
Operating a vessel on the water requires a solid understanding of safety practices, navigation rules, and proper equipment usage. Mastering these concepts ensures not only personal safety but also the wellbeing of others sharing the waterways. This guide provides an overview of critical skills and knowledge needed to confidently handle responsibilities on the water.
From understanding navigation markers to interpreting weather patterns, there are numerous aspects to consider when preparing for maritime activities. Familiarity with these topics helps avoid common mistakes and promotes a safe, enjoyable experience.
Safety regulations, emergency procedures, and environmental awareness play a crucial role in responsible vessel operation. Whether you are new to this or seeking to enhance your expertise, this resource offers valuable insights to navigate the process effectively.
Understanding Boating Safety Principles

Ensuring safety on the water is a fundamental part of operating any vessel. Knowing how to prevent hazards and respond to unexpected situations helps protect everyone on board and others sharing the environment. Familiarity with core practices and recommended guidelines creates a foundation for secure and responsible activity.
Key Safety Guidelines
Preparation begins with checking essential equipment, such as flotation devices, communication tools, and navigation aids. Regular maintenance of the vessel ensures it is seaworthy and equipped to handle various conditions. Adhering to right-of-way rules and maintaining situational awareness minimizes risks and helps prevent accidents.
Responding to Emergencies
Understanding how to react in critical situations, such as capsizing or severe weather, can make a significant difference. Practicing man-overboard drills and familiarizing yourself with emergency signals ensures readiness during crises. Always prioritize safety over speed or convenience to maintain control in challenging scenarios.
Essential Equipment for Safe Boating
Proper preparation involves equipping your vessel with tools and devices designed to ensure safety and compliance with regulations. The right gear not only protects passengers but also simplifies navigation and communication in various conditions. Knowing what to carry on board is a critical aspect of responsible operation.
Must-Have Safety Gear
- Life jackets: Ensure that each person has access to a properly fitted flotation device approved for use.
- Fire extinguishers: Carry at least one extinguisher suitable for onboard fires, and ensure it is easily accessible.
- Navigation lights: Functional lighting is essential for visibility during low-light conditions or nighttime operation.
- First aid kit: Include medical supplies for minor injuries and ensure it is stored in a waterproof container.
- Sound-producing devices: Items such as whistles or air horns are necessary for signaling in emergencies.
Additional Items for Smooth Operation
- Communication tools: A VHF radio or mobile device can be a lifeline in case of emergencies.
- Anchor and line: Having a reliable anchor ensures you can secure the vessel when needed.
- Tool kit: Basic tools and spare parts can assist with minor mechanical issues while on the water.
- Charts and compass: These are vital for navigation, especially in unfamiliar areas or when electronic devices fail.
Carrying these essentials not only enhances safety but also ensures preparedness for unexpected situations, allowing for a more secure and enjoyable experience.
Rules of the Waterway Explained

Understanding navigation laws and behavioral guidelines on the water is essential for maintaining order and preventing accidents. These principles ensure smooth interaction between operators and safeguard both vessels and passengers. Mastering these rules enhances confidence and promotes a harmonious environment.
Right-of-Way Priorities
One of the fundamental aspects of navigation is knowing who has the right of way. Larger ships with limited maneuverability, vessels under sail, and those involved in fishing activities often take precedence. Smaller or more agile crafts must yield in such cases. Always approach crossings and overtaking scenarios with caution, signaling intentions clearly to avoid confusion.
Key Navigation Practices
Maintaining safe speeds, adhering to marked channels, and keeping a proper lookout are vital habits for every operator. Recognizing and responding to buoys, markers, and lights helps define safe zones and directs traffic flow. Additionally, avoiding restricted areas and respecting designated swimming zones are critical to ensure everyone’s safety.
By respecting these guidelines and staying vigilant, you contribute to a secure and efficient shared waterway experience.
Navigation Basics Every Boater Should Know
Effective navigation is a cornerstone of safe and efficient travel on the water. Familiarity with essential techniques and tools ensures that you can plan routes, avoid hazards, and reach destinations with confidence. Understanding the fundamental principles of navigation is critical for smooth operation.
Charts and maps play a key role in identifying water depths, obstacles, and traffic patterns. Learning to interpret these resources accurately helps you anticipate potential risks and select the safest paths. Coupled with a compass, they provide a reliable guide even when electronic systems fail.
Another important aspect is recognizing navigation aids such as buoys, markers, and lights. These indicators communicate critical information about safe channels, shallow areas, and restricted zones. Paying attention to their positioning and color coding enhances your ability to make informed decisions while on the move.
Staying aware of your surroundings, maintaining proper speed, and following established guidelines contribute to a secure and enjoyable experience on the water. With a strong foundation in navigation skills, you can approach every journey with confidence.
Interpreting Buoys and Markers
Buoys and markers are essential tools for guiding watercraft safely through various environments. They communicate important information about navigation routes, hazards, and permissible activities in specific areas. Understanding their meanings and functions is critical for safe operation.
These aids are designed with standardized colors, shapes, and symbols to convey distinct messages. Recognizing their significance helps operators stay within safe zones, avoid shallow waters, and comply with waterway regulations. Below is a table summarizing common types and their purposes.
| Type | Description | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Red Buoys | Cylindrical shape, red color | Mark the right side of the channel when returning from open water |
| Green Buoys | Conical shape, green color | Indicate the left side of the channel when returning from open water |
| Yellow Markers | Square or triangular symbols | Highlight cautionary zones or special areas |
| White Buoys | White with orange markings | Provide warnings or designate restricted zones |
By learning to interpret these navigational aids accurately, you can better understand waterway layouts and make informed decisions to ensure a safe journey.
Weather Conditions and Boating Precautions
Understanding weather conditions is crucial for ensuring safety on the water. Changes in temperature, wind, and precipitation can significantly impact vessel stability and navigation. Being aware of potential weather hazards and taking the necessary precautions can help avoid accidents and improve your overall boating experience.
Before setting out, always check weather forecasts and be aware of the following common conditions that can affect your journey:
- Wind – Strong winds can make it difficult to control your vessel and can increase the risk of capsizing or colliding with objects.
- Storms – Sudden storms can bring heavy rain, lightning, and high waves. It’s important to seek shelter immediately if you see dark clouds or hear thunder.
- Fog – Reduced visibility from fog can make navigation challenging. Always slow down and use navigational lights to stay visible to others.
- Temperature – Cold temperatures can lead to hypothermia if you fall into the water. Dress appropriately and have emergency equipment ready in case of an emergency.
In addition to monitoring weather forecasts, consider these precautions before heading out:
- Check your vessel’s condition and ensure all safety equipment is in good working order.
- Ensure everyone on board wears a life jacket, especially in rough weather conditions.
- Have a communication device on hand, such as a marine radio or fully charged phone.
- Plan your route and keep an eye on the weather throughout your trip. If conditions worsen, be prepared to head back or seek safe harbor.
By staying informed and prepared, you can mitigate the risks posed by adverse weather conditions and enjoy a safer, more enjoyable experience on the water.
Emergency Procedures for Boating Incidents
Accidents on the water can occur unexpectedly, and it is essential to know how to react in such situations. Prompt and appropriate responses can make a significant difference in minimizing damage and ensuring the safety of everyone on board. Knowing emergency procedures and having a clear plan in place are key to handling boating incidents effectively.
In the event of an emergency, the first step is to stay calm and assess the situation. Identify the type of incident, whether it’s a collision, fire, capsize, or mechanical failure, and determine the severity. Once the problem is identified, the following actions should be taken:
- Call for Help: Use a marine radio or mobile phone to contact the nearest emergency services or the coast guard. Provide your location and a description of the incident.
- Ensure Safety: Make sure all passengers are accounted for and wearing life jackets. If anyone is injured, provide first aid if possible while waiting for help to arrive.
- Prevent Further Damage: If a fire is present, use a fire extinguisher if available. In case of a collision or grounding, check for fuel leaks and take necessary steps to prevent environmental damage.
- Prepare for Evacuation: If the vessel is sinking or unsafe, prepare to abandon ship. Have life rafts or life jackets ready and ensure everyone knows how to use them.
It’s also important to regularly practice emergency drills with everyone on board so that everyone is familiar with the proper actions in case of an incident. Familiarizing yourself with safety protocols and having the necessary equipment on hand increases your ability to handle any unforeseen emergencies efficiently.
Life Jacket Usage and Importance
Wearing a life jacket is one of the most crucial safety measures when spending time on the water. These devices are designed to keep individuals afloat in the event of an emergency, reducing the risk of drowning. Regardless of swimming ability, life jackets provide an essential layer of protection that can save lives.
Why Life Jackets Are Essential
Life jackets serve as a safeguard in various situations, especially when unexpected events like capsizing, sudden falls, or exhaustion occur. They help maintain buoyancy, ensuring that individuals remain afloat until rescue efforts can be made or they reach safety.
- Prevents Drowning: The primary function of a life jacket is to prevent drowning by providing buoyancy and keeping the head above water.
- Supports Safety During Emergencies: In case of accidents, life jackets offer vital support, giving individuals a chance to survive until help arrives.
- Promotes Visibility: Many life jackets are brightly colored, making it easier for rescuers to spot individuals in distress.
How to Use Life Jackets Correctly
Simply wearing a life jacket is not enough. It is important to ensure it fits properly and is worn correctly to maximize its effectiveness. Here are some key guidelines:
- Proper Fit: Ensure the life jacket fits snugly but comfortably. It should not be too tight or too loose. Check that the straps are secure and that the jacket does not ride up when you are in the water.
- Wear at All Times: Always wear a life jacket while on the water, even if you are in a stationary vessel or a calm area. Accidents can happen unexpectedly.
- Check Condition: Regularly inspect life jackets for signs of wear and tear, such as rips, broken straps, or deflation in inflatable models.
By understanding the importance of life jackets and using them correctly, you can significantly enhance your safety and ensure a more secure experience while navigating the waters.
Legal Requirements for Operating a Boat
Operating a vessel requires knowledge of specific legal guidelines designed to ensure the safety of all individuals on the water. These rules can vary depending on the region, type of watercraft, and the purpose of the activity. Understanding these regulations is essential to avoid penalties and ensure safe navigation.
Before taking a vessel out on the water, certain legal conditions must be met. These may include licensing, registration, and compliance with safety regulations. Below are some key legal requirements to be aware of:
| Requirement | Description |
|---|---|
| Operator Certification | Many regions require boat operators to complete a boating safety course and obtain a certification before operating certain types of vessels. |
| Vessel Registration | Most boats need to be registered with the local government or maritime authority. This provides identification for the vessel and is often required to operate legally. |
| Minimum Age Requirements | Operators must meet a minimum age requirement, which varies by jurisdiction and type of boat being used. |
| Safety Equipment | All vessels must carry essential safety equipment, including life jackets, fire extinguishers, and sound signaling devices, based on the size and type of the boat. |
| Alcohol Laws | Similar to operating a motor vehicle, consuming alcohol while operating a vessel is regulated. Operators may face legal consequences for operating under the influence. |
Familiarizing yourself with these regulations helps ensure responsible and legal operation. Always check local laws for any updates or specific requirements that may apply to your particular situation.
Environmental Practices for Responsible Boating
Ensuring the protection of natural water environments is a crucial responsibility for anyone using vessels. By adopting eco-friendly habits, individuals can reduce their impact on aquatic ecosystems and maintain the health of waterways. Responsible practices help preserve aquatic life, prevent pollution, and protect the beauty of the environment.
There are several essential actions that can be taken to promote environmental sustainability while on the water:
- Minimize Waste: Dispose of all waste properly, including trash, oil, and fuel. Never throw waste into the water to avoid contamination of the aquatic ecosystem.
- Fuel Management: Always ensure that fuel is handled carefully to prevent spills. Use spill-proof containers and refuel at designated areas to avoid leakage into the water.
- Wildlife Awareness: Keep a safe distance from wildlife and avoid disturbing their natural habitats. Follow established guidelines to protect birds, fish, and other creatures.
- Use of Non-toxic Materials: When cleaning or maintaining your vessel, opt for environmentally safe products that will not harm the water or its inhabitants.
- Maintain Your Vessel: Regularly inspect and maintain your boat to ensure it operates efficiently and reduces emissions. A well-maintained vessel is less likely to pollute the environment.
By following these practices, individuals can contribute to preserving the health of waterways for future generations while enjoying their time on the water. Each responsible decision helps reduce the negative impact on marine and freshwater environments.
Signals and Communications on the Water

Effective communication on the water is essential for ensuring safety and coordinating activities between vessels. Whether it’s signaling for assistance or indicating navigation intentions, clear and understood signals play a critical role in preventing accidents and promoting smooth movement on the water.
Various signaling systems are used to convey messages, including visual, auditory, and radio-based methods. Each method has specific rules that should be followed for proper communication.
Visual Signals
Visual signals are one of the most common methods for conveying information between vessels. These signals include flags, lights, and hand gestures. They are essential for alerting nearby vessels about your intentions or any emergency situation.
| Signal | Meaning |
|---|---|
| Daytime flag (Red) | Indicates distress or emergency situation |
| Flashing white light | Signals a request for assistance |
| Hand wave | Indicates a greeting or desire to communicate |
Auditory Signals

Auditory signals, typically made using a horn or whistle, are crucial for alerting nearby vessels or signaling intentions such as turning or stopping. The length and frequency of sound vary depending on the situation. These signals are particularly important in low visibility conditions, such as fog or night travel.
- One short blast: Indicates a vessel is altering course to port.
- Two short blasts: Indicates a vessel is altering course to starboard.
- Five short blasts: Used to signal danger or confusion.
By understanding and using these signals correctly, individuals can contribute to safer and more coordinated operations on the water, ensuring both their own safety and that of others around them.
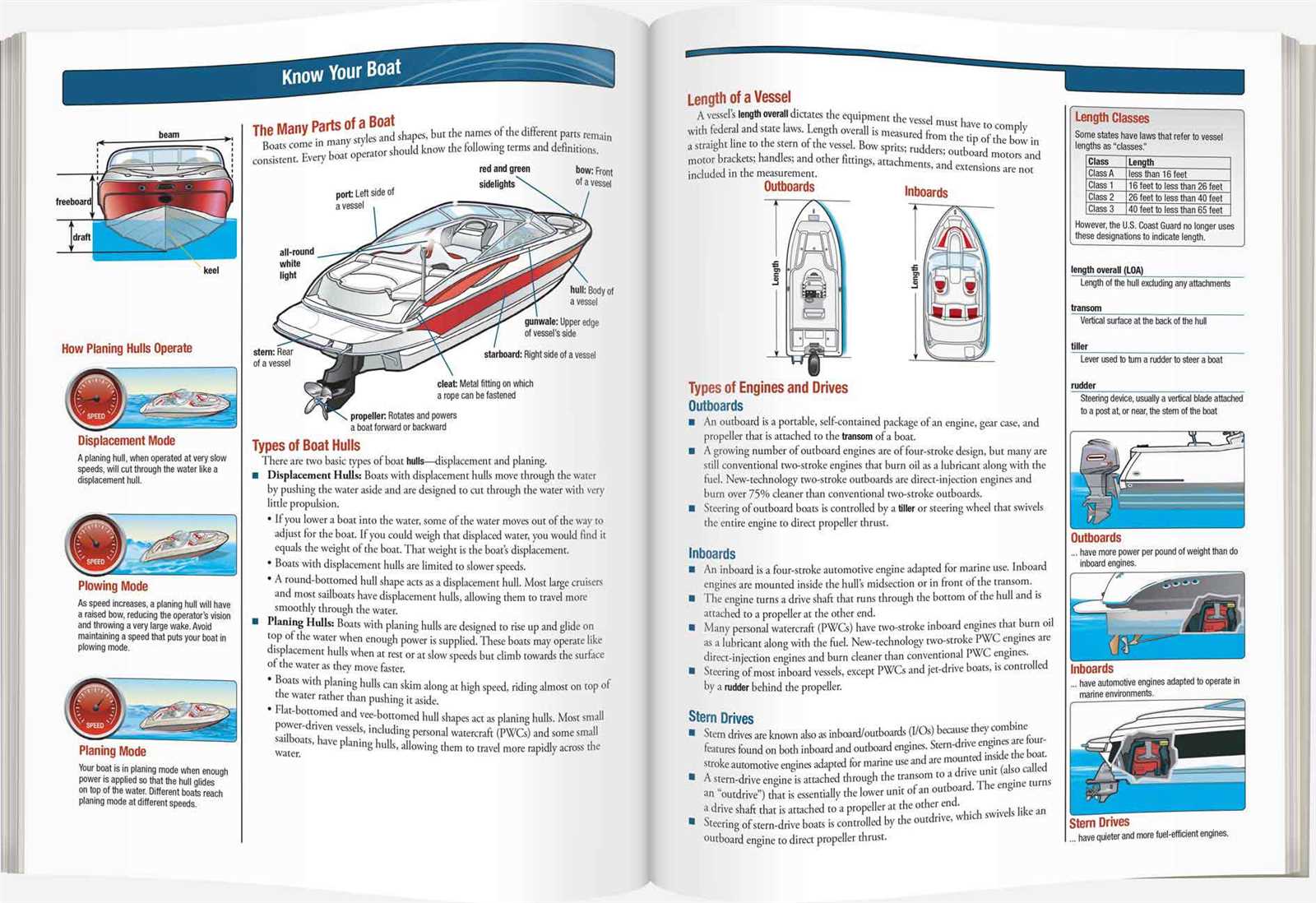
Understanding Hull Types and Designs
The shape and structure of a vessel’s hull significantly impact its performance, stability, and suitability for various water activities. Different hull designs are engineered to cater to specific needs, whether for speed, load-bearing capacity, or stability in rough waters. Understanding the features of each type can help individuals make informed choices about the vessel that best suits their intended use.
Common Hull Types
There are several distinct hull designs, each offering advantages in specific conditions. Some hulls are better suited for calm, protected waters, while others are built for open, turbulent seas. Below are a few of the most common hull types:
- Displacement Hull: Designed for slower speeds, this type pushes through the water, creating a wake. It is ideal for larger boats used for long-distance travel or carrying heavy loads.
- Planing Hull: This hull lifts out of the water at higher speeds, allowing for quicker movement across the surface. It is commonly found in performance and recreational vessels.
- Catamaran Hull: Featuring two parallel hulls, this design offers stability and is efficient at high speeds. It is often used in both leisure and commercial crafts.
Hull Design Features
In addition to hull types, the design elements also play a crucial role in determining how the vessel performs on water. Key design features include:
- V-Shaped Hull: This type cuts through waves effectively, offering a smooth ride in rough waters. It is commonly used in offshore boats and larger vessels.
- Flat Bottom Hull: Ideal for calm waters, this design offers stability and a shallow draft, making it perfect for lakes and rivers.
- Chine: The angle where the hull sides meet the bottom of the vessel can affect performance. A sharp chine offers better handling at higher speeds, while a rounded chine provides greater stability at lower speeds.
By understanding hull types and design features, individuals can select the most suitable vessel for their needs, whether it’s for recreational purposes, commercial use, or navigation in varying water conditions.
Preventing Collisions with Other Vessels

Maintaining safety on the water requires awareness of other vessels and an understanding of how to avoid collisions. Navigating busy waterways, whether in ports or open waters, demands careful attention, adherence to regulations, and proper handling of the vessel. Proactively taking steps to avoid accidents can prevent costly damages and ensure everyone’s safety.
Key Prevention Strategies

Following a few important guidelines can significantly reduce the risk of a collision:
- Keep a Safe Distance: Always maintain an appropriate distance from other vessels to allow for safe maneuvering. The closer the vessels, the less time there is to react to unexpected changes.
- Observe Right of Way Rules: Knowing who has the right of way helps prevent confusion and ensures safe passage. Always yield to vessels that have priority according to the navigation rules.
- Use Proper Signaling: Communicate intentions clearly with sound signals or visual markers. This helps other vessels anticipate your movements and take necessary precautions.
- Maintain a Proper Speed: Operating at safe speeds gives more time to react to sudden obstacles or the movements of nearby vessels. Adhere to speed limits, especially in congested areas.
Common Collision Avoidance Techniques

When you encounter other vessels, understanding specific maneuvers to avoid collisions can make a big difference:
- Adjust Speed: Reducing speed is often the best way to prevent an accident, especially when navigating near other boats or in crowded areas.
- Alter Course: If a collision seems imminent, changing course is a quick way to create space between vessels. However, the maneuver should be done in a way that doesn’t confuse or endanger others.
- Signal Intentions Early: Always signal any course change well in advance to give other vessels enough time to react. Use horn signals or other recognized markers as needed.
- Use Radar and GPS: Modern technology can assist in detecting nearby vessels, particularly in low-visibility conditions. Ensure that radar and navigation systems are used effectively.
By practicing these techniques and staying vigilant, you can ensure safer operations and reduce the likelihood of accidents on the water.
Handling Fuel and Fire Safety
Proper management of fuel and fire hazards is essential to ensuring the safety of any watercraft operation. The risk of fire can arise from improper fuel handling or malfunctioning equipment. Understanding safety protocols and having the correct procedures in place can prevent disasters and help manage emergencies effectively.
Safe Fuel Handling Practices
Fuel is highly flammable, making its handling a critical part of safe watercraft operations. Follow these guidelines to minimize the risk:
- Always Refuel in Well-Ventilated Areas: Avoid fueling in enclosed spaces. Proper ventilation helps to disperse any fumes, preventing potential ignition sources from causing a fire.
- Use Proper Fueling Equipment: Always use fuel lines, nozzles, and containers that are in good condition and designed for the type of fuel you are using. This reduces the chance of spills or leaks.
- Turn Off Engines and Electrical Systems: Never fuel your vessel with the engine running. Make sure all electrical devices, including lights and radios, are turned off to prevent sparks.
- Check for Leaks Regularly: Before and after fueling, inspect the fuel lines, tanks, and other related equipment for any signs of leaks or damage. Immediate repairs should be made to avoid fire hazards.
Fire Prevention and Response
Preventing a fire is always better than having to manage one. Here are some key measures to reduce fire risks:
- Install Fire Extinguishers: Ensure your vessel is equipped with a suitable fire extinguisher for the type of fire that could occur. Keep it easily accessible and check it regularly to ensure it’s in working order.
- Keep Flammable Materials Secure: Store fuel, lubricants, and other flammable materials in designated, secure containers away from heat sources.
- Have an Emergency Response Plan: Familiarize yourself with emergency fire procedures, including how to use the fire extinguisher and how to safely evacuate if necessary. Quick action can save lives and prevent widespread damage.
- Install Fire and Gas Detectors: Consider installing detectors that can sense fire or gas leaks. These devices can alert you early to dangers, allowing for quicker action.
By following these safety practices, you reduce the risks associated with fuel and fire hazards, creating a safer environment for everyone on board.
Anchoring Techniques for Stability
Properly securing a vessel is essential for maintaining its stability and ensuring it remains stationary in varying water conditions. The right anchoring technique can help prevent drifting, protect the vessel from rough weather, and ensure safety for everyone on board. Understanding the different methods of anchoring and knowing when to use them is crucial for a successful experience on the water.
There are several anchoring techniques that can be employed depending on the specific conditions and needs. The main goal is to achieve a secure hold to prevent unnecessary movement while also maintaining comfort and safety.
- Proper Anchor Selection: Choose an anchor that suits the size and type of the vessel as well as the nature of the seabed. A lightweight anchor is better for calm conditions, while a heavy-duty one is needed for rocky or sandy bottoms.
- Correct Placement: Always anchor in calm, sheltered areas. When dropping the anchor, aim to ensure it lands on solid ground and sinks properly to grip the seabed.
- Anchor Scope: The scope refers to the ratio of the length of the anchor line to the depth of the water. A longer scope offers better holding power. A ratio of 5:1 is typically recommended in calm conditions, and a 7:1 ratio in rougher waters.
- Using Multiple Anchors: In challenging conditions, or when wanting additional stability, consider deploying two anchors. This technique is known as “doubling up,” where one anchor is placed at the bow and another at the stern to prevent drifting in multiple directions.
- Checking the Hold: After anchoring, assess the vessel’s position regularly to ensure it remains steady. If movement occurs, the anchor may need to be reset or repositioned.
By mastering anchoring techniques, vessel operators can ensure better control and stability, regardless of the conditions encountered. Properly anchoring a vessel is an essential skill that enhances both safety and overall boating enjoyment.
Basic Maintenance for Your Vessel
Regular upkeep is essential for ensuring the longevity, safety, and performance of your watercraft. Simple maintenance tasks can help identify potential issues early, improve the vessel’s functionality, and prevent costly repairs in the future. A well-maintained vessel operates more efficiently and remains safer for those on board.
Basic maintenance should be done regularly to avoid problems that may arise from neglect. This includes tasks related to the engine, exterior, and onboard systems that help keep everything running smoothly.
- Engine Care: Regularly inspect the engine for any signs of wear or damage. Change the oil and replace the fuel filters as recommended by the manufacturer. Ensure the cooling system is functioning properly, and check for leaks or signs of corrosion.
- Battery Maintenance: Inspect the battery for corrosion or leaks. Clean the terminals and ensure the battery is charged and secure. If the vessel is not used regularly, disconnect the battery to prevent discharge.
- Hull Inspection: Examine the hull for cracks, chips, or signs of damage. Clean the bottom of the vessel and remove any growth, such as algae or barnacles, which can affect performance. Apply anti-fouling paint if necessary.
- Deck and Interior Upkeep: Regularly clean the deck and the interior of the vessel. Check all safety equipment, such as life jackets and fire extinguishers, to ensure they are in good condition and accessible.
- Cleaning and Waxing: Regularly wash and wax the exterior to protect the finish and reduce the build-up of dirt and grime. This also helps prevent UV damage and corrosion from saltwater exposure.
- Inspecting the Propeller: Periodically check the propeller for any damage or debris. Ensure that it is securely attached and functioning properly to avoid performance issues.
By staying on top of these basic maintenance tasks, you can ensure that your vessel remains in good working condition, operates efficiently, and is ready for the water at all times. Regular maintenance not only extends the life of the vessel but also enhances the overall boating experience.
Frequently Asked Questions About Boating Exams
When it comes to operating a watercraft, there are important skills and knowledge that must be mastered. Many individuals looking to gain proficiency in boating often have questions about the requirements and process for certification or testing. Below are some commonly asked questions that can help clarify common doubts and provide useful insights for those preparing to take the required assessments.
What is the purpose of boating certification?

Boating certification ensures that individuals understand key safety protocols, navigational rules, and emergency procedures. It aims to create a safer environment on the water, reducing the risks associated with operating a vessel. Having this certification also helps the operator navigate legal requirements and improves overall boating experience.
How do I prepare for the test?

Preparation for a boating test typically involves studying materials that cover essential topics, such as vessel operation, safety regulations, weather conditions, and navigation. Many resources, including online courses and practice quizzes, are available to help learners familiarize themselves with the required knowledge. Hands-on practice and familiarity with the boat itself are also important components of preparation.
Is there an age requirement to take the test?
The age requirement varies depending on local regulations. In many areas, individuals must be a certain age before they can take the certification exam, usually ranging from 12 to 16 years old. However, younger individuals may be able to operate a vessel under certain supervision or conditions.
Are there any fees associated with the certification?
Yes, there are often fees associated with both the coursework and the certification exam. These fees cover the costs of materials, administration, and sometimes the examination process itself. The amount can vary depending on the location and the type of certification being obtained.
How long does the certification last?
The validity of boating certification typically ranges from 3 to 10 years, depending on the governing body. After this period, renewal may be required, which could involve a brief refresher course or re-assessment to ensure that the operator’s knowledge is up-to-date.
By answering these common questions, individuals can better prepare themselves for the necessary assessments, making the process clearer and more manageable. Understanding the requirements and preparation needed for certification helps ensure a successful and safe experience on the water.