
Mastering the skills required to operate heavy machinery in a warehouse or construction setting is crucial for ensuring both efficiency and safety. Those looking to pass certification tests must demonstrate a strong understanding of key principles and practices related to equipment handling. This guide offers practical insights into the core concepts and requirements that every candidate should know.
Preparation involves not only learning about equipment features and operating techniques, but also understanding the safety measures that are integral to minimizing risks. Test-takers need to be familiar with the most common scenarios they may face while on the job and how to handle them properly. The goal is to provide reliable knowledge that supports safety standards and helps reduce workplace accidents.
Success depends on a combination of theoretical knowledge and hands-on experience. By reviewing the crucial areas of concern, individuals can confidently approach the assessment process and ensure they are well-prepared to work with heavy machinery under safe conditions. Proper understanding of operational protocols and hazard management is essential for a smooth certification journey.
Safe Equipment Handling Test Insights
Successfully passing the certification process for material handling machinery requires more than just a basic understanding of how the equipment works. Candidates must also demonstrate an awareness of essential safety protocols, maintenance checks, and proper usage to ensure smooth and hazard-free operation. A well-rounded knowledge base is key to passing any related assessment and working efficiently in a high-risk environment.
Being prepared for the assessment involves understanding the critical aspects of machinery management, from the basics of load handling to emergency procedures. A candidate must be able to identify potential risks and understand how to prevent accidents while operating heavy machinery. This includes learning about safe maneuvering techniques, the significance of thorough equipment inspections, and how to respond to potential hazards.
Mastery of these essential concepts not only aids in passing the certification process but also promotes long-term safety in the workplace. Proper preparation ensures that the individual can handle the machinery confidently and without compromising safety standards, making it possible to work efficiently and securely in a variety of environments.
Understanding Equipment Safety Requirements
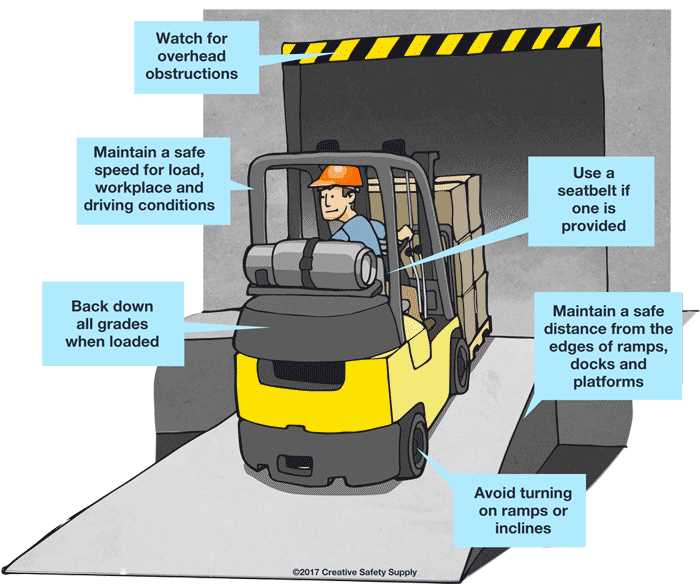
When working with heavy machinery, it is crucial to understand the fundamental safety principles that ensure the well-being of both the user and the surrounding environment. These guidelines are designed to minimize risks and promote responsible handling of the equipment. Proper knowledge and adherence to these safety standards can significantly reduce accidents and improve overall operational efficiency.
Each piece of machinery has specific safety measures that must be followed to prevent injuries and equipment malfunctions. These include procedures for inspecting equipment before use, maintaining proper load capacities, and knowing how to respond to potential hazards. Understanding these requirements is essential for anyone who plans to work with heavy machinery in any setting.
| Safety Aspect | Key Requirements |
|---|---|
| Pre-Operational Inspection | Check for mechanical issues, fluid levels, and tire condition. |
| Load Handling | Ensure loads are balanced and within the equipment’s capacity. |
| Environmental Awareness | Identify hazards such as uneven surfaces or obstacles in the path. |
| Emergency Procedures | Know how to handle sudden malfunctions or accidents. |
By becoming familiar with these essential safety requirements, individuals can ensure they operate machinery in a way that minimizes risk and maintains safety standards throughout their tasks. Continuous learning and adherence to safety protocols are vital to maintaining a secure work environment.
Key Equipment Handling Procedures to Know

When working with heavy machinery, it’s essential to follow specific procedures to ensure safe and efficient operation. These practices are designed to promote proper handling, minimize risks, and enhance productivity. Mastering these fundamental techniques is necessary for anyone working in environments where machinery is in regular use.
Proper handling requires a deep understanding of equipment functionality and the specific tasks it is used for. It’s important to follow established procedures to ensure that the machinery operates correctly and safely in any environment. The following are some key procedures every user should be familiar with:
- Pre-Use Inspections: Always check the equipment for any visible damage or mechanical issues before starting work. This includes inspecting the tires, brakes, fluid levels, and load capacity.
- Correct Loading Techniques: Ensure loads are balanced and positioned securely to avoid tipping or shifting during movement. The load should not exceed the machine’s weight limit.
- Safe Maneuvering: Always operate equipment at a controlled speed. Avoid sudden movements and be aware of surroundings, especially in tight or crowded spaces.
- Proper Parking: After use, ensure that the equipment is parked on a level surface and that the load is lowered to the ground. Engage the parking brake to prevent movement.
- Emergency Protocols: Understand how to react in the event of an emergency. Familiarize yourself with the procedures for malfunction or hazardous situations.
By following these essential procedures, users can enhance their operational efficiency while minimizing potential hazards. These practices contribute to a safer workplace and are essential for long-term success in handling machinery.
Common Questions on Equipment Stability

Understanding the principles of machinery stability is crucial for ensuring safe and efficient operations. Stability plays a key role in preventing accidents, particularly when handling heavy loads or operating in challenging environments. A lack of awareness about stability can lead to tipping, accidents, and costly damages. This section answers some of the most frequently asked questions about how to maintain proper balance and stability when using heavy equipment.
One of the most common concerns is how to maintain balance while transporting loads. Proper load placement, as well as understanding the limits of the machinery, are key factors in maintaining stability. The center of gravity, both of the equipment and the load, needs to be carefully considered to prevent dangerous tipping. Additionally, external factors like terrain and weather conditions can affect stability, making it essential to adjust operating methods accordingly.
- How does load positioning affect stability? The load should be positioned as low as possible and centered to maintain balance. Avoid lifting loads too high, as it can shift the center of gravity and increase the risk of tipping.
- What role does surface type play in stability? Uneven, slippery, or soft surfaces can compromise the stability of the machine. Always ensure that the equipment is operated on stable, level ground.
- How does speed impact stability? Operating at high speeds increases the risk of losing control and can reduce the machine’s stability, especially when turning or navigating obstacles.
- Why is load weight important? Exceeding the machine’s weight capacity can cause instability, making it difficult to control the equipment and putting both the user and the load at risk.
By understanding these fundamental aspects of machinery stability, users can prevent accidents and ensure smoother, safer operations. Proper awareness and technique are essential for maintaining balance in a variety of working conditions.
Top Hazards in Equipment Operation

When handling heavy machinery, operators face a variety of potential risks that can lead to accidents and injuries. Understanding these hazards is critical to ensuring a safe working environment. By identifying and addressing common threats, the likelihood of accidents can be minimized, leading to safer and more efficient operations. This section highlights some of the most common risks involved in equipment handling and offers guidance on how to manage them effectively.
Common Risks and Their Causes
Many hazards stem from improper handling, lack of training, or environmental factors. Inadequate knowledge of equipment limits, poor maintenance, or unsafe work practices can contribute to dangerous situations. Identifying these risks and taking steps to mitigate them is essential for anyone working with machinery.
| Hazard | Cause | Prevention |
|---|---|---|
| Overturning | Improper load handling or uneven ground | Ensure proper load balance and operate on level surfaces |
| Collisions | Inattention, poor visibility, or overcrowded areas | Use spotters, ensure clear sightlines, and follow traffic patterns |
| Pinning | Inadequate space or poor maneuvering | Maintain safe distances and maneuver carefully in tight spaces |
| Falling Loads | Poorly secured or unbalanced loads | Check load stability before lifting and transport at low heights |
Managing Risks Effectively

By understanding the main hazards and implementing proactive measures, operators can reduce the likelihood of accidents. Proper training, regular equipment inspections, and awareness of surroundings are crucial steps in minimizing risks. Maintaining a safety-first attitude and adhering to established protocols will help ensure the well-being of everyone in the work environment.
Load Handling Best Practices

Efficient and secure handling of materials is essential when using heavy machinery to transport goods. Proper techniques ensure that loads are moved safely, preventing accidents, damage, and unnecessary delays. Following best practices for load handling not only protects the equipment but also contributes to a safer and more productive work environment. This section outlines the key practices to keep in mind when managing loads.
First and foremost, it’s crucial to understand the weight and balance of the load before attempting to move it. Load distribution affects the stability of the machinery, and improper positioning can lead to tipping or uneven movement. Additionally, knowing the weight limits of both the equipment and the load is essential to avoid overloading, which can result in equipment failure or unsafe conditions.
- Proper Load Positioning: Always keep the load as low as possible to maintain stability. The load should be centered and evenly distributed to prevent tipping.
- Securing the Load: Ensure that the load is secured tightly to avoid shifting during movement. Use appropriate strapping, blocking, or other securing methods.
- Check Load Size: Ensure the load size is appropriate for the equipment being used. Avoid overhanging loads that can affect visibility or create instability.
- Clear Pathways: Always ensure the path is clear of obstacles before moving the load. This reduces the risk of collision and improves efficiency.
- Controlled Movement: Avoid sudden movements or sharp turns when transporting loads. Move at a steady speed to maintain control of the equipment.
By following these best practices, the handling of materials can be done more effectively and safely, reducing the risk of accidents or equipment damage. Proper load management plays a crucial role in creating a productive and secure work environment for all involved.
Pre-Operational Safety Checks
Before engaging any machinery for operation, it’s critical to conduct a thorough safety inspection to ensure the equipment is functioning correctly and ready for use. These checks help identify potential issues that could lead to accidents, equipment malfunctions, or delays. By performing pre-operational inspections, operators can reduce the likelihood of failures and enhance overall safety in the workplace.
Key Areas to Inspect

A comprehensive safety check includes several key areas that should be thoroughly examined before each use. These areas are vital to ensuring that the machinery is safe and operational. Below are the primary components to inspect:
- Visual Inspection: Look for any obvious signs of damage or wear, such as cracked tires, broken lights, or bent parts.
- Fluid Levels: Check the oil, hydraulic fluid, and coolant levels to ensure proper function and to prevent overheating or mechanical failure.
- Brakes: Test the braking system to make sure it responds quickly and effectively when engaged. Ensure that the parking brake is functioning properly.
- Load Handling Equipment: Inspect the lifting arms, forks, and other load-handling components for any signs of damage, wear, or misalignment.
- Warning Lights and Horn: Test all safety features such as lights, horns, and alarms to confirm they are functioning to alert others in the work area.
Performing the Inspection
To conduct the inspection, follow a systematic approach to check each of the components mentioned above. Start by turning off the equipment and performing a walk-around to visually inspect the machine. Test the equipment’s functionality by operating it at low speeds to verify that all systems are working as expected. If any issues are identified during the inspection, they should be addressed before operation to ensure safety and efficiency.
Regular pre-operational checks are a simple yet effective way to ensure equipment is in optimal condition, reducing the risk of accidents and equipment downtime. Consistent inspections create a safer, more productive work environment for everyone involved.
How to Pass Your Equipment Certification

Successfully passing a machinery certification test requires more than just understanding the basics of equipment operation. It involves a combination of knowledge, hands-on practice, and awareness of safety standards. Proper preparation is key to ensuring you not only pass the test but also gain the confidence and skills needed for safe and efficient machinery handling. This section will guide you through the essential steps to help you pass the certification process with ease.
The first step is to familiarize yourself with the key concepts and terminology related to the equipment you will be tested on. Understanding the technical aspects, such as load capacity, stability, and basic maintenance requirements, is essential. In addition to theoretical knowledge, hands-on experience is crucial. Make sure to practice operating the machinery in various scenarios to build your confidence and competence. This combination of theory and practice will significantly improve your chances of passing the test successfully.
- Study the Basics: Learn the fundamental concepts such as load handling, stability, and emergency procedures. Ensure you understand the specific requirements for the type of machinery you will be certified to use.
- Gain Practical Experience: Spend time operating the equipment under supervision, focusing on mastering the controls and maneuvering in different environments.
- Understand Safety Protocols: Safety is paramount, so make sure you are familiar with all safety guidelines, such as proper loading techniques, avoiding collisions, and maintaining clear visibility.
- Take Practice Tests: Practice with mock tests to become familiar with the format of the certification process. This can help reduce test anxiety and ensure you are prepared for all types of questions.
- Ask Questions: If there’s something you don’t understand, don’t hesitate to ask for clarification. It’s better to ask questions during your training than to struggle with unclear concepts during the test.
By combining theoretical study with hands-on practice and a solid understanding of safety practices, you can significantly improve your chances of passing the certification test. The key is consistent preparation and focusing on the areas that are most likely to be tested. Stay focused, be confident, and approach the test with a positive mindset for the best results.
Traffic and Pedestrian Safety in Material Handling

Ensuring the safety of both vehicle operators and pedestrians within a worksite is critical for preventing accidents and maintaining a smooth workflow. The movement of heavy machinery in areas with pedestrian traffic requires careful planning and strict adherence to safety protocols. Effective traffic management and pedestrian awareness can significantly reduce the risk of accidents and enhance overall productivity in the workplace.
To maintain a safe environment, it is essential to establish clear rules and guidelines for both vehicle operators and pedestrians. These rules should cover areas such as speed limits, designated pathways, and proper communication between workers. By creating a traffic control plan and educating all personnel on these procedures, the chances of accidents can be minimized.
Key Safety Measures for Vehicles

- Designate Routes: Clearly mark vehicle paths and ensure operators stick to designated lanes to avoid crossovers with pedestrian walkways.
- Speed Limits: Establish and enforce speed limits within the workspace to prevent sudden movements and give operators more time to react to unexpected obstacles.
- Warning Signals: Use horns, lights, and other warning signals to alert pedestrians when machinery is approaching, especially at intersections or blind corners.
- Regular Maintenance: Ensure that all vehicles are well-maintained, with functioning brakes, lights, and horns to guarantee optimal performance and safety.
Pedestrian Safety Practices

- Clear Pathways: Pedestrians should always stay on designated walkways and avoid walking through areas where machinery operates. Signs and barriers should be used to keep pedestrian paths separate from vehicle routes.
- Awareness: Pedestrians must remain alert at all times, especially when moving near operating machinery. Avoid distractions such as mobile phones and always make eye contact with operators before crossing paths.
- Proper Training: Ensure that all workers are trained on how to safely navigate the work environment and what to do if they encounter a moving vehicle.
- Personal Protective Equipment: Pedestrians should wear appropriate protective gear such as high-visibility vests to enhance their visibility and reduce the risk of accidents.
By implementing these traffic management and pedestrian safety strategies, work environments can be made safer, preventing collisions and injuries. Both vehicle operators and pedestrians must work together to ensure a harmonious and risk-free workflow in any industrial setting.
Understanding Load Capacity Limits
Knowing the maximum load capacity of handling equipment is essential for ensuring safe operation and avoiding accidents. Overloading can lead to equipment malfunctions, increased risk of tipping, and potential harm to both operators and bystanders. To maintain a safe work environment, it’s crucial to understand how to calculate and respect load limits, and how various factors can affect the equipment’s capacity. Proper training and attention to these limits ensure that loads are handled efficiently without compromising safety.
Factors Influencing Load Capacity
The load capacity of any handling machine can be influenced by several factors that are important to consider before lifting or transporting heavy items. These factors include:
- Load Center: The further the load is from the machine’s center of gravity, the lower the capacity. It’s vital to ensure that the load is positioned as close to the center as possible.
- Lift Height: As the lift height increases, the load capacity decreases. Understanding the impact of height on stability is crucial, especially when stacking or lifting at greater heights.
- Surface Conditions: Uneven or slippery surfaces can affect the stability of the equipment. It’s essential to adjust the load capacity based on the terrain or environment in which the equipment operates.
- Attachment Usage: Using additional attachments (such as extended forks or lifting beams) can reduce the machine’s overall capacity. Always check the manufacturer’s guidelines to adjust the load limits accordingly.
How to Determine Safe Load Capacity

To determine the safe load capacity, operators must refer to the machine’s specifications, usually displayed on a label or in the operator’s manual. The load capacity is typically listed for different configurations, including lift height and load center distance. It’s important to consult these guidelines before each use and never exceed the recommended capacity. Additional safety practices, such as load testing and ensuring balanced loads, can further help in determining the safe operating limits.
Respecting the load capacity ensures efficient and safe handling of materials, reduces the risk of accidents, and contributes to the longevity of the equipment. Proper education and consistent attention to these limits are vital components of maintaining a safe working environment.
Inspection Checklist for Equipment Users
Before using any material handling equipment, a thorough inspection is necessary to ensure it is in proper working condition. Regular checks help prevent accidents, identify wear and tear, and ensure the longevity of the machinery. By following a standard inspection checklist, operators can quickly assess the condition of the equipment, making sure it is safe to use and ready for operation. This process is essential for maintaining workplace safety and preventing downtime due to equipment failure.
Key Areas to Inspect
- Brakes: Check that the braking system is responsive, ensuring that both the service and parking brakes are functioning properly.
- Steering: Test the steering mechanism for smooth operation and any signs of excessive wear or damage.
- Tyres: Inspect tyres for proper inflation, tread wear, and any visible damage. Uneven wear or under-inflated tyres can affect stability.
- Hydraulic System: Look for any signs of leakage and test the lift and tilt functions to ensure smooth operation.
- Lights and Horn: Ensure that all lights, including headlights, tail lights, and indicators, are functioning. The horn should be tested for loudness and clarity.
- Load Handling Components: Examine forks, mast, and other lifting mechanisms for any visible damage or wear. Ensure the load backrest is secure.
- Battery and Electrical System: Check the battery charge level, connections, and condition of cables. Electrical issues can lead to malfunction during use.
How to Perform the Inspection

Each inspection should follow a systematic approach, beginning with a visual check and followed by functional tests. The operator should start by walking around the equipment to visually check for any obvious signs of damage or defects. Next, perform a series of functional checks, including testing the lift, tilt, and steering functions. Any issues found during the inspection should be documented and reported immediately for repair. Remember, operators should never use equipment if any safety-related issues are detected.
By adhering to a regular inspection routine, operators ensure that the equipment remains in good working condition, reducing the likelihood of accidents and costly repairs. Regular checks not only promote safety but also enhance the productivity and efficiency of daily operations.
Types of Material Handling Equipment and Their Use
Various types of material handling machines are designed to meet specific needs in different environments. These machines differ in size, power, and the type of loads they can carry. Depending on the nature of the task, selecting the right type of machine can significantly improve efficiency, safety, and productivity. From basic lifting tasks to handling heavy or specialized loads, each machine serves a distinct purpose in a warehouse or construction setting.
Here are some of the most common types of material handling equipment, each designed for specific types of tasks:
| Type | Primary Use | Advantages |
|---|---|---|
| Counterbalance Machines | Used for moving pallets and lifting heavy loads in tight spaces. | Versatile and ideal for general warehouse work. |
| Reach Trucks | Designed for working in narrow aisles and reaching high shelving units. | Great for high stacking in warehouses with limited space. |
| Order Pickers | Used to pick individual items from shelves, especially in smaller warehouses. | Efficient for quick retrieval of goods. |
| Stand-Up Trucks | Ideal for moving loads in confined spaces or short distances. | Compact design and ease of maneuverability. |
| Heavy Duty Machines | Designed for lifting and moving extremely heavy or large loads. | Best for industrial environments or construction sites. |
Each type of machine offers specific benefits, making it crucial to choose the right one based on your operational needs. Whether you need a machine for heavy lifting, navigating tight aisles, or handling oversized goods, understanding the purpose and advantages of each type can help you make an informed decision that ensures both safety and efficiency in your daily tasks.
Training and Certification Requirements for Material Handling Equipment
Before using material handling machines, individuals must undergo proper training to ensure they understand both the equipment’s operation and the safety protocols necessary to prevent accidents. Certification is required in many regions to confirm that workers possess the necessary skills and knowledge to operate the machines safely and effectively. This process is essential for reducing workplace injuries and improving operational efficiency.
Key Training Components

- Equipment Familiarization: Operators must understand the specific controls, functions, and capabilities of the machine they will be using.
- Safety Protocols: Proper training ensures that operators are aware of the correct safety measures to follow during operation, including how to handle hazardous situations.
- Load Handling Techniques: Correct procedures for lifting, stacking, and transporting materials are taught to minimize the risk of accidents and equipment damage.
- Environment Awareness: Training includes understanding how to navigate different environments safely, such as tight aisles, crowded warehouses, or outdoor job sites.
Certification Process

Certification typically involves both theoretical and practical assessments. The process can vary by location, but it generally includes:
- Theoretical Training: This includes learning about equipment features, safety regulations, and how to handle various situations.
- Practical Assessment: Operators must demonstrate their ability to operate the machine in real-world conditions under the supervision of a certified trainer.
- Recertification: In many cases, certification must be renewed periodically to ensure that operators remain up to date with any changes in regulations or technology.
Proper certification not only ensures compliance with regulatory standards but also boosts workplace safety and productivity. Investing in thorough training for all individuals who use material handling equipment is essential for maintaining a safe and efficient working environment.
Material Handling Equipment Maneuvering Techniques for Safety
Proper handling of material transport vehicles is crucial for maintaining safety in environments where they are used. Maneuvering these machines efficiently and securely involves understanding the limitations of the equipment, the layout of the workspace, and following best practices to prevent accidents. Mastering these techniques can help operators avoid collisions, reduce the risk of tipping, and ensure smooth, controlled movements when navigating tight spaces.
Essential Maneuvering Techniques
- Slow and Steady Movements: Always maneuver at slow speeds, particularly in areas with limited visibility or when turning tight corners. Rapid movements can lead to loss of control.
- Use of Rearview Mirrors: When reversing, constantly check mirrors and ensure there is a clear path. If necessary, have a spotter to guide the process in blind areas.
- Turning Techniques: Make wide turns whenever possible, and avoid sharp, sudden movements. This helps maintain balance and prevent tipping, especially when carrying loads.
- Correct Use of Brakes: Engage brakes gently to ensure smooth stops. Abrupt braking can cause the equipment to lurch or tip, especially with heavy loads.
- Load Positioning: Keep the load as low as possible while maneuvering. High loads can affect the machine’s center of gravity and increase the risk of tipping.
Best Practices for Navigating Confined Spaces
- Assess the Environment: Before moving, take time to evaluate the layout of the area. Look for obstacles or tight spaces that may require extra care while maneuvering.
- Use Clear Markings: In busy areas, ensure paths are clearly marked and free of debris to maintain a safe flow of traffic.
- Maintain Safe Distances: Always maintain a safe distance between your vehicle and walls, other machines, and pedestrians. This ensures sufficient space for adjustments during tight maneuvers.
By practicing these techniques, workers can avoid common risks associated with material transport equipment. Efficient, cautious handling not only ensures the well-being of the personnel but also contributes to the overall safety and productivity of the workplace.
Common Material Handling Certification Mistakes to Avoid
When preparing for a certification assessment, individuals often make several common mistakes that can hinder their chances of success. Whether it’s misunderstanding important guidelines, neglecting crucial safety protocols, or overlooking key operational principles, these errors can lead to confusion and potentially dangerous outcomes. Identifying and avoiding these pitfalls is essential for ensuring a smooth and successful evaluation process.
Key Mistakes to Avoid During Certification
- Failing to Study Properly: Many candidates assume they can rely solely on hands-on experience without reviewing the theoretical knowledge required. It’s important to balance practical skills with understanding safety regulations and equipment handling protocols.
- Ignoring Pre-Use Inspections: Skipping the step of inspecting the equipment before use is a common oversight. This step is critical for ensuring everything is in working order and that no safety hazards are present.
- Underestimating the Importance of Safety Gear: Some individuals neglect the need for proper safety gear or fail to use it consistently. Ensuring that personal protective equipment (PPE) is worn at all times is a fundamental aspect of the assessment.
- Overloading the Equipment: Many candidates make the mistake of overloading material transport equipment, which can result in instability or malfunction. Always ensure that the load does not exceed the maximum weight capacity.
- Inadequate Communication: Not communicating clearly with spotters or other workers can lead to accidents. Effective communication during operation is key to ensuring a safe environment.
How to Prepare and Succeed
- Thorough Review of Guidelines: Take time to understand all the regulations, manufacturer instructions, and safety guidelines related to material handling operations.
- Practice Regularly: Hands-on practice is essential for building muscle memory and confidence in operating the equipment safely and effectively.
- Stay Calm and Focused: During the assessment, it’s important to stay focused, maintain composure, and approach each task with care to avoid rushed decisions that can lead to mistakes.
By understanding and avoiding these common mistakes, candidates can approach their certification process with greater confidence, increasing their chances of passing successfully while ensuring the safety of themselves and others.
How to Improve Material Handling Safety Skills
Enhancing safety skills when working with material handling equipment requires a combination of knowledge, practical experience, and continuous awareness of best practices. Whether you’re a beginner or have been working with such equipment for years, there’s always room to refine your technique. Focusing on safety doesn’t just protect the individual operator but also ensures the well-being of coworkers and the integrity of the work environment.
To improve these skills, it’s important to stay updated on the latest safety guidelines, regularly assess and practice key maneuvers, and always be mindful of the potential hazards that exist in the workplace. Continuous learning and self-assessment can significantly reduce the likelihood of accidents and injuries.
Practical Tips for Enhancing Safety Skills

- Stay Informed: Regularly review updated safety standards, manufacturer guidelines, and operational procedures to ensure you’re following best practices.
- Engage in Regular Training: Participate in hands-on training sessions, simulations, and safety drills to practice critical maneuvers and response times under various conditions.
- Focus on Awareness: Continuously scan the environment for potential hazards such as obstacles, uneven ground, or other workers, and adjust your operations accordingly.
- Enhance Communication Skills: Clear and effective communication with coworkers, especially when navigating shared spaces, is key to preventing accidents.
- Practice Slow and Steady Movements: Avoid rushing when handling equipment. Take the time to perform every task methodically to ensure stability and control.
Key Areas for Continuous Improvement
- Vehicle Inspections: Regularly inspect the equipment before use to identify any defects or maintenance needs. A well-maintained machine is far safer to operate.
- Load Handling: Practice properly distributing weight and handling loads at a safe height to prevent tipping and ensure stability.
- Adapt to Environmental Changes: Recognize how changes in weather, lighting, or workspace layout affect your ability to operate safely, and adjust accordingly.
By prioritizing these practices and continuously refining your approach, you can greatly enhance your safety skills, ensuring not only your own well-being but also contributing to a safer workplace for everyone involved.
Emergency Procedures to Follow for Material Handling Equipment
In any work environment that involves operating heavy machinery, knowing the correct emergency procedures is crucial. When an unexpected situation arises, swift and correct actions can prevent further damage or injury. Whether it’s a mechanical failure, an environmental hazard, or an accident, knowing how to respond can make a significant difference in ensuring the well-being of everyone involved and minimizing damage to equipment or the surrounding area.
Every workplace should have established protocols for handling emergencies, and it is essential that all personnel are trained on how to respond effectively. These procedures should be reviewed regularly and practiced to ensure they become second nature in the event of a real emergency.
Key Emergency Steps to Follow

- Stop and Assess the Situation: Immediately cease any operations to prevent further issues. Assess the environment for hazards such as fire, spills, or structural damage.
- Notify Supervisors and Emergency Personnel: Contact the appropriate supervisors and emergency response teams. Clear communication is vital in coordinating the response efforts.
- Use Emergency Equipment: If applicable, use emergency shut-off buttons or other safety mechanisms to isolate the machinery or hazardous materials from causing additional harm.
- Evacuate if Necessary: If the situation presents an immediate danger, follow established evacuation routes to ensure all personnel can exit the area safely.
- Provide First Aid: If injuries occur, provide immediate first aid and seek medical attention. Keep a first aid kit nearby and ensure personnel are trained in basic life-saving techniques.
Common Emergency Scenarios and Procedures
| Scenario | Procedure |
|---|---|
| Mechanical Failure | Immediately stop the equipment, notify maintenance staff, and ensure that the equipment is isolated from power sources. |
| Spilled Load | Stop all movement, secure the area, and clean up the spill if safe. Notify the supervisor and evacuate if necessary. |
| Collision or Injury | Stop the equipment, check for injuries, provide first aid, and call for medical assistance if needed. Secure the scene for investigation. |
| Fire | Activate the fire alarm, use the nearest fire extinguisher to suppress the fire if trained, and evacuate the area as per protocol. |
Having a clear and practiced emergency response plan ensures that all personnel can react swiftly and efficiently in times of crisis. Regular drills and proper training are key components in making sure that everyone knows their role and can respond appropriately when an emergency arises.