
In today’s fast-paced business environment, organizations face a variety of challenges that could impact their long-term success. Understanding how to address these obstacles effectively requires a deep understanding of various strategies and techniques aimed at minimizing potential negative outcomes. This section will provide insights into essential topics that are crucial for anyone preparing to tackle assessments on this subject.
Comprehending the fundamentals of identifying and addressing vulnerabilities plays a significant role in strengthening an organization’s ability to navigate uncertainty. By focusing on core principles, individuals can enhance their ability to foresee potential disruptions and take appropriate measures to reduce the likelihood of such events.
Building a comprehensive understanding of the factors influencing decision-making and protective strategies is key. The ability to apply these concepts in real-world scenarios can significantly improve organizational resilience, and prepare you for success in evaluating these complex areas.
Enterprise Risk Management Exam Questions and Answers

Successfully navigating assessments related to identifying and addressing potential threats requires a solid grasp of core principles. This section will provide a thorough overview of key concepts, challenges, and scenarios commonly encountered in evaluations, helping to strengthen your knowledge and readiness. By understanding the underlying frameworks and approaches, you will be better equipped to respond effectively to various case studies and practical situations.
Key Concepts and Principles
At the heart of this discipline lies the ability to recognize critical challenges and evaluate their potential impact on an organization. A clear understanding of fundamental concepts, such as identification techniques, assessment methods, and protective measures, is essential for developing effective responses. Mastering these areas will ensure that you’re prepared for any scenario that might arise in an assessment environment.
Practical Scenarios and Approaches
Practical application of theoretical knowledge is crucial in this field. The scenarios you may encounter often test your ability to think critically and apply structured techniques to solve problems. By studying sample situations and understanding the appropriate steps to take in response, you’ll be able to confidently navigate the challenges presented in your assessments.
Key Concepts in Risk Management
Understanding the core principles that drive organizational preparedness is crucial for tackling challenges that could affect stability and success. This section explores the fundamental ideas that form the foundation for identifying vulnerabilities, assessing their potential impact, and developing strategies to minimize or eliminate harm. A solid grasp of these concepts is essential for anyone aiming to navigate this complex field effectively.
Identifying Potential Threats
One of the primary steps in any comprehensive strategy is identifying possible obstacles that may hinder an organization’s progress. This involves evaluating both internal and external factors that could disrupt operations. Tools such as risk identification matrices and scenario analysis are used to help spot potential challenges before they escalate, allowing for proactive planning and action.
Evaluating the Impact
Once threats are identified, it is crucial to assess their potential consequences. This requires understanding both the likelihood of occurrence and the severity of each challenge. By applying methodologies like probability assessments and impact analysis, one can prioritize which issues require immediate attention and which can be addressed over time. A balanced approach ensures that resources are allocated efficiently to protect key assets.
Understanding Risk Identification Methods
Recognizing potential obstacles is the first step in preparing for unexpected disruptions. Effective identification allows organizations to address weaknesses proactively before they escalate into significant challenges. This section delves into various approaches used to pinpoint vulnerabilities and examine how each method contributes to building a more resilient strategy. By mastering these techniques, individuals can anticipate problems and develop well-informed action plans.
Common Approaches to Identifying Challenges
There are several strategies available to identify potential threats to an organization. The following methods are commonly used to gain a comprehensive understanding of possible disruptions:
- Brainstorming Sessions: Gathering a team to discuss potential challenges, leveraging collective expertise and diverse perspectives.
- Interviews and Surveys: Collecting input from stakeholders and employees to identify less obvious threats.
- Historical Data Analysis: Reviewing past incidents and trends to predict future vulnerabilities.
- SWOT Analysis: Analyzing internal strengths and weaknesses, along with external opportunities and threats, to uncover potential risks.
Tools for Effective Identification
In addition to traditional methods, various tools can enhance the process of recognizing vulnerabilities:
- Risk Assessment Matrices: These visual tools help prioritize threats based on their likelihood and impact.
- Checklists: Structured lists of potential issues based on industry best practices or past experiences.
- Software Solutions: Advanced tools that use algorithms and historical data to predict future challenges.
Assessing Risk Impact and Likelihood
Evaluating the potential effects of challenges and their probability is crucial for effective decision-making. Understanding how likely an event is to occur and the magnitude of its impact allows organizations to prioritize resources and strategies. This section focuses on methods and tools used to assess both the probability of an issue happening and its potential consequences, helping to focus efforts on the most significant threats.
Methods for Assessing Impact
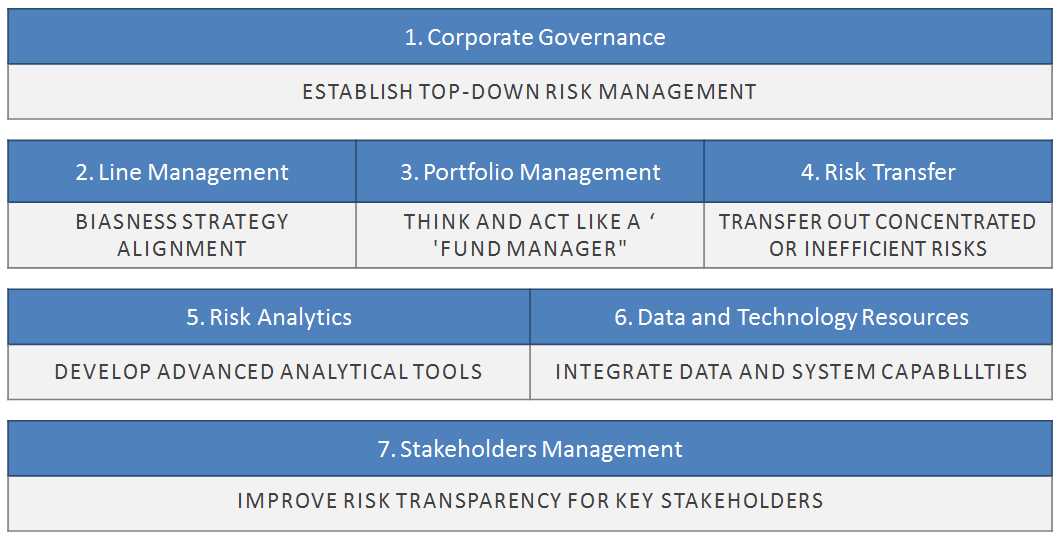
Once a potential threat has been identified, the next step is to understand how much damage it could cause. Several approaches can help quantify the consequences, allowing for better prioritization of responses:
- Qualitative Assessment: Describing potential outcomes in terms of severity (e.g., minor, moderate, critical) to understand the range of possible impacts.
- Quantitative Assessment: Using data, metrics, and statistical models to estimate financial or operational losses resulting from a disruption.
- Scenario Analysis: Exploring different scenarios to evaluate how various conditions might influence the consequences of an event.
Evaluating Likelihood of Occurrence
Understanding how likely a particular event is to happen is just as important as assessing its potential impact. Several techniques help estimate the probability of an issue arising:
- Expert Judgement: Relying on experienced professionals to provide insights based on their knowledge of the field and historical trends.
- Probability Scales: Using predefined scales (e.g., 1-5 or 1-10) to assign likelihood scores based on past data or expert opinion.
- Historical Data Analysis: Reviewing past occurrences and patterns to estimate the frequency of similar events in the future.
Risk Mitigation Strategies Explained
Once potential challenges have been identified and evaluated, the next step is to develop effective strategies to reduce their impact. Mitigation techniques are essential for minimizing negative outcomes and ensuring organizational stability. This section explores various approaches to addressing vulnerabilities, outlining both proactive and reactive methods for dealing with potential threats.
Proactive Approaches to Minimizing Threats
Proactive strategies focus on preventing problems before they occur. These measures help in reducing the likelihood of disruptive events and can significantly lessen the potential consequences. Common approaches include:
- Prevention Plans: Implementing processes and safeguards to stop challenges from arising in the first place.
- Training and Awareness: Educating staff and stakeholders about potential dangers and how to avoid them.
- Redundancy Systems: Building backup systems and processes to ensure continuity in case of failure.
Reactive Measures for Handling Unexpected Events
In cases where threats have already materialized or are imminent, reactive strategies are employed to minimize damage. These methods help in swiftly addressing issues and recovering as quickly as possible:
- Contingency Plans: Preparing detailed response plans for various scenarios to guide quick decision-making during a crisis.
- Resource Allocation: Directing resources to the most critical areas to mitigate immediate impacts.
- Insurance and Financial Reserves: Using financial tools to cover potential losses or liabilities.
Critical Risk Management Frameworks
To effectively navigate potential threats, organizations rely on structured frameworks that provide guidelines for identifying, assessing, and addressing challenges. These frameworks offer systematic approaches that help decision-makers create consistent strategies and ensure long-term resilience. In this section, we explore key frameworks that have become standards in safeguarding against unforeseen disruptions and optimizing organizational stability.
Widely Used Frameworks
Several frameworks are recognized for their effectiveness in guiding organizations through the complexities of dealing with potential vulnerabilities. Here are some of the most commonly applied:
- ISO 31000: This international standard outlines principles and guidelines for establishing a robust approach to dealing with uncertainties, focusing on integrating risk processes into all aspects of the organization.
- COSO ERM Framework: The Committee of Sponsoring Organizations (COSO) provides a comprehensive model that helps organizations improve governance, performance, and sustainability by effectively identifying and managing potential threats.
- Bowtie Method: A visual approach that identifies the cause-and-effect relationships between risks, their consequences, and the controls in place to manage them.
Benefits of Structured Frameworks
Implementing a clear, structured framework offers numerous advantages, including:
- Consistency: A standard approach ensures that all threats are assessed and handled in a uniform manner across the organization.
- Improved Decision-Making: Frameworks provide decision-makers with the tools to prioritize resources and respond effectively to potential challenges.
- Enhanced Accountability: By establishing clear roles and processes, frameworks ensure that everyone understands their responsibilities in managing uncertainties.
Examining Risk Control Techniques
Effectively managing uncertainties involves implementing techniques to reduce their impact or eliminate them altogether. These control methods are essential for minimizing potential disruptions and ensuring smooth operations. In this section, we will explore various techniques used to manage hazards, focusing on both preventative and corrective approaches to limit negative outcomes.
Preventative Measures to Address Challenges
Preventative control techniques focus on eliminating potential issues before they occur. These measures are designed to reduce the likelihood of disruptions and ensure the stability of ongoing activities. Common preventative techniques include:
- Process Redesign: Modifying existing workflows or operations to eliminate vulnerabilities and prevent errors or failures.
- Regular Monitoring: Implementing continuous oversight to identify and address potential problems before they escalate.
- Staff Training: Educating employees to recognize potential challenges early and act appropriately to prevent adverse events.
Corrective Actions for Managing Unexpected Issues
Even with the best preventative measures in place, unexpected events can still arise. Corrective actions are employed to address and mitigate the effects of such incidents. These techniques include:
- Incident Response Plans: Developing structured plans to quickly respond to unforeseen events and reduce their impact on operations.
- Damage Control Systems: Implementing procedures to limit the effects of disruptions once they occur, minimizing downtime or financial losses.
- Continuous Improvement: Analyzing past events to improve future preparedness and make necessary adjustments to processes or systems.
Enterprise Risk Management Process Overview
Successfully navigating uncertainties requires a structured process that integrates the identification, evaluation, and mitigation of potential challenges into everyday business operations. This systematic approach helps organizations anticipate problems and take proactive steps to avoid or minimize their effects. In this section, we will provide an overview of the essential stages involved in managing potential disruptions and ensuring long-term stability.
The process begins with understanding the environment and identifying threats that could hinder the achievement of organizational goals. Afterward, the focus shifts to evaluating the likelihood and impact of each potential issue. Once priorities are established, effective strategies are developed to address the most critical challenges. Finally, ongoing monitoring and adaptation ensure that the organization remains resilient, even in the face of unforeseen obstacles.
Common Risk Management Pitfalls
While developing strategies to handle uncertainties, organizations often face several common challenges that can hinder the effectiveness of their efforts. These pitfalls can result in missed opportunities or even increased exposure to potential threats. In this section, we will examine some of the most frequent mistakes made during the process and how they can be avoided.
Common Challenges in Identifying Threats
One of the first stages of addressing uncertainties is identifying potential issues. However, there are several pitfalls that organizations can encounter during this phase:
- Incomplete Assessment: Failing to consider all possible sources of disruption can leave vulnerabilities unaddressed.
- Overlooking Minor Threats: Ignoring smaller challenges, which may seem insignificant, can lead to larger problems down the line.
- Bias in Identification: Relying too heavily on past experiences or biases may cause key threats to be overlooked.
Challenges in Evaluating and Addressing Issues
Even when potential issues are identified, missteps during the evaluation and response stages can lead to ineffective solutions:
- Underestimating Impact: Failing to fully assess the consequences of certain events can lead to inadequate planning or resources being allocated.
- Overcomplicating Solutions: Implementing overly complex strategies can be difficult to maintain and may not be as effective in addressing immediate needs.
- Lack of Flexibility: Not adapting to changes or new information can leave organizations vulnerable when circumstances evolve.
Risk Management in Financial Sectors
In the financial industry, handling potential challenges is critical to maintaining stability and protecting assets. Given the complexity and volatility of financial markets, institutions must employ thorough processes to identify, assess, and mitigate possible threats that could disrupt operations or affect profitability. This section delves into the specific methods and strategies used by financial organizations to safeguard their interests and ensure long-term success.
Financial institutions face a unique set of challenges due to market fluctuations, regulatory requirements, and the interconnectedness of global economies. Managing these challenges requires a combination of proactive planning, effective monitoring, and quick responses to emerging issues. By understanding the key techniques used within the financial sector, organizations can better navigate the uncertainties they encounter.
Legal Aspects of Risk Management
In any organization, understanding the legal framework surrounding the handling of potential challenges is crucial. Legal considerations shape the processes and strategies used to address uncertainties, as businesses must comply with various laws and regulations. This section explores how legal factors influence the way organizations approach the identification, assessment, and mitigation of risks while ensuring compliance with relevant legal standards.
Key Legal Considerations in Managing Uncertainty
There are several important legal aspects that organizations must consider when addressing challenges, including liability, compliance with regulatory requirements, and the protection of intellectual property. These factors directly affect decision-making and the development of effective strategies. Below are some of the main legal concerns that organizations must navigate:
| Legal Concern | Impact on Strategy |
|---|---|
| Compliance with Regulations | Ensures that the organization follows all applicable laws and industry standards to avoid penalties or legal action. |
| Contractual Obligations | Helps prevent breaches of contract that could result in legal disputes or financial loss. |
| Liability Issues | Addresses potential legal liabilities from accidents, employee actions, or third-party claims, mitigating the risk of lawsuits. |
| Intellectual Property Protection | Safeguards proprietary information and assets from theft or unauthorized use that could undermine competitive advantage. |
Ensuring Legal Compliance in Risk Mitigation
To effectively address potential challenges, organizations must integrate legal compliance into their strategies. This involves staying updated on changes in laws and regulations and ensuring that risk reduction measures are aligned with legal requirements. Regular audits, employee training on legal responsibilities, and consultations with legal professionals are some of the best practices to ensure ongoing compliance.
Building a Risk Management Plan
Creating an effective strategy to handle potential disruptions is vital for any organization aiming to secure its operations and achieve long-term goals. A comprehensive plan allows businesses to prepare for uncertainties, minimize negative impacts, and ensure continuity. This section outlines the key steps involved in developing a robust strategy that addresses various challenges and prepares an organization for unforeseen circumstances.
The first step in building a plan is to identify all potential threats that could affect the organization. Once these threats are recognized, they must be evaluated based on their likelihood and possible impact. After prioritizing these risks, businesses can then develop targeted strategies for prevention, reduction, or response. Continuous monitoring and updating of the plan ensure that it remains relevant and effective as the environment evolves.
Evaluating Risk Management Tools
In order to effectively navigate uncertainties, organizations must utilize a variety of tools designed to assess, track, and mitigate potential challenges. Evaluating these tools is essential for determining their effectiveness in addressing specific needs. This section examines different tools available for organizations to integrate into their strategies and discusses how to assess their suitability based on various criteria.
Tools for handling potential threats can vary in complexity and functionality. Some are designed for simple tracking and reporting, while others offer more advanced features like predictive analytics and scenario modeling. Below is a comparison of common tools used to support decision-making in uncertain situations:
| Tool | Features | Advantages | Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Risk Assessment Software | Helps in identifying, evaluating, and prioritizing potential threats. | Streamlines assessment processes, offers data visualization. | May require training and integration with other systems. |
| Incident Tracking Systems | Monitors incidents and tracks actions taken to resolve them. | Improves response time and accountability. | Requires regular updates and maintenance. |
| Predictive Analytics Tools | Uses historical data to forecast future events and potential threats. | Helps in proactive decision-making and preparedness. | May be costly and require specialized knowledge to use effectively. |
| Scenario Modeling Tools | Simulates various possible situations to understand their impact. | Assists in evaluating multiple outcomes and planning responses. | Can be complex to implement and interpret. |
Choosing the right tools depends on the specific needs of an organization, as well as the complexity of the challenges they face. By carefully evaluating the features, advantages, and potential limitations of each tool, businesses can ensure they have the necessary resources to handle future uncertainties effectively.
Corporate Governance and Risk Management
Effective leadership and oversight are crucial for ensuring an organization remains resilient in the face of challenges. Corporate governance plays a central role in setting the framework within which decisions are made, ensuring that potential challenges are identified, assessed, and addressed in a timely manner. Strong governance practices provide a clear structure for managing uncertainties and safeguarding long-term sustainability.
Incorporating sound governance principles into organizational processes helps align decision-making with strategic objectives. It ensures that responsibilities are well-defined, accountability is maintained, and the necessary resources are allocated to address potential disruptions. Below are key elements that highlight the relationship between governance and effective uncertainty management:
Key Elements of Corporate Governance
- Board Oversight: The board of directors plays a pivotal role in overseeing strategies that ensure the organization is prepared for future uncertainties.
- Accountability: Clear accountability mechanisms ensure that individuals and teams are held responsible for identifying and addressing challenges.
- Transparency: Transparent processes and communication foster trust and enable stakeholders to understand how challenges are being managed.
- Strategic Alignment: Effective governance ensures that decisions are in line with the organization’s overall goals, optimizing its ability to handle disruptions.
Integrating Governance into Risk Management Framework
Incorporating governance into an organization’s decision-making framework enhances its ability to assess potential challenges and respond proactively. By establishing clear roles and responsibilities, organizations can better navigate uncertainties and take informed actions. Moreover, continuous evaluation and adaptation of governance structures help ensure that they remain relevant and effective as conditions evolve.
Risk Communication in Organizations
Clear, effective communication is essential for any organization facing uncertainties and potential challenges. Proper communication ensures that all stakeholders are aware of potential threats and are equipped with the necessary information to make informed decisions. When the flow of information is seamless and transparent, an organization can respond more efficiently to obstacles and adapt its strategies accordingly.
In organizations, communication regarding potential issues should be structured and consistent. Leaders must ensure that all levels of the organization understand the nature of the challenges, the impacts they may have, and the strategies in place to address them. This involves sharing relevant data, explaining the rationale behind decisions, and fostering an environment where questions and concerns can be raised openly. Below are key components that form an effective communication strategy within an organization:
Key Components of Effective Communication
- Transparency: Sharing accurate, timely, and relevant information with all stakeholders builds trust and fosters confidence in decision-making.
- Consistency: Regular updates and clear messaging ensure everyone remains on the same page and minimizes confusion.
- Responsiveness: Being receptive to feedback and adjusting communications as new information becomes available ensures continued alignment with organizational objectives.
- Clarity: Avoiding jargon and using clear, straightforward language helps to ensure that all stakeholders, regardless of their role, understand the key messages being communicated.
Methods of Risk Communication
Organizations can utilize various communication channels to share information about challenges and strategies. Below is a table of common communication methods used within organizations:
| Method | Description | Advantages |
|---|---|---|
| Meetings | Face-to-face or virtual gatherings to discuss issues, strategies, and updates. | Direct communication, real-time interaction, opportunity for immediate feedback. |
| Reports | Written documents detailing assessments, updates, and action plans. | Formal documentation, comprehensive detail, referenceable over time. |
| Emails | Electronic messages used to communicate updates, changes, or important announcements. | Efficient, accessible, easy to track communication. |
| Presentations | Visual and verbal presentations used to convey information to groups. | Engaging, visual aids support understanding, good for large groups. |
Case Studies on Enterprise Risks
Understanding the challenges organizations face is crucial for developing effective strategies and preparing for unforeseen challenges. Real-world case studies provide valuable insights into how different companies address uncertainties, plan for potential obstacles, and respond to unexpected events. By examining these scenarios, one can better understand how to navigate and mitigate challenges that may arise in the future.
These case studies highlight various aspects of potential threats, from operational to financial, and how organizations approach the identification, assessment, and resolution of these issues. The following examples explore different situations in which companies experienced significant setbacks or hurdles, and how they responded to minimize damage and recover effectively:
Case Study 1: Financial Crisis in a Retail Business
- Background: A large retail chain experienced a significant downturn during an economic crisis, impacting consumer spending and overall sales.
- Challenges Faced: Decreased demand, inventory issues, and loss of market share to competitors.
- Actions Taken: The company implemented a cost-cutting strategy, adjusted its marketing approach, and diversified its product offerings to adapt to changing consumer preferences.
- Outcome: Although the company faced short-term losses, it eventually recovered by focusing on customer loyalty and innovative product solutions.
Case Study 2: Cybersecurity Breach in a Tech Firm
- Background: A tech company specializing in cloud-based services suffered a cybersecurity breach, leading to sensitive customer data being compromised.
- Challenges Faced: Damage to reputation, legal complications, loss of customer trust, and potential regulatory fines.
- Actions Taken: The company immediately initiated a security audit, notified affected customers, and implemented stronger cybersecurity measures to prevent future incidents.
- Outcome: While the breach affected short-term sales and customer confidence, the firm rebuilt its brand by demonstrating transparency and commitment to securing customer data.
Case Study 3: Natural Disaster Impact on Manufacturing
- Background: A manufacturing company in a flood-prone region faced operational shutdowns due to an unexpected natural disaster.
- Challenges Faced: Damage to facilities, disruption of production, and delays in delivering orders to clients.
- Actions Taken: The company implemented a business continuity plan, re-established supply chains, and introduced disaster preparedness training for staff.
- Outcome: The company managed to resume operations quickly and strengthened its resilience by investing in infrastructure upgrades and more effective emergency protocols.
Preparing for the Risk Management Exam
Preparing for an assessment in this field requires a strategic approach, as it encompasses a wide range of concepts and practices. To perform well, it is essential to understand the key topics, methodologies, and tools used to address challenges within organizations. Effective preparation involves not only reviewing theoretical knowledge but also practicing the application of these principles to real-world scenarios.
One of the first steps in preparing for such an assessment is to familiarize yourself with the core concepts that will likely be tested. Focus on understanding the frameworks, tools, and techniques used to identify, evaluate, and address potential threats. Additionally, understanding how organizations plan for uncertainties, implement controls, and respond to crises will be crucial.
Key Areas to Focus On
- Frameworks: Study the different frameworks used to structure and approach uncertainty in organizations. These can provide a structured methodology for identifying challenges and creating solutions.
- Tools and Techniques: Familiarize yourself with various tools that assist in identifying potential threats and assessing their likelihood and impact. These tools are integral in helping organizations take proactive steps.
- Case Studies: Reviewing real-world examples of organizations facing difficulties will help you understand how theoretical concepts are applied in practice. Focus on how companies address issues such as financial instability, operational failures, and security breaches.
- Regulations and Compliance: Understanding the legal and regulatory frameworks that govern the industry is essential. Be prepared to discuss how organizations comply with industry standards and legal requirements to mitigate challenges.
Effective Study Strategies
- Active Practice: Solve practice problems and case studies to familiarize yourself with the types of scenarios that may arise in the assessment. This will help reinforce your knowledge and improve problem-solving skills.
- Group Discussions: Engaging in discussions with peers or colleagues can provide new perspectives on complex topics and help clarify difficult concepts.
- Review Key Texts: Go over textbooks, notes, and online resources that focus on the core principles. Summarize and condense the material to focus on the most critical concepts.
- Mock Assessments: Taking mock tests will help you gauge your readiness and identify areas where further study is needed.
By focusing on these areas and adopting a structured study plan, you can approach the assessment with confidence and a solid understanding of how to tackle the challenges presented. Focus on both theoretical knowledge and practical application, and you’ll be well-prepared for success.
Sample Exam Questions and Answers
When preparing for an assessment in this field, practicing with sample scenarios is an effective method to reinforce your understanding of key concepts. By working through various questions, you can familiarize yourself with the types of situations you may face and sharpen your ability to apply theoretical knowledge to practical challenges. Below are a few examples of typical questions, along with explanations of the best approaches to answering them.
Sample Scenarios
| Question | Correct Approach |
|---|---|
| What is the first step in addressing a potential threat within an organization? | Identification is the first step. You must recognize the issue or potential threat before taking further action. This could involve conducting a thorough analysis of the internal and external environment to identify possible vulnerabilities. |
| Which method is best for evaluating the severity of a challenge? | Impact Assessment allows you to evaluate how a particular event would affect the organization. This can involve examining financial, operational, or reputational consequences in various scenarios. |
| What is the most effective way to mitigate potential problems in a project? | Risk Mitigation Strategies should focus on reducing the likelihood of an event occurring, or minimizing its impact if it does. This may involve using controls, adopting preventive measures, or transferring the responsibility. |
| How can organizations ensure compliance with regulatory standards? | Monitoring through regular audits, reporting, and staying updated with legal requirements is essential. It ensures that the organization remains compliant with both industry and government regulations, reducing the likelihood of penalties or non-compliance issues. |
Approach to Problem Solving
When confronted with similar scenarios during the assessment, remember to structure your answers systematically. Begin by identifying the core issue, followed by assessing its impact and likelihood. Afterward, propose suitable strategies to address the issue, ensuring that you explain the rationale behind your choices. Providing clear and concise reasoning will help demonstrate your understanding of the concepts in practice.