to produce an enhanced effect.
- Antagonistic Effects: When one drug reduces or neutralizes the effect of another.
- Common Side Effects: Focus on the most frequent and severe reactions to commonly prescribed medications.
By reviewing these topics in detail, you’ll gain a better understanding of how medications function and how to safely manage their use in clinical practice. Familiarizing yourself with these areas will not only increase your test performance but also improve your ability to apply this knowledge in real-world scenarios.
How to Approach Medication Calculations
Calculating medication dosages accurately is a critical skill for anyone in the healthcare field. These calculations ensure that patients receive the correct amount of medication, which is essential for their safety and well-being. Whether working with liquid medications, oral tablets, or injectable substances, understanding how to approach these calculations is key to success in clinical practice.
Understanding Key Concepts
Before diving into calculations, it’s important to familiarize yourself with the core concepts that underpin them. Some of the essential elements include:
- Dosage Form: Know the difference between various forms of medication (e.g., tablets, liquids, injectables) and their respective units of measurement.
- Concentration: Understand the concentration of a medication, such as mg/mL or g/L, and how to use this information in calculations.
- Unit Conversions: Be comfortable converting between different units of measurement (e.g., milligrams to grams, milliliters to liters).
Step-by-Step Approach
Approaching medication calculations methodically will help ensure accuracy. The following steps provide a clear process to follow:
| Step | Action |
|---|---|
| Step 1 | Identify the desired dosage and the available medication concentration. |
| Step 2 | Set up the equation based on the given values and what needs to be calculated. |
| Step 3 | Perform the necessary arithmetic to determine the correct dosage or volume. |
| Step 4 | Double-check your work for accuracy, ensuring the units are consistent and the calculations make sense. |
By following these steps, you can avoid errors and become more efficient in performing medication calculations. Practice regularly to build confidence and ensure proficiency in these essential tasks.
Common Mistakes to Avoid During the Exam
When preparing for a high-stakes assessment in the healthcare field, it’s easy to fall into certain traps that can cost valuable points. Many candidates make simple yet avoidable errors that could have been prevented with careful attention and effective strategies. Being aware of these common mistakes can help you navigate the test more confidently and effectively.
- Misreading Questions: Always take the time to carefully read each question. Misunderstanding the wording can lead to incorrect answers, even if you know the material well.
- Skipping Instructions: Pay close attention to any instructions or specific details provided in the question, such as units of measurement or the required method for calculation.
- Overlooking Units: Failing to keep track of units when performing calculations can lead to mistakes. Always ensure that your answers have consistent units and that conversions are done properly.
- Rushing Through the Test: Speed can be important, but rushing through questions without careful consideration may result in careless mistakes. Manage your time but allow yourself enough time to think through each problem.
- Second-Guessing Yourself: Once you’ve chosen an answer, avoid overthinking and changing your responses unless you are certain you made an error. Trust your initial judgment unless you spot a clear mistake.
- Not Reviewing Answers: If time permits, always review your answers before submitting the test. This final check can help you spot any overlooked mistakes or missed instructions.
By staying mindful of these common pitfalls, you can minimize errors and increase your chances of achieving a successful outcome. Remember, preparation and a calm, methodical approach are essential to overcoming these challenges.
Effective Time Management Techniques
Mastering time management is essential when preparing for any important assessment. Efficiently allocating your study time ensures that you cover all necessary topics while avoiding last-minute stress. By implementing structured techniques, you can maximize your productivity and stay focused throughout the preparation process.
- Prioritize Key Topics: Identify the most critical subjects that require more attention and allocate additional time to those areas. Focus on your weaknesses to build confidence in those topics.
- Set Realistic Goals: Break your study sessions into manageable goals, such as completing a chapter or mastering a specific concept. This helps you track your progress and stay motivated.
- Use Time Blocks: Implement the Pomodoro technique or other time-blocking methods. Study for 25-30 minutes, then take a short break. This helps maintain focus and prevents burnout.
- Create a Study Schedule: Plan your study sessions in advance. Set aside specific hours for each topic, and ensure that you balance study time with relaxation to avoid fatigue.
- Avoid Multitasking: Focus on one task at a time. Multitasking may seem efficient, but it can reduce the quality of your learning and waste valuable time.
By integrating these techniques into your preparation routine, you can manage your time effectively, reduce anxiety, and improve your performance. Consistency and planning are the keys to making the most of your study sessions and ensuring a successful outcome.
Essential Pharmacology Resources for Study
Having the right study materials is critical for effective preparation in healthcare-related assessments. Accessing high-quality resources can enhance your understanding of key concepts and boost your confidence. Whether you’re relying on books, online tools, or study groups, using the best materials available will significantly improve your learning process.
Printed Materials
Books and printed study guides remain invaluable for thorough understanding and review. Key resources should cover foundational topics and provide practice problems to test your knowledge. Consider using:
- Textbooks: Comprehensive textbooks that explain core concepts, terminology, and clinical applications.
- Study Guides: Summarized versions of textbooks that offer concise explanations and practice questions for focused review.
- Practice Question Banks: Books that provide practice questions mimicking real-world scenarios and assessments.
Online Platforms and Tools
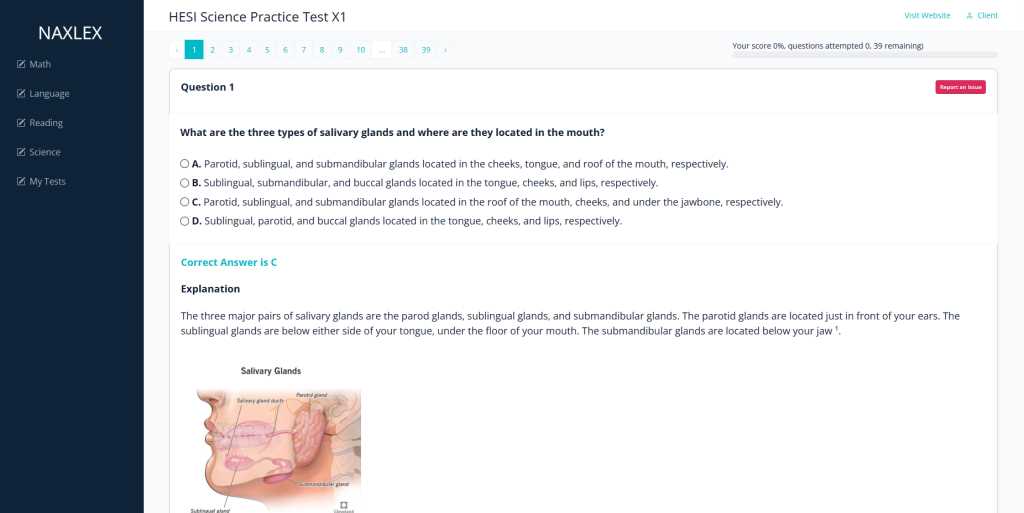
Digital tools and websites offer interactive and up-to-date content that can supplement traditional study methods. These platforms provide flexibility, allowing you to study at your own pace. Useful resources include:
- Interactive Websites: Platforms offering tutorials, quizzes, and flashcards tailored to healthcare subjects.
- Video Lessons: Educational videos that break down complex topics into easy-to-understand visual explanations.
- Mobile Apps: Apps that help reinforce key topics through gamified learning and on-the-go practice.
Study Groups and Peer Support
Collaborating with peers can provide different perspectives and deepen your understanding of challenging topics. Study groups foster discussion, allowing for shared resources and solutions to difficult problems. Consider joining:
- Online Forums: Communities where students can share insights, resources, and solutions to questions.
- In-Person Study Groups: Local or class-based groups that meet regularly to review material together.
Leveraging a combination of these resources will ensure a well-rounded study approach, increasing your ability to recall information and apply it effectively during assessments.
Understanding Drug Classifications
In the healthcare field, understanding the classification of medications is essential for providing safe and effective care. Medications are categorized into different groups based on their effects on the body, mechanisms of action, and therapeutic uses. Familiarity with these categories helps healthcare professionals make informed decisions and ensures the proper use of medications in various clinical settings.
Drug classifications are typically organized by the way a medication works or its intended purpose. Some common categories include:
- Analgesics: Medications designed to relieve pain by acting on the nervous system.
- Antibiotics: Drugs used to treat infections by killing or inhibiting the growth of bacteria.
- Antidepressants: Medications used to manage mood disorders by affecting neurotransmitters in the brain.
- Antihypertensives: Drugs aimed at lowering blood pressure, often used in the treatment of cardiovascular conditions.
- Diuretics: Medications that help remove excess fluid from the body, typically used for conditions like hypertension and heart failure.
Each classification contains various subclasses or individual medications that work in slightly different ways but achieve similar results. By understanding how these medications interact with the body, healthcare providers can tailor treatment plans to meet the unique needs of each patient.
Mastering the different drug classifications and their mechanisms is crucial for anyone working in the medical field, as it directly impacts both the effectiveness and safety of patient care.
Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics Essentials
Understanding the processes by which drugs move through the body and their effects on various systems is fundamental in healthcare. Two key concepts in this area are the absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion (ADME) of drugs, as well as their biological effects on target tissues. These processes help explain how medications work, how they should be administered, and how their effects can be maximized while minimizing potential side effects.
The study of drug movement within the body (pharmacokinetics) and the study of their effects on the body (pharmacodynamics) are interconnected and provide essential information for making clinical decisions.
Pharmacokinetics Overview

Pharmacokinetics refers to the journey a drug takes through the body, from administration to elimination. It involves several key stages:
- Absorption: How the drug enters the bloodstream from the site of administration.
- Distribution: How the drug spreads throughout the body and reaches various tissues.
- Metabolism: The process by which the body breaks down the drug, usually in the liver.
- Excretion: The elimination of the drug from the body, primarily through the kidneys.
Each stage of pharmacokinetics plays a crucial role in determining the drug’s concentration at the site of action, which impacts its effectiveness and potential for adverse effects.
Pharmacodynamics Overview
Pharmacodynamics focuses on the interactions between the drug and the body, specifically how the drug produces its effects. Key concepts include:
- Receptor Binding: How a drug binds to receptors on cells or tissues to initiate its effect.
- Therapeutic Effects: The desired actions of a drug that lead to symptom relief or disease management.
- Side Effects: Unintended effects that can occur as a result of the drug interacting with other systems in the body.
Pharmacodynamics helps explain the potency, duration, and intensity of a drug’s effects, guiding healthcare professionals in selecting the most appropriate treatment for their patients.
By mastering both pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics, healthcare providers can optimize drug therapy, ensuring that medications are used safely and effectively to improve patient outcomes.
Preparing for Drug Interactions Questions
Understanding how different medications interact with each other is critical for ensuring patient safety. Drug interactions can alter the effects of one or more medications, leading to unexpected side effects, reduced efficacy, or even harmful reactions. Being well-prepared for questions related to drug interactions is essential for making informed clinical decisions and preventing potential complications.
To successfully address questions related to drug interactions, it is important to focus on several key areas. These include understanding the types of interactions, the mechanisms involved, and the clinical implications for patients. Here are some tips for preparing effectively:
Types of Drug Interactions
Drug interactions can be classified into various categories based on their nature:
- Pharmacokinetic Interactions: These occur when one drug alters the absorption, distribution, metabolism, or excretion of another drug, affecting its concentration in the bloodstream.
- Pharmacodynamic Interactions: These interactions occur when two drugs have additive, synergistic, or antagonistic effects on the same physiological process or receptor.
- Chemical Interactions: Some drugs may chemically react when mixed together, rendering them ineffective or causing harmful reactions.
Identifying High-Risk Interactions
Certain drug interactions pose higher risks than others, particularly those involving medications with narrow therapeutic windows. It’s crucial to be aware of medications that are more likely to interact:
- Blood thinners and anticoagulants: These can interact with a variety of drugs, potentially increasing the risk of bleeding or clot formation.
- Antibiotics: Some antibiotics can affect the metabolism of other medications, potentially altering their effectiveness.
- Antiarrhythmic drugs: These medications can interact with other cardiac drugs, potentially causing dangerous heart rhythm disturbances.
By focusing on these common interactions, you can better anticipate and identify potential problems during clinical assessments.
Preparing for questions on drug interactions involves more than memorizing specific pairings of medications. A deep understanding of the mechanisms behind these interactions, the ability to identify high-risk combinations, and the knowledge of how to manage and mitigate these risks are all essential for making safe, informed decisions in patient care.
Reviewing Common Adverse Drug Effects
Medications, while essential for treating various conditions, can sometimes lead to unintended harmful effects. These adverse reactions can vary in severity, from mild discomfort to serious health complications. Being familiar with common side effects and understanding how to manage them is crucial for both healthcare professionals and patients to ensure safe and effective treatment outcomes.
Adverse drug effects can occur in any patient, but some groups of medications are more likely to cause specific reactions. Below are common categories of side effects and examples of drugs often associated with these issues:
Types of Adverse Drug Effects
Adverse reactions to medications can be classified into several categories based on their nature and impact on the body:
- Allergic Reactions: These occur when the immune system mistakenly identifies a drug as harmful. Symptoms can range from mild skin rashes to severe anaphylaxis.
- Gastrointestinal Disturbances: Many medications can cause nausea, vomiting, constipation, or diarrhea, especially antibiotics and painkillers.
- CNS Effects: Central nervous system disturbances like dizziness, confusion, or headaches are common with medications affecting the brain, such as sedatives or pain relievers.
- Hematologic Effects: Some drugs can impact the blood, leading to issues such as anemia, low platelet count, or increased risk of bleeding.
Managing and Preventing Adverse Effects
While it may not be possible to completely eliminate the risk of side effects, healthcare providers can take steps to minimize them:
- Patient Education: Inform patients about potential side effects and the importance of reporting any unusual symptoms.
- Adjusting Dosages: Lowering the dose of a medication may reduce the likelihood or severity of side effects.
- Monitoring: Regular monitoring of patients receiving high-risk drugs can help identify adverse effects early, allowing for timely intervention.
By reviewing common adverse drug effects and understanding how to manage them, healthcare professionals can ensure that treatment is as safe and effective as possible. Proactive care and communication are key to minimizing risks and improving patient outcomes.
Tips for Memorizing Drug Names
Memorizing the names of medications can be a daunting task, especially given the vast number of drugs and their complex names. However, with the right strategies, it is possible to recall them more efficiently. Developing effective techniques to remember drug names can help improve retention and recall, making it easier to associate medications with their uses, dosages, and potential side effects.
Utilizing Mnemonics and Associations
One of the most effective ways to remember drug names is by using mnemonics or memory aids. By creating associations between drug names and their characteristics, you can make the information more relatable and easier to recall. Some useful techniques include:
- Phonetic Rhymes: Create rhymes or songs that help you remember the names. For example, turning complex names into catchy tunes can make them stick in your memory.
- Group Drugs by Class: Grouping medications by their drug class or therapeutic use can make it easier to remember related drugs. For example, antibiotics, pain relievers, and antidepressants can all be studied as categories with shared characteristics.
- Visual Cues: Associating a drug name with a visual image can help. Imagine an image that represents the drug’s effect or purpose, like thinking of a “happy face” for antidepressants.
Repetition and Active Recall

Repetition is a tried-and-true method for memorization. The more frequently you review drug names, the more likely they are to stick in your long-term memory. Active recall, which involves testing yourself on the drug names instead of simply reading them, can also be incredibly effective. Some strategies for repetition and active recall include:
- Flashcards: Create flashcards with the drug name on one side and its use, side effects, and classification on the other. Reviewing these cards regularly can enhance retention.
- Spaced Repetition: Review the names at increasing intervals, starting with frequent reviews and gradually spacing them out as you become more familiar with the material.
- Practice Tests: Take practice tests or quizzes to reinforce your knowledge and test your recall under time constraints.
By combining mnemonic techniques with repetition and active recall, you can make memorizing drug names more manageable. These strategies, when used consistently, will help improve your ability to remember and retain the names of medications over time.
How to Handle Complex Question Formats
When preparing for an assessment, it’s essential to understand how to tackle questions that are presented in a variety of formats. These questions can range from multiple-choice and true/false to more complicated scenarios that require critical thinking and application of knowledge. Being prepared to approach these formats strategically will help you remain calm and confident during the test.
There are several common types of questions that might challenge you. Understanding the structure and anticipating how to handle each type can make a significant difference in your performance.
Understanding Different Question Types
Each question format requires a specific approach. Some common types include:
| Question Type | Strategy |
|---|---|
| Multiple Choice | Read all options carefully before selecting an answer. Eliminate obviously wrong answers and focus on the most logical choice. |
| True/False | Look for qualifying words like “always” or “never.” These words can help you determine the accuracy of a statement. |
| Scenario-Based | Break down the scenario step by step. Identify key clues in the question, and apply your knowledge to each element. |
| Matching | Group related terms or concepts together. Use process of elimination if you’re unsure about some answers. |
Effective Time Management
Time management is key when dealing with more complicated questions. Allocate a set amount of time for each question or section. If a question is particularly tricky, don’t linger on it too long; move on and return to it later if time allows. This will ensure that you address every question without feeling rushed.
By preparing ahead of time and practicing different question formats, you’ll be better equipped to handle even the most complex scenarios. This approach will enhance your problem-solving skills and improve your ability to apply knowledge under pressure.
Exam-Day Tips for Confidence
On the day of an assessment, feeling confident and composed can significantly impact your performance. How you approach the day can influence how well you manage stress and handle the pressure of answering challenging questions. Implementing a few simple strategies can help you stay calm, focused, and ready to succeed.
Start by getting a good night’s sleep before the assessment day. Rest is crucial for memory recall and mental clarity. A well-rested mind is more alert and able to think critically when faced with difficult questions.
Another important tip is to eat a nutritious breakfast. Avoid heavy, greasy meals that may make you feel sluggish. Instead, opt for foods that provide long-lasting energy, such as whole grains, protein, and fruits.
Once you’re at the testing location, take a moment to center yourself. Deep breathing exercises or a short meditation session can help calm your nerves and reduce feelings of anxiety. Remember, you’ve prepared for this, and you’re capable of handling whatever comes your way.
As you begin answering questions, stay mindful of your pacing. Don’t rush through the questions, but avoid lingering too long on any one question. If you’re unsure about an answer, move on and come back to it later if time allows.
Lastly, trust your preparation. You’ve dedicated time and effort to studying and mastering the material. Confidence comes from knowing you’ve put in the work. On the day of the assessment, remind yourself that you are prepared and capable of succeeding.
Common HESI Pharmacology Exam Mistakes
When preparing for any important assessment, there are certain pitfalls that many candidates fall into. Understanding these common errors can help you avoid them and ensure you are better prepared when it’s time to take the test. The mistakes often involve misinterpreting questions, overlooking key details, or mismanaging time during the assessment.
One frequent mistake is rushing through the questions. Many candidates feel pressured by time and attempt to answer too quickly, leading to careless mistakes. It’s important to read each question carefully and take the time to understand exactly what is being asked before selecting an answer.
Another common error is second-guessing yourself. After selecting an answer, it’s tempting to change it based on doubt or a momentary thought. This often results in choosing the wrong option. Trust your first choice unless you’re absolutely certain there’s a mistake.
Failing to manage time properly can also be detrimental. It’s easy to get stuck on difficult questions, but it’s essential to move on and return to them if necessary. Managing your time allows you to give adequate attention to all questions, ensuring you don’t miss out on easy ones simply because you spent too much time on one challenging item.
Additionally, many candidates overlook the importance of reviewing answers when time allows. Not revisiting questions and answers can result in missed mistakes or incomplete answers that could have been corrected with a second look.
Lastly, neglecting to thoroughly review study materials, especially key concepts and details, can also lead to mistakes. Ensure you focus on both broad topics and the specific details that may be tested. Failing to master this balance can leave gaps in your knowledge and impact your performance.
Staying Calm During the Final Assessment
Taking a high-stakes test can be a nerve-wracking experience, but staying calm and focused is crucial for optimal performance. Many candidates feel anxiety or stress when the pressure is on, but with the right strategies, it’s possible to maintain a clear mind and approach each question with confidence.
One effective approach is practicing deep breathing techniques. When you feel anxiety creeping in, take a few moments to breathe deeply and slowly. This helps to reduce stress and refocus your thoughts. Here are some other helpful techniques to stay calm:
- Visualize Success: Picture yourself calmly answering questions and successfully completing the test. Visualization can boost your confidence and reduce nervousness.
- Stay Present: Focus only on the question in front of you, rather than worrying about how many questions are left or what score you might get. Staying in the moment helps you avoid overwhelming yourself.
- Practice Relaxation Exercises: Before the test, try practicing relaxation techniques such as progressive muscle relaxation. This can help ease any tension in your body during the assessment.
- Take Breaks: If the assessment allows, take brief moments to stretch or relax your muscles to release any tension that may be building up.
- Positive Self-Talk: Remind yourself that you’ve prepared well and are capable of handling the challenge. Positive affirmations can reduce stress and increase your self-assurance.
Maintaining a calm demeanor will not only help you think clearly but will also allow you to make better decisions and avoid rushing through questions. By staying relaxed, you’ll increase your chances of performing at your best.