
When it comes to mastering complex biological systems, thorough preparation is essential for success. Understanding the intricacies of human anatomy and physiology requires more than memorization–it involves connecting concepts, visualizing processes, and applying knowledge in practical scenarios. This section will guide you through the essential topics and strategies needed to perform well in your upcoming evaluation.
Building a solid foundation starts with reviewing core principles and focusing on the most commonly tested areas. Whether you’re studying the nervous, muscular, or cardiovascular systems, each chapter contributes to a broader understanding of how the human body functions. Strengthening your grasp of these systems will not only help with exam questions but also enhance your overall comprehension.
Effective study techniques, coupled with a focused review of key content, will enable you to approach the assessment with confidence. Keep in mind that success lies in applying knowledge to real-world scenarios, reinforcing your understanding through practice, and avoiding common pitfalls. Use these insights to sharpen your preparation and increase your chances of achieving a top score.
A&P 2 Final Exam Answers
To succeed in your upcoming assessment, it’s crucial to have a clear understanding of key topics and how they interconnect. Mastery of the human body’s systems is not just about recalling information but also about applying it in various contexts. This section provides valuable insights into the most essential areas you need to focus on, ensuring you are fully prepared.
Critical systems such as the nervous, cardiovascular, and musculoskeletal systems are often central to the test. Familiarizing yourself with their functions, interactions, and structures will allow you to answer a variety of questions with ease. Focus on understanding the mechanisms behind these systems, as this deeper understanding will make it easier to recall relevant details under time constraints.
In addition to content knowledge, test-taking strategies play an important role in achieving success. Knowing how to approach different types of questions, from multiple-choice to short-answer, can significantly impact your performance. Practice with previous questions and review materials to identify areas where you need further study, ensuring you are well-rounded in your preparation.
Key Concepts for A&P 2 Final Exam
Understanding the core principles of human biology is essential for success in your upcoming assessment. Focusing on critical systems and their functions will give you the foundation needed to tackle a range of questions. This section highlights the most important topics, helping you prioritize areas for study and strengthen your knowledge.
The nervous system plays a central role in regulating bodily functions and responding to environmental changes. Understanding its structure, including neurons and synaptic transmission, is crucial for answering related questions. Similarly, a deep dive into the musculoskeletal system will enable you to explain how muscles and bones interact to support movement.
Another key area is the cardiovascular system, which involves the heart and blood vessels in maintaining circulation and oxygen delivery. Reviewing how blood flow is regulated and how various factors influence cardiovascular health will be essential. Additionally, grasping the digestive and respiratory systems is vital for understanding how the body processes nutrients and exchanges gases, respectively.
Understanding the Nervous System for Exams
The nervous system is one of the most complex and essential systems in the human body. It coordinates various functions, from basic reflexes to complex behaviors. A strong understanding of how the nervous system works is critical for answering questions related to its structure, function, and disorders. This section explores the key aspects that are often tested, with a focus on neural pathways, signaling, and system interactions.
Key Components of the Nervous System
The nervous system can be divided into two main parts: the central nervous system (CNS) and the peripheral nervous system (PNS). The CNS consists of the brain and spinal cord, while the PNS includes all other neural elements. Understanding how these components work together to transmit signals throughout the body is crucial for success.
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Central Nervous System | Processes and interprets information from the body, controls complex functions. |
| Peripheral Nervous System | Transmits sensory and motor information between the CNS and body. |
Neural Signaling and Pathways
Neural signaling relies on electrical impulses that travel along neurons. These signals are transmitted across synapses with the help of neurotransmitters. Key topics to focus on include action potentials, synaptic transmission, and the role of different neurotransmitters in regulating bodily functions.
Important Musculoskeletal System Topics
The musculoskeletal system is fundamental for movement, providing structure and support to the body. It encompasses bones, muscles, tendons, and ligaments, all working in harmony to allow for locomotion and stability. Understanding the key components and their interactions is essential for mastering this topic and performing well in assessments.
Key areas to focus on include bone structure and function, which covers the types of bones, their role in protecting organs, and their involvement in mineral storage. Additionally, understanding muscle anatomy and contraction is vital, as it explains how muscles generate force and facilitate movement through contraction mechanisms like the sliding filament theory.
Another critical aspect is the joint function, which explores how bones are connected and how movements are facilitated by synovial fluid and cartilage. Reviewing common joint disorders and their impact on movement will also help provide a comprehensive understanding of this system.
Digestive System Review for A&P 2
The digestive system plays a vital role in processing nutrients and eliminating waste, providing the body with the energy it needs to function. It involves a complex series of organs and processes that work together to break down food, absorb essential nutrients, and remove indigestible components. A thorough understanding of this system is crucial for mastering its key functions and mechanisms.
Important topics to focus on include the structure and function of the gastrointestinal tract, which includes organs such as the stomach, small intestine, and large intestine. Understanding how food moves through these areas and is broken down into nutrients is central to understanding digestion. Additionally, the role of accessory organs like the liver, pancreas, and gallbladder in secreting digestive enzymes and bile is critical for the complete digestion process.
Another key area is the process of nutrient absorption, particularly in the small intestine. Here, nutrients from digested food are absorbed into the bloodstream, supporting the body’s energy and metabolic needs. Focusing on the mechanisms of nutrient transport and absorption will help solidify your grasp of this essential process.
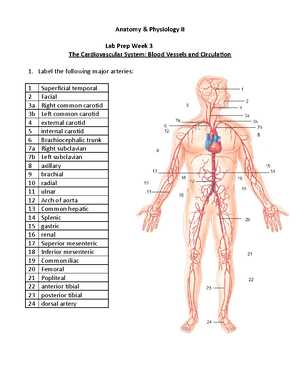
Cardiovascular System Key Points
The cardiovascular system is crucial for maintaining the flow of blood, which transports oxygen, nutrients, and waste products throughout the body. Understanding its structure and function is vital for any comprehensive study of human biology. This section highlights the essential components and processes involved in the cardiovascular system.
Major Components of the Cardiovascular System
The cardiovascular system consists of the heart, blood vessels, and blood. These elements work together to ensure proper circulation and metabolic function. Key areas to focus on include:
- The Heart: A muscular organ responsible for pumping blood throughout the body.
- Blood Vessels: Arteries, veins, and capillaries that transport blood to and from various body parts.
- Blood: The fluid that carries oxygen, nutrients, and waste products between organs and tissues.
Circulation and Blood Flow
Understanding how blood circulates through the body is essential. The heart pumps blood through two primary circulatory routes:
- Pulmonary Circulation: Transports deoxygenated blood from the heart to the lungs and returns oxygenated blood to the heart.
- Systemic Circulation: Delivers oxygenated blood from the heart to the rest of the body and returns deoxygenated blood back to the heart.
Focusing on the functioning of each circulation route and the role of the heart valves in maintaining unidirectional blood flow will help solidify your understanding of cardiovascular processes.
Respiratory System Essentials for the Exam
The respiratory system is essential for gas exchange, delivering oxygen to the bloodstream and removing carbon dioxide. Understanding its structure, processes, and function is vital for any test that covers human physiology. This section provides an overview of the most important components and concepts related to respiration.
Key Components of the Respiratory System
The respiratory system includes several key structures that work together to facilitate breathing and gas exchange. These components are:
- Nasal Cavity: The passage where air is filtered, moistened, and warmed before entering the lungs.
- Trachea and Bronchi: Airways that carry air into the lungs, dividing into smaller bronchioles for further distribution.
- Lungs: The organs responsible for exchanging gases through tiny air sacs called alveoli.
- Diaphragm: The primary muscle involved in breathing, expanding and contracting the chest cavity.
Mechanism of Breathing
Breathing involves two main processes: inhalation and exhalation. During inhalation, the diaphragm contracts, and air is drawn into the lungs. During exhalation, the diaphragm relaxes, pushing air out of the lungs. Understanding how these movements correlate with pressure changes in the thoracic cavity is essential for understanding the mechanics of breathing.
Renal System and Its Role in A&P
The renal system plays a crucial role in maintaining the body’s internal balance by regulating fluid and electrolyte levels, filtering waste, and ensuring proper waste elimination. Its primary organs, the kidneys, work together to carry out these essential functions. Understanding the structure and processes of the renal system is key for grasping how the body maintains homeostasis.
Key Functions of the Renal System
The renal system carries out several vital functions that contribute to overall health. These include:
- Filtration of Blood: The kidneys filter waste products, toxins, and excess substances from the bloodstream.
- Regulation of Fluid Balance: The kidneys help maintain the body’s water and electrolyte levels by adjusting the volume of urine produced.
- Acid-Base Balance: The kidneys help maintain a stable pH level in the body by excreting hydrogen ions and reabsorbing bicarbonate.
- Excretion of Waste: The renal system eliminates metabolic waste, such as urea, from the body through urine.
Kidney Structure and Function

The kidneys are made up of millions of functional units called nephrons, which filter blood and produce urine. Each nephron consists of a glomerulus, where blood is filtered, and a renal tubule, where necessary substances are reabsorbed, and waste is secreted. Understanding the roles of these structures in filtration and reabsorption is crucial for a comprehensive understanding of the renal system.
Endocrine System Overview for A&P 2
The endocrine system plays a pivotal role in regulating various bodily functions through the secretion of hormones. These chemical messengers help control processes such as metabolism, growth, reproduction, and stress responses. By understanding the key glands, hormones, and feedback mechanisms involved, you can gain insight into how the body maintains homeostasis and responds to internal and external stimuli.
The primary components of the endocrine system include several glands that secrete hormones into the bloodstream. These hormones are responsible for coordinating activities in different organs and tissues. Key glands include the pituitary gland, thyroid, adrenal glands, and pancreas, each producing specific hormones that target different areas of the body.
In addition to the hormones themselves, it’s important to understand how negative and positive feedback loops regulate hormone levels. These feedback mechanisms ensure that hormone production remains balanced, preventing overproduction or deficiency that could disrupt bodily functions.
Study Tips for A&P 2 Final Exam
Preparing for an advanced course assessment requires focused effort and effective study strategies. The material covered in this subject is broad and complex, so having a structured approach is essential for mastering key concepts and performing well. In this section, we will explore some of the best study techniques to help you succeed.
One of the most effective methods is active learning, which involves engaging with the material rather than passively reading or memorizing. Try summarizing what you’ve learned in your own words, teaching the material to others, or creating mind maps to visualize complex systems and processes. This active involvement will reinforce your understanding and improve retention.
Another useful technique is spaced repetition. Instead of cramming all the information in one sitting, break down your study sessions over a period of time. Revisiting topics periodically helps strengthen memory and reduces stress as the assessment approaches.
Commonly Tested A&P 2 Terms
In any advanced human biology course, there are several terms and concepts that frequently appear on assessments. These terms represent fundamental processes, structures, and systems that are essential to understanding how the body functions. Familiarity with these terms will help you prepare effectively and ensure a comprehensive grasp of the subject matter.
Key Anatomical and Physiological Terms
Below is a list of commonly tested terms that you should be familiar with. These terms cover a range of biological systems and physiological processes:
| Term | Description |
|---|---|
| Homeostasis | The body’s ability to maintain a stable internal environment despite external changes. |
| Metabolism | The chemical reactions that occur within the body to maintain life, including energy production and utilization. |
| Endocrine System | The system responsible for hormone production and regulation of body functions like growth and metabolism. |
| Neurotransmitters | Chemical messengers that transmit signals across synapses in the nervous system. |
| Circulatory System | The system that transports oxygen, nutrients, and waste products throughout the body via the heart and blood vessels. |
Physiological Processes to Know
In addition to the key terms, understanding the physiological processes that these terms represent is crucial. These include:
- Cellular Respiration: The process by which cells produce energy from glucose and oxygen.
- Neurotransmission: The process by which nerve cells communicate with each other using chemical signals.
- Muscle Contraction: The physiological process by which muscles generate force to produce movement.
Physiology vs Anatomy in the Final Exam

Understanding the distinction between structure and function is crucial when preparing for assessments in advanced biology. While both anatomy and physiology are interrelated, they focus on different aspects of the body. Anatomy deals with the physical structures of the body and their relationships to each other, while physiology focuses on how these structures work and interact to maintain the body’s overall function. Grasping these concepts will help you approach the material with a clearer perspective and improve your ability to answer complex questions.
Key Differences Between Anatomy and Physiology
In order to succeed, it’s important to recognize the specific areas each field covers:
- Anatomy: Focuses on the physical structure and organization of the body, including organs, tissues, and cells.
- Physiology: Studies the mechanisms and processes by which the body functions, such as metabolism, circulation, and nervous system activity.
Approaching Questions Related to Anatomy and Physiology
When preparing for your assessment, try to approach questions with a dual focus: first, identify the anatomical structure or system involved, and then understand how that structure contributes to a specific physiological process. For example, understanding how the heart’s anatomy supports its role in circulation (physiology) can help you answer both structure and function questions.
Effective Review Methods for A&P 2

When preparing for advanced assessments in biology, reviewing the material efficiently is crucial for success. Given the vast amount of content covered, it’s essential to utilize strategies that allow for active engagement with the material, improving retention and understanding. In this section, we will explore methods that will help you effectively review key concepts and reinforce your knowledge.
Active Recall and Spaced Repetition
Active recall is one of the most effective study techniques. It involves testing yourself on the material rather than simply re-reading notes. By recalling information without the aid of reference materials, you strengthen your memory and improve your ability to retrieve information under pressure. Combine this technique with spaced repetition, which involves revisiting the material at increasing intervals over time. This method helps reinforce learning and minimizes the chances of forgetting important concepts.
Visual Aids and Study Groups
Incorporating visual aids such as diagrams, charts, and flashcards can significantly enhance your understanding, particularly for complex systems or processes. Many students find that creating their own visuals, such as mind maps or flow charts, helps them better grasp relationships between different concepts. Additionally, studying with peers in a group setting can provide different perspectives and help clarify confusing topics. Group discussions encourage active participation, which further solidifies understanding and memory.
Common Mistakes in A&P 2 Finals
When preparing for assessments in advanced biology, it’s easy to overlook certain details or make common errors that can affect your performance. These mistakes often stem from misunderstandings or failure to grasp key concepts, which can lead to avoidable errors during the test. In this section, we will highlight some of the most frequent pitfalls students encounter and provide tips on how to avoid them.
Overlooking Key Concepts
One of the most common mistakes is failing to focus on fundamental concepts, which can have a ripple effect on more complex topics. It’s easy to get lost in the details, but a strong understanding of basic principles is crucial for tackling more challenging questions.
- Neglecting to understand core systems (e.g., circulatory, digestive, nervous systems) can lead to confusion when faced with related questions.
- Ignoring the interconnections between structures and functions may cause errors when explaining physiological processes.
Misinterpreting Questions
Another frequent issue is misunderstanding the wording of the questions. This can result in providing the wrong answer, even if the student knows the correct material. Here are a few common mistakes:
- Misreading questions that ask for “functions” versus “structures.” Confusing these can lead to answers that don’t fully address the question.
- Failing to recognize terms that require detailed explanation versus a simple answer. For example, “Describe” versus “List” can change the depth of your response.
To minimize these mistakes, always read each question carefully and make sure you understand what is being asked before answering.
How to Prepare for Multiple Choice Questions
Multiple choice questions can often feel like a guessing game, but with the right preparation, they can become one of the most manageable parts of any assessment. The key to success lies in understanding the material deeply and practicing strategies that can help you confidently navigate through the options. In this section, we’ll provide effective tips to help you prepare for multiple choice questions and improve your chances of selecting the correct answer.
Master the Material
Before you even think about practicing questions, ensure that you have a thorough understanding of the material. Here’s how you can strengthen your knowledge:
- Review key concepts, terms, and processes regularly to reinforce your understanding.
- Focus on areas that have historically been difficult or unclear.
- Create flashcards to test yourself on definitions and important facts.
Strategies for Answering
Once you’re confident in your knowledge, it’s time to focus on strategies for answering multiple choice questions effectively:
- Eliminate Incorrect Options: Often, one or more choices are obviously wrong. Eliminate them to narrow down your options.
- Look for Keywords: Pay close attention to words like “always,” “never,” or “most likely,” as they often signal extreme answers.
- Read All Choices: Even if the first answer seems correct, read through all the options to ensure you’re not missing something better.
- Guessing with Confidence: If you’re unsure, try to make an educated guess based on your knowledge of the subject.
By mastering both the material and the strategies for answering, you can approach multiple choice questions with confidence and improve your performance significantly.
Practical Applications in A&P 2 Final Exam
Understanding the theoretical aspects of human biology is essential, but being able to apply that knowledge in real-world situations is just as important. In this section, we’ll explore how key physiological and anatomical concepts are applied in practical settings, helping you bridge the gap between theory and practice. These applications can be particularly helpful in answering questions that require more than just memorization.
Real-World Relevance of Physiology and Anatomy
Many of the concepts you study have direct applications in healthcare, medicine, and even everyday life. Here are some examples:
- Understanding the Circulatory System: Knowledge of blood flow, heart function, and the circulatory system is crucial for diagnosing and treating cardiovascular conditions.
- Respiratory Mechanics: The principles of gas exchange and lung function are applied in treating respiratory diseases and monitoring oxygen levels in patients.
- Musculoskeletal Health: A deep understanding of muscles, bones, and joints is critical for physical therapy, rehabilitation, and preventing injuries.
Applying Knowledge in Clinical Settings
In clinical practice, the ability to identify symptoms, understand underlying causes, and apply solutions is paramount. Here’s how to think about application in practical settings:
- Diagnostic Procedures: An understanding of anatomy and physiology helps healthcare professionals conduct physical exams, interpret lab results, and make informed decisions about patient care.
- Treatment and Therapy: Whether prescribing medication or designing physical therapy plans, understanding how the body responds to various treatments is essential.
- Prevention and Education: Educating patients on healthy lifestyle choices, disease prevention, and proper body mechanics requires knowledge of the body’s systems and their interactions.
By recognizing how theoretical knowledge connects to practical applications, you will not only enhance your test performance but also better appreciate the real-world impact of your studies.