
Understanding and interpreting heart rhythms are essential skills for healthcare professionals. Accurate identification of various heart conditions can significantly impact patient care and treatment outcomes. Mastering these skills not only ensures better clinical decision-making but also prepares individuals for important assessments in the field of cardiology.
Recognizing irregularities in heart rhythms requires a deep understanding of electrocardiograms (ECGs) and the physiological processes that influence them. Through consistent practice and focused study, it is possible to improve one’s ability to distinguish between normal and abnormal patterns, allowing for quicker and more reliable diagnoses.
For those preparing for a certification or proficiency assessment, it is crucial to familiarize oneself with common arrhythmias, their underlying causes, and the methods used to evaluate them. This knowledge serves as the foundation for making informed decisions when faced with real-world clinical scenarios.
AACN Identifying Dysrhythmias Exam Answers
When preparing for a cardiology proficiency assessment, it is crucial to develop a strong foundation in heart rhythm recognition. This involves understanding the characteristics of normal and abnormal cardiac activity and being able to quickly differentiate between various conditions. Mastery of these skills allows healthcare providers to make informed decisions that can directly impact patient health outcomes. The following content explores the key components needed to succeed in rhythm recognition assessments.
Understanding Common Heart Rhythm Irregularities
To excel in rhythm recognition, one must familiarize themselves with the common conditions that will be tested. The ability to quickly identify and categorize these rhythms based on their specific features is essential. Some of the most frequently encountered irregularities include atrial fibrillation, ventricular tachycardia, and heart block. Knowing the key traits of each, such as their timing, frequency, and the way they appear on an ECG, will greatly improve accuracy when taking a proficiency test.
Key ECG Features to Focus On
Each rhythm disorder has unique ECG patterns that distinguish it from other conditions. Understanding these patterns is crucial for success. When interpreting the heart’s electrical activity, focus on elements like the P wave, QRS complex, and T wave. Recognizing their normal appearance and how they change during irregular rhythms will enable a clear understanding of the underlying issue. These characteristics will often be a focal point in assessment questions.
| Rhythm | ECG Characteristics | Clinical Significance |
|---|---|---|
| Atrial Fibrillation | Irregularly irregular rhythm, absent P waves | Increased stroke risk, requires rate control |
| Ventricular Tachycardia | Wide QRS complexes, rapid heart rate | Potential for cardiac arrest, requires immediate intervention |
| First Degree Heart Block | Prolonged PR interval, normal QRS complex | Generally benign, may progress to more severe block |
By focusing on the essential ECG features of these and other common rhythm disorders, healthcare professionals can significantly improve their chances of success in assessments related to heart rhythm interpretation.
Overview of Dysrhythmia Recognition
Recognizing irregular heart rhythms is a critical skill for healthcare professionals. Accurate interpretation of cardiac activity plays a central role in diagnosing conditions that can range from benign to life-threatening. Understanding how to differentiate between normal and abnormal patterns is essential for effective patient care. Mastery of this skill allows for quicker, more accurate decision-making and better patient outcomes in clinical settings.
Heart rhythm disorders can take many forms, each with unique characteristics that require careful analysis. By studying the electrical impulses that regulate the heart, healthcare providers can develop a keen eye for distinguishing various patterns. Key components of heart rhythms, such as the P wave, QRS complex, and T wave, provide valuable clues that help in making accurate assessments.
Successful rhythm recognition also involves understanding the physiological implications of these disorders. Different conditions can cause varying levels of disruption to the heart’s function, and recognizing these disruptions is the first step toward appropriate treatment. Whether through basic electrocardiogram (ECG) analysis or more advanced techniques, being able to identify and classify these irregularities is essential for timely intervention and effective care.
Key Concepts for Exam Preparation
Preparing for a proficiency assessment in heart rhythm recognition requires a thorough understanding of essential concepts. A solid foundation in the basic principles of ECG interpretation, coupled with the ability to recognize common cardiac abnormalities, is crucial. Focused study on these key topics helps ensure that you can quickly and accurately identify heart conditions when faced with clinical scenarios or assessment questions.
Understanding ECG Waveforms
ECGs are the primary tool used for analyzing heart rhythms. Familiarizing yourself with the various components of the waveform, such as the P wave, QRS complex, and T wave, is essential. Each element represents a different phase of the heart’s electrical activity, and being able to interpret their patterns will allow for a better understanding of both normal and abnormal rhythms. Mastery of these waveforms is foundational to successful rhythm recognition.
Common Arrhythmias and Their Characteristics
Another critical area of study is the various types of arrhythmias, each of which has distinct features. Conditions like atrial fibrillation, ventricular tachycardia, and heart block each present unique ECG patterns. Understanding the specific characteristics of these disorders–such as heart rate, regularity, and waveform abnormalities–will aid in differentiating between similar rhythms and contribute to more accurate diagnoses.
Common Dysrhythmias in the Exam
In any proficiency assessment related to heart rhythm recognition, certain cardiac conditions are more likely to appear due to their prevalence and clinical significance. Understanding the features of these conditions is essential for accurate interpretation and quick diagnosis. Familiarity with common irregularities allows professionals to efficiently identify and assess them during practical evaluations or real-world scenarios.
Atrial Fibrillation
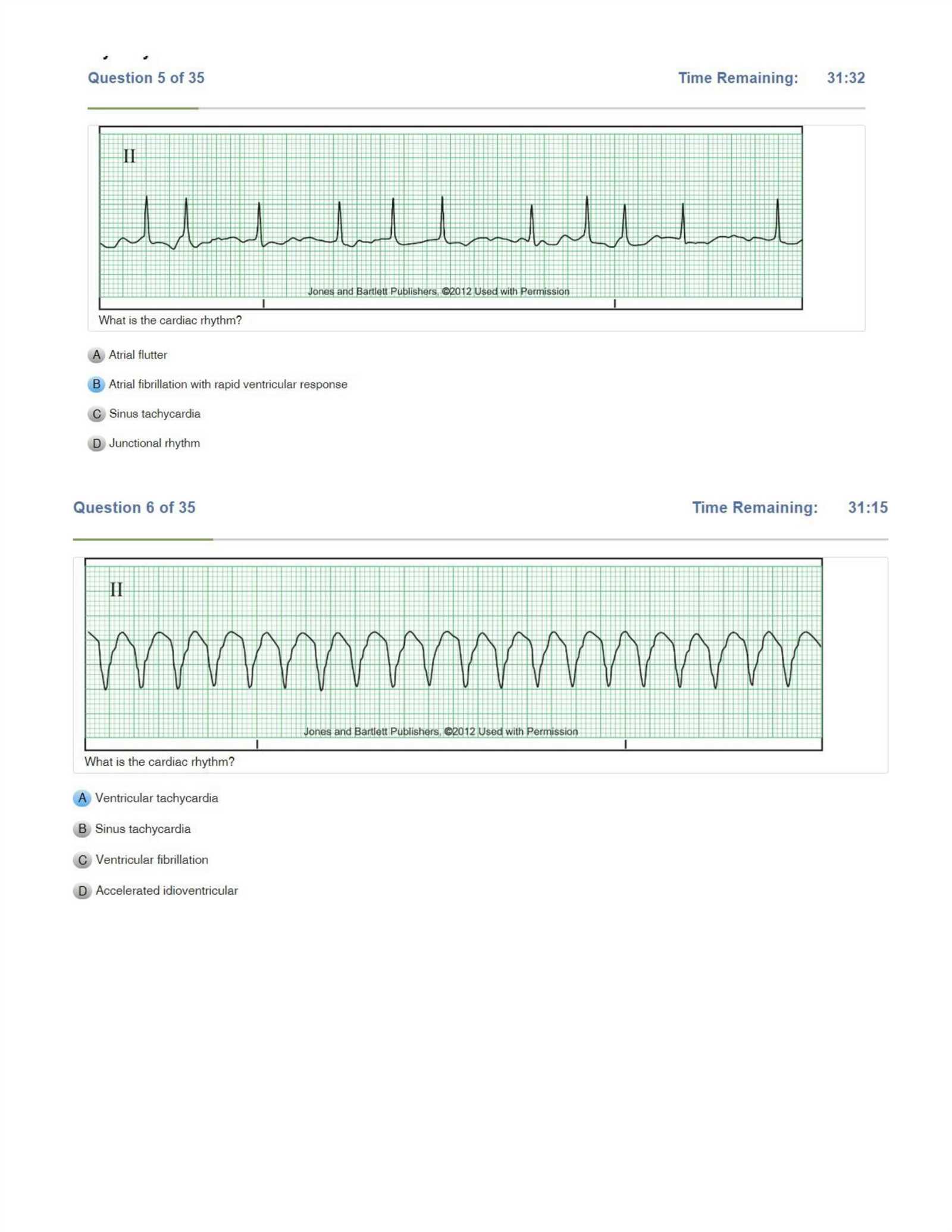
Atrial fibrillation is one of the most frequently encountered arrhythmias in assessments. It is characterized by an irregularly irregular rhythm, absence of distinct P waves, and varying ventricular rates. This condition often indicates a heightened risk of stroke and may require immediate medical management to prevent complications.
- Irregularly irregular rhythm
- Absent P waves
- Rapid ventricular response
Ventricular Tachycardia
Ventricular tachycardia (VT) is a potentially life-threatening arrhythmia marked by a rapid heart rate originating from the ventricles. In ECG readings, VT often presents with wide QRS complexes and a consistent, fast rate. Immediate intervention is necessary to prevent deterioration into more severe conditions like ventricular fibrillation.
- Wide QRS complexes
- Rapid heart rate (over 100 bpm)
- Can lead to cardiac arrest if untreated
First Degree Heart Block
First degree heart block is a relatively benign condition where the electrical impulses are delayed between the atria and ventricles. This results in a prolonged PR interval on the ECG but does not typically cause significant symptoms. It is important to differentiate this condition from more severe heart blocks.
- Prolonged PR interval (greater than 0.20 seconds)
- Normal QRS complexes
- Generally asymptomatic
By understanding these common arrhythmias, healthcare professionals can be better prepared to recognize them during assessments and clinical practice. Recognizing these key conditions will ensure effective diagnosis and appropriate management strategies.
Understanding ECG Waveforms and Intervals
Electrocardiograms (ECGs) are an essential tool for assessing the heart’s electrical activity. A clear understanding of the various waveforms and intervals is crucial for accurately interpreting heart rhythms. Each component of the ECG provides valuable information about the different phases of the cardiac cycle, helping healthcare professionals identify both normal and abnormal patterns. By learning to analyze these waveforms and intervals, you can gain deeper insights into the underlying cardiac conditions and make more informed clinical decisions.
The primary components of an ECG include the P wave, QRS complex, and T wave. These elements correspond to specific actions within the heart’s electrical system. In addition to these waveforms, several intervals, such as the PR interval and QT interval, are important indicators of cardiac function and can help differentiate between various heart conditions.
By understanding the relationship between these waveforms and intervals, professionals can effectively identify arrhythmias, assess heart function, and determine the need for further intervention. Mastery of this fundamental knowledge is a key aspect of rhythm recognition and is essential for accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
Critical Values in Dysrhythmia Analysis
In the analysis of heart rhythm abnormalities, certain key values are critical for accurate diagnosis and effective treatment. These values help determine the severity of the condition and guide clinical decision-making. Understanding these measurements is essential for professionals working with patients who may present with arrhythmias or other cardiac issues. By focusing on these critical values, healthcare providers can identify life-threatening conditions and intervene in a timely manner.
Among the most important metrics in rhythm analysis are heart rate, PR interval, QRS duration, and QT interval. Deviations from the normal ranges of these values can signal the presence of various conditions, from benign arrhythmias to more dangerous disorders that require immediate attention. Close attention to these values is necessary for differentiating between normal and abnormal rhythms and for determining the appropriate course of action.
In addition to these intervals, the regularity of the rhythm and the morphology of the ECG waveforms also play significant roles in the analysis. Variations in waveform shape, amplitude, or timing can indicate underlying pathologies that may not be immediately apparent from the heart rate alone. By carefully assessing these critical values, healthcare professionals can provide better care and ensure the best possible outcomes for their patients.
Steps to Identify Arrhythmias Effectively
Accurately recognizing heart rhythm disorders is crucial for healthcare professionals to make timely and appropriate decisions. Effective rhythm analysis requires a systematic approach that includes a step-by-step process to assess the heart’s electrical activity. By following these steps, professionals can confidently identify various abnormalities and determine the most appropriate interventions.
The first step in identifying arrhythmias is to assess the overall rhythm of the heart. This involves determining whether the rhythm is regular or irregular. Next, you should measure the heart rate to assess whether it falls within a normal range. Once you have these basic measurements, it’s important to examine the individual components of the ECG, such as the P wave, QRS complex, and T wave, to ensure they follow a normal pattern. Any deviations from the expected pattern could indicate an underlying rhythm disorder.
In addition to waveform analysis, consider the relationship between the P wave and the QRS complex. This will help you determine whether the heart’s electrical impulses are being conducted normally or if there are delays or blocks in the system. By following these systematic steps, healthcare professionals can identify and classify arrhythmias more effectively, ensuring timely treatment and improving patient outcomes.
Heart Rate and Rhythm Interpretation Tips
Accurate interpretation of heart rate and rhythm is essential for diagnosing and managing various cardiac conditions. By carefully evaluating the rate and regularity of heartbeats, healthcare professionals can identify potential abnormalities and determine appropriate treatment plans. A systematic approach to rhythm analysis can help avoid misinterpretation and ensure effective patient care.
Start by assessing the heart rate. A quick way to determine the rate is by measuring the distance between R waves on the ECG. From there, you can calculate the number of beats per minute. For a more precise interpretation, also check for regularity. An irregular rhythm may indicate an arrhythmia or a fluctuation in heart activity. Pay attention to any pauses or extra beats as these can signal more complex issues.
Another important tip is to evaluate the relationship between the P wave and the QRS complex. A normal rhythm shows a consistent P wave before each QRS complex. If there is a delay or absence, it could point to conduction delays or blocks. Understanding these fundamental elements can significantly improve your ability to identify various rhythm disturbances quickly and accurately.
| Rhythm Type | Heart Rate | Pattern |
|---|---|---|
| Atrial Fibrillation | Variable | Irregularly Irregular |
| Ventricular Tachycardia | Rapid (>100 bpm) | Wide QRS Complex |
| Sinus Bradycardia | Slow ( | Regular |
By focusing on these tips and consistently practicing rhythm interpretation, you can become more proficient in detecting abnormal heart rhythms and responding effectively to clinical situations.
Common Mistakes to Avoid on the Exam
When preparing for a test focused on assessing knowledge of cardiac rhythm abnormalities, it’s important to be aware of common errors that can affect performance. These mistakes can lead to misinterpretation of heart rhythms, inaccurate assessments, and ultimately, poor exam results. By understanding the most frequent pitfalls and taking steps to avoid them, you can improve your accuracy and confidence during the assessment process.
Rushing Through the Analysis
One of the most common mistakes is rushing through the rhythm analysis. Many candidates may try to identify patterns too quickly without fully examining all the components of the ECG. It’s important to take the time to evaluate each segment, from the P wave to the T wave, and assess the relationship between these components. Skipping over these steps can lead to missing critical details that can change the interpretation of the rhythm.
Ignoring Subtle Variations in Rhythm
Another mistake is overlooking subtle variations or irregularities in the heart rhythm. Some arrhythmias present with only minor deviations that can be easily missed if you are not paying close attention. For example, slight changes in the timing of the P waves or a delayed QRS complex can indicate conduction issues or the presence of an arrhythmia. Recognizing even the smallest irregularities can significantly enhance your diagnostic accuracy.
By taking a methodical approach, avoiding haste, and being mindful of minor variations, you can reduce the likelihood of errors and improve your performance in rhythm analysis tests.
Study Strategies for Success
To perform well in any assessment related to heart rhythm abnormalities, it is essential to adopt effective study strategies. Proper preparation involves not only understanding the theoretical concepts but also practicing practical skills. By following a structured study plan, you can ensure comprehensive knowledge and improve your ability to analyze and interpret cardiac rhythms accurately.
Develop a Study Schedule
Creating a study schedule is one of the most crucial steps in preparation. A well-organized timetable helps you allocate sufficient time for each topic, preventing last-minute cramming. Make sure to break down complex subjects into manageable sections and review them regularly.
- Set specific time blocks for each topic.
- Prioritize areas where you feel less confident.
- Review material consistently to reinforce memory.
Utilize Various Learning Resources
Using a variety of study resources can enhance your understanding and provide a broader perspective. In addition to textbooks, consider incorporating online tutorials, videos, and practice ECG strips to build practical skills. These resources can provide visual aids that are crucial for mastering rhythm interpretation.
- Watch video tutorials on rhythm analysis.
- Practice with sample ECGs to improve interpretation skills.
- Participate in online forums or study groups for discussion.
By following these study strategies and staying consistent, you can build the knowledge and confidence needed to succeed in rhythm analysis assessments.
Role of Medication in Dysrhythmia Management
Medications play a critical role in the management of abnormal heart rhythms, offering both symptomatic relief and long-term control. Depending on the type and severity of the rhythm disorder, different drugs can be used to restore normal heart function, control the rate, or prevent dangerous complications. Proper medication management is essential for reducing the risks associated with arrhythmias and improving patient outcomes.
Several classes of medications are commonly prescribed for managing irregular heartbeats. These drugs work in various ways, either by slowing down the heart rate, stabilizing the electrical activity, or reducing the likelihood of abnormal rhythms. It is important to match the right medication to the specific type of arrhythmia for effective treatment.
Common Classes of Medications
- Antiarrhythmic drugs – These help restore the normal rhythm by modifying the electrical activity of the heart.
- Beta-blockers – These reduce the heart rate and can help prevent episodes of arrhythmia.
- Calcium channel blockers – These drugs slow the electrical conduction and are used in rate control.
- Anticoagulants – These are used to reduce the risk of blood clots that may form due to abnormal heart rhythms.
Medication Considerations and Monitoring
When treating heart rhythm issues, healthcare providers must consider the patient’s overall health, the underlying cause of the abnormal rhythm, and any other medical conditions. It is important to regularly monitor the patient’s response to medication and adjust dosages as needed to avoid side effects or complications.
- Regular ECG monitoring to assess the effectiveness of treatment.
- Frequent blood tests to check for potential side effects, especially with long-term use of certain drugs.
- Adjusting medications as needed based on clinical response and patient tolerance.
By properly utilizing medications, it is possible to manage abnormal heart rhythms effectively and prevent serious complications, significantly improving patient quality of life.
Using the ECG to Identify Conditions
The electrocardiogram (ECG) is an invaluable tool for diagnosing and monitoring various heart conditions. By analyzing the electrical signals of the heart, healthcare providers can gain insights into the heart’s rhythm, rate, and overall function. The ECG provides a graphical representation that helps detect abnormalities in heart activity, offering crucial information for treatment decisions.
Correct interpretation of ECG waveforms is essential for identifying a range of cardiac issues, from minor irregularities to life-threatening conditions. Understanding the different components of the ECG and how they correlate with heart function is fundamental for accurate diagnosis and effective management of heart conditions.
Key Components of an ECG
- P Wave – Represents atrial depolarization and is an indicator of atrial activity.
- QRS Complex – Reflects ventricular depolarization and provides information on the ventricles’ electrical activity.
- T Wave – Represents ventricular repolarization and can reveal issues with heart muscle recovery.
- PR Interval – The time taken for electrical signals to travel from the atria to the ventricles, helping assess conduction delays.
Common Conditions Identified via ECG

Various heart conditions can be recognized through characteristic changes in the ECG pattern. Some of the most common include:
- Arrhythmias – Irregular heart rhythms that can present as too fast, too slow, or erratic rhythms.
- Myocardial Infarction – Heart attack, typically indicated by abnormal ST-segment elevations or depressions.
- Heart Block – A delay or blockage in the electrical conduction system, often identified by prolonged PR intervals.
- Electrolyte Imbalances – Issues such as high or low potassium levels, which can alter the shape of the T wave or other segments of the ECG.
By studying these key components and understanding how they relate to different cardiac conditions, healthcare providers can effectively use the ECG to diagnose and manage various heart disorders.
Recognizing Life-Threatening Arrhythmias
Prompt identification of critical cardiac rhythm abnormalities is essential for saving lives. Some heart conditions are particularly dangerous and can rapidly progress to a life-threatening state if not addressed immediately. Recognizing these irregular rhythms is crucial for providing timely interventions and preventing catastrophic outcomes. Understanding the common signs and symptoms, as well as the characteristics on an electrocardiogram (ECG), is key in identifying these conditions early.
There are several types of dangerous arrhythmias that healthcare professionals need to be able to recognize quickly. These conditions can cause the heart to beat too fast, too slow, or erratically, disrupting the blood flow to vital organs, including the brain. The ECG is one of the most important diagnostic tools used to identify these life-threatening situations.
Common Life-Threatening Arrhythmias

| Arrhythmia | ECG Characteristics | Potential Risk |
|---|---|---|
| Ventricular Fibrillation | Rapid, erratic electrical impulses with no defined rhythm or waveform. | Causes the heart to quiver instead of pumping blood, leading to cardiac arrest. |
| Ventricular Tachycardia | Fast, wide QRS complexes at a rate of over 100 beats per minute. | Can deteriorate into ventricular fibrillation if untreated, leading to sudden death. |
| Atrial Fibrillation | Irregularly irregular rhythm with no distinct P waves and variable ventricular response. | Increases the risk of stroke and can lead to heart failure if not managed properly. |
| Asystole | No electrical activity seen on the ECG; flatline. | Complete cessation of heart activity, requiring immediate resuscitation efforts. |
Signs and Symptoms to Watch For

In addition to ECG findings, certain symptoms can indicate that a patient is experiencing a life-threatening rhythm disturbance. These include:
- Chest pain – Often associated with arrhythmias caused by underlying coronary artery disease.
- Shortness of breath – Difficulty breathing may result from insufficient cardiac output.
- Dizziness or fainting – Reduced blood flow to the brain can cause loss of consciousness or near-fainting spells.
- Palpitations – Patients may feel rapid or irregular heartbeats, which could signal a serious arrhythmia.
Recognizing these critical conditions and acting quickly can mean the difference between life and death. Proper training and familiarity with the ECG features of these dangerous arrhythmias are essential for timely intervention and optimal patient outcomes.
Importance of Clinical Practice for the Exam
Clinical practice plays a vital role in preparing for any certification or assessment related to cardiac rhythm interpretation. While theoretical knowledge provides the foundation, hands-on experience allows you to apply what you’ve learned in real-world settings. Practicing in clinical environments enhances your ability to recognize and respond to critical situations, making it an essential component of effective preparation. This practical exposure reinforces learning, builds confidence, and helps in the development of quick decision-making skills that are crucial during the assessment and in actual clinical practice.
Real-World Application of Theoretical Knowledge
In a clinical setting, you encounter a wide range of scenarios that challenge your understanding of cardiac rhythms. The opportunity to observe patients in different states of health and disease helps solidify theoretical knowledge. Clinical practice helps you connect ECG patterns with actual patient symptoms, giving you a more holistic understanding of the conditions you are studying.
Developing Critical Thinking and Decision-Making Skills
Working with patients gives you the chance to improve your clinical judgment and the ability to make informed decisions under pressure. In many cases, identifying abnormal heart rhythms and knowing how to respond quickly can save lives. By practicing with real patient data, whether through simulations or direct patient care, you develop a faster, more accurate approach to identifying issues and intervening appropriately.
Moreover, frequent exposure to diverse cases in clinical settings helps you become familiar with rare and complex conditions that may not be covered in textbooks. This experience is invaluable as it prepares you to handle unexpected situations with a calm and knowledgeable approach during assessments or in practice.
Examining Sinus Rhythms and Variations
Understanding normal heart rhythms and their variations is fundamental in assessing cardiac health. Sinus rhythm is the most common and stable heart rhythm, originating from the sinoatrial (SA) node. However, even within normal sinus rhythm, variations can occur, reflecting different physiological conditions or mild abnormalities. Recognizing these variations is crucial for distinguishing between what is normal and what may require further investigation or intervention. By understanding the nuances of sinus rhythms and their possible fluctuations, healthcare professionals can better monitor patients and respond to potential issues before they escalate.
Normal Sinus Rhythm Characteristics
A normal sinus rhythm (NSR) is characterized by a consistent rhythm and heart rate, typically ranging from 60 to 100 beats per minute in a resting adult. The rhythm is initiated by the SA node, and each beat is followed by a regular, evenly spaced wave on the ECG. This rhythm is considered the “default” for a healthy heart and serves as a baseline for comparing other rhythms. In a normal sinus rhythm, the P wave, QRS complex, and T wave appear in a predictable and consistent manner, with a steady PR interval and normal heart rate.
Common Variations in Sinus Rhythm
While sinus rhythm is the most common and stable pattern, certain variations can occur under specific conditions. These include:
- Sinus Arrhythmia: A common variation in heart rate where the rhythm speeds up during inspiration and slows down during expiration. This is often seen in young, healthy individuals and is typically benign.
- Sinus Tachycardia: A faster-than-normal heart rate, usually over 100 beats per minute, which can occur in response to stress, exercise, fever, or other conditions.
- Sinus Bradycardia: A slower-than-normal heart rate, typically under 60 beats per minute, which may be seen in athletes or during sleep, but can also indicate underlying health issues in other cases.
Recognizing and understanding these variations is key to accurately interpreting ECGs and providing appropriate patient care. Whether the rhythm is slightly altered due to normal physiological processes or indicative of a potential issue, a thorough understanding of sinus rhythms and their variations is essential for making informed clinical decisions.
Final Review and Exam Day Tips
Preparing for an assessment that tests your knowledge and skills in clinical settings requires both focused study and careful planning for the day of the evaluation. As the test approaches, it’s important to consolidate your understanding of key concepts and refine your test-taking strategies. This final review process not only reinforces your knowledge but also boosts your confidence. Additionally, understanding how to approach the test day itself can make a significant difference in your performance. Proper preparation, both mentally and practically, will help you stay calm and focused during the assessment.
Last-Minute Review Techniques
As you enter the final stages of preparation, here are some effective strategies to make sure you’re ready:
- Focus on Weak Areas: Review topics or concepts that you find challenging. Use practice questions, review guides, or flashcards to test your understanding.
- Practice with Simulated Scenarios: If possible, engage in practice exercises or simulations that mirror the real assessment format. This will help you become familiar with the types of questions or tasks you will face.
- Review Key Formulas and Patterns: Make sure you’re comfortable with any critical formulas, rhythms, or patterns that are frequently tested. This could include things like normal heart rate ranges, ECG waveforms, or common conditions.
Test Day Tips
The day of the evaluation can be nerve-wracking, but proper preparation can ease anxiety. Here are some helpful tips for staying focused and calm:
- Get a Good Night’s Sleep: A well-rested mind is more alert and focused. Aim to get at least 7-8 hours of sleep the night before the test.
- Eat a Healthy Breakfast: A nutritious meal will provide sustained energy throughout the day. Avoid heavy, greasy foods that might make you feel sluggish.
- Arrive Early: Give yourself plenty of time to arrive at the testing location. Arriving early reduces stress and allows you to get settled before the assessment starts.
- Stay Calm and Focused: During the test, take deep breaths to stay calm. If you encounter a difficult question, move on and return to it later. Don’t let one question derail your progress.
- Manage Your Time: Keep track of the time during the assessment. Don’t spend too long on any one question, and make sure you pace yourself to complete the entire evaluation.
With the right strategies and mindset, you’ll be in the best position to succeed. Remember to trust in your preparation, stay confident, and approach the assessment with a clear, focused mind.