
In any competitive field, understanding key principles and frameworks is essential for success. Developing the ability to address various challenges efficiently requires a solid grasp of fundamental concepts and techniques. This section focuses on essential topics that help prepare for evaluations in business strategy settings.
Familiarity with real-world scenarios is crucial when tackling theoretical problems. The ability to analyze different situations, assess strategies, and provide insightful recommendations is often tested. Mastering these elements will enable individuals to approach tasks confidently and demonstrate their understanding in practical applications.
Strategic planning, market analysis, and competitive positioning are some of the core areas that candidates are expected to be proficient in. By honing skills in these domains, one can navigate complex questions with ease and accuracy, ensuring a high level of performance.
Marketing Management Sample Exam Questions
In any assessment focusing on business strategy, it is important to understand the types of scenarios that might be presented. The goal is to evaluate one’s ability to solve complex problems and make informed decisions. Understanding the structure of tasks can greatly improve preparedness for such evaluations.
Typical challenges may involve analyzing a company’s positioning within a competitive landscape, evaluating customer behavior patterns, or making strategic recommendations based on available data. Each task requires a combination of theoretical knowledge and practical problem-solving skills.
Additionally, participants may encounter exercises that test their ability to develop coherent plans and strategies aimed at addressing specific business challenges. These tasks often require clear reasoning, critical thinking, and the application of industry best practices to achieve optimal results.
Understanding Key Marketing Management Concepts
To tackle complex scenarios effectively, it’s essential to grasp the foundational principles that drive strategic decisions. These core ideas lay the groundwork for developing effective strategies, managing resources efficiently, and meeting organizational goals. A strong understanding of these concepts enhances one’s ability to approach various tasks with confidence and clarity.
Core Elements in Strategic Planning
Strategic planning encompasses a variety of activities aimed at identifying objectives, formulating methods to achieve them, and evaluating the results. Key areas include identifying target audiences, choosing the right approaches for growth, and understanding competitive dynamics. Mastering these elements is crucial for shaping successful strategies.
Importance of Consumer Insights
Analyzing consumer behavior and preferences is a fundamental aspect of creating tailored approaches. By understanding what drives consumer choices, businesses can design more effective strategies that resonate with their audience. This understanding leads to better customer retention and acquisition rates.
| Concept | Description | Application |
|---|---|---|
| Target Audience | Identifying specific groups of potential customers | Improves product relevance and customer engagement |
| Competitive Analysis | Evaluating strengths and weaknesses of competitors | Helps develop more effective differentiation strategies |
| Resource Allocation | Distributing resources to maximize outcomes | Ensures efficient use of budget and personnel |
Common Marketing Strategies in Exams

When preparing for assessments related to business planning and strategy, understanding key approaches used to achieve organizational success is crucial. Often, these strategies focus on how businesses position themselves in competitive markets, reach their target audiences, and differentiate their offerings. Recognizing these common tactics will help students effectively respond to related tasks.
One common strategy involves segmentation, where businesses divide a larger market into smaller groups based on shared characteristics. This allows companies to tailor their offerings to specific needs, improving customer satisfaction and increasing market share. Another prevalent approach is differentiation, where companies seek to make their products or services stand out from competitors by emphasizing unique features or superior quality.
Cost leadership is also widely discussed. This strategy focuses on becoming the lowest-cost provider in a particular market segment, often through economies of scale or operational efficiencies. By reducing costs, businesses can offer competitive pricing, attracting a larger customer base without sacrificing profitability.
Preparing for Marketing Analysis Questions
Effective preparation for business analysis tasks requires an understanding of how to evaluate data, interpret market trends, and make strategic decisions based on findings. Developing these skills enables individuals to respond to complex scenarios with logical reasoning and evidence-based conclusions. Being able to identify key patterns and insights is crucial when tackling analytical challenges.
Key Areas to Focus On
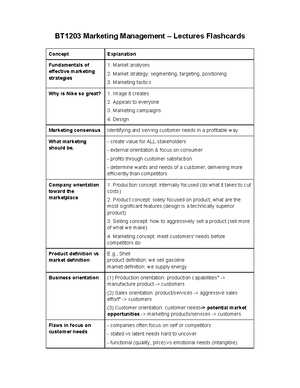
Familiarity with various analytical frameworks and tools is essential. These are often used to assess different aspects of business performance, including consumer behavior, market trends, and competitive positioning. Some of the most important areas to focus on include:
- SWOT Analysis: Understanding the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats of a business.
- PESTEL Analysis: Analyzing political, economic, social, technological, environmental, and legal factors that impact an organization.
- Competitive Analysis: Identifying key competitors and evaluating their strategies to understand how to outperform them.
Approach to Data Interpretation
When approaching business data, it is essential to be able to identify the most relevant information and draw meaningful conclusions. This involves evaluating trends, understanding consumer needs, and forecasting potential outcomes. A few tips for interpreting data effectively include:
- Ensure all data sources are credible and relevant to the task.
- Look for patterns and correlations that could inform strategic decisions.
- Use quantitative and qualitative data to provide a comprehensive view of the market.
How to Approach Marketing Case Studies

Case studies often present real-world scenarios that require a thoughtful analysis of business challenges and the application of relevant strategies. These tasks assess one’s ability to evaluate a situation, identify critical issues, and propose practical solutions. A structured approach is essential to effectively address these complex tasks.
When faced with a case study, the first step is to thoroughly read and understand the scenario. It’s important to identify key factors that will influence the decision-making process. This includes recognizing the goals, challenges, available resources, and potential obstacles that the company may face. Once these elements are identified, it becomes easier to formulate a strategy.
Steps to Follow
To approach a case study methodically, consider following these steps:
- Identify the problem: Understand the primary challenge or issue the company is facing.
- Analyze available data: Review any provided information, including market conditions, customer insights, and financial data.
- Evaluate alternatives: Consider multiple strategies or actions that could address the issue at hand.
- Develop a solution: Choose the best course of action based on the analysis, and justify your decision with solid reasoning.
- Consider implementation: Think about how the solution can be effectively implemented, including required resources and potential risks.
Best Practices for Success
To ensure a strong response to a case study, consider these best practices:
- Stay organized and present your ideas clearly and logically.
- Support your solution with data or evidence wherever possible.
- Be mindful of potential risks or limitations in your proposed solution.
- Focus on practical, feasible recommendations that align with the company’s capabilities and objectives.
Evaluating Consumer Behavior in Exams
Understanding how individuals make purchasing decisions and how they respond to different influences is a crucial aspect of business strategy. When preparing for assessments that explore these topics, it’s important to grasp the underlying psychological and social factors that drive consumer choices. This knowledge enables one to analyze behavior patterns and predict how consumers will react to various market stimuli.
In assessments, tasks related to consumer behavior often require identifying the factors influencing purchasing decisions, such as cultural, social, or personal elements. Understanding these influences allows for the development of effective strategies tailored to target audiences.
| Factor | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Cultural | The shared values, customs, and traditions that shape consumer preferences. | A family-oriented ad campaign targeting specific cultural values. |
| Social | Influences from groups, peers, and social networks that affect decision-making. | Peer pressure influencing consumers to purchase a trending product. |
| Personal | Individual characteristics such as lifestyle, income, and occupation that impact buying behavior. | A high-income individual choosing luxury products based on personal taste. |
By analyzing these factors, one can better understand how consumers make choices and tailor strategies that align with these insights. A strong ability to evaluate these elements will contribute to success in answering related tasks.
Important Theories for Marketing Management
In business strategy, various theoretical frameworks guide decision-making and influence how organizations interact with consumers. Understanding these key concepts is essential for addressing challenges and creating effective strategies. These theories help professionals analyze consumer behavior, identify opportunities, and shape overall business direction.
Key Frameworks to Master
Several important theories are commonly used in business strategy to explain consumer behavior and market dynamics. Familiarity with these models is crucial for applying relevant approaches in real-world situations:
- The Product Life Cycle (PLC) Theory: This model explains the stages a product goes through from introduction to decline, helping businesses plan marketing strategies at each phase.
- Porter’s Five Forces: A framework for analyzing the competitive forces in an industry, helping companies assess the strength of their market position.
- Segmentation, Targeting, and Positioning (STP): A process for dividing a market into smaller segments, targeting specific groups, and positioning products to appeal to those groups effectively.
Psychological and Behavioral Insights
Several theories also explore the psychological aspects of consumer behavior, offering insights into how consumers make purchasing decisions:
- Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs: This theory suggests that individuals prioritize their needs in a hierarchical order, starting with basic needs and moving toward self-actualization.
- The Theory of Planned Behavior: A psychological model that predicts how individuals’ intentions and attitudes influence their actions, particularly in the context of purchasing decisions.
- Buyer Decision Process: This model outlines the stages a consumer goes through when making a purchase, from problem recognition to post-purchase behavior.
Mastering these theories allows professionals to approach business challenges with a deeper understanding of both market forces and consumer psychology, providing a solid foundation for strategic decisions.
Marketing Research and Data Interpretation
In any business strategy, gathering relevant information and analyzing it effectively is key to making informed decisions. Research provides valuable insights into consumer preferences, market trends, and competitive forces. Proper data interpretation helps businesses identify opportunities and potential challenges, leading to more effective decision-making.
To analyze data accurately, it is essential to understand various research methods, such as surveys, focus groups, and observational studies. These approaches allow businesses to collect qualitative and quantitative data that can provide a clearer picture of consumer behavior and market dynamics. Once the data is gathered, interpreting it correctly becomes the next critical step.
Effective interpretation involves identifying patterns, trends, and anomalies within the data. It requires an understanding of statistical tools and techniques to analyze large datasets and draw actionable conclusions. Moreover, it’s important to consider external factors, such as economic conditions or social trends, that could influence the data.
By mastering the art of research and data interpretation, companies can stay ahead of the competition, improve their products or services, and develop targeted strategies that resonate with their customers.
Effective Time Management During Exams

When faced with time-sensitive tasks, organizing and allocating time effectively is crucial to performing well. Proper time management allows individuals to prioritize tasks, minimize stress, and ensure all areas are addressed within the given time frame. It’s essential to approach these challenges with a structured strategy to maximize efficiency.
Time management during assessments requires careful planning and discipline. Instead of rushing through questions or overthinking one section, it’s important to allocate time based on the difficulty of the task and the weight of each question. By managing time effectively, you can ensure that each part of the test receives appropriate attention.
Key Strategies for Success
To optimize time during an assessment, consider these practical tips:
- Prioritize tasks: Identify the most time-consuming or complex questions and tackle them first, ensuring you have sufficient time for each section.
- Allocate specific time limits: Set a time limit for each question or task. Use a watch or timer to track your progress and stay on schedule.
- Stay focused: Avoid distractions and keep your attention on the task at hand. This will help you maintain a steady pace and avoid wasting precious minutes.
Final Tips for Efficient Time Use

To further enhance time efficiency during assessments, consider the following recommendations:
- Practice under timed conditions: Simulate test scenarios in advance to build your speed and familiarity with time constraints.
- Review your answers: If time permits, allocate a few minutes at the end to review your answers and correct any mistakes.
With practice and discipline, managing time effectively during assessments can greatly improve performance and reduce anxiety.
Developing Successful Marketing Plans
Creating an effective plan is essential for achieving business goals and reaching target audiences. A well-structured strategy helps organizations align their resources, set clear objectives, and implement tactics that drive success. By focusing on key elements, businesses can develop comprehensive approaches that ensure long-term growth and sustainability.
The first step in crafting a successful strategy is understanding the market landscape, identifying the audience, and analyzing competitors. This research forms the foundation for making informed decisions and selecting the best tactics. Additionally, clear goals and measurable objectives are necessary to track progress and determine the plan’s effectiveness.
To build a solid plan, it’s important to incorporate the following elements:
- Market Research: Gather insights about customer preferences, trends, and challenges to ensure the strategy is relevant.
- Target Audience: Define the specific groups you want to reach and tailor messages to their needs.
- Positioning: Establish a unique value proposition that differentiates your product or service from competitors.
- Tactics: Choose the most effective channels and activities to execute the strategy, such as advertising, promotions, or content creation.
- Budget: Allocate resources wisely to ensure all initiatives are supported and costs are controlled.
- Metrics: Define key performance indicators (KPIs) to measure the success and adjust the plan as needed.
By carefully considering these components, businesses can develop a strategy that not only meets short-term goals but also positions them for long-term success. Regular evaluation and adjustments are crucial to ensure the plan remains aligned with changing market dynamics and business priorities.
Focus on SWOT Analysis in Marketing
Understanding the internal and external factors influencing a business is essential for developing a comprehensive strategy. One of the most effective tools for this is the SWOT framework, which helps identify strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats that impact decision-making. By utilizing this approach, companies can better assess their position in the market and plan accordingly.
The first step in conducting a SWOT analysis is identifying the internal strengths and weaknesses. Strengths could include a strong brand, efficient processes, or loyal customers. On the other hand, weaknesses might relate to gaps in resources, poor customer perception, or operational inefficiencies. Recognizing these internal factors is crucial for improving the business’s overall effectiveness.
Next, the analysis shifts to examining external factors such as opportunities and threats. Opportunities could arise from emerging market trends, new technologies, or changes in consumer behavior. Conversely, threats may include economic downturns, competitive pressures, or regulatory changes. Understanding these elements allows a business to capitalize on favorable conditions while mitigating potential risks.
By combining insights from both internal and external factors, businesses can create strategies that leverage their strengths, address weaknesses, exploit opportunities, and prepare for threats. Regularly updating a SWOT analysis helps companies stay adaptive and proactive in a constantly evolving marketplace.
Addressing Product Life Cycle Questions

The journey of a product from its introduction to its eventual decline is crucial to understand for effective business strategy. Recognizing the various stages a product goes through can help businesses make informed decisions about resource allocation, marketing tactics, and future development. Whether a product is in its growth phase or nearing the end of its life cycle, each stage requires unique strategies to maximize profitability and sustain market relevance.
Understanding the product life cycle helps in addressing specific challenges associated with each stage. By analyzing customer demands, competition, and market trends, companies can tailor their approach to ensure continued success or smooth phase transitions.
Key Stages in the Product Life Cycle
Here are the typical stages a product goes through, each requiring different strategies:
- Introduction: At this stage, the focus is on creating awareness and gaining initial customers. Heavy investment in advertising and promotion may be necessary.
- Growth: As the product gains traction, businesses focus on expanding their market share, optimizing distribution channels, and increasing brand loyalty.
- Maturity: In this stage, competition increases. The focus shifts to differentiation, brand positioning, and maintaining customer loyalty.
- Decline: When the product reaches its decline phase, businesses often consider reducing costs, discontinuing the product, or finding ways to revitalize it through innovation.
Strategies for Each Stage
Tailoring strategies to the specific needs of each phase is essential for prolonging a product’s lifecycle. Some strategies include:
- Introduction Phase: Focus on educating customers and building a solid brand foundation.
- Growth Phase: Enhance product visibility, expand reach, and ensure scalability.
- Maturity Phase: Diversify offerings, use loyalty programs, and improve customer experience to maintain market position.
- Decline Phase: Consider product diversification, repositioning, or gradually phasing out the product while preparing for new innovations.
By carefully analyzing the product life cycle and adjusting strategies accordingly, businesses can ensure their products remain competitive and aligned with market demands, optimizing profits throughout their lifespan.
Branding and Positioning in Exam Papers
Understanding the concept of establishing a unique identity in the market is crucial for any business. In an academic context, questions related to how brands differentiate themselves from competitors and carve out a distinct position in the consumer’s mind are essential. These concepts, often discussed in case studies and theoretical problems, help in evaluating a company’s approach to capturing market share and sustaining consumer loyalty.
At the core of brand development is the process of positioning, which determines how a product or service is perceived in the minds of potential customers. This involves emphasizing particular attributes or values that resonate with the target audience, setting the brand apart from others. When approached in academic assessments, questions often challenge students to demonstrate an understanding of these strategies and apply them in real-world scenarios.
Key Elements of Branding
Several factors contribute to the strength of a brand. These include the following:
- Brand Identity: The visual elements, name, and messaging that distinguish the brand from others.
- Brand Loyalty: The emotional connection and repeat patronage of customers towards a particular brand.
- Brand Image: How a brand is perceived by consumers, shaped by experiences, reputation, and marketing efforts.
Effective Positioning Strategies
For brands to succeed, they must occupy a distinct position in the market. Some strategies include:
- Cost Leadership: Offering products at the lowest price while maintaining quality.
- Differentiation: Emphasizing unique features or benefits that set the brand apart from competitors.
- Focus Strategy: Targeting a specific niche market to cater to unique customer needs.
When answering questions on this topic in exams, it’s important to analyze how these strategies are implemented by brands in different industries and evaluate their effectiveness in achieving long-term success.
Pricing Strategies and Their Implications
Setting the right price for a product or service plays a crucial role in shaping its success in the market. Different approaches to pricing reflect varying business objectives, from maximizing profits to building customer loyalty. The strategic decisions surrounding pricing are often influenced by factors such as competition, market demand, and customer perceptions of value. Understanding the implications of these choices is essential for businesses aiming to remain competitive and meet their financial goals.
Each pricing strategy carries its own advantages and challenges. The right choice depends on the target market, product type, and overall business strategy. When analyzing these strategies in academic contexts, it is important to consider both short-term and long-term outcomes, including how pricing affects consumer behavior, market positioning, and profitability.
Common Pricing Approaches
Businesses often adopt a variety of pricing methods to achieve their desired outcomes. Here are some common strategies:
- Penetration Pricing: Setting a low initial price to quickly attract customers and gain market share. This approach is often used in competitive markets or when launching a new product.
- Skimming Pricing: Setting a high initial price and gradually lowering it over time. This strategy is often used for innovative products or those with little competition.
- Value-Based Pricing: Pricing based on the perceived value of a product to the customer, rather than on the cost of production or market conditions.
- Psychological Pricing: Using pricing techniques, such as setting a price just below a round number (e.g., $9.99 instead of $10), to influence consumer behavior.
Implications of Pricing Decisions
The implications of pricing decisions are far-reaching. Choosing the wrong pricing strategy can lead to lost revenue, damaged brand perception, or missed opportunities. For instance:
- Customer Perception: A high price can signal quality, while a low price may attract bargain shoppers but risk diluting the brand.
- Competitive Positioning: Pricing too high may make it difficult to compete with established players, while pricing too low could undermine a company’s profitability.
- Profitability: Prices must cover costs and deliver sufficient margin, ensuring the business remains financially viable.
When discussing pricing strategies in academic settings, it’s important to evaluate how each strategy impacts not only the bottom line but also consumer trust and brand image over time.
Analyzing Market Segmentation Questions

When evaluating how to divide a broad consumer or business market into smaller, more manageable groups, it is essential to understand the factors that influence this process. Effective segmentation involves categorizing the market based on shared characteristics, needs, and behaviors. The primary goal is to identify groups of customers who are likely to respond similarly to specific offerings. In academic discussions, understanding the various techniques and methodologies for segmenting markets is crucial for making strategic decisions in business environments.
Segmentation is not only about dividing markets, but also about selecting the right segments to target. This involves evaluating the potential of each segment in terms of profitability, reach, and alignment with the company’s overall objectives. Analyzing segmentation strategies in academic contexts often includes examining the key criteria used to group consumers and the practical implications of these choices.
Types of Market Segmentation
Market segmentation can be based on various characteristics. Below are some common methods:
- Demographic Segmentation: Categorizing consumers based on factors like age, income, gender, education, or occupation.
- Geographic Segmentation: Grouping customers based on location, such as country, region, city, or climate.
- Behavioral Segmentation: Dividing the market according to consumer behaviors, including purchasing patterns, brand loyalty, or product usage.
- Psychographic Segmentation: Grouping individuals based on lifestyle, personality traits, values, and interests.
Evaluating the Effectiveness of Segmentation
Once a market is segmented, businesses must analyze the potential of each segment and determine its feasibility. The effectiveness of segmentation strategies can be measured by factors such as:
| Factor | Importance |
|---|---|
| Reach | How easily a segment can be accessed through marketing channels. |
| Profitability | The financial potential of the segment based on its size, spending power, and purchasing habits. |
| Consistency | The uniformity of behaviors and needs within the segment, ensuring the market responds similarly to marketing strategies. |
| Alignment with Brand | The degree to which the segment’s preferences align with the company’s product offerings or mission. |
In the context of academic analysis, it’s important to assess how well a business can serve the identified segments. Companies must also consider whether the segments will evolve over time and how the segmentation strategy will need to adapt accordingly.
Understanding Marketing Metrics and KPIs

To make informed decisions and assess the performance of business strategies, it is vital to measure key factors that reflect the success or areas for improvement. These indicators help evaluate the effectiveness of various initiatives, providing insights that guide future actions. Knowing how to select and interpret the right metrics is crucial for understanding the impact of efforts and ensuring that objectives are being met.
In any strategic approach, it’s essential to identify the most relevant indicators. These include quantitative data points that reveal customer engagement, sales performance, and overall business health. By tracking these measures, organizations can fine-tune their strategies to optimize results and achieve set goals.
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
KPIs are specific, measurable elements that align directly with the goals of a business. They are used to assess performance and determine whether objectives are being met. Common KPIs include:
- Conversion Rate: The percentage of visitors who take a desired action, such as making a purchase or signing up for a service.
- Customer Retention Rate: A measure of how well a business keeps its customers over time.
- Return on Investment (ROI): A metric that evaluates the profitability of a particular investment or strategy.
- Customer Lifetime Value (CLV): The total revenue a business can expect from a single customer throughout their relationship.
Common Metrics for Performance Evaluation
In addition to KPIs, several other metrics are valuable for analyzing the effectiveness of business activities. These include:
- Website Traffic: Measures the number of visitors to a website, indicating interest in the brand or product.
- Engagement Rate: Tracks interactions with content, such as likes, shares, and comments, reflecting the level of audience involvement.
- Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC): The cost associated with acquiring a new customer, including marketing and sales expenses.
- Churn Rate: The percentage of customers who stop using a product or service within a given period.
By tracking these metrics and KPIs, organizations can better understand how well their efforts align with their goals, allowing for timely adjustments to improve performance and optimize strategies.
Tips for Writing Strong Responses
Crafting well-structured, thoughtful responses is key to demonstrating your understanding of key concepts and your ability to apply them. A strong reply not only addresses the main points but also showcases your analytical skills and ability to communicate effectively. By following a few essential strategies, you can ensure that your responses are clear, concise, and compelling.
Key Strategies for Effective Responses
- Understand the Prompt: Carefully read the prompt to ensure you fully comprehend the question. Focus on what is being asked and identify key terms to guide your response.
- Use Clear Structure: Organize your thoughts logically. Start with an introduction that outlines your main ideas, followed by body paragraphs that provide detailed explanations, and finish with a strong conclusion summarizing your key points.
- Be Concise: Avoid unnecessary information or overly long explanations. Keep your response focused on the topic and present your points as clearly and succinctly as possible.
- Support Your Claims: Whenever possible, back up your points with examples, data, or real-world applications. This will strengthen your argument and show that you can apply theoretical knowledge to practical situations.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Vague Answers: Avoid generalizations. Ensure your points are specific and relevant to the question.
- Over-complicating Responses: Keep your answers simple and focused. Don’t try to include too many ideas in one response.
- Lack of Organization: Disorganized answers can be difficult to follow. Always structure your response in a clear, logical way.
- Ignoring the Question: Stay on topic. If the question asks for an analysis or evaluation, make sure your response addresses those aspects directly.
By applying these techniques, you can craft strong, persuasive responses that demonstrate both your knowledge and your ability to communicate effectively. This approach will help you excel in your evaluations and showcase your expertise in the subject matter.