
Successfully passing certification assessments in the healthcare field requires not only knowledge but also the ability to apply that knowledge under pressure. For anyone aiming to excel in clinical laboratory practices, understanding key concepts and mastering procedures is crucial. This guide offers a structured approach to mastering the essential aspects of blood collection and analysis techniques that are commonly tested.
The process involves detailed attention to anatomy, patient safety, and proper collection methods. Whether you are reviewing procedures or brushing up on specific protocols, this resource serves as a comprehensive tool for those looking to excel in their assessment. Focusing on the most frequently asked questions and standard practices will greatly increase your confidence and performance.
Mastering this material will provide you with the confidence to navigate through your assessments smoothly. By understanding the underlying principles and testing strategies, you can approach each section with ease and accuracy. Prepare effectively by studying important topics and reviewing essential methods that are commonly evaluated in medical tests.
Phlebotomy Final Exam Answer Key
Understanding the critical aspects of blood collection and laboratory analysis is essential for those seeking certification in healthcare-related fields. To achieve success in assessments, it’s important to review the various processes, safety protocols, and technical skills commonly tested. By focusing on key areas such as sample collection methods, patient interaction, and proper procedure adherence, candidates can ensure they are well-prepared for any evaluation.
This section provides a detailed overview of the necessary concepts and procedures often included in professional testing. It highlights the essential techniques, common errors to avoid, and tips for interpreting practical tasks. Mastery of these topics will not only help you answer questions with confidence but also improve your overall competence in the field.
With a thorough understanding of standard practices, you will be equipped to handle different types of assessments effectively. Review of critical steps, from patient preparation to specimen handling, will ensure you’re ready to perform accurately and professionally. Emphasizing precision, safety, and efficiency is key to excelling in practical tests and succeeding in your certification journey.
Overview of Phlebotomy Exam Structure

Assessments in healthcare fields, especially those involving laboratory and clinical procedures, follow a structured format designed to evaluate practical and theoretical knowledge. Understanding the general structure of these evaluations is essential for effective preparation. These tests typically assess both your ability to apply techniques and your understanding of protocols and safety measures.
Key Areas Covered in Assessments
The structure usually includes various sections that focus on different aspects of healthcare practice. Some key areas typically covered are:
- Collection techniques and methods
- Patient preparation and safety protocols
- Understanding laboratory equipment and tools
- Common errors and troubleshooting
- Professional and ethical behavior in medical environments
Test Formats and Question Types
Depending on the testing organization, the structure may involve both written and practical components. Below are common formats used in these types of assessments:
- Multiple-choice questions to test theoretical knowledge
- Practical demonstrations to evaluate hands-on skills
- Short-answer questions focused on procedures and terminology
Understanding the test structure allows you to prioritize study areas, ensuring a well-rounded approach to both practical and theoretical components. With proper preparation, you can confidently approach each section of the assessment with the required knowledge and skills.
Key Topics to Focus On
When preparing for a certification assessment in healthcare practices, it is important to concentrate on the most relevant areas that are frequently tested. Mastering these topics will help you demonstrate both your theoretical knowledge and practical abilities. Focus on understanding the procedures, techniques, and safety protocols that are central to patient care and laboratory practices.
Essential Areas to Study
Here are the key topics that should be prioritized during preparation:
- Blood collection techniques and best practices
- Proper patient identification and safety measures
- Handling and labeling of specimens
- Understanding anatomical landmarks for accurate sampling
- Infection control practices and hygiene standards
- Knowledge of laboratory equipment and tools
- Common complications and troubleshooting during procedures
Important Concepts to Review

Additionally, the following concepts are crucial for understanding the underlying principles of healthcare testing:
- Phlebotomy terminology and definitions
- Ethical considerations and professional conduct
- Regulatory guidelines and patient confidentiality
- Understanding blood circulation and vein identification
Focusing on these topics will ensure that you are well-prepared to perform procedures with accuracy and confidence while also demonstrating a comprehensive understanding of the key concepts in healthcare testing.
Common Questions on Phlebotomy Exams
During certification assessments in the healthcare field, certain questions and topics tend to be more frequently tested. These commonly addressed subjects often focus on both practical skills and theoretical knowledge essential for performing clinical tasks. Preparing for these common queries helps ensure you’re ready to tackle the most relevant and challenging aspects of your assessment.
Frequently Asked Topics
Here are some typical questions that candidates may encounter in their assessments:
- What are the proper techniques for blood collection?
- How do you identify and prepare a patient for a procedure?
- What are the most common complications during blood draws and how to avoid them?
- What are the different types of blood samples and their uses?
- How do you handle and store specimens after collection?
- What are the steps for ensuring patient safety during medical procedures?
- How do you troubleshoot common issues in the collection process?
Test Scenarios and Challenges
In addition to theoretical questions, practical scenarios are often presented to evaluate real-world problem-solving. These may include:
- Handling difficult veins or patient discomfort
- Managing sample contamination or incorrect labeling
- Dealing with emergency situations in a medical setting
Familiarity with these common questions and scenarios ensures that you are equipped with the knowledge and confidence to excel in your assessment. Reviewing these topics thoroughly will allow you to demonstrate both practical competency and a deep understanding of the required procedures.
Understanding Blood Collection Techniques
Blood collection is a fundamental skill in healthcare, essential for diagnostic testing and patient care. Mastering the various techniques used for obtaining blood samples ensures accuracy, patient safety, and the reliability of results. It is crucial to understand the different methods and when to apply them, as well as how to minimize discomfort and complications for patients.
The process involves multiple steps, from patient identification and preparation to the actual collection of the sample. Proper technique not only ensures that the sample is viable for testing but also helps prevent potential errors, such as contamination or improper labeling. Familiarity with the most common procedures, such as venipuncture, capillary draws, and arterial sampling, is essential for success in any clinical setting.
Key considerations include choosing the right site for collection, using appropriate equipment, and following safety protocols to reduce the risk of infection or injury. Additionally, understanding how to handle specimens after collection is just as important to ensure that they remain intact and uncontaminated until analysis. Mastery of these techniques is vital for anyone seeking to perform this critical role with competence and professionalism.
Correct Procedures for Phlebotomy Tests
Following the correct procedures for blood collection is essential to ensure accurate test results and maintain patient safety. Each step of the process, from preparation to sample handling, must be performed with precision and care. Proper technique minimizes the risk of contamination, reduces discomfort, and prevents errors that could affect the outcome of diagnostic testing.
It begins with ensuring the patient is correctly identified and comfortable, as well as preparing the necessary equipment, such as sterile needles, collection tubes, and gloves. Selecting the appropriate site for collection, whether it be a vein or capillary, is a crucial part of the process. The collection itself must be performed following established protocols to ensure that the sample is viable and uncontaminated.
Once the sample is collected, proper labeling and documentation are essential to avoid any mix-up or mistakes. Afterward, the specimen must be handled carefully and transported to the laboratory under appropriate conditions to preserve its integrity. Adhering to these steps guarantees that the blood collection process is completed correctly and efficiently, providing reliable results for patient diagnosis.
How to Interpret Lab Results
Interpreting laboratory results is a critical skill for healthcare professionals, as it directly impacts patient care decisions. Accurate interpretation involves understanding normal ranges, recognizing abnormal values, and knowing when further investigation is required. The ability to analyze test results effectively ensures timely and accurate diagnoses, which is essential for appropriate treatment planning.
Lab results typically provide numerical values, which are compared to reference ranges based on healthy individuals. Anomalies or deviations from these ranges can indicate potential health issues that may require additional testing or intervention. Professionals must also consider the patient’s medical history, symptoms, and other factors that could influence the results.
Below is an example table illustrating some common lab tests and their reference ranges, which can help guide the interpretation process:
| Test | Normal Range | Possible Abnormal Findings |
|---|---|---|
| Hemoglobin | 13.8-17.2 g/dL (male), 12.1-15.1 g/dL (female) | Low levels may indicate anemia; high levels could suggest dehydration or lung disease. |
| White Blood Cell Count | 4,500-11,000 cells/µL | Elevated levels may suggest infection or inflammation; low levels could indicate immune system issues. |
| Platelet Count | 150,000-450,000 cells/µL | Low levels may indicate bleeding disorders; high levels could suggest risk of clotting. |
By understanding these values and the potential causes of deviations, healthcare providers can make informed decisions about next steps in patient care. Effective interpretation of lab results is essential in ensuring that each patient receives the most appropriate and timely treatment.
Phlebotomy Safety and Protocols
Ensuring the safety of both patients and healthcare workers is a top priority in any clinical procedure. Proper safety measures and protocols are essential to prevent accidents, minimize infection risks, and maintain a sterile environment. Healthcare providers must follow specific guidelines to ensure procedures are performed correctly and safely.
Essential Safety Measures
Key safety practices include:
- Personal protective equipment (PPE): Always use gloves, face shields, and protective gowns to minimize exposure to bodily fluids.
- Needle safety: Dispose of needles and sharp instruments immediately in appropriate containers to prevent needle-stick injuries.
- Hygiene protocols: Proper hand washing and sanitization of all equipment help reduce the risk of contamination and infection.
Protocol for Safe Blood Collection

Following a systematic approach ensures both patient safety and the accuracy of collected samples:
- Confirm patient identity and inform them about the procedure to reduce anxiety.
- Select the proper site for sample collection, ensuring it is free of infection or scarring.
- Use sterile equipment and maintain a clean workspace at all times.
- Monitor the patient during and after the procedure for any signs of complications, such as dizziness or hematoma formation.
By adhering to these safety protocols, healthcare professionals can reduce the risk of infection, injury, and errors during patient care. Proper training and vigilance in following safety guidelines are essential for maintaining a safe clinical environment.
Test Preparation Tips for Success
Effective preparation is crucial for achieving success in any assessment. To ensure that you perform at your best, it is essential to not only review the content but also adopt strategies that improve both understanding and recall. Preparation goes beyond memorizing facts–it requires mastering key concepts, practicing hands-on skills, and managing test-day stress.
Study Strategies

Here are some key tips to help you prepare effectively:
- Review core concepts: Focus on understanding the principles behind the procedures and techniques, rather than simply memorizing terms.
- Practice with sample scenarios: Work through practice questions or case studies to apply your knowledge to real-world situations.
- Use visual aids: Diagrams, charts, and videos can help reinforce complex information and provide a clearer understanding of processes.
Time Management and Focus

Proper time management is vital in the lead-up to your assessment. Break down your study sessions into manageable chunks and give yourself breaks to maintain focus. Stay organized and set clear, achievable goals for each session. The night before the test, ensure you have a good night’s rest to be well-rested and mentally sharp.
By adopting these strategies and staying consistent with your preparation, you will be well-equipped to approach the assessment with confidence and knowledge. Success comes from a balanced approach to studying, practice, and preparation for the day of the test.
Study Materials for Phlebotomy Exams
To succeed in any assessment related to blood collection and analysis, it is important to have the right study resources. These materials help reinforce theoretical knowledge, practical techniques, and overall comprehension. A combination of textbooks, online resources, and hands-on practice ensures a comprehensive approach to mastering the subject.
Essential Study Resources
Here are some key materials to consider when preparing:
- Textbooks: Books that cover anatomy, medical terminology, and clinical procedures provide a strong foundation. Look for updated editions with detailed explanations and practice questions.
- Online Courses: Interactive learning platforms offer video tutorials, quizzes, and discussions that can enhance your understanding and test readiness.
- Flashcards: Use digital or physical flashcards to review key terms, procedures, and safety protocols regularly. This method is great for active recall.
- Practice Questions: Many websites and study guides offer sample questions that simulate real-world assessments. These can help you familiarize yourself with the format and structure of questions.
Hands-On Practice
While theoretical knowledge is important, practical skills are equally vital. Here are a few ways to develop your technique:
- Practice with simulators: Some institutions offer practice mannequins or virtual simulators to help you develop blood collection skills in a controlled environment.
- Study groups: Join a study group where you can practice techniques on each other and discuss difficult concepts. Group learning often helps clarify challenging material.
By using these diverse study materials and strategies, you will be well-prepared to confidently face any challenges and succeed in the assessment process.
Time Management During the Exam
Effective time management is crucial when facing any assessment. Properly allocating time to each section and question helps ensure that you can complete the test confidently without rushing through any part of it. Successful candidates understand the importance of pacing themselves throughout the duration of the test and being mindful of the time they spend on each task.
Prioritize and Plan
Before diving into the questions, take a moment to quickly scan through the entire test. This allows you to get an overview of the structure and identify any sections that may require more time or focus. Once you’ve assessed the test, allocate your time based on the number of questions and the complexity of each section.
- Quick Questions First: Start with the questions that you find easiest. This will help you build momentum and ensure that you tackle straightforward tasks first.
- Time per Question: Keep track of time and assign an average amount of time for each question. If you’re stuck on a question, move on and come back to it later if time permits.
- Leave Time for Review: Reserve the last few minutes to review your answers. This will give you a chance to catch any mistakes or misinterpretations.
Stay Calm and Focused
As the clock ticks down, it’s essential to remain calm. Anxiety can waste valuable time, so take deep breaths and keep a steady pace. If you find yourself spending too much time on one question, remind yourself that each part of the assessment is important, and your focus should remain on completing it as efficiently as possible.
By managing your time wisely, you can ensure that you give each section the attention it deserves while completing the test within the allotted time. This strategy reduces stress and helps improve your performance.
How to Avoid Common Mistakes
During any assessment, it’s easy to make errors that could affect your performance. Recognizing and avoiding common mistakes is key to achieving better results. By adopting proactive strategies and staying focused, you can minimize these errors and approach the test with confidence.
Tips to Avoid Mistakes
- Read Instructions Carefully: One of the most common mistakes is failing to thoroughly read the instructions. Misunderstanding the requirements of a task can lead to errors that could have been easily avoided.
- Don’t Rush Through Questions: Rushing through questions can lead to careless mistakes. Take your time, read each question carefully, and ensure you understand it before answering.
- Review Your Work: After completing a section, quickly review your answers to make sure you’ve answered each question properly. Double-check for any skipped questions or errors.
Stay Organized and Focused
- Stay Calm Under Pressure: Anxiety can cloud your judgment and increase the chances of making mistakes. Keep calm, breathe, and focus on one question at a time.
- Manage Time Effectively: Poor time management can lead to rushed responses and overlooked questions. Plan your time wisely and ensure you leave enough time for each section.
By being mindful of these common mistakes and using the strategies mentioned, you will be better prepared to perform at your best. Avoiding these pitfalls can make all the difference in achieving success.
Important Terminology in Blood Collection
In the field of blood collection, a clear understanding of specific terminology is essential for success. Familiarizing yourself with these terms will not only help you communicate effectively but also enhance your ability to understand procedures, protocols, and safety measures. Mastering these key terms will contribute to a deeper comprehension of the entire process.
Key Terms to Know
- Venipuncture: The process of obtaining a blood sample by inserting a needle into a vein. This technique is commonly used for diagnostic testing.
- Capillary Blood Collection: A method of obtaining blood from the capillaries, often performed using a lancet. This is typically used for smaller sample requirements.
- Hematology: The branch of medicine concerned with the study of blood and its disorders. Understanding hematology is crucial for interpreting test results accurately.
- Anticoagulant: A substance that prevents blood from clotting. These are often used in blood collection tubes to ensure accurate test results.
- Serum: The clear, yellowish fluid that remains after blood has clotted. It contains antibodies and is often used for testing purposes.
Understanding the Vocabulary
Knowing the terminology surrounding blood collection helps ensure that you can perform tasks correctly and communicate effectively with colleagues and healthcare professionals. Each term has its own specific meaning and application, contributing to your overall competence in the field.
By mastering this terminology, you will feel more confident and prepared when handling various procedures, interpreting results, and interacting with others in the healthcare setting.
Understanding the Anatomy for Blood Collection
In any practice involving blood collection, a thorough understanding of human anatomy is essential. Knowing the key structures involved, such as veins, arteries, and the circulatory system, helps ensure that procedures are carried out safely and effectively. It is important to identify the right sites for blood collection and to be familiar with how to handle various anatomical challenges that may arise during the process.
Key Anatomical Concepts
- Veins: Veins are the primary vessels used for blood collection. They carry deoxygenated blood back to the heart. Knowledge of major veins, like the median cubital vein, helps ensure accurate and comfortable sample collection.
- Arteries: Arteries carry oxygen-rich blood away from the heart. While they are not typically used for blood collection, understanding their location and function is important to avoid accidental puncture during procedures.
- Capillaries: Small vessels that connect veins and arteries, capillaries are often used for blood collection in certain situations, such as fingerstick or heelstick methods.
- Skin Layers: Understanding the layers of the skin, such as the epidermis and dermis, is essential for knowing the appropriate depth for needle insertion and minimizing patient discomfort.
- Circulatory System: Familiarity with how blood circulates throughout the body allows for the proper identification of the best collection sites and a better understanding of the impact of different medical conditions on the process.
Practical Applications of Anatomical Knowledge
Knowing the anatomy relevant to blood collection helps prevent complications such as bruising, hematomas, and unnecessary discomfort for the patient. It also enables practitioners to make informed decisions when faced with difficult collection sites, improving both safety and accuracy during procedures.
By understanding the anatomical structures involved, you can ensure the highest standards of care and achieve the best results in your blood collection practices.
Ethics and Best Practices for Blood Collection
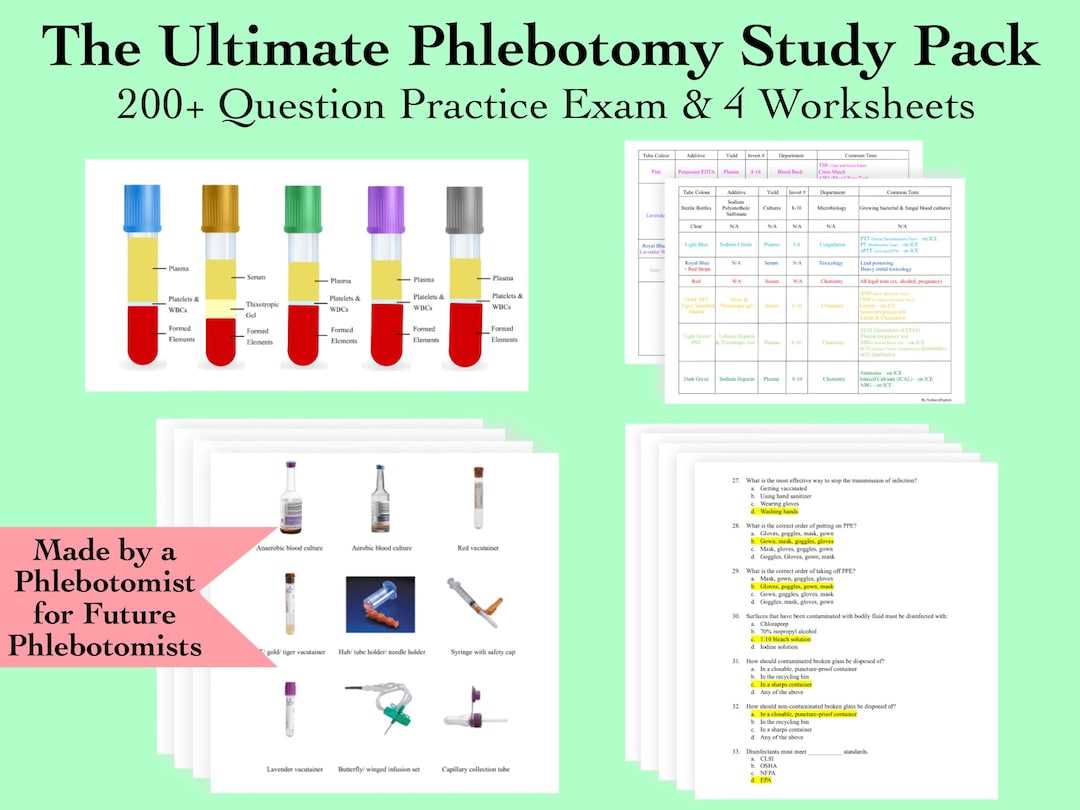
Ethics and best practices are essential in any healthcare practice, especially when performing tasks that directly involve patients’ health and well-being. In the field of blood collection, practitioners must maintain high standards of professionalism, respect patient confidentiality, and ensure the safety and comfort of those undergoing the procedure. Adhering to ethical guidelines not only promotes trust but also helps to prevent complications and ensures that the procedure is carried out properly.
Core Ethical Principles
The foundation of ethical practice in blood collection revolves around a few key principles that guide professional behavior and ensure patient rights are respected.
- Informed Consent: It is vital to obtain explicit consent from patients before performing any procedure. They must understand what is happening and have the right to decline.
- Confidentiality: Ensuring that patient information, including test results, is kept confidential is crucial for building trust and upholding privacy standards.
- Non-Discrimination: All patients, regardless of background, should receive the same level of care, dignity, and respect.
- Accountability: Practitioners must be accountable for their actions, ensuring that all procedures are performed according to established guidelines and protocols.
Best Practices in Blood Collection
Best practices refer to the highest standards of care when performing blood collection. They involve a combination of technical skill, proper preparation, and communication with patients. Adhering to these practices minimizes errors and enhances the overall patient experience.
| Practice | Description |
|---|---|
| Proper Identification | Verify the patient’s identity to prevent errors in blood collection and ensure that samples are correctly matched to the patient. |
| Cleanliness and Sterility | Always use sterile equipment and clean the collection site thoroughly to reduce the risk of infection. |
| Comfort and Communication | Make sure to communicate with the patient about the procedure and ensure their comfort throughout the process. |
| Correct Technique | Use the appropriate technique and tools for the type of blood collection being performed to ensure accuracy and minimize discomfort. |
By integrating these ethical principles and best practices, healthcare professionals can maintain a high level of professionalism, improve patient outcomes, and foster trust and respect in the healthcare setting.
What to Expect During the Assessment

When preparing for a certification or competency assessment, it’s important to understand the structure and expectations of the process. The assessment will test both theoretical knowledge and practical skills related to the procedures and techniques you have learned. You can expect a combination of multiple-choice questions, practical tasks, and scenario-based problems designed to evaluate your ability to apply knowledge in real-world situations.
Typically, the assessment will be divided into two main sections: a written part, which assesses your understanding of key concepts, and a practical part, which requires you to demonstrate hands-on skills in a controlled environment. Each section is designed to evaluate different aspects of your proficiency, ensuring that you are well-equipped for real-world situations.
Written Portion
The written part of the assessment will likely include various types of questions that cover core topics, such as:
- Technical knowledge: Questions may cover topics such as anatomy, safety protocols, and proper techniques.
- Regulatory standards: You may be asked about ethical practices, patient confidentiality, and compliance with healthcare regulations.
- Problem-solving: Scenario-based questions will assess your ability to make decisions and troubleshoot challenges that could arise during procedures.
Practical Portion
The practical portion will require you to demonstrate your ability to perform various tasks effectively. You might be asked to:
- Prepare equipment: Ensure all necessary tools are available, sterile, and correctly set up.
- Collect samples: You will be asked to perform blood draws or other relevant tasks while following proper safety protocols.
- Handle complications: If challenges arise, you will need to show how you handle them calmly and efficiently, such as managing patient discomfort or dealing with difficult situations.
Throughout the assessment, you will be evaluated on your technical proficiency, communication skills, and ability to follow safety protocols. It’s important to remain focused, calm, and organized to demonstrate your competence in both theoretical and practical aspects of your training.
How to Review Assessment Responses
After completing an assessment, reviewing your responses thoroughly is essential for identifying areas of strength and potential improvement. This process not only helps you understand where you succeeded but also highlights areas where further study and practice may be necessary. Proper review strategies will allow you to reinforce your understanding and make adjustments before applying your knowledge in real-world scenarios.
The review process should involve a step-by-step evaluation of each section of the assessment. This includes revisiting both theoretical questions and practical tasks, ensuring that your understanding of each concept aligns with the expected outcomes. It is also crucial to analyze any mistakes or uncertainties you encountered and determine how to address them moving forward.
Steps for Reviewing Written Responses
When reviewing your written responses, focus on the following steps to maximize your learning:
- Identify Correct and Incorrect Responses: Go through each question and compare your responses with the correct ones. This will help you recognize patterns in your understanding and identify knowledge gaps.
- Understand the Rationale Behind the Correct Answers: For each question you answered correctly, try to understand why that specific response is correct. This ensures that you fully grasp the concept, rather than just memorizing the answer.
- Analyze Mistakes: If you made an error, investigate why the mistake happened. Was it a misunderstanding of the question, or did you lack certain knowledge? This step is vital for improving your future performance.
- Review Key Terms and Concepts: Focus on any terminology or concepts you struggled with during the assessment. Revisit textbooks, notes, or online resources to deepen your understanding of these critical areas.
Steps for Reviewing Practical Responses
The practical portion of the assessment evaluates your hands-on skills. When reviewing this part of the assessment, consider the following steps:
- Reflect on Task Execution: For each task you completed, assess whether you followed the correct procedures and protocols. Were there any steps missed or done incorrectly?
- Evaluate Your Time Management: Reflect on how efficiently you completed each task. Did you manage your time well, or were there delays in performing certain procedures?
- Assess Your Communication Skills: Effective communication is crucial during practical tasks. Think about how clearly you communicated with others, especially in situations requiring patient interaction or team collaboration.
- Identify Areas for Improvement: If you faced difficulties during the practical tasks, list specific areas to work on. This might include improving your dexterity, better preparing your workspace, or practicing complex techniques.
Regularly reviewing your performance, both written and practical, will ensure that you are always refining your skills and reinforcing your knowledge. It provides a clear path for improvement, helping you become more confident and proficient in your field.