
When preparing for any assessment related to child health, understanding core concepts and practical skills is essential. These evaluations test knowledge across various topics, focusing on care techniques, medical conditions, and patient management strategies. Mastery of these areas can significantly improve confidence and readiness for real-world applications.
Through a structured approach to studying, candidates can familiarize themselves with common scenarios and practices often encountered in clinical settings. A clear understanding of both theory and hands-on skills forms the foundation for success, whether for entry-level positions or advanced roles in the field.
Thorough preparation not only helps in mastering theoretical knowledge but also equips professionals with the practical insight needed to respond to diverse challenges. With a focus on real-life situations, this comprehensive guide provides crucial tips and strategies for tackling assessment tasks effectively.
Essential Concepts in Child Health Care
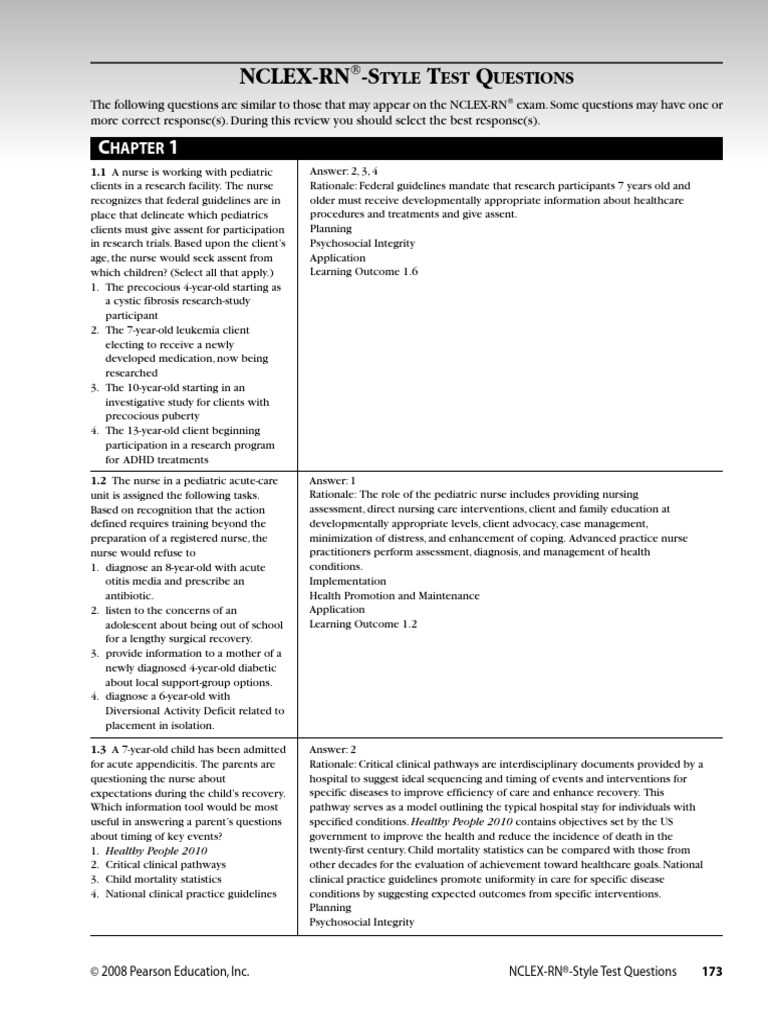
Understanding the fundamental principles of caring for young patients is crucial for any healthcare professional. Key concepts in this area involve the integration of medical knowledge, clinical skills, and effective communication with both children and their families. This foundation forms the basis of quality care and ensures the well-being of the child across various stages of development.
One of the core components involves recognizing developmental milestones and understanding how they affect treatment and care plans. This knowledge helps in assessing the child’s overall health and identifying any potential concerns early on. Additionally, staying informed about common conditions that affect children and their specific needs plays a major role in providing appropriate care and interventions.
Another vital aspect is the ability to work in partnership with families. Supporting caregivers and educating them about managing the child’s health is essential for ensuring continuity of care outside of the clinical setting. These concepts together help in delivering holistic and effective healthcare for younger populations.
Understanding Key Child Care Principles
Effective care for young patients requires a deep understanding of their unique needs and challenges. It involves not only addressing immediate health concerns but also supporting long-term growth and development. The key to successful treatment lies in recognizing the physical, emotional, and psychological factors that influence a child’s well-being. Building trust and ensuring comfort are equally important as medical interventions.
Comprehensive Approach to Care
Incorporating a holistic approach is essential when managing a child’s health. This includes monitoring developmental milestones, understanding the role of nutrition, and identifying early signs of common illnesses. Care plans should be flexible, adapting to the evolving needs of the child while ensuring family involvement throughout the process. Education for caregivers is crucial in promoting better health outcomes and preventing future complications.
Importance of Communication
Clear and compassionate communication plays a critical role in delivering effective care. Children may not always be able to express their symptoms or needs clearly, which makes it essential for caregivers and healthcare providers to be observant and attentive. Explaining procedures and treatment options in a way that is both understandable and reassuring can reduce anxiety and build a sense of security.
Common Conditions in Child Health Care
Children are susceptible to a variety of health conditions that differ significantly from those seen in adults. These conditions often require specific approaches to diagnosis, treatment, and ongoing care. Recognizing the most common issues in young patients allows healthcare providers to take appropriate steps in managing them and minimizing complications.
Respiratory infections are one of the most frequent concerns, including conditions such as asthma, pneumonia, and bronchitis. These illnesses can range from mild to severe and require careful monitoring of symptoms to ensure proper treatment. Additionally, gastrointestinal disorders, such as dehydration, gastroenteritis, and food allergies, are prevalent and often necessitate quick intervention to prevent further health issues.
Another common category of health concerns involves infectious diseases like chickenpox, measles, and ear infections. Vaccinations play a significant role in preventing many of these illnesses, but they still remain a source of concern for parents and caregivers. Proper diagnosis and early treatment are key to managing these conditions effectively.
Top Skills in Child Health Care to Master
To provide optimal care for young patients, there are several key skills that every healthcare professional should focus on mastering. These abilities are critical for assessing, diagnosing, and treating children, while ensuring comfort and safety throughout their care. From clinical techniques to effective communication, each skill plays a vital role in delivering high-quality service.
Below is a table outlining some of the most important skills in this field:
| Skill | Description |
|---|---|
| Assessment and Diagnosis | Accurately identifying symptoms, understanding growth milestones, and evaluating developmental progress. |
| IV Insertion and Fluid Management | Administering intravenous fluids and medications while minimizing discomfort and complications. |
| Family Education and Support | Providing caregivers with the knowledge and tools to manage their child’s health at home. |
| Effective Pain Management | Recognizing pain cues and implementing strategies to alleviate discomfort in children. |
| Emergency Response | Quickly assessing and providing interventions during urgent health situations. |
By mastering these core competencies, professionals can ensure they are fully equipped to care for young patients in any clinical setting, making a significant impact on both immediate and long-term health outcomes.
Important Topics to Focus on for Child Health Care Assessments
When preparing for assessments in the field of child health care, it’s essential to focus on the most relevant topics that are commonly tested. These areas encompass a wide range of knowledge, from understanding common illnesses to mastering specific clinical procedures. By familiarizing oneself with these key subjects, individuals can enhance their preparedness and confidently approach any evaluation.
Core Knowledge Areas
A strong grasp of developmental stages, common medical conditions, and pediatric pharmacology is vital. Professionals should be able to identify typical signs of illness and developmental delays, understand appropriate medication dosages, and offer guidance on preventive care. In addition, the ability to assess vital signs and interpret results accurately is crucial for effective decision-making.
Practical Application of Care Techniques
Equally important is mastering the practical application of various care techniques, including administering injections, managing hydration, and addressing emergencies. These skills are often evaluated through scenario-based questions that test the ability to respond effectively in real-life situations. Proficiency in these areas ensures that individuals are well-prepared to handle the dynamic nature of working with young patients.
How to Approach Child Health Care Case Studies
Case studies are an essential part of understanding real-world scenarios in the field of child health. These practical exercises allow individuals to apply their knowledge to solve problems, assess conditions, and make decisions that are critical for patient outcomes. Properly approaching case studies requires a combination of critical thinking, clinical knowledge, and effective problem-solving strategies.
Step-by-Step Analysis
Start by thoroughly reviewing the case details and identifying key information, such as the patient’s age, medical history, symptoms, and any relevant environmental factors. Focus on understanding the underlying issues presented in the case, whether they are related to chronic conditions, acute illnesses, or developmental concerns. This initial assessment will guide the direction of your treatment plan and recommendations.
Implementing a Comprehensive Care Plan
After identifying the key issues, create a comprehensive care plan that addresses the child’s immediate needs while considering long-term goals. This plan should incorporate not only medical treatments but also the roles of caregivers, necessary lifestyle changes, and any further diagnostic steps. Ensure that the approach is adaptable, as each child’s response to treatment may vary, and continuous evaluation is necessary for optimal outcomes.
Medication Dosage and Administration for Children
Administering the correct dosage of medication is a critical aspect of ensuring effective treatment for young patients. The process requires a precise understanding of drug types, appropriate dosages, and safe methods of administration. Children, depending on their age, weight, and health status, may require different approaches than adults, making it essential to follow proper guidelines to avoid potential complications.
Accurate dosing is crucial, as children are more vulnerable to side effects or overdoses due to their developing bodies. Healthcare providers must consider various factors, such as the child’s age, weight, and medical condition, when determining the appropriate medication and dosage. Below is a table highlighting key considerations for medication management in younger patients:
| Factor | Consideration |
|---|---|
| Age | Different age groups require specific dosing adjustments based on their developmental stage. |
| Weight | Medication dosages are often calculated based on the child’s weight to ensure accuracy. |
| Route of Administration | The method of delivering medication (oral, intravenous, etc.) affects absorption rates and efficacy. |
| Medical History | Pre-existing conditions and allergies must be considered to avoid adverse reactions. |
| Drug Interactions | Ensure that prescribed medications do not interact negatively with other treatments the child may be taking. |
By carefully evaluating these factors and adhering to recommended guidelines, healthcare providers can administer medications safely and effectively, minimizing risks and maximizing therapeutic outcomes for children.
Strategies for Effective Child Pain Management

Managing pain in young patients requires a nuanced approach that takes into account both their physical and emotional needs. Children may have difficulty expressing their discomfort, which makes it essential for healthcare providers to recognize non-verbal cues and adopt strategies that not only alleviate pain but also reduce anxiety and fear. A holistic approach, addressing both the cause and the experience of pain, is key to providing the most effective care.
One important strategy is the use of age-appropriate communication to understand the child’s pain level and ensure that the treatment approach is tailored to their needs. In addition to pharmacological interventions, non-pharmacological methods such as distraction, relaxation techniques, and comfort positioning can be incredibly effective in managing pain in children. It is also crucial to involve the child’s caregivers in the pain management process, as their presence can provide emotional support and contribute to the child’s sense of security.
By combining these strategies with a compassionate approach, healthcare providers can significantly improve the overall comfort and well-being of young patients while managing pain effectively.
Critical Procedures in Child Health Care Explained
In child health care, there are several vital procedures that require precise technique and a clear understanding of the patient’s needs. These procedures are fundamental in ensuring the safety, well-being, and comfort of young patients, especially during critical situations. Mastery of these procedures helps healthcare professionals respond effectively and efficiently to a variety of health challenges that children may face.
Essential Procedures for Immediate Care

Some procedures are performed in urgent situations and require quick, accurate actions to stabilize the child. These may include:
- Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation (CPR) for infants and children
- Intubation to secure the airway in severe respiratory distress
- IV insertion for fluid and medication administration
- Managing severe allergic reactions (e.g., using epinephrine)
Routine Procedures for Ongoing Care
Beyond emergencies, there are also procedures that are essential for ongoing care, such as:
- Monitoring and recording vital signs (heart rate, temperature, respiratory rate)
- Administering vaccines and immunizations
- Wound care and dressing changes for minor injuries
- Providing nutritional support through feeding tubes or intravenous nutrition
Understanding these procedures, practicing them under supervision, and knowing when to use them can significantly improve outcomes in young patients, making them a critical aspect of health care in children.
Developmental Milestones in Child Health Care

Tracking the progress of a child’s development is an essential part of ensuring their overall well-being. Health professionals monitor various milestones to assess whether a child is developing at a typical rate across multiple domains–physical, cognitive, emotional, and social. Identifying any delays or issues early on allows for prompt intervention and support to help the child reach their full potential.
Key Physical and Cognitive Milestones

Children undergo significant changes during their early years, with milestones varying depending on their age group. These milestones are generally categorized as:
- Physical Development: Gross and fine motor skills, such as crawling, walking, and hand-eye coordination.
- Cognitive Development: Early learning abilities, including object recognition, problem-solving skills, and language acquisition.
Social and Emotional Milestones
In addition to physical and cognitive development, emotional and social growth is equally important. These milestones help determine how children interact with others, regulate their emotions, and develop social bonds. Key milestones include:
- Social Skills: Interaction with peers, sharing, and understanding social cues.
- Emotional Development: Expression of emotions, forming attachments, and beginning to understand feelings.
Each milestone offers insights into a child’s growth trajectory, and any deviations from expected development should be addressed with appropriate care and support. This approach ensures that children receive the guidance they need for healthy development across all areas.
Common Child Health Emergencies and Responses
In the care of young patients, certain health emergencies can arise unexpectedly. These situations often require immediate intervention to stabilize the child and prevent long-term complications. Being prepared to respond to these emergencies is vital for ensuring the best outcomes. Recognizing common emergencies and knowing the appropriate actions to take can save lives and minimize distress for both the child and their family.
Some of the most frequent emergencies that may require urgent attention include:
- Respiratory Distress: Difficulty in breathing due to conditions like asthma or foreign object aspiration. Immediate action includes clearing the airway and administering oxygen.
- Severe Allergic Reactions: Anaphylaxis can occur due to insect stings, food allergies, or medications. The use of epinephrine and ensuring a clear airway is critical.
- Fever and Sepsis: High fever, particularly in infants, can indicate an infection. Prompt treatment with fluids and antibiotics may be necessary.
- Head Injuries: Trauma to the head, such as a fall, can lead to concussion or bleeding. Monitoring for signs of brain injury and seeking medical attention is essential.
- Choking: Blockage of the airway can occur when children put objects in their mouth. The Heimlich maneuver or back blows may be required to clear the obstruction.
In each of these situations, it is crucial to remain calm and take swift action. Immediate intervention can often make the difference between a full recovery and long-term complications. Healthcare providers must be equipped with the knowledge and skills to recognize signs of distress early and act effectively.
Pediatric Assessment Techniques for Nurses

Accurate assessment of a child’s health is fundamental in providing quality care. Effective evaluation involves not only recognizing physical symptoms but also understanding developmental stages and behavioral cues that can offer insight into the child’s overall condition. Mastery of these techniques enables healthcare providers to make informed decisions and tailor interventions accordingly.
Observation and Physical Examination

In the assessment of a child, observation plays a crucial role. A nurse should observe the child’s general appearance, behavior, and mobility. Key aspects include:
- General Appearance: Observing the child’s skin color, posture, and responsiveness to the environment.
- Behavioral Cues: Noting signs of distress, irritability, or lethargy, which can indicate pain or illness.
- Physical Examination: Assessing vital signs, auscultating lung and heart sounds, and checking reflexes or muscle tone for abnormalities.
Developmental and Cognitive Assessment

Beyond physical observations, it is also essential to evaluate developmental progress. Healthcare providers assess:
- Motor Skills: Evaluating whether the child can perform age-appropriate tasks like sitting, walking, or fine motor skills.
- Cognitive Function: Assessing the child’s ability to communicate, recognize objects, or follow instructions.
By integrating these techniques, healthcare providers can better understand the child’s health status and detect potential issues early. This comprehensive approach is key to ensuring optimal care for young patients.
Understanding Child Nutrition and Growth
Proper nutrition is essential in the early stages of life, as it lays the foundation for healthy development and long-term well-being. Adequate intake of nutrients supports growth, cognitive development, and the functioning of vital organs. A balanced diet tailored to a child’s age and individual needs is crucial for ensuring they reach their growth potential.
Key Components of Child Nutrition
Children require a variety of nutrients, each serving a specific function to support their growth and development. These include:
- Proteins: Important for tissue growth and repair, particularly in the developing muscles and organs.
- Carbohydrates: Provide energy for physical activity and brain function, especially important as children become more active.
- Fats: Essential for brain development, hormone production, and absorption of fat-soluble vitamins.
- Vitamins and Minerals: Vital for immune function, bone health, and other bodily processes. Calcium, iron, and vitamin D are particularly important during the growing years.
Growth Patterns and Monitoring

Growth in children follows certain patterns, with changes in height, weight, and body composition occurring at different rates depending on age. Regular monitoring of growth metrics helps identify potential health concerns early on. Healthcare providers track these changes using growth charts to ensure that children are developing according to their expected milestones.
Understanding the relationship between nutrition and growth is fundamental to promoting optimal health outcomes. Proper dietary habits not only support immediate health but also influence the child’s future development and disease prevention.
Role of Family in Pediatric Care
Family involvement is a critical component in the care and recovery of children, as they are often the primary source of emotional and physical support. The relationship between healthcare providers and families plays an essential role in ensuring a child’s well-being, both in the hospital setting and at home. Families provide valuable insights into the child’s behavior, preferences, and medical history, which can greatly enhance the quality of care provided.
Families help create a supportive and familiar environment that can ease a child’s anxiety during treatment. They also play a key role in the child’s recovery process, following treatment plans and providing emotional comfort. Involving family members in decision-making processes empowers them, fostering trust and cooperation between the caregivers and healthcare team.
In addition to emotional support, family members are often involved in the daily care routine, administering medications, ensuring proper nutrition, and promoting rehabilitation. This close collaboration allows for a more holistic approach to care and strengthens the child’s overall health outcomes.
Preventive Care in Pediatric Care

Preventive care plays a crucial role in promoting long-term health and well-being in children. By focusing on early detection and prevention, healthcare providers can reduce the risk of chronic conditions, improve quality of life, and support healthy development. Proactive measures such as vaccinations, regular screenings, and health education help build a foundation for a healthier future.
Some key aspects of preventive care for children include:
- Immunizations: Vaccinations are essential in protecting children from various contagious diseases, ensuring both individual and community health.
- Routine Screenings: Regular check-ups and screenings help detect early signs of developmental delays, vision or hearing problems, and other health issues that may require intervention.
- Healthy Lifestyle Promotion: Encouraging physical activity, a balanced diet, and adequate sleep helps prevent obesity, diabetes, and other lifestyle-related conditions.
- Parental Guidance: Educating parents on the importance of health habits, safety practices, and mental well-being is vital in establishing positive routines at home.
By integrating these strategies into regular care practices, healthcare providers can reduce the occurrence of preventable diseases and conditions, setting the stage for children to grow and thrive in a healthy environment.
Ethical Considerations in Pediatric Care
Providing care to young patients presents unique ethical challenges that require thoughtful consideration. These challenges arise from the need to balance the child’s best interests with the rights and decisions of the parents or guardians. Healthcare providers must navigate complex situations where the child’s capacity for understanding may be limited, and the decisions made can significantly impact their future health and well-being.
Key ethical considerations include:
- Informed Consent: In pediatric care, obtaining consent involves clear communication with parents or legal guardians, while also considering the child’s understanding and involvement in the decision-making process.
- Confidentiality: Protecting a child’s privacy is essential, even though parents typically have access to their child’s health information. Providers must ensure that sensitive information is shared only with authorized individuals.
- Best Interest of the Child: Healthcare decisions should prioritize the child’s well-being, taking into account both medical needs and the potential impact on their development and quality of life.
- Autonomy and Respect: As children grow, they should be gradually involved in decisions about their care, respecting their developing autonomy while still considering the guidance of their caregivers.
- End-of-Life Decisions: When faced with serious illnesses, healthcare providers must navigate difficult decisions regarding treatment options, balancing life-sustaining interventions with the wishes of the family and the child’s prognosis.
By addressing these ethical concerns with sensitivity and care, healthcare professionals can ensure that they uphold the dignity and rights of both the child and their family while providing the best possible care.