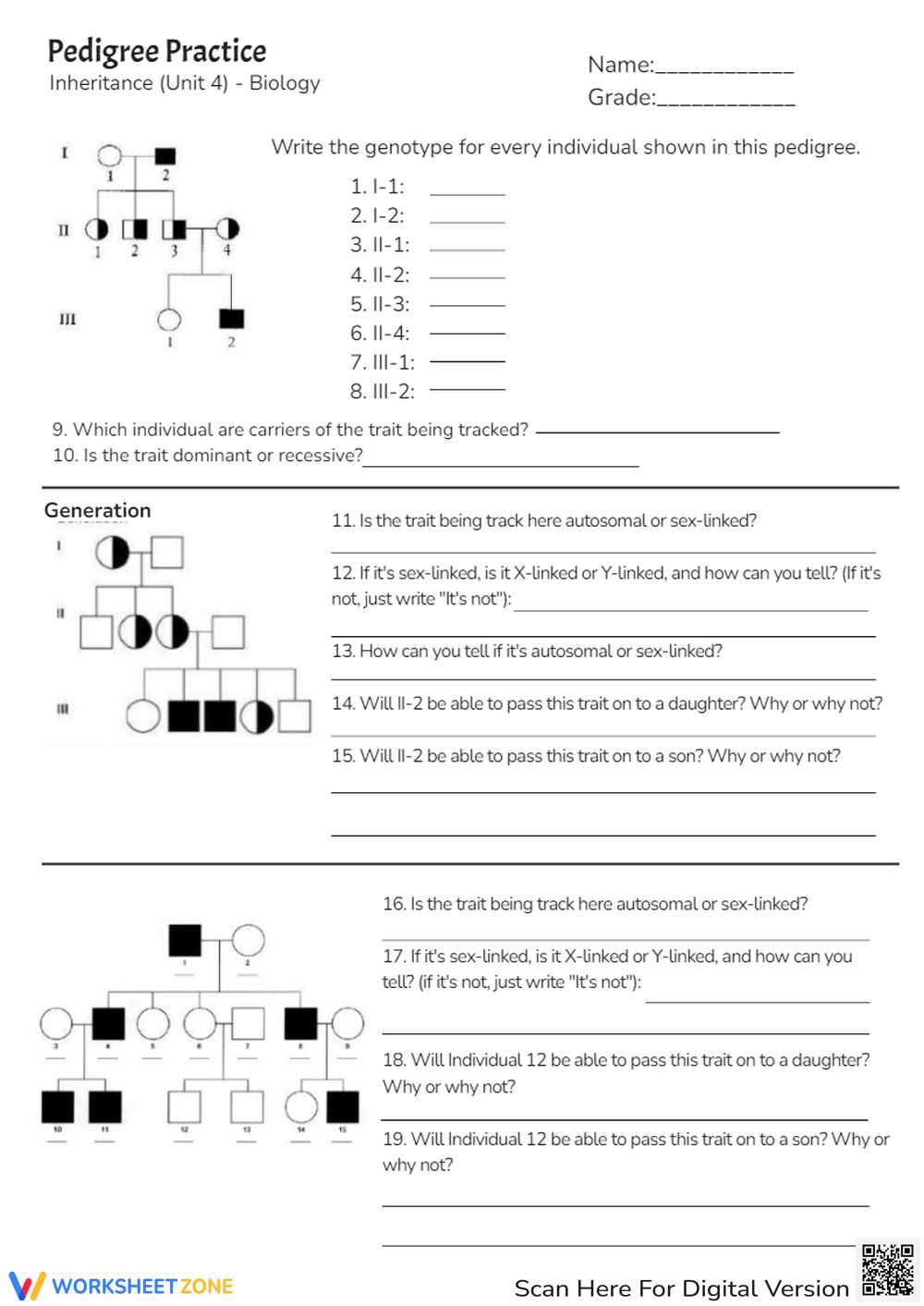
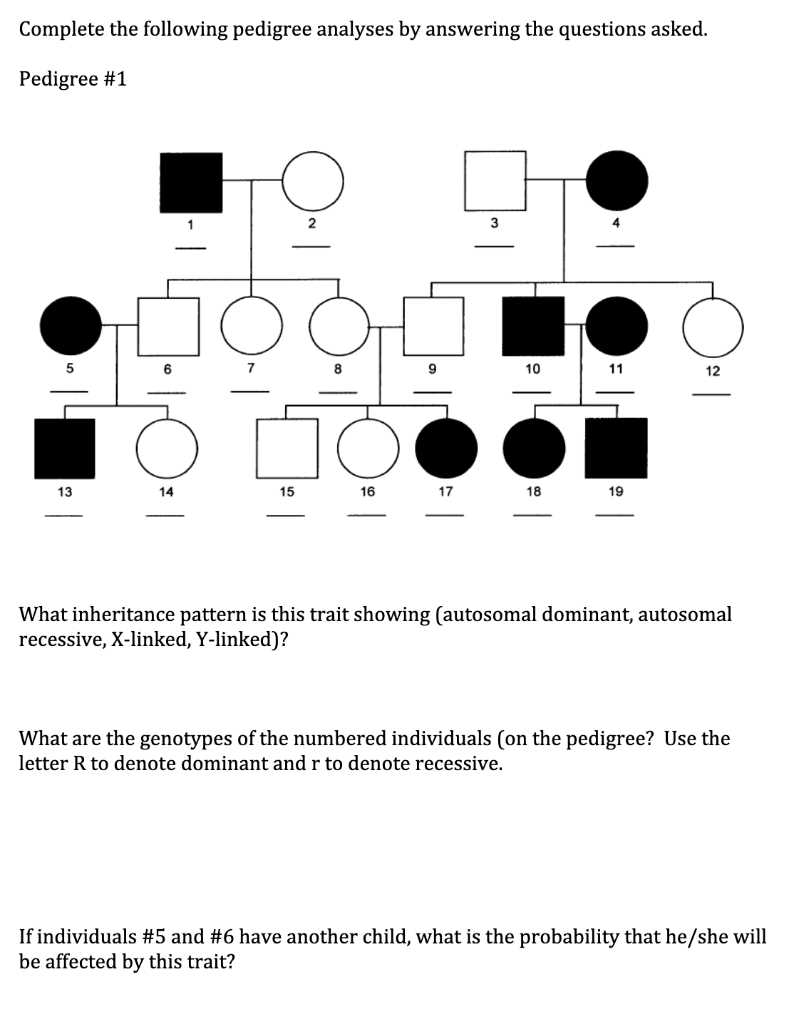
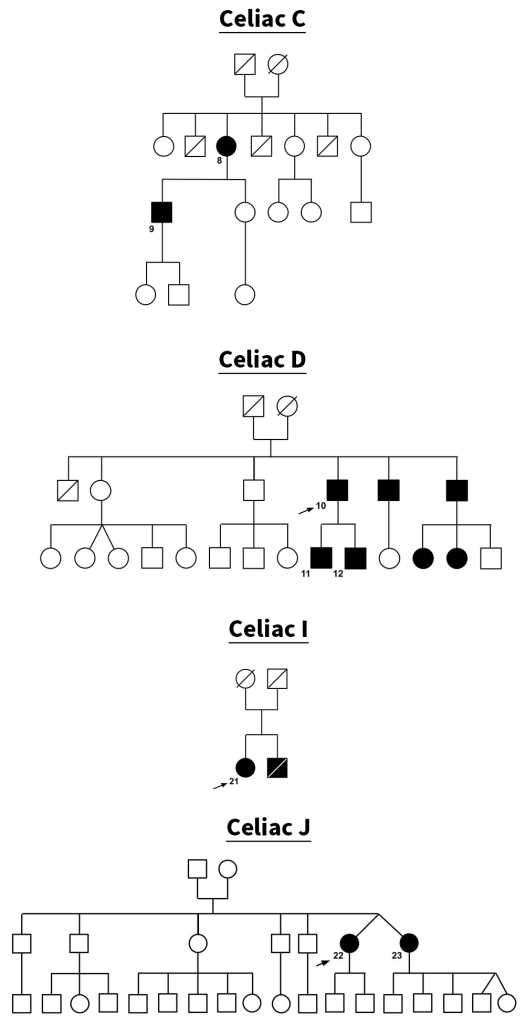
When it comes to understanding a dog’s background, many owners and breeders seek to uncover the details of their animal’s lineage. Knowing the ancestry of a dog can provide valuable insights into its characteristics, health history, and potential for certain traits. This knowledge plays a significant role in breeding practices, as well as in ensuring the overall well-being of the animal.
There are various aspects to consider when looking into a dog’s family tree. Whether it’s identifying inherited traits, understanding the origins of specific breeds, or verifying genetic connections, each piece of information contributes to a broader picture. By examining the history of a dog’s ancestors, owners can make more informed decisions regarding health, care, and breeding choices.
In this section, we will delve into common topics related to dog lineage, focusing on how to interpret records, the importance of genetic diversity, and the significance of heritage in breeding. A deeper understanding of these elements can enhance both the care and breeding of dogs, ensuring healthier, well-adjusted animals.
Lineage Inquiries and Clarifications
Many dog owners often seek to understand the deeper aspects of their dog’s ancestry, wondering about the genetic background that shapes their pets. The details of a dog’s lineage can reveal important information, from inherited traits to potential health risks. Understanding these elements helps owners make informed decisions on breeding, care, and overall well-being.
Questions arise when trying to trace a dog’s background accurately. How can one verify the connections between different generations? What factors determine the quality of a dog’s genetic history? In this section, we will address common concerns, offering guidance on interpreting records, recognizing key factors in lineage, and understanding the role of genetics in a dog’s development.
Whether you are interested in exploring the health implications of a dog’s genetic makeup or simply curious about its breed origins, this guide will help clarify common uncertainties. We’ll dive into various aspects of canine heritage, offering practical advice for those looking to better understand their dogs’ ancestry.
What is a Lineage in Dogs
The lineage of a dog is a detailed record of its ancestry, showing the connection between generations of dogs. This family history is crucial for understanding a dog’s genetic makeup, including traits passed down from its ancestors. It provides insight into a dog’s potential behavior, health, and physical attributes.
A dog’s background can be traced through a chart that lists the names and other details of its forebears. This chart serves as a map of a dog’s genetic inheritance, helping breeders and owners track the presence of specific characteristics. It also plays an important role in maintaining or improving breed standards, ensuring dogs inherit desirable traits while minimizing the risks of inherited diseases.
For dog breeders, a clear understanding of a dog’s heritage is essential for making informed breeding decisions. It allows them to plan matings with the aim of producing healthy puppies with the best traits from both parents. By analyzing the family history, breeders can reduce the risk of genetic disorders and improve the overall health of the breed.
How to Read a Lineage Chart
Reading a dog’s family history chart is an important skill for understanding its genetic background. These charts display the connections between a dog and its ancestors, often extending several generations. By interpreting the information correctly, owners and breeders can learn about inherited traits, health risks, and potential for certain behaviors.
Understanding the Structure
The chart typically consists of a series of boxes representing individual dogs, with lines connecting them to show their relationships. The top part of the chart usually represents the dog’s parents, while subsequent generations are shown below. Each box will often contain details like the dog’s name, breed, registration number, and sometimes health records or achievements. The lines connecting the boxes represent the direct lineage, such as mother to offspring or father to offspring.
Interpreting Key Information
Focus on specific details when examining a lineage chart. Look for any markings or notations that indicate inherited traits or health issues in previous generations. Some charts also include information about championships or other accolades, which can be important for breeders aiming to maintain or improve certain qualities in the breed. Understanding these key elements helps in making educated decisions regarding breeding and health management.
Why Lineage Records Matter for Breeding
Understanding a dog’s ancestry is essential for responsible breeding practices. By tracing the lineage, breeders can make informed decisions that maximize the chances of producing healthy and well-tempered offspring. Without this information, it would be difficult to predict the genetic traits passed down through generations, which could lead to undesirable outcomes for the breed.
Ensuring Genetic Health
One of the primary reasons for tracking a dog’s ancestry is to identify potential genetic health issues. By examining the family history, breeders can spot recurring health problems that may be inherited, such as hip dysplasia or heart conditions. This knowledge allows breeders to select mating pairs that minimize the risk of passing on these issues, promoting healthier puppies.
Preserving Breed Standards
Another important aspect of knowing a dog’s family background is the ability to maintain or improve breed standards. Certain traits, both physical and behavioral, are characteristic of a specific breed. By using lineage records, breeders can ensure that future generations continue to meet these standards, contributing to the consistency and quality of the breed as a whole.
Common Misconceptions About Lineage Records
There are several myths and misunderstandings surrounding a dog’s ancestry chart that can lead to confusion, especially among new breeders or dog owners. These misconceptions can sometimes influence breeding decisions or mislead owners into making assumptions about a dog’s genetics and health.
One common myth is that a clear family history guarantees a dog will be healthy and free from genetic disorders. While a well-documented family tree can help identify potential health risks, it does not eliminate the possibility of hidden genetic conditions. Health issues may still arise even if no problems appear in previous generations.
Another misconception is that having a strong lineage always means a dog will perform better in competitions or shows. While ancestry can contribute to certain traits, such as appearance and behavior, individual dogs may still vary widely in terms of temperament and skills, regardless of their background.
It’s important to approach lineage charts with a critical eye and not assume that all the information on them guarantees specific outcomes. Understanding the context and limitations of these records is essential for making responsible decisions when it comes to breeding and dog care.
Understanding Inbreeding and Lineage Records
Inbreeding occurs when closely related dogs are bred together, often with the intent of preserving specific traits within a breed. However, this practice can have unintended consequences on the genetic health of the offspring. By examining the family history of a dog, breeders can identify patterns of inbreeding and assess the potential risks of this practice.
Inbreeding can lead to a higher likelihood of passing down genetic disorders, as closely related dogs may share similar genetic defects. This can result in health problems that affect the dog’s overall well-being and quality of life. Breeders who track the family history of their dogs are better equipped to avoid mating dogs that share the same genetic weaknesses, promoting healthier offspring.
While some inbreeding may be necessary to maintain certain breed standards or traits, it is important to balance this with genetic diversity. Healthy breeding practices involve careful selection of mates that can contribute to the vitality and long-term health of the breed. By understanding the risks of inbreeding, breeders can make informed decisions that improve the genetic pool and ensure better outcomes for future generations.
How to Verify a Dog’s Ancestry
Confirming a dog’s family background is crucial for breeders and owners who want to ensure the accuracy of the lineage. Proper verification ensures that the dog’s genetic history aligns with the claimed ancestry, which can impact breeding decisions, health testing, and overall care. Several methods can be used to confirm a dog’s background.
Check Official Registrations
One of the most reliable ways to verify a dog’s family history is by checking official breed registries. These organizations maintain detailed records of registered dogs and their ancestry. Here’s how to start:
- Obtain the dog’s registration number from the breeder or owner.
- Search the registry’s online database or contact them directly to confirm the dog’s lineage.
- Ensure the dog’s ancestors are also listed, as this will provide additional verification of the claimed family history.
Genetic Testing
Another effective method is through DNA testing, which can confirm a dog’s genetic background and identify any hidden lineage details. DNA tests can reveal:
- Breed composition and ancestral origins.
- Health markers and potential genetic disorders.
- Linkages to known genetic lines in the database of the testing company.
By combining registry verification and genetic testing, dog owners can ensure the accuracy of a dog’s ancestry, leading to better-informed decisions about breeding and health care.
Top Sources for Lineage Information
When it comes to tracking a dog’s ancestry, several reliable sources can provide valuable insights. These platforms and organizations maintain extensive records that allow breeders and owners to verify the history and genetic background of a dog. Utilizing these sources ensures that you have accurate and trustworthy information for breeding decisions and care practices.
| Source | Description | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| American Kennel Club (AKC) | The AKC is a well-known registry that maintains detailed records on purebred dogs in the U.S. | Breed registration and history |
| UK Kennel Club | UK’s official kennel club offers a similar service to AKC, focusing on breed standards and dog ancestry. | International pedigree verification |
| Breed-specific Registries | Many breeds have their own specialized registry, providing in-depth information about lineage and standards. | Specific breed ancestry |
| DNA Testing Services | Several companies offer genetic testing, revealing detailed information about a dog’s genetic makeup and heritage. | Genetic analysis and health screening |
| International Canine Genetic Testing Database | A global database that connects genetic testing results across different dog breeds. | Global lineage and genetic mapping |
Each of these sources offers unique benefits, depending on your specific needs, whether you are verifying a dog’s registration, exploring its genetic history, or confirming health traits. By utilizing these trusted platforms, you can ensure the accuracy of a dog’s ancestry records.
The Role of Lineage Records in Health Testing
Understanding a dog’s ancestry is a vital part of assessing potential genetic health risks. By examining a dog’s family background, breeders and veterinarians can identify common hereditary conditions and make informed decisions about health testing. This proactive approach helps in preventing the spread of genetic disorders within the breed and promotes the well-being of future generations.
| Health Condition | Importance of Ancestral Records | Testing Method |
|---|---|---|
| Hip Dysplasia | Tracking family history helps identify the likelihood of genetic predisposition to joint issues. | X-rays and DNA testing for specific markers |
| Progressive Retinal Atrophy (PRA) | Lineage data can highlight potential carriers of this eye condition. | DNA test for specific mutations |
| Heart Diseases | Family history allows early detection of hereditary cardiovascular conditions. | Cardiac evaluations and genetic screening |
| Epilepsy | Knowing the dog’s ancestors can pinpoint the likelihood of inherited epilepsy. | Genetic testing and seizure monitoring |
| Von Willebrand’s Disease | Ancestral records assist in recognizing dogs that may carry this bleeding disorder. | Blood tests and genetic screening |
By utilizing lineage records, breeders can ensure they are taking the necessary steps to reduce the risk of passing on genetic diseases. Health testing, when combined with thorough ancestral knowledge, enhances the health and vitality of future generations.
How Lineage Affects Dog Value
The family background of a dog plays a significant role in determining its market value. Breeders and potential buyers often look at a dog’s ancestral records to assess its genetics, traits, and overall potential. A strong lineage can increase a dog’s worth, while a lack of documented ancestry may reduce its appeal, especially for purebred breeds.
Influence on Breeding Potential
Dogs with a well-documented lineage, especially those from champion bloodlines, are often more valuable for breeding purposes. Their genetic traits, such as temperament, size, and health, are predictable, making them desirable for producing quality offspring. Breeders are willing to pay more for dogs that come from proven lines with minimal genetic issues.
Market Demand and Buyer Preference
Potential dog owners, particularly those looking for specific characteristics, are willing to pay a premium for dogs with verified ancestry. A strong family background ensures that the dog will meet breed standards, increasing its attractiveness to buyers. In addition, buyers who are looking for pets with health guarantees or specific traits may be more inclined to invest in a dog with a documented lineage.
In conclusion, a dog’s ancestry can have a significant impact on its value, influencing both breeders and buyers. Understanding the family history not only helps in breeding decisions but also plays a critical role in determining a dog’s worth in the marketplace.
Can Lineage Predict Behavior Traits
Understanding a dog’s behavior often begins with analyzing its family history. While environmental factors and training play a significant role, certain behavioral traits may be inherited from the dog’s ancestors. By examining a dog’s bloodline, it’s possible to make educated predictions about its temperament, responsiveness, and overall behavioral tendencies.
Many breeds are known for specific behavioral characteristics, such as loyalty, intelligence, or protectiveness. These traits are often passed down through generations, with some dogs showing strong tendencies based on their lineage. For example, certain breeds might be predisposed to being more independent, while others may be naturally more social and affectionate.
Behavioral Traits from Ancestry
By analyzing family records, breeders can identify trends in behavior that are common among specific bloodlines. Dogs from a strong, well-documented lineage might exhibit consistent characteristics, such as an increased ability to train or a particular sensitivity to certain stimuli. This insight helps breeders match dogs with the right homes, based on the expected behavior traits.
Limitations of Behavioral Predictions
It’s important to note that while a dog’s lineage can provide valuable clues, it does not guarantee specific behavioral outcomes. Each dog is an individual, and its environment, upbringing, and training are crucial factors that shape its behavior. Therefore, while ancestry can provide insight, it cannot fully predict a dog’s behavior.
In conclusion, examining a dog’s lineage can offer useful information about its potential behavioral traits, but it should not be relied upon as the sole indicator of how the dog will behave. A combination of genetic predispositions and environmental influences ultimately determines the dog’s personality and actions.
Lineage vs DNA Testing: Key Differences
Both family history records and genetic testing provide valuable insights into a dog’s ancestry, but they serve different purposes. While family records offer a documented history of a dog’s relatives, genetic testing reveals specific information about its DNA. Understanding the key differences between these two methods helps breeders and dog owners make informed decisions about their pets.
Lineage Documentation
Family history records trace the ancestry of a dog through generations, providing information about its parents, grandparents, and other relatives. These records often include details about physical traits, achievements, and sometimes health issues within the family line. Key points of lineage documentation include:
- Identification of breed-specific traits passed down through generations
- Recognition of notable ancestors, such as champion dogs
- Understanding of potential hereditary health issues based on family history
Genetic Testing
Genetic testing, on the other hand, directly analyzes a dog’s DNA to identify specific genes that influence its health, behavior, and physical traits. This testing can provide more precise information than family records and is capable of detecting genetic disorders or conditions that may not be apparent from lineage alone. Key benefits of genetic testing include:
- Detection of inherited genetic diseases and predispositions
- Analysis of breed composition in mixed-breed dogs
- Accurate assessment of traits that may not be visually obvious
In summary, while both lineage documentation and genetic testing offer valuable insights, they serve different functions. Lineage records provide a broad view of a dog’s ancestry and physical traits, while genetic testing offers precise information about its genetic makeup, allowing for a deeper understanding of potential health risks and characteristics.
How to Build a Dog Lineage Chart
Creating a detailed family record for a dog involves collecting information about its ancestors, tracing back multiple generations to understand its genetic background and traits. This record helps breeders make informed decisions about pairing dogs and predicting potential offspring characteristics. Building a comprehensive lineage chart requires careful research, accurate documentation, and organization of the dog’s ancestral history.
Step 1: Gather Information
The first step in constructing a dog’s family history is to collect as much information as possible about the dog’s parents, grandparents, and great-grandparents. Start by asking the breeder for records or any available documentation on the dog’s relatives. If no formal records are available, you may need to reach out to the dog’s previous owners or look for information through dog registries and breed clubs.
Step 2: Verify the Data
Once you’ve gathered initial information, it’s important to verify its accuracy. Cross-check the details with breed registries, kennel clubs, or other reputable sources to ensure that all the information is correct. Look for consistency in the details such as birth dates, titles, achievements, and health records of the relatives. Verification is crucial to ensure that the lineage is accurately documented.
Step 3: Organize the Information
After gathering and verifying the data, the next step is to organize it in a clear and accessible format. You can use software tools or templates to build a visual chart that shows the relationship between the dog and its ancestors. The chart should include names, dates, health status, and any notable achievements. Organizing this information in a tree-like structure helps visualize the family history clearly.
Step 4: Keep the Record Updated
Building a family history is not a one-time task. As new generations are born, it’s important to keep the record updated with information about the offspring and their achievements. Maintaining an up-to-date lineage chart helps track the traits and health of future generations, providing valuable insight into breeding practices.
In conclusion, constructing a dog’s family history chart is a process that requires attention to detail, accurate data collection, and organization. When done correctly, it can provide a wealth of information that helps breeders make informed decisions and ensure the health and well-being of future generations.
International Registration Organizations for Dog Lineages
In the world of dog breeding, various global bodies are responsible for the official recognition and documentation of a dog’s family history. These organizations play a crucial role in ensuring that breeders have access to reliable and standardized records that trace the lineage of individual dogs. Such institutions offer a framework for registration, verification, and tracking of pedigrees, enabling breeders to make informed decisions while maintaining breed standards.
1. Fédération Cynalogique Internationale (FCI)
The FCI is one of the most prominent organizations when it comes to dog lineage registration worldwide. Based in Belgium, the FCI works with national kennel clubs to ensure that dog breed standards are met and recognized internationally. It oversees the registration of dogs in over 80 countries and plays a key role in organizing international competitions and events.
2. American Kennel Club (AKC)
Based in the United States, the AKC is one of the most well-known organizations for dog registration. The AKC maintains a vast database of breed information and provides a trusted platform for registering dogs. In addition to registration, the AKC offers health testing, training, and events, which are valuable resources for breeders worldwide. It is highly respected within the industry and serves as an important reference for pedigree documentation in North America.
3. The Kennel Club (UK)
The Kennel Club is the UK’s leading authority on dog breeding and registration. It maintains a comprehensive registry of purebred dogs in Britain, promoting responsible breeding practices while maintaining breed standards. The Kennel Club also supports health testing initiatives to reduce the prevalence of inherited conditions within breeds.
4. Canadian Kennel Club (CKC)
The Canadian Kennel Club, similar to its counterparts in the U.S. and UK, provides a standardized platform for dog registration and lineage documentation in Canada. The CKC works closely with breeders to uphold breed standards and offers various services for health, training, and events. It is widely regarded as a credible source for lineage verification in the Canadian dog breeding community.
5. United Kennel Club (UKC)
Based in the United States, the UKC is known for recognizing a diverse range of breeds and promoting the recognition of mixed-breed dogs through its “Total Dog” philosophy. It offers registration services for dogs of varying backgrounds and is committed to the promotion of responsible breeding practices and ethical standards.
In conclusion, these organizations play a key role in maintaining the integrity of dog breeding by providing reliable and internationally recognized systems for registering dogs and tracing their family histories. Breeders who wish to maintain high standards and ensure their dogs’ health and well-being can turn to these trusted institutions for guidance and support.
The Importance of Lineage in Dog Shows
In competitive dog events, the lineage of a dog plays a crucial role in determining its eligibility and success. Understanding the family history of a dog is essential for judges who evaluate the breed standards and characteristics of each participant. The documentation of a dog’s ancestry not only highlights its genetic makeup but also offers insights into its traits and potential performance in various competitions.
1. Evaluating Conformance to Breed Standards
One of the primary factors in dog shows is whether a dog meets the specific standards of its breed. These standards are often shaped by the dog’s genetic history, which influences its appearance, behavior, and health. Knowing a dog’s ancestry helps judges assess whether the dog conforms to these standards, making lineage a key criterion in competition. It also provides insight into the breeding practices that have shaped the dog’s traits over generations.
2. Ensuring Ethical Breeding Practices
By tracking a dog’s family background, breeders can ensure that they follow ethical practices by avoiding inbreeding or the propagation of undesirable traits. Ethical breeding is a cornerstone of responsible dog ownership, and accurate lineage documentation helps to maintain the integrity of the breed. This information is not only valuable for participating in shows but also contributes to the overall health and well-being of the dog community.
Conclusion: Lineage is integral to the evaluation process in dog shows, impacting everything from breed conformity to the ethical standards upheld by breeders. Having access to reliable information about a dog’s ancestry ensures that the right traits are emphasized and that the dog’s lineage is accurately represented in competitions.
How Lineage Records Contribute to Genetic Diversity
Understanding the family history of an animal plays a vital role in promoting healthy breeding practices and preserving genetic variety. By tracking ancestry, breeders can make informed decisions to prevent the risk of genetic issues that can arise from close relationships between individuals. These records allow for the careful selection of breeding pairs to maintain or increase genetic diversity, which is crucial for the overall health of a species.
1. Avoiding Inbreeding
One of the most significant risks in breeding is inbreeding, which can lead to an increase in inherited diseases and reduce genetic diversity. Lineage tracking helps breeders identify related individuals, minimizing the chance of breeding closely related animals. This process helps maintain a stronger gene pool and encourages the breeding of animals with diverse backgrounds, reducing the occurrence of genetic disorders.
2. Enhancing Long-Term Health

- Disease Resistance: By maintaining genetic diversity, animals are less likely to inherit recessive genetic conditions, leading to a healthier population.
- Physical Fitness: Genetic variety can result in animals that are physically more resilient and adaptable to different environments and conditions.
- Fertility Rates: A diverse gene pool often improves the fertility of offspring, ensuring a stronger future generation.
3. Promoting Evolutionary Adaptation
Genetic diversity is essential for a species’ ability to adapt to changing environments. A broader gene pool allows for greater evolutionary flexibility, enabling future generations to respond better to environmental pressures such as disease outbreaks or climate change. Tracking ancestry over generations ensures that breeders continue to introduce new genetic material into the population, allowing for ongoing adaptation and survival.
Conclusion: By carefully managing lineage information, breeders play a crucial role in maintaining the long-term health and vitality of a species. The preservation of genetic diversity ensures not only the well-being of individual animals but also the strength of future generations.
Lineage and the Future of Dog Breeding
The practice of tracking a dog’s ancestry has always been central to responsible breeding. As the field evolves, understanding family backgrounds continues to be a key factor in ensuring healthy, balanced, and genetically diverse populations. However, with advancements in technology and new breeding techniques, the role of lineage documentation is undergoing significant changes, influencing the future direction of dog breeding practices.
1. Embracing Genetic Testing for Better Decisions
With the rise of DNA analysis, breeders now have access to more precise tools to evaluate genetic traits, health risks, and inherited conditions. These advancements supplement traditional methods of recording ancestry and provide a more comprehensive understanding of a dog’s genetic makeup. As a result, breeders can make more informed decisions, reducing the risk of genetic disorders and promoting better long-term health for the breed.
- Health Screening: DNA tests allow for early identification of potential genetic diseases, enabling breeders to prevent passing on harmful traits.
- Optimizing Breed Quality: By combining family history with genetic markers, breeders can select pairs that are more likely to produce strong, healthy offspring.
- Tailoring Breeding Strategies: Genetic data provides valuable insights into traits that might not be visible but are inherited, helping breeders to fine-tune breeding goals.
2. Shaping Ethical Breeding Practices
As ethical concerns around dog breeding grow, it is increasingly important to consider the implications of genetic manipulation. The ability to track bloodlines and analyze genetic data helps breeders maintain high standards, avoiding practices that prioritize appearance over health. The future of dog breeding will likely see a shift toward a more welfare-centered approach, ensuring that health, temperament, and genetic diversity are prioritized.
- Reducing Inbreeding: By identifying genetic relationships and minimizing inbreeding, breeders can help prevent the spread of hereditary diseases.
- Promoting Welfare: Ethical breeding will focus not only on the dog’s lineage but also on temperament, behavior, and physical well-being, ensuring that dogs thrive in family environments.
- Transparency: With more accessible records, owners and potential buyers will have greater access to information, promoting trust and accountability within the breeding community.
3. Integrating Technology with Tradition
While traditional breeding methods based on documented family lines remain valuable, the future of the field lies in the integration of modern technology. Advancements like genetic mapping, artificial intelligence, and digital databases will allow for more precise tracking of lineage and traits. This combination of old and new methods will enable breeders to optimize breeding practices while ensuring that the health and welfare of the dogs are prioritized.
Conclusion: As dog breeding continues to evolve, the understanding of ancestry and genetic makeup will remain essential. By combining traditional knowledge with new technological innovations, breeders can create healthier, more diverse populations and ensure a bright future for the dogs in their care.