To effectively handle critical medical situations, healthcare professionals must be well-prepared for emergency scenarios that require advanced life-saving techniques. Practicing and mastering the key procedures involved in these high-pressure moments is essential for success in life-threatening conditions.
Simulating real-life challenges helps improve decision-making abilities and ensures that responses are quick and accurate under pressure. Comprehensive preparation not only boosts confidence but also sharpens the skills needed to manage complex situations efficiently.
Through targeted review and active participation in mock scenarios, medical teams can reinforce their knowledge and refine their techniques. This process allows them to identify gaps in understanding and correct any uncertainties before facing real-life emergencies.
ACLS Practice Exam Questions and Answers
Preparing for certification in advanced life support requires not only theoretical knowledge but also the ability to apply concepts in real-world situations. The process involves understanding various medical protocols, treatment options, and emergency response strategies. Practicing with relevant scenarios allows healthcare professionals to sharpen their skills and gain confidence in their ability to act swiftly during critical moments.
Key Areas to Focus On
In order to effectively manage life-threatening situations, it is crucial to review the most important areas, including cardiovascular emergencies, airway management, and drug administration. Understanding the specific procedures involved in each of these areas prepares individuals for the decision-making required in real-time scenarios. Simulating various cases ensures readiness when actual emergencies arise.
Techniques for Effective Study
To maximize preparation, it is beneficial to incorporate a variety of learning tools such as quizzes, case studies, and scenario-based drills. These methods allow individuals to test their knowledge, identify areas that need further review, and improve their performance under stress. Regular practice not only increases retention but also develops a deeper understanding of complex medical protocols.
Understanding ACLS Certification Requirements
Obtaining certification in advanced life-saving techniques is a key step for healthcare providers aiming to manage critical medical emergencies. The process involves meeting specific training prerequisites and demonstrating competence in handling life-threatening situations. This certification ensures that professionals are equipped with the knowledge and practical skills to act effectively in emergencies.
Prerequisites for Certification
Before pursuing certification, individuals must fulfill certain educational and experience requirements. These prerequisites are designed to ensure that candidates possess the foundational knowledge necessary for advanced training. Key requirements include:
- Basic life support certification
- Relevant healthcare experience, typically in emergency or intensive care settings
- Completion of a recognized course in advanced life support procedures
Certification Process
The process to achieve certification typically involves two main components: completing an accredited training program and passing a skills assessment. During training, candidates are taught how to manage critical situations, such as cardiac arrest and respiratory distress, using evidence-based guidelines. To achieve certification, individuals must:
- Participate in theoretical learning through online modules or in-person sessions
- Engage in hands-on practice through simulations and case studies
- Successfully complete a skills test to demonstrate practical application of learned techniques
Once all requirements are met, candidates receive official certification, which is valid for a set period before requiring renewal through continuing education and re-assessment.
Key Concepts in ACLS Protocols

Effective management of critical health emergencies requires a clear understanding of established guidelines that prioritize rapid intervention and systematic care. These protocols outline a series of steps designed to address life-threatening situations efficiently, ensuring that healthcare providers respond appropriately to conditions such as cardiac arrest, stroke, and respiratory failure.
Core Principles of Emergency Response

The foundation of these protocols lies in quick and accurate decision-making. Healthcare providers must be able to assess the situation rapidly and apply the correct treatment sequence. Key principles include:
- Immediate Action: Prioritizing life-saving measures such as chest compressions, defibrillation, and airway management.
- Continuous Monitoring: Regular assessment of the patient’s vital signs and adjusting interventions as necessary.
- Team Coordination: Clear communication and collaboration among medical team members to ensure seamless care delivery.
Advanced Techniques and Medications
In addition to basic life support measures, advanced protocols involve the use of medications and specialized equipment. Healthcare providers are trained to administer specific drugs, such as epinephrine or amiodarone, depending on the clinical scenario. These treatments are designed to stabilize the patient’s condition and support recovery. Additionally, advanced airway management, including intubation and the use of mechanical ventilation, may be required to ensure optimal oxygen delivery during resuscitation efforts.
Importance of ACLS for Healthcare Providers
Advanced medical training is crucial for healthcare professionals to ensure they are fully equipped to handle critical situations where fast action can mean the difference between life and death. The ability to respond quickly and effectively in emergencies, such as cardiac arrest, respiratory failure, and stroke, requires specialized knowledge and skills that are honed through comprehensive education and hands-on experience.
Improved Patient Outcomes: Healthcare providers trained in advanced life-saving techniques are more likely to deliver timely and effective care. By mastering essential protocols, they can stabilize patients during emergencies, increasing the chances of survival and reducing long-term complications.
Confidence in Critical Moments: In high-stress situations, it is easy to feel overwhelmed. However, healthcare professionals who have undergone rigorous training are better prepared to stay calm, assess the situation, and make informed decisions. This confidence is key to delivering the best care under pressure.
Team Collaboration: Effective emergency response often involves coordination between multiple healthcare providers. Advanced training programs teach the importance of clear communication, role clarity, and seamless teamwork, which are vital in ensuring that all necessary interventions are applied without delay.
Common ACLS Exam Question Types
When preparing for certification in advanced life support, understanding the types of scenarios and content commonly tested is essential. The assessment typically covers a broad range of situations that healthcare professionals might face in high-pressure environments. It is designed to evaluate not only theoretical knowledge but also the practical application of advanced life-saving procedures.
Scenario-Based Questions
These questions often present real-world situations that require immediate decision-making. They test the ability to quickly identify the correct course of action, such as:
- Determining the appropriate response for a patient in cardiac arrest.
- Choosing the correct medication for specific medical emergencies.
- Identifying symptoms of life-threatening conditions such as stroke or respiratory distress.
Multiple-Choice Questions on Protocols
These questions focus on assessing familiarity with detailed protocols and procedures. Candidates are asked to select the most accurate answer from several options, which often include:
- Correct drug dosages and administration routes for various conditions.
- The proper steps for airway management and ventilation techniques.
- The sequence of actions required during specific emergency interventions.
Case Study Simulations

In these scenarios, participants must analyze a patient’s condition, interpret vital signs, and decide on a comprehensive treatment strategy. Case study simulations test both knowledge and practical decision-making skills in complex situations.
How to Prepare for ACLS Exams

Preparation for certification in advanced life-saving techniques requires a focused and systematic approach. To successfully navigate the assessment, healthcare professionals must not only master theoretical concepts but also develop the practical skills necessary to respond effectively in high-stress situations. Structured preparation strategies can greatly enhance both knowledge retention and performance under pressure.
Effective Study Methods
To ensure a comprehensive understanding of the material, it’s essential to combine different learning techniques. Below is a suggested study plan to help candidates prepare efficiently:
| Study Method | Description | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Interactive Courses | Participate in online or in-person courses that offer both theoretical lessons and practical exercises. | Enhances retention through hands-on experience and expert guidance. |
| Scenario-Based Drills | Engage in case simulations that mimic real-life emergencies to test decision-making skills. | Builds confidence in applying protocols under pressure. |
| Review Protocols | Study key guidelines and procedures, focusing on the most commonly tested areas. | Improves familiarity with standard practices and reduces the likelihood of mistakes. |
| Group Study Sessions | Collaborate with colleagues to discuss case studies and complex concepts. | Encourages knowledge sharing and clarifies difficult topics. |
By following a structured approach and focusing on the most critical areas, candidates can significantly increase their chances of passing the assessment with confidence and competence.
Study Tips for ACLS Practice Tests
Preparing for an assessment in advanced life support requires a strategic approach to studying. To achieve success, it’s essential to focus on mastering key concepts, understanding critical protocols, and practicing the application of these skills in emergency scenarios. Effective study habits can greatly enhance retention and ensure readiness when faced with real-life situations.
One of the most effective ways to prepare is by using practice tests and mock scenarios. These tools not only reinforce the material but also help identify areas where additional review is needed. By simulating real exam conditions, individuals can gain confidence and improve their ability to recall important details under pressure.
Effective Study Techniques
To make the most of your study sessions, consider the following techniques:
- Active Recall: Focus on actively retrieving information from memory rather than passively reading or reviewing notes. This strengthens retention and helps with long-term learning.
- Timed Practice Sessions: Practice under timed conditions to simulate the real exam environment. This will improve your time management skills and reduce stress.
- Review Mistakes: After completing practice tests, carefully review your incorrect answers. Understanding why a particular response is wrong is just as important as knowing the correct one.
- Group Study: Collaborate with peers to test each other and discuss complex concepts. Group study can help clarify difficult material and enhance understanding through shared knowledge.
Incorporating these study methods into your preparation will not only improve your knowledge but also boost your confidence when approaching the actual test.
Overview of ACLS Algorithms

In critical care situations, clear and structured guidelines are essential for making rapid decisions that can save lives. These guidelines are typically organized into a series of step-by-step procedures, known as algorithms, which guide healthcare professionals through the appropriate responses to various emergencies. These procedures ensure that life-saving interventions are performed in the correct order, with minimal delay and maximum efficiency.
Key Algorithms in Advanced Life Support
Several algorithms form the backbone of response protocols in emergencies such as cardiac arrest, arrhythmias, and stroke. Each algorithm is designed to address specific clinical scenarios, ensuring that healthcare providers have a clear course of action. The main algorithms include:
- Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation (CPR) Algorithm: Provides a systematic approach to performing chest compressions, defibrillation, and other critical actions during a cardiac arrest.
- Advanced Airway Management Algorithm: Focuses on securing and maintaining the airway to ensure proper oxygenation and ventilation.
- Post-Cardiac Arrest Care Algorithm: Guides the management of patients after the restoration of spontaneous circulation, ensuring continued stabilization and assessment.
- Acute Coronary Syndrome Algorithm: Details the steps for managing chest pain, heart attack symptoms, and related conditions.
Understanding the Algorithm Structure
Each algorithm consists of a series of actions to be taken in a specific order, often accompanied by decision points. At each step, healthcare providers must assess the patient’s condition and select the appropriate intervention. These steps typically involve:
- Assessment: Initial evaluation of vital signs, rhythm, and clinical symptoms.
- Interventions: Administration of medications, electrical therapy (such as defibrillation), or airway management techniques.
- Reassessment: Continuous monitoring of the patient’s response to interventions, with adjustments as necessary.
By following these structured pathways, healthcare professionals can ensure they are providing timely and effective care in emergency situations, ultimately improving patient outcomes.
Managing Cardiac Arrest in ACLS
Cardiac arrest is a critical emergency that requires immediate and effective intervention. Rapid recognition of the condition and prompt application of life-saving techniques can significantly improve the chances of survival. The management process involves a series of coordinated steps designed to restore circulation, oxygenate the body, and address the underlying causes of the arrest.
Key Steps in Cardiac Arrest Management
When a patient is in cardiac arrest, there are several key actions that must be taken immediately to improve the likelihood of a successful resuscitation. The following steps are central to managing a cardiac arrest event:
- Immediate Recognition: Identifying signs of cardiac arrest, such as unresponsiveness and absent pulse, is the first step in initiating the appropriate response.
- Call for Help: Promptly activating the emergency response system ensures that additional resources, such as advanced care teams, are mobilized quickly.
- Chest Compressions: Begin high-quality chest compressions without delay. Compressions should be deep and fast, at a rate of 100 to 120 per minute, to maintain blood flow to vital organs.
- Defibrillation: If the rhythm is shockable, early defibrillation is crucial. Use an automated external defibrillator (AED) to deliver a shock as soon as possible.
- Airway Management: Ensure the airway is open, and administer rescue breaths to provide oxygenation, especially if advanced airway techniques are available.
Post-Resuscitation Care
After restoring circulation, the patient must be continuously monitored and managed to ensure stability. Key actions include:
- Ongoing Monitoring: Regularly assess vital signs, including heart rate, blood pressure, and oxygen saturation levels.
- Therapeutic Hypothermia: Cooling the patient may be considered to reduce brain injury and improve neurological outcomes in certain cases.
- Identifying the Cause: Efforts should be made to diagnose the underlying cause of the arrest, whether it be a heart attack, arrhythmia, or another condition, and treat it accordingly.
Effective management of cardiac arrest relies on timely interventions, teamwork, and adherence to established protocols. By following these critical steps, healthcare providers can significantly increase the chances of survival and improve long-term outcomes for patients.
Advanced Airway Management in ACLS
Securing the airway is a critical component of managing any life-threatening emergency. In situations where a patient’s breathing is compromised or absent, advanced techniques are required to ensure adequate oxygenation and ventilation. These methods go beyond basic measures and are designed to manage the airway effectively, even in complex or difficult cases.
Key Techniques in Advanced Airway Management
When basic airway methods, such as head-tilt-chin-lift or mouth-to-mouth ventilation, are insufficient, more advanced procedures come into play. These techniques are essential in providing a secure airway in patients who require prolonged or more controlled ventilation. Some of the most commonly used advanced airway management strategies include:
- Endotracheal Intubation: Inserting a tube into the trachea to secure the airway and facilitate mechanical ventilation. This technique is often performed by trained healthcare providers in critical care settings.
- Supraglottic Airway Devices: Devices such as the laryngeal mask airway (LMA) or i-gel are inserted into the airway to maintain patency and allow for ventilation without the need for endotracheal intubation.
- Cricothyroidotomy: A surgical procedure to create an emergency airway when other methods are not possible, typically performed when there is an obstruction preventing intubation.
Considerations for Airway Management
Effective airway management requires not only the proper technique but also constant assessment and adjustment based on the patient’s condition. Several factors must be considered, including:
- Timing: Immediate intervention is crucial to prevent brain injury due to hypoxia. Delayed or ineffective airway management can lead to irreversible damage.
- Airway Clearance: Removing any obstruction, such as blood, vomit, or foreign bodies, is vital to ensuring a clear path for oxygen and ventilation.
- Oxygenation Monitoring: Continuous monitoring of oxygen levels and ventilation effectiveness should be done to ensure proper delivery of oxygen to vital organs.
In emergency situations, advanced airway management is an essential skill for healthcare providers. Mastery of these techniques ensures that patients receive the necessary care to maintain oxygenation and survive life-threatening events.
ACLS Pharmacology and Medications
In life-threatening emergencies, medications play a crucial role in stabilizing the patient, correcting underlying conditions, and facilitating recovery. Pharmacological interventions are designed to address various cardiac and respiratory issues, such as arrhythmias, ischemia, and hypoxia. Understanding the medications used in advanced resuscitation is essential for healthcare professionals to effectively manage critical situations.
Medications are administered to restore normal heart rhythm, improve oxygenation, or support the circulatory system. These drugs are often chosen based on the patient’s condition, with specific protocols determining which medications should be given at different stages of care. Proper dosing and timely administration can greatly impact the patient’s prognosis.
Common Medications Used in Emergencies
Several medications are frequently used to manage patients in life-threatening conditions. These include:
- Adrenaline (Epinephrine): This potent vasoconstrictor and inotrope is used to increase heart rate and improve blood flow, especially during cardiac arrest.
- Amiodarone: A powerful antiarrhythmic used to treat ventricular arrhythmias, helping to stabilize the heart’s electrical activity.
- Lidocaine: Another antiarrhythmic drug used to treat ventricular arrhythmias, often administered when other medications are ineffective.
- Atropine: Used to increase heart rate in cases of bradycardia (slow heart rate), typically administered in emergency situations where the heart rate is dangerously low.
- Magnesium Sulfate: Used to manage torsades de pointes and other specific arrhythmias, particularly when electrolyte imbalances are suspected.
Administration Routes and Considerations
Medications can be administered through various routes, depending on the clinical situation. The most common methods include intravenous (IV), intraosseous (IO), and endotracheal routes. Each method has its advantages and limitations, and the choice of route depends on the patient’s access and urgency of the situation.
- IV Administration: The preferred method for most medications during resuscitation, offering rapid absorption and effective delivery.
- IO Administration: Used when intravenous access is difficult to obtain, providing fast access to the circulatory system through the bone marrow.
- Endotracheal Administration: In certain circumstances, medications can be delivered via the endotracheal tube when other routes are unavailable.
Proper knowledge of pharmacology, as well as the indications, contraindications, and dosing of medications, is essential for effective resuscitation and patient management. Healthcare professionals must be familiar with these pharmacological agents and be prepared to use them in a timely and efficient manner during critical events.
Interpreting ECGs in ACLS Exams
Understanding the interpretation of electrocardiograms (ECGs) is vital for healthcare providers in emergency situations. ECGs are used to monitor the heart’s electrical activity, and recognizing abnormal patterns is essential for diagnosing conditions like arrhythmias, ischemia, and heart attacks. In high-stress clinical environments, timely and accurate ECG interpretation can make a significant difference in patient outcomes.
ECGs are a critical part of resuscitation efforts, providing real-time data that guide treatment decisions. Healthcare professionals need to quickly identify different arrhythmias and other cardiac abnormalities, and recognize when immediate interventions are required. This skill is often tested during advanced certification assessments to ensure that providers can respond efficiently during life-threatening emergencies.
Common ECG Rhythms in Emergency Situations
Recognizing common arrhythmias is essential for effective patient management. Below are some of the most common patterns healthcare professionals need to identify:
| Rhythm | Description | Action |
|---|---|---|
| Ventricular Fibrillation | Irregular, chaotic electrical activity with no identifiable QRS complexes or P waves. The heart is not pumping blood effectively. | Immediate defibrillation is required. |
| Ventricular Tachycardia | Fast, abnormal heart rhythm originating from the ventricles. Can lead to loss of pulse if untreated. | Defibrillation or medication to restore normal rhythm. |
| Atrial Fibrillation | Irregular heart rhythm with no distinct P waves. Often leads to decreased cardiac output. | Medication to control rate or rhythm, sometimes synchronized cardioversion. |
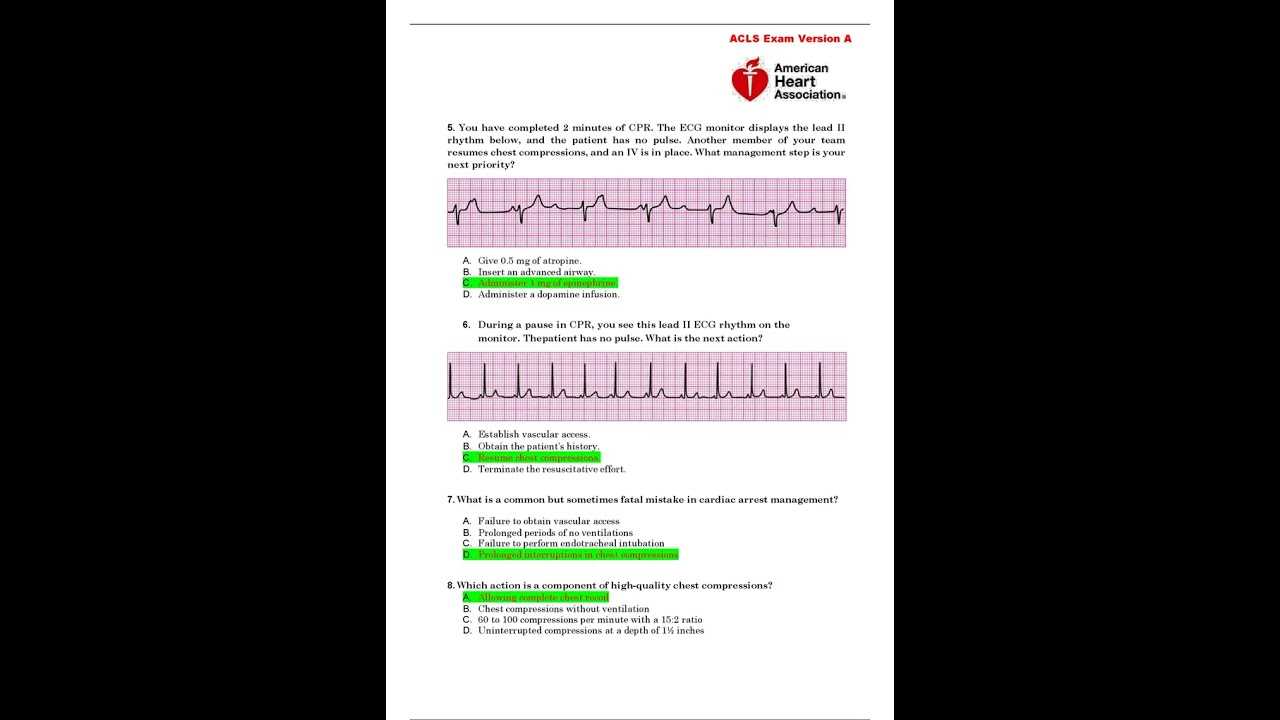
| Asystole | Complete absence of electrical activity. No heart contractions. | CPR and administration of epinephrine. |
| Bradycardia | Slower than normal heart rate, often with irregular rhythm. | Consider atropine administration or pacing if symptomatic. |
Key Considerations in ECG Interpretation
When interpreting ECGs, it is important to focus on several key elements:
- Heart Rate: The number of heartbeats per minute, which can help determine whether the heart is functioning too slowly (bradycardia) or too quickly (tachycardia).
- Rhythm Regularity: Whether the heart rhythm is regular or irregular. Irregular rhythms may indicate issues such as atrial fibrillation or other arrhythmias.
- Waveform Patterns: The P waves, QRS complexes, and T waves should be analyzed to assess the heart’s electrical conduction.
- Intervals: The PR interval, QRS duration, and QT interval can provide important information about conduction delays or abnormal patterns.
Properly interpreting ECGs in emergency scenarios requires practice and a deep understanding of cardiac physiology. Healthcare providers must be able to make quick decisions based on these readings, often under pressure, to ensure the best possible patient care.
ACLS Pediatric and Neonatal Considerations
Managing pediatric and neonatal patients in emergency situations requires specialized knowledge and tailored approaches. The physiological differences between children, infants, and adults significantly affect how medical interventions should be applied. In cases of cardiac arrest or respiratory distress, quick and accurate assessments are crucial to providing effective care for younger patients. Healthcare professionals need to be well-prepared to recognize the unique needs of these vulnerable populations and implement life-saving techniques appropriately.
The primary difference in treating pediatric and neonatal patients lies in their smaller size, faster metabolism, and different cardiovascular responses. These factors influence medication dosages, the technique for airway management, and the methods of providing chest compressions or defibrillation. A solid understanding of these nuances is necessary for delivering the best outcomes in critical situations.
Pediatric Resuscitation: Key Differences
Pediatric resuscitation follows many of the same principles as adult resuscitation, but adjustments are required to account for a child’s smaller anatomy and unique physiological responses. Here are a few important aspects to consider:
- Airway Management: Smaller airways in children require more delicate handling, with specialized tools such as pediatric-sized endotracheal tubes.
- Chest Compressions: Depth and rate of compressions differ between children and adults. The recommended compression depth for children is about one-third of the chest’s anterior-posterior diameter.
- Defibrillation: For pediatric patients, defibrillation should use a lower energy setting. Pediatric pads or manual defibrillators should be used when available.
Neonatal Resuscitation Considerations
Newborns in distress require immediate intervention, but their treatment protocols are distinct from both adult and pediatric care. Neonatal resuscitation focuses heavily on ensuring the airway is clear and providing oxygenation. Special considerations include:
- Oxygenation: Neonates may need supplemental oxygen or positive pressure ventilation, but over-oxygenation must be avoided to prevent complications such as retinopathy of prematurity.
- Heart Rate Assessment: Neonates with a heart rate below 60 beats per minute require immediate chest compressions in addition to positive pressure ventilation.
- Fluid Management: Proper fluid resuscitation is crucial for neonatal patients. In cases of hypovolemic shock, balanced fluid therapy is often the first step.
Understanding these differences and preparing for the challenges associated with pediatric and neonatal emergencies will ensure healthcare providers are ready to intervene effectively in critical situations. Ongoing training and familiarity with the latest protocols are essential for successful outcomes when treating younger patients in distress.
Practice Exam Strategies for Success
Preparing for a certification or assessment test requires more than just reviewing materials; it involves a strategic approach to ensure success. By understanding the format of the test and practicing under realistic conditions, you can improve your chances of performing well. Effective preparation involves time management, mastering key concepts, and developing test-taking skills that help navigate difficult questions efficiently. A well-rounded strategy not only builds confidence but also enhances overall knowledge retention.
Using practice tests as part of your study plan helps identify areas of strength and weakness, allowing you to focus your efforts on the most critical areas. Simulating the actual testing environment can also reduce anxiety, giving you the mental clarity needed for optimal performance on test day. Knowing how to approach different types of questions can make a significant difference in your success rate.
Time Management Tips
One of the most important aspects of preparing for a test is managing your time effectively. Here are a few tips to help you stay on track:
- Set a Time Limit: Try to complete each practice test within the allotted time to develop a sense of pacing.
- Focus on the Clock: Avoid spending too much time on one question. If unsure, move on and come back later.
- Break Down the Material: Divide your study sessions into manageable time blocks and take regular breaks to maintain focus.
Understanding the Test Structure
Familiarizing yourself with the structure of the test can significantly enhance your performance. It’s essential to understand how questions are framed and the weight of different sections. Here’s how you can approach the structure:
- Identify Common Themes: Many tests focus on specific core topics. Understanding these themes helps prioritize your study material.
- Practice Under Test Conditions: Simulating actual test conditions, including time limits and distractions, will better prepare you for the real experience.
- Review Correct and Incorrect Answers: After completing practice sessions, take time to review both the correct and incorrect answers. This helps reinforce learning and identify patterns in mistakes.
Incorporating these strategies into your study plan can lead to greater success, making the preparation process more efficient and less stressful. By staying organized and focused, you increase your likelihood of achieving your certification goals and performing well under test conditions.
Understanding Rhythm Interpretation
Interpreting heart rhythms accurately is essential for making critical decisions during emergency situations. Understanding various cardiac rhythms allows healthcare providers to diagnose and treat life-threatening conditions effectively. Correct identification of these rhythms helps guide treatment plans and interventions, leading to better patient outcomes. By mastering the interpretation of electrocardiograms (ECGs) or heart monitors, medical professionals can distinguish between normal and abnormal rhythms, which is crucial in emergencies.
Recognizing rhythm abnormalities involves a systematic approach that includes identifying the rate, regularity, and morphology of the heartbeats. This knowledge helps in assessing the urgency of the situation, such as whether immediate intervention is required or if a more cautious approach is appropriate. By practicing rhythm recognition and treatment protocols, healthcare providers can increase their readiness and confidence when faced with real-world clinical scenarios.
Key Rhythms to Identify
Several key heart rhythms are commonly encountered in emergency situations, each requiring a different approach. Here are some essential rhythms to recognize:
- Normal Sinus Rhythm: Characterized by a consistent heart rate between 60 and 100 beats per minute with regular intervals. No treatment is needed unless symptoms develop.
- Bradycardia: A slower-than-normal heart rate, typically below 60 beats per minute, which may require interventions like atropine if symptomatic.
- Tachycardia: A rapid heart rate, usually over 100 beats per minute, which may require treatment depending on whether it is regular or irregular.
- Atrial Fibrillation: An irregular rhythm that can cause blood clots and increase stroke risk, often requiring anticoagulation therapy or cardioversion.
- Ventricular Fibrillation: A life-threatening, erratic rhythm that leads to ineffective heart pumping and requires immediate defibrillation to restore a normal rhythm.
Steps for Rhythm Interpretation
To accurately interpret heart rhythms, it is crucial to follow a structured method. Here are the basic steps:
- Assess the Rate: Count the number of beats per minute. A normal rate ranges from 60 to 100 bpm.
- Check Regularity: Determine whether the intervals between heartbeats are consistent.
- Examine the P Waves: Identify whether the P waves are present and consistent, as this indicates atrial depolarization.
- Measure the QRS Complex: Ensure that the QRS complex is narrow (less than 0.12 seconds) for a normal rhythm.
- Evaluate the ST Segment: Look for elevation or depression in the ST segment, which may indicate ischemia or injury.
By mastering rhythm interpretation, healthcare providers can make informed decisions that improve patient care and prevent complications during critical moments. Regular practice and continuous education on rhythm recognition are essential for maintaining competence in this area.
Testing Your Knowledge with Quizzes
One of the most effective ways to gauge your understanding and reinforce the concepts you’ve learned is by taking various quizzes designed to test your knowledge. These quizzes offer a dynamic approach to reviewing key topics, providing a hands-on opportunity to identify areas that need improvement. By answering challenging scenarios, you can assess your preparedness for real-world clinical situations and solidify your learning.
Participating in quizzes can also help you become familiar with the format and style of clinical challenges. As you progress through each quiz, you’ll develop a stronger understanding of core principles and identify patterns in questions that are commonly encountered. This active learning method not only improves retention but also helps boost confidence when it comes to applying your knowledge in practical settings.
Benefits of Taking Quizzes
Engaging in quizzes offers several advantages for those preparing for clinical assessments:
- Enhanced Retention: Quizzes help reinforce information and improve long-term memory retention, especially when reviewing complex medical concepts.
- Immediate Feedback: By reviewing answers right after completing a quiz, you can identify correct and incorrect responses, providing insight into areas needing further attention.
- Increased Confidence: Regular testing helps you become more confident in your decision-making ability, improving your overall performance in high-pressure scenarios.
- Self-Assessment: Taking quizzes allows you to evaluate your knowledge level and track your progress over time, guiding your focus for further study.
Types of Quizzes You May Encounter
Quizzes typically cover a broad range of topics, offering multiple-choice questions, case studies, and scenario-based inquiries. Here’s a table highlighting some common types of quizzes and their focus areas:
| Type of Quiz | Focus Area |
|---|---|
| Multiple-Choice | Testing knowledge on key protocols, drug dosages, and procedural steps. |
| Case Studies | Assessing the application of learned concepts to real-life situations. |
| Scenario-Based | Analyzing critical thinking in emergency response scenarios. |
| Timed Quizzes | Simulating pressure situations, requiring quick decision-making. |
By consistently engaging with quizzes that challenge your knowledge, you will be better prepared to face real-world clinical challenges. These exercises allow you to fine-tune your decision-making skills, ensuring you’re equipped to manage complex patient care situations effectively.
Exam Simulation and Mock Tests
Simulating real-world assessments is an essential step in preparation. These simulations offer a realistic environment where you can apply your knowledge, refine your skills, and familiarize yourself with the types of challenges you will face. Mock tests replicate the pressure and time constraints of actual clinical scenarios, helping to improve your response time and decision-making abilities. By practicing under simulated conditions, you can approach real-life situations with greater confidence and precision.
Using simulation tools can bridge the gap between theoretical learning and hands-on experience. They present a variety of complex cases, requiring you to make critical decisions swiftly. The feedback you receive after completing each simulation is invaluable, highlighting areas of improvement and reinforcing your strengths. Regular exposure to mock tests enhances your ability to manage high-stakes situations effectively, sharpening both your theoretical and practical skills.
Why Use Simulations and Mock Tests?
Mock tests and simulation sessions offer a host of benefits that go beyond typical study methods:
- Real-World Readiness: They replicate real clinical situations, preparing you for the types of challenges you’ll encounter in professional settings.
- Time Management: By practicing under timed conditions, you’ll become adept at managing pressure and making decisions within the limited time available.
- Knowledge Application: These tests push you to apply theoretical knowledge in a practical context, reinforcing your understanding of procedures and protocols.
- Self-Evaluation: Simulations provide a comprehensive assessment of your skills, helping you identify areas where further improvement is needed.
How Mock Tests Are Structured
Mock tests typically include a variety of scenarios designed to challenge your clinical knowledge and decision-making abilities. Here’s a breakdown of the types of tests and their focus areas:
| Test Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Timed Scenarios | Recreate high-pressure situations where quick decision-making is essential. |
| Case Studies | Detailed patient scenarios requiring a step-by-step approach to diagnosis and treatment. |
| Multiple Choice | Test knowledge of protocols, dosages, and common procedures. |
| Role-Playing | Interactive simulations where you take on a specific role, making decisions as if you were treating a patient. |
By regularly engaging with mock tests and simulations, you will refine your skills, ensuring that you are well-prepared for actual clinical assessments. This hands-on experience is invaluable in honing your decision-making abilities and enhancing your overall performance in critical care environments.
What to Expect During Certification Assessments
Certification assessments are designed to evaluate your competence in handling critical situations, applying protocols, and making decisions under pressure. These assessments are structured to test both theoretical knowledge and practical skills, ensuring that candidates are fully prepared to respond effectively in emergency medical scenarios. The format typically includes a combination of written tests, practical simulations, and real-time decision-making exercises that challenge your ability to assess and manage life-threatening conditions.
Throughout the assessment process, you can expect a variety of tasks, each designed to test different aspects of your clinical skills. It is important to stay calm and methodical, as the situations presented will require quick, yet accurate decision-making. Whether you are handling a patient scenario or answering knowledge-based questions, the focus will be on your ability to perform under pressure while adhering to established guidelines and protocols.
Key Components of the Assessment
Here’s a breakdown of what you may encounter during the assessment:
- Written Test: This part of the assessment will evaluate your understanding of key medical principles, protocols, and guidelines. Expect questions that test your theoretical knowledge, including drug dosages, emergency procedures, and algorithmic steps for various medical emergencies.
- Practical Scenarios: Hands-on simulations where you will be expected to perform medical interventions in a controlled environment. These scenarios will typically focus on managing cardiac arrest, airway management, and other critical situations.
- Role-Playing Exercises: In some cases, you may be asked to engage in role-playing activities where you take on the role of a healthcare provider, responding to simulated emergencies while demonstrating proper medical techniques.
- Skills Testing: You may be asked to demonstrate certain clinical skills, such as CPR, defibrillation, or intubation, under the watchful eye of an instructor or evaluator.
Tips for Success
To succeed in your assessment, consider the following strategies:
- Prepare Thoroughly: Review relevant protocols, procedures, and guidelines. Familiarize yourself with the most common emergency situations and their appropriate management strategies.
- Stay Calm: The ability to stay composed under pressure is crucial. Remember to breathe, focus on the task at hand, and proceed methodically.
- Practice Hands-On Skills: If possible, practice practical skills regularly. Simulations, mannequins, and hands-on drills can help you hone your ability to respond quickly and accurately.
- Review Feedback: After each practice scenario, review the feedback provided. This will help you identify areas for improvement and refine your approach for future simulations.
By understanding the structure of the assessment and preparing adequately, you can approach the process with confidence, ensuring that you are fully equipped to handle the responsibilities of a healthcare provider in critical situations.