
Exploring the world of sound involves more than just listening–it’s about recognizing patterns, understanding structures, and analyzing the emotional impact of different elements. Whether you’re preparing for an assessment or simply deepening your knowledge, gaining insight into these areas will enhance your ability to interpret various compositions and styles.
Developing a strong foundation in recognizing key components like rhythm, harmony, and melody allows you to fully appreciate the complexity of any piece. This section will provide the tools necessary to approach questions with clarity and precision, ensuring you can identify and explain the various elements that contribute to the creation of an auditory experience.
With a methodical approach and focused practice, you’ll gain confidence in your ability to assess and interpret a wide range of auditory works. Sharpening your critical thinking skills and honing your listening techniques will empower you to succeed and deepen your connection to the art form.
Music Appreciation Exam Answers
When preparing for assessments related to sound analysis, it’s essential to understand the various aspects that make up the structure and essence of a composition. Mastering the ability to identify instruments, styles, and elements will help you respond confidently to questions that require deep understanding. This section will focus on how to approach different types of inquiries and improve your knowledge of key topics.
Key Areas to Focus On
One of the most crucial areas to focus on is recognizing musical forms and structures. Understanding the way different sections of a piece fit together allows you to describe its flow and impact accurately. Additionally, it’s important to familiarize yourself with various genres and their distinguishing characteristics, from classical to contemporary, ensuring that you can identify them during assessments.
Effective Study Strategies
To maximize your performance, practice listening and analyzing compositions in detail. Pay attention to how rhythm, harmony, and instrumentation contribute to the overall effect. Developing a routine where you actively engage with sound will help solidify your ability to answer questions and explain your reasoning clearly.
Key Concepts for Music Appreciation Exams
To excel in assessments related to the study of sound, it’s important to familiarize yourself with foundational concepts that will allow you to interpret and analyze compositions effectively. A solid understanding of core principles will enable you to approach different questions with clarity and precision.
Fundamental Elements of Sound
There are several key aspects to consider when analyzing a piece of sound art. These elements form the building blocks of any composition and are essential for any assessment. The primary concepts include:
- Rhythm: The pattern of beats and time structure in a piece.
- Harmony: The combination of different notes played or sung together to create a pleasing effect.
- Melody: A sequence of notes that are perceived as a single entity.
- Texture: The layering of sounds that make up the overall sonic quality.
- Form: The structure or arrangement of a musical work, including repetition, contrast, and variation.
Understanding Historical Context
A deep understanding of different historical periods and their associated styles will help you identify and appreciate the evolution of sound over time. Be sure to study:
- Classical Era: Known for its formal structure and emphasis on orchestral arrangements.
- Romantic Period: Focused on emotional expression and greater dynamic range.
- Contemporary Music: Often experimental, using modern techniques and electronic elements.
Grasping these concepts will not only help you in identifying characteristics but also in discussing their significance within the broader context of sound history. Understanding how these elements interconnect is key to answering questions effectively.
Understanding Different Music Eras
To truly grasp the evolution of sound, it’s important to study the various historical periods that shaped its development. Each era brings with it distinct characteristics, reflecting the cultural, social, and technological changes of the time. Understanding these shifts allows for a deeper comprehension of how different styles and techniques emerged and evolved.
Classical and Romantic Periods
The Classical period is known for its emphasis on structure and balance, with composers focusing on clear forms and orchestral arrangements. It was a time of refinement and simplicity, with the music often following precise rules and patterns.
The Romantic era, in contrast, marked a shift toward emotional expression and individualism. Composers sought to convey deeper emotions and explore more dynamic contrasts, making the sound more dramatic and personal. Major figures like Beethoven and Chopin pushed the boundaries of harmony and orchestration, creating pieces that still resonate today.
Modern and Contemporary Movements
In the 20th and 21st centuries, sound began to break free from traditional constraints. The Modern era introduced new methods, such as dissonance and atonality, reflecting the rapidly changing world. With the rise of technology, the Contemporary period has seen a blend of electronic experimentation and diverse genres, reflecting the complexities of contemporary life.
Familiarity with these eras not only helps in identifying pieces but also in understanding the cultural context behind each work. This knowledge is essential for interpreting different styles and their impact on the present-day landscape of sound.
Common Music Terminology and Definitions
In the study of sound and its elements, understanding the language used to describe compositions is essential. Familiarity with key terms allows you to effectively analyze and communicate about various pieces. The following terms are frequently used to discuss the structure and characteristics of different works.
Fundamental Terms
These terms are the foundation of understanding any composition and are crucial when discussing the technical aspects:
- Tempo: The speed at which a piece is performed, often described in beats per minute.
- Pitch: The perceived frequency of a sound, determining its highness or lowness.
- Dynamics: The volume variations in a piece, from soft (piano) to loud (forte).
- Interval: The distance between two pitches, which can define the mood or tension in a composition.
- Chords: A combination of three or more notes played simultaneously, forming the harmonic foundation of a piece.
Advanced Concepts
As you dive deeper into sound analysis, you’ll encounter more complex terminology that helps explain intricate features:
- Modulation: The process of changing from one key to another within a piece.
- Counterpoint: The technique of combining two or more independent melodies to create harmony.
- Fugue: A contrapuntal composition where a theme is introduced and developed through repetition and variation.
- Sonata Form: A structure commonly used in classical compositions, involving exposition, development, and recapitulation.
Having a strong grasp of these terms not only aids in describing what you hear but also deepens your understanding of how a piece is constructed and its emotional impact.
How to Analyze a Musical Composition
Analyzing a composition involves more than just listening–it’s about understanding the underlying structure, identifying key elements, and exploring how they work together to create an emotional and intellectual experience. By breaking down a piece into its core components, you can gain deeper insight into its meaning and the techniques used by the composer.
The first step in analyzing any work is to listen actively and attentively. Focus on identifying the different sections of the piece and how they relate to each other. Pay attention to the rhythm, tempo, and dynamics, as they provide clues about the mood and emotional trajectory of the composition.
Next, examine the structure of the piece. Identify recurring themes or motifs and analyze how they evolve throughout the composition. Understanding the form–whether it’s a sonata, symphony, or more modern structure–will help you recognize patterns and anticipate how the piece progresses.
Additionally, it’s essential to consider the instrumentation and arrangement. Listen for how different instruments interact and complement each other. This can reveal the texture of the piece, whether it’s dense with layers or more sparse and transparent.
Finally, reflect on the emotional and intellectual impact of the composition. How does the music make you feel? What kind of atmosphere does it create? By considering these aspects, you can gain a fuller understanding of how all the elements come together to create a cohesive and meaningful experience.
Preparing for a Music Appreciation Test
Success in assessments related to the study of sound requires more than just passive listening; it demands a structured approach to understanding key concepts, terminology, and the ability to analyze various compositions. Preparation is crucial, and focusing on the right areas will help you feel confident and ready to tackle any question that comes your way.
Building a Solid Foundation
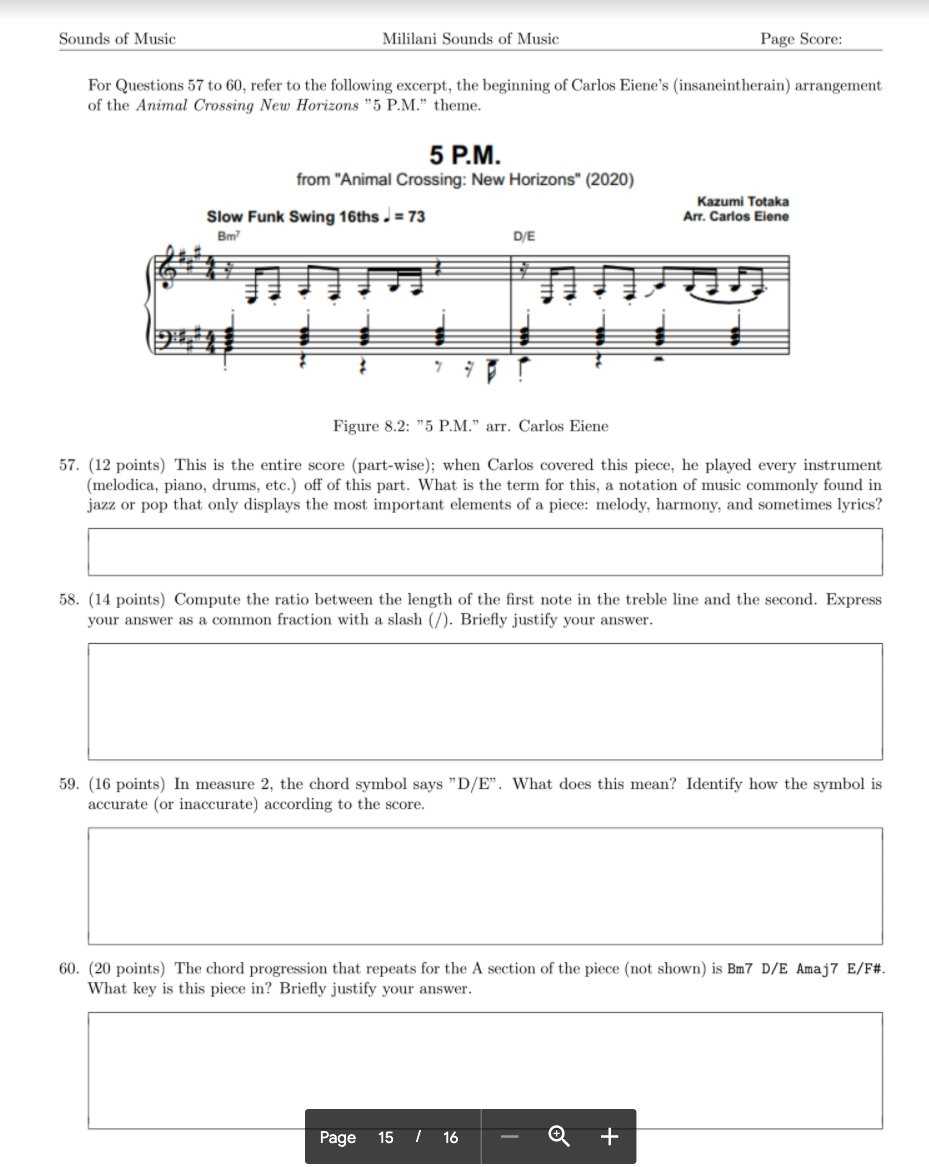
Start by reviewing fundamental concepts that form the backbone of the subject. Familiarize yourself with essential terms such as rhythm, harmony, and form. Understanding the different components of a composition will allow you to answer questions with greater precision and detail. You should also be able to identify key elements such as tempo and dynamics, as they are often central to analysis.
Practical Tips for Effective Study
In addition to theoretical knowledge, active listening is vital. Spend time listening to different styles and genres, focusing on identifying their unique characteristics. Take notes while you listen, noting down any recurring themes, motifs, or instruments. This practice will help you recognize these elements during assessments. Don’t forget to review any assigned materials, including lecture notes or recommended readings, as they often provide valuable insights into important topics.
Lastly, try mock tests or practice questions to simulate the testing environment. This will help you become familiar with the format of questions and manage your time effectively when answering them.
Famous Composers You Should Know
Throughout history, certain individuals have shaped the landscape of sound through their groundbreaking compositions. These renowned figures have influenced countless styles and techniques, leaving a legacy that continues to resonate in contemporary works. Becoming familiar with these composers will deepen your understanding and appreciation of the art form.
Here are some of the most iconic figures whose works are essential to know:
- Ludwig van Beethoven: Known for pushing the boundaries of classical forms, Beethoven’s work bridges the gap between the Classical and Romantic eras. His symphonies and piano sonatas remain central to classical repertoire.
- Johann Sebastian Bach: A master of counterpoint and harmonic structure, Bach’s compositions, especially his fugues and concertos, are fundamental to the development of Western music.
- Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart: Mozart’s ability to blend technical skill with emotional depth has made his operas, symphonies, and chamber works timeless.
- Pyotr Ilyich Tchaikovsky: Known for his expressive melodies and emotional depth, Tchaikovsky’s ballets and symphonic works have become iconic in the romantic tradition.
- Frédéric Chopin: Renowned for his poetic piano compositions, Chopin’s works are admired for their technical brilliance and emotional depth.
Understanding the contributions of these composers not only allows you to identify their styles but also helps you trace the development of musical techniques across eras. Each of these figures made distinct contributions that shaped the evolution of sound, influencing everything from orchestration to thematic development.
Tips for Memorizing Music Terms
Learning terminology related to sound and composition can be challenging, but with the right strategies, it becomes easier to retain and recall important concepts. Effective memorization techniques can help you grasp complex terms and apply them when needed, especially during assessments or discussions.
Active Engagement with Terms
One of the most effective ways to memorize terms is through active engagement. Instead of simply reading definitions, try using them in context. When you learn a new term, listen for it in pieces you are studying, or write sentences using the word. This helps to strengthen your memory by associating terms with real-world examples.
Visual Aids and Mnemonics
Creating visual aids like flashcards or diagrams can be extremely helpful. Use images or symbols to represent abstract concepts, which can make them easier to remember. Additionally, mnemonics or acronyms can help simplify complex definitions by turning them into easy-to-recall phrases.
| Term | Mnemonic | Definition |
|---|---|---|
| Tempo | “Tigers Eat Meat, Often” | The speed at which a piece is played. |
| Harmony | “Happy Angels Rest On Nighty Yards” | The combination of different notes played together. |
| Pitch | “Piano Is Timeless, Crystal Harmony” | The perceived highness or lowness of a sound. |
By breaking terms down into smaller, manageable chunks and regularly practicing their meanings, you’ll improve your ability to recall and use them with confidence. Integrating these techniques into your study routine will ensure a strong grasp of terminology, making it easier to discuss and analyze compositions.
Essential Listening Skills for Exams
When preparing for assessments involving sound analysis, developing strong listening skills is crucial. These skills allow you to identify key elements within a piece, understand its structure, and analyze its emotional and intellectual content. Active and focused listening is the foundation for performing well in any related test or evaluation.
Active Listening Techniques
Active listening involves fully engaging with the composition, concentrating on its details rather than passively hearing the sounds. Begin by identifying different sections, noting changes in tempo, dynamics, and the overall flow. Try to isolate individual instruments or voices to understand how they contribute to the piece as a whole. This approach will help you recognize important patterns and structures during assessments.
Identifying Key Elements
When listening to a piece for analysis, focus on identifying the core components such as rhythm, harmony, and melody. Pay attention to recurring motifs or themes, as they often form the basis for the structure of the composition. By honing your ability to spot these elements, you can improve both your listening comprehension and analytical skills.
Additionally, practice identifying different musical genres, styles, and historical periods. Understanding the characteristics of each can give you a broader context for your analysis, making it easier to identify specific features and place them within the right framework.
Popular Music Genres in Study
In any comprehensive study of sound and composition, exploring the various genres that have shaped artistic expression is essential. Each genre carries distinct characteristics, techniques, and cultural influences that contribute to the evolution of music. Understanding these categories can deepen your ability to analyze and appreciate the diversity within this field.
Here are some of the most influential genres that are often studied in detail:
- Classical: Known for its complex structures and intricate harmonies, this genre spans from the Baroque period to the Romantic era, with composers such as Beethoven and Mozart setting foundational standards.
- Jazz: Emerging in the early 20th century, jazz is characterized by improvisation, swing rhythms, and syncopated beats. It incorporates a wide range of influences, from blues to ragtime.
- Rock: A genre that evolved from rhythm and blues, rock emphasizes strong beats and electric instruments. Its diverse subgenres, including punk, progressive, and alternative rock, have shaped modern culture.
- Pop: With catchy melodies and accessible structures, pop music has a global appeal. Artists like Michael Jackson and Madonna have defined the genre’s evolution.
- Hip-hop: Originating in the 1970s, hip-hop blends rhythm with spoken word, focusing on lyrical expression and social commentary. It is one of the most influential genres in contemporary culture.
By studying these genres, you gain a better understanding of their historical context, the innovation behind their development, and their impact on other styles and genres. Each genre brings something unique to the table, offering a rich array of sounds, techniques, and cultural significance.
Interpreting Musical Elements and Forms
Understanding the various components that make up a composition is key to analyzing and appreciating its structure and impact. These elements, such as rhythm, harmony, and form, work together to create a cohesive piece, each contributing a unique aspect to the overall experience. Interpreting how these components interact allows for a deeper appreciation of the work and its intended emotional or intellectual message.
Key Elements to Focus On
When analyzing a piece, start by focusing on the individual elements that shape its sound and structure. Elements like rhythm define the pace and movement of the composition, while harmony creates the emotional undercurrent. The melody, on the other hand, is often the most recognizable part, drawing listeners in with its distinctive tune. Understanding how each of these components interacts with others helps in identifying the overall feel and intent of the piece.
Common Forms and Their Significance
Musical forms refer to the overarching structure that a piece follows, guiding its progression and helping to organize the various elements. Common forms include the sonata form, ternary form, and binary form, each offering a different way to organize sections within a composition. Recognizing these patterns allows listeners to better understand how a piece develops and evolves, contributing to a richer listening experience.
By examining both the individual elements and the broader form of a composition, you can uncover the underlying structure and gain a deeper understanding of its design and artistic value.
Study Methods for Music Appreciation
Effective study techniques are essential for mastering the concepts and skills needed to excel in any field of auditory art. Developing a deep understanding requires not just passive listening but active engagement with the material. By applying structured study methods, you can improve both your analytical and interpretative skills, making it easier to identify key components and understand their significance within a piece.
Here are some practical methods to enhance your learning experience:
- Active Listening: Focus on engaging with the piece on a deeper level. Listen multiple times, paying attention to different aspects such as rhythm, harmony, and instrumentation each time.
- Note-taking: While listening, jot down notes about what stands out. This can include identifying specific themes, changes in tempo, or unique characteristics that you notice.
- Practice Regularly: Consistent review and practice will reinforce key concepts. Listening to various compositions from different periods and genres can help you recognize patterns and styles more easily.
- Group Study: Collaborating with others can provide fresh perspectives. Discussing different interpretations and analyses can deepen your understanding and help you retain important information.
- Visual Aids: Using sheet music or diagrams can enhance your understanding of the structure and components of a composition. It allows you to see how the elements are arranged and interact.
By combining these techniques, you can improve your ability to analyze, interpret, and remember important concepts, setting yourself up for success in your studies.
Understanding Music Theory Basics
Grasping the fundamental principles that govern sound and its arrangement is key to truly understanding any composition. These principles form the foundation that guides both the creation and analysis of auditory works. By mastering the basics, you’ll gain a deeper insight into how different elements work together to produce harmony and rhythm in a piece.
Core Elements of Sound
At the heart of any composition lies the interaction of several key components that create its unique identity. These components include:
- Pitch: The highness or lowness of a note, fundamental to creating melodies and harmonies.
- Rhythm: The timing of notes and rests, which dictates the movement of a piece.
- Harmony: The combination of different pitches played together, supporting the main melody.
- Tempo: The speed at which a composition is played, which can dramatically affect the mood.
- Dynamics: The variations in loudness or softness throughout a piece.
Building Blocks of Theory
Understanding the structure and organization of sound is vital for recognizing how composers shape their works. The following elements form the foundation of theory:
- Scales: A series of notes ordered by pitch, often used as the basis for melodies and harmonies.
- Chords: Groups of notes played simultaneously, typically built on the notes of a scale.
- Intervals: The distance between two pitches, crucial for creating melodies and harmonies.
- Key Signatures: Indications of the key of a composition, helping to establish the tonality and mood.
- Time Signatures: Notations that define the meter of a piece, indicating how beats are grouped.
By familiarizing yourself with these basic principles, you’ll have the tools to break down and understand the structure of any composition, making it easier to analyze and appreciate the nuances of a piece.
Identifying Instruments in a Composition
Recognizing the different instruments used in a performance or a recorded piece can significantly enhance your understanding and enjoyment of the work. Each instrument contributes its unique sound, texture, and role, creating a distinctive sonic landscape. By familiarizing yourself with the characteristics of various instruments, you can begin to identify their presence and contribution to the overall composition.
Common Instrument Families
In any performance, instruments can typically be categorized into several families, each with its own distinctive timbre. The most common families include:
- String Instruments: Instruments like the violin, cello, and guitar are known for their resonant, melodic qualities. They can produce a wide range of dynamics and tones, from smooth and lyrical to sharp and piercing.
- Wind Instruments: This group includes instruments like the flute, clarinet, and trumpet. Wind instruments often produce bright, clear tones, and they play a key role in melody and harmony.
- Percussion Instruments: Instruments like the drums, cymbals, and tambourine provide rhythm and drive to a piece. They can create both subtle background effects and bold, powerful sounds.
- Keyboard Instruments: Instruments such as the piano and organ produce a rich, full sound and are essential for both harmonic and melodic contributions in many works.
Techniques for Identifying Instruments
To effectively identify instruments, focus on listening for certain characteristics that distinguish each one. Pay attention to:
- Timbre: The unique tonal quality of an instrument. For example, a violin has a bright, airy tone, while a bassoon sounds deeper and more resonant.
- Pitch Range: Some instruments, like the flute, produce higher pitches, while others, like the bass guitar, are lower and more grounded.
- Articulation: The way notes are attacked and released. Instruments like the trumpet have sharp, clear attacks, while the string section may have smoother transitions.
- Volume and Dynamics: Some instruments can dominate the soundscape, while others blend in more quietly. Percussion often provides dramatic shifts in volume, while string instruments may shift gradually.
By developing a keen ear for these attributes, you can start recognizing the various instruments in any performance, improving your ability to analyze and appreciate the textures within a piece.
Common Mistakes in Music Exams
Many students face challenges when preparing for assessments related to performing arts, and there are several frequent pitfalls that can hinder success. Understanding and avoiding these common mistakes can significantly improve your performance. These errors often arise from misunderstanding the material, misapplying knowledge, or not following proper preparation strategies.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Here are some of the most common mistakes that can negatively impact results:
- Inadequate Preparation: Rushing through practice sessions or failing to give enough time to review concepts can lead to a lack of confidence. It’s important to create a detailed study schedule that allows enough time for each topic or technique.
- Misinterpreting Instructions: Often, students fail to carefully read or understand the questions or guidelines provided. This can lead to incorrect answers or misapplied techniques. Always take the time to read through the instructions thoroughly.
- Neglecting Theory: While practical skills are important, neglecting the theoretical aspects of the subject can cause gaps in understanding. Ensure you balance both practical and theoretical study.
- Overlooking Details: Small details such as dynamics, tempo markings, or articulation can make a big difference. Not paying attention to these finer aspects can cause you to miss key elements in your response.
- Inconsistent Practice: Practicing irregularly or in short bursts rather than having consistent, focused sessions can result in uneven skill development. Set regular, structured practice times to reinforce concepts.
- Focusing Too Much on One Area: Concentrating too heavily on one aspect, such as performance or memorization, at the expense of others, can lead to an unbalanced preparation. Ensure a holistic approach to studying, addressing all aspects of the assessment.
Tips for Overcoming Mistakes
To improve your chances of success, consider these tips:
- Clarify Uncertainties: Don’t hesitate to ask questions if something is unclear. Seek clarification from instructors or peers to ensure that you fully understand the material.
- Review and Reflect: After each study session or practice, take time to review your performance. Reflect on what went well and what can be improved for next time.
- Practice Under Test Conditions: Simulating the actual test conditions can help reduce anxiety and increase your familiarity with the format. Practice completing tasks within the time limit and in an environment free from distractions.
- Stay Organized: Keep your study materials, notes, and resources well-organized to easily access information when needed. This reduces stress and enhances focus.
By recognizing and addressing these common errors, you can prepare more effectively and approach your assessments with confidence.
How to Answer Music Appreciation Questions
When responding to questions about the performing arts, it’s essential to focus on clarity, accuracy, and demonstrating a deep understanding of the subject matter. The way you approach each question can significantly affect the quality of your response. Here are some useful strategies for effectively tackling these types of queries.
Approach to Answering Questions
To provide a strong response, follow these key steps:
- Understand the Question: Take time to carefully read each question to ensure you understand what is being asked. Break the question down into parts if necessary, and identify any keywords or specific topics you need to address.
- Use Clear and Concise Language: Write your answers in a straightforward and clear manner. Avoid overly complex sentences or unnecessary jargon. Keep your explanations to the point and focused on the question.
- Provide Specific Examples: Whenever possible, use examples from known compositions or performances to support your response. This shows you have a practical understanding of the material and can apply theoretical knowledge.
- Be Organized: Structure your response logically. Start with an introduction to your answer, followed by the main body with supporting details, and conclude with a concise summary if needed.
- Stay Relevant: Stick to the topic at hand. Avoid diverging into unrelated areas, as this can confuse your response and detract from the clarity of your points.
Table of Key Points to Keep in Mind
| Tip | Description |
|---|---|
| Understand the Question | Carefully read each query to grasp its meaning before formulating your response. |
| Use Clear Language | Keep your answers simple and easy to understand, avoiding unnecessary complexity. |
| Provide Examples | Support your points with concrete examples, showing practical knowledge. |
| Stay Organized | Structure your response logically to improve readability and flow. |
| Be Relevant | Ensure that all information in your response directly relates to the question asked. |
By following these strategies, you can answer questions with confidence and demonstrate a thorough understanding of the material. This approach will also help you avoid common pitfalls and ensure that your responses are clear, precise, and relevant.