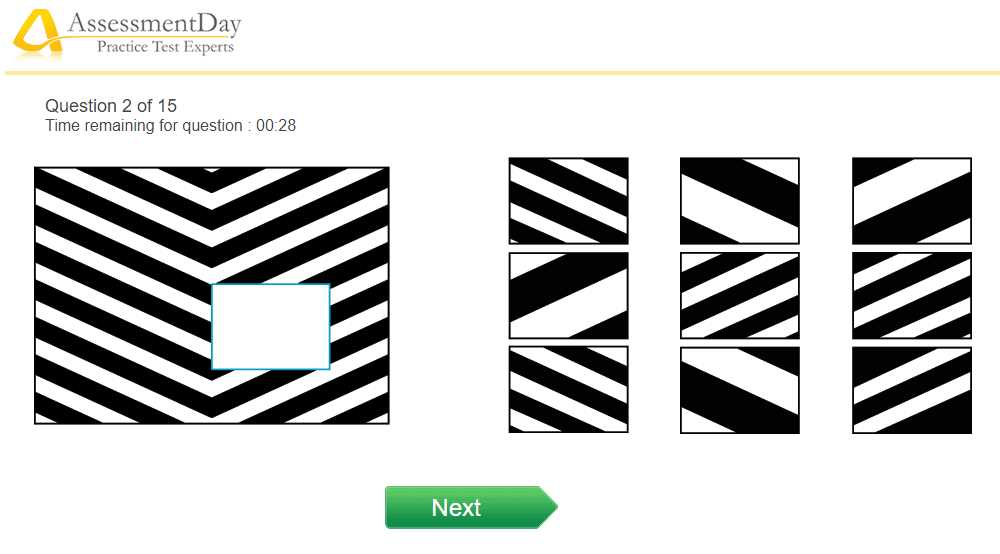
Understanding complex problems that require sharp reasoning is crucial for academic achievements. These challenges test your ability to think critically, make quick decisions, and apply knowledge effectively under time pressure. By preparing for such tests, you can enhance your mental agility and problem-solving capabilities.
Preparation plays a significant role in improving your performance. Familiarity with various problem types allows you to develop efficient strategies, manage time effectively, and reduce errors. Success depends not only on raw intelligence but also on the ability to approach difficult tasks systematically and calmly.
To excel in these assessments, it is essential to practice regularly and sharpen your analytical skills. Breaking down complicated tasks into smaller, manageable parts enables you to stay focused and organized, ultimately leading to better outcomes. By honing these skills, you’ll build confidence and prepare yourself for a variety of challenges in both academic and professional environments.
Mastering Reasoning Challenge Preparation
Effective preparation for intellectual assessments requires more than just memorizing facts. It involves developing a methodical approach to solving problems, improving analytical abilities, and enhancing mental flexibility. Through consistent practice, you can refine your skills and increase your chances of success in high-pressure situations.
Key Elements of Effective Preparation
- Understanding Problem Types – Familiarize yourself with different categories of challenges, such as pattern recognition, deductive reasoning, and sequence puzzles.
- Practice Regularly – Consistent practice is crucial. Working through a variety of exercises sharpens your ability to identify patterns and apply logical steps quickly.
- Time Management – Develop strategies for solving problems efficiently, allowing you to manage time effectively during an actual assessment.
- Critical Thinking – Strengthen your ability to approach problems from different angles and question assumptions.
Recommended Strategies for Success
- Start with Simpler Tasks – Begin with easier exercises to build confidence and gradually progress to more complex scenarios.
- Analyze Mistakes – Review incorrect solutions to identify patterns in your thought process and avoid making the same errors again.
- Break Down Complex Problems – Divide complicated challenges into smaller, more manageable parts to make them easier to tackle.
- Stay Calm Under Pressure – Practice staying focused and composed when faced with difficult problems, as stress can cloud judgment.
Key Concepts in Reasoning Challenges
To perform well in assessments that test cognitive abilities, it’s essential to grasp the underlying principles and techniques that govern problem-solving. A deep understanding of core ideas will allow you to approach tasks with clarity and confidence, making it easier to navigate complex scenarios and find solutions efficiently.
Fundamental Principles to Understand
- Deductive Reasoning – The process of drawing specific conclusions based on general principles. This skill is essential for making valid inferences and solving problems systematically.
- Inductive Reasoning – Making generalizations based on specific observations. This skill helps in recognizing patterns and predicting outcomes.
- Pattern Recognition – Identifying repeated sequences or trends in a set of data. Recognizing patterns aids in simplifying complex problems and predicting future results.
- Abstract Thinking – The ability to think beyond the immediate and consider different perspectives, which helps in solving unconventional problems.
Essential Techniques for Success

- Elimination Method – Narrowing down options by systematically ruling out incorrect choices, making it easier to focus on the most likely solutions.
- Logical Sequences – Understanding how one step leads to another. This approach helps you stay organized and approach problems in a logical, step-by-step manner.
- Working with Variables – Using symbols or placeholders to represent unknown values. This allows you to create more flexible solutions and model different scenarios.
- Critical Evaluation – Constantly assessing the validity of your reasoning process. Questioning assumptions ensures you’re on the right track and helps you avoid logical errors.
How to Approach Logical Reasoning
When faced with tasks that test your reasoning abilities, it’s crucial to adopt a methodical and structured approach. This allows you to break down complex challenges into manageable steps, minimizing errors and improving your efficiency. A well-planned strategy not only helps in finding the right solution but also in navigating through difficult scenarios with confidence.
Steps for Effective Problem-Solving
- Understand the Problem – Carefully read through the task to ensure you comprehend what is being asked. Pay attention to details and identify the key elements that need to be addressed.
- Identify Relevant Information – Filter out unnecessary data and focus on the critical points that will lead you to the solution. This helps in avoiding distractions.
- Develop a Plan – Map out a clear approach or sequence of steps. Organizing your thoughts beforehand makes it easier to tackle the task methodically.
- Consider Multiple Approaches – Think about different strategies or solutions. This allows you to select the most effective one and improves your flexibility in problem-solving.
Common Techniques to Use
- Start Simple – Begin with straightforward elements of the problem to build momentum and gradually move towards more complex parts.
- Eliminate Irrelevant Options – Remove clearly incorrect possibilities to narrow down your choices, making it easier to focus on the most plausible solutions.
- Use Visual Aids – Drawing diagrams, charts, or tables can help organize information more clearly and reveal patterns that might be missed in text alone.
- Check for Consistency – Ensure that your conclusions follow logically from the premises, and that all steps align with the problem’s parameters.
Common Types of Reasoning Challenges
Assessments designed to test cognitive abilities often involve a variety of problem types, each requiring different approaches and strategies. Understanding the most common formats can help you prepare more effectively and increase your chances of success. By recognizing patterns in the problems, you can quickly identify the appropriate method for solving them.
Frequently Encountered Problem Types
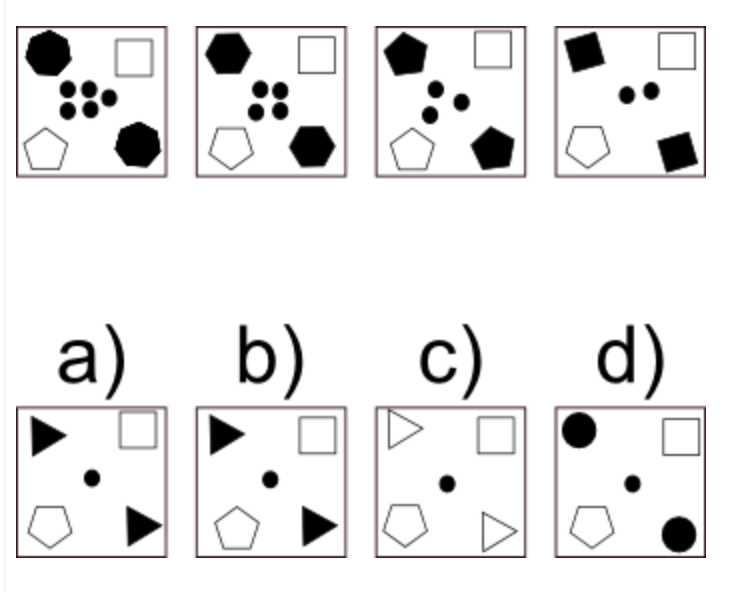
- Pattern Recognition – Tasks that require identifying sequences or repeated elements in a set of data. These are common in tasks related to numbers, shapes, or letters.
- Deductive Reasoning – Problems where conclusions must be drawn from general statements or premises. These require careful evaluation of given information to reach a logically sound conclusion.
- Inductive Reasoning – These challenges involve making generalizations based on specific observations or examples. The goal is to detect underlying trends or patterns.
- Classification – Organizing a set of items or concepts into groups based on shared characteristics or criteria. These tasks test your ability to identify relationships and categorize information accurately.
- Analogies – Comparing two sets of items or concepts and identifying relationships between them. These problems often require identifying logical parallels or connections.
Additional Types of Challenges
- Mathematical Reasoning – Tasks that involve using mathematical principles, such as algebra, geometry, or number theory, to find solutions or make predictions.
- Verbal Reasoning – Problems that test your ability to understand, interpret, and analyze written information. These tasks often require drawing inferences or evaluating arguments.
- Spatial Reasoning – Challenges that involve visualizing objects, their positions, or their movements in space. These tasks are common in puzzles that deal with shapes or diagrams.
- Logical Sequences – Tasks where you must predict the next element in a series based on a pattern. These problems test your ability to recognize consistent progressions.
Effective Strategies for Solving Reasoning Problems
Approaching complex tasks that require sharp thinking demands more than just understanding the surface-level details. It’s about employing methods that help break down challenges into simpler steps, reducing cognitive overload and improving accuracy. With the right strategies, you can solve difficult problems faster and with greater precision.
Key Approaches to Enhance Problem-Solving
- Understand the Full Scope – Begin by thoroughly analyzing the task to ensure you’re addressing all aspects. Missing key details early on can lead to unnecessary errors later.
- Work in Stages – Divide the problem into smaller, manageable sections. Tackling one part at a time prevents feeling overwhelmed and increases efficiency.
- Look for Patterns – Identifying recurring themes or structures in the problem can provide valuable insights, allowing you to predict outcomes or determine missing elements.
- Use Elimination – When faced with multiple choices, rule out obviously incorrect options. This narrows your focus and makes it easier to spot the right solution.
Advanced Techniques for Success
- Test Hypotheses – Don’t hesitate to try different approaches. Testing assumptions can reveal the best path forward and help refine your solution.
- Visualize the Problem – Drawing diagrams, charts, or other visual aids can help simplify complex tasks and clarify relationships between elements.
- Stay Organized – Keep your work neat and structured. Writing down key points, calculations, or conclusions prevents confusion and makes reviewing your process easier.
- Think in Reverse – In some cases, considering the problem backward can lead to a more direct solution. Tracing the end result and working backward may expose shortcuts or missing links.
Importance of Practice in Reasoning Assessments
Regular practice is essential for honing cognitive abilities and excelling in tasks that require critical thinking. By repeatedly engaging with challenging problems, you build familiarity with different types of scenarios and improve your ability to solve them efficiently. Consistent training not only increases your speed but also boosts your confidence when faced with unfamiliar tasks.
Benefits of Repeated Practice
- Improved Speed – Regular exposure to problems helps you recognize patterns faster, allowing you to solve them more quickly during high-pressure situations.
- Enhanced Problem-Solving Skills – With each practice session, you develop a deeper understanding of various techniques, enabling you to apply the most effective strategies when tackling new challenges.
- Familiarity with Task Formats – Practicing different types of problems makes you more adept at identifying the correct approach for each situation, reducing the risk of errors due to misunderstanding the task.
- Increased Confidence – As you solve more problems, you build self-assurance in your abilities, which helps you stay calm and focused during assessments.
Strategies for Effective Practice
- Set Specific Goals – Focus on improving particular skills or addressing areas where you struggle the most. This targeted approach leads to better results.
- Mix Problem Types – Work on a variety of challenges to ensure you’re well-rounded and capable of handling diverse scenarios during actual tasks.
- Track Progress – Keep a record of your practice sessions to monitor improvements and identify areas where additional focus is needed.
- Simulate Real Conditions – Try to replicate the time constraints and conditions of the actual task to make your practice sessions more realistic and beneficial.
Tips for Analyzing Logical Puzzles
Successfully solving puzzles that challenge your reasoning skills requires a strategic approach. Analyzing these problems effectively involves breaking down the given information, identifying key components, and considering various solutions. By refining your approach, you can improve both your accuracy and efficiency in solving these challenges.
Steps for Analyzing Puzzles
- Read Carefully – Pay close attention to every detail of the puzzle. Often, the smallest piece of information can unlock the entire solution.
- Identify Key Elements – Determine the critical facts and variables within the puzzle. Highlight or note them to ensure you focus on what is most important.
- Look for Constraints – Many puzzles contain hidden restrictions or conditions. Recognizing these limitations helps narrow down potential solutions and eliminates unnecessary options.
- Organize Information – If the puzzle involves multiple variables, create tables, charts, or lists to better visualize the relationships between them. This can make the connections clearer.
Approaching Complex Scenarios
- Work Backwards – In some cases, solving the puzzle in reverse order can make it easier to identify patterns or rules that weren’t obvious at first.
- Break Down the Problem – Decompose the puzzle into smaller, manageable parts. Tackling each piece individually can prevent you from feeling overwhelmed.
- Test Possible Solutions – Don’t be afraid to try different approaches. Testing various possibilities can help you quickly eliminate incorrect solutions and move toward the right one.
- Stay Patient – Puzzles can be tricky, and it’s easy to feel frustrated. Take breaks if needed, but always return with a fresh perspective to approach the problem with renewed focus.
Time Management in Reasoning Tests
Effective time management is crucial when faced with tasks that test your cognitive abilities. Allocating time wisely ensures that you can approach each problem systematically without feeling rushed. By developing a strategy for managing your time, you can enhance your performance and reduce stress during challenging assessments.
Strategies for Efficient Time Use
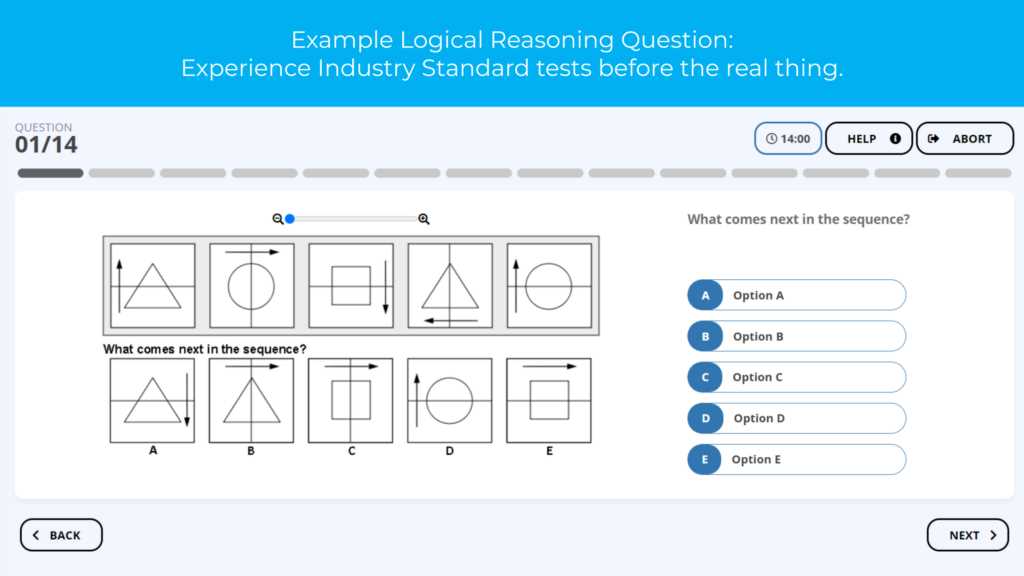
- Prioritize Tasks – Quickly assess the difficulty of each problem. Start with the ones that are easiest for you, building momentum before tackling more complex ones.
- Set Time Limits – Allocate a specific amount of time for each question or task. Try to stick to it to avoid spending too much time on any one part of the assessment.
- Move On When Stuck – If you find yourself struggling with a particular problem, don’t waste too much time on it. Move to the next one and return later with a fresh perspective if needed.
- Use Shortcuts – Familiarize yourself with techniques that allow you to solve problems more quickly, such as pattern recognition, elimination, or breaking down tasks into smaller parts.
Improving Speed Without Sacrificing Accuracy
- Practice Under Time Constraints – Simulate real conditions during practice sessions by timing yourself. This will help you become accustomed to the pressure and improve your ability to work efficiently.
- Stay Calm – Rushing can lead to careless mistakes. Focus on staying calm and collected, which will help you work more methodically and avoid errors.
- Monitor Your Progress – Periodically check your time to ensure you’re on track. Adjust your approach if you find you’re falling behind on your planned schedule.
Understanding Logical Fallacies
Identifying errors in reasoning is essential for evaluating arguments and drawing sound conclusions. These mistakes, known as fallacies, can mislead or distort the reasoning process, leading to faulty judgments. By recognizing common fallacies, you can improve your critical thinking skills and avoid being swayed by invalid reasoning.
Fallacies can occur in various forms, from appealing to emotions rather than facts, to presenting false dilemmas or irrelevant information. Understanding these pitfalls allows you to scrutinize arguments more effectively and engage in more reasoned, logical discussions.
Critical Thinking for Test Success
Effective problem-solving during assessments requires more than just recalling information. It demands the ability to analyze, evaluate, and synthesize data in a way that leads to well-reasoned conclusions. By developing strong critical thinking skills, you can approach challenges with confidence, carefully considering all angles before making decisions.
Key Elements of Critical Thinking
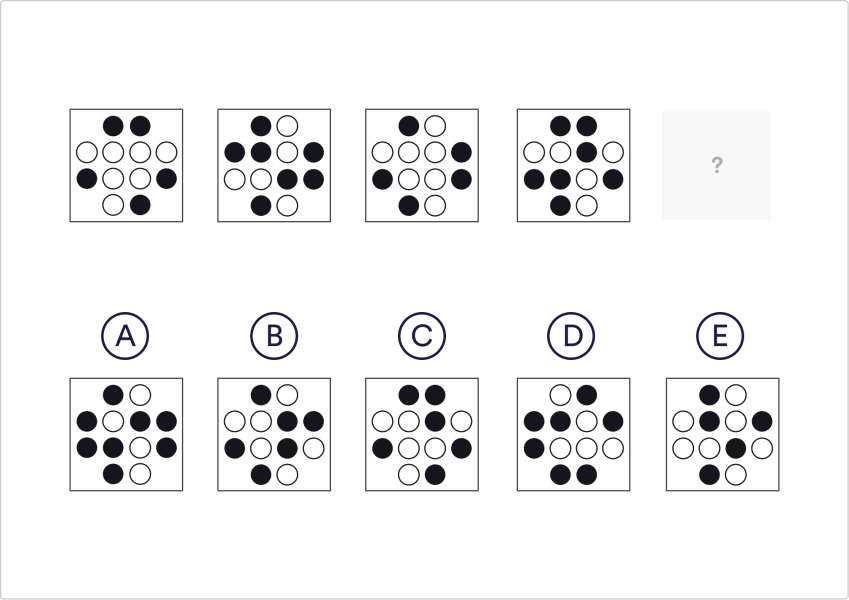
- Analysis – Break down complex problems into smaller, more manageable parts. Understand the structure and relationships of the information presented.
- Evaluation – Assess the validity and relevance of the data. Look for inconsistencies or gaps that might affect your conclusions.
- Inference – Draw logical conclusions based on the information at hand, taking into account both explicit details and implied meanings.
- Reflection – Consider different perspectives and revisit your reasoning. Critical thinkers constantly question their assumptions and refine their approaches.
Strategies for Improving Critical Thinking
- Ask Probing Questions – Challenge yourself to dig deeper. Instead of simply accepting information, question its source, relevance, and accuracy.
- Practice Active Listening – When presented with problems or scenarios, actively engage with the material. Take notes and summarize key points to ensure full comprehension.
- Consider Alternative Solutions – Don’t settle for the first solution that comes to mind. Explore multiple approaches and evaluate their merits before committing to one.
- Develop Logical Arguments – Train yourself to construct well-structured arguments. Focus on supporting your conclusions with strong evidence and clear reasoning.
Common Mistakes to Avoid in Reasoning Tests
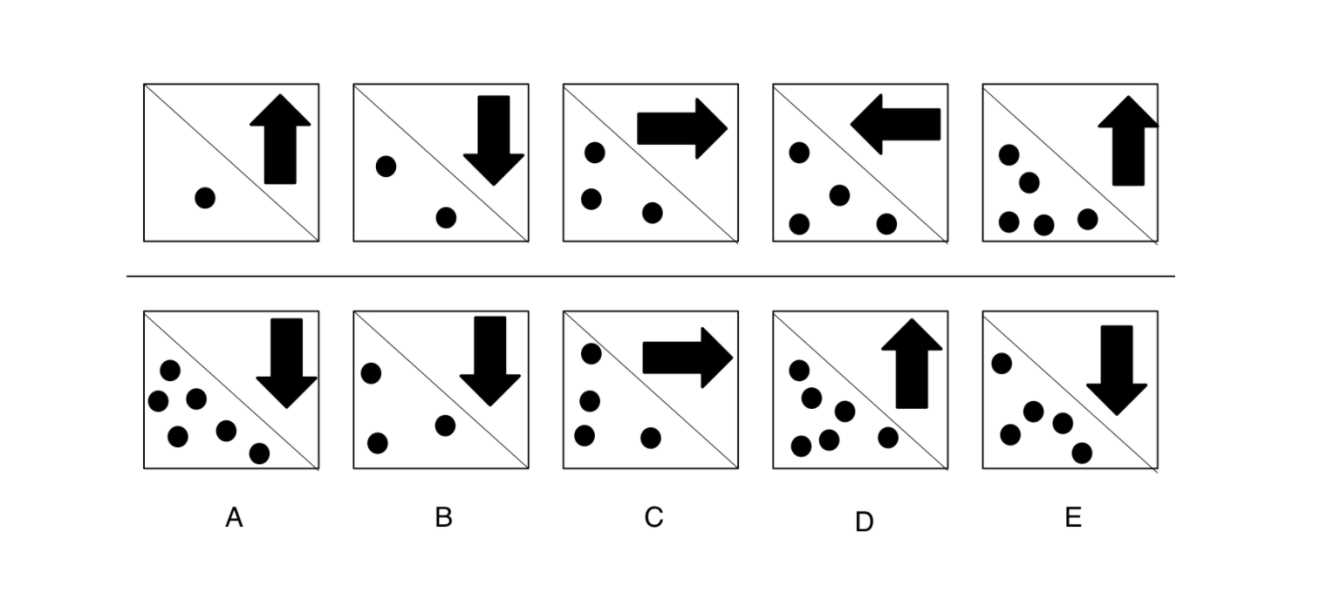
When tackling complex challenges, it’s easy to fall into common traps that can undermine your performance. Many of these mistakes occur due to rushing, misinterpreting the information, or failing to double-check your work. By being aware of these pitfalls, you can take proactive steps to avoid them and increase your chances of success.
Typical Errors to Watch For
- Rushing Through Problems – Trying to complete tasks too quickly can lead to careless mistakes. Always pace yourself to ensure accuracy before moving on to the next challenge.
- Misunderstanding the Problem – It’s crucial to read each task carefully and understand all of its components before attempting a solution. Skipping this step often leads to incorrect answers.
- Overlooking Key Information – Sometimes, crucial details are hidden within the problem. Be sure to read all the instructions and data thoroughly to avoid missing critical elements.
- Ignoring Time Constraints – While it’s important to take your time, managing the clock is essential. Don’t get too caught up on one problem; keep track of the overall time to ensure you address all tasks.
How to Prevent These Mistakes
- Stay Calm and Focused – Anxiety can cloud your judgment. Take deep breaths and approach each challenge methodically, one step at a time.
- Review Your Work – Before finalizing your answers, take a few minutes to check your work. Even small errors can have a significant impact on your results.
- Practice Regularly – The more familiar you are with different problem types, the less likely you are to fall into common traps. Practice under timed conditions to build confidence and efficiency.
How to Improve Critical Thinking Skills
Enhancing your ability to think critically is a valuable skill that can improve decision-making, problem-solving, and reasoning. This process involves developing a deeper understanding of concepts, considering different perspectives, and evaluating information more effectively. With consistent practice and the right strategies, you can sharpen your mind and approach complex problems with greater confidence.
Improving your reasoning abilities requires intentional effort. By engaging in activities that challenge your thinking and adopting effective techniques, you can strengthen your cognitive skills and become more adept at navigating difficult tasks.
Effective Techniques for Enhancing Thinking Abilities
- Engage in Brain-Training Exercises – Solve puzzles, play strategy games, or engage in exercises that require deep thought. These activities stimulate your mind and promote sharper reasoning.
- Read Widely – Reading diverse materials–books, articles, or academic papers–helps expose you to different viewpoints and ways of thinking. It also improves your ability to analyze and synthesize information.
- Ask Thoughtful Questions – Cultivate the habit of questioning the reasoning behind arguments and ideas. This helps you develop a deeper understanding of concepts and encourages thoughtful analysis.
- Reflect on Your Thought Process – Regularly evaluate your reasoning steps to identify areas where you can improve. Self-reflection enhances awareness of how you approach challenges and helps you refine your methods.
Building a Routine for Continuous Improvement
- Practice Regularly – Consistent practice is key to developing critical thinking. The more you engage with complex problems, the more natural it will become to analyze them from multiple angles.
- Seek Feedback – Don’t be afraid to ask for feedback on your reasoning from peers, mentors, or colleagues. Constructive criticism helps you recognize blind spots and develop a more thorough approach.
- Break Problems into Smaller Parts – When faced with a complex challenge, divide it into manageable components. This approach makes it easier to analyze and solve problems step by step.
Resources for Reasoning Test Preparation
Preparing for a test that challenges your problem-solving and reasoning skills requires access to the right tools and materials. A variety of resources, from practice exercises to detailed guides, can help you improve your approach and increase your chances of success. Utilizing these materials effectively allows you to build a strong foundation and familiarize yourself with the types of challenges you may encounter.
Whether you prefer online courses, books, or interactive problem sets, there are several ways to enhance your preparation. Below is a table of some helpful resources that can support your study process.
| Resource Type | Description | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Books | Printed or digital books provide comprehensive overviews of reasoning techniques and exercises to practice. | “Critical Thinking for Beginners”, “Mastering Problem Solving” |
| Online Courses | Interactive learning platforms offer guided lessons, quizzes, and exercises tailored to enhance reasoning skills. | Coursera, Udemy, Khan Academy |
| Practice Tests | Simulated assessments allow you to practice under timed conditions, helping you prepare for the actual test. | TestPrep, PracticeTests.com |
| Apps | Mobile applications offer on-the-go exercises and challenges, making it easy to practice reasoning skills in spare moments. | Lumosity, Peak, Brilliant |
| Study Groups | Collaborating with peers can provide insights and different perspectives on solving problems effectively. | Local study groups, online forums |
How to Handle Complex Reasoning Challenges
Tackling intricate problems requires a systematic approach to break down the information and identify key elements. When faced with a complex scenario, it’s essential to stay calm, focus on the task at hand, and apply structured techniques to analyze and resolve the problem. By following a clear strategy, you can handle even the most difficult challenges with greater ease and precision.
Approaches to Simplifying Complex Tasks
- Break the Problem Down – Divide the issue into smaller, more manageable parts. Analyze each component individually before reassembling them to form the solution.
- Identify Key Information – Highlight the most relevant facts or data points. Often, unnecessary details can cloud your judgment, so focus on the essentials.
- Look for Patterns – Spotting trends or recurring themes can simplify the process of solving complex tasks. This helps in identifying the right approach more quickly.
- Use Process of Elimination – In some cases, ruling out incorrect options can narrow down your possibilities, helping you find the correct answer faster.
Organizational Tools to Aid in Problem-Solving
Using structured tools can help you stay organized and clear-headed while addressing challenging problems. The following table outlines some useful strategies and their applications.
| Tool/Technique | Purpose | Application |
|---|---|---|
| Flowcharts | Visualize the steps and relationships between elements. | Helps map out the sequence of actions or decisions in a problem. |
| Diagrams | Illustrate complex concepts or structures. | Useful for organizing data or showing relationships between entities. |
| Tables | Organize facts or options systematically. | Helpful for comparing multiple variables or filtering through possibilities. |
| Mind Maps | Brainstorm ideas and visually connect key elements. | Effective for exploring different angles or potential solutions. |
How to Stay Focused During the Test
Maintaining concentration during a challenging assessment is crucial for achieving success. Distractions can hinder your ability to think clearly, leading to mistakes or oversights. To stay on track, it’s important to adopt strategies that minimize interruptions and help you stay engaged with the material. By using techniques to manage your mental energy and focus, you can improve your performance and avoid common pitfalls.
Techniques for Maintaining Focus
- Prioritize Deep Breathing – Calm your mind and reduce anxiety by practicing controlled breathing. This can help you stay centered and focused on the task at hand.
- Set Time Limits for Each Task – Giving yourself a set amount of time for each problem helps prevent overthinking and encourages a steady pace throughout the assessment.
- Minimize Distractions – Find a quiet environment free from distractions. If you’re working online or on a computer, close unnecessary tabs or apps that may divert your attention.
- Take Short Breaks – If allowed, take a brief pause after completing sections. A few seconds to stretch or relax can refresh your mind and restore focus.
Maintaining Motivation During Long Tests

- Stay Positive – Cultivate a positive mindset by reminding yourself of your preparation and capability. Positive reinforcement can reduce stress and keep you motivated.
- Visualize Success – Mentally picture yourself successfully solving problems and moving through the assessment. Visualization can enhance focus and boost confidence.
- Break Tasks into Smaller Segments – Instead of feeling overwhelmed by the length of the test, tackle it in smaller parts. This helps keep you engaged and ensures each section feels more manageable.
Sample Reasoning Challenges for Practice
Practicing with various scenarios is an essential part of developing your reasoning abilities. By solving sample problems, you can enhance your problem-solving skills and become more familiar with the types of challenges you might encounter. Below are several examples that will help you prepare and sharpen your critical thinking capabilities.
| Challenge Type | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Pattern Recognition | Identify a sequence or pattern within a set of items. | What comes next in the sequence: 2, 4, 8, 16, ? |
| Deductive Reasoning | Use logic to deduce an answer from given statements or facts. | All roses are flowers. All flowers have petals. Does a rose have petals? |
| Analytical Thinking | Break down a complex scenario into smaller, manageable components. | If John is taller than Mark and Mark is taller than Sarah, who is the tallest? |
| Numerical Reasoning | Apply mathematical logic to solve numerical problems. | If 5x = 25, what is x? |
| Verbal Reasoning | Understand relationships between words and concepts. | If “apple” is to “fruit”, then “carrot” is to what? |
Improving Speed in Problem Solving
In any assessment or challenge, the ability to solve problems quickly and accurately is a crucial skill. Speed doesn’t only come from understanding the material but also from practicing efficient techniques that allow you to navigate complex tasks with ease. By honing certain strategies, you can develop a faster problem-solving approach while maintaining accuracy.
Techniques for Speed Improvement
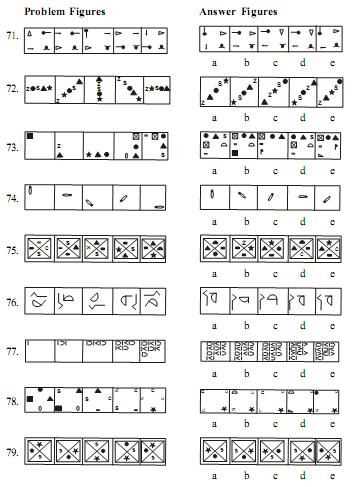
- Practice Regularly – Consistent practice with varied problems will help you recognize patterns faster and develop intuitive solutions.
- Master Time Management – Set time limits for each task or problem. This will help you avoid spending too much time on any single part and improve your pacing.
- Develop Shortcuts – Learn to recognize shortcuts or methods that speed up the process, such as eliminating impossible options quickly or simplifying steps in multi-part problems.
- Work on Mental Agility – Train your brain to think faster by solving problems under pressure. Mental exercises and games like chess or puzzles can help sharpen your quick-thinking skills.
- Stay Calm Under Pressure – Speed and accuracy go hand in hand with a calm mindset. Practicing relaxation techniques, such as deep breathing, can help you maintain focus during challenging tasks.
Tools to Help Increase Efficiency
- Timed Drills – Engage in timed practice drills to improve both your speed and problem-solving accuracy.
- Flashcards – Use flashcards for quick recall of key concepts or formulas. This improves the speed at which you can apply these principles during problem solving.
- Process Flow Charts – Visual aids like flow charts can help you quickly identify steps or actions required to solve a problem without wasting time on unnecessary decision-making.