
Preparing for assessments in the field of design and construction requires a deep understanding of various core principles. This section will guide you through the most important topics, offering insights and strategies to help you tackle a variety of challenges effectively. By mastering the material, you can approach each task with confidence and skill.
Strategic preparation is essential for success. Recognizing the patterns in tasks and anticipating what may be tested allows you to focus your efforts efficiently. From theoretical knowledge to practical application, the key is in balancing both areas to demonstrate proficiency.
By examining common subjects and practical examples, this guide will provide the tools needed to navigate through complex topics. Whether it’s theory, design, or technical skills, you’ll find valuable insights to strengthen your readiness and improve performance.
Architecture Exam Questions and Answers
Successfully navigating through assessments in the field of design involves understanding both the theoretical concepts and practical applications that are typically evaluated. This section will explore common types of challenges one may face and provide essential strategies for addressing them with clarity and precision. It is crucial to be well-prepared across a range of topics to demonstrate a deep understanding of the subject matter.
Key areas often tested include:
- Design Principles: Understanding the fundamental rules that guide the creation of functional, aesthetic structures.
- Construction Techniques: Demonstrating knowledge of materials, methods, and processes used in building development.
- Historical Context: Recognizing important periods, movements, and architects that shaped the industry.
- Sustainability Practices: Applying eco-friendly and energy-efficient approaches to design and construction.
- Building Codes and Regulations: Showing an understanding of legal and safety standards that govern the construction of structures.
When preparing for such assessments, it’s important to review past challenges to identify recurring themes. Familiarity with specific subjects can help boost confidence and improve performance under timed conditions.
Practical application also plays a significant role in the evaluation process. Here are some example areas to focus on:
- Design Schemes: Be prepared to present well-thought-out solutions to design problems, incorporating appropriate materials and methods.
- Technical Drawings: Demonstrating proficiency in reading and creating accurate blueprints and schematics is essential.
- Case Studies: Analyzing real-world examples of buildings and developments, discussing their design, structure, and impact.
With careful study and a focused approach, mastering these areas can significantly increase your chances of performing well in assessments related to design and construction fields.
Key Topics to Study for Architecture Exams
To succeed in assessments related to the design and construction field, it is essential to focus on critical areas that are often tested. A well-rounded understanding of both theoretical principles and hands-on skills is necessary. Below are some of the main subjects that frequently appear, which will help build a strong foundation for success.
Design Fundamentals
Having a solid grasp of design basics is vital for creating functional and innovative solutions. Key topics in this area include:
- Form and Space: Understanding how to balance aesthetics with functionality in creating usable spaces.
- Human Factors: Designing with consideration for comfort, safety, and accessibility.
- Material Selection: Knowledge of the properties and applications of different construction materials.
- Design Methodologies: Familiarity with approaches like concept development, sketching, and modeling.
Technical Knowledge
In addition to theoretical knowledge, practical understanding is crucial. Focus on mastering these technical areas:
- Structural Systems: Learning about different types of load-bearing systems, including beams, columns, and foundations.
- Building Codes: Familiarity with legal regulations that govern construction processes and safety standards.
- Energy Efficiency: Knowledge of sustainable design practices and energy-efficient building systems.
- Construction Methods: Understanding how buildings are constructed, from foundation to finishing touches.
By dedicating time to mastering these essential topics, you can develop a comprehensive understanding of the field, which will help you navigate the various challenges presented in assessments.
Common Exam Questions in Architecture

When preparing for assessments in the field of design and construction, it’s essential to be familiar with the types of topics that are frequently tested. This section will explore typical subjects and problem-solving scenarios that often appear, helping to build a comprehensive understanding of what to expect. Mastery of these areas will enhance your ability to address a variety of challenges with confidence and clarity.
Key Topics Often Covered
Below are some of the most common areas that are assessed, along with examples of the types of problems you might encounter:
| Topic | Sample Problem |
|---|---|
| Design Principles | Describe how you would design a small residential building while ensuring maximum energy efficiency. |
| Construction Techniques | What are the most effective methods for ensuring structural integrity in high-rise buildings? |
| Building Codes | Explain the importance of fire safety regulations in commercial buildings and how they impact design. |
| Historical Influences | Identify key architectural movements from the 20th century and explain their influence on modern construction. |
| Sustainable Practices | Discuss how green roofs can contribute to sustainability in urban environments. |
Problem-Solving Scenarios
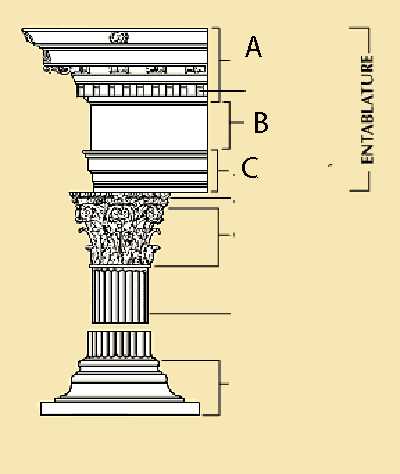
In addition to theoretical knowledge, practical problem-solving is also commonly tested. Here are a few typical scenarios you may encounter:
- Technical Drawings: Be prepared to interpret architectural drawings, identify mistakes, and propose corrections.
- Site Analysis: Assess the suitability of a location for a new building, considering factors such as topography and environmental impact.
- Design Challenges: Solve complex design problems by integrating creative solutions with functional requirements.
Familiarity with these common scenarios will help you approach your assessments with confidence, ensuring you’re prepared for a wide range of challenges.
How to Prepare for Architecture Tests
Success in design assessments requires a strategic approach that combines in-depth knowledge with effective time management. Preparing for these challenges involves understanding core principles, practicing problem-solving techniques, and refining your technical skills. A focused and organized study plan is key to mastering the material and performing confidently under pressure.
Start by reviewing the fundamentals: Ensure you have a solid understanding of the basic concepts and methods that are commonly evaluated. This includes topics like structural systems, building materials, design theory, and safety standards. A clear grasp of these subjects will serve as a foundation for more advanced studies.
Practice with real-world scenarios: Applying theoretical knowledge to practical situations is crucial. Work through design problems, sketch concepts, and study case studies to improve your ability to solve complex challenges. Hands-on practice will also help you become more comfortable with technical drawing and using architectural software.
Time management: Break down your study sessions into manageable blocks, focusing on different areas during each. Practice under timed conditions to simulate the pressure of an actual test, ensuring you’re able to perform efficiently and accurately. Prioritize weaker areas, but don’t neglect to review your strengths as well.
Stay updated: The field of design is always evolving, so it’s important to stay current with new trends, technologies, and regulations. Follow industry news, attend workshops, or participate in online forums to keep your knowledge fresh and relevant.
By focusing on these strategies, you’ll be better equipped to handle various types of challenges, whether they involve creative design, technical applications, or legal considerations.
Understanding Architectural Design Principles
Designing functional and visually appealing spaces requires a deep understanding of core principles that guide the creation of built environments. These principles are the foundation of every successful structure, ensuring it meets both aesthetic and practical needs. Mastering these concepts will allow you to approach every project with clarity and confidence.
Key Concepts in Design
The most important aspects to grasp when considering design include:
- Form and Function: Balancing the visual appeal with the intended use of the space. Every element should serve both a practical and artistic purpose.
- Space Planning: Understanding how to effectively utilize space to create a harmonious, functional environment that encourages movement and interaction.
- Proportion and Scale: Ensuring that all elements are appropriately sized in relation to each other, as well as the overall structure, to create a sense of balance.
- Material Selection: Choosing the right materials not only for their aesthetic value but also for their functionality, durability, and sustainability.
- Lighting and Ventilation: Incorporating natural and artificial lighting, along with proper ventilation, to enhance the comfort and energy efficiency of the space.
Principles of Sustainability

In modern design, sustainability plays a crucial role. Key considerations include:
- Energy Efficiency: Using design strategies to reduce energy consumption, such as passive heating, cooling, and efficient insulation.
- Eco-friendly Materials: Opting for renewable or recycled materials to minimize environmental impact while maintaining high performance.
- Natural Resources: Designing with consideration for water usage, natural light, and other sustainable elements that reduce the building’s ecological footprint.
Mastering these design principles provides a strong foundation for creating spaces that are not only visually compelling but also functional, efficient, and sustainable.
Important Architectural Theory Concepts
Understanding the fundamental concepts of design theory is essential for anyone working in the built environment. These theoretical ideas not only inform the creative process but also shape the way we approach construction, spatial organization, and the relationship between form and function. A strong grasp of these concepts provides a framework for thoughtful and innovative design.
Space and Place: The concept of space is central to design, encompassing both the physical dimensions of a space and the way it is perceived by those who inhabit it. Place, on the other hand, refers to the cultural, historical, and emotional significance that a particular space can hold, creating a deeper connection to the environment.
Human-Centered Design: This theory emphasizes designing with a focus on the needs, comfort, and experiences of the people who will use the space. It integrates aspects such as ergonomics, accessibility, and environmental psychology to ensure that built spaces are functional, welcoming, and inclusive.
Contextualism: Understanding the context in which a building or structure is placed is crucial. This theory argues that design should respond to its environment–whether natural, social, or historical–to create a cohesive and meaningful relationship between the building and its surroundings.
Modernism: Rooted in the early 20th century, modernism focuses on simplicity, functionalism, and the use of new materials and technologies. It rejects ornamental elements in favor of clean lines, open spaces, and efficient use of resources.
Postmodernism: As a reaction to modernism, postmodernism embraces complexity, contradiction, and a playful approach to design. This theory incorporates historical references, diverse styles, and bold forms to create structures that evoke emotion and stimulate thought.
Structuralism: This theory suggests that the design of buildings should be informed by the underlying systems and structures that support them. It emphasizes organization, order, and clarity, both in the physical structure and the way people move and interact within the space.
These key theoretical concepts are essential for developing a holistic understanding of design practices, helping professionals approach each project with both creativity and analytical insight.
Typical Questions on Building Codes
Understanding the rules and regulations that govern the construction of buildings is essential for anyone working in the field. These guidelines ensure that structures are safe, accessible, and comply with legal and environmental standards. Below are some common topics that often come up when discussing building codes, along with examples of what might be asked.
Key Areas of Focus
When preparing for assessments, it’s important to familiarize yourself with the core areas of building codes. Some typical areas include:
- Fire Safety: What are the fire resistance ratings required for different building materials? How do building codes address fire exits and emergency evacuation?
- Structural Integrity: What are the load-bearing requirements for floors, walls, and roofs? How should seismic or wind forces be accounted for in the design?
- Accessibility: What regulations exist to ensure that buildings are accessible to individuals with disabilities? Considerations such as ramps, door widths, and bathroom facilities.
- Energy Efficiency: How do building codes promote sustainable construction? What insulation and energy-saving materials are mandated in certain climates?
Code Compliance and Enforcement
Questions in this area often focus on the practical application of building codes and how compliance is monitored:
- Permits and Inspections: What are the steps to ensure a project complies with local building codes? How do permits and inspections play a role in the process?
- Non-compliance Issues: What happens if a building fails to meet required standards? What penalties or corrective actions might be imposed?
- Updating Codes: How often are building codes updated? What is the process for implementing new or revised regulations?
Mastering the fundamental principles of building codes and understanding how they apply to real-world projects will ensure that you’re well-prepared for discussions and assessments on this crucial topic.
Effective Study Tips for Architecture Exams
Preparing for assessments in design-related fields requires a focused approach that balances theoretical knowledge with practical application. To perform well, it’s essential to engage with the material in a structured way, ensuring both breadth and depth of understanding. The following study tips will help you streamline your preparation and maximize your effectiveness.
Organize Your Study Sessions
Plan ahead: Break down the topics into smaller, manageable sections. Create a study schedule that allocates time for each area based on its difficulty and your comfort level with the material. This will help you avoid feeling overwhelmed and ensure you cover all essential subjects.
Prioritize key topics: Focus on the areas that are most likely to be tested. Review past materials or practice exercises to identify recurring themes or subjects that have historically been emphasized. This targeted approach can help you allocate your time wisely.
Engage with Practical Exercises
Hands-on practice: It’s crucial to apply what you’ve learned through practice exercises. Work on design problems, case studies, or simulated challenges to strengthen your problem-solving skills. This will not only deepen your understanding but also help you become more comfortable with applying theoretical concepts in real-world contexts.
Utilize visual aids: Diagrams, flowcharts, and sketches can greatly enhance your understanding. For subjects that are visually complex, create your own diagrams or refer to existing ones to help internalize the material. This approach is especially useful for technical topics or concepts related to spatial design.
Take regular breaks: Avoid cramming or studying for long hours without rest. Regular breaks will keep your mind fresh and improve your overall productivity. Use techniques like the Pomodoro method to balance focused study time with short breaks to maintain efficiency.
By staying organized, practicing consistently, and focusing on key concepts, you’ll be well-prepared to tackle any challenge that comes your way in the field of design assessments.
Time Management Strategies for Exams
Effective time management is crucial when preparing for any assessment. Allocating sufficient time to review all necessary materials, while ensuring you don’t overwork yourself, can make all the difference. Implementing strategic approaches to how you organize and use your time will help you stay focused and productive without feeling overwhelmed.
Set clear goals: Before you begin studying, define specific goals for each session. Identify the topics you want to cover and set achievable targets for each study period. This will give you direction and keep you from drifting off course.
Create a study schedule: Break down your preparation into manageable time blocks. Divide your study time into focused intervals, typically 25-50 minutes, followed by short breaks. This will help you maintain concentration and avoid burnout. Use a calendar or planner to visualize your schedule and track your progress.
Prioritize tasks: Focus on the most important or difficult topics first, tackling them when your mind is fresh. This ensures that you’re giving your best effort to the areas that need the most attention. Once the challenging subjects are covered, you can work on easier material with greater ease.
Avoid procrastination: Start early and stay consistent. Procrastination can lead to last-minute stress and poor performance. By beginning your preparation ahead of time and sticking to your schedule, you’ll reduce anxiety and improve the quality of your work.
Review and adjust: Regularly assess your progress to ensure you’re on track. If you find yourself spending too much time on one area or not enough on another, adjust your approach accordingly. Flexibility in your time management is key to staying effective.
By planning your time thoughtfully and sticking to a well-organized schedule, you’ll be able to manage your workload efficiently, ensuring you’re fully prepared for the challenges ahead.
Mastering Architectural History for Exams
Grasping the evolution of building styles, influential periods, and key figures is essential when preparing for assessments in the design field. Understanding how past developments shape current practices not only enriches knowledge but also enhances the ability to analyze and appreciate design concepts. This section explores effective strategies for mastering the subject of architectural history.
Focus on Key Periods and Movements
One of the most effective ways to approach the study of design history is by breaking down the material into distinct periods and movements. Concentrating on major architectural eras will help you connect styles, ideas, and technological advancements over time. Key movements such as the Renaissance, Baroque, Modernism, and Postmodernism should be prioritized, with particular attention to their defining features, philosophies, and notable practitioners.
- Renaissance: Explore the revival of classical design principles and the impact of figures like Brunelleschi and Michelangelo.
- Modernism: Study the rise of functionalism, minimalism, and the works of Le Corbusier and Frank Lloyd Wright.
- Postmodernism: Understand the rejection of rigid modernist principles and the return to ornamentation, exemplified by architects like Robert Venturi.
Utilize Visual Learning Tools
Visual aids: As architectural history is rich in visual detail, using images, diagrams, and drawings can greatly enhance your retention of key concepts. Focus on learning the distinct characteristics of styles through images of iconic buildings and structures. Sketches and architectural plans will help you link theoretical knowledge to real-world examples.
Interactive learning: Consider using digital tools and virtual tours of historical buildings to better understand the context in which these structures were created. Many resources are available that allow you to explore architectural sites and gain a deeper appreciation for their design elements.
By focusing on critical periods and utilizing visual tools, you can deepen your understanding of how design has evolved and better prepare for assessments on the subject.
How to Approach Technical Drawing Questions
When it comes to design assessments that involve creating or interpreting technical drawings, it’s essential to approach the task with precision and a clear understanding of key concepts. These tasks require both a strong foundation in drawing techniques and the ability to visualize and represent objects accurately. This section provides practical strategies for tackling such challenges effectively.
Understand the Basics of Technical Drawing

Before attempting any complex tasks, it’s important to master the fundamental elements of technical drawing. This includes understanding the different types of lines, scales, projections, and symbols used to represent structures and components. A clear grasp of these basics will enable you to approach more complex drawings with confidence.
Key concepts to review:
- Scale: Ensure that all elements are drawn proportionally and that the correct scale is used.
- Projection: Learn the differences between orthographic projection, isometric projection, and perspective drawing.
- Symbols: Familiarize yourself with standard symbols for electrical, plumbing, and other mechanical elements.
Work Through Step-by-Step Processes
When faced with a drawing problem, it’s helpful to break it down into manageable steps. Start by reviewing the prompt carefully to understand the requirements, then proceed methodically through the drawing process.
| Step | Action |
|---|---|
| 1 | Analyze the task and gather all necessary information, including dimensions and required views. |
| 2 | Sketch the basic outline of the structure or component. |
| 3 | Add detail gradually, ensuring each element is aligned with the specified measurements. |
| 4 | Check for accuracy, ensuring that all lines, angles, and dimensions match the requirements. |
Tip: Double-check your work, especially the measurements and proportions. Small errors can lead to significant mistakes in the final drawing.
By mastering these basic techniques and following a structured approach, you’ll be able to tackle any drawing-related challenge with precision and efficiency.
Essentials of Sustainable Design Assessments
In assessments focused on eco-friendly building practices, it is crucial to understand the fundamental principles that guide the creation of energy-efficient, environmentally conscious structures. These principles encompass a broad range of concepts, from the use of sustainable materials to the incorporation of renewable energy sources. A comprehensive grasp of these topics will help ensure that you can effectively address challenges related to sustainable design.
Key Areas to Focus On

When preparing for assessments related to sustainability in the built environment, there are several key areas that are vital for success. Understanding these concepts will not only provide a solid foundation but will also help in applying these principles to real-world scenarios.
- Energy Efficiency: Learn how to design buildings that use less energy by implementing insulation, passive heating, and cooling techniques.
- Green Materials: Study the environmental impact of materials, focusing on those that are renewable, non-toxic, and recyclable.
- Water Conservation: Explore methods to reduce water usage, such as rainwater harvesting and low-flow fixtures.
- Waste Management: Understand how to minimize construction waste and utilize sustainable disposal methods.
- Indoor Air Quality: Familiarize yourself with strategies for creating healthy indoor environments, including proper ventilation and non-toxic materials.
Common Principles in Sustainable Design
The following principles are foundational when approaching eco-friendly design projects:
- Design for Durability: Creating structures that are long-lasting and require minimal maintenance reduces the need for resources over time.
- Optimize Natural Resources: Maximize natural light and ventilation, reducing reliance on artificial lighting and climate control systems.
- Energy Modeling: Use energy simulation tools to predict energy consumption and optimize the building’s performance before construction begins.
By focusing on these essential areas and principles, you will be better prepared to approach sustainability-focused challenges with a well-rounded understanding of eco-friendly design practices.
Architectural Software and Assessment Topics

In the field of building design, proficiency in various software tools is essential for tackling complex tasks and solving design-related challenges. These tools play a critical role in visualizing concepts, performing calculations, and ensuring accuracy in designs. Understanding how to effectively use architectural software can provide a significant advantage when addressing challenges related to sustainable practices, structural integrity, and spatial planning.
Key Software Tools to Master
Different software programs are tailored for specific tasks in the design process. Whether it’s drafting, 3D modeling, or simulation, knowing which tool to use and how to utilize its features effectively is essential. Below are some key tools that are often featured in assessments:
- AutoCAD: A leading software for creating detailed 2D and 3D drawings, essential for drafting floor plans, elevations, and technical schematics.
- Revit: A Building Information Modeling (BIM) tool that helps in planning, designing, and managing building projects in a collaborative environment.
- SketchUp: Known for its user-friendly interface, SketchUp is widely used for creating 3D models, particularly in early design phases.
- Rhino: A powerful tool for 3D modeling and design, especially useful for complex and organic shapes that require high precision.
- V-Ray: A rendering software that integrates with other design tools to produce photorealistic visualizations of building models.
How to Use Software in Assessments
When preparing for assessments that involve design tasks, familiarity with how to leverage software tools for different purposes is crucial. Here’s how to approach tasks effectively:
- Practice Regularly: Ensure you are comfortable with the tool’s interface, shortcuts, and core functions.
- Understand Software Limitations: Each tool has its strengths and weaknesses, so it’s essential to choose the right software for the task at hand.
- Focus on Precision: Whether creating 2D drawings or 3D models, always prioritize accuracy to avoid errors in your design.
- Utilize Tutorials: If you encounter a challenge with a tool, online tutorials can help you understand complex features and workflows.
- Time Management: During assessments, allocate time to each software task based on its complexity, allowing for thorough yet efficient completion.
Mastering the right software is a vital aspect of succeeding in design-based assessments. By improving your skills with these tools, you can tackle tasks with greater ease and efficiency, leading to better outcomes in both practical applications and evaluation scenarios.
What to Expect in Practical Design Tests

When preparing for hands-on assessments, it’s important to understand the type of tasks that will challenge your skills in real-world applications. These tests are designed to evaluate how well you can apply theoretical knowledge in practice, focusing on your ability to solve problems, use design tools, and communicate ideas effectively. In these situations, you may be asked to create detailed drawings, develop conceptual designs, or solve practical problems using your technical expertise.
Types of Tasks You May Encounter
Practical design assessments can vary widely depending on the focus of the test, but generally, you can expect to face several types of challenges:
- Design Challenges: You may be given a brief that requires you to come up with a functional and creative design for a specific project, such as a building or space planning.
- Technical Drafting: Tasks often require you to produce accurate technical drawings, including floor plans, elevations, or sections, using drafting software or hand-drawing techniques.
- Problem-Solving Exercises: These tasks test your ability to identify and resolve issues that could arise during the design or construction phases, such as structural integrity or material selection.
- Model Making: You may be asked to create a physical or digital model of a design to showcase spatial arrangements or structural elements.
Preparing for the Assessment
To excel in practical tests, thorough preparation is key. Here are some steps to ensure you are ready:
- Familiarize Yourself with Common Tools: Make sure you are proficient with the software or tools you’ll need for the test, whether it’s CAD software, sketching tools, or 3D modeling programs.
- Practice Problem-Solving: Work through design problems and technical challenges regularly to enhance your ability to think critically and quickly on your feet.
- Refine Your Technical Drawing Skills: Focus on improving the accuracy and clarity of your sketches and technical drawings to communicate your ideas effectively.
- Understand the Brief: Read and analyze the given task carefully to ensure you address all aspects of the problem in your solution.
- Time Management: Allocate sufficient time for each part of the task and prioritize efficiently, ensuring you complete each section without rushing.
Hands-on tests are an excellent way to showcase your practical abilities and demonstrate how well you can apply your knowledge to real-life scenarios. By preparing thoroughly and practicing the necessary skills, you can approach these challenges with confidence and perform effectively in assessments.
Case Studies and Test Question Examples

In preparing for assessments, reviewing real-world scenarios and example challenges is crucial for understanding how to approach tasks effectively. Case studies provide insights into how specific problems are solved, offering a practical view of what might be expected during assessments. Examining sample scenarios allows you to develop problem-solving strategies, refine technical skills, and improve your ability to apply theory in real-life situations. By analyzing these cases, you can learn how to structure your responses and highlight key details relevant to the task at hand.
Case Study Examples
Below are several examples of real-world cases that you may encounter during practical assessments. These cases help you understand the kind of problem-solving required and how to manage the design process effectively:
| Case Study | Key Focus Areas |
|---|---|
| Residential Building Design | Space planning, sustainability, material selection, building regulations compliance |
| Office Space Layout | Ergonomics, workflow optimization, lighting, acoustics, and HVAC systems |
| Public Park Design | Landscaping, environmental considerations, accessibility, integration with surrounding area |
| Urban Development Project | Infrastructure, community integration, sustainability, zoning laws, traffic management |
Example Challenges
Here are a few sample challenges that reflect the kind of tasks you may be asked to solve:
- Design a Sustainable Office Building: Create a floor plan for an office space that maximizes natural light and minimizes energy consumption. Be sure to incorporate eco-friendly materials and sustainable design principles.
- Renovation of a Historical Landmark: Propose a renovation plan for a historical building, ensuring the preservation of its key architectural features while introducing modern amenities.
- Urban Space Optimization: Redesign a public square to enhance its functionality for community events while ensuring ease of access for all users, including people with disabilities.
By reviewing case studies and practicing with sample challenges, you can better prepare for the types of practical tasks that will be presented. These examples help you develop a systematic approach to problem-solving and refine your technical skills, making it easier to tackle real-world challenges with confidence.
Building a Strong Foundation for Assessments

Establishing a solid base of knowledge and skills is essential for successfully navigating practical assessments. To perform at your best, it’s crucial to understand the core concepts, theories, and methods that underpin your field of study. A strong foundation allows you to approach complex challenges with clarity and confidence, making it easier to apply your learning in real-world scenarios. By systematically strengthening your core understanding, you set yourself up for long-term success, ensuring you’re prepared to tackle various types of tasks with efficiency and precision.
Key Areas to Focus On
Focusing on the most fundamental areas will help you build a comprehensive understanding. These are some of the critical aspects to focus on during your preparation:
- Design Principles: Understanding the essential design philosophies, aesthetics, and functionality ensures that you can create balanced and practical solutions.
- Building Regulations: Familiarity with codes, safety standards, and environmental guidelines is crucial for ensuring that your designs comply with legal and ethical requirements.
- Material Knowledge: A deep understanding of the properties and uses of different materials helps you make informed decisions about your designs and structures.
- Structural Integrity: Gaining knowledge of load-bearing systems, materials strength, and structural calculations allows you to develop sound and safe designs.
- Sustainability: Integrating environmentally conscious strategies into your designs ensures that your work is both practical and responsible.
Building Practical Skills
In addition to theoretical knowledge, practical skills are essential for creating effective solutions in real-world contexts. Working on hands-on projects, using design software, and participating in group activities can help you hone these skills. Regular practice is key to reinforcing what you’ve learned and making sure you can apply your knowledge effectively under pressure.
By focusing on these fundamental areas and developing practical skills, you’ll be well-equipped to excel in assessments. A strong foundation not only boosts your confidence but also prepares you for tackling a wide range of challenges with expertise and creativity.