Understanding cardiac rhythms is essential for healthcare professionals, particularly nurses working in critical care environments. Accurate identification and timely intervention can significantly impact patient outcomes. The ability to recognize abnormal heart patterns and respond appropriately is a crucial skill that every nurse must develop.
To succeed in this area, it’s important to familiarize oneself with various types of heart irregularities, as well as the tools and techniques used to diagnose and treat them. With proper knowledge and practice, nurses can gain the confidence needed to handle these challenges effectively.
Utilizing reliable resources and studying common heart rhythm scenarios will enable nurses to improve their proficiency. By focusing on real-world cases, it becomes easier to connect theoretical knowledge with practical application, ensuring better patient care in emergencies.
Cardiac Rhythm Mastery Guide for Nurses

Gaining a deep understanding of heart rhythms and their irregularities is crucial for nursing professionals, particularly those involved in critical care. Mastery of this subject allows for precise assessment, rapid decision-making, and effective intervention in high-pressure situations. Nurses equipped with the right knowledge are better prepared to handle emergency cardiac events and improve patient outcomes.
The process of preparing for this area of nursing practice involves both theoretical study and hands-on experience. By focusing on the different types of heart irregularities, as well as the related diagnostic techniques, nurses can strengthen their ability to recognize and address various conditions swiftly and accurately.
A comprehensive guide can be a valuable resource in this learning journey, helping nurses not only familiarize themselves with essential concepts but also practice critical thinking skills in real-world scenarios. Below is a table highlighting key topics that should be understood for effective mastery in this field:
| Topic | Description |
|---|---|
| Heart Rhythm Identification | Recognizing various types of heart rhythms, both normal and abnormal, to ensure accurate diagnoses. |
| Electrocardiogram Interpretation | Understanding how to read ECG strips and identifying signs of irregularities. |
| Medication Management | Familiarizing oneself with drugs used to treat arrhythmias and their proper administration. |
| Cardiac Emergency Protocols | Knowing the correct steps to take in a cardiac emergency, including advanced interventions. |
| Patient Monitoring Techniques | Developing proficiency in monitoring patients with cardiac conditions for early signs of complications. |
By carefully studying these key topics, nurses can enhance their ability to handle a wide range of cardiac-related issues, ensuring the best possible care for their patients. Additionally, continuous practice and learning will build confidence and expertise in managing complex heart conditions.
Understanding Cardiac Rhythms for Nurses
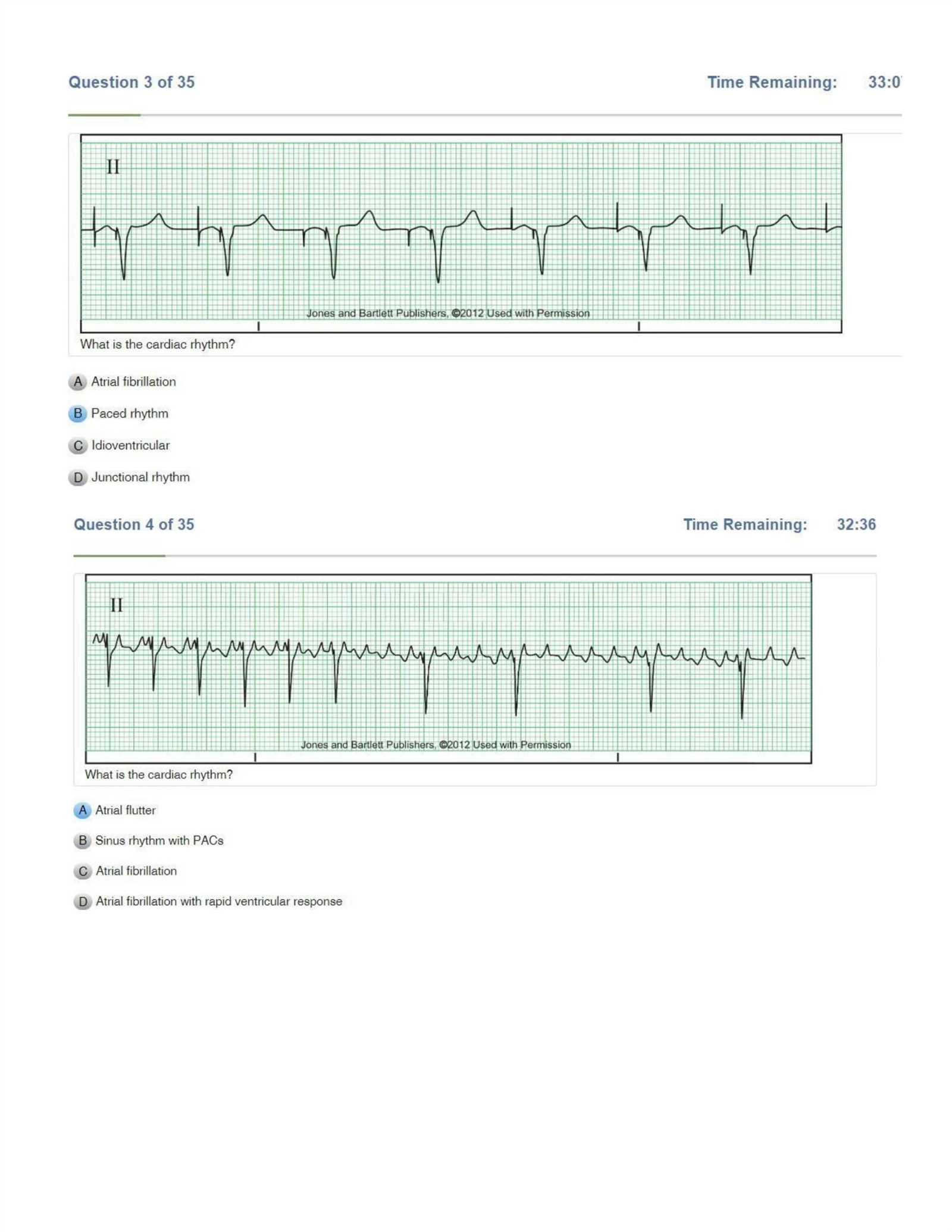
As healthcare professionals, nurses play a critical role in identifying and managing irregular heart patterns. These abnormalities can range from minor disturbances to life-threatening conditions, and recognizing them quickly is essential for effective patient care. Understanding the underlying mechanisms, classification, and treatment options is key to managing these conditions with confidence and accuracy.
For nurses, it is crucial to become familiar with how the heart functions under normal and abnormal circumstances. By mastering the basics of heart rhythms, such as the electrical conduction system, nurses can detect potential issues earlier, leading to quicker interventions and better patient outcomes. Building this knowledge not only supports clinical practice but also aids in the interpretation of diagnostic tests and patient monitoring.
In this section, we will explore the various types of cardiac arrhythmias, their symptoms, and the strategies nurses use to assess and manage them effectively in the clinical setting. Understanding these rhythms enhances the nurse’s ability to make informed decisions and provide timely, life-saving interventions when necessary.
How Practice Resources Can Enhance Your Knowledge
Utilizing reliable practice materials can significantly improve your understanding of complex healthcare concepts, especially when it comes to mastering irregular heart rhythms. These resources provide both theoretical knowledge and practical insights, allowing healthcare professionals to gain confidence in recognizing and managing heart conditions.
Benefits of Using Practice Materials
- Enhanced Learning – Reviewing detailed examples and scenarios helps reinforce key concepts, making it easier to apply knowledge in real-world situations.
- Increased Speed and Accuracy – Regular practice improves the ability to quickly identify abnormal rhythms, leading to more efficient decision-making during emergencies.
- Improved Diagnostic Skills – Working through practice questions sharpens diagnostic abilities, helping professionals interpret results with greater precision.
How to Make the Most of These Resources

- Consistent Practice – Regularly reviewing and working through questions will build a deeper understanding and boost retention of critical information.
- Simulate Real Scenarios – Practice materials often present case studies that simulate real clinical situations, allowing users to test their knowledge under pressure.
- Analyze Results – Review incorrect answers to identify areas that need improvement and focus future study efforts on those topics.
By leveraging these valuable resources, healthcare professionals can strengthen their knowledge and readiness, ensuring they are well-equipped to handle critical situations involving heart rhythm disturbances.
Key Concepts in Cardiac Rhythm Diagnosis
Accurately diagnosing irregular heart rhythms is essential for effective patient care. By understanding the key factors that contribute to these conditions, healthcare professionals can identify issues earlier and implement appropriate interventions. Mastering the concepts that underpin rhythm analysis allows for better clinical decision-making and improved patient outcomes.
Important Factors in Diagnosing Heart Rhythms
- Electrical Conduction System – Understanding how electrical impulses travel through the heart is essential for recognizing abnormalities.
- ECG Interpretation – Analyzing electrocardiogram results is crucial for identifying various rhythm disturbances and their severity.
- Patient History – A comprehensive patient history, including medical conditions and medications, can offer valuable insight into potential rhythm problems.
- Clinical Symptoms – Symptoms such as dizziness, shortness of breath, or chest pain often indicate underlying rhythm issues.
Common Types of Cardiac Rhythms
| Rhythm | Characteristics | Possible Causes |
|---|---|---|
| Sinus Tachycardia | Increased heart rate above 100 bpm | Exercise, fever, anxiety |
| Atrial Fibrillation | Irrregular, rapid heart rate with no clear P waves | Hypertension, heart disease, stress |
| Ventricular Fibrillation | Rapid, chaotic rhythm leading to ineffective heart pumping | Myocardial infarction, cardiomyopathy |
| Bradycardia | Slow heart rate below 60 bpm | Hypothyroidism, heart block, medications |
By mastering these concepts, healthcare providers can effectively recognize and manage a variety of cardiac rhythm disorders. This foundational knowledge supports clinical practice and enhances patient safety during diagnostic and treatment procedures.
Study Tips for Cardiac Rhythm Questions
Preparing for questions related to heart rhythm disorders requires focused study and effective strategies. Understanding key concepts and practicing real-life scenarios helps develop the skills needed to accurately interpret various conditions. By honing your knowledge and testing your comprehension, you can improve both your theoretical and practical abilities.
Break Down Complex Concepts – Start by understanding the fundamentals of how the heart works and how electrical impulses influence heart rhythms. This foundational knowledge is crucial for recognizing irregularities and understanding their causes. Once these basics are clear, focus on more complex conditions and their diagnostic criteria.
Practice with Real-World Scenarios – Apply your knowledge by reviewing case studies and rhythm strip examples. This helps to build confidence in diagnosing different types of heart issues. The more exposure you get to various cases, the better prepared you will be for any situation that may arise.
Focus on Common Patterns – Not all heart rhythm disturbances are equally common. Prioritize learning the most frequently encountered patterns, such as atrial fibrillation, sinus tachycardia, and bradycardia. Knowing these rhythms well will make it easier to identify them quickly and accurately in real-life scenarios.
Use Practice Questions – Testing yourself with practice questions is an excellent way to reinforce your learning. It helps you become more familiar with how questions are structured and the types of information that are most likely to be asked. Focus on understanding why the correct answer is right and why the others are incorrect.
Review Mistakes – After practicing, take the time to review the questions you got wrong. Understanding why you missed certain answers will help you identify areas that need improvement, making your study sessions more effective. Regularly reviewing mistakes will reinforce your understanding and prevent them from being repeated.
Common Cardiac Rhythm Patterns in Nursing
In nursing practice, it’s essential to recognize and understand the most common patterns of heart irregularities. Identifying these disturbances early enables timely intervention and improves patient outcomes. Nurses play a critical role in monitoring patients for signs of these conditions and responding appropriately to prevent further complications.
Frequent Heart Rhythm Disorders
There are several key heart rhythm disorders that nurses commonly encounter in clinical settings. Understanding the distinguishing characteristics of each condition allows healthcare professionals to act quickly and confidently. Below are some of the most frequent rhythm abnormalities:
- Atrial Fibrillation – Characterized by rapid and irregular heartbeats, often leading to blood clots and stroke risk.
- Bradycardia – A slower-than-normal heart rate, typically under 60 beats per minute, which may cause dizziness or fainting.
- Tachycardia – An abnormally fast heart rate, typically above 100 beats per minute, which can result in shortness of breath and chest pain.
- Ventricular Fibrillation – A life-threatening condition where the heart’s electrical activity becomes chaotic, leading to ineffective pumping.
Recognizing Patterns in Clinical Practice
Nurses must develop a keen eye for identifying these rhythms by using tools like electrocardiograms (ECGs) and clinical observation. Early detection allows for timely intervention, such as administering medications or preparing for more advanced treatments like defibrillation. Consistent practice and knowledge of these common patterns are essential for improving patient care in cardiac emergencies.
Mastering Electrocardiogram (ECG) Interpretation
Interpreting electrocardiograms (ECGs) is a critical skill for healthcare professionals, particularly when monitoring heart health and diagnosing rhythm disorders. An ECG provides a visual representation of the heart’s electrical activity, making it essential for identifying abnormalities such as arrhythmias, ischemia, or other cardiac conditions. Mastery of ECG interpretation allows healthcare providers to make informed decisions and deliver timely interventions.
Key Components of an ECG
Understanding the different components of an ECG strip is fundamental for accurate interpretation. Each wave and interval represents a specific phase of the heart’s electrical cycle. Key elements to focus on include:
- P wave – Represents atrial depolarization, which triggers the contraction of the atria.
- QRS complex – Represents ventricular depolarization, which triggers the contraction of the ventricles.
- T wave – Represents ventricular repolarization, the recovery phase of the ventricles after contraction.
- PR interval – The time it takes for the electrical impulse to travel from the atria to the ventricles.
- QT interval – Represents the time it takes for the ventricles to contract and recover.
Steps for Effective ECG Interpretation
To interpret an ECG strip effectively, it is important to follow a structured approach. This ensures that no critical information is overlooked and helps in identifying irregularities:
- Identify the Rate: Calculate the heart rate by counting the number of R waves in a 10-second interval and multiplying by six.
- Examine Rhythm: Check if the rhythm is regular or irregular by assessing the consistency of the R-R intervals.
- Analyze P Waves: Ensure that the P waves are present and consistent, indicating proper atrial activity.
- Evaluate the PR Interval: Measure the PR interval to ensure it falls within the normal range (0.12 to 0.20 seconds).
- Assess the QRS Complex: Ensure that the QRS complex is narrow (less than 0.12 seconds) unless there is a known bundle branch block.
- Look for Abnormalities: Check for signs of ischemia, infarction, or arrhythmias, such as ST-segment elevation or depression, or irregular beats.
With consistent practice and attention to detail, mastering ECG interpretation becomes a powerful tool for diagnosing and managing cardiac conditions effectively. By recognizing patterns and abnormalities early, healthcare providers can offer better patient care and prevent more serious complications.
Important Cardiac Rhythm Medications to Know
Understanding the medications used to treat heart rhythm disorders is crucial for healthcare professionals. These drugs help manage abnormal heart rates, restore normal rhythm, and prevent complications such as stroke or heart failure. It is essential to be familiar with the different classes of medications, their mechanisms of action, and when they are indicated in patient care.
Antiarrhythmic Medications – These are the primary class of drugs used to treat irregular heart rhythms. They work by altering the electrical impulses within the heart to restore a normal rhythm. Common antiarrhythmic drugs include:
- Amiodarone – A potent antiarrhythmic often used to treat life-threatening arrhythmias like ventricular tachycardia or atrial fibrillation.
- Lidocaine – Typically used for ventricular arrhythmias, especially after a heart attack or during surgery.
- Flecainide – A medication used for supraventricular arrhythmias, particularly in patients without underlying heart disease.
Beta-Blockers – These medications are commonly prescribed to slow the heart rate and control arrhythmias related to high blood pressure or anxiety. They block the effects of adrenaline, reducing the heart’s workload and lowering the risk of arrhythmic episodes. Common examples include:
- Metoprolol – Often used for chronic conditions like hypertension and heart failure to control heart rate and reduce arrhythmia risks.
- Atenolol – A beta-blocker that helps in controlling atrial fibrillation and improving overall heart function.
Calcium Channel Blockers – These drugs help manage arrhythmias by inhibiting calcium from entering heart cells, which slows the electrical conduction and reduces the heart rate. They are particularly useful for conditions like atrial fibrillation and hypertension. Some common medications include:
- Diltiazem – A calcium channel blocker that slows the heart rate, often used in atrial fibrillation and supraventricular tachycardia.
- Verapamil – Another calcium channel blocker used to control ventricular rate and alleviate symptoms in atrial fibrillation.
Anticoagulants – Medications that help reduce the risk of blood clots in patients with arrhythmias like atrial fibrillation. These drugs help prevent stroke by thinning the blood, making it less likely to clot. Key anticoagulants include:
- Warfarin – A long-established blood thinner used to prevent clots in patients with abnormal heart rhythms.
- Apixaban – A newer anticoagulant that works to prevent stroke in patients with atrial fibrillation.
By understanding the role and proper use of these medications, healthcare providers can effectively manage patients with abnormal heart rhythms, improving patient outcomes and reducing complications. It’s essential for nurses and medical professionals to stay updated on the latest treatment protocols and medication options to deliver the best care possible.
Managing Cardiac Emergencies Effectively
Cardiac emergencies require swift and efficient intervention to prevent life-threatening complications. Timely and appropriate management can make the difference between recovery and severe consequences, including death. Healthcare professionals must be well-prepared to assess, diagnose, and treat these emergencies in a systematic manner. Effective management involves recognizing symptoms early, applying appropriate interventions, and providing ongoing monitoring to stabilize the patient.
Steps for Immediate Response
When faced with a cardiac emergency, the first priority is to ensure patient safety and begin necessary interventions. The following steps are crucial:
- Assess the patient’s condition: Quickly evaluate the patient’s consciousness, airway, breathing, and circulation (ABCs). Ensure the patient is stable enough to continue treatment.
- Monitor vital signs: Obtain immediate measurements of heart rate, blood pressure, oxygen levels, and respiratory rate. Monitoring these will help guide further treatment.
- Administer oxygen: Provide supplemental oxygen to maintain adequate oxygenation, especially if the patient shows signs of hypoxia.
- Prepare for defibrillation if needed: For patients with life-threatening arrhythmias like ventricular fibrillation, immediate defibrillation can restore a normal rhythm.
Key Interventions in Cardiac Emergencies
In cardiac emergencies, a range of interventions can be applied depending on the nature of the emergency. These may include pharmacological treatments, procedural interventions, or both. Some common treatments include:
- Medications: Administering antiarrhythmic drugs, anticoagulants, or vasopressors based on the specific condition. Medications help stabilize heart rhythm and prevent complications.
- Cardioversion: For certain arrhythmias, synchronized electrical shocks can be delivered to restore a normal rhythm, usually when medications are ineffective.
- Advanced airway management: In some cases, the patient may need advanced airway support such as intubation to secure the airway and ensure proper ventilation.
- CPR (Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation): If the heart stops beating, immediate CPR is necessary to provide oxygen to vital organs until defibrillation or further treatment can be administered.
By acting quickly and following evidence-based protocols, healthcare providers can significantly improve outcomes in patients experiencing cardiac emergencies. Ongoing education and training in emergency response are key to ensuring that all team members are prepared to handle such critical situations effectively.
Essential ECG Rhythm Strips to Recognize
Being able to accurately identify and interpret ECG rhythm strips is crucial for healthcare professionals involved in cardiac care. Recognizing various heart rhythms quickly allows for timely intervention and improves patient outcomes. This section highlights some of the most common and important ECG patterns that every healthcare provider should be familiar with.
Common ECG Rhythms and Their Significance
Understanding the characteristics of common ECG rhythms is essential for making accurate diagnoses and providing appropriate treatments. Here are several key rhythms to recognize:
- Normal Sinus Rhythm: This is the baseline rhythm, indicating a regular heart rate between 60 and 100 beats per minute. The P-wave, QRS complex, and T-wave appear normal and consistent.
- Atrial Fibrillation: This rhythm is marked by irregular, rapid electrical activity in the atria. It is characterized by an absence of distinct P-waves and an irregularly irregular ventricular response.
- Ventricular Tachycardia: A life-threatening arrhythmia, ventricular tachycardia presents with a fast heart rate originating in the ventricles. It is typically seen with wide, bizarre QRS complexes.
- Ventricular Fibrillation: This is a chaotic electrical activity in the ventricles, leading to ineffective pumping. The rhythm is irregular with no identifiable QRS complexes, P-waves, or T-waves, and is a medical emergency.
- Third-Degree Heart Block: A complete block in the conduction between the atria and ventricles. The atria and ventricles beat independently, resulting in a slow and irregular ventricular rhythm.
Importance of Early Recognition
Quick recognition of abnormal rhythms can prevent complications such as stroke, heart failure, or even death. By knowing how to identify these common patterns on an ECG strip, healthcare providers can initiate the appropriate treatment immediately, whether it involves medication, electrical therapy, or other interventions. Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial to improving patient outcomes in cardiac emergencies.
Role of Nurses in Dysrhythmia Care
Nurses play a crucial role in the care and management of patients with abnormal heart rhythms. Their responsibilities go beyond basic monitoring; they are instrumental in early detection, patient education, and collaboration with the healthcare team to ensure timely and effective treatment. Nurses are often the first line of defense when it comes to recognizing signs of irregular cardiac rhythms, and their ability to respond quickly can significantly impact patient outcomes.
In addition to monitoring vital signs and assessing the patient’s condition, nurses are responsible for administering medications, managing advanced life support protocols, and ensuring that patients are comfortable and well-informed throughout their care. Their role in educating patients about the nature of their condition, as well as the treatment options available, is essential in promoting long-term health and preventing recurrence of rhythm disturbances.
As part of a multidisciplinary team, nurses are also involved in coordinating care plans and helping to implement therapeutic interventions, including medication adjustments, electrical therapies, and lifestyle changes. Their expertise in interpreting cardiac rhythms and responding to emergencies helps to optimize treatment strategies and improve patient safety.
Understanding Sinus and Atrial Rhythms
Sinus and atrial rhythms are fundamental to the understanding of normal and abnormal heart electrical activity. These rhythms originate from the sinus node or atrial tissue and play a key role in maintaining proper heart function. Accurate recognition of these patterns is critical in diagnosing potential issues related to the heart’s electrical system.
Sinus Rhythms: Characteristics and Importance
Sinus rhythms are considered the standard heart rhythms, originating from the sinoatrial (SA) node, which is the natural pacemaker of the heart. Here are some key characteristics of sinus rhythms:
- Regular Rhythm: The heart rate remains steady, typically between 60-100 beats per minute in adults.
- P-Wave: Each beat is preceded by a consistent P-wave, indicating atrial depolarization.
- QRS Complex: The QRS complex follows each P-wave in a 1:1 ratio, signifying the conduction of electrical impulses through the ventricles.
- Normal Duration: The intervals between beats, including the PR and QRS intervals, remain within normal ranges.
Atrial Rhythms: Understanding Variations
Atrial rhythms refer to those that originate within the atria, either in the SA node or another pacemaker in the atrium. While these rhythms are typically normal, variations can indicate potential heart conditions. Common atrial rhythms include:
- Atrial Flutter: Characterized by rapid, regular atrial contractions, often producing a sawtooth pattern on the ECG.
- Atrial Fibrillation: A disorganized, irregular rhythm, where the atria quiver instead of contracting normally, leading to an irregular ventricular response.
- Premature Atrial Contractions (PACs): Early beats originating from the atria that can cause a skipped or extra heartbeat.
Recognizing sinus and atrial rhythms is crucial in diagnosing underlying conditions and determining appropriate interventions. By understanding their characteristics, healthcare providers can ensure proper care and improve patient outcomes.
Comprehensive Dysrhythmia Exam Preparation
Thorough preparation for assessments related to heart rhythm disturbances is essential for anyone involved in cardiac care. Mastering the key concepts and becoming familiar with various rhythm patterns enables healthcare professionals to approach the subject confidently and efficiently. Proper preparation goes beyond memorization; it involves understanding the underlying physiology, recognizing different rhythm disturbances, and applying appropriate interventions.
One effective way to prepare is by reviewing common rhythm types and their characteristics. This includes becoming proficient in identifying normal rhythms as well as recognizing abnormal patterns that may indicate underlying issues. Additionally, it’s important to familiarize oneself with common treatments and interventions for each type of irregularity, from pharmacological options to more advanced procedures like cardioversion.
Studying the tools used for rhythm assessment, such as electrocardiograms (ECGs), is also critical. Knowing how to interpret an ECG strip accurately can make the difference between quick diagnosis and delay in treatment. Focus on understanding the timing of intervals, waveforms, and their significance in different arrhythmic conditions.
Incorporating practice questions and case studies into your study routine is an excellent way to simulate real-world scenarios. This not only reinforces theoretical knowledge but also develops critical thinking skills necessary for effective decision-making during patient care.
Advanced Dysrhythmia Topics for Nurses
For nurses working in the field of cardiac care, understanding advanced topics related to heart rhythm disorders is crucial. These concepts go beyond basic rhythm recognition and require in-depth knowledge of complex conditions that can affect a patient’s cardiovascular system. A deeper grasp of these subjects not only improves patient outcomes but also enhances the nurse’s ability to make informed decisions under pressure.
Advanced topics in this area often involve understanding the pathophysiology behind various rhythm disturbances and the potential risks they pose. Nurses must be familiar with the latest interventions and treatment protocols that are tailored to each specific arrhythmic condition. This includes pharmacological treatments, electrical cardioversion, and the use of devices such as pacemakers and defibrillators.
Complex Arrhythmias and Their Management
Complex arrhythmias, such as ventricular fibrillation or atrial flutter, can be life-threatening if not managed correctly. Nurses must understand the nuances of these conditions, including how they develop, their symptoms, and the appropriate emergency interventions. Advanced training allows nurses to identify these rhythms quickly and initiate the correct interventions, such as defibrillation or medication administration, to stabilize the patient.
Cardiac Devices and Their Role in Rhythm Management
As part of advanced cardiac care, nurses should be well-versed in the use of implantable devices that help manage rhythm disorders. These devices, such as implantable cardioverter defibrillators (ICDs) and pacemakers, play a significant role in preventing life-threatening arrhythmias. Understanding how these devices work and their troubleshooting protocols is essential for providing comprehensive care to patients who rely on them for rhythm stabilization.
Improving Speed and Accuracy in Exams
Achieving both speed and accuracy during assessments requires a combination of preparation, focus, and effective strategies. Whether you are tackling multiple-choice questions or solving complex problems, mastering these skills is essential for performing well under pressure. A disciplined approach to studying and applying time-management techniques can significantly enhance your performance.
To improve your ability to quickly and accurately respond to questions, consider the following strategies:
- Understand the Core Concepts: Before attempting any questions, ensure that you have a solid understanding of the key topics. This foundational knowledge will help you recall information more quickly and reduce the chances of making errors.
- Practice Regularly: Regular practice with timed tests helps you become familiar with the format and structure of the questions, improving both your speed and precision.
- Work on Time Management: Allocate specific time limits to different sections or question types. This practice will help you avoid spending too much time on one question, ensuring you can address all items within the time frame.
- Learn to Prioritize: Tackle questions you feel most confident about first, leaving more challenging ones for later. This strategy ensures that you secure easy points early on, reducing stress as you approach more difficult questions.
By incorporating these techniques into your study routine, you can improve your ability to answer questions quickly while maintaining accuracy. This combination of skills is vital for achieving success in any type of assessment.
Resources for Exam Success

Achieving success in any assessment requires more than just studying the material; it involves having access to the right resources that can enhance your learning experience and help you perform at your best. Online platforms and educational tools offer a wealth of resources that can guide you through complex topics, provide practice opportunities, and help you build confidence. These resources are designed to support learners in mastering challenging concepts and improving their test-taking strategies.
Here are some valuable resources to consider for boosting your exam preparation:
- Interactive Practice Tests: Engage with practice tests that simulate real exam conditions. These resources help you become familiar with the format of questions, improve your time management, and identify areas where further study may be needed.
- Study Guides and Review Materials: Comprehensive study guides offer in-depth explanations of key concepts, often with step-by-step solutions. These materials help reinforce learning and ensure that all important topics are covered.
- Online Communities and Forums: Join online forums where you can interact with peers, discuss difficult topics, and share tips and strategies. Collaborating with others can help deepen your understanding and offer new perspectives on problem-solving.
- Video Tutorials and Webinars: Visual learning resources such as video tutorials and webinars allow you to see complex topics explained in real-time. These resources are particularly helpful for visual learners and those who prefer interactive content.
- Flashcards and Quizzes: Use digital flashcards and quizzes to reinforce key facts and concepts. These tools are ideal for quick reviews and can be accessed anytime to fit your study schedule.
Leveraging these resources will give you a well-rounded approach to preparing for any assessment. By practicing with interactive tools, reviewing important topics, and connecting with other learners, you can improve your performance and increase your chances of success.