The study of the human body requires a deep understanding of its various systems and functions. Whether you are revisiting key concepts or preparing for a challenging assessment, mastering these foundational topics is crucial for success. Grasping the intricacies of body structures, their roles, and how they interact provides essential insights into health and disease.
Organ systems such as the cardiovascular, respiratory, and musculoskeletal networks are complex yet vital for maintaining life. A thorough understanding of how each system works independently and together will significantly enhance your ability to recall important information. Focusing on the core principles of each system helps ensure clarity when faced with detailed questions.
As you dive into the detailed study of cellular functions, tissue types, and organ roles, it is essential to actively engage with the material. Visual aids, such as diagrams and charts, can aid in recalling complex relationships between systems. Preparing effectively means not only memorizing facts but also understanding how these systems collaborate to keep the body functioning.
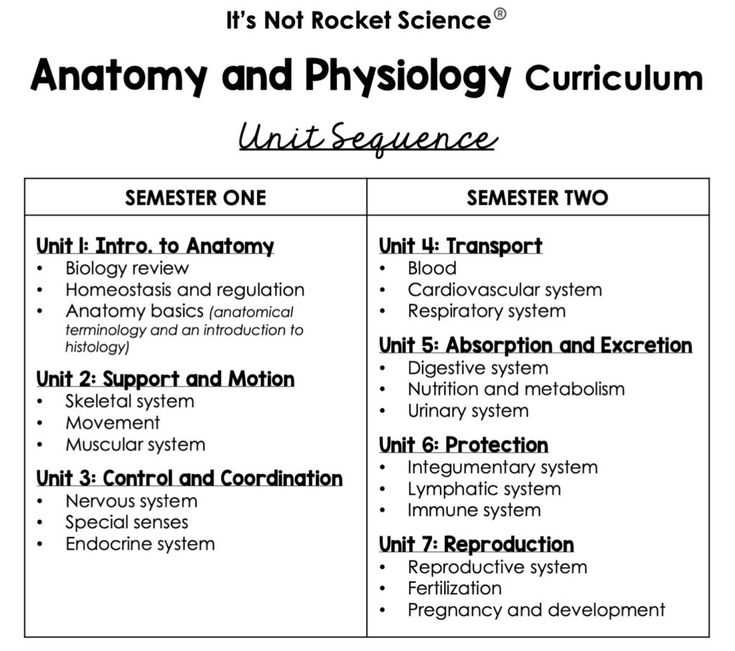
Anatomy and Physiology Semester 1 Final Exam Answers
When preparing for assessments focused on the human body, it is essential to have a solid grasp of the main concepts. These include understanding how the body’s systems work, the relationships between organs, and the fundamental processes that support life. This section offers a structured approach to reviewing key topics that often appear in evaluations, helping you ensure mastery of core material.
Key Systems to Focus On
Several systems are critical to human function, each with its own set of key concepts. The circulatory system, respiratory functions, and musculoskeletal mechanics are all integral to the body’s overall operation. Gaining a deep understanding of each system’s anatomy and roles prepares you for more complex questions.
| System | Key Concept | Critical Information |
|---|---|---|
| Circulatory | Blood flow and heart function | Understanding how oxygen and nutrients are delivered to tissues |
| Respiratory | Breathing process and gas exchange | Recognizing how oxygen is absorbed and carbon dioxide removed |
| Musculoskeletal | Bone structure and muscle movement | Understanding the role of joints, muscles, and bones in mobility |
Important Tips for Studying
To perform well on these assessments, active study techniques such as creating diagrams, summarizing key points, and practicing with sample questions are invaluable. This not only improves retention but also strengthens the ability to apply knowledge in practical scenarios. Focus on understanding mechanisms behind each function rather than just memorizing terms.
Key Topics for Semester 1 Exam
To excel in evaluations related to the study of the human body, it’s essential to focus on core concepts that encompass various systems and functions. Understanding how different parts of the body interact and support life is crucial. This section outlines the fundamental topics that are often central to assessments, ensuring comprehensive preparation for any challenge.
Essential Body Systems
The most important systems to understand include the circulatory, respiratory, and musculoskeletal systems. Mastering how these systems function individually and in coordination with others is key to answering questions accurately. A strong grasp of the underlying processes will enable you to tackle more complex topics effectively.
Cellular Function and Structure
Equally important is the understanding of cellular activities, tissue types, and the structural components that make up the body. Knowing how cells interact within organs and tissues to perform vital functions forms the foundation for more detailed questions about body processes. This knowledge also supports the ability to explain how the body adapts to internal and external changes.
Understanding Human Body Systems
To truly comprehend how the human body functions, one must explore the various systems that work in harmony to maintain life. Each system plays a crucial role in the overall health and well-being of an individual. Understanding the structure, function, and interconnections between these systems is essential for a deeper appreciation of human biology.
Major Systems in the Body
There are several key systems within the body that contribute to its complex operations. Each system has specific roles and components, but they all work together to ensure survival. Below are the primary systems you should focus on:
- Circulatory System: Transports blood, nutrients, gases, and wastes to and from the cells.
- Respiratory System: Facilitates the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide in the lungs.
- Musculoskeletal System: Provides structure, support, and enables movement.
- Nervous System: Controls and coordinates body activities, responding to internal and external stimuli.
- Digestive System: Breaks down food, absorbs nutrients, and eliminates waste.
- Endocrine System: Secretes hormones that regulate growth, metabolism, and other processes.
Interconnectivity Between Systems
Each system in the body does not operate in isolation. Instead, they are highly interdependent. For example, the respiratory system provides oxygen to the blood, which is then circulated by the cardiovascular system to various tissues. Similarly, the nervous system plays a role in regulating the functions of many of these systems. Understanding these interconnections is vital for answering complex questions about body functions.
- The circulatory and respiratory systems work together to deliver oxygen to tissues and remove carbon dioxide.
- The digestive and circulatory systems collaborate to provide essential nutrients to the body’s cells.
- The nervous and musculoskeletal systems are essential for movement and coordination.
Cell Structure and Function Review

The human body is composed of trillions of cells, each performing vital functions that contribute to overall health. Understanding the structure of cells and the roles of their various components is fundamental to grasping how tissues and organs operate. This section reviews key cellular structures and their functions, which are essential for maintaining life.
Key Components of a Cell
Each cell is made up of several components that work together to carry out necessary processes. Below are the main structures found in most cells:
- Cell Membrane: The outer layer that controls what enters and leaves the cell.
- Nucleus: The control center of the cell, containing genetic material (DNA) that directs cellular activities.
- Cytoplasm: The gel-like substance inside the cell that supports organelles and allows for chemical reactions.
- Mitochondria: Often referred to as the powerhouse of the cell, they generate energy in the form of ATP.
- Ribosomes: Responsible for protein synthesis, essential for cell growth and function.
- Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER): A network of membranes involved in the synthesis and transport of proteins and lipids.
- Golgi Apparatus: Processes and packages proteins and lipids for transport within or outside the cell.
- Lysosomes: Contain enzymes that break down waste materials and cellular debris.
Functions of Cellular Structures
Each part of the cell has a specific function that is essential to the survival of the organism. Below is a breakdown of how these components contribute to the cell’s overall function:
- Energy Production: Mitochondria produce ATP, which is the energy currency of the cell, allowing it to perform necessary functions.
- Protein Synthesis: Ribosomes create proteins that are essential for cell structure and function, while the endoplasmic reticulum aids in their transport.
- Waste Management: Lysosomes help to break down waste materials, preventing the buildup of harmful substances.
- Cellular Communication: The cell membrane’s selective permeability allows it to communicate with its environment, maintaining homeostasis.
Important Musculoskeletal System Concepts
The musculoskeletal system is essential for movement, support, and protection of the body’s internal structures. It is made up of bones, muscles, joints, and connective tissues, all of which work together to allow for mobility and provide structural integrity. Understanding the core concepts of this system is vital for anyone studying the functions of the human body.
Key Structures in the Musculoskeletal System

The musculoskeletal system consists of various components that serve distinct functions but work in tandem to support movement and stability. Below are the major structures to understand:
- Bones: Provide a rigid framework that supports the body, protects vital organs, and facilitates movement by serving as attachment points for muscles.
- Muscles: Responsible for generating force and facilitating movement through contraction and relaxation. There are three main types: skeletal, smooth, and cardiac.
- Joints: Areas where two or more bones meet, allowing for flexibility and movement. They can be classified as synovial, cartilaginous, or fibrous, depending on the degree of movement they allow.
- Tendons: Connect muscles to bones, transmitting the force generated by muscles to produce movement.
- Ligaments: Connect bones to other bones at joints, providing stability and preventing excessive movement.
Functions of the Musculoskeletal System

The musculoskeletal system not only supports the body but also enables a wide range of functions. Understanding these functions is crucial for a complete grasp of how this system contributes to overall health:
- Movement: Muscles contract to move bones at joints, enabling various actions such as walking, running, and lifting objects.
- Support: The skeleton provides a structural framework that supports the body’s weight and allows for upright posture.
- Protection: Bones, particularly those of the skull and ribcage, protect vital organs such as the brain, heart, and lungs.
- Mineral Storage: Bones store essential minerals like calcium and phosphorus, which can be released into the bloodstream when needed.
- Hematopoiesis: Bone marrow produces blood cells, playing a crucial role in immune function and oxygen transport.
Digestive System: Key Functions
The digestive system plays a vital role in breaking down food, absorbing nutrients, and eliminating waste. It involves a complex series of processes that work together to convert food into energy and vital building blocks for the body. Understanding these functions is crucial for comprehending how the body nourishes itself and maintains overall health.
Essential Processes in Digestion

The digestive system involves multiple stages to ensure food is broken down properly and nutrients are absorbed effectively. These processes include:
- Ingestion: The intake of food and liquids through the mouth, the first step in the digestive process.
- Mechanical Digestion: The physical breakdown of food, such as chewing and the churning action in the stomach, which helps to increase surface area for enzyme activity.
- Chemical Digestion: The use of enzymes and digestive fluids to break down food into simpler molecules that can be absorbed by the body.
- Absorption: Nutrients from digested food are absorbed into the bloodstream through the walls of the small intestine.
- Excretion: The removal of waste products and undigested materials from the body through defecation.
Organs Involved in Digestion
The digestive process is carried out by a series of organs that work together to ensure food is processed and nutrients are efficiently absorbed. Key organs include:
- Mouth: The entry point for food, where mechanical digestion begins with chewing and chemical digestion starts with saliva.
- Esophagus: A muscular tube that moves food from the mouth to the stomach through peristalsis (wave-like contractions).
- Stomach: A muscular organ that further breaks down food through mechanical churning and the secretion of digestive enzymes and acids.
- Small Intestine: The primary site for nutrient absorption, where digested food interacts with enzymes and bile to be absorbed into the bloodstream.
- Large Intestine: Absorbs water and electrolytes from undigested food, forming solid waste for elimination.
Cardiovascular System Breakdown
The cardiovascular system is crucial for transporting blood, oxygen, nutrients, and waste products throughout the body. It consists of the heart, blood vessels, and blood, all of which play a role in maintaining homeostasis and ensuring the proper function of all organs. Understanding how these components work together is essential for grasping the system’s overall function.
Major Components of the Cardiovascular System
The cardiovascular system is made up of several key elements that perform specific functions in circulation and nutrient exchange. Below is an overview of the main components:
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Heart | Pumps blood throughout the body, ensuring that oxygen, nutrients, and hormones are delivered to tissues, and waste products are removed. |
| Arteries | Carry oxygen-rich blood away from the heart to various parts of the body. |
| Veins | Return deoxygenated blood back to the heart from the body. |
| Capillaries | Tiny blood vessels that facilitate the exchange of oxygen, nutrients, and waste products between blood and tissues. |
Key Functions of the Cardiovascular System
This system is responsible for several vital functions, all of which contribute to the body’s overall well-being. The main functions include:
- Circulation: The heart pumps blood through the arteries to deliver oxygen and nutrients to cells, while veins return waste-laden blood to be processed and expelled.
- Temperature Regulation: Blood helps regulate body temperature by distributing heat throughout the body.
- Immune Response: Blood carries white blood cells that protect against infection, disease, and foreign invaders.
- Waste Removal: The cardiovascular system helps transport waste products to organs such as the kidneys for excretion.
Nervous System Exam Preparation
The nervous system is integral to controlling and coordinating all bodily functions. It manages everything from voluntary movements to involuntary processes such as breathing and heartbeat regulation. A solid understanding of this system is essential for mastering concepts related to how the body responds to internal and external stimuli. Proper preparation can help ensure a thorough grasp of the system’s structure, functions, and pathways.
Core Topics to Focus On

When preparing for assessments related to the nervous system, it’s important to focus on several key areas. These topics encompass the structure, function, and interactions of the system’s components:
| Topic | Focus Areas |
|---|---|
| Neurons | Understand the structure of neurons, including dendrites, axons, and synapses, and their role in transmitting electrical impulses. |
| Central Nervous System | Study the brain and spinal cord, focusing on their roles in processing and relaying information. |
| Peripheral Nervous System | Learn the functions of nerves outside the brain and spinal cord, including sensory and motor pathways. |
| Neurotransmitters | Know the chemical messengers used by neurons to communicate with each other across synapses. |
| Reflex Arcs | Review the process by which sensory information is converted into a rapid, automatic response. |
Study Techniques for Success
Effective study techniques can greatly enhance your understanding of the nervous system. Here are some strategies to consider:
- Active Recall: Test yourself regularly on key concepts to reinforce memory retention and understanding.
- Diagram Practice: Draw or label diagrams of neurons, the brain, and nervous pathways to better visualize structures and connections.
- Flashcards: Use flashcards to memorize important terms, functions, and processes related to the nervous system.
- Practice Questions: Solve practice questions to apply your knowledge and identify areas for further review.
Respiratory System Essentials
The respiratory system plays a vital role in ensuring that the body receives enough oxygen while removing carbon dioxide, a waste product of cellular processes. This system consists of various organs and structures that work together to facilitate gas exchange. A thorough understanding of how the system functions, from inhalation to exhalation, is essential for comprehending its role in maintaining homeostasis and overall health.
Key structures in the respiratory process include the lungs, airways, and diaphragm. These components work in unison to ensure the proper flow of air into the body and the expulsion of waste gases. Additionally, the regulation of breathing rate and depth is influenced by both internal and external factors, which help maintain balance in the body.
In addition to basic functions, the respiratory system also interacts with the circulatory system to deliver oxygen to tissues and organs throughout the body. This process of oxygen transport and carbon dioxide removal is critical for sustaining life, and any disruption in this system can lead to serious health complications.
Endocrine Glands and Their Roles
The body’s regulatory systems rely heavily on chemical signals to coordinate a wide range of processes. One such system is the group of glands responsible for producing hormones, which act as messengers to regulate metabolism, growth, mood, and many other bodily functions. These glands secrete their products directly into the bloodstream, enabling them to affect distant organs and tissues.
Each gland in the endocrine system has a specific function that contributes to maintaining balance in the body. The hormones they produce control vital processes, from energy production to reproductive health. Understanding the roles of these glands is essential for recognizing how they influence overall health and well-being.
Examples of key endocrine glands include the thyroid, adrenal glands, pituitary gland, and pancreas. Each one plays a critical role in regulating bodily functions through hormonal secretion, impacting everything from stress response to blood sugar levels.
Study Tips for Exam Success
Effective preparation is key to performing well in assessments. By adopting the right strategies and maintaining consistency in your study routine, you can improve retention and understanding of complex material. The right approach can make a significant difference in how well you recall information when needed and help you build confidence for the upcoming test.
Key Strategies for Success
There are several proven techniques that can enhance your ability to grasp difficult concepts and retain critical information. Incorporating these strategies into your study plan can help streamline your preparation:
- Active Learning: Engage with the material by taking notes, creating diagrams, or explaining concepts in your own words. This helps reinforce learning.
- Time Management: Break your study sessions into manageable chunks and set realistic goals. Spacing out your study time prevents burnout and improves focus.
- Practice Retrieval: Test yourself regularly with practice questions or flashcards. This active recall process strengthens your memory and helps identify weak areas.
- Group Study: Collaborate with classmates to discuss key topics. Group study sessions can provide different perspectives and fill in knowledge gaps.
Creating a Productive Environment
Your study environment can greatly impact your focus and productivity. To maximize your efficiency, consider the following tips:
- Choose a Quiet Space: Find a quiet, distraction-free area where you can concentrate fully on your work.
- Organize Materials: Keep all necessary study materials–books, notes, and other resources–easily accessible and organized to avoid wasting time looking for them.
- Take Regular Breaks: Short breaks between study sessions help refresh your mind and prevent fatigue. Use techniques like the Pomodoro method to stay focused.
Common Mistakes to Avoid in Exams
When preparing for assessments, it’s important to be aware of the common errors that can negatively impact your performance. Recognizing these mistakes early allows you to take proactive measures to avoid them and improve your chances of success. In this section, we’ll explore the most frequent pitfalls students encounter and provide tips on how to sidestep them.
Key Pitfalls to Watch Out For
Avoiding these typical mistakes will help you approach your studies with a more strategic mindset. By being mindful of these challenges, you can ensure that you are fully prepared and confident when the test day arrives:
- Rushing Through Questions: Taking your time to read each question thoroughly is essential. Avoid the temptation to rush through, as this can lead to misunderstandings or missed details.
- Neglecting to Review Instructions: Many students overlook the instructions for each section. Always read the instructions carefully to understand the expectations and avoid unnecessary mistakes.
- Not Managing Time Effectively: Poor time management can result in incomplete answers. Make sure to allocate sufficient time to each section and prioritize questions based on their weight or difficulty.
- Leaving Out Important Details: Be sure to provide clear, detailed responses. Omitting important information can cost valuable points, even if your answer is otherwise correct.
- Overlooking Review Opportunities: Take the time to review your answers before submitting. Often, you can catch small errors or realize that you’ve missed a critical point.
How to Minimize Mistakes
By staying organized and practicing good habits, you can avoid these common errors. Here are some additional tips to help minimize mistakes during your preparation and assessment:
- Practice Under Test Conditions: Simulate real test conditions when practicing to get comfortable with timing and managing pressure.
- Stay Calm and Focused: Anxiety can lead to careless errors. Practice mindfulness or breathing exercises to remain calm during the test.
- Seek Clarification When Necessary: If a question is unclear, don’t hesitate to ask for clarification. Ensuring you understand the task is vital to answering correctly.
Best Resources for Semester 1 Review
Preparing for the assessment at the end of the course requires careful planning and the use of the best study materials. Using the right resources can enhance your understanding and retention of key concepts, ensuring that you are well-equipped for the challenge ahead. In this section, we’ll explore some of the most effective tools and materials for comprehensive review.
Top Study Guides and Textbooks
When reviewing complex topics, having the right textbooks and study guides is essential. These resources provide detailed explanations, practice problems, and visual aids that will help reinforce your knowledge:
- Comprehensive Textbooks: Choose textbooks that cover all major systems and processes in detail. They should provide clear explanations, diagrams, and summaries of key concepts.
- Review Books: Specialized review books are designed for quick study and summarizing important information. These can be especially helpful for revising before the assessment.
- Online Practice Questions: Many websites and platforms offer practice questions and mock quizzes that simulate the test experience. Practicing with these tools can help you familiarize yourself with the format and the types of questions you may encounter.
Supplementary Digital Tools
In today’s digital age, there are plenty of online resources that can provide interactive learning experiences. These tools offer flexibility and engage students through multimedia and interactive features:
- Educational Websites: Websites like Khan Academy or Quizlet offer free lessons, flashcards, and quizzes that cover various topics in depth. They provide an engaging way to study, especially for visual learners.
- Video Tutorials: Platforms like YouTube or Coursera have video tutorials that break down complex subjects into digestible lessons, which can be especially useful for reinforcing difficult concepts.
- Interactive Apps: Apps designed for student review, such as Anki or Brainscape, use spaced repetition and active recall to help improve memory retention and test readiness.
Using a combination of these resources will not only deepen your understanding but also allow you to engage with the material from different angles, improving both comprehension and recall when it matters most.
Physiology of Human Tissues Explained
The human body is composed of a variety of tissues, each serving a unique function that is essential for maintaining overall health and stability. Understanding how these tissues work together to perform vital tasks provides insight into the complexity of the body’s functions. In this section, we will explore the different types of tissues and how they contribute to bodily processes.
Types of Tissues and Their Functions
The human body contains four primary types of tissue, each with specific roles in the functioning of organs and systems. Below is a breakdown of each type and its general purpose:
- Epithelial Tissue: This type of tissue forms protective layers that line the surfaces of organs, blood vessels, and cavities. It also plays a key role in absorption, secretion, and sensation.
- Connective Tissue: This tissue provides structural support and binds other tissues together. It includes a wide range of tissues, such as bone, cartilage, blood, and lymph, each having specialized functions.
- Muscle Tissue: Composed of cells capable of contraction, muscle tissue is responsible for movement. It can be categorized into skeletal, smooth, and cardiac muscle, each contributing to different bodily movements and functions.
- Nervous Tissue: Nervous tissue is involved in communication and control throughout the body. It consists of neurons and supporting cells, facilitating the transmission of electrical impulses and coordinating responses.
How Tissues Work Together
While each tissue type has a specific role, they often work together to support larger functions in the body. For instance, epithelial and connective tissues collaborate to form organs like the skin, while muscle and nervous tissues coordinate movement and response. This dynamic interrelationship allows the body to carry out complex tasks efficiently.
Understanding the physiology of human tissues provides a foundation for recognizing how disruptions in one type of tissue can affect the entire body. It emphasizes the importance of maintaining tissue health to ensure the proper functioning of all systems within the body.
Review of Human Development Stages
Human growth is a continuous process that begins at conception and progresses through various stages of life. Each phase is marked by significant physical, cognitive, and emotional changes. Understanding these stages helps to clarify how humans evolve from infancy to adulthood, highlighting the milestones and challenges encountered along the way.
The developmental process is often divided into specific periods that correspond to key transitions in a person’s life. These stages are not just defined by age but by the different biological and psychological developments that occur. Below is a breakdown of these stages and their main characteristics.
- Infancy: The first stage of life, from birth to around two years, is characterized by rapid physical growth, sensory development, and the beginning of motor skills. Infants also start forming basic emotional and social bonds.
- Early Childhood: This stage, from two to six years, is marked by continued growth in motor skills, language acquisition, and early cognitive development. Children also begin to develop a sense of independence and social awareness.
- Middle Childhood: Spanning ages six to twelve, this period focuses on the refinement of skills, both physical and mental. Cognitive abilities like memory, problem-solving, and logical thinking advance significantly, along with social relationships.
- Adolescence: Occurring from approximately twelve to eighteen years, adolescence is a time of significant physical, emotional, and sexual development. This stage is often defined by the search for identity, independence, and deeper peer relationships.
- Adulthood: After eighteen years, individuals enter adulthood, which can be broken into early, middle, and late adulthood. Early adulthood focuses on career and relationship-building, while middle adulthood deals with reflection on life achievements and potential changes. Late adulthood is marked by the reflection on one’s legacy and physical aging.
Each of these stages plays an essential role in shaping a person’s life. Understanding human development offers a comprehensive view of how people grow and adapt over time, with each phase contributing to the broader context of the human experience.
Exam Strategies for Anatomy Questions
When preparing for assessments involving the study of the body’s structures, it’s crucial to approach the material methodically. A comprehensive understanding of body systems, organs, and their interconnections can be overwhelming without a clear strategy. This section provides effective methods to tackle questions related to the body’s structural components, ensuring you’re well-equipped to recall information quickly and accurately during the test.
The key to success lies in active learning and organizing knowledge in a way that makes it easy to retrieve under pressure. By using a combination of memory techniques, visualization, and practice questions, you can enhance your ability to recall detailed information when needed.
Effective Study Techniques
- Active Recall: Instead of passively reviewing notes, test yourself on what you can remember. This method strengthens neural pathways related to the material, improving long-term retention.
- Visualization: Associate structures with their locations or functions. Creating mental images of organs, tissues, and systems can significantly enhance your ability to recall details.
- Practice with Diagrams: Many questions involve labeling diagrams or identifying structures. Practicing with blank diagrams can help you become familiar with the visual aspects of body systems.
Test-Taking Tips

- Read Questions Carefully: Ensure you understand exactly what the question is asking. Some questions may test detailed knowledge, while others may focus on broader concepts.
- Focus on Key Structures: For questions that involve the location or function of specific body parts, concentrate on major systems, organs, or regions that are frequently covered.
- Eliminate Wrong Answers: If you’re unsure of an answer, rule out the most unlikely choices first. This increases your chances of selecting the correct response.
By applying these techniques and strategies, you can approach questions with confidence, ensuring that you’re prepared to recall critical details efficiently and accurately during the assessment.