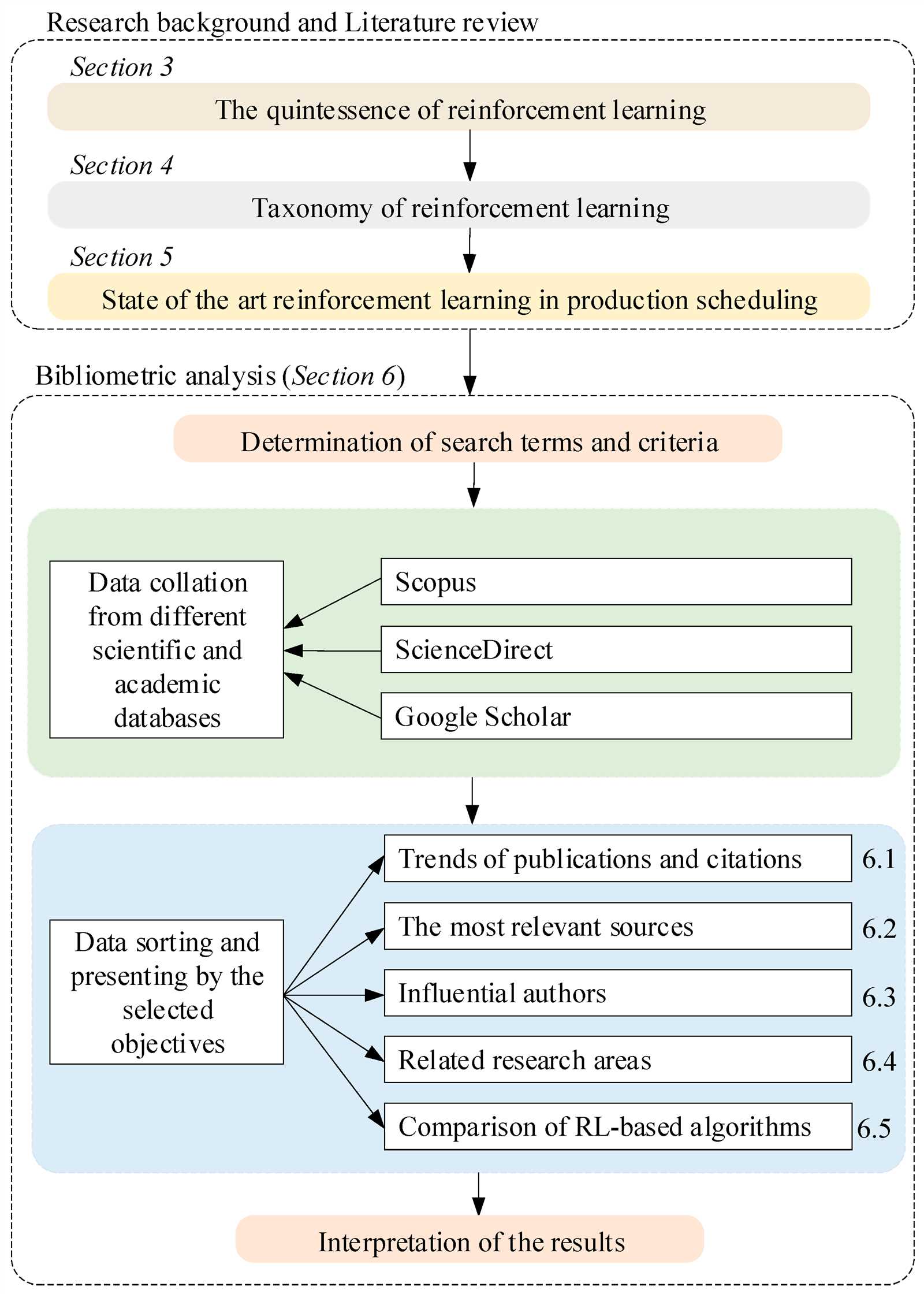
The process of shaping behavior in educational settings is influenced by various strategies designed to increase engagement and motivation. These methods help in establishing consistent patterns that promote desired outcomes over time. By understanding how certain factors can drive persistence and effort, educators can apply targeted approaches to improve student performance and retention.
In this discussion, we will explore the fundamental principles that explain how external factors impact the learning process. Emphasis will be placed on identifying the mechanisms behind student reactions and the long-term effects of positive stimulation. Effective techniques can encourage continuous progress, offering a sustainable approach to improving overall results.
We will also look into practical applications that demonstrate the success of these methods in real-world situations. By examining both theoretical frameworks and classroom examples, educators can better understand how to implement these strategies for maximum impact. Real-life examples will highlight the benefits of structured interventions that aim to foster a productive learning environment.
Understanding Key Principles of Behavior and Learning
This part of the study focuses on the underlying mechanisms that drive consistency and growth in behavior. By examining how specific factors influence a learner’s actions, we can uncover the core elements that contribute to long-term success. The goal is to identify the processes that create lasting changes and foster continuous improvement in educational settings.
At its core, this approach emphasizes how external influences can shape learning patterns and encourage perseverance. Whether through strategic interventions or natural responses to stimuli, the method seeks to establish a positive feedback loop that reinforces productive behavior. The focus is on creating an environment where progress is continually supported and enhanced, ultimately leading to better engagement and achievement.
Understanding these dynamics provides valuable insights for educators looking to improve their teaching methods. By recognizing the connections between external triggers and internal motivation, educators can design more effective learning experiences. This process helps build a framework that encourages students to maintain focus and effort over time, ultimately achieving their full potential.
Key Concepts in Behavior and Motivation Dynamics
At the heart of learning theory lies the understanding of how external factors influence a learner’s actions over time. By identifying the core principles that drive persistence and engagement, we can better understand how specific strategies lead to sustained progress. These concepts highlight the connection between input and outcome, establishing patterns that encourage the repetition of desired behaviors.
One crucial aspect of this approach is the role of positive stimuli in shaping actions. Through consistent and timely reinforcement, individuals are more likely to continue exhibiting targeted behaviors. Reinforcement techniques are designed to strengthen responses, making them more likely to occur in the future. These strategies work by creating a cycle of success that motivates the learner to persist in their efforts.
Another important concept is the gradual build-up of effort, where initial actions pave the way for increasingly complex behaviors. As the individual experiences success, they gain confidence, which encourages further action and development. By recognizing these patterns, educators can design more effective learning environments that foster long-term growth and mastery.
How Momentum Affects Learning Outcomes
The process of learning is deeply influenced by the speed and consistency with which students engage with tasks. When learners experience continuous success, their motivation and confidence grow, leading to a cycle that drives further progress. This cycle of repeated success not only enhances the ability to perform specific tasks but also improves overall learning efficiency.
The Impact of Continuous Success
When learners achieve consistent positive results, they build a sense of accomplishment that propels them forward. This sense of success acts as a powerful motivator, encouraging students to tackle more challenging material and deepen their understanding. The cumulative effect of these experiences reinforces their commitment and willingness to keep pushing towards their goals.
How Persistence Leads to Mastery
Persistence is key to mastering any new skill. As learners continue to make progress, even small victories contribute to the development of expertise. The feeling of competence gained through successive achievements encourages students to stay engaged and explore more complex concepts. Ultimately, this process fosters a deeper level of understanding and retention of knowledge.
Analyzing Core Principles of Behavioral Influence
This section focuses on the fundamental concepts that guide the shaping of behavior and learning outcomes. By understanding how different factors work together to influence actions, we can better identify the key elements that contribute to successful learning strategies. The principles discussed here aim to explain the processes that lead to sustained effort and long-term progress in educational settings.
The Role of External Influences
External factors play a significant role in directing and reinforcing student behavior. Whether through structured feedback, rewards, or other stimuli, these elements help create an environment where positive actions are continuously supported. The consistency of these external factors encourages learners to stay engaged, reinforcing the behaviors that lead to growth and improvement.
Internal Motivation and Growth
While external factors are essential, internal motivation also drives long-term success. A learner’s own desire to achieve and improve can act as a powerful force that sustains effort even in the face of challenges. By fostering intrinsic motivation, educators can encourage self-driven growth, helping students to develop a deeper connection to their learning process. Understanding this dynamic is key to designing strategies that promote continuous engagement and achievement.
Impact of External Stimuli on Student Behavior
The way external rewards and feedback influence student behavior is crucial to understanding how learning takes place. Positive interactions, such as praise or tangible rewards, can significantly affect how students approach tasks and persist in their efforts. By consistently reinforcing desired behaviors, educators can create an environment that encourages repeated positive actions, ultimately fostering a culture of achievement.
The Role of Positive Feedback
Positive feedback serves as a powerful tool in shaping student behavior. When learners are recognized for their efforts, they are more likely to repeat those actions in the future. This kind of acknowledgment helps build confidence and encourages students to continue striving for success. It also establishes a sense of accountability, where students understand that their actions are being noticed and valued.
Impact of Tangible Rewards
Tangible rewards, such as certificates, grades, or other incentives, can be effective in maintaining motivation, particularly when linked to specific achievements. These rewards provide an immediate sense of accomplishment, reinforcing the connection between effort and outcome. However, it is essential to use such incentives strategically to ensure they support long-term motivation rather than just short-term compliance.
| Type of Feedback | Impact on Behavior | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Positive Praise | Encourages repetition of desired behavior | Verbal praise for completing an assignment |
| Tangible Rewards | Motivates further effort and engagement | Certificates or prizes for achieving goals |
| Constructive Criticism | Promotes reflection and improvement | Feedback on areas for improvement after a test |
Examples of Progress in Education
In the educational process, positive cycles of engagement and achievement can lead to continuous progress. As students experience success in one area, their confidence and motivation grow, enabling them to take on more challenging tasks. These cycles of improvement not only enhance individual performance but also contribute to a more productive and engaging learning environment.
Building Confidence Through Small Wins
One common example of this dynamic is the process of achieving small goals over time. When students complete tasks successfully, even minor ones, they gain a sense of accomplishment that encourages them to continue progressing. For example, a student who consistently scores well on quizzes may feel more confident tackling larger projects or tests. These early successes serve as stepping stones toward greater achievements, creating a pattern of positive outcomes that motivate further effort.
The Snowball Effect of Continued Effort
Another example can be seen in the way continued effort leads to increasing mastery. As students accumulate knowledge and skills, their growing expertise enables them to tackle more complex problems with ease. This snowball effect means that once a learner gains momentum, it becomes easier to maintain and build upon their progress. For instance, a student who regularly practices math problems will find that their ability to solve more difficult equations improves steadily, leading to more frequent successes.
The Role of External Rewards in Motivation
External rewards play a crucial part in shaping a learner’s motivation and engagement. When students receive acknowledgment for their efforts, it reinforces their drive to continue participating and working towards their goals. These rewards can range from verbal praise to tangible incentives, each playing a distinct role in encouraging persistence and fostering enthusiasm for learning.
In education, motivation is often fueled by the recognition of effort, which in turn increases the likelihood of desired behaviors being repeated. Positive outcomes, such as praise, grades, or rewards, can strengthen the connection between effort and success, encouraging students to stay committed. The following are some of the primary ways in which external rewards influence motivation:
- Immediate Feedback: Positive responses provided right after an achievement motivate students to maintain their focus and effort.
- Incentives for Achievement: Tangible rewards, such as certificates or small prizes, boost motivation by offering an immediate sense of accomplishment.
- Recognition of Progress: Acknowledging milestones encourages students to keep progressing towards their goals, reinforcing their belief in their abilities.
These external motivators create a cycle where students learn that their efforts lead to positive results, which in turn fuels further action. However, it’s important to strike a balance between external rewards and fostering intrinsic motivation, ensuring that students remain driven by personal growth and not solely by the expectation of rewards.
- Setting Clear Expectations: Ensuring that students know what is expected of them and how their efforts will be rewarded can provide clarity and focus.
- Celebrating Small Wins: Acknowledging even small accomplishments helps maintain enthusiasm and momentum, which can build toward larger achievements.
Common Misunderstandings in Behavioral Progress Theory
While the theory of behavior and progress is widely accepted, there are several misconceptions that can lead to confusion when applying these principles in educational settings. Often, individuals may misunderstand how certain factors influence actions and outcomes, leading to ineffective strategies or unrealistic expectations. It is essential to address these misunderstandings to fully grasp how to support and guide learners toward sustained improvement.
Here are some of the most common misconceptions:
- Immediate Results Are Guaranteed: One of the biggest misunderstandings is that positive outcomes will occur instantly after reinforcing a behavior. In reality, behavioral change takes time and requires consistent effort over an extended period.
- Rewards Are the Only Motivator: While external rewards are important, relying solely on them can undermine intrinsic motivation. Students who are motivated only by rewards may struggle to engage in the absence of external incentives.
- More Reinforcement Equals Better Results: Some believe that the more rewards or feedback provided, the better the outcomes. However, excessive reinforcement can lead to dependency, diminishing the long-term effectiveness of the strategy.
- One-Size-Fits-All Approach: Another common misconception is that the same approach will work for all students. The reality is that each individual responds differently to various types of feedback and reinforcement, requiring personalized strategies for optimal results.
To avoid these pitfalls, educators and learners should recognize that behavioral improvement is a gradual process, and different individuals may need varying levels of support and encouragement. By acknowledging these common misunderstandings, more effective learning environments can be created, where growth is sustained through a balanced and thoughtful approach.
- Focus on Consistency: Gradual and consistent reinforcement over time produces more lasting change than immediate or excessive rewards.
- Emphasize Intrinsic Motivation: It’s crucial to foster internal motivation so that students engage with their learning for personal satisfaction, not just external validation.
- Adapt Strategies to Individual Needs: Understand that different learners may require unique approaches to stay engaged and motivated.
Common Misunderstandings in Behavioral Progress Theory
While the theory of behavior and progress is widely accepted, there are several misconceptions that can lead to confusion when applying these principles in educational settings. Often, individuals may misunderstand how certain factors influence actions and outcomes, leading to ineffective strategies or unrealistic expectations. It is essential to address these misunderstandings to fully grasp how to support and guide learners toward sustained improvement.
Here are some of the most common misconceptions:
- Immediate Results Are Guaranteed: One of the biggest misunderstandings is that positive outcomes will occur instantly after reinforcing a behavior. In reality, behavioral change takes time and requires consistent effort over an extended period.
- Rewards Are the Only Motivator: While external rewards are important, relying solely on them can undermine intrinsic motivation. Students who are motivated only by rewards may struggle to engage in the absence of external incentives.
- More Reinforcement Equals Better Results: Some believe that the more rewards or feedback provided, the better the outcomes. However, excessive reinforcement can lead to dependency, diminishing the long-term effectiveness of the strategy.
- One-Size-Fits-All Approach: Another common misconception is that the same approach will work for all students. The reality is that each individual responds differently to various types of feedback and reinforcement, requiring personalized strategies for optimal results.
To avoid these pitfalls, educators and learners should recognize that behavioral improvement is a gradual process, and different individuals may need varying levels of support and encouragement. By acknowledging these common misunderstandings, more effective learning environments can be created, where growth is sustained through a balanced and thoughtful approach.
- Focus on Consistency: Gradual and consistent reinforcement over time produces more lasting change than immediate or excessive rewards.
- Emphasize Intrinsic Motivation: It’s crucial to foster internal motivation so that students engage with their learning for personal satisfaction, not just external validation.
- Adapt Strategies to Individual Needs: Understand that different learners may require unique approaches to stay engaged and motivated.
Reinforcement Strategies for Effective Learning
Effective learning is driven by strategic approaches that encourage positive behaviors and sustain motivation. The use of well-planned methods to recognize and reward progress can significantly enhance a student’s commitment to their studies. By integrating various techniques, educators can create an environment where learners feel valued, motivated, and inspired to continue their educational journey.
Positive Feedback and Recognition
Providing students with timely and meaningful feedback is one of the most powerful ways to reinforce learning. Recognition of both effort and achievement strengthens students’ belief in their capabilities, boosting their self-confidence and encouraging continued engagement. Positive reinforcement can take various forms:
- Verbal Praise: Acknowledging students’ hard work with encouraging words motivates them to keep pushing forward.
- Public Recognition: Highlighting achievements in front of peers can build confidence and foster a sense of accomplishment.
- Certificates or Awards: Tangible rewards like certificates provide a sense of formal recognition that can further incentivize future success.
Setting Clear and Achievable Goals
Another effective strategy is goal-setting. When students know what they are working towards and understand how to achieve it, they are more likely to stay focused and motivated. Clear, achievable goals provide direction and a sense of purpose in the learning process. Breaking larger goals into smaller, more manageable steps also allows students to experience regular successes, which boosts their morale and momentum.
- SMART Goals: Encourage students to set goals that are Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound.
- Tracking Progress: Allow students to track their progress toward their goals, providing regular opportunities for reflection and adjustment.
- Celebrating Milestones: Recognize and celebrate key milestones as students reach them, reinforcing their efforts and encouraging them to keep progressing.
By implementing these strategies, educators can create an environment where students feel supported, engaged, and motivated to continue advancing in their learning journey. Through consistent positive feedback and clear goal-setting, students are more likely to stay committed and reach their full potential.
Linking Positive Feedback to Long-Term Success
Establishing a connection between consistent positive feedback and long-term achievement is crucial for sustainable growth in any learning process. When students consistently experience acknowledgment for their efforts, they begin to understand that their actions have lasting consequences. This cycle of feedback helps to foster intrinsic motivation, which is essential for ongoing success in both academic and personal development.
The key to ensuring that feedback leads to long-term results lies in making the process meaningful and goal-oriented. Short-term rewards may provide immediate satisfaction, but it is the reinforcement of effort toward larger goals that truly cultivates resilience and perseverance. By linking positive recognition to a sense of progress, students are more likely to maintain their motivation and push through challenges.
Building Sustainable Habits Through Feedback
For reinforcement to have a lasting impact, it must be integrated into a student’s routine in a way that promotes the development of productive habits. Regular, consistent feedback plays a key role in shaping these habits. Here’s how:
- Consistency: Providing steady and predictable reinforcement helps students internalize the importance of effort and progress, making it easier to form lasting habits.
- Long-Term Goal Focus: Reinforcing the connection between daily actions and long-term aspirations encourages students to stay focused on their bigger picture rather than short-term rewards.
- Building Confidence: Regular positive feedback boosts students’ self-belief, which can help them tackle more complex challenges and setbacks in the future.
Creating a Supportive Environment for Growth
Another essential factor in linking positive reinforcement to long-term success is creating an environment that continually supports the learner’s progress. This environment goes beyond just the classroom setting; it includes relationships, resources, and tools that consistently promote growth. A supportive environment encourages students to view feedback not just as praise but as a tool for improvement, shaping their ability to persist in the face of difficulties.
- Encourage Reflection: Regularly asking students to reflect on their achievements and setbacks helps them see how feedback is directly tied to their growth.
- Provide Meaningful Challenges: Students should be given tasks that challenge their current abilities, encouraging them to apply themselves fully and see tangible results from their efforts.
- Foster Collaboration: Learning environments that encourage peer collaboration and shared feedback can provide additional reinforcement, helping students grow both individually and as part of a community.
By aligning reinforcement strategies with long-term goals and creating a supportive environment, students are more likely to remain motivated and committed to their learning, achieving sustainable success in the long run.
Research Findings on Positive Feedback and Learning Progress
Extensive studies have shown that consistent positive feedback significantly enhances the learning process, encouraging greater effort and sustained engagement. The effectiveness of feedback in educational settings goes beyond mere praise; it influences how students perceive their capabilities and motivates them to persist through challenges. Research indicates that well-structured recognition of progress plays a critical role in shaping students’ attitudes towards learning and their long-term achievements.
One key finding is the importance of timing and consistency in feedback. When students receive immediate recognition following their efforts, they are more likely to internalize the reinforcement and apply themselves more vigorously in subsequent tasks. Furthermore, the consistency of feedback influences the development of positive learning habits, which are essential for continued progress. The data suggests that reinforcement, when applied systematically, encourages students to push through setbacks and reinforces their belief in their ability to succeed.
Studies have also revealed that positive reinforcement fosters a growth mindset, which is crucial for lifelong learning. When students are regularly acknowledged for their progress, they develop a deeper understanding that skills can be improved through effort, rather than being limited by innate abilities. This mindset shift promotes resilience, leading to improved performance even in the face of difficulty.
Moreover, research highlights the importance of aligning feedback with the goals and expectations of the learner. Tailoring recognition to specific learning objectives helps students understand the direct connection between their actions and the outcomes they are striving for. This alignment boosts motivation and helps them stay focused on their long-term goals.
In conclusion, the findings emphasize that feedback, when strategically applied, has a profound impact on students’ learning experiences. By reinforcing effort and aligning recognition with individual progress, educators can foster an environment where students are motivated to continue learning and achieving their goals over time.
Improving Learning with Progressive Learning Techniques

Incorporating effective techniques that build on learners’ progress can significantly enhance their ability to absorb new concepts and stay motivated. By creating a learning environment that rewards incremental progress, students are more likely to engage actively and persistently. These techniques help to create a cycle of positive reinforcement, where small successes contribute to larger achievements, and the momentum of progress encourages continued effort.
The key to these techniques lies in focusing on both short-term gains and long-term goals. While immediate rewards can spark motivation, it is the ongoing reinforcement of progress towards larger objectives that fosters deep learning. Applying such strategies requires consistency, clarity, and an understanding of individual learning needs, which helps to maintain momentum and sustain focus throughout the learning process.
Strategies for Maintaining Engagement
There are several techniques that can help maintain engagement and promote continuous improvement in the learning journey. These include:
- Chunking Information: Breaking down complex topics into smaller, manageable parts allows students to build confidence as they master each segment, creating a sense of accomplishment.
- Frequent Feedback: Regular and timely feedback helps students stay on track, ensuring they understand how their efforts are contributing to their progress.
- Clear Milestones: Setting clear, achievable milestones provides students with specific targets to aim for, which can boost motivation and enhance a sense of purpose.
Creating a Growth-Oriented Environment
Creating an environment that emphasizes progress rather than perfection can greatly impact a student’s ability to maintain focus and achieve long-term success. This involves encouraging learners to view challenges as opportunities for growth rather than obstacles. Educators can achieve this by:
- Promoting a Positive Mindset: Encouraging students to focus on their improvement rather than solely on outcomes can foster resilience and persistence.
- Celebrating Small Wins: Acknowledging even small achievements helps build confidence and reinforces the idea that progress is a continuous journey.
- Fostering Collaboration: Encouraging students to work together and share their successes strengthens their commitment to learning and creates a supportive environment.
By incorporating these techniques, educators can foster an atmosphere where students are motivated by their own progress, ultimately leading to a more engaging and successful learning experience.
Overcoming Challenges with Positive Feedback Strategies
Educational environments are often full of obstacles that can hinder students’ progress and motivation. However, addressing these challenges through well-structured feedback can have a transformative effect on a learner’s ability to navigate difficulties and remain focused on their goals. By implementing consistent reinforcement techniques, educators can guide students through challenges while maintaining their motivation and promoting continuous improvement.
When faced with setbacks, learners often feel discouraged, which can lead to disengagement and decreased performance. However, strategically applied feedback can turn these setbacks into opportunities for growth. By focusing on the progress students are making and highlighting their efforts, educators can help them regain their confidence and sustain momentum through tough situations.
Common Educational Obstacles
Students face a variety of challenges in their learning journey. Below are some of the most common hurdles:
- Loss of Confidence: When students struggle with new concepts, they may begin to doubt their abilities, which can lead to further difficulties.
- Lack of Motivation: Prolonged challenges can cause students to lose interest in the material, making it harder for them to stay engaged.
- Overwhelming Content: Large amounts of information or complex tasks can overwhelm students, causing frustration and a lack of focus.
How Feedback Helps Overcome Obstacles
Positive feedback strategies can address these challenges in several ways. Below is a table outlining how different forms of feedback can help students overcome common obstacles:
| Challenge | Feedback Strategy | Effect |
|---|---|---|
| Loss of Confidence | Highlighting progress and small achievements | Boosts self-esteem and restores belief in abilities |
| Lack of Motivation | Providing encouragement and setting clear goals | Increases engagement and fosters a sense of purpose |
| Overwhelming Content | Breaking down tasks into manageable steps | Reduces stress and helps students feel more in control |
By using targeted feedback techniques, educators can transform these obstacles into learning opportunities, fostering resilience, and encouraging ongoing success. This approach not only supports students during difficult moments but also empowers them to take ownership of their learning and persevere through challenges.
Overcoming Challenges with Positive Feedback Strategies
Educational environments are often full of obstacles that can hinder students’ progress and motivation. However, addressing these challenges through well-structured feedback can have a transformative effect on a learner’s ability to navigate difficulties and remain focused on their goals. By implementing consistent reinforcement techniques, educators can guide students through challenges while maintaining their motivation and promoting continuous improvement.
When faced with setbacks, learners often feel discouraged, which can lead to disengagement and decreased performance. However, strategically applied feedback can turn these setbacks into opportunities for growth. By focusing on the progress students are making and highlighting their efforts, educators can help them regain their confidence and sustain momentum through tough situations.
Common Educational Obstacles
Students face a variety of challenges in their learning journey. Below are some of the most common hurdles:
- Loss of Confidence: When students struggle with new concepts, they may begin to doubt their abilities, which can lead to further difficulties.
- Lack of Motivation: Prolonged challenges can cause students to lose interest in the material, making it harder for them to stay engaged.
- Overwhelming Content: Large amounts of information or complex tasks can overwhelm students, causing frustration and a lack of focus.
How Feedback Helps Overcome Obstacles
Positive feedback strategies can address these challenges in several ways. Below is a table outlining how different forms of feedback can help students overcome common obstacles:
| Challenge | Feedback Strategy | Effect |
|---|---|---|
| Loss of Confidence | Highlighting progress and small achievements | Boosts self-esteem and restores belief in abilities |
| Lack of Motivation | Providing encouragement and setting clear goals | Increases engagement and fosters a sense of purpose |
| Overwhelming Content | Breaking down tasks into manageable steps | Reduces stress and helps students feel more in control |
By using targeted feedback techniques, educators can transform these obstacles into learning opportunities, fostering resilience, and encouraging ongoing success. This approach not only supports students during difficult moments but also empowers them to take ownership of their learning and persevere through challenges.
Practical Applications of Key Learning Strategies
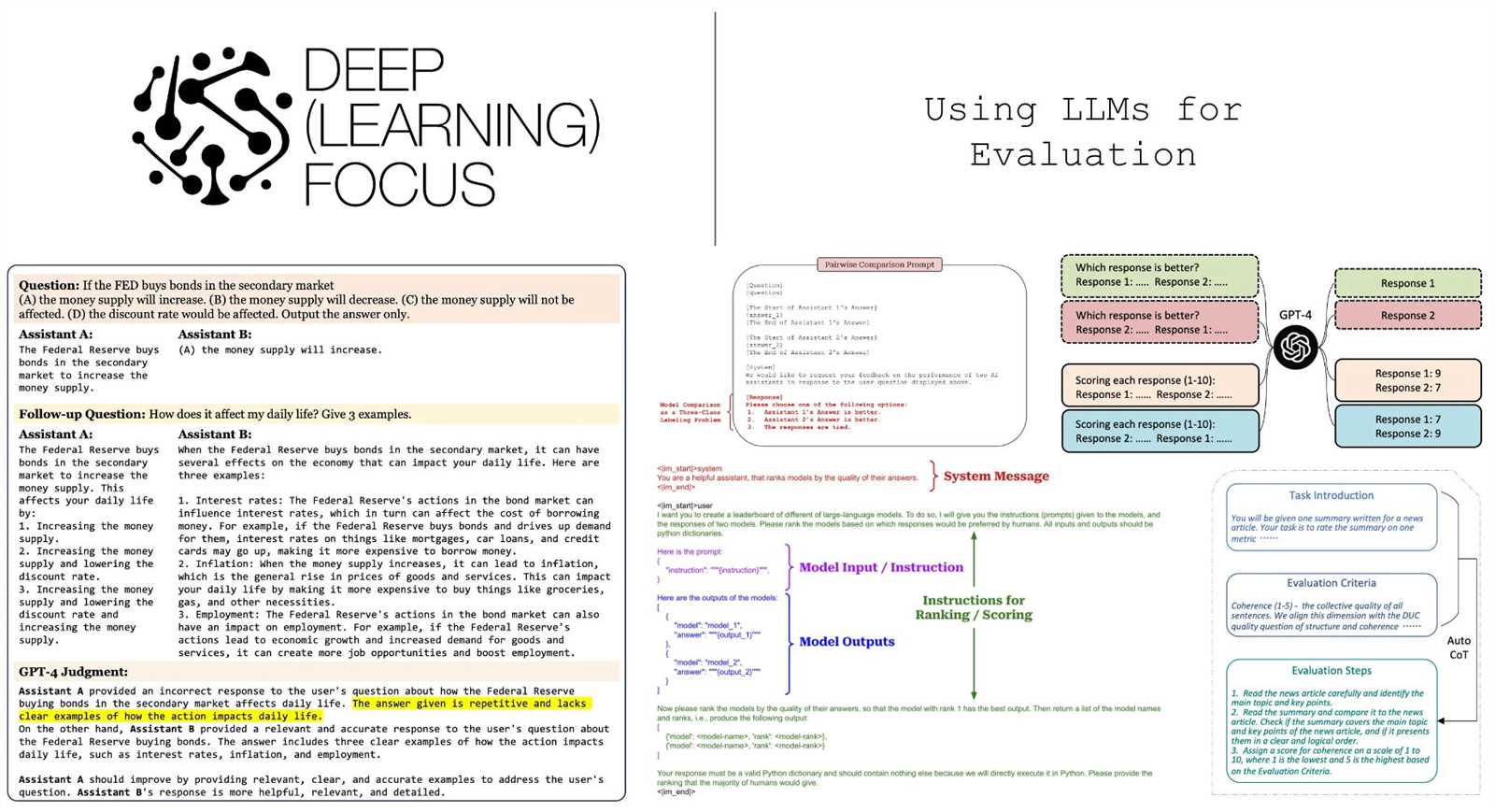
Understanding key concepts and strategies is essential for applying them effectively in real-world scenarios. In educational settings, this knowledge can be directly translated into practical techniques that enhance learning and boost performance. By using these strategies thoughtfully, educators and students alike can optimize the learning process, overcome challenges, and achieve desired outcomes.
The principles discussed can be applied across various disciplines and learning environments, fostering deeper understanding and helping individuals develop essential skills. Whether in the classroom, workplace, or self-directed learning, the following applications can provide a structured approach to implementing these methods.
Effective Classroom Applications
- Behavioral Adjustments: Tailoring teaching methods to suit individual learning needs and promoting consistent progress through positive feedback.
- Task Breakdown: Simplifying complex tasks into manageable segments, allowing students to experience consistent success and build confidence.
- Active Engagement: Using interactive techniques that encourage active participation, such as group discussions and hands-on activities, to maintain interest and foster learning.
Applications for Self-Study and Personal Growth
- Goal Setting: Establishing clear, achievable goals to maintain focus and motivation throughout the learning process.
- Consistent Reflection: Regularly assessing personal progress and adjusting learning strategies to stay on track and address areas of improvement.
- Building Resilience: Developing strategies to stay motivated and persistent in the face of setbacks, focusing on long-term success rather than immediate results.
By incorporating these practical strategies into daily learning routines, individuals can create a more effective and fulfilling educational experience. These techniques not only help with immediate learning goals but also contribute to long-term growth and mastery of complex subjects.
Future Directions for Reinforcement Momentum
As the field of adaptive learning systems evolves, the exploration of new methodologies and algorithms is crucial to further enhance their performance. Researchers are focusing on improving the efficiency and scalability of decision-making processes through various innovative approaches. The integration of new concepts could lead to more sophisticated models capable of handling increasingly complex tasks.
Emerging Strategies in Algorithm Development
Future advancements will likely center around the refinement of algorithms, optimizing how systems predict and adapt to dynamic environments. These techniques could allow for better handling of long-term dependencies and uncertain scenarios, opening new possibilities for real-time decision-making.
Exploring New Applications

The potential applications of these advanced systems extend far beyond traditional domains, reaching areas such as autonomous systems, healthcare, and finance. As technologies improve, the scope of their use in practical, real-world situations will broaden, making them more accessible and effective across industries.
| Focus Area | Key Innovations | Potential Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Algorithm Efficiency | Improved learning rates, reduced resource consumption | Faster, more effective models with minimal computational cost |
| Scalability | Handling larger datasets and environments | Systems can manage increasingly complex tasks with ease |
| Application Scope | Expansion into new sectors such as healthcare and finance | Wider adoption and impact across industries |