
Understanding how to interpret heart rhythms is a crucial skill for anyone pursuing a career in healthcare. Whether you’re preparing for an upcoming certification or simply looking to sharpen your diagnostic abilities, practicing key concepts is essential. This section will guide you through various methods for improving your ability to identify and assess different heart patterns, using simulated scenarios to enhance your learning experience.
By focusing on real-world scenarios and working through challenging heart rhythm sequences, you can build confidence in your diagnostic skills. Developing a systematic approach to evaluating each rhythm can drastically improve both accuracy and speed. This method allows you to familiarize yourself with the most common patterns and anomalies, strengthening your ability to respond effectively in clinical settings.
Effective preparation involves recognizing not only the normal waves but also the variations that may indicate underlying health conditions. The more you engage with these exercises, the better you’ll understand the intricacies of rhythm identification. Each test will help you fine-tune your approach, making you more adept at spotting subtle irregularities and ensuring more reliable assessments in practice.
EKG Practice Exam with Answers
Building proficiency in heart rhythm interpretation requires a structured approach to identifying and assessing different patterns. One effective way to enhance your skills is through a variety of simulated scenarios designed to test your knowledge and application of diagnostic techniques. By engaging in these exercises, you can familiarize yourself with common heart rhythm types, as well as less frequent but equally important anomalies.
Each scenario presents a unique set of challenges, enabling you to apply what you’ve learned in a practical context. The goal is to refine your ability to quickly and accurately analyze heart rhythms, distinguishing between normal and abnormal patterns. These exercises are designed to help you think critically and improve your decision-making under pressure, which is essential for real-life situations.
Additionally, reviewing the provided solutions after completing the exercises will help you understand why specific interpretations are correct or incorrect. This feedback loop strengthens your diagnostic ability, highlighting areas where further attention may be needed. With consistent practice, your understanding of the various patterns will deepen, leading to greater confidence and expertise in the field.
Understanding the Basics of EKG
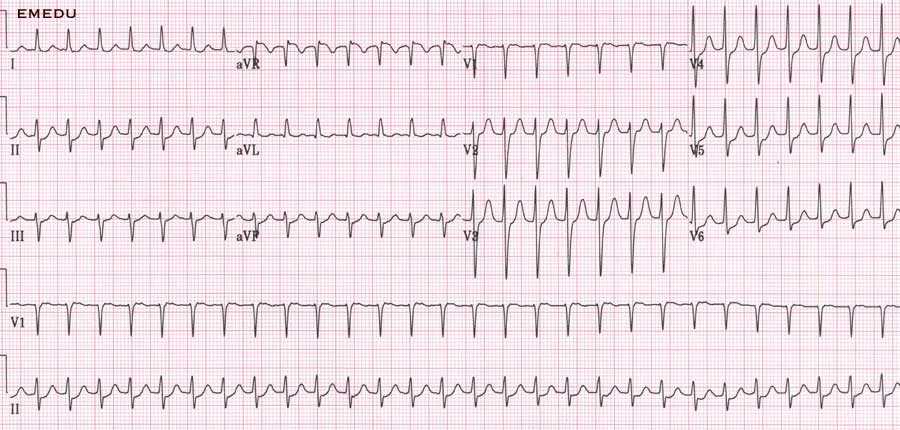
To effectively interpret heart rhythms, it’s crucial to first understand the foundational concepts behind how the heart functions electrically. The heart generates electrical impulses that control the rhythm of each heartbeat, and these impulses can be measured and recorded through specific diagnostic methods. By mastering the fundamentals of these electrical signals, you can more easily identify abnormalities and gain a deeper understanding of the heart’s behavior.
The Heart’s Electrical System
The heart’s electrical system is responsible for regulating the heartbeat. It starts in the sinoatrial (SA) node, which acts as the natural pacemaker, sending electrical impulses that travel through the heart, causing it to contract and pump blood. These signals can be traced as they move through the heart, providing valuable insights into its overall function.
Components of the Signal
To properly assess heart function, it’s important to recognize the key components of the electrical signal. The primary waves and intervals include the P wave, QRS complex, and T wave. Each represents a specific stage in the electrical activity of the heart, from the contraction of the atria to the contraction of the ventricles and the recovery phase.
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| P wave | Represents atrial depolarization (contraction). |
| QRS complex | Represents ventricular depolarization (contraction). |
| T wave | Represents ventricular repolarization (recovery). |
By learning to recognize and understand these key signals, you lay the groundwork for more advanced interpretations and can better assess heart function during diagnostic procedures.
Common EKG Patterns and Waveforms
Identifying the various heart rhythm patterns and their corresponding waveforms is essential for accurate diagnosis. The electrical impulses generated by the heart produce distinct waves that can be analyzed to assess its condition. Recognizing these common patterns is the first step toward understanding the heart’s electrical activity and detecting any abnormalities.
Each rhythm and waveform represents a specific phase in the heart’s cycle, from contraction to relaxation. Below are some of the most common patterns encountered in diagnostic assessments:
- Normal Sinus Rhythm: Represents a steady and regular rhythm originating from the heart’s natural pacemaker.
- Atrial Fibrillation: A rapid and irregular rhythm originating from the atria, leading to an uncoordinated contraction of the heart muscle.
- Ventricular Tachycardia: A fast heart rate originating from the ventricles, often indicating a serious underlying issue.
- Bradycardia: An abnormally slow heart rate, typically below 60 beats per minute.
- Premature Ventricular Contractions (PVCs): Early heartbeats originating from the ventricles, often creating irregularities in rhythm.
Each of these rhythms can be distinguished by the specific appearance of their waveforms on a graph. For instance, the normal sinus rhythm will show evenly spaced waves, while conditions like atrial fibrillation or ventricular tachycardia will exhibit more erratic patterns.
Understanding these common patterns helps in both identifying abnormalities and responding to potential health concerns. With repeated exposure and practice, recognizing these waveforms becomes second nature, allowing for faster and more accurate evaluations in clinical settings.
Key Skills for EKG Interpretation
To effectively analyze and interpret heart rhythms, several essential skills are required. These abilities allow healthcare professionals to quickly and accurately assess the heart’s electrical activity, helping to identify normal patterns as well as potential abnormalities. Mastery of these skills ensures that the interpreter can make informed decisions in both routine and emergency situations.
Fundamental Abilities for Accurate Analysis
Understanding the core components of heart rhythms is the first step toward developing proficiency in interpretation. The following abilities are critical:
- Wave Identification: Recognizing the P wave, QRS complex, and T wave is fundamental to understanding the phases of the heart cycle.
- Rhythm Recognition: Being able to distinguish between regular and irregular rhythms helps in diagnosing conditions such as arrhythmias.
- Time Interval Measurement: Accurately measuring the intervals between waves, such as the PR interval and QT interval, helps identify conduction delays and other issues.
- Heart Rate Calculation: Determining the heart rate by counting the number of beats over a specific time frame is crucial for diagnosing tachycardia and bradycardia.
Advanced Skills for Complex Interpretations
As experience grows, the ability to analyze more complex rhythms and variations becomes increasingly important. Some advanced skills include:
- Identifying Arrhythmias: Recognizing irregular rhythms like atrial fibrillation or ventricular tachycardia requires keen attention to detail and experience.
- Assessing Heart Blocks: Understanding different types of heart block, such as first-degree or complete block, is key to accurate diagnosis.
- Understanding Ischemic Changes: Recognizing ST segment changes can provide vital clues about potential myocardial infarctions or ischemia.
By honing these skills, healthcare providers can enhance their ability to interpret heart rhythms, ultimately leading to more accurate diagnoses and better patient outcomes.
How to Prepare for EKG Exams
Preparation for assessing heart rhythms involves a combination of knowledge acquisition, hands-on practice, and effective strategies to ensure success in diagnostic evaluations. The process requires both theoretical understanding and the ability to apply this knowledge in real-world scenarios. By following a structured approach to preparation, individuals can develop the confidence and skills needed to excel.
Building a Strong Knowledge Base
Before attempting any diagnostic tests or simulations, it is essential to have a solid grasp of the fundamental concepts. Key areas to focus on include:
- Understanding Cardiac Physiology: Familiarize yourself with the heart’s electrical system and how different rhythms are generated.
- Mastering Waveforms: Learn to identify the various waves and intervals in heart rhythm recordings, such as the P wave, QRS complex, and T wave.
- Recognizing Abnormalities: Study common arrhythmias and other irregularities, such as tachycardia, bradycardia, and atrial fibrillation.
Effective Hands-On Practice
Theoretical knowledge alone is not enough; practical experience is equally important. Some strategies for hands-on preparation include:
- Simulated Scenarios: Engage in as many practice scenarios as possible to improve pattern recognition and diagnostic decision-making.
- Timed Practice Sessions: Simulate timed assessments to improve your ability to analyze rhythms under pressure and manage time effectively.
- Review and Feedback: After each practice session, review your results and seek feedback to identify areas for improvement.
By combining comprehensive knowledge with hands-on practice, you will be well-prepared to assess heart rhythms accurately and confidently when the time comes.
Top EKG Questions for Practice
One of the most effective ways to reinforce your understanding of heart rhythm analysis is by engaging with a variety of challenging questions. These questions help to test your knowledge, refine your diagnostic skills, and prepare you for real-life situations where quick and accurate assessments are necessary. By working through these key queries, you can strengthen your ability to recognize common and complex heart patterns.
Essential Questions for Building Expertise
Here are some critical questions that will test your ability to identify and interpret various rhythms and abnormalities:
- What is the significance of a prolonged QT interval? Understanding this could help in identifying risks for arrhythmias and potential cardiac issues.
- How do you differentiate between atrial fibrillation and atrial flutter? Recognizing subtle differences in rhythm can lead to more accurate diagnoses.
- What does a wide QRS complex indicate? The width of the QRS complex can provide insights into ventricular conduction abnormalities.
- What is the normal range for heart rate based on rhythm interpretation? Calculating heart rate helps identify whether the rhythm is too fast or too slow.
- How would you identify a second-degree heart block? Understanding the variations in AV conduction is crucial for diagnosing different types of heart blocks.
Advanced Diagnostic Questions
As you grow more comfortable with basic concepts, these advanced questions will challenge your deeper understanding of heart rhythm disturbances:
- How would you recognize a ventricular tachycardia from a supraventricular tachycardia? Identifying the origin of the rhythm is key to proper treatment.
- What do ST segment changes indicate in a clinical setting? Recognizing ischemic changes or infarctions is critical for emergency care.
- What is the role of the P wave in detecting atrial abnormalities? Abnormalities in the P wave can help identify atrial arrhythmias or other conditions.
- What does a delta wave suggest in relation to the heart’s conduction system? Identifying this wave pattern could point to specific conditions like Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome.
By continuously testing your knowledge with such questions, you can enhance your ability to accurately interpret heart rhythms and improve your diagnostic skills for clinical practice.
Analyzing EKG Strips Accurately
Accurate interpretation of heart rhythm patterns is a vital skill in clinical practice. By closely analyzing the graphical representation of electrical activity, healthcare professionals can detect normal and abnormal rhythms, ultimately guiding patient care. Effective analysis involves a combination of technical knowledge, systematic evaluation, and attention to detail.
The key to interpreting rhythm strips lies in methodically assessing each component of the trace. From waveforms to intervals, every detail provides crucial information about the heart’s electrical conduction. By following a structured approach, one can ensure that no abnormalities are overlooked, and all vital information is accurately recorded.
Step-by-Step Approach to Accurate Analysis
To improve your ability to interpret heart rhythm recordings, consider these steps:
- Identify the P Wave: This small upward deflection represents atrial depolarization. Ensure that it is present and consistent in normal rhythms.
- Examine the PR Interval: Measure the time between the P wave and the QRS complex to assess the conduction between the atria and ventricles. A prolonged PR interval could indicate a block.
- Assess the QRS Complex: This is the most significant deflection, representing ventricular depolarization. A wide QRS complex may indicate a ventricular conduction delay or abnormality.
- Check the T Wave: The T wave represents ventricular repolarization. Any abnormalities in its shape or direction could signal potential cardiac issues, such as ischemia or electrolyte imbalances.
- Measure the Heart Rate: Calculating the heart rate is essential to determine whether the rhythm is too fast or slow, which may point to tachycardia or bradycardia.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
While interpreting heart rhythm strips, it’s important to avoid common errors that can lead to misdiagnosis:
- Ignoring Subtle Abnormalities: Even small deviations, such as a slight change in the T wave or a prolonged PR interval, may be indicative of a serious underlying condition.
- Overlooking Rate Calculation: An incorrect heart rate can lead to misinterpretation of the rhythm. Always double-check your calculations, especially in irregular rhythms.
- Failing to Recognize the Overall Rhythm: Pay attention to the consistency of the rhythm throughout the entire strip. A single abnormality may not be as important as the overall rhythm pattern.
By using a systematic approach and avoiding common pitfalls, you can ensure a thorough and accurate analysis of heart rhythm strips, ultimately leading to better patient outcomes.
Identifying Normal and Abnormal EKGs

Interpreting heart rhythm recordings accurately is essential in diagnosing and managing cardiovascular health. The ability to distinguish between normal and abnormal patterns is critical for providing timely and appropriate care. A comprehensive understanding of typical waveforms, intervals, and overall rhythm characteristics allows clinicians to make informed decisions based on recorded electrical activity.
While normal heart rhythms follow a predictable pattern, deviations can indicate underlying health issues. By systematically assessing various components, such as waveform shapes, intervals, and regularity, one can identify whether the heart’s electrical activity is functioning as expected or if there are signs of disturbances such as arrhythmias or conduction blocks.
Recognizing Normal Rhythms
A normal rhythm is characterized by consistent, well-defined waveforms and intervals. Some key features to look for in a typical heart rhythm include:
- Consistent P Waves: Regularly appearing before each QRS complex, signaling normal atrial depolarization.
- Normal PR Interval: The time between the P wave and QRS complex should be between 120-200 milliseconds, indicating healthy atrioventricular conduction.
- Regular QRS Complex: A narrow, sharp QRS complex suggests normal ventricular depolarization, typically lasting between 60-100 milliseconds.
- Even Heart Rate: A rate between 60-100 beats per minute is considered normal for adults at rest.
- Consistent T Waves: Smooth, upright T waves indicate proper ventricular repolarization.
Identifying Abnormalities
Abnormal rhythms can range from minor variations to life-threatening conditions. Some common irregularities include:
- Bradycardia: A slower than normal heart rate (less than 60 bpm), which may indicate underlying issues like heart block or drug effects.
- Tachycardia: An abnormally fast heart rate (over 100 bpm), often a result of stress, fever, or a variety of arrhythmias.
- Premature Beats: Early heartbeats, either atrial or ventricular, that disrupt the normal rhythm.
- Irregularly Irregular Rhythm: Conditions like atrial fibrillation, where there is no discernible pattern, and the rhythm is erratic.
- Prolonged Intervals: An extended PR interval (first-degree block) or a prolonged QT interval, both of which may signal conduction delays or electrolyte disturbances.
By recognizing the difference between normal and abnormal patterns, clinicians can effectively assess cardiac health, prioritize further testing, and implement necessary interventions to manage any underlying conditions.
How to Spot Heart Arrhythmias
Recognizing irregular heart rhythms is crucial in diagnosing and managing potential cardiovascular issues. Arrhythmias, or disturbances in the heart’s electrical activity, can vary from harmless to life-threatening. By carefully examining the recorded heart signals, healthcare professionals can identify abnormal rhythms and take prompt action to prevent complications.
The key to spotting arrhythmias lies in understanding normal cardiac patterns and being able to detect deviations. A systematic approach to analyzing heart rhythm strips helps differentiate between normal and abnormal rhythms, enabling early detection of conditions like atrial fibrillation, ventricular tachycardia, or heart blocks.
Signs of Arrhythmias to Look For
When reviewing heart rhythms, certain signs may indicate the presence of an arrhythmia. Key features to observe include:
- Irregular Heartbeat: A rhythm that lacks a consistent pattern, often seen in conditions like atrial fibrillation or premature ventricular contractions.
- Abnormal Heart Rate: A heart rate that is either too fast (tachycardia) or too slow (bradycardia) may signal an underlying issue, such as sinus tachycardia or heart block.
- Prolonged or Shortened Intervals: Extended PR intervals or a long QT interval can indicate conduction abnormalities, which might lead to arrhythmias like first-degree heart block or long QT syndrome.
- Premature Beats: Early beats that disrupt the regular rhythm, such as premature atrial contractions or premature ventricular contractions, which are often seen in arrhythmic conditions.
- Absent or Abnormal Waves: Missing P waves, irregular QRS complexes, or abnormal T waves may suggest various types of arrhythmias, including atrial flutter or ventricular fibrillation.
Common Types of Arrhythmias
Some of the most common arrhythmias include:
- Atrial Fibrillation: An irregular and often rapid rhythm originating in the atria, which can lead to stroke or other complications if left untreated.
- Ventricular Tachycardia: A fast and potentially dangerous rhythm originating in the ventricles, often requiring immediate medical attention.
- Bradycardia: A slower-than-normal heart rate, which can result from heart block or other electrical system issues.
- Heart Block: A delay or blockage in the electrical signals between the atria and ventricles, often leading to slow or irregular heartbeats.
By being vigilant and using a systematic approach to rhythm analysis, healthcare providers can spot arrhythmias early and intervene when necessary, reducing the risk of severe complications and improving patient outcomes.
Common Mistakes in EKG Interpretation
Accurate heart rhythm analysis is a vital skill for clinicians, but misinterpretations can occur even with experienced professionals. Common errors often stem from overlooked details, rushed evaluations, or a misunderstanding of the clinical context. Recognizing these mistakes is key to improving diagnostic accuracy and preventing incorrect assessments that could affect patient care.
The complexity of heart rhythm patterns, along with the need for timely decisions, makes it easy to overlook certain nuances. By understanding typical mistakes, healthcare providers can refine their interpretation skills and reduce the chances of errors that could lead to misdiagnosis or inappropriate treatment.
Overlooking Subtle Abnormalities
Small deviations in rhythm can often be missed if the heart trace is not analyzed carefully. Some common oversights include:
- Missed Early Beats: Premature contractions, whether atrial or ventricular, can sometimes be overlooked, leading to a misinterpretation of the overall rhythm.
- Ignoring Minor Interval Changes: Small but significant prolongations of the PR or QT intervals might be dismissed, even though they can indicate serious conditions such as heart block or long QT syndrome.
- Misidentifying Waveforms: Confusing P waves or T waves with other elements in the recording can result in an inaccurate rhythm classification, especially in complex rhythms like atrial fibrillation.
Failure to Consider Clinical Context
It’s important to remember that the clinical context is essential when interpreting heart rhythm strips. Common mistakes include:
- Not Accounting for Patient Symptoms: Relying solely on the recorded rhythm without considering the patient’s clinical presentation can lead to misinterpretation of benign versus potentially dangerous patterns.
- Ignoring Medication Effects: Certain medications can alter the heart’s electrical patterns, leading to misinterpretation if the clinician does not account for their influence.
- Overlooking Normal Variants: Some variations in heart rhythm, such as sinus arrhythmia, are normal in certain patient populations but might be mistaken for pathological arrhythmias if not considered in context.
By being aware of these common mistakes, healthcare professionals can enhance their accuracy in interpreting heart rhythms, ultimately leading to better patient outcomes and more effective management of cardiac health.
Importance of Practice in EKG Mastery
Mastering the art of heart rhythm interpretation requires consistent effort and regular exposure to a variety of cardiac patterns. Familiarity with different heart signals and their variations is key to developing expertise in this field. As with any medical skill, repetition enhances the ability to quickly and accurately recognize both normal and abnormal patterns, allowing clinicians to make informed decisions under pressure.
The process of honing this skill involves a deep understanding of the heart’s electrical activity, but it also requires ongoing practice to ensure proficiency. The more exposure a healthcare professional has to a range of rhythm strips, the better they can differentiate between common variations and potentially dangerous arrhythmias. Continuous practice allows one to develop an intuition for reading heart signals, improving both diagnostic confidence and speed.
Building Confidence Through Repetition
One of the most significant benefits of regular exposure to heart rhythm strips is the development of confidence. Over time, healthcare professionals can become more comfortable identifying patterns and anomalies, which leads to quicker assessments in real clinical situations. The more you work with real or simulated recordings, the more instinctive your analysis becomes.
- Enhanced Speed: Repetition helps clinicians recognize patterns faster, reducing the time it takes to analyze a rhythm strip during patient care.
- Improved Accuracy: Frequent practice helps refine the eye for spotting subtle abnormalities that might otherwise be missed during a brief review.
- Increased Familiarity: Constant practice helps professionals become more familiar with the diverse range of heart rhythms, making it easier to spot deviations from the norm.
Learning Through Exposure to a Wide Variety of Patterns
Exposure to a variety of cases is essential for mastering heart rhythm interpretation. Different arrhythmias present in unique ways, and becoming familiar with these differences is essential for correct diagnosis. By practicing with a wide range of rhythm strips, professionals can better distinguish between conditions that may initially appear similar.
- Diverse Scenarios: Working with a variety of strips that include different heart rates, intervals, and abnormal patterns builds the experience needed to identify the subtle differences in rhythms.
- Simulated Cases: Using simulations or mock heart rhythm tests provides the benefit of repeated exposure to challenging cases without the pressure of real-time decision-making.
- Real-World Application: Engaging in hands-on experience or working alongside experienced clinicians helps contextualize theoretical knowledge, bridging the gap between learning and clinical application.
In summary, regular practice plays a crucial role in refining the skills needed for accurate heart rhythm interpretation. Through consistent exposure to various heart patterns, clinicians can improve both their speed and precision, ultimately contributing to better patient care and outcomes.
Using EKG Exams for Self-Assessment
Self-assessment plays an important role in the journey to mastering heart rhythm interpretation. Engaging in periodic self-evaluation helps clinicians identify strengths and weaknesses in their ability to analyze heart signals. By working through various rhythm challenges, individuals can assess their current knowledge, track their progress, and refine their diagnostic skills over time.
Taking time to evaluate one’s performance allows for a deeper understanding of areas that require further study. With targeted self-assessment, healthcare professionals can build a more structured approach to improving their skills, leading to greater confidence and accuracy in clinical settings. Whether through mock scenarios or self-guided assessments, evaluating one’s progress provides valuable feedback that can guide future learning efforts.
Benefits of Self-Assessment in Skill Development
Regular self-assessment provides several key advantages in the development of heart rhythm interpretation skills. These include:
- Identifying Knowledge Gaps: By reviewing one’s responses and performance, individuals can pinpoint areas where further study or practice is needed.
- Tracking Progress: Regular self-assessments offer a way to monitor improvement over time, helping individuals gauge their growing proficiency.
- Enhancing Problem-Solving Skills: Self-assessment encourages critical thinking and helps individuals improve their ability to quickly identify and address issues during real-world situations.
Effective Self-Assessment Techniques

For self-assessment to be truly effective, it is important to approach it with intention. Here are some strategies for making the most out of self-evaluation:
- Simulated Scenarios: Engage in mock cases or simulations that mirror real-world challenges. This helps test one’s ability to quickly and accurately interpret heart rhythm patterns.
- Regular Practice: Repetition is key to improving heart rhythm interpretation. Regular self-assessment exercises help reinforce learned skills and expose areas that need attention.
- Review and Reflect: After completing self-assessments, take time to review your mistakes and reflect on how to improve. This reflective process leads to greater self-awareness and continuous growth.
Incorporating self-assessment into the learning process ensures that clinicians can maintain high standards of practice. By systematically evaluating one’s skills and knowledge, individuals can remain committed to improving their expertise and stay prepared for the challenges of diagnosing heart conditions effectively.
Step-by-Step Guide to EKG Practice
Mastering heart signal interpretation requires a structured and methodical approach. Following a clear, step-by-step process can significantly enhance your ability to analyze and understand heart rhythm patterns accurately. This guide outlines the key stages in refining your diagnostic skills, from familiarizing yourself with the basics to tackling complex cases confidently.
By adopting a systematic approach, you can build a strong foundation and progressively advance your abilities. Consistent practice with targeted exercises ensures that you not only develop competence but also maintain high levels of proficiency over time.
Step 1: Learn the Fundamentals
The first step in mastering heart rhythm analysis is gaining a solid understanding of the basic components. Begin by studying key concepts and terminology, including the different waveforms, intervals, and segments that make up the heart signal. This foundational knowledge will provide the context needed to interpret more complex patterns accurately.
- Understand the heart’s electrical activity: Familiarize yourself with the movement of ions and how it generates the signals measured during heart rhythm analysis.
- Learn the basic components: Know the main waveforms, such as the P wave, QRS complex, and T wave, and their corresponding physiological meanings.
- Study measurement intervals: Understand the significance of intervals such as the PR interval, QT interval, and RR interval for accurate rhythm interpretation.
Step 2: Engage in Regular Exercises
Once the basics are clear, the next step is to engage in focused exercises designed to strengthen your diagnostic abilities. Regular practice with various heart rhythms will enhance your ability to spot patterns, recognize abnormalities, and make accurate assessments.
- Start with simple rhythms: Begin by working through basic, normal heart rhythms to become comfortable identifying common patterns.
- Progress to complex cases: Gradually introduce more challenging rhythms, including arrhythmias, and work on identifying irregularities.
- Simulate real-world scenarios: Create mock situations that mimic what you may encounter in clinical practice to test your skills under pressure.
Step 3: Evaluate and Reflect on Your Performance
After completing exercises or simulated cases, it’s essential to assess your performance. Reflecting on your mistakes and successes will provide insights into areas of improvement and solidify your learning.
- Review your answers: After working through exercises, compare your results with reference materials or guidelines to check for accuracy.
- Identify areas for improvement: Focus on recurring mistakes or areas where you hesitate, and dedicate more time to refining these skills.
- Track your progress: Keep a record of your practice sessions and note areas where you have improved over time, providing motivation and insight into your development.
By following this structured approach and regularly engaging in exercises, you can build a strong foundation in heart rhythm analysis. With practice, reflection, and continuous learning, you will gain the confidence and expertise needed to accurately assess and diagnose heart conditions.
How to Approach Complex EKG Questions
When faced with challenging scenarios that require heart rhythm interpretation, it’s essential to approach the problem methodically. Breaking down complex cases into manageable steps can help you navigate through them more effectively and avoid common pitfalls. Mastering this approach will enhance your ability to make accurate assessments and improve your decision-making skills in clinical situations.
The key to solving difficult cases lies in understanding the core principles, identifying the essential patterns, and maintaining a logical sequence throughout your analysis. This section will guide you through an organized approach to tackle intricate questions related to heart signal interpretation.
Step 1: Identify the Key Elements
Complex cases often involve a variety of different signals and irregularities. Begin by identifying the primary components of the signal, such as the P wave, QRS complex, and T wave. Pinpointing these elements allows you to focus on what is most important for interpretation.
- Locate the rhythm: Is the heart rate normal, fast, or slow? Determine whether the rhythm is regular or irregular to get a clearer understanding of the pattern.
- Assess intervals and segments: Measure the intervals and segments between key components to look for abnormalities such as prolonged intervals or shortened segments.
- Note the waveforms: Ensure that all waveforms (P, QRS, T) are present and look for any deviations from the expected shape or size.
Step 2: Analyze and Compare Against Known Patterns
Once you’ve identified the core components, compare the given signal against common heart rhythm patterns. This helps you recognize abnormalities that may indicate specific conditions or arrhythmias.
- Compare against normal rhythms: Begin by reviewing the standard rhythms for comparison. If there are any deviations, it’s important to determine whether they suggest an issue.
- Look for irregularities: Identify unusual features like premature beats, abnormal waveforms, or inconsistent intervals, which could point to a potential diagnosis.
- Use a systematic approach: Apply a consistent method for analyzing each rhythm you encounter, checking for specific characteristics like heart rate, rhythm, and morphology.
Step 3: Evaluate Clinical Context
Complex cases often require you to factor in the clinical context in addition to the technical analysis of the signals. Consider the patient’s background, symptoms, and history when making an interpretation.
- Consider the patient’s health status: Take into account whether the patient has a history of heart disease, recent surgery, or other factors that could influence the rhythm.
- Look for clinical signs: Pay attention to any clinical symptoms that may provide additional context, such as dizziness, chest pain, or fainting.
- Integrate all information: Bring together your analysis of the waveform, intervals, and patient symptoms to make a comprehensive evaluation.
By using this systematic approach, you can effectively tackle complex questions related to heart rhythm interpretation. Take the time to practice and apply these steps regularly to build confidence and proficiency in dealing with challenging cases.
Time Management During EKG Exams
Effective time management is crucial when it comes to interpreting heart rhythm data within a limited timeframe. In high-pressure situations, such as assessments or real-world applications, the ability to analyze signals efficiently while maintaining accuracy can make a significant difference in the outcome. Organizing your time helps ensure that you approach each task systematically, avoiding unnecessary stress and reducing the likelihood of errors.
Developing a strategy to allocate time wisely throughout the process not only boosts performance but also enhances confidence. This section explores techniques for managing your time effectively, ensuring that every minute counts when interpreting complex heart rhythm data.
Step 1: Prioritize Tasks Based on Complexity
Some signals may require more time to analyze than others. It is essential to evaluate the complexity of each case and prioritize accordingly. Here’s how you can allocate your time:
- Simple signals: If the pattern is straightforward and within normal limits, take a brief moment to confirm its consistency and move on quickly.
- Complex cases: More intricate rhythms or abnormal patterns will demand additional attention. Spend extra time here but try not to linger too long.
- Problematic rhythms: If you encounter a particularly challenging case, briefly skip it and return later, ensuring you manage time effectively across all questions.
Step 2: Use a Structured Approach
Sticking to a structured method helps you make quick decisions and prevents you from getting bogged down in minor details. By developing a consistent approach for every analysis, you save valuable seconds without compromising accuracy. Below is a breakdown of an efficient approach:
| Step | Time Allocation | Task Description |
|---|---|---|
| Step 1 | 1-2 minutes | Quickly identify the heart rate and rhythm. |
| Step 2 | 2-3 minutes | Examine intervals and waveforms for any abnormalities. |
| Step 3 | 2 minutes | Compare the identified pattern against known rhythms. |
| Step 4 | 1 minute | Make a decision about the overall interpretation. |
By adhering to this structure, you ensure that each task is completed efficiently while still leaving enough time to address more complicated cases. The goal is to maintain a steady pace throughout the process.
Step 3: Practice Time-Management Strategies
Becoming proficient at managing time during rhythm interpretation takes practice. Here are a few tips to help you improve your time management skills:
- Time yourself: During practice sessions, set a timer for each rhythm you analyze to simulate exam conditions.
- Take breaks: Periodically rest your mind to stay sharp and avoid burnout, which can lead to mistakes under pressure.
- Evaluate your performance: After each session, review the time spent on each case to identify areas for improvement.
By refining your time management skills, you’ll be better prepared to handle any challenge efficiently, ensuring that you not only complete each task on time but also deliver precise and confident results.
Why Correct Answering Matters in EKG Exams

Providing accurate responses when assessing heart rhythms is essential for both immediate patient care and long-term health outcomes. Precision in identifying normal and abnormal signals directly affects clinical decisions, treatment plans, and patient safety. Inaccurate interpretations can lead to delayed diagnoses, inappropriate treatments, or missed life-threatening conditions.
In high-stakes settings, such as medical evaluations or certification assessments, every detail counts. Correctly interpreting signals demonstrates both competence and confidence, qualities that are vital for healthcare professionals. This section explores why getting the correct answers is crucial, not only for passing tests but for improving overall clinical performance.
Improved Clinical Decision-Making
Accurate identification of heart patterns plays a pivotal role in determining the most appropriate course of action. Whether managing routine care or emergency situations, decisions based on correct interpretations help ensure that patients receive timely interventions, improving their chances of recovery. By honing your ability to recognize signals correctly, you are better equipped to:
- Diagnose heart conditions early: Spotting irregular rhythms early can lead to quicker, more effective treatments.
- Minimize the risk of complications: Timely intervention based on proper diagnosis reduces the likelihood of adverse outcomes.
- Enhance patient trust: When patients see that their healthcare provider can accurately assess their condition, it builds confidence in the care they are receiving.
Ensuring Patient Safety
Incorrectly analyzing heart rhythm data can have serious consequences, including unnecessary procedures or treatments. For example, misinterpreting a benign arrhythmia as a serious condition might result in invasive treatments that could otherwise be avoided. Similarly, overlooking a critical arrhythmia can delay necessary interventions. Achieving accuracy ensures that:
- Inappropriate treatments are avoided: Correct interpretation prevents the application of unnecessary or harmful interventions.
- Life-threatening conditions are identified: Fast, correct diagnoses allow for swift action in high-risk cases like heart attacks or strokes.
- Confidence in the healthcare process is maintained: When the analysis is accurate, patients can trust that they are receiving the best possible care.
In summary, the ability to interpret heart signals correctly is not just a test skill–it is an essential part of being an effective and trustworthy healthcare provider. Each answer matters, as the choices made impact patient outcomes and the overall effectiveness of treatment strategies.
Strategies for Mastering EKG Knowledge
Mastering the interpretation of heart rhythm patterns is crucial for anyone looking to excel in healthcare settings. Building a solid foundation in understanding the different rhythms, abnormalities, and their clinical implications requires dedication and the use of effective strategies. By employing the right techniques, one can improve both their theoretical knowledge and practical skills, leading to enhanced accuracy and confidence in identifying various conditions.
This section highlights strategies that will help learners improve their understanding and ability to interpret heart patterns accurately, ensuring better performance in clinical practice and evaluations. Whether you are a novice or an experienced practitioner, these methods can elevate your comprehension and application of rhythm analysis.
1. Study Key Concepts and Terminology
A strong grasp of the terminology and fundamental concepts is the first step in mastering heart rhythm analysis. Focus on understanding the underlying principles of rhythm formation, wave structures, and the different types of arrhythmias. Knowing the basic components, such as:
- P waves, QRS complexes, and T waves: These are the basic building blocks of a heart rhythm and understanding each component’s role is essential.
- Heart rate calculation: Learning how to quickly and accurately calculate heart rates will help you identify abnormalities faster.
- Rhythm interpretation: Familiarize yourself with common rhythm patterns, including their normal and abnormal forms.
2. Practice Regularly with Real-World Scenarios

Consistent practice is key to refining your ability to analyze heart rhythms. The more exposure you have to real-world cases, the better equipped you will be to recognize different patterns and abnormalities. Utilize resources like:
- Interactive software: These tools simulate real scenarios and allow for hands-on practice in rhythm analysis.
- Case studies: Reviewing case studies helps connect theory to practice, allowing you to see how different heart patterns affect patient outcomes.
- Mock assessments: Practice tests or simulated evaluations provide a low-stakes environment for improving your skills and gaining confidence.
By practicing regularly, you’ll develop the ability to quickly identify and interpret heart rhythms accurately, which is essential in both learning and clinical settings. Over time, this hands-on experience will solidify your knowledge and reduce the likelihood of errors when analyzing actual cases.