
In today’s digital landscape, safeguarding sensitive information is more critical than ever. Effective protection strategies play a pivotal role in preventing unauthorized access, data breaches, and potential risks to privacy. These methods help organizations assess and address vulnerabilities, ensuring the integrity of operations and communication.
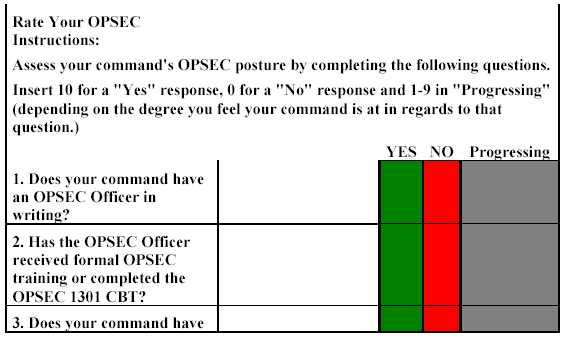
Comprehending the essence of these protective measures involves looking beyond just technical tools. It requires a deep understanding of how data can be exposed and what practices can be employed to mitigate threats. From personal to organizational security, maintaining confidentiality and minimizing risk are at the heart of these efforts.
By adopting a proactive approach, businesses and individuals can strengthen their defense systems, ensuring that their valuable assets remain secure. In this section, we explore key strategies that focus on managing and limiting the potential for information leaks and security breaches.
What Are Security Measures in Response to Risks
In the context of protecting sensitive information, specific strategies are designed to address potential vulnerabilities and safeguard critical assets. These practices focus on identifying threats, assessing risks, and implementing solutions to mitigate potential exposure. By evaluating all potential weaknesses, organizations can adopt the right security protocols to preserve confidentiality and integrity.
Key Components of Risk Response Strategies
Security measures aimed at minimizing vulnerabilities typically include several layers of protection. These efforts are not limited to one solution but rather a combination of tactics to cover various areas of concern:
- Risk assessment: Identifying potential weaknesses within systems and processes.
- Data protection: Ensuring the secure storage and transfer of sensitive information.
- Incident response: Preparing for and managing any breaches or security failures.
- Employee training: Educating staff about the best practices for maintaining confidentiality and security.
Practical Applications and Examples
These protective measures are widely used in various sectors, from government agencies to private corporations. In high-stakes environments, ensuring that confidential data is not exposed requires constant vigilance. Implementing these protocols helps avoid compromising critical information, whether in digital communication or physical operations.
By focusing on these fundamental strategies, organizations can create a robust framework that not only identifies potential risks but also effectively manages and reduces them, maintaining security throughout their operations.
Importance of Operational Security in Responses
Effective security measures are crucial for protecting sensitive information and preventing unauthorized access during critical operations. By ensuring that the right precautions are in place, organizations can minimize the risk of leaks and attacks, preserving both the integrity and confidentiality of their data. Operational security plays a pivotal role in crafting responses to security challenges, offering a structured approach to risk management.
Without proper precautions, even the smallest security lapse can lead to significant vulnerabilities. This is why implementing a comprehensive strategy to secure communication and data during sensitive operations is necessary for maintaining privacy and safety across all levels of operation.
| Security Focus | Impact of Inaction |
|---|---|
| Data Encryption | Exposes sensitive information to unauthorized parties |
| Access Control | Increases the likelihood of unauthorized access |
| Employee Training | Leads to accidental data exposure and breaches |
| Incident Response Planning | Delays reaction times during critical breaches |
By focusing on these elements, organizations can prevent costly security breaches and maintain operational efficiency, even in the most challenging situations. Each layer of operational security ensures that the integrity of critical data is upheld, and response times are optimized in the event of a potential threat.
Key Principles of Operational Security in Protection
Effective security practices are built upon several core principles that guide the protection of sensitive information and the prevention of unauthorized access. These principles help organizations identify risks, control vulnerabilities, and establish reliable protocols to protect both physical and digital assets. The foundation of a strong security framework relies on these essential guidelines, ensuring that each layer of security is both comprehensive and effective.
Risk identification and management is one of the cornerstones of a solid security strategy. By understanding potential threats, organizations can implement measures to minimize exposure and mitigate possible attacks. Whether in data storage, communication, or personnel management, recognizing weak points allows for more targeted and efficient protection efforts.
Data confidentiality and integrity are equally vital. Ensuring that sensitive information is accessible only to authorized individuals reduces the likelihood of leaks or unauthorized alterations. Implementing strong encryption, access controls, and secure communication channels further enhances protection and maintains the trust of stakeholders.
Continuous monitoring and response complete the security cycle. Regular assessments and real-time monitoring help detect vulnerabilities or breaches quickly. Having a well-prepared response plan ensures that any security incident can be addressed swiftly, minimizing damage and restoring system integrity.
How Security Measures Protect Sensitive Data
Protecting sensitive data is essential for maintaining privacy and ensuring the safety of personal, corporate, and governmental information. The application of specific security measures helps to secure valuable data from unauthorized access, breaches, and potential threats. By implementing effective strategies, organizations can reduce risks and protect critical assets from exposure.
Encryption is one of the most powerful tools in safeguarding sensitive data. By transforming data into unreadable code, it ensures that even if information is intercepted, it cannot be accessed or understood without the proper decryption key. This process is critical in securing data during transmission over networks or while stored in databases.
Access control further strengthens protection by restricting data access to only those who are authorized. Through the use of passwords, biometric verification, and multi-factor authentication, organizations can limit who can view or modify sensitive information, reducing the risk of internal or external threats.
Regular audits and monitoring are also vital to ensuring the ongoing protection of sensitive data. Continuous surveillance of systems and networks helps identify any unusual activity that could indicate a potential breach. Early detection allows organizations to act swiftly, minimizing any potential damage to data integrity.
Common Misconceptions About Security Measures
When it comes to protecting sensitive information, there are many misunderstandings surrounding the best practices and methods used to ensure security. These misconceptions can lead to vulnerabilities or ineffective strategies, ultimately putting critical data at risk. It’s important to recognize and address these common myths to better safeguard information.
- Only technical solutions matter: Many believe that advanced software or tools are the only way to secure data. However, proper security requires a combination of technical measures, well-defined procedures, and employee awareness.
- Security is a one-time task: Another misconception is that once security protocols are in place, they no longer require attention. In reality, security is an ongoing process that demands constant evaluation and updates to stay ahead of emerging threats.
- All threats come from outside: While external attacks are a concern, internal threats are equally important. Employees, whether malicious or accidental, can be a source of significant risk if proper access controls and training are not implemented.
- Encryption is enough: While encryption is a powerful tool, it’s only one layer in a broader security strategy. Without additional measures such as access control, monitoring, and incident response planning, encryption alone cannot guarantee total protection.
By understanding these misconceptions, organizations can build a more comprehensive and effective security framework that addresses both internal and external risks, ensuring sensitive data remains protected at all times.
Steps to Develop Effective Security Responses
Creating effective strategies to protect sensitive information involves a structured approach that addresses potential vulnerabilities, establishes protocols, and ensures quick responses to threats. By following a clear and organized plan, organizations can minimize risks and enhance their overall security posture. Each step should be tailored to the unique needs of the organization while maintaining a focus on risk reduction and data protection.
1. Assess and Identify Risks
The first step in developing an effective security strategy is to evaluate potential threats. Identifying risks involves reviewing existing systems, processes, and data flows to pinpoint weak points that could be targeted by attackers. Regular risk assessments ensure that new vulnerabilities are recognized and addressed in a timely manner.
2. Define Protective Measures
Once risks are identified, the next step is to implement protective measures. This includes adopting encryption, setting up access controls, and establishing clear policies for data handling and sharing. A multi-layered defense approach is crucial to ensuring that sensitive information is safeguarded at all stages, from storage to transmission.
By following these foundational steps, organizations can develop robust security strategies that not only prevent breaches but also enable quick recovery in case of a security incident. Regular updates and continuous monitoring are key to maintaining an effective defense against evolving threats.
The Role of Security Measures in Risk Management
In risk management, one of the most critical elements is ensuring that sensitive information is protected from threats that could compromise confidentiality, integrity, and availability. Effective security protocols help organizations assess potential risks and develop strategies to mitigate them. These protective measures play a vital role in minimizing the impact of threats and ensuring the smooth operation of business activities.
Risk Identification and Prevention
Identifying potential risks is the first step in any security strategy. By understanding where vulnerabilities exist–whether within systems, processes, or personnel–organizations can address those weaknesses before they are exploited. Prevention strategies are designed to minimize the likelihood of an attack or data breach, effectively reducing overall risk exposure.
Mitigation and Response Strategies
Once risks are identified, developing mitigation measures is essential. This may involve creating strong access controls, encrypting sensitive data, or training employees to recognize and avoid common threats. In the event of a breach, a well-prepared response plan ensures that organizations can react quickly to limit the damage and recover swiftly.
By integrating these protective measures into a comprehensive risk management framework, organizations can strengthen their defenses, prevent potential losses, and maintain a secure environment for their operations and data. Security strategies are an ongoing process that adapts as new risks emerge, helping organizations stay ahead of evolving threats.
How to Assess Security Measure Effectiveness
Evaluating the effectiveness of security protocols is essential to ensuring that protective strategies are functioning as intended. Regular assessment helps organizations identify any weaknesses or gaps in their defense mechanisms and make necessary adjustments. The process involves reviewing security measures from multiple angles, including their ability to prevent, detect, and respond to threats.
1. Define Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
Establishing clear metrics is crucial in assessing the effectiveness of any security strategy. These indicators should reflect how well the measures prevent breaches, minimize risks, and protect sensitive information. Common KPIs include:
- Incident response time: How quickly the system can detect and respond to a breach.
- Data loss prevention: The ability to prevent unauthorized access and data leaks.
- Employee adherence: The level of compliance with security protocols among staff.
2. Conduct Regular Testing and Audits
Ongoing testing is an integral part of evaluating security effectiveness. This may involve conducting penetration tests, vulnerability scans, or simulated attack scenarios to assess how well systems stand up to real-world threats. Regular audits, both internal and external, also help ensure that security measures are up to date and functioning correctly.
3. Collect Feedback and Data
Gathering feedback from both employees and external stakeholders can provide valuable insights into the success of security practices. Surveys, interviews, and security incident reports offer data on potential areas of improvement. By actively engaging with those who interact with security systems daily, organizations can better understand the strengths and weaknesses of their protocols.
Through these assessments, organizations can ensure that their security measures remain effective, adapting to new threats and challenges as they arise. Regular evaluation keeps systems robust and responsive to emerging risks, providing continuous protection for sensitive data.
Security Measures and Their Impact on Communication
Effective communication is essential in both personal and organizational settings. However, the way sensitive information is shared must be protected to avoid potential breaches. Implementing strong protective measures helps safeguard communication channels from unauthorized access, ensuring that information remains confidential and secure. The integration of security protocols into communication practices is crucial in reducing the risk of data exposure and maintaining trust between parties.
Ensuring Confidentiality in Communication
Confidentiality is one of the most critical aspects of secure communication. By employing encryption, secure messaging platforms, and access control, sensitive messages can be protected from prying eyes. This minimizes the risk of information leakage, especially in environments where the exchange of private or proprietary data is frequent. Furthermore, limiting access to only authorized individuals enhances trust and ensures that only those with the proper credentials can view or share certain information.
Maintaining Integrity and Authenticity
In addition to confidentiality, data integrity and authenticity play vital roles in communication security. Security protocols ensure that messages are not tampered with during transmission, and that recipients can verify the identity of the sender. This is crucial for preventing malicious attacks like phishing or impersonation. Implementing measures like digital signatures, authentication checks, and secure channels prevents unauthorized individuals from altering or falsifying communications.
By embedding security into communication practices, organizations can safeguard sensitive information from external threats and ensure that both internal and external communications remain secure and trustworthy. These protective measures help organizations protect their reputation, comply with regulations, and maintain operational efficiency in a secure environment.
Security Measures in Cybersecurity Defense
In the field of cybersecurity, protective measures are critical to defending against a variety of threats, from data breaches to malicious attacks. Implementing effective security protocols helps organizations to reduce vulnerabilities and increase their resilience against cyber threats. By adopting a proactive approach to defense, organizations can safeguard sensitive data, secure communication channels, and ensure business continuity.
Identifying Vulnerabilities and Threats
The first step in a robust cybersecurity defense strategy is identifying potential vulnerabilities. This involves reviewing systems, applications, and networks to pinpoint weak points that could be exploited by attackers. Regular assessments, such as penetration testing and vulnerability scans, allow organizations to stay ahead of evolving threats by addressing security gaps before they are targeted. Early detection of potential risks ensures that defenses are reinforced and risks are minimized.
Layered Defense Approach
A layered defense strategy is essential in cybersecurity. By implementing multiple layers of protection, such as firewalls, intrusion detection systems, encryption, and multi-factor authentication, organizations can ensure that even if one line of defense is compromised, others will still provide protection. This approach helps to mitigate the impact of attacks and prevent unauthorized access to critical systems and data. A well-designed layered defense system ensures a strong, multi-faceted barrier against cyber threats.
Through a combination of proactive risk identification and layered defense measures, organizations can build a resilient cybersecurity infrastructure that minimizes the potential impact of cyber threats. These measures work together to ensure that sensitive data remains protected and business operations are not disrupted by malicious activities.
Security Measures and Privacy Protection
Ensuring privacy is a fundamental aspect of any security strategy, especially when dealing with sensitive personal or organizational data. Privacy protection involves safeguarding individual rights and maintaining confidentiality by controlling how data is accessed, shared, and stored. Implementing strong protective measures reduces the risk of unauthorized access, ensuring that private information remains secure from external threats.
Key Methods for Protecting Privacy
Privacy protection relies on a variety of methods and best practices that help prevent data leakage and unauthorized access. Some of the most effective strategies include:
- Data Encryption: Ensuring that all sensitive data is encrypted during storage and transmission, making it unreadable to unauthorized parties.
- Access Control: Limiting access to sensitive information based on roles and ensuring that only authorized personnel can view or modify it.
- Secure Communication Channels: Using secure communication tools like encrypted emails and messaging platforms to protect privacy during exchanges of information.
Monitoring and Compliance
To ensure privacy is maintained, continuous monitoring of systems and compliance with relevant data protection regulations is essential. Regular audits, checks, and assessments ensure that privacy policies are followed and that any vulnerabilities are identified before they can be exploited. Following global privacy standards like GDPR or CCPA further strengthens an organization’s ability to protect private data.
By embedding privacy protection measures into daily operations and digital processes, organizations not only secure sensitive information but also build trust with customers and clients. These proactive measures are vital to maintaining confidentiality and mitigating the risks associated with data breaches and privacy violations.
Training Teams to Understand Security Measures
Effective training is essential for ensuring that teams fully understand the importance of security measures and how to apply them in their daily activities. When employees are educated about best practices, they are better equipped to protect sensitive information, prevent data breaches, and maintain a secure environment. Comprehensive training programs help teams recognize potential threats and respond appropriately to mitigate risks, strengthening the organization’s overall defense strategy.
It is crucial to tailor training sessions to the specific needs and roles within the team. While some members may need in-depth technical knowledge, others may require a more general understanding of security protocols. By offering diverse training formats, such as workshops, e-learning modules, and hands-on simulations, organizations can ensure that their teams stay informed and prepared for any potential security challenges.
Ongoing education and regular updates are also key to maintaining a strong security posture. As threats evolve, so too should the knowledge and skills of the team. Providing refresher courses and staying current with the latest security trends ensures that the team remains proactive and effective in addressing emerging threats.
Security Measures in Government and Military
In government and military operations, the protection of sensitive information is paramount. Safeguarding critical data and communication channels ensures that national security is maintained and that operations remain secure from external threats. Security protocols are implemented at every level to mitigate risks and ensure that classified information does not fall into the wrong hands. The stakes are particularly high in these sectors, making robust security practices indispensable for operational success.
Key Security Strategies in Government and Military
Governments and military organizations employ a range of security measures to protect sensitive information, ranging from classified documents to communications. The following strategies are essential for maintaining security:
| Security Measure | Description |
|---|---|
| Encryption | Ensuring that all communications and sensitive data are encrypted to prevent unauthorized access. |
| Access Control | Restricting access to critical data based on roles and clearance levels to ensure that only authorized personnel have access. |
| Secure Communication Channels | Using secure lines of communication, such as encrypted emails or military-grade messaging systems, to avoid interception. |
Training and Awareness for Security Personnel
In addition to technical measures, personnel training is essential for maintaining operational security. Government and military staff are regularly trained to identify potential threats, recognize suspicious activities, and act swiftly in response to security breaches. This comprehensive training ensures that employees and officers at every level understand the importance of their role in maintaining security and confidentiality.
By implementing these robust security measures and continually educating personnel, government and military organizations can effectively protect sensitive information and ensure the integrity of their operations in the face of emerging threats.
Challenges in Implementing Security Measures
Implementing robust security practices can be a complex and challenging task, especially when dealing with sensitive information. Organizations must address various obstacles to ensure that security protocols are effective and consistently followed. These challenges range from technical difficulties to human factors, all of which must be managed to maintain a secure environment. Overcoming these barriers is essential for safeguarding data and protecting against threats.
Technical and Resource Constraints
One of the primary challenges in implementing security measures is the availability of technical resources. Organizations may lack the necessary tools, infrastructure, or expertise to deploy advanced security technologies. Additionally, budget constraints can limit the ability to invest in the latest security systems, leaving critical systems vulnerable. Overcoming these challenges often requires prioritizing security initiatives and seeking cost-effective solutions that still meet the required standards.
Human Factors and Training
Another significant challenge is ensuring that all employees are properly trained and aware of the importance of security. Even with the best technical systems in place, human error remains one of the most common causes of security breaches. Employees may inadvertently expose sensitive information through negligence or lack of awareness. Ongoing training and a culture of security consciousness are essential to mitigate these risks and ensure that personnel understand their role in maintaining security.
By addressing both technical and human challenges, organizations can strengthen their security posture and reduce the likelihood of a successful attack. Consistent evaluation, training, and investment in technology are key steps toward overcoming these obstacles.
Future Trends in Security Strategy Approaches
As technology continues to evolve, the landscape of security strategies is also changing. Organizations are constantly adapting to new threats, and the approaches they use to protect sensitive information are becoming increasingly sophisticated. The future of security will be shaped by innovations in technology, changes in organizational needs, and the emergence of new vulnerabilities. Understanding these future trends is essential for staying ahead of potential risks and ensuring that security practices remain effective in an ever-evolving environment.
Advancements in Artificial Intelligence and Automation
One of the most significant trends in the future of security will be the increased integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and automation. These technologies will play a pivotal role in identifying threats, automating responses, and enhancing overall security protocols. AI can analyze vast amounts of data to detect patterns and potential vulnerabilities that would be difficult for humans to identify. Automation will help streamline repetitive tasks, reduce human error, and improve response times to security incidents.
Emphasis on Data Privacy and Compliance
As privacy concerns continue to rise, organizations will place even more emphasis on data protection and compliance with privacy regulations. The increasing amount of personal and sensitive data being collected means that companies must adopt stringent measures to ensure that data is not only secure but also handled in accordance with legal standards. Future security strategies will prioritize data encryption, secure data storage, and compliance with global privacy laws such as GDPR and CCPA.
By embracing these emerging trends, organizations can enhance their ability to protect sensitive data and stay ahead of evolving security threats. The future of security will involve a combination of innovative technologies, strict privacy regulations, and an ever-vigilant approach to risk management.