
In the world of project management, there are various certifications that can significantly enhance your career prospects. These credentials validate your knowledge and ability to apply best practices in real-world situations. However, the path to obtaining such qualifications can be challenging, requiring a strong understanding of the core principles, processes, and methodologies. Preparing for a certification test involves more than just studying theory; it’s about honing your practical skills and gaining confidence in applying concepts to scenarios that may arise during the assessment.
One of the most effective ways to prepare is by familiarizing yourself with practice materials that simulate the structure and type of content you may encounter. By engaging with sample assessments, you will not only test your knowledge but also improve your ability to think critically under pressure. It’s crucial to focus on both the content and the strategic approach to tackling complex situations, ensuring you’re ready for the challenges ahead. Practicing with realistic examples enhances your chance of success and allows you to gauge your readiness for the actual test.
Throughout your preparation, understanding the relationship between the framework and practical application will be key. It’s not only about memorizing terms or definitions; it’s about applying those principles effectively in a variety of contexts. With the right materials and a well-planned approach, you can set yourself up for success and confidently face any assessment related to project management methodologies.
Prince2 Agile Exam Questions and Answers
In preparation for certification assessments, it is essential to engage with relevant practice materials that replicate the format and type of content you may encounter. These resources not only help you review key concepts but also allow you to develop strategies for tackling the test’s various challenges. The ability to apply theoretical knowledge to practical scenarios is a crucial skill for success. By familiarizing yourself with mock tests, you can gauge your understanding and refine your approach to different types of tasks and case studies.
Key Areas to Focus On
When preparing for this type of qualification, it’s important to focus on the main principles and processes that will be tested. Understanding the framework’s structure, roles, and practices is fundamental. In addition, knowing how to adjust these concepts in dynamic project settings is a valuable skill. Practice exercises that focus on real-life examples will strengthen your ability to apply theoretical knowledge effectively. This approach will ensure that you are ready for both multiple-choice scenarios and scenario-based problems.
Strategies for Success
To improve your performance, it’s crucial to learn not only the material but also how to approach the test strategically. Time management is key–ensuring that you allocate appropriate time for each question and don’t rush through difficult areas. It’s also important to familiarize yourself with the types of scenarios that require critical thinking, as these often test your ability to adapt to changing project requirements. Practice under timed conditions to simulate the exam experience and build confidence for the actual assessment.
Understanding Prince2 Agile Framework
The success of any project relies heavily on having a well-defined methodology that guides the team through the various stages of development. A structured framework is essential for managing both the process and people involved. It integrates flexibility with control, ensuring that project objectives are met while adapting to the unique challenges that arise throughout the lifecycle. This approach helps create a balanced environment where deliverables can be achieved efficiently and with a high level of stakeholder satisfaction.
Key Components of the Framework
At the core of this approach are several principles that provide direction and consistency. These principles are designed to be flexible enough to apply to various types of projects, from small-scale initiatives to complex, large-scale undertakings. By focusing on iterative cycles, continuous feedback, and clear roles and responsibilities, the framework ensures that progress is monitored and adjustments can be made when necessary. This adaptability is one of its greatest strengths, allowing for optimal decision-making in uncertain or rapidly changing conditions.
Roles and Responsibilities
Understanding the roles within the framework is crucial to its successful implementation. Every participant has a specific function, contributing to the overall project success. These roles range from those responsible for defining the project vision to those ensuring the day-to-day operations are running smoothly. Below is a summary of the main roles involved:
| Role | Description |
|---|---|
| Project Manager | Responsible for overseeing the project and ensuring that objectives are met within scope, time, and budget. |
| Team Member | Contributes to the execution of project tasks, ensuring quality and timely delivery. |
| Stakeholder | Individuals or groups who have an interest in the project’s outcome and can impact its success. |
| Customer | Provides feedback and requirements, ensuring the project delivers value and meets expectations. |
Key Concepts of Agile Methodology
Effective project management requires more than just following a set of instructions; it involves adapting to changes, embracing flexibility, and ensuring continuous collaboration. This approach is designed to foster responsiveness to evolving requirements and promote iterative improvements. By prioritizing customer feedback, incremental delivery, and team involvement, this methodology encourages sustainable progress throughout the project’s lifecycle. Understanding its fundamental principles is key to successfully applying it in real-world scenarios.
Core Principles
- Collaboration Over Contract Negotiation: Prioritize ongoing collaboration with stakeholders over rigid contracts and documentation.
- Responding to Change: Embrace flexibility and adaptability, allowing the project to adjust to changing conditions and feedback.
- Frequent Delivery: Deliver small, functional increments of the project regularly to ensure continuous progress and value.
- Customer-Centric Focus: Ensure that the customer’s needs and feedback are prioritized throughout the development process.
Iterative Process
One of the key aspects of this approach is its iterative nature. Instead of completing the entire project in one go, work is broken into smaller, manageable chunks, delivered incrementally. This allows teams to continuously evaluate progress, adapt to new information, and make necessary adjustments along the way. Key features of this process include:
- Short Development Cycles: Work is completed in small, time-boxed cycles known as sprints or iterations.
- Continuous Feedback: Regular feedback from stakeholders helps shape the direction and improve the product incrementally.
- Frequent Reassessment: At the end of each cycle, progress is reviewed, and adjustments are made for the next phase of development.
How to Approach Exam Questions
Approaching assessments effectively requires a strategic mindset. It’s not just about recalling information but about thinking critically and analyzing the best way to apply your knowledge to various scenarios. This process involves reviewing the material, understanding the underlying principles, and practicing how to respond to different challenges. A well-structured approach can make a significant difference in how well you perform under pressure and manage your time during the test.
Key Strategies for Effective Test-Taking

There are several techniques that can help you approach each task with clarity and confidence. The most important strategy is understanding the structure of the test and practicing with mock scenarios. In addition, managing time efficiently, focusing on key concepts, and reading each prompt thoroughly will ensure that you answer each section accurately.
| Strategy | Description |
|---|---|
| Understand the Format | Familiarize yourself with the test layout and types of tasks you will encounter. This helps reduce uncertainty during the assessment. |
| Time Management | Allocate time wisely for each section, ensuring you don’t rush through difficult tasks but still leave enough time for all questions. |
| Careful Reading | Read every question or scenario carefully. Pay attention to details and ensure you understand what’s being asked before responding. |
| Eliminate Wrong Options | If you are unsure about an answer, eliminate clearly incorrect options first, increasing your chances of selecting the right one. |
Tips for Effective Time Management
Effective time management is crucial when preparing for any assessment, as it ensures that you can complete all sections within the allotted time while maintaining accuracy and focus. Organizing your time allows you to avoid last-minute rushes and reduces stress, leading to a more confident and productive performance. Proper planning and prioritization are key to staying on track and tackling each task methodically.
Prioritize Key Areas
Start by identifying the most important sections or areas where you may need extra attention. Allocate more time to complex tasks that require critical thinking or detailed responses. By prioritizing the areas that challenge you the most, you ensure that you’re able to give them the necessary focus without being overwhelmed.
Use Time Blocks
Break down your available time into smaller blocks dedicated to specific tasks or sections. This approach helps you stay focused and ensures that no part of the assessment is neglected. For example, if you have 60 minutes for a series of tasks, divide that time into 15-minute segments and set clear goals for what you want to achieve in each block. This structure makes the test feel more manageable and prevents you from spending too much time on one question.
Practice with Timed Scenarios
One of the best ways to prepare for managing time effectively is by simulating test conditions. Practice with mock tasks under timed conditions to get a feel for pacing and to refine your ability to quickly assess and answer questions. This exercise helps build confidence and reduces anxiety on the day of the actual assessment.
Stay Calm and Adjust When Needed
If you find yourself spending too much time on a difficult question, don’t hesitate to move on and come back to it later. Adjusting your strategy in real-time is an important skill that can help you stay on track. Remaining calm under pressure and making quick decisions about how to manage your time will ensure you make steady progress throughout the assessment.
Common Exam Pitfalls to Avoid
While preparing for an assessment, it is just as important to be aware of common mistakes that can derail your performance. Many individuals fall into certain traps that hinder their ability to perform at their best. These pitfalls, such as poor time management, misunderstanding questions, or rushing through sections, can negatively impact your score. Recognizing and avoiding these missteps can make a significant difference in achieving a successful outcome.
Rushing Through Questions

One of the most common mistakes is rushing through tasks, either out of impatience or anxiety. This can lead to careless errors and overlooked details, ultimately costing valuable points. Take your time to carefully read each task and understand what is being asked. Approaching each question methodically will ensure you don’t miss important information that could change the outcome of your answer.
Overlooking Instructions
Another frequent pitfall is failing to follow the instructions provided for each task. Ignoring specific directions, such as word limits or formatting requirements, can lead to confusion and frustration. Always pay close attention to the instructions, as they often provide valuable context and help you tailor your responses effectively. Skipping this step can result in unnecessary mistakes that could easily be avoided with a more careful reading of the guidelines.
Detailed Overview of Key Principles
Every structured approach to project management is built upon a foundation of core principles that guide decision-making, ensure consistency, and promote successful outcomes. These principles form the bedrock for how teams approach tasks, handle risks, and manage resources throughout the course of the project. A clear understanding of these fundamental concepts is essential for effective planning and execution, enabling teams to stay aligned with the project’s objectives and navigate challenges efficiently.
By adhering to these principles, project teams can ensure they maintain a focus on the most important aspects of the project, making informed decisions and adapting strategies as necessary. These principles are designed to be flexible enough to apply to any type of project while still providing the structure needed to achieve clear and measurable results.
Principle 1: Focus on Business Justification
Every project should be driven by a clear and ongoing business need. This principle emphasizes the importance of aligning the project’s objectives with organizational goals. If the project no longer provides value or if the justification for its continuation becomes unclear, it may need to be reassessed or even terminated. Ensuring continuous business justification helps keep the project on track and prevents unnecessary investments in unproductive efforts.
Principle 2: Learn from Experience

Project teams should continuously review past lessons and experiences, applying them to current efforts. This principle encourages a culture of learning, where teams actively seek insights from previous projects, both successful and failed, to improve decision-making and avoid repeating mistakes. By fostering a learning environment, teams can adapt more quickly to changing circumstances and refine their processes for better results.
Principle 3: Defined Roles and Responsibilities
Clear roles and responsibilities ensure that everyone involved in the project understands their tasks and the expectations placed on them. This principle stresses the importance of defining the roles of key stakeholders, including the project manager, team members, and external contributors. A well-defined structure promotes accountability, streamlines communication, and enhances overall team coordination.
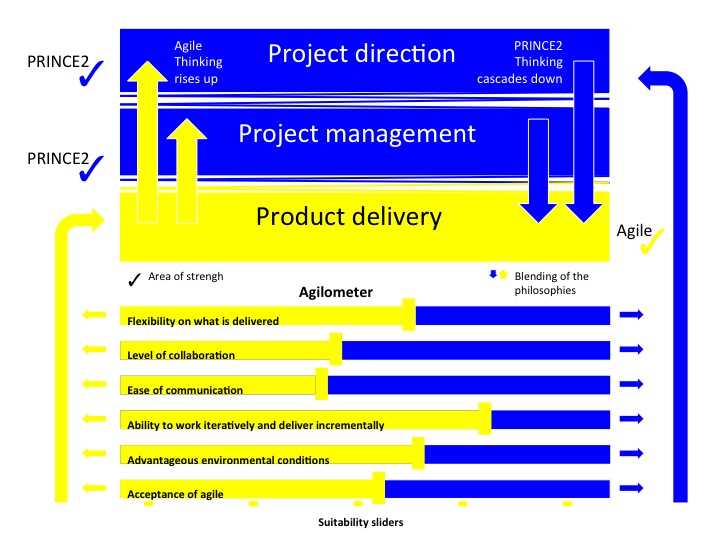
How Flexible Practices Align with Structured Methodologies
In project management, combining structured approaches with flexible methods can create a powerful framework that supports both control and adaptability. The goal is to blend the rigor of a formal methodology with the responsiveness of iterative techniques, ensuring that projects remain on track while adapting to changing requirements. Understanding how these approaches complement each other is crucial for delivering projects that are both efficient and able to respond to evolving customer needs.
Complementing Control with Flexibility

Structured methods provide a solid foundation for ensuring that projects are properly planned, executed, and monitored. They offer clear guidelines and roles, ensuring that the scope, risks, and resources are carefully managed throughout the lifecycle. On the other hand, flexible practices focus on continuous delivery and rapid adaptation, allowing teams to respond to feedback quickly and refine their approach as they progress. By integrating the two, organizations can maintain oversight while remaining agile enough to meet changing demands and unexpected challenges.
Improving Stakeholder Engagement
One of the key areas where flexibility aligns with structure is in stakeholder engagement. Traditional methodologies emphasize stakeholder involvement at key stages, often at the beginning and end of the project. Flexible practices, however, encourage ongoing collaboration throughout the project’s lifecycle. This continuous engagement ensures that the final outcome better meets the needs of the client or end-user, while the structured elements help to keep communication clear and decisions aligned with project objectives.
Sample Questions for Assessment Preparation
When preparing for any structured certification, it’s essential to practice with sample tasks that reflect the types of challenges you will encounter. These practice items not only help familiarize you with the format but also provide an opportunity to assess your understanding of key concepts and your ability to apply them in different contexts. By reviewing sample scenarios, you can enhance your readiness and identify areas where you may need further improvement.
Understanding Key Concepts
One of the most effective ways to prepare is to focus on questions that assess your understanding of the core principles and concepts. Below are examples of practice tasks that cover a range of important topics:
- Scenario-Based Evaluation: You are managing a project with a constantly evolving scope. How would you ensure that the project stays aligned with its initial goals while accommodating changes effectively?
- Process Focus: Given a set of predefined stages, which process should be followed when facing a critical risk that could affect the project’s timeline?
- Team Collaboration: How would you approach the task of facilitating communication between stakeholders with differing priorities?
Applying Knowledge to Practical Situations
In addition to conceptual understanding, you must be able to apply your knowledge to real-world situations. These sample tasks focus on testing your ability to integrate theoretical frameworks with practical application:
- Prioritization Challenge: You are faced with multiple urgent tasks, each requiring your attention. What method would you use to prioritize the tasks, ensuring that the project continues moving forward efficiently?
- Risk Management: Describe the steps you would take to identify, assess, and mitigate a potential risk that could jeopardize the delivery of a key milestone.
- Stakeholder Engagement: A key stakeholder has expressed dissatisfaction with the direction of the project. How would you handle the situation to ensure their concerns are addressed without derailing the project?
Answering Multiple Choice Questions Effectively
Multiple-choice tasks are a common assessment format that tests both your knowledge and your ability to think critically under time constraints. While these tasks may seem straightforward, answering them effectively requires careful analysis of each option and an understanding of how to eliminate incorrect choices. A strategic approach can help you maximize your chances of selecting the right answer and avoid common pitfalls.
To improve your performance, it’s essential to employ a systematic approach to each task. Begin by carefully reading the question and considering what is being asked before reviewing the possible answers. Then, evaluate each choice based on your knowledge of the subject, eliminating those that are obviously incorrect. This process will help you narrow down your options and increase your likelihood of selecting the correct response.
Steps to Effectively Tackle Multiple Choice Tasks
| Step | Description |
|---|---|
| Step 1: Read the Question Carefully | Ensure you fully understand what is being asked. Pay attention to keywords such as “most important” or “least likely,” as these can guide your selection process. |
| Step 2: Eliminate Obvious Incorrect Answers | Cross out any options that you know are definitely wrong. This will leave you with fewer options to consider, making it easier to focus on the most plausible ones. |
| Step 3: Evaluate the Remaining Options | Carefully consider the remaining choices. Think about the key principles and concepts involved, and select the one that best aligns with what you’ve learned. |
| Step 4: Check for Clues in the Question | Sometimes, the question itself may contain hints or context that can help you choose the correct option. Look for these cues before finalizing your answer. |
| Step 5: Avoid Overthinking | Don’t second-guess yourself too much. Often, the first answer that comes to mind is the correct one. If you’re unsure, go with your intuition, but ensure you’ve followed the process above. |
By using this structured approach, you can tackle multiple-choice tasks more efficiently, making sure you’re selecting the answer based on logic and knowledge rather than guesswork. With practice, this strategy will help you boost your performance and reduce the likelihood of errors in time-sensitive assessments.
Real-World Scenarios and Solutions
In any professional environment, real-world situations often present challenges that require more than just theoretical knowledge. Effective problem-solving involves applying learned concepts to address practical issues. By examining a few scenarios, you can better understand how to navigate complex situations and apply your expertise to create successful outcomes. This approach enhances your ability to think critically and respond with confidence when faced with unexpected situations.
Scenario 1: Managing Project Scope Changes
In dynamic environments, changes to the project scope are inevitable. The key to handling such adjustments is managing expectations and balancing flexibility with control. Here’s a breakdown of a typical scenario:
- Situation: The project’s scope has expanded midway due to a client request, resulting in potential delays.
- Challenge: How to incorporate these changes without compromising the original objectives or timeline.
- Solution: Implementing a structured change control process helps assess the impact, gain stakeholder approval, and adjust plans accordingly.
Scenario 2: Addressing Team Communication Gaps
Effective communication is crucial for any project’s success. However, when team members are spread across different locations or departments, communication gaps can occur.
- Situation: Team members from different departments are not aligned on project milestones, causing delays.
- Challenge: How to improve com
How to Interpret Agile Terms in Exams
When encountering specialized terminology in assessments, it is essential to understand not only the definitions but also the context in which they are used. Many terms are widely understood but may take on specific meanings depending on the situation or framework being applied. The ability to interpret these terms correctly ensures that you can answer questions accurately and demonstrate a comprehensive understanding of the concepts involved.
Understanding Key Terminology
To tackle questions that feature unfamiliar or complex terms, break them down into simpler components. Here are a few commonly used terms and how to approach their interpretation:
- Iteration: A short, time-boxed period during which a set of tasks or objectives is completed. In assessments, look for clues in the question to determine whether it’s referring to a specific phase or cycle of a process.
- Backlog: A prioritized list of tasks or deliverables that need to be completed. When seeing this term, think about how it aligns with project timelines and resource allocation.
- Increment: A tangible outcome or deliverable that results from completing a set of tasks or goals within a cycle. In some scenarios, it refers to a part of the final product being built incrementally.
- Velocity: The rate at which tasks are completed or work is delivered over time. Be sure to understand whether the question refers to actual performance metrics or theoretical expectations.
Contextual Clues
Interpreting terms in assessments requires more than just recognizing the words. Pay close attention to the surrounding context, as it will help you determine the correct approach. For instance:
- Scenario-based questions: These questions provide a situation and ask how you would apply a term or concept. In such cases, the context will clarify whether the term refers to a process, tool, or methodology.
- Multiple-choice questions: In questions with multiple answer choices, the wording can often point to the most accurate interpretation. Eliminate answers that don’t align with the core definition or context presented.
- Key phrases: Phrases like “continuous improvement,” “adaptive planning,” or “collaboration” signal a focus on flexibility, communication, and ongoing refinement. These terms often have nuanced meanings in specific frameworks, so understanding their practical application is key.
By focusing on both the specific meaning of the term and its practical application within the context of the question, you can enhance your ability to interpret terms effectively and answer related questions with confidence.
Exploring the Process Model
The process model for any framework or methodology is designed to provide structure and clarity for delivering projects successfully. It maps out the stages and key activities involved, outlining how the project should progress from initiation to completion. Understanding the structure of the process model allows project managers and teams to ensure consistent delivery, effective resource management, and alignment with goals.
Core Stages of the Process Model
The process model is typically divided into key stages, each with specific objectives and tasks that guide the team towards a successful project outcome. Here are the core stages that are commonly found in most models:
- Initiation: The initial phase where project goals, objectives, scope, and stakeholders are identified. This stage sets the foundation for the entire project.
- Planning: In this phase, detailed plans for execution are created, covering timelines, resources, risk management, and deliverables. It sets expectations for the team and the client.
- Execution: The phase where the bulk of work takes place. Tasks are completed according to the plan, and regular checks are done to ensure alignment with project objectives.
- Monitoring and Controlling: This stage involves tracking project progress, managing changes, and ensuring the project stays on track. Any deviations from the plan are addressed during this phase.
- Closure: After successful delivery, the project is finalized, and lessons learned are documented. The closure phase also includes handing over deliverables and closing out the project.
Integrating Flexibility with Structure
One of the key features of a well-designed process model is its ability to balance structure with flexibility. A good process model should provide clear guidelines and checkpoints but also allow for adjustments as necessary based on project needs. This adaptability is critical in dynamic environments where changes may arise unexpectedly.
- Regular Reviews: Frequent reviews allow teams to assess whether progress is on track and make adjustments if required. These reviews contribute to the overall adaptability of the process.
- Feedback Loops: Continuous feedback from stakeholders ensures that expectations are met and that necessary changes can be incorporated. This feedback loop helps in refining the deliverables throughout the project’s lifecycle.
By understanding the core stages and principles that govern a project process model, teams can confidently manage their projects from start to finish, ensuring smooth execution and timely delivery.
Understanding Roles in a Project Framework

In any project management methodology, the roles assigned to team members are crucial for ensuring a smooth and effective project flow. These roles define responsibilities, authority, and the contribution of each individual towards the project’s success. By understanding how different roles interact and collaborate, teams can better navigate the complexities of project execution and ensure clear communication and efficient decision-making.
Key Project Roles and Responsibilities
Each role within a project framework comes with its own set of expectations and duties. These roles help ensure that the project remains on track and that the team is focused on delivering high-quality results. Below are some common roles that can be found within such frameworks:
- Project Sponsor: The individual who provides overall direction and support for the project. They ensure that the project aligns with the organization’s goals and provide the necessary resources.
- Project Manager: Responsible for day-to-day project management, ensuring the project meets its deadlines, stays within budget, and achieves its objectives. They coordinate between stakeholders and manage resources.
- Team Members: These are the individuals who carry out the work to meet the project’s goals. Each team member typically specializes in a specific area of expertise, contributing to the overall progress of the project.
- Stakeholders: People who have an interest in the project’s outcome, such as clients, end users, and other departments. Stakeholders provide feedback, approval, and direction throughout the project lifecycle.
Collaborating to Achieve Success
Successful project management hinges on the collaboration between these roles. Clear communication between the project manager, team members, and stakeholders ensures that any challenges are addressed early and that the project’s progress is regularly reviewed. In addition, the flexibility of some roles allows for the agile adaptation to changes, which is essential for maintaining project momentum in fast-paced environments.
- Regular Check-ins: Frequent status updates and meetings help to ensure that all members are aligned and that issues are quickly identified and resolved.
- Adaptability: Certain roles, like the project manager, must be adaptable to changing requirements and manage the project scope effectively.
In summary, understanding the roles and how they function together within a project framework is essential for achieving project success. The interactions between these roles drive the project’s progress and ensure that goals are met effectively and efficiently.
Best Resources for Preparation
Effective preparation for any certification or assessment requires utilizing the right resources to enhance understanding and build confidence. Whether you’re new to the field or looking to refine your knowledge, selecting the best materials is crucial for mastering the concepts and performing well. Various tools, from textbooks to online platforms, can offer different perspectives and practice opportunities to strengthen your skills and comprehension.
Top Materials for Studying
There are a wide range of study materials available, each offering different benefits. From comprehensive textbooks to practice tests and online courses, the options are abundant. Below are some of the most recommended resources to consider when preparing:
Resource Type Description Recommended For Official Guides Detailed manuals offering in-depth explanations of principles and frameworks, typically provided by certification bodies. Newcomers looking for structured learning Practice Tests Simulated questions that mirror the style and difficulty of actual assessments, helping you gauge your knowledge and time management. Those wanting to improve test-taking skills Online Courses Interactive, video-based lessons that offer flexibility in studying and often include quizzes and assignments for better retention. Self-motivated learners seeking visual content Strategies to Pass the Certification
Successfully obtaining a certification requires not only understanding the core concepts but also mastering how to approach the assessment itself. Whether you’re preparing for your first certification or aiming to improve your performance, having a solid strategy is essential. By focusing on structured learning, practicing under exam conditions, and applying effective time management techniques, you can increase your chances of success.
Start by breaking down the study material into manageable sections. Instead of attempting to cover everything at once, focus on specific areas each day. Create a study schedule that allows for consistent review, helping to reinforce key concepts without feeling overwhelmed. Make use of various learning methods, such as reading, watching instructional videos, and practicing with sample questions, to reinforce your understanding from different angles.
Simulating exam conditions through practice tests is another effective strategy. By timing yourself during these sessions, you will get used to the pacing and learn how to prioritize your time effectively. It’s also helpful to review your mistakes after each practice test, ensuring that you understand the reasoning behind the correct answers. This reflective process will improve your ability to make decisions quickly and confidently during the actual test.
Additionally, developing a strategy for the day of the assessment is key. Ensure you get adequate rest the night before, and approach the exam with a calm and focused mindset. Arrive early, review any last-minute notes, and make sure you’re familiar with the exam environment. During the exam itself, read each question carefully, eliminate obviously incorrect answers, and focus on managing your time effectively across all sections.