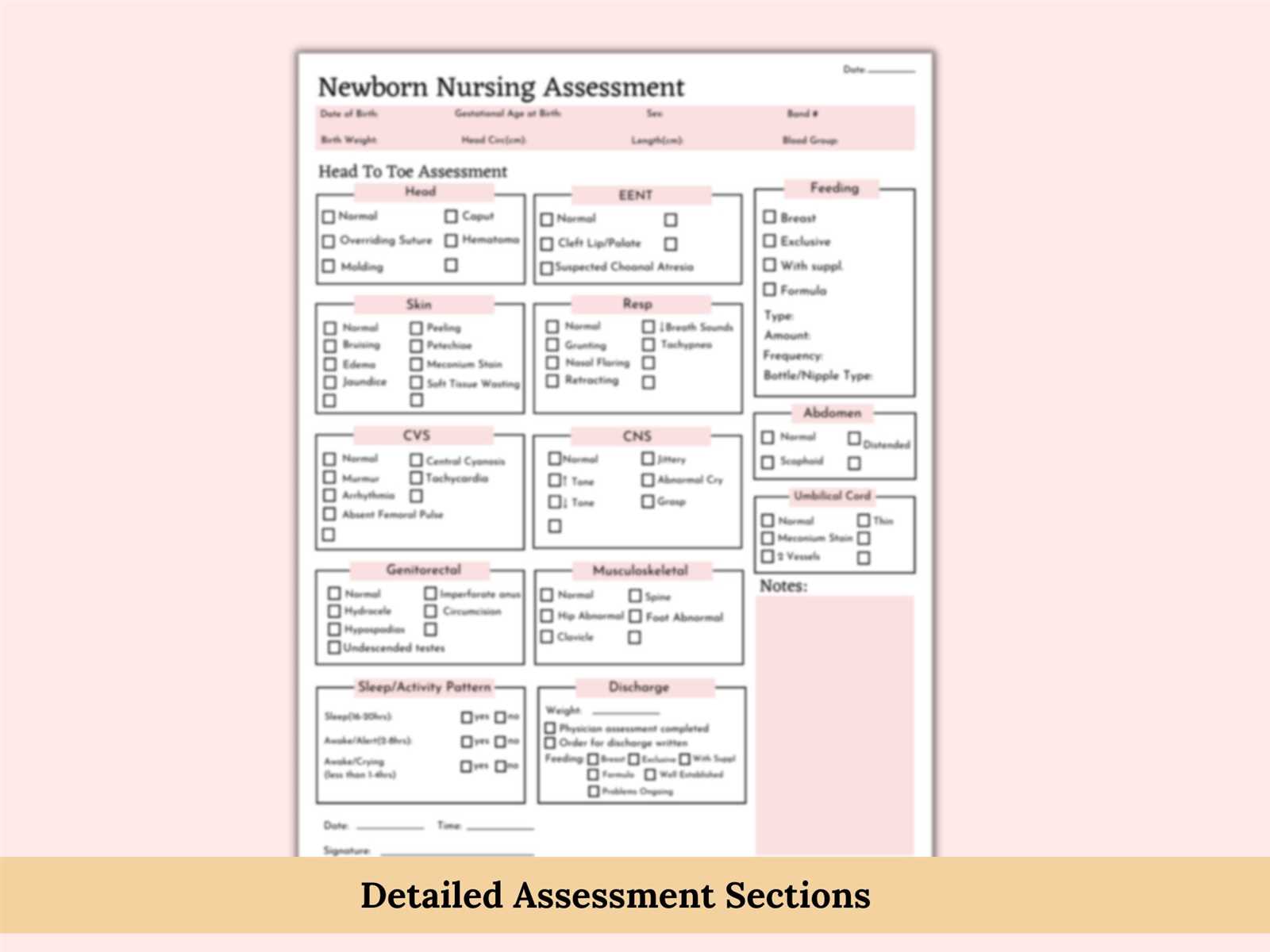
Ensuring a thorough and accurate evaluation of a baby’s well-being is a critical aspect of early care. Healthcare providers use structured methods to assess various health parameters and identify potential concerns. This process helps to ensure that infants are developing properly and that any health issues are detected early.
Understanding the essential steps involved in the assessment allows medical professionals to maintain a standardized approach to checking key body systems. By following a detailed framework, they can systematically record findings and track progress, making it easier to provide quality care throughout the early stages of life.
Effective documentation during these evaluations serves not only as a reference for ongoing care but also as a way to communicate important observations to parents or caregivers. Clear and concise records are essential for tracking changes over time and ensuring the infant’s optimal development.
Newborn Physical Exam Template Overview
Conducting a comprehensive assessment of an infant’s health is a vital practice in early care. A well-organized framework ensures that all necessary aspects of development and bodily functions are carefully reviewed. By following a structured approach, healthcare providers can ensure that no critical area is overlooked and that any potential health issues are identified promptly.
This structured approach helps professionals systematically document their observations, providing a clear record of the infant’s health status. Such documentation serves as a foundation for future assessments, allowing caregivers to track progress and detect any changes that might require attention.
By utilizing a consistent method, medical staff can provide thorough care and support to families, addressing concerns while ensuring that infants are receiving the best possible start in life. A detailed evaluation not only promotes effective communication between healthcare providers and parents but also plays a key role in long-term health management.
Key Components of a Newborn Exam
A thorough assessment of an infant’s health involves checking several vital aspects of their development and well-being. Each part of the body and physiological system must be reviewed to ensure proper function and identify any potential concerns. The process includes evaluating physical attributes, reflexes, organ functions, and overall growth.
General Health and Measurements
Monitoring general health and taking accurate measurements are essential in understanding an infant’s progress and identifying potential issues. Key areas to observe include:
- Weight, length, and head circumference
- Skin tone and texture
- Overall appearance and responsiveness
Systematic Evaluation of Body Functions
After checking general health, more specific systems are evaluated to ensure proper function. These include:
- Cardiovascular system: Heart rate, rhythm, and blood pressure
- Respiratory system: Breathing patterns and lung sounds
- Neurological reflexes: Reactions such as rooting, grasping, and the Moro reflex
- Musculoskeletal system: Range of motion and muscle tone
Importance of a Detailed Physical Assessment
Carefully assessing an infant’s health from the very beginning is essential for identifying early signs of potential health issues. A comprehensive evaluation helps healthcare providers spot abnormalities and ensures that each part of the body is functioning correctly. Early detection of any problems can significantly impact the success of treatment and long-term outcomes.
Early Detection of Health Concerns
A detailed health check allows for the identification of developmental delays or conditions that may not be immediately obvious. Addressing issues early can lead to better management and fewer complications later on. Key aspects to observe include:
| Area of Concern | Potential Issues | Benefits of Early Detection |
|---|---|---|
| Musculoskeletal System | Joint deformities or tightness | Early intervention can prevent long-term mobility issues |
| Neurological Reflexes | Delayed or absent reflexes | Helps identify neurological disorders or developmental delays |
| Cardiovascular System | Abnormal heart sounds or irregular heart rate | Allows for early cardiac monitoring and treatment |
Tracking Progress Over Time
A detailed assessment also establishes a baseline for tracking the infant’s growth and development. By monitoring changes over time, healthcare providers can ensure that the infant is meeting milestones and adjust care plans if necessary.
Step-by-Step Guide for Newborn Evaluation
Performing a thorough assessment of an infant’s health involves several key steps to ensure that all areas of development and bodily functions are reviewed systematically. A step-by-step approach helps healthcare professionals maintain consistency and accuracy throughout the process, ensuring no aspect is overlooked.
Preparing for the Evaluation
Before beginning the assessment, ensure that all necessary tools and equipment are ready. This includes a scale, measuring tape, thermometer, stethoscope, and a clean examination area. The infant should be calm and comfortable, ideally in a quiet room with proper lighting. Begin by gathering any relevant medical history and details about the delivery.
Systematic Review of Body Systems
The evaluation process can be broken down into the following steps:
- General Appearance: Assess the infant’s responsiveness, skin color, and overall appearance.
- Head and Neck: Examine for any abnormalities, such as molding of the skull or abnormal head shape.
- Chest and Abdomen: Listen for heart and lung sounds, and check the abdomen for any signs of distention or tenderness.
- Extremities: Check the movement and positioning of arms and legs, and assess muscle tone.
- Reflexes: Test for standard reflexes such as rooting, sucking, and the Moro reflex.
By following these steps, healthcare providers can ensure that they are performing a comprehensive evaluation that covers all critical areas of infant health.
How to Document Newborn Findings

Proper documentation of an infant’s health findings is crucial for effective care management and communication between healthcare providers. Accurate records allow for tracking changes over time, ensuring that any potential concerns are addressed promptly. Clear documentation also serves as a legal and medical reference, providing a comprehensive history for future evaluations.
Key Aspects to Document
When documenting an infant’s health status, several key elements should be noted:
- Physical Measurements: Record weight, length, and head circumference accurately, as these are essential indicators of growth and development.
- Skin and Appearance: Note any signs of jaundice, rashes, or other visible concerns.
- Respiratory and Cardiovascular Findings: Document heart rate, respiratory rate, and any irregular sounds.
- Reflexes and Movement: Clearly record the presence or absence of key reflexes such as sucking, rooting, and grasping.
- Feeding Patterns: Include details on feeding behavior, whether breast or bottle-fed, and any difficulties observed.
Using a Standardized Format
Adopting a consistent format for documenting findings helps ensure that all critical information is included and easily accessible. Standardized forms or digital systems can streamline this process, making it more efficient and reducing the likelihood of missing important details.
Common Abnormalities to Look For
While conducting a thorough health check, it is essential to be aware of potential irregularities that may indicate underlying issues. Identifying abnormalities early allows for timely interventions, ensuring better outcomes for the infant. Common areas that require attention include the skin, respiratory system, and musculoskeletal structure.
Skin and Appearance
Several skin-related conditions can arise during the early stages of life. These include:
- Jaundice: A yellowish tint to the skin and eyes, which may signal liver dysfunction or other health issues.
- Rashes: The presence of red, bumpy, or scaly skin could be a sign of infections, allergies, or dermatitis.
- Birthmarks: Most are harmless, but certain types, like port-wine stains, may require monitoring.
Musculoskeletal and Neurological Issues
Abnormalities in muscle tone or movement can signal potential developmental concerns. These might include:
- Clubbed Feet: A condition where the feet are turned inward, which may require treatment or corrective procedures.
- Abnormal Reflexes: Lack of typical reflexes such as the Moro or rooting reflex may indicate neurological issues.
- Hip Dysplasia: Signs of misaligned hip joints, which may result in limited movement or clicking sounds.
Tools Required for a Newborn Exam
To perform a thorough health assessment of an infant, several tools and instruments are necessary to ensure accurate measurements and observations. These items help healthcare professionals systematically evaluate the infant’s physical condition and document the findings effectively. Proper preparation and use of these tools allow for a comprehensive evaluation of all body systems.
- Stethoscope: Essential for listening to heart and lung sounds, checking for irregularities in the cardiovascular and respiratory systems.
- Thermometer: Used to measure the infant’s body temperature, helping to identify signs of fever or hypothermia.
- Scale: A sensitive scale is required to measure the infant’s weight accurately, a key indicator of health and development.
- Measuring Tape: Used to measure length and head circumference, which are vital parameters for tracking growth.
- Ophthalmoscope: A tool used to examine the eyes and check for abnormalities in the eye structures or signs of infections.
- Reflex Hammer: Used to test the infant’s reflexes, which are important for assessing neurological function.
- Penlight: A small flashlight used to check the pupil reaction to light and assess neurological function.
Having these tools ready and knowing how to use them correctly ensures that every aspect of the infant’s health is evaluated accurately and efficiently.
Ensuring Accurate Measurements and Recordings
Accurate measurements and precise documentation are critical when assessing an infant’s health. Ensuring that each parameter is recorded correctly allows for a reliable baseline and facilitates tracking growth and development over time. Consistency in measurement techniques and the careful recording of findings are essential for identifying potential issues and making informed decisions about care.
To achieve accurate results, it is important to use the right tools and methods. For example, when measuring weight, using a scale designed for infants will provide more reliable results than a standard adult scale. Similarly, when documenting length, ensuring the infant is positioned correctly will prevent discrepancies in the recorded data.
It is also crucial to document findings immediately and clearly to avoid errors that might arise from memory lapse or misinterpretation. Whether recording physical measurements or observations of reflexes, the information should be noted in a systematic and consistent manner. Proper documentation serves not only as a record for future reference but also as a tool for ongoing monitoring and potential interventions.
Timing and Frequency of Newborn Exams
Properly scheduling health assessments during the early stages of life is crucial for monitoring the infant’s development and identifying any potential issues. Regular evaluations help to establish a baseline for health and ensure that any concerns are addressed promptly. The timing and frequency of these assessments are guided by both medical recommendations and the infant’s specific health needs.
Typically, initial checks are performed shortly after birth, followed by follow-up evaluations during the first few weeks of life. The frequency of these assessments may vary based on the infant’s health condition and the healthcare provider’s guidelines.
| Age | Recommended Assessment | Frequency |
|---|---|---|
| Immediately after birth | Initial health check, vital signs | One-time |
| 1-3 days | Postpartum evaluation | One-time |
| 1 week | Follow-up check, weight, reflexes | One-time |
| 2 months | Routine check, vaccination review | Regular |
| 4-6 months | Growth and development assessment | Regular |
Adhering to these schedules ensures that the infant’s health is closely monitored and allows for early detection of any abnormalities or developmental concerns.
Growth Milestones During Physical Exams
Tracking an infant’s development through regular assessments provides key insights into their growth and health. Identifying developmental milestones is critical for understanding whether the infant is progressing as expected and for spotting any concerns that may need further attention. These milestones include a range of physical, motor, and sensory abilities that evolve during the early stages of life.
Physical Growth and Measurements
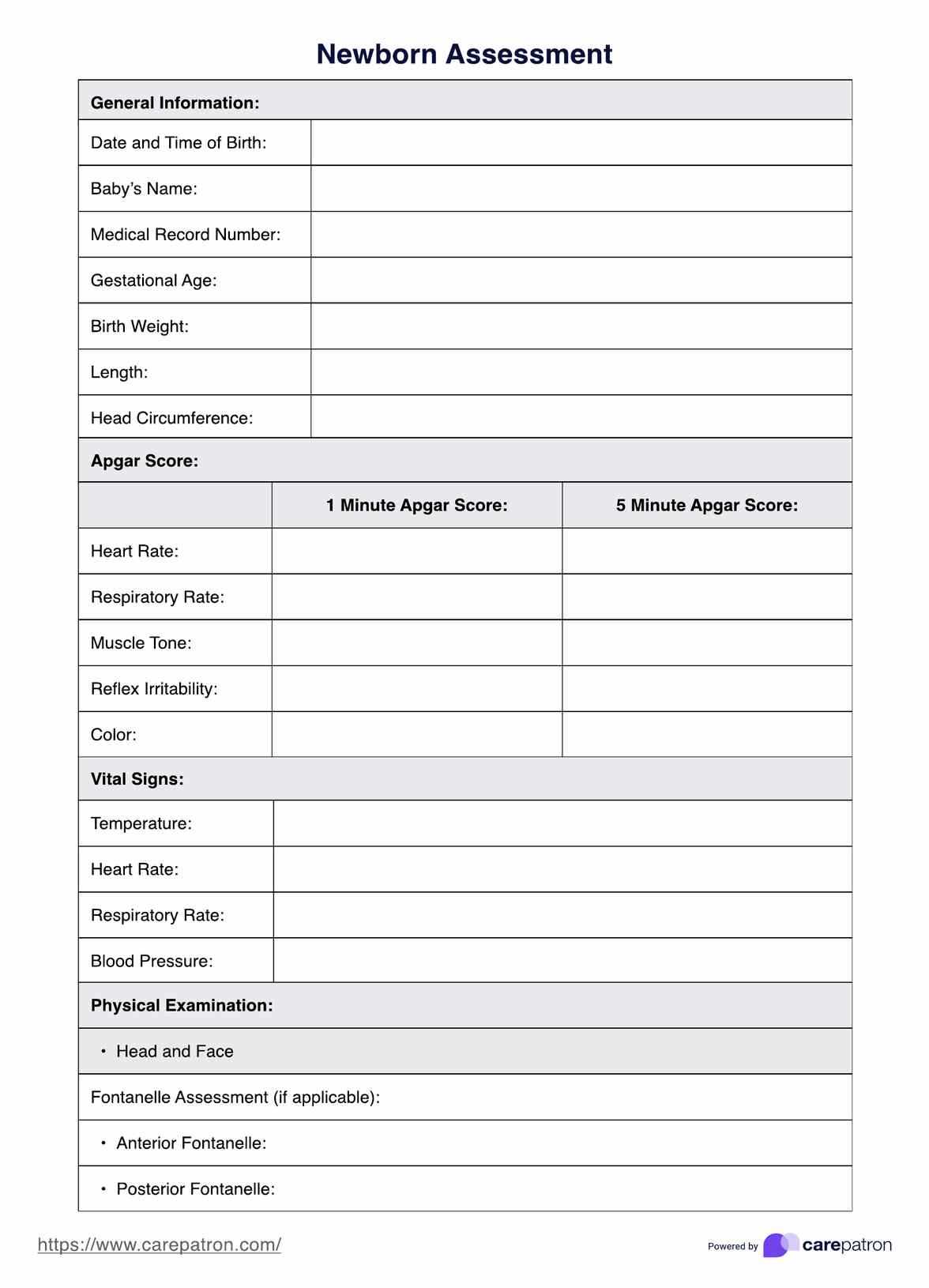
During health checks, healthcare providers monitor key physical markers that indicate growth progress. These include:
- Weight: Regular weight measurements help to assess nutritional intake and overall health.
- Length: Tracking the length of the infant ensures proper growth and can highlight potential growth restrictions.
- Head Circumference: Monitoring the size of the head can provide insights into brain development.
Motor and Developmental Milestones
As the infant grows, healthcare providers also assess motor skills and reflex development. Key milestones include:
- Motor Skills: By 2-3 months, infants typically begin to lift their heads during tummy time and follow objects with their eyes.
- Reflexes: Reflexes such as the rooting and Moro reflex are commonly observed in the early months to assess neurological function.
- Muscle Tone: Observing muscle tone and coordination helps ensure that muscle development is on track.
By consistently tracking these milestones, healthcare professionals can ensure that the infant is developing properly and address any potential concerns at an early stage.
Skin and Head Assessment in Newborns
Evaluating the condition of an infant’s skin and head is a critical part of the overall health check. These areas can reveal important information about the infant’s well-being and developmental progress. Observing any abnormalities or changes in the skin or head is essential for early detection of potential health concerns.
Skin Observations
When assessing the skin, healthcare providers look for a range of characteristics that can indicate overall health. Some key observations include:
- Skin Color: A healthy infant typically has pinkish skin, although slight blue tones on the hands and feet are common in the first few hours. Persistent discoloration may signal circulatory issues.
- Skin Integrity: The skin should be intact without rashes, cuts, or abrasions. Common conditions such as jaundice or birthmarks may be noted during the assessment.
- Texture: The texture of the skin is another indicator of health. Dryness or peeling skin can occur naturally after birth but should be monitored.
- Lanugo: Fine body hair, known as lanugo, is typically present in the early days after birth. Its presence or absence can be noted during the assessment.
Head and Skull Observations
The head and skull are also thoroughly examined to ensure proper development. Important factors to check include:
- Fontanelles: The soft spots on the skull, known as fontanelles, are assessed for size and tension. A bulging fontanel may indicate increased intracranial pressure, while a sunken one can suggest dehydration.
- Shape: The shape of the head is checked for any signs of molding or abnormalities. Mild molding can occur during birth, but it should resolve naturally within a few days.
- Scalp: The scalp is examined for any lesions, infections, or birthmarks that may require further attention.
- Neck Muscles: The neck is also assessed for symmetry and strength, which helps ensure proper alignment and motor development.
By carefully observing and documenting these features, healthcare professionals can identify early signs of potential concerns, ensuring prompt intervention if necessary.
Cardiovascular and Respiratory Examination Tips
Assessing the cardiovascular and respiratory systems is a crucial part of evaluating an infant’s health. The heart and lungs play vital roles in overall well-being, and early detection of any irregularities can help prevent or address potential health issues. By carefully observing certain signs and using appropriate techniques, healthcare professionals can gather essential information about these systems.
Cardiovascular System Assessment

The heart is examined to ensure proper function and blood circulation. Important points to observe include:
- Heart Rate: A normal heart rate should fall within a specific range. An excessively fast or slow heart rate may indicate an underlying issue.
- Heart Sounds: Listening for abnormal heart sounds, such as murmurs, can help detect issues like congenital heart defects. Regular heartbeats with no unusual sounds are typically a good sign.
- Peripheral Pulses: Checking pulses in the arms and legs is important to ensure good blood flow throughout the body.
- Color: Observing the skin color can provide clues about blood circulation. Bluish tones around the lips or extremities could signal circulatory problems.
Respiratory System Assessment
Proper lung function is vital for oxygenation and overall health. When assessing the respiratory system, consider the following:
- Respiratory Rate: The rate at which the infant breathes should be checked. A higher-than-normal rate may indicate respiratory distress.
- Breathing Patterns: Irregular or labored breathing can point to problems such as infections or lung conditions.
- Oxygen Saturation: Measuring oxygen saturation helps ensure that the body is receiving adequate oxygen. Low saturation levels can be a warning sign for respiratory difficulties.
- Chest Movement: The chest should expand symmetrically. Uneven movement or retractions may indicate respiratory distress.
By systematically checking these components, healthcare providers can assess whether an infant’s cardiovascular and respiratory systems are functioning properly and detect any early signs of concern.
Neurological Check for Infants
Assessing the neurological function in an infant is essential for identifying any potential issues with brain and nervous system development. Early recognition of neurological abnormalities can lead to more effective interventions and treatments. This evaluation involves checking the infant’s reflexes, muscle tone, responsiveness, and sensory abilities to ensure proper neurological function.
Key Areas of Focus
During the neurological evaluation, certain key aspects should be monitored:
- Motor Responses: Assessing how well the infant moves their limbs or body can help detect any motor impairments. Proper coordination of movements indicates normal neurological function.
- Reflexes: Reflexes are automatic responses to specific stimuli, and they can reveal how well the nervous system is functioning. Common reflexes, such as the Moro or rooting reflex, should be present in healthy infants.
- Posture and Muscle Tone: Observing the infant’s posture and muscle tone is critical. An infant should have good muscle tone and exhibit proper body posture.
- Response to Stimuli: How the infant reacts to light, sound, and touch can provide important clues about their neurological health.
Neurological Development Milestones
Infants reach certain neurological milestones during their early months. Understanding these milestones helps healthcare providers track normal development:
| Age | Milestone |
|---|---|
| 0-2 Months | Startling reflex, ability to track objects with eyes |
| 2-4 Months | Head control, recognition of familiar voices |
| 4-6 Months | Hand-eye coordination, reaching and grasping |
| 6-12 Months | Rolling over, sitting up, babbling sounds |
By evaluating these components, healthcare professionals can assess the neurological development and identify any issues that may require attention. Regular checks ensure that any abnormalities are detected early and can be addressed promptly.
Eye and Hearing Screening Procedures
Screening for vision and hearing issues in infants is a crucial part of early developmental assessments. These tests help identify potential sensory impairments that may affect communication and learning abilities. Detecting problems early allows for timely interventions, promoting better outcomes for the infant’s overall development.
Eye Screening Process
The assessment of visual function is an essential component of infant care. Early detection of vision problems can prevent further complications as the child grows. Common eye screening techniques include:
- Visual Tracking: Observing whether the infant can follow a moving object or light with their eyes. This checks for basic visual coordination.
- Pupillary Response: Checking how the pupils react to changes in light. A proper response is an indication of normal visual function.
- Red Reflex Test: This test involves using a light source to check for any abnormalities in the eye, such as cataracts or other obstructions.
Hearing Screening Process
Detecting hearing impairments early is vital for language development and social interactions. Several tests can help assess auditory health in infants:
- Otoacoustic Emissions (OAE): A small probe placed in the infant’s ear measures sounds generated by the inner ear in response to a click or tone.
- Auditory Brainstem Response (ABR): This test records brainwave responses to sounds played through earphones, helping to assess how well the auditory pathways are functioning.
- Behavioral Observation: In some cases, simple observation can provide clues about an infant’s hearing ability, such as their reaction to loud noises.
Screening Results and Follow-Up
If an infant shows signs of hearing or vision issues, follow-up procedures should be scheduled promptly. Early treatment can significantly improve long-term outcomes for sensory development. The following table outlines common results and the necessary actions:
| Screening Test | Normal Result | Action if Abnormal |
|---|---|---|
| Visual Tracking | Follows objects or light | Referral to a pediatric ophthalmologist |
| Pupillary Response | Equal constriction to light | Further eye examination |
| Red Reflex Test | Clear, uniform red reflection | Referral for a detailed eye exam |
| OAE Test | Normal emissions detected | Further hearing evaluation if no response |
| ABR Test | Normal brainwave responses | Referral for audiological follow-up |
By ensuring regular screening of vision and hearing, healthcare professionals can detect and address potential issues early, contributing to healthier developmental milestones and better overall outcomes for the infant.
Communicating Findings to Parents
Sharing assessment results with parents is a critical part of healthcare practice. The way in which information is conveyed can influence how parents feel about their child’s health and development. It is essential to deliver findings clearly, compassionately, and in a way that is both informative and supportive.
When communicating results, healthcare professionals should focus on being empathetic and transparent, ensuring that parents understand the context and significance of the findings. Whether the outcome is positive or indicates a need for further investigation, providing clear next steps is vital for fostering trust and cooperation.
Key Approaches for Effective Communication
- Be Clear and Concise: Use straightforward language to explain the findings. Avoid medical jargon unless the parents are familiar with it, and provide definitions when necessary.
- Offer Support and Reassurance: Acknowledge any concerns the parents may have and reassure them that the next steps are manageable. If follow-up care or referrals are needed, explain these processes calmly and clearly.
- Provide Written Information: Offering written materials or resources can help parents process the information after the conversation. This allows them to revisit the details at their own pace.
- Encourage Questions: Create an open dialogue where parents feel comfortable asking questions. This not only helps to clarify uncertainties but also strengthens the partnership between the healthcare provider and the parents.
Handling Sensitive or Concerning Results
In cases where the findings may be concerning, it is important to address the issue with sensitivity. The healthcare provider should:
- Express empathy and understanding, recognizing the emotional weight of the information.
- Offer clear next steps, including any referrals, tests, or additional evaluations that may be needed.
- Provide the opportunity for the parents to express their emotions or concerns, and address them with care and respect.
By maintaining an open, empathetic approach, healthcare providers can ensure that parents leave the discussion with a clear understanding of their child’s health and the actions needed moving forward.
Legal Considerations in Newborn Evaluations
During the assessment of an infant’s health, healthcare professionals must be aware of various legal obligations and considerations. These include ensuring informed consent, maintaining confidentiality, and adhering to established protocols. A thorough understanding of these legal aspects is essential to safeguard both the wellbeing of the child and the rights of the parents or guardians.
It is important for practitioners to understand that their responsibilities extend beyond medical knowledge to include legal and ethical practices. Each step taken in evaluating the infant must comply with regulations and standards set by medical boards, laws governing patient care, and relevant healthcare policies.
Informed Consent and Parental Authorization
Obtaining informed consent is one of the foundational legal principles in healthcare. Before conducting any procedure or evaluation, the healthcare provider must ensure that the parents or guardians fully understand the process, the purpose of the assessment, and any potential risks or benefits involved. This consent must be documented to protect both the healthcare provider and the parents legally.
- Clear Communication: The practitioner should explain the purpose and nature of the evaluation in simple terms, ensuring that parents are well informed.
- Documentation: A written record of consent must be obtained from the parents or guardians, which includes their understanding of the process and their agreement to proceed.
- Right to Refuse: Parents have the legal right to refuse certain procedures. This refusal must be acknowledged and documented as well.
Confidentiality and Data Protection
Confidentiality is another crucial aspect of legal compliance in healthcare. All personal health information, including any findings from the assessment, must be handled with strict confidentiality. Healthcare providers must ensure that this information is stored securely and only shared with authorized individuals or entities, in accordance with relevant laws such as HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act) in the United States.
- Secure Record Keeping: All information gathered during the evaluation must be kept in a secure manner, whether electronically or in paper format.
- Sharing of Information: Information should only be shared with other healthcare providers or agencies involved in the infant’s care, and only with the explicit consent of the parents or guardians.
- Parental Access: Parents have the right to access their child’s medical records and should be provided with the appropriate channels to do so.
By addressing these legal considerations, healthcare providers can ensure they are meeting their professional and ethical obligations, while also building trust with parents and guardians. Understanding and respecting these responsibilities ensures that care is provided in a lawful, transparent, and compassionate manner.