
Understanding the factors that influence property markets is essential for anyone looking to navigate the complexities of the housing sector. This section delves into the key variables that shape market behaviors, focusing on how shifts in demand, supply, and external forces affect property values and investment strategies.
The local landscape is constantly changing, influenced by a variety of elements ranging from interest rates to shifts in consumer preferences. By analyzing these fluctuations, we can gain a deeper understanding of what drives decisions in the market and how they impact long-term profitability.
In addition to internal factors, external forces like government regulations and broader financial systems play a crucial role in steering market movements. Grasping these connections can provide valuable insights for anyone preparing to make informed decisions in the property field.
Shifting Patterns in the Property Market
The performance of the housing sector is deeply connected to various forces that continually shape its landscape. From governmental policy changes to shifts in consumer behavior, the movement of this market depends on a complex interplay of factors that influence both buyers and sellers alike. Understanding these shifts is crucial for grasping how property values fluctuate and how investors can strategically position themselves.
Key influences such as the cost of borrowing, population dynamics, and employment rates all play significant roles in determining the health of the market. These elements impact purchasing decisions, availability of housing, and investment opportunities across regions. Tracking how these factors evolve provides critical insights into future movements in the property world.
Additionally, market cycles–whether booming or declining–are often reflective of broader economic conditions. Understanding the phases of these cycles can be vital for predicting when to enter or exit the market, making it essential for those studying the property sector to stay informed about current conditions and anticipated shifts.
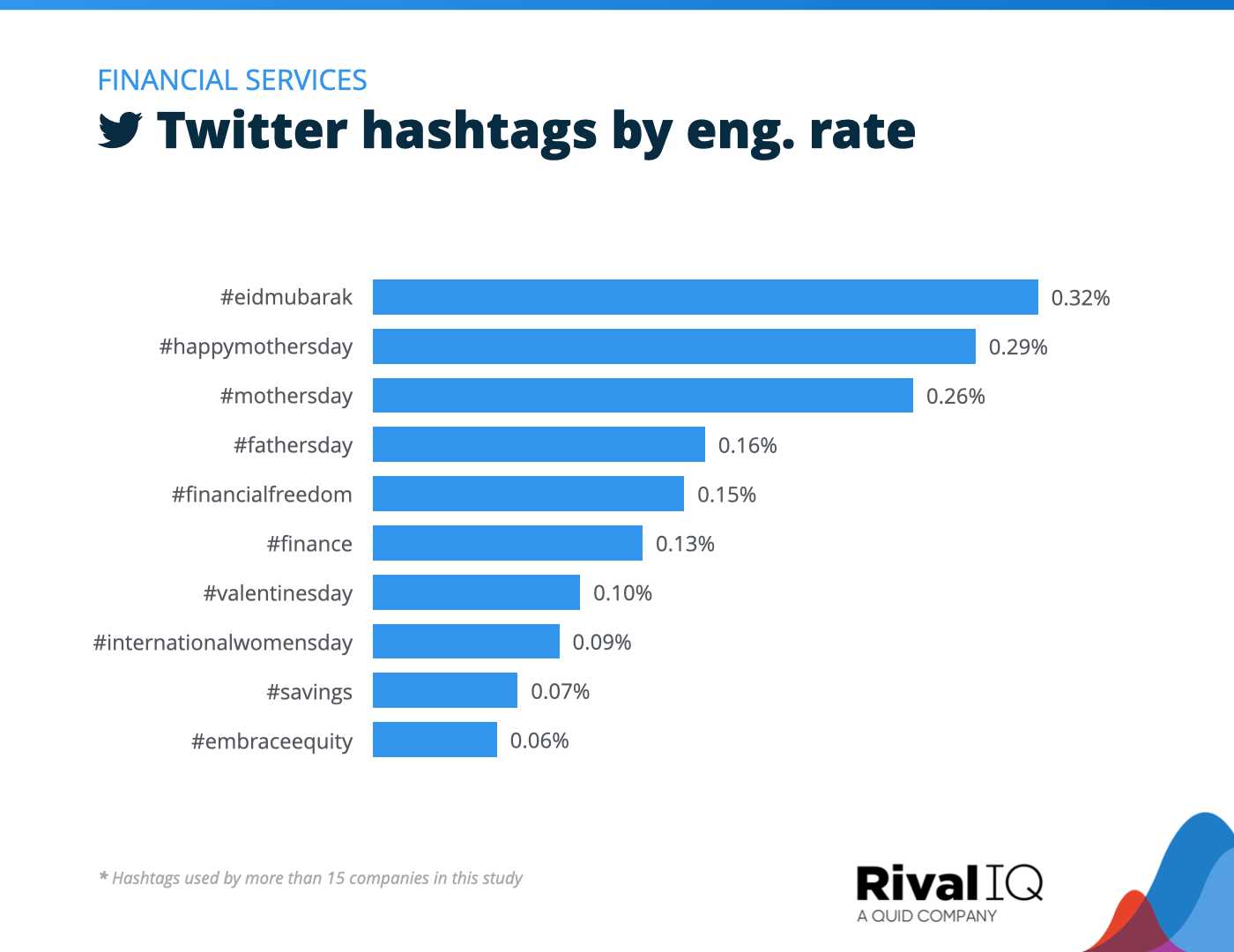
Understanding California’s Housing Market Fluctuations
The housing market in many regions, especially within larger metropolitan areas, experiences constant fluctuations influenced by a range of factors. These shifts often reflect changing demands, adjustments in the supply of properties, and external pressures such as interest rates or employment trends. Grasping these variations is key to predicting market behavior and making informed decisions.
Several core elements contribute to the ups and downs of the market, from shifts in consumer purchasing power to the introduction of new housing policies. Additionally, natural events such as population growth or migration patterns can heavily influence demand, further driving these market cycles.
| Factor | Effect on Housing Market |
|---|---|
| Interest Rates | Higher rates can reduce affordability, leading to decreased demand, while lower rates typically stimulate buying activity. |
| Population Growth | Increases demand for housing, particularly in urban centers, which can lead to price hikes. |
| Government Policies | Regulations such as rent control or tax incentives can impact both property values and availability of homes. |
| Employment Rates | A healthy job market boosts confidence and demand for housing, while high unemployment can depress activity. |
Understanding these factors and how they interconnect can provide valuable insight into market shifts, allowing participants to make better choices when entering or exiting the housing market. Knowledge of these elements is essential for anyone seeking to understand or navigate the ever-changing dynamics of housing markets.
Impact of Interest Rates on Property Values
The cost of borrowing money is a major factor influencing the housing sector. Fluctuations in interest rates can directly affect how affordable homes are for potential buyers, which in turn influences property values. When borrowing becomes more expensive, the demand for housing tends to decrease, putting downward pressure on prices. Conversely, when borrowing costs are lower, demand often increases, driving prices up.
How Interest Rates Affect Buyer Behavior
Interest rates primarily impact buyers’ ability to finance property purchases. When rates are high, monthly mortgage payments increase, making it more difficult for buyers to afford homes. This reduced purchasing power leads to lower demand and may cause a dip in property prices. On the other hand, when rates decrease, buyers can secure lower monthly payments, often resulting in increased demand and higher property values.
Long-Term Effects on the Market
While short-term changes in interest rates can cause immediate shifts in the market, long-term trends tend to have a more sustained impact on property values. Over time, sustained low or high rates can either stabilize or destabilize the market, influencing both property prices and investment strategies. Understanding these patterns is essential for making informed decisions in the property sector.
| Interest Rate Environment | Effect on Housing Market |
|---|---|
| High Rates | Decreased affordability leads to lower demand, putting downward pressure on property values. |
| Low Rates | Increased affordability stimulates higher demand, driving property prices upwards. |
| Stable Rates | Provides consistency in the market, allowing property values to stabilize and increase gradually. |
The relationship between interest rates and property values is a crucial aspect to understand for anyone involved in the housing sector, whether as a buyer, seller, or investor. Monitoring interest rate movements allows participants to anticipate market shifts and make more strategic decisions.
Role of Employment Growth in Property Markets
The growth of job opportunities in a region plays a crucial role in shaping housing demand and, consequently, property values. As employment levels rise, more people are able to afford homes, leading to greater competition in the market. This increased demand can drive up property prices, benefiting both sellers and investors. Conversely, when employment opportunities decrease, housing demand tends to fall, which can lead to price stabilization or declines.
In areas with high job growth, people are more likely to relocate in search of new opportunities. This influx of workers increases the need for both rental properties and homes for sale. Additionally, as more individuals find stable employment, their purchasing power grows, making it easier for them to secure financing for home purchases.
Strong job markets also contribute to overall economic stability, which can make a region more attractive for investment. Areas with consistently low unemployment rates tend to experience more stable property values, as people are less likely to face financial hardships that might force them to sell their homes. In contrast, regions suffering from high unemployment often see more volatile property markets.
Impact of Employment Growth on Housing Demand:
As more jobs are created, housing demand increases, leading to potential price increases in surrounding areas.
Employment growth not only drives demand for housing but also influences the types of properties that are in demand. In regions where high-paying jobs are prevalent, luxury homes or larger properties may see a rise in interest. In contrast, areas with a focus on lower-wage employment may see more demand for affordable housing or rental units.
Analyzing Supply and Demand in Property Markets
The balance between the availability of homes and the desire of buyers plays a central role in determining property prices and overall market stability. When supply exceeds demand, prices tend to decrease, as sellers compete to attract buyers. Conversely, when demand outstrips supply, competition increases, often driving prices up. Understanding this dynamic is essential for those involved in property transactions, whether for investment or personal purchase.
The key to analyzing this balance lies in closely monitoring changes in both the number of available properties and the factors influencing buyer behavior. Shifts in population, economic conditions, and consumer preferences all contribute to variations in demand, while changes in construction activity, land availability, and zoning regulations influence the supply side of the market.
| Market Condition | Effect on Property Prices |
|---|---|
| High Demand, Low Supply | Prices rise due to increased competition among buyers for fewer properties. |
| Low Demand, High Supply | Prices fall as sellers reduce their asking prices to attract buyers. |
| Balanced Supply and Demand | Prices stabilize, leading to a more predictable and steady market. |
In regions where growth is rapid or there are shifts in demographics, demand can surge quickly, outpacing the rate at which new properties are built. This can lead to higher prices and, in some cases, housing shortages. Conversely, oversupply–often due to overconstruction or changes in economic conditions–can result in price declines and increased competition among sellers.
Real Estate Investment Patterns in California
Investment patterns in the housing sector often reflect broader shifts in both local and national markets. By examining the patterns in property investment, we can understand the strategies and decisions that influence both short-term and long-term gains. These patterns are driven by a combination of factors, including market sentiment, financing conditions, and investor expectations about future growth in property values.
In many regions, investors focus on particular types of properties, such as residential, commercial, or mixed-use developments. In times of economic expansion, there is typically a greater focus on acquiring higher-value properties or new developments, while during periods of uncertainty, more conservative approaches may dominate. The location of these investments also plays a critical role, as urban centers often attract more attention due to their higher demand and potential for growth.
The behavior of individual investors also differs from institutional players, with the former often seeking rental income or capital appreciation, while large firms might focus on larger-scale projects, seeking diversified portfolios across regions. These distinctions contribute to the overall dynamics of the market, shaping the flow of capital and the construction of new properties.
Regional Economic Differences Across California
The economic landscape within a state can vary greatly between regions, influencing everything from property demand to investment strategies. These variations are driven by factors such as industry presence, demographic trends, and local policies. Understanding the distinct characteristics of each region is vital for anyone navigating the housing market, as what works in one area may not necessarily apply to another.
In some regions, a focus on high-tech industries and innovation drives rapid growth and increases demand for both commercial and residential properties. In others, agricultural sectors or tourism play a more prominent role in shaping the local economy, with unique implications for housing prices and development patterns. These regional differences are key in understanding how markets function and the best opportunities for investment.
Below are some of the major regional distinctions across the state:
- Urban Centers: Major cities like Los Angeles and San Francisco are characterized by a fast-paced economy, high cost of living, and a demand for luxury housing and office spaces.
- Technology Hubs: Regions like Silicon Valley and the surrounding Bay Area are heavily influenced by the tech sector, with a focus on high-paying jobs and the demand for upscale properties.
- Agricultural Areas: Central California’s agricultural economy tends to have lower property prices, with investment opportunities often centered around farmland or agricultural operations.
- Coastal Regions: Coastal communities often attract high demand due to their desirable locations, driving up property values in areas such as San Diego and Santa Barbara.
- Mountain and Desert Areas: Areas like Palm Springs and Lake Tahoe experience fluctuations in demand due to seasonal factors and tourism-driven economies.
These variations highlight the importance of considering regional nuances when making property decisions, whether buying, selling, or investing. Each area’s unique economic foundation shapes the market in different ways, and recognizing these differences can be the key to success in property transactions.
Government Policies Affecting Property Markets
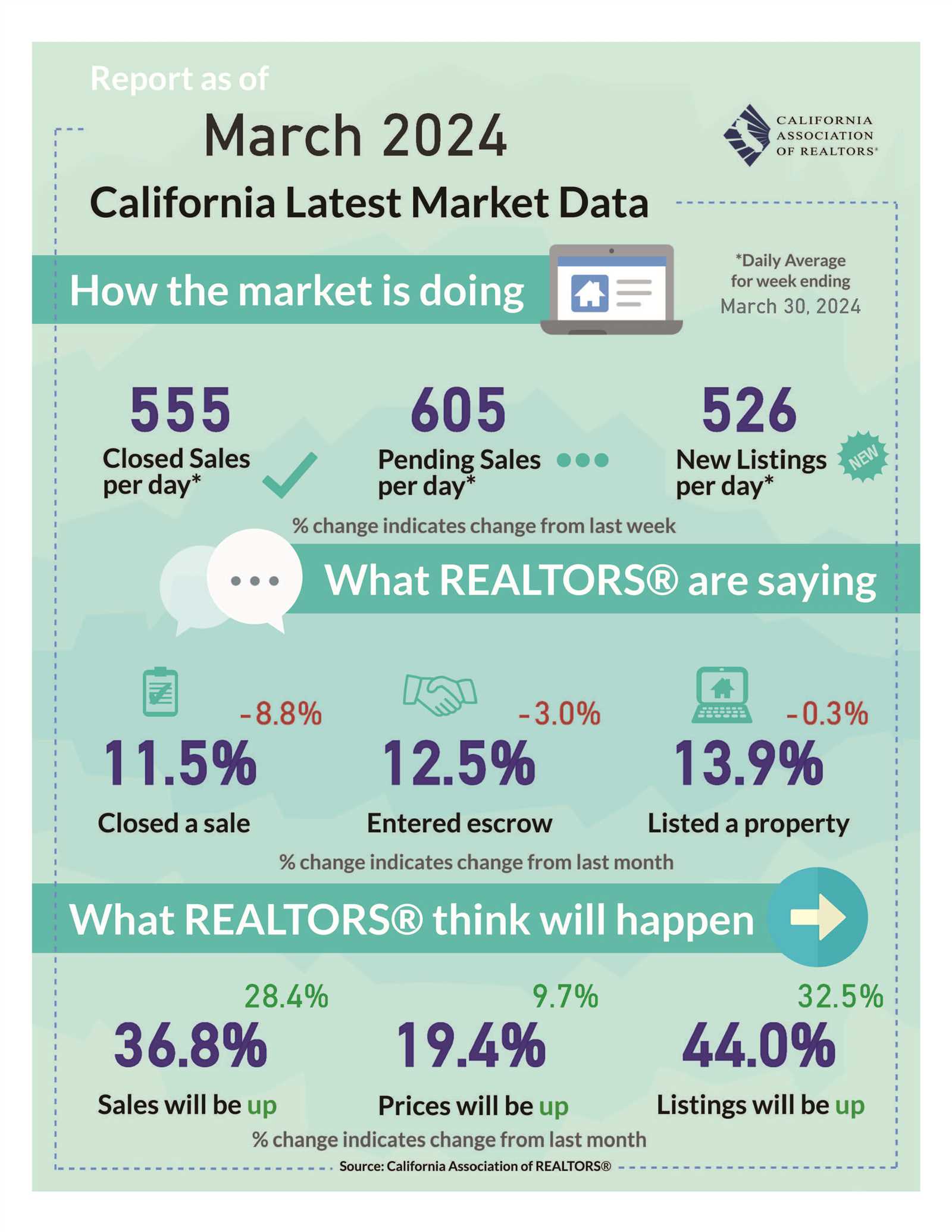
Government regulations and policies play a pivotal role in shaping the dynamics of the housing market. These policies influence everything from construction practices to affordability and market access. By implementing zoning laws, tax incentives, and interest rate adjustments, authorities can either stimulate or slow down demand for properties, affecting both buyers and investors.
Local, state, and federal policies can have significant effects on property values. For instance, the introduction of rent control measures may limit rental prices, which can influence investor interest in residential properties. On the other hand, policies that incentivize development or offer tax breaks for first-time buyers can boost demand and drive market growth.
Some key areas where government intervention impacts the property sector include:
- Zoning and Land Use Regulations: These rules determine where and how properties can be developed, directly impacting the availability of land for housing and commercial projects.
- Tax Incentives and Credits: Government-issued tax breaks for homebuyers or developers can encourage investment in specific markets, stimulating both demand and supply.
- Rent Control and Tenant Protection Laws: These policies aim to provide stability in rental markets by regulating how much landlords can charge, which can affect the profitability of rental properties.
- Interest Rate Policies: Central banks adjust interest rates to manage inflation and economic growth, which directly impacts mortgage affordability and overall demand for properties.
- Affordable Housing Programs: Initiatives to support the construction of affordable housing influence the accessibility of properties for low- to moderate-income individuals and families.
In conclusion, government policies are a powerful tool that can either stimulate or restrict property market activity. Investors and homebuyers alike must stay informed of the latest regulations and understand how these policies can impact their decisions in the housing sector.
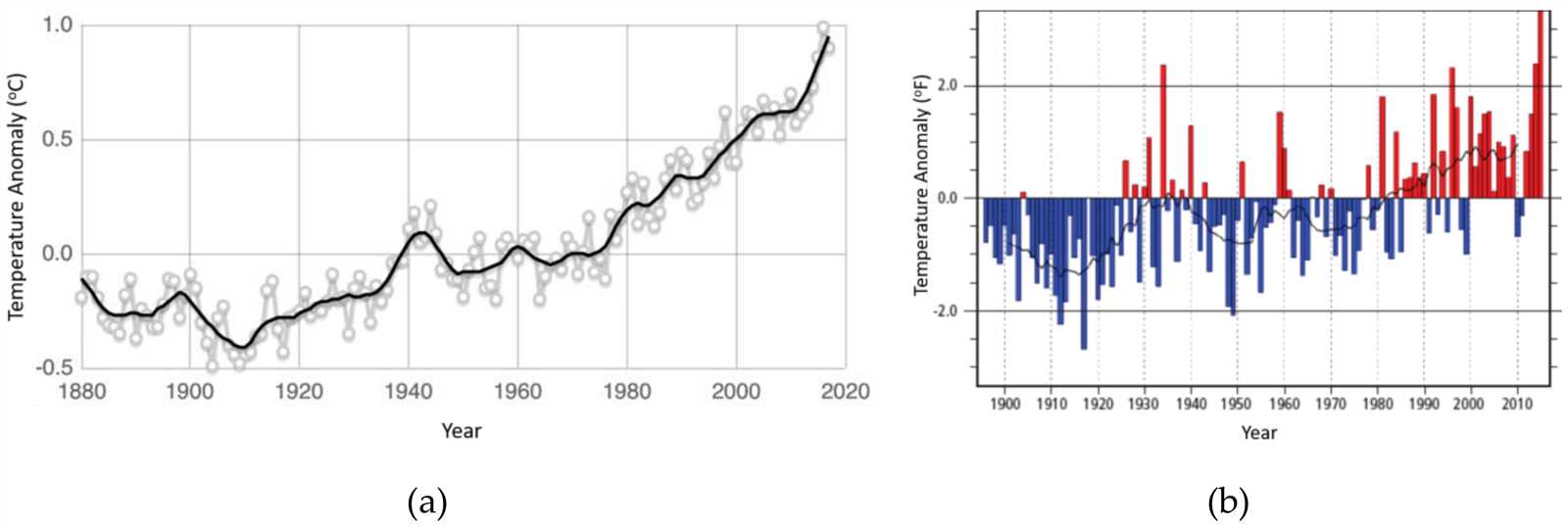
How Inflation Shapes Real Estate Decisions
Inflation is a key factor that can dramatically influence decisions within the property market. As prices for goods and services rise, the cost of owning, buying, and renting properties can also increase. This can alter buyer and investor behavior, leading to shifts in demand, financing options, and overall market activity.
When inflation is high, purchasing power decreases, making it more expensive to acquire property. For many potential homeowners or investors, this may lead to hesitation, causing them to delay purchases or seek more affordable options. On the other hand, inflation can sometimes drive people to invest in property as a hedge against rising costs, believing that property values will appreciate over time.
The Impact on Financing and Interest Rates
As inflation rises, central banks often respond by increasing interest rates to control inflationary pressures. Higher interest rates make borrowing more expensive, which can dampen demand for property, as higher monthly mortgage payments may become unaffordable for many buyers. This can lead to a slowdown in sales and a reduction in property prices, particularly in markets that rely heavily on financing.
Investor Behavior and Property Values
Inflation can also affect investor strategies. With increasing prices and costs, many investors view property as a safe investment that will retain its value or even appreciate over time. However, those who rely on rental income may face higher operational costs, including maintenance and taxes, which can affect profitability. As a result, some may choose to divest from certain sectors or adjust rental rates to cover the rising expenses.
In conclusion, inflation has a profound effect on property decisions. Whether buying, selling, or investing, understanding its influence on costs, financing, and overall market conditions is crucial for navigating the property landscape effectively.
Analyzing Market Cycles and Timing
Understanding the natural cycles that occur within property markets is essential for making informed decisions. These cycles typically move through phases of expansion, peak, contraction, and recovery, each presenting different opportunities and risks for buyers, sellers, and investors. Recognizing the current phase of the market can help individuals optimize the timing of their transactions, whether they are looking to purchase, sell, or invest.
During periods of expansion, demand increases, leading to higher prices and more competition among buyers. This is typically a good time for sellers to take advantage of rising property values. Conversely, in a contraction phase, the market cools, with prices stabilizing or declining, which may favor buyers looking for more affordable options.
Timing the market accurately can be challenging, as external factors such as interest rates, economic policies, and broader market sentiment can all influence the length and intensity of each cycle. However, by closely monitoring these shifts, market participants can position themselves to take advantage of favorable conditions and avoid making decisions during less favorable times.
Foreign Investment and Its Market Impact
International investors play a significant role in shaping property markets across various regions. Their participation can bring both positive and negative effects, depending on the scale of investment and the focus of the capital influx. Foreign capital often targets high-demand areas, leading to increased property values, which can impact local buyers and market dynamics.
When foreign investors enter the market, they typically invest in prime locations, driving up prices and increasing competition. This can create challenges for domestic buyers, especially those in lower price ranges, who may find it more difficult to secure property. At the same time, the influx of investment can also stimulate the construction sector, creating jobs and potentially boosting the local economy.
Positive Market Impacts

There are several benefits that come with foreign investment, including increased liquidity and diversification of the market. The capital provided by international buyers can help fund new developments, infrastructure projects, and renovations, which can improve the overall property landscape.
Challenges and Potential Risks
However, excessive foreign investment can lead to affordability issues, especially in highly desirable cities. When foreign capital outpaces local purchasing power, it can exacerbate housing shortages and drive prices beyond the reach of many residents.
| Impact | Positive Effect | Negative Effect |
|---|---|---|
| Property Prices | Increase in property values in prime locations | Potential for inflated prices and decreased affordability |
| Market Liquidity | Increased market activity and opportunities for sellers | Potential market instability due to foreign demand shifts |
| Construction and Jobs | Growth in new development projects and employment | Potential over-reliance on foreign capital for growth |
In conclusion, foreign investment can have a profound impact on the local property market. While it can bring significant benefits, it is crucial to balance this capital influx with policies that protect local buyers and ensure a stable, accessible market for all participants.
Technological Advancements in Real Estate
In recent years, the property market has been greatly influenced by innovations in technology. These developments have reshaped how transactions are conducted, how properties are marketed, and even how buyers and sellers interact. Technology has made it easier to access information, streamline processes, and enhance decision-making, leading to more efficient and transparent practices within the industry.
From virtual tours to automated valuation models, technological tools have transformed the way both professionals and consumers approach property decisions. Buyers can now explore listings from anywhere in the world, while sellers benefit from improved marketing strategies and enhanced property exposure. Technology is also aiding in the development of smarter cities, with advanced infrastructure and data-driven planning techniques.
Key Technological Tools in Property Transactions
- Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR): These tools allow potential buyers to take virtual tours of properties, offering an immersive experience without needing to visit in person.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI is used to predict market trends, assist in property valuation, and recommend properties based on a user’s preferences.
- Blockchain: This technology is revolutionizing property transactions by providing secure, transparent, and efficient ways to complete contracts and transfers.
- Big Data and Analytics: With large-scale data analysis, investors and developers can make more informed decisions about where to build, what types of properties to develop, and how to price them.
The Future of Property Technology
The future of the property market is increasingly intertwined with technological advancements. As artificial intelligence continues to improve, we can expect even more personalized experiences for buyers and sellers. Moreover, the use of smart technologies in properties, such as energy-efficient systems and automated home controls, is likely to grow, making homes more sustainable and desirable.
In conclusion, technological innovations are rapidly changing the landscape of the property industry. Those who embrace these advancements are likely to stay ahead of the curve and capitalize on new opportunities that emerge within the sector.
Environmental Changes and Property Values
Environmental factors play a significant role in shaping the demand and value of properties. As climate conditions change and sustainability becomes a larger focus, the long-term viability of certain locations and property types is being reevaluated. Natural events, such as floods, droughts, and wildfires, alongside shifts in governmental policies related to environmental protection, are influencing real estate decisions in profound ways.
In recent years, property buyers and investors have become more conscious of environmental risks, which have led to a growing interest in sustainable homes and eco-friendly buildings. These changes in environmental awareness are affecting both residential and commercial markets, influencing everything from construction standards to property valuations.
Key Environmental Factors Affecting Property Values
- Climate Risks: Increased risks from flooding, hurricanes, wildfires, and other natural disasters are making certain areas less desirable and can negatively impact property values.
- Energy Efficiency: Properties with energy-saving features, such as solar panels and high-efficiency heating and cooling systems, are becoming more valuable as buyers seek ways to reduce their environmental footprint.
- Air and Water Quality: Areas with poor air or water quality may see a decrease in property demand, as buyers look for healthier living environments.
- Government Regulations: Local and regional policies designed to mitigate environmental impacts, such as zoning restrictions or green building incentives, can have a significant effect on property development and valuation.
Impact of Sustainable Design on Property Values
Buildings and homes that integrate sustainable design elements are often valued higher, as buyers increasingly look for properties that align with their values on environmental conservation. The demand for green buildings, whether residential or commercial, is expected to continue growing as sustainability becomes more integrated into urban planning and real estate development.
In conclusion, as environmental concerns rise, both buyers and sellers must carefully consider how environmental factors impact property values. From reducing carbon footprints to managing climate risks, the role of sustainability in the real estate market will only expand in the years to come.
Tax Implications on Real Estate Transactions
The impact of taxation on property transactions is a critical consideration for buyers, sellers, and investors alike. Various tax policies affect the profitability and overall cost of purchasing, owning, and selling property. Whether it’s capital gains taxes, property taxes, or deductions available for property-related expenses, these factors can significantly influence decision-making in the market.
Taxes not only determine the net returns on investment but also shape the demand and supply of properties. The structure of tax laws, which can differ depending on location, plays a crucial role in the financial viability of real estate transactions. For instance, changes in property tax rates or the introduction of tax incentives for sustainable developments can create favorable conditions for both buyers and developers.
Key Taxes Affecting Property Transactions
- Capital Gains Tax: When a property is sold for more than its purchase price, the profit is typically subject to capital gains tax. The tax rate can vary based on how long the property was held and the individual’s tax bracket.
- Property Taxes: Property taxes are recurring costs based on the assessed value of the property. These taxes are often a significant consideration for both property owners and potential buyers, as they can affect the affordability of ownership.
- Transfer Taxes: Transfer taxes are imposed when a property changes ownership. These taxes can add an additional layer of cost to the transaction and vary by jurisdiction.
- Tax Deductions for Homeowners: Homeowners may be eligible for tax deductions on mortgage interest, property taxes, and certain home improvements, which can influence purchasing decisions.
Tax Strategies for Real Estate Investors
For investors, understanding the tax implications of various strategies is essential for maximizing returns. The ability to leverage tax deductions, such as depreciation on rental properties, or take advantage of 1031 exchanges to defer capital gains taxes, can substantially improve profitability in the long term. Careful tax planning is necessary to optimize the financial outcomes of real estate investments.
In conclusion, tax considerations are a vital component of real estate transactions and investments. Buyers and sellers must remain informed about local tax laws and incentives to make informed financial decisions and navigate the complexities of the market.
The Role of Mortgages in Market Trends
Mortgages are a key factor in shaping the dynamics of the property market. They provide buyers with the means to purchase properties without requiring full upfront payment, which, in turn, influences both demand and pricing patterns. The availability and terms of mortgage loans can significantly affect market movement, as changes in lending policies, interest rates, or borrower qualifications can either stimulate or suppress buyer activity.
The cost of borrowing, especially in relation to interest rates, plays a central role in determining housing affordability. When interest rates are low, mortgages become more accessible, leading to increased demand for properties. Conversely, higher rates can make borrowing more expensive, cooling the market and potentially leading to price corrections. Understanding how mortgage conditions impact market behavior is essential for both investors and homebuyers.
Impact of Interest Rates on Mortgage Affordability
Interest rates directly influence how much buyers can afford to borrow. As these rates fluctuate, they can shift the balance of purchasing power within the market. When rates are low, monthly mortgage payments are generally lower, allowing buyers to afford more expensive homes. On the other hand, rising rates increase monthly payments, which can limit buyers’ ability to enter the market or afford higher-priced properties.
- Lower Rates: Reduced borrowing costs encourage more people to take out mortgages, stimulating demand in the housing market.
- Higher Rates: Increased mortgage payments can reduce buyer interest, particularly among first-time buyers or those with less disposable income.
The Impact of Lending Standards on Buyer Behavior
Lending standards, such as credit score requirements and down payment ratios, also shape the landscape of the property market. Stricter lending standards can make it more difficult for individuals to secure mortgages, reducing the pool of potential buyers. Conversely, more relaxed lending practices can increase demand by allowing a wider range of people to qualify for loans.
- Strict Lending Practices: When banks impose higher credit score or down payment requirements, fewer people qualify for mortgages, leading to a slowdown in sales and potentially lower home prices.
- Relaxed Lending Standards: Easier access to credit encourages more buyers to enter the market, which can drive up property demand and increase prices.
In conclusion, mortgages are a crucial element in shaping property market conditions. By influencing purchasing power, affordability, and overall demand, the availability and terms of mortgage loans have a direct impact on market movement and pricing strategies.
Population Growth and Housing Demand
As the number of people in a region increases, the need for suitable housing rises correspondingly. A growing population drives up demand for residential properties, putting pressure on both the availability and pricing of homes. This dynamic is often seen in areas experiencing rapid demographic expansion, where the influx of new residents leads to higher competition for available properties and a shift in market conditions.
Population growth can stem from various factors, including migration from other regions, higher birth rates, or increased life expectancy. Regardless of the source, an expanding population requires an adequate supply of housing to accommodate the increased demand. Failure to meet this need can result in rising property values, especially in densely populated urban centers.
Impact of Migration on Housing Needs
Migration patterns, both within and between countries, play a significant role in shaping housing demand. As more people move to specific areas in search of better job opportunities, lifestyle changes, or lower living costs, the local housing market can experience rapid shifts in demand.
- Increased Influx: A surge in population due to migration can lead to overcrowding and increased competition for available homes, driving up prices.
- Outward Migration: When residents move away from a particular area, it may result in decreased demand for housing, which could cause property values to stabilize or decline.
The Role of Urbanization in Housing Markets
Urbanization is another significant factor influencing housing demand. As more individuals move into city centers, the need for both housing units and infrastructure grows. With limited space available in highly urbanized areas, housing prices can increase, leading to challenges in affordability for new residents. In turn, this can push some buyers to seek housing in suburban or rural areas, further driving growth and changes in demand patterns.
- Urban Growth: As cities expand, developers and investors often focus on creating high-density housing to meet the demand, which may increase property values in those areas.
- Suburban Shift: In response to high city prices, more people may choose to live in suburban areas, leading to greater demand for homes outside of metropolitan centers.
Ultimately, the relationship between population growth and housing demand is a fundamental factor that shapes property markets. As population sizes fluctuate, so too does the need for appropriate living spaces, which in turn influences market dynamics and price points.
Market Trends in Commercial Real Estate
The landscape of commercial property is constantly evolving, driven by factors such as shifting business needs, technological advancements, and changes in consumer behavior. As industries grow and adapt, the demand for office spaces, retail locations, and industrial facilities fluctuates, creating unique opportunities and challenges for investors, developers, and tenants alike. Understanding the forces shaping the commercial property market is key to making informed decisions in this dynamic environment.
Shifts in Office Space Demand
The rise of remote work, along with changing preferences for flexible office environments, has had a profound impact on the demand for traditional office spaces. Many companies are rethinking their office requirements, with some downsizing their physical footprints while others adopt hybrid models that combine in-person and virtual workforces. As a result, certain markets are seeing a decline in demand for large, long-term office leases, while others are benefiting from the need for smaller, flexible workspaces.
- Reduced Need for Traditional Offices: Businesses are increasingly adopting remote work policies, leading to fewer tenants seeking large office buildings.
- Rise in Flexible Spaces: The demand for co-working spaces and flexible office leases is on the rise as businesses prioritize agility and cost-efficiency.
The Shift in Retail Locations
The retail sector has experienced significant disruption due to the growth of e-commerce, changing consumer habits, and the shift to online shopping. Physical retail locations are increasingly being reimagined to meet new consumer expectations. In some cases, retail properties are being repurposed for different uses, such as fulfillment centers or experiential spaces that offer unique customer experiences beyond traditional shopping.
- Decline in Traditional Retail Leases: As online shopping continues to grow, the demand for large, traditional retail stores has decreased in many markets.
- Experiential Retail: Some retail locations are evolving into spaces that offer entertainment, dining, or interactive experiences, rather than focusing solely on products.
Understanding these shifts and responding to changes in business needs and consumer expectations will be crucial for those involved in the commercial property sector. Whether through reimagining office space or adapting retail properties to new market demands, staying ahead of these developments will ensure success in a constantly evolving marketplace.
Predicting Future Real Estate Movements
The ability to forecast future shifts in the property market is essential for investors, developers, and industry professionals seeking to make informed decisions. While no prediction can be entirely precise, understanding the key drivers that influence market fluctuations helps in identifying potential opportunities and risks. By analyzing historical data, examining current market conditions, and considering external factors such as policy changes or technological innovations, experts can form projections about the direction the market is likely to take.
Factors Impacting Future Property Movements
Several factors play a critical role in determining the direction of the property market. The most influential of these include:
- Interest Rates: Changes in borrowing costs can significantly affect both buyer demand and investor activity. Rising rates typically dampen demand, while lower rates can spur more activity in both residential and commercial sectors.
- Population Growth: As the population grows, so does the demand for housing and business space. Regions experiencing population influxes often see increased pressure on property values and rental rates.
- Technological Advancements: Innovations such as smart homes, virtual reality tours, and automation in construction and property management can alter market dynamics, creating new opportunities or making certain property types more desirable.
Anticipating Market Shifts
While it’s impossible to predict exact outcomes, some key indicators can give valuable insight into where the market is headed:
- Real-Time Data: Monitoring market data such as property sales, pricing trends, and inventory levels offers clues as to the current state of demand and supply. These data points help gauge whether the market is in an expansionary or contractionary phase.
- Government Policies: Legislation and policy changes, particularly in taxation or zoning, can greatly influence the market. For example, changes in housing laws or commercial property tax incentives may drive development or create new opportunities in specific areas.
By carefully evaluating these factors, industry professionals can develop strategies that anticipate potential shifts, positioning themselves for long-term success in the ever-evolving property landscape.