
Efficient stopping mechanisms are crucial for the safety and reliability of modern vehicles. These systems use compressed air to ensure consistent and powerful deceleration, making them a preferred choice for large trucks, buses, and other heavy-duty vehicles. Understanding how these systems function can help improve safety measures and prevent unexpected malfunctions.
Key components involved in these setups include air reservoirs, valves, and pneumatic cylinders, all working together to provide reliable performance under various driving conditions. In this guide, we explore the common issues that arise, how to maintain these systems, and offer practical solutions to ensure they function optimally throughout their lifespan.
By addressing frequent concerns, we aim to equip both new and experienced users with the knowledge necessary to handle common challenges, troubleshoot effectively, and optimize system performance. Whether you’re a vehicle technician or just looking to understand how these systems operate, this section provides valuable insights to enhance your understanding.
Understanding Compressed Vehicle Stopping Systems
Efficient deceleration mechanisms are essential for the safe operation of heavy-duty vehicles. These systems use the power of compressed gases to provide stopping force, ensuring that even the largest trucks and buses can slow down or stop effectively. The mechanisms behind these setups can raise several questions regarding their functionality, maintenance, and troubleshooting. Here, we address some of the most common inquiries about these systems to help users understand their operation better.
How Do Compressed Systems Function?
In vehicles that use pneumatic systems, compressed air is stored in reservoirs and directed through various components to activate the stopping mechanism. When the driver applies pressure to the control system, the compressed air is released, causing a response in the vehicle’s stopping apparatus. This process ensures the vehicle slows down steadily and securely. Regular checks and maintenance are essential to keep these systems functioning smoothly.
Common Issues with Compressed Systems
Like any mechanical system, pneumatic stopping setups can encounter issues over time. Understanding these problems can help prevent downtime and ensure safety on the road. The most common issues include air leaks, faulty valves, and worn seals. Below is a table listing some typical problems and their potential causes:
| Problem | Potential Cause | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Air Loss | Damaged hoses or seals | Inspect and replace faulty components |
| Delayed Response | Clogged valves or lines | Clean or replace valves and air lines |
| Inconsistent Stopping Force | Low air pressure | Check air pressure levels and refill if necessary |
| System Failure | Faulty compressor | Inspect and repair or replace compressor |
Proper maintenance, including regular inspections and timely repairs, is critical to ensure that these systems remain reliable and functional. Addressing minor issues early can prevent more serious failures, contributing to the overall safety and performance of the vehicle.
How Do Compressed Vehicle Stopping Systems Work?
In modern vehicles, especially larger ones like trucks and buses, deceleration relies on the controlled release of compressed gases. This method provides the necessary force to slow or stop a vehicle effectively. The system uses a series of components, including reservoirs, valves, and pneumatic cylinders, to create the required pressure and apply it precisely when needed. Understanding how these parts interact helps in grasping how the entire mechanism functions to ensure safety on the road.
The process begins with the compression of air, which is stored in specialized tanks. When the driver engages the control system, the compressed gas is released into the system. This causes pistons to activate, which in turn applies force to the vehicle’s stopping mechanisms. This response is quick, reliable, and essential for controlling large vehicles under heavy loads.
Routine maintenance and inspections are critical to keep the system running smoothly. Regular checks ensure that air pressure is sufficient, components are not worn, and the system is free from leaks. Without these precautions, the effectiveness of the stopping system could be compromised, leading to potential hazards on the road.
Common Compressed Vehicle Stopping System Problems
Like any complex mechanical system, pneumatic deceleration setups can experience various issues over time. Understanding these common problems can help prevent performance loss and ensure optimal safety. Recognizing early signs of failure allows for timely repairs and avoids costly downtime. Below are some of the most frequent challenges users face with these systems.
- Loss of Pressure: One of the most critical issues is a drop in air pressure, which can lead to reduced stopping power. This could be caused by leaks, faulty valves, or a malfunctioning compressor.
- Delayed Response: If the vehicle’s response time is slower than usual when applying the stopping mechanism, it may indicate a clog in the air lines or an issue with the valve that controls air release.
- Uneven Performance: Inconsistent force during deceleration may suggest a problem with the distribution of air to different sections of the system, often due to worn-out components or air supply interruptions.
- Component Wear: Over time, parts such as seals, hoses, or diaphragms can deteriorate. Regular checks can prevent total failure by identifying these signs early.
- Air Tank Contamination: Dirt and moisture buildup in air tanks can interfere with air flow, leading to inefficient operation. Periodic maintenance and cleaning are required to avoid this issue.
Regular inspections and prompt attention to any of these issues are essential for maintaining safety and reliability in a vehicle’s stopping system. Addressing minor concerns quickly can extend the life of the system and prevent major failures.
How to Inspect Compressed Vehicle Stopping Systems
Regular inspections of vehicle deceleration systems are essential to ensure optimal performance and safety. These systems rely on various components working in harmony, so checking each part for wear and tear, leaks, and overall functionality is key to preventing malfunctions. Proper inspection helps identify potential issues early, reducing the risk of system failure during operation.
Visual and Physical Checks
Begin by visually inspecting all external components, including hoses, valves, and cylinders. Look for any signs of wear, cracks, or leaks. Pay particular attention to the connections and seals, as these are often the areas where air can escape. Use your hands to feel for any unusual vibrations or sounds that may indicate a problem. Leaks are a common issue that can easily be detected by listening closely or using soapy water to spot escaping air bubbles.
Pressure and Functionality Tests
Next, check the pressure levels in the system. Insufficient pressure can cause delayed response times or even complete failure of the stopping mechanism. Test the control system by applying pressure and observing the response. If the system reacts slowly or inconsistently, there may be an issue with the valve or air lines. Pressure gauges should be calibrated regularly to ensure accuracy during testing.
Ensure the air reservoirs are free from moisture and dirt, as contaminants can affect the efficiency of the entire system. Regularly drain any moisture from the tank to prevent buildup and corrosion.
By conducting thorough inspections at regular intervals, you can help ensure that the deceleration system remains in top condition, reducing the risk of unexpected failures on the road.
Key Components of Compressed Vehicle Stopping Systems
Efficient vehicle stopping relies on a complex network of components working together seamlessly. Each part plays a crucial role in ensuring the system functions effectively, from generating and storing pressure to controlling its release. Understanding the essential elements of these systems can help ensure they are properly maintained and operated for maximum performance.
The core components of this system include the pressure reservoirs, control valves, cylinders, and the compressor. Each part must work in harmony to provide reliable deceleration when needed. Regular maintenance and understanding the role of each component are essential for preventing system failures and ensuring safety on the road.
Pressure Reservoirs
The reservoirs are responsible for storing the compressed gas necessary for deceleration. These tanks must be large enough to hold enough pressure for the entire vehicle, ensuring it can stop safely under various conditions. Regular checks for leaks and corrosion are crucial to maintaining proper pressure levels.
Control Valves
Valves direct the flow of air throughout the system. When the driver engages the stopping mechanism, these valves release the compressed air to activate the cylinders. They must be free from blockages or wear, as malfunctions can lead to delayed or inconsistent responses. Regular cleaning and lubrication of these valves help maintain smooth operation.
Compressor
The compressor generates the pressure needed to fill the reservoirs. It is powered by the engine and operates continuously to ensure a steady supply of air for deceleration. Proper maintenance of the compressor is vital to prevent pressure drops and ensure that the system can perform reliably when needed.
Pneumatic Cylinders
Cylinders are the final component in the system that translates air pressure into mechanical force, applying pressure to the vehicle’s stopping mechanism. Over time, seals inside the cylinders can wear out, leading to leaks and reduced performance. Regular inspection of these cylinders helps identify issues before they result in system failure.
Compressed Vehicle Stopping System Maintenance Tips
Regular upkeep is essential for ensuring the reliability and safety of stopping systems in large vehicles. Proper maintenance can prevent unexpected failures, extend the life of key components, and keep the system running smoothly. By following a few straightforward guidelines, vehicle owners and operators can reduce the likelihood of malfunctions and costly repairs.
- Check Pressure Regularly: Maintaining the correct air pressure is critical for proper system function. Regularly inspect pressure gauges to ensure they are reading correctly, and verify that the pressure is within the recommended range.
- Inspect for Leaks: Leaks are a common problem in compressed systems. Look for signs of escaping gas around hoses, valves, and connections. If you detect a leak, replace the affected part promptly to avoid reduced performance.
- Drain Moisture from Reservoirs: Moisture can build up in air reservoirs, which can affect the system’s performance. Periodically drain water from the tanks to prevent rust and corrosion that could impair operation.
- Clean Air Filters: Clogged filters can restrict airflow, leading to poor performance. Regularly clean or replace the filters to ensure unrestricted airflow and maintain optimal pressure.
- Lubricate Moving Parts: Regular lubrication of moving components like valves and cylinders ensures smooth operation and prevents premature wear. Use the manufacturer-recommended lubricants for optimal results.
- Inspect Hoses and Connections: Over time, hoses can degrade, leading to cracks or ruptures. Check for signs of wear, such as bulges or abrasions, and replace any damaged hoses to avoid leaks or system failure.
By following these maintenance steps, vehicle operators can ensure that their stopping systems remain efficient, reliable, and safe, minimizing the risk of failure and enhancing overall vehicle performance.
Understanding Compressed Vehicle Stopping System Pressure
Pressure management is a vital aspect of ensuring that the stopping mechanism in large vehicles works efficiently. The pressure within the system directly affects its responsiveness and overall performance. Proper understanding of how pressure is generated, stored, and controlled is essential for the safe operation of these systems. When pressure levels are too low or too high, the entire system’s effectiveness can be compromised, leading to safety hazards.
How Pressure is Managed
The system generates pressure using a compressor that draws in air and stores it in pressure reservoirs. This compressed air is then released through valves to activate the mechanical components responsible for slowing the vehicle. It’s essential to maintain the right balance, as either too little or too much pressure can cause operational issues.
Importance of Monitoring Pressure
Regular monitoring of pressure levels is crucial for system efficiency. Low pressure can cause delayed responses when decelerating, while excessive pressure might lead to system overload or even damage. Proper maintenance, including checking pressure gauges and draining moisture from reservoirs, is necessary to avoid pressure-related issues.
| Pressure Range | Effect on Performance |
|---|---|
| Too Low | Delayed response time, reduced stopping power |
| Optimal | Immediate and reliable deceleration |
| Too High | Potential system overload, possible damage to components |
By maintaining the correct pressure levels and performing regular system checks, operators can ensure that the system operates effectively, minimizing the risk of malfunction and enhancing safety on the road.
What Causes Compressed Vehicle Stopping System Failure?
System failure in a vehicle’s deceleration mechanism can be a serious safety concern. Understanding the common causes of failure can help in identifying issues before they result in an emergency. A variety of factors can lead to a breakdown in performance, ranging from mechanical wear to environmental conditions. Regular checks and maintenance are essential to keeping the system in working order.
Common Causes of System Failure
There are several factors that can lead to failure in the compressed vehicle stopping system. The most frequent causes include insufficient pressure, component wear, and contamination in the system. Poor maintenance practices or neglecting early signs of malfunction can also contribute to a sudden breakdown. Below are some of the primary reasons for system failure:
| Cause | Impact |
|---|---|
| Low Pressure | Delayed response, reduced stopping ability |
| Worn Components | Leaks, loss of efficiency, complete failure |
| Moisture Contamination | Corrosion, clogging of valves, inconsistent performance |
| Improper Maintenance | Unnoticed wear, undetected leaks, system overload |
Preventing System Failures
To avoid catastrophic failures, regular inspection and timely maintenance are crucial. Checking for leaks, draining moisture, monitoring pressure levels, and replacing worn components can significantly reduce the risk of failure. Ensuring the system operates optimally helps maintain vehicle safety and performance over time.
Vehicle Stopping Mechanism Adjustment Techniques
Proper adjustment of the vehicle’s stopping system is essential for maintaining optimal performance and safety. Over time, components in the system may wear down or shift, requiring regular adjustments to ensure consistent and reliable deceleration. Proper tuning of these systems helps prevent issues such as delayed response or uneven wear, which can lead to larger malfunctions. Understanding the right techniques for adjustment is key to maintaining the integrity of the system.
Steps for Proper System Adjustment

Adjusting the stopping system requires attention to detail and adherence to manufacturer guidelines. The main goal is to ensure that all components are aligned and functioning as intended. Below are the general steps involved in adjusting the system:
- Step 1: Check for proper pressure levels before adjusting the system.
- Step 2: Inspect key components for wear or misalignment.
- Step 3: Adjust the control valve to ensure smooth operation.
- Step 4: Test the system to confirm correct response and deceleration.
Common Adjustment Issues
During adjustment, common problems may arise, such as incorrect valve settings or uneven pressure distribution. These issues can lead to poor system performance if not addressed promptly. Below are some of the most frequent adjustment-related issues:
- Uneven Pressure: This can cause inconsistent stopping force and delayed reaction time.
- Misaligned Components: Misalignment can lead to irregular wear and poor system function.
- Improper Valve Settings: Incorrect valve settings may result in sluggish or uneven deceleration.
By regularly adjusting the system and addressing any issues early, operators can ensure that their vehicle’s stopping system remains reliable and performs as expected, helping to maintain safety on the road.
Signs of Worn Vehicle Stopping System Parts
Recognizing when parts in the vehicle’s stopping system are worn out is crucial for ensuring reliable performance and safety. Over time, various components such as valves, cylinders, and seals can degrade, leading to inefficiency or even complete failure if left unchecked. Identifying these warning signs early can prevent costly repairs and safety hazards, allowing for timely maintenance and part replacements.
Common Indicators of Wear
As components in the stopping mechanism wear, they can exhibit certain signs that indicate a need for attention. Below are some of the most common indicators of worn-out parts:
- Uneven or Slow Response: If the vehicle takes longer than usual to decelerate, it could be a sign that components like valves or cylinders are losing their effectiveness.
- Leaking Fluid: Fluid leaks around the system’s connections often indicate worn seals or damaged hoses that need replacing.
- Excessive Noise: Unusual sounds such as hissing or grinding can point to problems like worn pistons or faulty valves.
- Inconsistent Stopping Power: If the stopping force feels weaker or erratic, it could mean that components like the regulator or compressor are worn and failing to maintain optimal pressure.
Maintaining System Integrity
Regular inspections and maintenance are essential to identify worn parts early. Ensuring that all parts are functioning correctly can prevent unexpected failures and maintain the vehicle’s stopping efficiency. By monitoring these warning signs, drivers and operators can address issues before they become dangerous or lead to expensive repairs.
Benefits of Pneumatic Systems Over Hydraulic Systems
Pneumatic systems offer several advantages over hydraulic counterparts, especially when it comes to large vehicles or heavy-duty machinery. While both types use fluid to generate pressure for stopping or controlling mechanisms, pneumatic systems rely on compressed gases, which bring unique benefits. These advantages include better efficiency, easier maintenance, and enhanced safety, making pneumatic systems a preferred choice in many industrial and commercial applications.
Key Advantages of Pneumatic Systems
There are several reasons why pneumatic systems are often favored over hydraulic systems, particularly for heavy-duty use. Below are some of the key benefits:
- Better Control in Extreme Conditions: Pneumatic systems can operate effectively in a wide range of temperatures and environments, while hydraulic systems may struggle in extreme conditions.
- Less Risk of Leaks: Since compressed gases are used instead of liquids, pneumatic systems are less prone to leakage, reducing maintenance costs and environmental hazards.
- Lower Operating Costs: Compressed air is more readily available and cost-effective compared to hydraulic fluid, which can be expensive and require frequent replenishment.
- Faster Response Time: Pneumatic systems can deliver faster responses due to the nature of compressed air, allowing for quicker stopping or activation in demanding situations.
Why Choose Pneumatic Systems?
The primary reason for choosing pneumatic systems over hydraulics lies in their simplicity and efficiency, particularly in commercial vehicles and heavy machinery. With fewer parts susceptible to wear and tear, these systems are often more durable and easier to maintain. Additionally, the cost-effectiveness and safety features further make pneumatic systems a reliable and practical solution for many industries.
How to Troubleshoot Vehicle Stopping Systems
Effective troubleshooting of a vehicle’s stopping system is essential for maintaining optimal performance and safety. If any part of the system malfunctions, it can affect the vehicle’s stopping power and reliability. Recognizing common issues early and understanding how to address them can prevent breakdowns and costly repairs. The process involves identifying symptoms, isolating the source of the problem, and applying the correct fixes to restore functionality.
Common Issues to Look For
When troubleshooting a stopping mechanism, several common problems can arise. Below are some of the typical symptoms and potential causes that should be investigated:
- Unresponsive or Sluggish Stopping Action: This could be caused by air pressure issues, leaks, or malfunctioning valves that are not maintaining the required pressure.
- Excessive Noise: Hissing or whistling sounds may indicate air leaks in the system, while grinding noises could signal internal component wear or contamination.
- Unusual Vibrations or Pulling: Uneven wear or misalignment in the system’s components can lead to unstable performance, causing the vehicle to pull to one side or experience erratic deceleration.
- Fluid Leaks: Leaks in the hoses or seals can lead to loss of pressure, which can impair the effectiveness of the system. Identifying the source of the leak is crucial.
Steps for Effective Troubleshooting
Once the problem is identified, troubleshooting involves several key steps to ensure the system is functioning properly. Here’s a general process to follow:
- Step 1: Perform a visual inspection to check for leaks, cracks, or damaged components.
- Step 2: Test system pressure levels to ensure they are within the recommended range.
- Step 3: Listen for any unusual sounds and isolate the source of leaks or malfunctioning parts.
- Step 4: Replace or repair damaged components, such as hoses, valves, or seals.
- Step 5: Test the system again to ensure proper functionality and responsiveness.
By following these steps and being proactive in addressing issues, vehicle operators can maintain a reliable stopping system and avoid unexpected failures on the road.
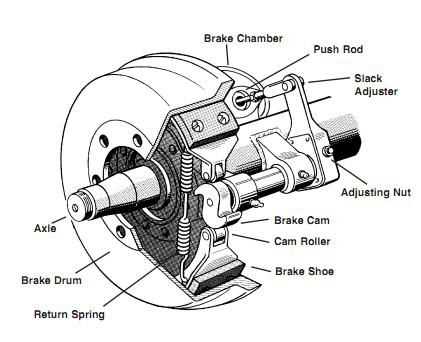
Valves and Their Roles in Vehicle Stopping Systems
Valves are critical components in any vehicle’s stopping system, playing a central role in controlling the flow and pressure of the system’s operational fluids. These devices manage the delivery of pressure to different parts of the system, ensuring efficient and safe stopping performance. Each type of valve serves a unique function, contributing to the overall reliability and responsiveness of the vehicle’s braking mechanism.
Types of Valves and Their Functions
There are various valves in a stopping system, each designed to perform specific tasks. Below are some of the main types and their respective roles:
- Quick Release Valve: This valve is responsible for quickly releasing pressure from the system when necessary, helping to maintain smooth and responsive operation.
- Relay Valve: The relay valve helps regulate the pressure and sends signals to the control mechanism, ensuring that pressure is applied evenly throughout the system.
- Pressure Protection Valve: This valve ensures that the system maintains the required pressure levels to avoid failures or irregular functioning.
- Check Valve: A check valve prevents the backward flow of pressure, ensuring that the fluid only flows in one direction to avoid potential issues with the operation.
- Modulating Valve: This valve controls the flow rate of pressure to specific components, allowing for smooth and precise adjustments to stopping power.
Maintaining Valve Efficiency
Proper maintenance of these valves is essential to ensure optimal performance and safety. Regular inspections should be carried out to identify any wear, leaks, or blockages that may hinder their function. Additionally, replacing faulty valves promptly can prevent system failures and extend the lifespan of other components within the system.
When to Replace Stopping System Shoes
The shoes in a vehicle’s stopping system are essential components that directly impact performance. Over time, they wear down due to constant friction, and understanding when to replace them is key to maintaining optimal safety and function. Regular monitoring of these components can prevent damage to other parts of the system and ensure reliable stopping power when needed most.
Signs That Shoes Need Replacing
There are several indicators that it might be time to replace the stopping system shoes. These signs include:
- Excessive Wear: If the shoes are worn down to a point where the material is significantly thinner than the recommended thickness, replacement is necessary.
- Poor Stopping Performance: If the vehicle takes longer to stop or exhibits reduced response, it could be a sign that the shoes are no longer effective.
- Noisy Operation: Unusual squealing or grinding noises during operation can indicate that the shoes are worn out or damaged.
- Visible Damage: Cracks, deep grooves, or other physical damage to the shoes are clear indicators that replacement is needed.
- Uneven Wear: If one shoe shows more wear than others, it could suggest an alignment issue or other mechanical problem that requires attention.
How to Ensure Proper Replacement
When replacing the shoes, ensure that the replacements are of high quality and compatible with the vehicle’s system. It’s also important to inspect related components, such as the drum or rotor, to ensure there is no additional damage that could affect performance. Regular maintenance checks should be scheduled to prevent premature wear and extend the life of the entire system.
How to Improve Stopping System Performance
Optimizing the performance of a vehicle’s stopping mechanism is crucial for safety and efficiency. Several factors contribute to its effectiveness, including the condition of components, proper maintenance, and regular inspections. By following key guidelines, drivers can ensure that the system operates at peak performance, providing reliable stopping power when needed most.
Key Factors for Improving Performance
To enhance the overall function of the stopping system, consider the following practices:
- Regular Maintenance: Frequent checks and servicing of all components ensure that wear and tear do not compromise the system’s efficiency. Pay close attention to wear patterns on shoes and related components.
- Proper Adjustment: Ensure all components are properly aligned and adjusted. Incorrect settings can lead to uneven wear, reduced stopping power, and potentially dangerous conditions.
- High-Quality Components: Always use high-quality replacement parts that meet the manufacturer’s standards. Cheap or incompatible parts can reduce system reliability and increase wear.
- Monitoring Air Pressure: Maintaining the proper pressure levels within the system is essential for consistent performance. Low or irregular pressure can lead to sluggish operation and increased wear.
- Efficient Use: Train drivers to use the stopping system efficiently. Avoiding excessive or harsh application can extend the lifespan of the components and prevent unnecessary damage.
Performing Regular Inspections
To ensure that the stopping system functions as expected, perform thorough inspections regularly. Look for any signs of damage, leaks, or wear in critical areas. Early detection of potential issues can save time and money, while also preventing breakdowns that could compromise safety on the road.
Stopping Mechanisms in Heavy Duty Vehicles
In heavy-duty vehicles, reliable stopping systems are essential for both safety and performance. These systems are designed to manage the high demands placed on vehicles that carry large loads or travel long distances. They are more robust than those in standard vehicles, offering greater power and control to ensure vehicles can stop safely under various conditions.
Why Heavy Duty Vehicles Require Special Systems

Heavy-duty vehicles face unique challenges due to their size, weight, and the loads they transport. A typical vehicle system might not be sufficient to handle the additional strain of frequent stopping and starting or long-haul braking. The use of a high-performance stopping mechanism is crucial for the following reasons:
- Increased Stopping Power: These systems provide the necessary force to stop large vehicles efficiently, even when fully loaded.
- Enhanced Safety: A properly functioning system reduces the risk of accidents, especially in emergencies or when driving on steep grades.
- Durability: The heavy-duty design is built to withstand harsh conditions, including frequent use and extreme temperatures.
- Improved Control: These systems offer precise control, allowing drivers to manage their vehicle more effectively, even in challenging driving situations.
Maintaining Optimal Performance
To ensure the stopping system in a heavy-duty vehicle continues to function properly, regular maintenance and monitoring are essential. Key maintenance practices include:
- Regular Inspection: Check all components regularly for signs of wear or damage. Early detection of issues can prevent costly repairs.
- System Calibration: Ensure the system is properly calibrated for the specific needs of the vehicle. Misadjustments can lead to reduced performance or safety hazards.
- Air Pressure Monitoring: For systems that rely on air pressure, it’s vital to maintain optimal levels to ensure consistent and reliable function.
- Component Replacement: Replace any worn or damaged parts promptly to maintain the system’s efficiency and avoid potential failure.