Success in any technical field relies on a clear understanding of the underlying principles and the ability to apply them effectively. By developing a structured approach to solving problems, individuals can build confidence and achieve accuracy, even when faced with complex scenarios.
This article provides insights into essential strategies for breaking down challenging tasks into simpler components. It emphasizes logical reasoning, critical thinking, and the importance of a systematic method for tackling intricate questions. With these tools, even the most daunting challenges become manageable.
Through a focus on practical applications and proven techniques, you’ll gain the skills needed to analyze problems, identify solutions, and approach tasks with efficiency. Prepare to deepen your understanding and refine your methods for optimal results.
Preparing for Geometry Final Exams Successfully
Effective preparation is the key to mastering complex topics and performing well under pressure. By organizing study sessions, reviewing key concepts, and applying strategies consistently, students can enhance their understanding and approach challenges confidently. Success in any subject lies in the ability to break down problems and apply learned techniques in real-world scenarios.
Focus on Core Concepts
Start by revisiting the most fundamental principles and understanding their interconnections. The ability to identify and understand core relationships is essential for tackling more advanced tasks. Ensure a deep comprehension of basic theories and practice their application in various settings to reinforce your grasp of the subject matter.
Practice Regularly to Build Confidence
Repetition is crucial for reinforcing concepts and improving problem-solving skills. Work through a variety of practice problems that test your knowledge and challenge your abilities. The more you practice, the more familiar and confident you become with the material. Keep track of areas that need improvement and focus on them during your study sessions to build overall competency.
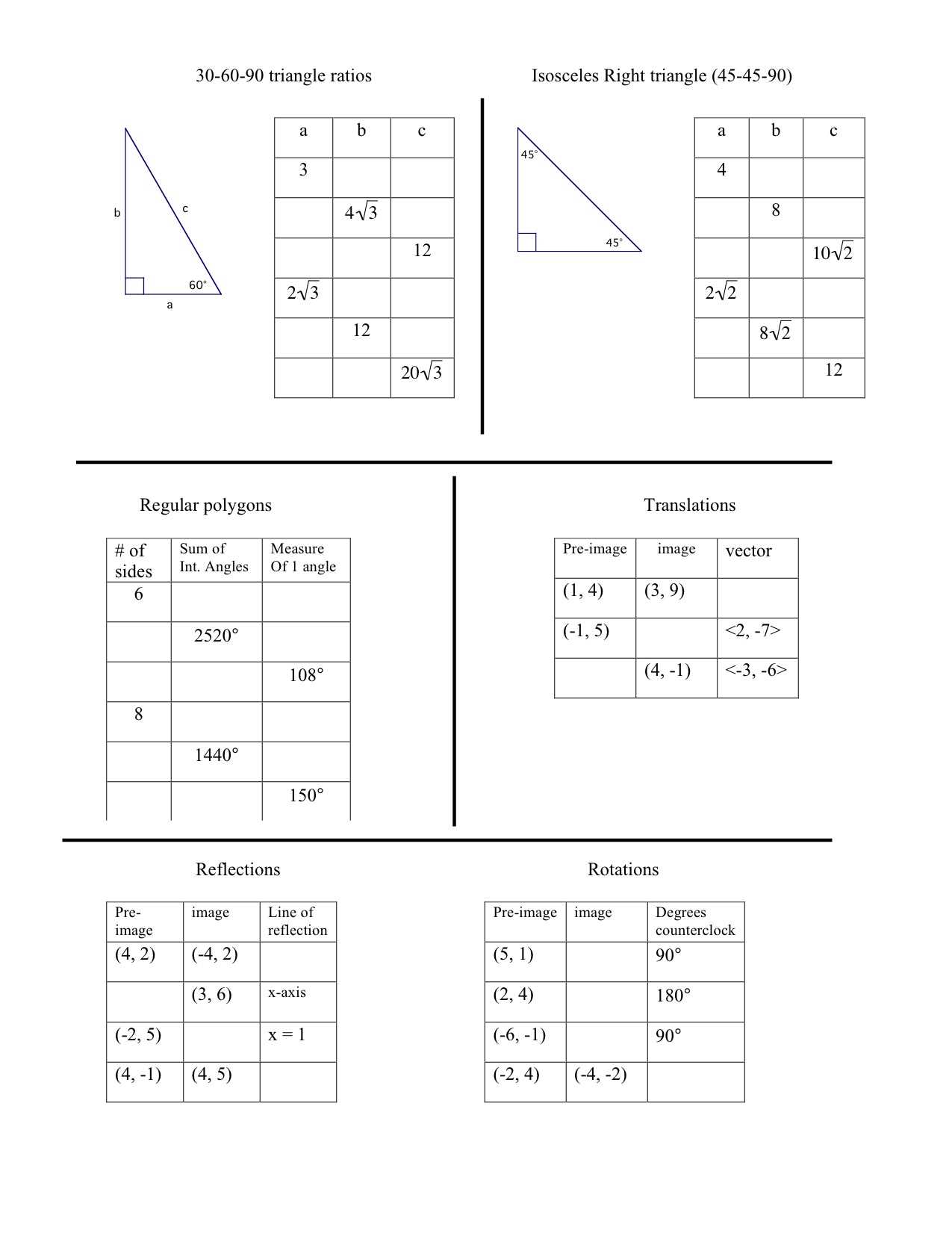
Key Formulas to Remember for Geometry Tests
Mastering essential equations is crucial when preparing for assessments in this field. Knowing the right formulas allows you to solve problems quickly and accurately. Below is a list of fundamental formulas that will help you approach different types of challenges with confidence.
Area and Perimeter Formulas
Understanding how to calculate areas and perimeters for various shapes is fundamental. These formulas are used frequently and should be memorized for quick reference.
- Area of a Rectangle: Length × Width
- Area of a Triangle: 1/2 × Base × Height
- Area of a Circle: π × Radius²
- Perimeter of a Rectangle: 2 × (Length + Width)
- Perimeter of a Circle (Circumference): 2 × π × Radius
Pythagorean Theorem
This formula is essential for solving problems related to right triangles. It helps you find the length of a side when the lengths of the other two sides are known.
- Pythagorean Theorem: a² + b² = c²
Volume and Surface Area Formulas
When dealing with three-dimensional objects, volume and surface area formulas are key. Memorizing these equations is necessary for tackling related questions efficiently.
- Volume of a Rectangular Prism: Length × Width × Height
- Surface Area of a Rectangular Prism: 2 × (Length × Width + Length × Height + Width × Height)
- Volume of a Cylinder: π × Radius² × Height
- Surface Area of a Cylinder: 2 × π × Radius × Height + 2 × π × Radius²
Familiarity with these formulas is crucial for solving problems quickly and accurately, ensuring you’re well-prepared for any challenges. Practice using these equations in various scenarios to strengthen your understanding and improve your problem-solving skills.
Solving Problems Involving Lines and Angles
Understanding the relationships between lines and angles is essential for solving various types of problems. Whether dealing with parallel lines, intersecting lines, or calculating angles formed by these lines, mastering these concepts is key to finding solutions efficiently. This section will explore common types of problems and the strategies you can use to approach them with confidence.
Working with Parallel Lines and Transversals
When two parallel lines are cut by a transversal, several important angle relationships come into play. These include corresponding angles, alternate interior angles, and consecutive interior angles. Recognizing these patterns allows you to solve problems involving these angles more easily.
- Corresponding Angles: Angles in the same position on two different lines.
- Alternate Interior Angles: Angles on opposite sides of the transversal but inside the parallel lines.
- Consecutive Interior Angles: Angles on the same side of the transversal and inside the parallel lines. These angles are supplementary.
Angle Relationships in Intersecting Lines
When two lines intersect, they form several pairs of angles, such as vertical angles and adjacent angles. Understanding these relationships is crucial for determining unknown angle measures.
- Vertical Angles: Angles that are opposite each other when two lines intersect. These angles are always equal.
- Adjacent Angles: Angles that share a common side and vertex. The sum of adjacent angles on a straight line is 180°.
By applying these principles and recognizing angle patterns, you can efficiently solve problems related to lines and angles. Practice with different scenarios will help solidify your understanding and improve your ability to approach these types of problems with confidence.
Understanding Properties of Geometric Figures
Each geometric shape has its own set of characteristics and rules that determine how its parts interact with each other. Whether dealing with polygons, circles, or three-dimensional solids, these properties help define the relationships between sides, angles, and other elements. A strong grasp of these attributes is essential when solving problems related to different shapes.
Properties of Common Two-Dimensional Shapes
Two-dimensional figures, such as squares, triangles, and circles, have unique properties that are fundamental to understanding their behavior in geometric problems. These properties often relate to the number of sides, angles, symmetry, and area calculations.
| Shape | Properties |
|---|---|
| Square | All sides are equal, all angles are 90°, opposite sides are parallel. |
| Equilateral Triangle | All sides are equal, all angles are 60°. |
| Circle | Has no sides, the distance from the center to any point on the circumference is the radius. |
Properties of Three-Dimensional Figures
In addition to two-dimensional shapes, three-dimensional solids also have distinct properties related to their volume, surface area, and the relationships between their faces, edges, and vertices. Understanding these properties is essential when working with solids in geometric problems.
| Shape | Properties |
|---|---|
| Cube | All faces are squares, all edges are equal in length, and it has 6 square faces. |
| Sphere | All points on the surface are equidistant from the center, has no edges or vertices. |
| Cylinder | Has two parallel circular bases, and a curved surface connecting the bases. |
By familiarizing yourself with these properties and practicing their application, you can gain a deeper understanding of how geometric shapes function and improve your problem-solving abilities.
How to Approach Coordinate Geometry Questions
When working with problems that involve points on a plane, it is essential to have a systematic approach. These questions often require you to analyze relationships between different points, lines, and shapes using their positions on a graph. Mastering this approach can simplify solving complex problems and help you understand the connections between geometric elements in a coordinate system.
Step 1: Understand the Given Information
Before diving into calculations, it’s important to carefully read and understand the provided details. Look for the coordinates of points and the equations of lines or curves. Pay attention to any special instructions, such as determining the distance between two points or finding the midpoint of a segment.
Step 2: Plot the Points on a Graph
Sometimes, drawing the problem can clarify the relationships between points and lines. By plotting the coordinates on a graph, you can visually identify important information and check for any patterns.
Step 3: Use Relevant Formulas
In many problems, you will need to apply specific formulas to calculate distances, slopes, midpoints, or areas. Common formulas to remember include:
- Distance Formula: d = √((x2 – x1)² + (y2 – y1)²)
- Slope Formula: m = (y2 – y1) / (x2 – x1)
- Midpoint Formula: Midpoint = ((x1 + x2) / 2, (y1 + y2) / 2)
Step 4: Solve Step-by-Step
Break down the problem into smaller steps. Start by finding the required values, such as the slope or distance, and use them to solve for the unknowns. Be sure to check your work at each stage to avoid mistakes.
Step 5: Interpret the Results
After solving, make sure to interpret your results within the context of the problem. For example, if you calculated the slope of a line, explain what it tells you about the line’s direction. If you’re finding the area of a triangle, ensure that your answer makes sense based on the given coordinates.
By following these steps, you can confidently tackle problems involving points, lines, and other shapes in a coordinate plane.
Effective Ways to Practice Geometry Proofs
Mastering the art of logical reasoning is essential when tackling problems that require justifying relationships between different shapes and figures. To be successful, it’s important to focus on building a strong foundation of concepts, identifying patterns, and applying them systematically in a step-by-step manner. Practicing these kinds of exercises can help you improve your reasoning skills and gain confidence in constructing rigorous arguments.
Understand the Basic Principles
Before diving into more complex tasks, make sure you’re familiar with the fundamental principles that govern relationships between geometric shapes. Recognize key properties, such as congruence, similarity, and parallelism, as well as theorems related to angles, triangles, and quadrilaterals. A clear understanding of these concepts provides the groundwork for constructing your logical steps.
Break Down the Problem into Steps
When faced with a proof, approach it like solving a puzzle. Begin by carefully analyzing the given information and figure out what you’re trying to prove. Break down the problem into smaller, manageable pieces and look for logical connections between them. Identify relationships between elements, such as shared angles or parallel lines, and consider how they can lead to the desired conclusion.
Use Diagrams to Visualize Relationships
Drawing clear diagrams is crucial when working on geometric arguments. Visual aids can help you identify relevant properties more easily and spot connections between figures. A well-drawn figure can also assist you in organizing your thoughts and staying on track as you work through each step of the proof.
Practice with Examples
To get better at proofs, practice is key. Start with simple examples and gradually increase the difficulty level. Work through a variety of problems that require different types of reasoning, from basic angle relationships to more advanced constructions involving polygons or circles. The more examples you work through, the more comfortable you’ll become with identifying proof strategies.
Study Proof Strategies
There are various strategies that can be employed in proofs, such as direct proof, proof by contradiction, or proof by induction. Understanding how and when to use these techniques is crucial. Studying different approaches allows you to approach a variety of problems with confidence and flexibility.
By consistently practicing, reviewing key concepts, and approaching each problem logically, you can sharpen your ability to create rigorous and coherent geometric arguments.
Identifying Patterns in Complex Geometry Problems
In many mathematical challenges, recognizing patterns is a critical skill that can simplify seemingly difficult problems. By spotting recurring relationships or regularities in shapes, lines, and angles, you can often reduce complex tasks to a series of straightforward steps. Developing the ability to identify such patterns helps in formulating strategies to tackle a wide range of problems effectively.
Look for Repeated Geometric Relationships

One of the first things to check when approaching a problem is whether any familiar geometric relationships appear. These may include parallel lines, similar triangles, or congruent angles. Identifying these repeating patterns can guide you towards relevant theorems or postulates that can simplify the problem-solving process.
Use Symmetry to Your Advantage
Symmetry is often present in complex problems and can be a powerful tool. Whether it’s axial symmetry or rotational symmetry, recognizing symmetrical properties can help break down a figure into smaller, more manageable sections. This can reveal hidden relationships or help prove certain properties without much effort.
As you solve problems, try to focus on the larger structure and identify how elements interact. Through consistent practice, you will improve your ability to see patterns that are not immediately obvious, ultimately making problem-solving faster and more intuitive.
Tips for Using Geometry Worksheets Effectively
When preparing for a challenging test, working through practice problems can be an invaluable strategy. Utilizing these materials correctly can boost your understanding and retention of key concepts. By focusing on structure, time management, and active problem-solving, you can ensure that each practice session enhances your skills and knowledge.
Prioritize Understanding Over Memorization
While practicing problems, it’s essential to focus on understanding the underlying concepts rather than simply memorizing formulas or procedures. Recognize how each step fits within the broader framework of the topic. This deeper understanding will make it easier to adapt your approach to different types of problems.
Break Down Problems Into Smaller Parts
Complex challenges can often seem overwhelming at first glance. Break them down into smaller, more manageable steps. This method allows you to focus on one element at a time, ensuring you don’t miss key details. Gradually, as you build confidence, you will be able to approach more difficult problems with greater ease.
Consistency and practice are key. Set aside time to regularly work through these exercises, tracking your progress and identifying areas where you may need to spend more time. This consistent effort will result in significant improvement over time.