When preparing for a certification in watercraft operation, it’s crucial to familiarize yourself with the key principles, safety protocols, and regulations. The process involves understanding various topics that are essential for safe and efficient navigation on the water. This guide is designed to help you tackle these topics with confidence and clarity.
By reviewing typical scenarios, rules of the water, and practical safety measures, you’ll gain the necessary knowledge to succeed. Whether you’re focused on operating a small vessel or a larger craft, mastering the core subjects ensures you’re ready to face real-world challenges with ease. Focus on practical skills, navigation techniques, and safety equipment, all of which will play a vital role during the test.
Study wisely and explore the different aspects that will be assessed. From understanding the operation of various water vehicles to knowing how to react in emergencies, preparing thoroughly will increase your chances of passing the certification process smoothly. Additionally, applying the knowledge gained in real-life scenarios will build your confidence and readiness.
Boat Exam Questions and Answers Guide
Preparing for a certification test in watercraft operation requires a solid understanding of various topics that assess both theoretical knowledge and practical skills. This guide provides insights into the most common subjects covered, along with practical advice on how to approach them effectively. Familiarity with these areas will help you confidently navigate the certification process.
Key aspects often tested include safety regulations, navigational rules, and equipment handling. Additionally, understanding how to manage different weather conditions, as well as how to respond to emergency situations, is crucial for anyone operating a water vehicle. By mastering these fundamental concepts, you’ll be well-equipped for both the theoretical assessment and real-world challenges.
| Topic | What to Focus On |
|---|---|
| Safety Measures | Essential gear, life-saving equipment, and emergency protocols |
| Navigation Rules | Markings, signals, and right-of-way regulations |
| Weather Conditions | Impact of different weather patterns on navigation |
| Watercraft Operations | Handling, maneuvering, and control techniques |
| Legal Responsibilities | Rules and regulations governing watercraft use |
By reviewing the most common areas of focus listed above, you’ll be able to concentrate your study efforts on the most critical topics. This approach will help streamline your preparation and ensure you’re ready to confidently tackle the practical and theoretical challenges ahead.
Understanding the Boat Exam Format
When preparing for a certification in watercraft operation, it’s essential to understand how the assessment process is structured. Knowing the format of the test can significantly improve your chances of success by helping you focus on the right areas and manage your time effectively. The assessment typically consists of multiple sections designed to evaluate your knowledge of key principles and practical skills required for safe operation.
The format may vary depending on the region or organization, but generally, you can expect the following types of assessments:
- Theoretical Section: Multiple-choice or true/false questions assessing your understanding of rules, regulations, and safety practices.
- Practical Skills Test: A hands-on evaluation of your ability to operate a water vehicle safely and competently.
- Emergency Protocols: Questions or tasks related to handling emergency situations, such as capsizing or navigating in rough conditions.
It’s important to familiarize yourself with the general structure of the test to avoid surprises. Many organizations provide practice tests or guidelines, which are highly recommended for better preparation.
- Start by reviewing all the basic regulations and operational procedures.
- Practice handling watercraft in various conditions to build confidence.
- Focus on emergency response techniques and equipment usage.
By understanding the exam structure and requirements, you can better organize your study plan and approach the certification with a clear, focused mindset.
Common Questions on Boat Safety Rules
Understanding safety protocols is crucial for anyone navigating the waters. These rules are designed to prevent accidents, protect individuals, and ensure that everyone enjoys their time on the water safely. Below are some of the most commonly asked topics related to safety practices that are essential for anyone taking part in watercraft activities.
Essential Safety Equipment
- What equipment is mandatory on board?
- How often should life jackets be checked for usability?
- Are fire extinguishers required, and where should they be placed?
- What other safety gear should always be accessible?
Operating Safely on the Water
- What are the speed limits in different water zones?
- How should one handle an unexpected storm or rough waters?
- What should you do in case of a collision or capsize?
- When is it necessary to use navigation lights or sound signals?
Knowing these basic safety rules will not only help you pass assessments but also ensure that you are fully prepared to act responsibly when out on the water. It’s important to always stay updated with the local regulations and equipment requirements specific to the area where you will be operating a vessel.
Preparing for Navigation and Signals
Effective navigation on the water relies heavily on understanding various signals, markings, and navigational aids. These systems are in place to guide operators and ensure safety while traveling across different bodies of water. Familiarity with these signs and techniques is crucial for avoiding obstacles, staying within legal boundaries, and ensuring a smooth journey.
To prepare adequately, it is important to recognize the key symbols and signals commonly used to communicate on the water. These can range from buoys and beacons to visual signals and sound alerts. A thorough understanding of these will help you respond appropriately in various situations.
| Signal Type | Description | Action Required |
|---|---|---|
| Red Buoy | Marks the right side of a channel when returning from open water | Pass on your left |
| Green Buoy | Marks the left side of a channel when returning from open water | Pass on your right |
| Flashing Light | Indicates a hazard or obstacle | Slow down and navigate with caution |
| Sound Signals | Used to indicate the intentions of another vessel | Respond according to the specific signal received |
Mastering these signals and becoming proficient in navigation techniques is essential for ensuring safety on the water. Understanding when and how to respond to different markers and signals will help you avoid accidents and stay on course, especially in unfamiliar areas or busy waterways.
Essential Rules for Safe Boating

Safety on the water is paramount, and understanding key regulations and best practices can prevent accidents and ensure a positive experience. There are several important rules that every operator must follow to protect themselves, their passengers, and others sharing the waterways. These rules cover a range of areas, from equipment requirements to operating procedures, and are designed to maintain order and minimize risks on the water.
Familiarity with these essential guidelines is not only important for legal compliance but also for personal safety. Following these practices ensures that you are prepared for various scenarios, from navigating in poor visibility to reacting appropriately in emergency situations.
- Always wear a properly fitted life jacket or personal flotation device (PFD).
- Be aware of local regulations, including speed limits and restricted zones.
- Ensure that your craft is equipped with all necessary safety equipment, such as fire extinguishers and signaling devices.
- Keep a safe distance from other vessels and avoid crowded areas when possible.
- Never operate a watercraft under the influence of alcohol or drugs.
- Maintain a proper lookout at all times to avoid collisions.
- Understand how to handle adverse weather conditions and rough waters.
By adhering to these key principles, you help create a safer environment for everyone on the water. A strong knowledge of these rules is a fundamental step toward responsible operation, ensuring that your time on the water is both enjoyable and secure.
Types of Boats and Their Regulations
There are many different types of watercraft, each with its own set of regulations that govern their operation. Understanding these classifications is essential for operators, as specific rules apply depending on the type of vessel being used. These regulations cover a wide range of aspects, including safety equipment requirements, speed limits, and operational zones.
Common Vessel Categories
Different types of water vehicles are subject to unique guidelines based on their size, purpose, and capacity. It’s important to be aware of the particular rules for each type to ensure compliance and safety on the water.
| Vessel Type | Common Regulations | Key Safety Requirements |
|---|---|---|
| Personal Watercraft (PWC) | Restricted speed in certain areas, must operate within sight of land | Life jackets, fire extinguishers, whistle |
| Motorized Yachts | Required to carry a minimum number of life jackets, must follow traffic lanes in certain zones | Life jackets for all passengers, navigational lights, sound signaling device |
| Rowboats and Canoes | Must stay within designated safe zones, restrictions on night navigation | Life jackets, sound signaling device (in some areas) |
| Sailboats | Must adhere to specific right-of-way rules when under sail | Life jackets, flares, fire extinguishers |
Understanding Local Variations
Each waterway may have specific rules that vary depending on local conditions, including speed limits, no-wake zones, and restrictions related to certain activities like fishing or swimming. It’s crucial to be aware of these localized regulations, especially when operating in unfamiliar areas.
By understanding the classifications and rules associated with each type of vessel, operators can ensure that they comply with legal standards, maintain safety, and avoid fines or penalties while navigating waterways.
Knowledge of Watercraft Types and Features
To navigate safely and efficiently on the water, it is essential to understand the different types of vessels available and their unique characteristics. Each type has its own set of features designed to serve specific purposes, whether for leisure, sport, or utility. Knowing the key attributes and capabilities of each vessel type helps operators make informed decisions and ensures safe operation.
The following list outlines some of the most common types of watercraft, along with their defining features:
- Personal Watercraft (PWC): These are small, motorized vessels designed for quick, agile movement. They are popular for recreational use and require minimal crew, usually just one or two people.
- Yachts: Larger vessels often used for longer journeys or luxury cruises. They are equipped with various amenities and require more crew members to operate.
- Fishing Vessels: These craft are designed specifically for fishing activities and are often equipped with storage for catches, specialized navigation tools, and safety equipment.
- Canoes and Kayaks: Small, manually-powered crafts used for recreational paddling, especially in calm waters. They are lightweight and easy to maneuver.
- Sailboats: Powered by wind, these vessels use large sails to move. They can be used for both recreation and competition and require a specific skill set for proper handling.
Each of these watercraft types may also feature specialized equipment depending on their intended use, such as motors, sails, safety devices, or storage compartments. Understanding the distinctions between them helps ensure that operators are fully prepared for different conditions on the water.
- Familiarize yourself with the typical capacities and limitations of each vessel type.
- Learn how to operate essential features such as the engine, sails, or paddles effectively.
- Understand how to maintain safety equipment specific to the vessel type.
By knowing the features and functions of various vessels, operators can enhance their skills, improve safety, and enjoy their time on the water to the fullest.
Boat Handling and Maneuvering Questions
Mastering the skills of operating a water vessel is crucial for ensuring smooth navigation and avoiding potential hazards. Understanding the techniques and principles behind effective movement, steering, and docking can make a significant difference in any journey. Whether you’re maneuvering through narrow channels, docking at a marina, or changing direction at high speed, having a solid grasp of handling techniques will improve both your safety and confidence on the water.
Essential Maneuvering Skills
When operating a vessel, it is important to be aware of various techniques to manage direction, speed, and stability. These skills include:
- Turning and Steering: Learn how to make smooth turns by adjusting the throttle and rudder appropriately, accounting for water currents and wind.
- Backing Up: Maneuvering in reverse requires practice to understand how the vessel responds to control inputs and environmental factors.
- Docking: Proper approach techniques, speed control, and understanding wind and tide conditions are essential for safe and effective docking.
- Emergency Maneuvers: Practice sharp turns and emergency stops to ensure you can react quickly if a situation arises.
Common Handling Challenges
While maneuvering a watercraft is relatively straightforward, certain challenges may arise. Some of the most common obstacles include:
- Strong Currents: Navigating in fast-moving water requires careful speed adjustments and awareness of current strength.
- Limited Visibility: Fog, rain, or low light can hinder maneuvering and may require slower speeds and extra caution.
- Wind Conditions: Wind can significantly affect the handling of a vessel, especially when navigating in open waters or when sailing.
By developing the ability to handle these challenges, you will be better equipped to manage your vessel in any environment, ensuring a safer and more enjoyable experience on the water.
Dealing with Emergency Situations on Water
Accidents and unexpected situations can arise at any time while on the water. Whether it’s a mechanical failure, sudden weather changes, or a medical emergency, being prepared to respond quickly and effectively is critical for ensuring safety. Understanding the basic steps to take in these situations, along with the necessary precautions, can make all the difference in minimizing harm and preventing further damage.
Being ready for an emergency means knowing how to handle various challenges, from capsizing to fire or collisions. Awareness of safety procedures, maintaining calm, and having the proper equipment are essential in managing these high-stress moments efficiently.
- Stay Calm: Panicking can make a situation worse. Take a deep breath and assess the circumstances before taking any action.
- Signal for Help: Use distress signals, such as flares, sound devices, or a radio, to alert others that you are in need of assistance.
- Use Life-Saving Equipment: Ensure that life jackets or personal flotation devices are immediately accessible to all passengers.
- Evacuate if Necessary: If the vessel is sinking or there is a fire, it may be necessary to abandon the vessel. Know the steps to safely evacuate and how to use life rafts if available.
- Stay Visible: If stranded or in distress, position yourself in a place where you can be seen from the shore or by passing vessels. Use bright colors and reflective gear to enhance visibility.
Being aware of these safety protocols, along with regularly checking equipment and staying informed about weather conditions, can prevent emergencies from escalating. In critical moments, swift and decisive actions can save lives and reduce the risk of injury or loss.
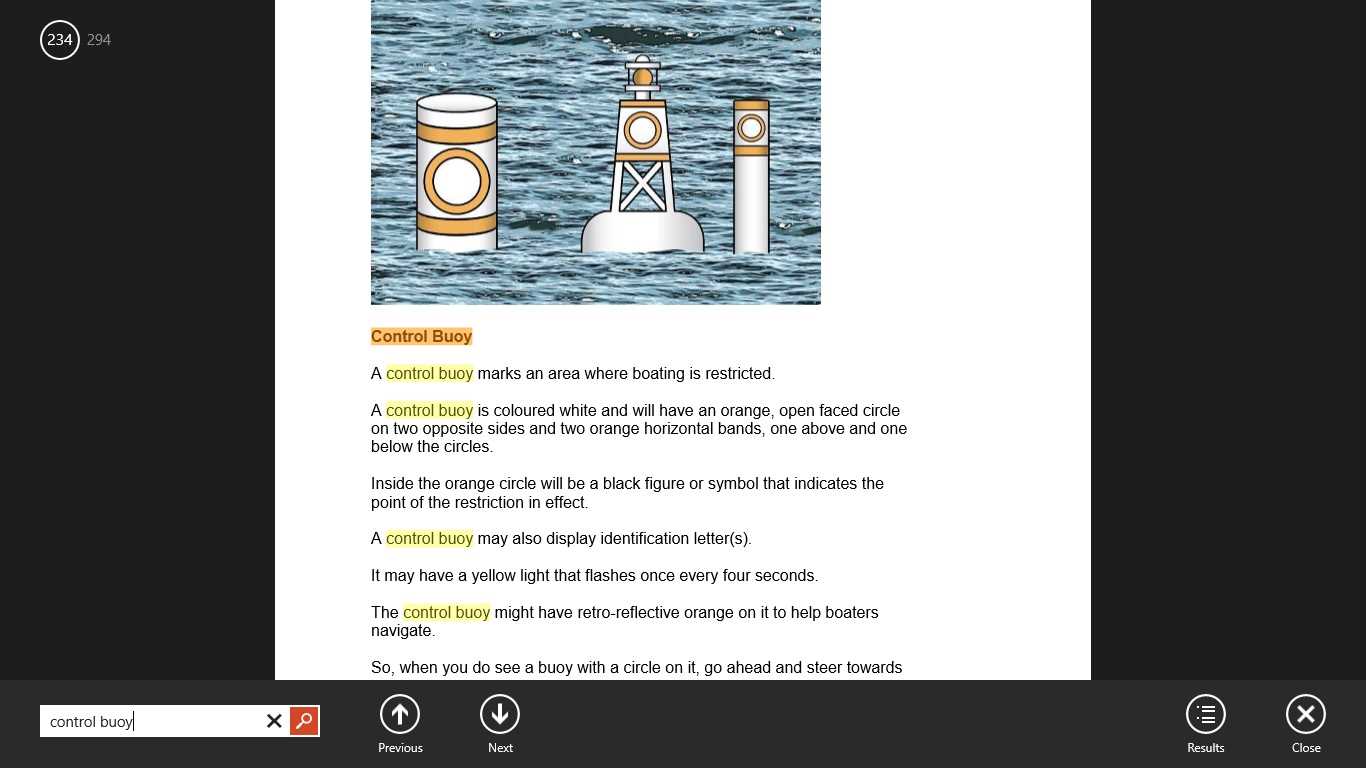
Understanding Buoyage and Marking Systems
In any waterway, markers and buoys are essential tools that provide critical information about navigation, safety, and hazards. These systems guide vessels safely through channels, warn of underwater obstacles, and indicate areas where certain activities are restricted or encouraged. Familiarity with how these markers are organized and what they represent is crucial for safe travel and proper decision-making while on the water.
Markers typically follow established international systems, each designed to represent specific information depending on location, function, and regional regulations. Understanding the color codes, shapes, and lights associated with these markers allows operators to interpret signals quickly and accurately, reducing the risk of accidents and improving overall navigation efficiency.
- Channel Markers: These are used to indicate the edges of safe navigable routes. They can be identified by different colors and shapes, such as red and green or cylindrical and conical markers.
- Dangerous Areas: Specific markers, often red with a black top, signal the presence of rocks, shoals, or other underwater hazards that could pose a danger to vessels.
- Safe Water Marks: These buoys indicate areas that are free from hazards and are typically found in the center of navigable channels. They are often white with red stripes.
- Special Marks: These markers denote specific areas where vessels should exercise caution or avoid altogether. They may include restricted zones like mooring areas or regions with environmental protections.
By understanding the meanings behind these signaling systems, operators can avoid potential hazards, plan more efficient routes, and ensure they are complying with all regulations. Recognizing and responding to the different types of markers is an essential skill for anyone operating on the water.
Importance of Weather Conditions in Boating

Weather plays a pivotal role in the safety and success of any water-based activity. Changes in temperature, wind patterns, precipitation, and visibility can significantly affect vessel stability, navigation, and overall safety. Understanding how to interpret weather forecasts and recognize early signs of changing conditions can make all the difference between a safe outing and a potentially dangerous situation.
Operators need to be aware of how various weather factors influence the behavior of the vessel, as well as how they interact with the surrounding environment. For example, high winds can lead to rough waves, while sudden storms may create hazardous visibility and increased risk of capsizing. Knowing how to react to these conditions, as well as when to avoid venturing out, is key to preventing accidents and ensuring a safe experience on the water.
- Wind: Strong gusts can affect maneuverability, especially for smaller vessels. High winds can also cause waves to grow larger, increasing the difficulty of maintaining control.
- Rain: Heavy rainfall can reduce visibility and create slippery conditions, making it harder to navigate or spot potential hazards in the water.
- Temperature: Extreme temperatures, both hot and cold, can have an impact on the functioning of equipment and increase the risk of hypothermia in the event of a fall into the water.
- Fog: Fog significantly reduces visibility, making navigation difficult and increasing the likelihood of collisions with other vessels or obstacles.
- Lightning: Thunderstorms with lightning can be extremely dangerous. Being on the water during a lightning storm increases the risk of being struck, which can cause injury or damage to equipment.
To mitigate risks, it is essential to always check weather reports before departure and keep an eye on any sudden changes while out on the water. By staying informed and prepared for unpredictable weather, operators can take proactive steps to avoid dangerous situations and protect everyone on board.
Safety Gear and Equipment Essentials
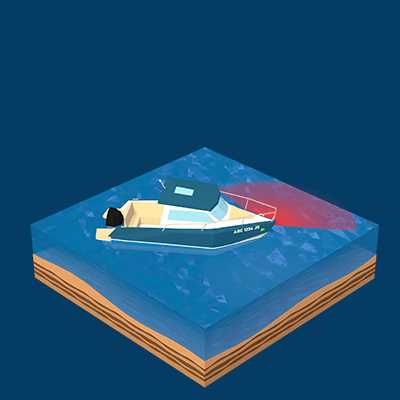
Proper safety equipment is crucial for preventing accidents and ensuring the well-being of everyone on board during water activities. Regardless of the type of excursion, having the right gear available can make the difference between a safe journey and a potentially life-threatening situation. It is essential to not only have the necessary items but also to ensure they are in good condition and easily accessible in case of an emergency.
There are several key pieces of safety gear that should always be on hand, including life-saving devices, communication tools, and weather protection equipment. Regular checks and maintenance of these items are vital, as their reliability can be critical when unforeseen circumstances arise.
- Personal Flotation Devices (PFDs): Every individual on board should have access to an appropriately sized life jacket or personal flotation device, which is essential for staying afloat in an emergency.
- First Aid Kit: A well-stocked first aid kit should contain supplies for treating minor injuries, such as bandages, antiseptics, and tools for splints or burns.
- Fire Extinguisher: Having a portable fire extinguisher on board is essential for quickly addressing small fires before they can escalate.
- Signaling Devices: Flares, whistles, or emergency signaling mirrors help attract attention in distress situations, enabling rescuers to locate you more easily.
- VHF Radio: A reliable VHF marine radio is crucial for communication with rescue teams or nearby vessels in case of emergencies.
- Weather Gear: Protective clothing, such as waterproof jackets and boots, along with a reliable weather radio, can help you stay dry and informed in the event of rain or storms.
By equipping yourself with these essentials and ensuring they are readily available, you increase the chances of a safe and successful trip. It’s not just about having the right tools but also knowing how to use them effectively when needed most.
How to Handle Dangerous Watercraft Situations
Understanding how to react in high-risk situations on the water is essential for ensuring safety and preventing accidents. Whether due to sudden weather changes, mechanical failure, or unexpected obstacles, knowing the proper steps to take can significantly reduce the potential for injury or damage. By remaining calm and following established protocols, you can address emergencies effectively and protect yourself and others from harm.
In critical situations, it is important to assess the situation quickly, prioritize actions, and have a clear plan for managing the emergency. This may involve stabilizing the vessel, signaling for help, or executing maneuvers to avoid hazards. Being prepared and trained for such scenarios enhances your ability to remain composed under pressure and make informed decisions.
Common Dangerous Situations and How to Respond
- Capsizing: If the vessel overturns, remain with it and try to stay calm. Use the flotation devices to stay afloat, and if possible, signal for assistance. Attempt to right the vessel if safe to do so.
- Collision: In the event of a collision, check for injuries immediately. If safe, assess damage to the vessel. Use a radio or signaling devices to alert nearby vessels for help, and be prepared to provide your location.
- Severe Weather: When faced with strong winds or thunderstorms, reduce speed and seek shelter if possible. Head towards the nearest safe harbor or secure location, but avoid navigating in poor visibility or turbulent conditions.
Key Safety Tips for Handling Emergencies

- Stay Calm: Panicking can worsen the situation. Take deep breaths and think through the next steps logically.
- Use Signaling Devices: Flare guns, whistles, or emergency lights help attract attention in distress situations.
- Know Emergency Procedures: Familiarize yourself with the emergency protocols for your vessel, and ensure all crew members are aware of them.
Being well-prepared and knowledgeable about how to handle dangerous situations can make a critical difference when facing an emergency. Always stay alert and practice emergency drills regularly to increase your ability to respond effectively in any scenario.
Rules for Operating a Vessel at Night
Operating a vessel after dark presents unique challenges and requires a heightened awareness of both visibility and safety. Navigating in low-light conditions demands extra caution due to reduced sightlines and the potential for unseen obstacles. Understanding the rules for nighttime operation ensures not only your safety but also the safety of others on the water.
Before heading out, it’s essential to check that your vessel is equipped with the necessary lighting and equipment to comply with nighttime navigation laws. Proper lighting helps increase visibility and allows other vessels to see you from a distance, reducing the risk of collisions. Additionally, it’s crucial to be aware of any specific regulations regarding nighttime operation in your area, as laws can vary by region.
Required Lights and Equipment
- Navigation Lights: Ensure that your vessel is equipped with the correct lights to indicate your position and direction. These typically include a white stern light, red and green sidelights, and an all-around white light visible from all directions when stopped.
- Flares and Signaling Devices: Carry distress flares or other signaling devices in case of an emergency. These should be easily accessible and ready for use.
- Reflective Gear: Wearing reflective vests and ensuring that your crew is similarly equipped helps improve visibility in the dark.
Best Practices for Nighttime Navigation
- Reduce Speed: Due to the limited visibility at night, it’s advisable to reduce speed to allow for more reaction time in case of obstacles or other vessels.
- Maintain a Safe Distance: Keep a safe distance from other vessels, particularly when navigating in busy waters. Be cautious when passing or approaching other crafts to avoid collisions.
- Stay Alert: At night, fatigue can set in more easily. Ensure you and your crew are well-rested and alert throughout your trip. Constant vigilance is key.
By following these rules and understanding the challenges of nighttime navigation, you can enhance your safety and that of others on the water. Always prioritize visibility, reduce speed, and stay prepared for any unforeseen circumstances.
Common Navigation and Charting Questions

Understanding how to navigate and read charts is essential for anyone operating on open waters. Navigational skills allow you to determine your position, avoid hazards, and plan the safest route to your destination. Mastery of charts and other navigational tools can greatly enhance your ability to handle diverse marine environments with confidence and precision.
When it comes to navigating through unfamiliar waters, having a solid understanding of key concepts such as latitude, longitude, compass headings, and depth readings is crucial. It’s also important to know how to interpret various symbols and markings found on nautical charts, which can provide vital information about submerged hazards, currents, and safe passages.
Here are a few common concerns that often arise when dealing with navigation and charting:
- How do I determine my position using charts? You can determine your position by referencing your current location against landmarks or by using GPS coordinates. Triangulating your position using multiple reference points is another method for more precise navigation.
- What are the different types of markers on charts? Nautical charts use a variety of symbols to indicate different types of markers, such as buoys, beacons, and light vessels. These markers are used to guide vessels through safe routes and indicate hazards.
- How do I calculate the distance between two points? To calculate the distance between two points on a chart, you can use the scale provided, or you can use GPS or a rangefinder to get the exact measurement. Accurate distance calculation is essential for planning safe travel times and estimating fuel usage.
- What is the significance of tide tables in navigation? Tide tables provide information on the times and heights of high and low tides. This data is crucial for planning navigation in shallow areas or when crossing sandbars, as tides can significantly affect water depth.
- How do I adjust for magnetic variation? Magnetic variation is the difference between true north and magnetic north, and it must be considered when setting compass headings. This adjustment can be made using the annual variation or deviation charts provided in most nautical publications.
By addressing these common concerns and thoroughly familiarizing yourself with charting practices, you can navigate with greater accuracy and avoid the risks posed by uncharted or hazardous waters.
Understanding Boating Traffic Regulations
Adhering to traffic regulations on the water is crucial for the safety and efficiency of navigation. Just like on the road, there are specific rules governing how vessels should interact to prevent collisions, ensure smooth traffic flow, and protect both people and the environment. Understanding these guidelines is essential for anyone navigating in crowded or regulated waters.
The key to safe maritime travel lies in recognizing the various rules that govern right of way, speed limits, and maneuvering near other vessels. These regulations help to avoid confusion and ensure that all waterway users can coexist safely. In some areas, there may also be local rules or restrictions based on weather, water depth, and wildlife preservation efforts.
Here are some important aspects of waterway traffic regulations:
- Right of Way Rules: These rules dictate who has priority in different situations, such as when crossing paths with another vessel or approaching docks. For example, when two vessels are heading toward each other, the vessel on the right generally has the right of way.
- Speed Limits: Many areas impose speed restrictions, especially near shorelines, harbors, or in narrow channels, to ensure safety and prevent erosion or wake damage. Always be aware of posted speed signs and adjust your speed accordingly.
- Navigation Lanes: Specific lanes may be designated for vessels of certain types, such as large commercial ships or recreational watercraft. It is important to follow these lanes to avoid accidents and ensure efficient traffic flow.
- Signal Use: Maritime traffic relies heavily on signals to indicate intentions, such as turning, slowing down, or stopping. Understanding the correct use of sound signals, like horns or whistles, can help communicate your next move to other nearby vessels.
- Special Areas: Certain areas, such as wildlife protection zones, shallow regions, or zones near bridges, may have additional rules or restrictions to protect the environment or prevent accidents. Make sure to familiarize yourself with these rules before entering such areas.
By following these regulations, you not only ensure the safety of your vessel and passengers but also contribute to the overall well-being of the waterway and its users. Knowing when to give way, how to navigate different zones, and how to communicate effectively will help you avoid potential hazards while cruising.
Boat Exam Question Tips and Strategies

Preparing for a knowledge-based assessment on maritime safety and operation requires a strategic approach. Whether you’re navigating through a series of theoretical evaluations or mastering specific regulatory guidelines, adopting a clear study strategy can enhance performance and boost confidence. The key lies in understanding the structure of the assessment and identifying common patterns that frequently appear during the process.
One effective approach is to break down the material into manageable sections and focus on the most frequently tested topics. These typically include safety protocols, traffic regulations, navigational procedures, and emergency responses. By familiarizing yourself with these core subjects, you can ensure a solid foundation in the areas most likely to be covered.
Here are some practical tips to help you approach the assessment with confidence:
- Practice with Sample Material: Working through practice questions or mock tests can simulate the experience and help you get comfortable with the format. It’s a great way to identify areas where you may need more focus or practice.
- Understand Key Concepts: Rather than memorizing individual facts, focus on grasping the underlying principles behind safety rules, navigational techniques, and emergency procedures. Understanding how concepts apply in real-world scenarios can make recalling information easier during the test.
- Review Mistakes: When reviewing your practice sessions, pay close attention to the questions you answered incorrectly. Understanding why you made an error will help reinforce the correct information and improve retention.
- Manage Your Time: Time management is critical when facing a timed assessment. Practice pacing yourself during practice tests to ensure you’re comfortable with the duration of the assessment. Learn to prioritize questions you’re sure about and come back to tougher ones later if needed.
- Stay Calm and Focused: Staying calm during the actual test is essential. Avoid rushing through questions, as this can lead to mistakes. Take your time to read each question thoroughly and review your answers before submitting them, if possible.
By following these strategies, you can effectively navigate the assessment process, increase your chances of success, and ensure you’re prepared for real-life maritime challenges. A well-organized study plan and a calm, focused mindset will go a long way in helping you achieve your goals.
How to Study for the Boat Exam
Preparing for a maritime knowledge assessment requires a structured approach to ensure you are well-equipped with the necessary skills and information. Success in these evaluations is achieved by thoroughly understanding key concepts, regulations, and safety practices essential for navigating and operating watercraft. A strategic study plan will help you tackle the subject matter effectively and build the confidence needed for the assessment.
First, it’s crucial to familiarize yourself with the core topics that will be covered in the evaluation. These often include rules of the waterway, safety procedures, navigational techniques, and how to respond to emergencies. Understanding these fundamental areas will provide a solid foundation for the exam.
Here are some key study strategies to help you prepare effectively:
- Break Down the Material: Rather than trying to study everything at once, divide the material into smaller sections. Focus on one topic at a time, such as safety regulations or traffic rules, and master it before moving on to the next subject.
- Create a Study Schedule: Plan your study sessions to allow enough time for each topic. A consistent study schedule helps avoid last-minute cramming and gives you the chance to review the material several times before the assessment.
- Use Practice Tests: Taking practice tests helps you get a feel for the structure of the assessment. It also allows you to identify areas where you may need to improve. Try to replicate test conditions by timing yourself and completing the tests under similar circumstances.
- Focus on Weak Areas: After completing practice questions, review your mistakes and dedicate extra time to the topics you find most challenging. Understanding why you got certain answers wrong will help you reinforce the correct information.
- Review Key Definitions: Definitions of important terms and concepts are often tested. Make sure you can clearly define and explain the most common terms related to safety, navigation, and maritime law.
- Stay Consistent: Regular study is more effective than cramming. Set aside a few hours each day to review the material and avoid overwhelming yourself with too much information at once.
By following these tips and maintaining a disciplined study routine, you will be well-prepared for the assessment. The more you familiarize yourself with the material, the more confident and prepared you will feel during the test. A structured approach to studying will ultimately help you understand the concepts, improve retention, and set you up for success.