
Preparing for assessments requires a clear understanding of the subject matter and the ability to apply knowledge effectively. Gaining insights into critical topics and honing problem-solving skills are essential steps to achieving top results. This guide aims to simplify complex ideas and offer practical tips to enhance your performance.
Understanding foundational ideas is crucial for building confidence in tackling challenging questions. By breaking down theoretical principles into manageable sections, learners can develop a deeper appreciation of their relevance and application.
Additionally, focusing on strategic learning techniques can significantly improve retention and recall. Time management, active participation in discussions, and consistent practice are just a few methods to ensure steady progress and better outcomes.
Understanding Core Concepts in Economics
Grasping the foundational ideas within this field involves breaking down theoretical frameworks and exploring how they relate to real-world situations. A clear comprehension of key principles allows for a better understanding of how various elements interact within larger systems. This section provides a straightforward approach to interpreting essential themes and their practical implications.
Key Theories and Their Applications
Familiarizing yourself with the primary theories enables a deeper understanding of their significance. By examining how abstract principles manifest in practical scenarios, you can identify patterns and make informed predictions. Analyzing specific case studies is an effective method to connect ideas with real-life outcomes.
Building Analytical Skills
Developing critical thinking is essential for interpreting data and identifying trends. Through structured analysis and problem-solving, learners can enhance their ability to assess complex scenarios. Practicing these skills consistently fosters a more intuitive grasp of intricate topics and prepares individuals to tackle challenging questions confidently.
Preparing Effectively for Your Exam
Achieving success in assessments requires thorough preparation and a structured approach to studying. By focusing on essential topics and refining problem-solving techniques, you can enhance your ability to address various challenges confidently. This section provides practical advice to streamline your preparation process.
Organizing Your Study Schedule
Time management is a crucial factor in efficient preparation. Begin by creating a detailed plan that allocates sufficient time to each subject area. Prioritize complex concepts while ensuring regular review of previously studied material. A balanced schedule helps maintain focus and prevents last-minute cramming.
Utilizing Resources and Practice
Supplementing your study with diverse materials, such as textbooks, online tools, and past papers, enhances understanding and application. Practicing with sample questions allows you to identify areas of improvement and build confidence in your abilities. Consistent practice is key to mastering complex ideas.
Analyzing Supply and Demand Dynamics
Understanding the interaction between availability and desire for goods or services is crucial for interpreting market behavior. These factors influence pricing, production, and consumption patterns, shaping the broader framework of trade and commerce. This section explores the core principles and their implications in various scenarios.
Key Factors Influencing Availability
Several elements affect the accessibility of products, including production costs, technological advancements, and resource availability. By examining these drivers, it becomes easier to predict how changes in one area may impact the entire system. Monitoring these shifts is essential for strategic decision-making.
Impact of Consumer Behavior
Preferences, income levels, and trends all play a significant role in shaping what individuals purchase. These patterns not only influence pricing but also guide producers in adjusting their offerings. Analyzing buyer tendencies provides valuable insights into future market conditions.
| Aspect | Effect on Availability | Effect on Pricing |
|---|---|---|
| Production Costs | Higher costs reduce availability | Prices increase to cover expenses |
| Consumer Preferences | Shift demand toward preferred products | Popular items may see price rises |
| Technological Advances | Boost production efficiency | Lower prices through reduced costs |
Mastering Microeconomic Theories and Applications
Exploring how individuals and businesses make decisions about resource allocation offers valuable insights into the mechanisms driving market activities. Understanding these foundational ideas helps explain how choices impact pricing, production, and consumption on a smaller scale. This section delves into key principles and their practical uses.
Examining Decision-Making Processes
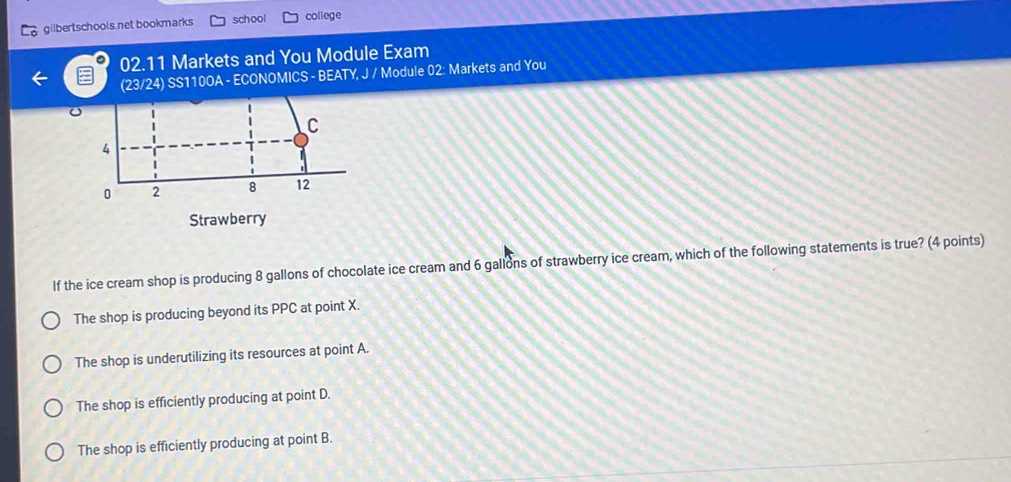
At the core of this area is the study of how participants weigh costs and benefits. Choices are often influenced by factors such as resource scarcity, available alternatives, and opportunity costs. Recognizing these elements allows for a clearer perspective on consumer and producer behavior.
Applying Theories to Real-World Scenarios
The ability to connect abstract concepts to practical situations is essential for thorough understanding. For instance, analyzing pricing strategies or production adjustments provides a tangible way to observe theoretical principles in action. Case studies and real-world examples serve as powerful tools for bridging the gap between theory and application.
Key Principles of Macroeconomics Simplified
Understanding the larger framework of financial and resource management at a national or global level provides insights into the overall functioning of markets. This area focuses on broad trends and collective outcomes rather than individual actions, offering a comprehensive view of economic systems. Simplifying these concepts helps make them accessible and applicable.
Exploring Market-Wide Interactions
Aggregate behavior, such as total production and consumption, is a cornerstone of this subject. By examining these patterns, it becomes possible to identify the factors driving growth, stability, and change. Monitoring indicators like output levels and employment rates provides a clear picture of overall performance.
The Role of Policies and External Factors
Governments and institutions play a critical role in shaping outcomes through fiscal and monetary measures. Additionally, global events, technological advancements, and trade agreements influence the balance of supply and demand. Analyzing these interactions helps predict shifts in large-scale trends and their potential impact on society.
Exam Strategies for Complex Economic Problems
Tackling intricate challenges requires a strategic approach to problem-solving, especially when dealing with complex scenarios that involve multiple variables. Developing a structured method not only improves accuracy but also enhances the ability to think critically under pressure. This section explores effective strategies to navigate such challenges successfully.
Breaking Down the Problem

Before diving into solutions, it’s essential to dissect the problem into manageable parts. Understanding each component allows for a more focused approach. Here’s how to start:
- Identify key concepts and terms.
- Analyze the relationships between variables.
- Look for any given data that will guide your approach.
Step-by-Step Solution Approach
Once the problem is broken down, it’s important to approach the solution methodically:
- Start with general principles and apply them to the specific situation.
- Make calculations where necessary and ensure accuracy at every step.
- Check for logical consistency in your solution.
- Review all assumptions and conclusions before finalizing your answer.
Common Mistakes to Avoid While Studying
Effective study habits are essential for mastering any subject, but there are several common pitfalls that can hinder progress. Being aware of these mistakes allows students to adopt better strategies and optimize their learning experience. This section outlines the key errors to avoid when preparing for complex assessments.
Rushing Through the Material

Trying to cover too much content in a short time often leads to shallow understanding and missed details. To avoid this mistake:
- Focus on mastering one concept at a time.
- Give yourself adequate time to review key points.
- Break study sessions into manageable intervals.
Neglecting Active Learning
Simply reading or passively reviewing notes is not enough to ensure deep understanding. Active engagement with the material leads to better retention and application. Here are some tips:
- Practice with exercises and examples.
- Teach concepts to someone else to reinforce your understanding.
- Ask questions and seek clarification when necessary.
Ignoring Previous Mistakes
Overlooking errors made in previous practice attempts can prevent improvement. It’s crucial to learn from these mistakes:
- Review feedback thoroughly.
- Understand why a mistake was made before moving on.
- Track progress and correct patterns of misunderstanding.
Using Data to Support Economic Analysis
Data plays a pivotal role in shaping sound analysis and drawing meaningful conclusions. By leveraging quantitative and qualitative information, one can uncover trends, validate theories, and strengthen arguments. This section emphasizes the importance of integrating data into the analytical process and how it can provide a clear and objective perspective on complex issues.
Types of Data in Analysis
When conducting in-depth analysis, various data types offer unique insights. These include:
- Qualitative data: Descriptive information that offers context and background to support analysis.
- Quantitative data: Numerical data used to establish patterns and validate hypotheses.
- Historical data: Past records and trends that provide a benchmark for future projections.
Integrating Data into Your Work
To effectively use data, it must be properly interpreted and integrated into your analysis:
- Ensure data is relevant and current to maintain accuracy.
- Use visual tools such as graphs and charts to enhance understanding.
- Consider the sources of your data to avoid biases and inaccuracies.
Exploring Global Market Trends and Impacts
Global markets are constantly evolving, influenced by a variety of factors such as technological advancements, geopolitical events, and shifts in consumer behavior. Understanding these trends is crucial for anticipating future movements and assessing their broader implications. In this section, we examine the key factors shaping global markets and the impacts they have on industries, economies, and societies at large.
Key Drivers of Global Market Trends

Several forces contribute to shaping the dynamics of global markets. These include:
- Technological innovation: Advancements in technology that drive new industries and change existing ones.
- Geopolitical events: Political decisions and international relations that can disrupt or enhance market activity.
- Consumer behavior: Shifts in preferences and spending patterns that influence demand for goods and services.
Impacts on Various Sectors
Understanding how these global market trends affect different sectors is key to adapting and thriving in a competitive environment. The effects can be seen in areas such as:
- International trade: Global supply chains and trade agreements that connect markets across borders.
- Labor markets: How job availability, skill demand, and wages are affected by global trends.
- Investment opportunities: Identifying sectors that are poised for growth or decline based on market shifts.
Practical Applications of Economic Policies
Economic policies are implemented to address real-world challenges and achieve specific goals within a society. By understanding how these policies are applied, we can assess their effectiveness in managing issues such as unemployment, inflation, and economic growth. This section explores the practical use of various economic strategies in shaping national and global outcomes.
Fiscal Policies and Government Spending
One of the most direct ways governments influence the economy is through fiscal policy, which involves adjusting government spending and taxation. These measures are designed to stimulate or slow down economic activity:
- Tax cuts: Reduce the tax burden on businesses and individuals to increase disposable income and spending.
- Public spending: Investing in infrastructure and social programs to boost demand and create jobs.
- Deficit management: Controlling national debt by adjusting spending and revenue collection strategies.
Monetary Policies and Interest Rates
Central banks utilize monetary policy to control the supply of money and influence interest rates, aiming to maintain price stability and promote sustainable growth:
- Interest rate adjustments: Raising or lowering rates to encourage or discourage borrowing and spending.
- Quantitative easing: Injecting money into the economy to stimulate activity when traditional methods are insufficient.
- Inflation control: Using monetary tools to keep inflation within a target range, stabilizing the currency.
Time Management Tips for Study Sessions
Effective time management is crucial for optimizing study sessions and achieving better results. By organizing your time wisely, you can ensure that you cover all necessary topics without feeling overwhelmed. This section offers strategies to help you manage your study time more efficiently, ensuring that each session is productive and focused.
Create a Structured Study Schedule
Planning your study sessions in advance allows you to allocate sufficient time to each subject or topic. A clear schedule helps prevent procrastination and ensures that all areas are given attention. Key strategies include:
- Set specific goals: Determine what you want to accomplish during each session, whether it’s mastering a particular concept or completing a set of practice questions.
- Break tasks into smaller segments: Instead of overwhelming yourself with long study sessions, divide your work into manageable chunks.
- Prioritize difficult topics: Tackle the most challenging subjects first, when your energy and focus are at their peak.
Minimize Distractions and Stay Focused
Staying focused is key to making the most of your study time. Distractions can severely hinder productivity, so it’s important to create a study environment that supports concentration:
- Find a quiet space: Choose a location free from distractions, such as your phone or loud environments.
- Use the Pomodoro technique: Study in short, focused intervals (e.g., 25 minutes of studying followed by a 5-minute break).
- Set clear boundaries: Inform others of your study times and avoid multitasking during your sessions.
Visualizing Economic Models with Graphs
Graphs are powerful tools for illustrating complex concepts and relationships in various fields of study. By presenting data visually, they allow for a clearer understanding of how different variables interact. In this section, we will explore how to use graphs to represent key concepts and models, enabling a more intuitive comprehension of theoretical frameworks and their practical applications.
When analyzing relationships between variables, graphs help to simplify abstract ideas and show their dynamics. For example, a simple line graph can demonstrate the relationship between supply and demand, helping to visualize how shifts in one curve affect the equilibrium price and quantity. The clarity provided by these visual aids makes it easier to analyze trends, predict outcomes, and assess the impact of different factors.
In addition to line graphs, other types of charts like bar graphs, scatter plots, and histograms can offer different perspectives on data, depending on the specific model being analyzed. Whether depicting the effects of policy changes or demonstrating market behavior, visualizing data can provide valuable insights that are often hard to grasp through numbers alone.
Improving Critical Thinking for Economic Essays
Critical thinking is essential when constructing well-argued essays that analyze complex ideas and concepts. It involves examining evidence, considering different perspectives, and formulating coherent arguments. By sharpening your critical thinking skills, you can better assess information, identify assumptions, and make informed conclusions that strengthen your writing.
One effective way to enhance critical thinking is by breaking down the argument into smaller components. This allows you to examine each point in detail and assess the validity of the evidence presented. By questioning the reliability of sources and identifying any gaps in the argument, you can refine your analysis and create a stronger, more persuasive essay.
Approaching Evidence and Sources
Evaluating sources critically is an essential part of developing a strong argument. Not all sources are equally credible, and distinguishing between reliable and unreliable information is key. Consider the following factors when assessing sources:
| Factor | Considerations |
|---|---|
| Author Expertise | Is the author qualified in the subject area? Are they a recognized authority? |
| Source Type | Is the source peer-reviewed, published in a reputable journal, or credible news outlet? |
| Evidence Support | Does the source provide empirical data or well-reasoned arguments to back up its claims? |
Evaluating Different Perspectives
Critical thinking also requires you to consider multiple viewpoints on an issue. By acknowledging counterarguments and weighing them against your position, you can demonstrate a deeper understanding of the topic. This approach not only enriches your essay but also shows your ability to think analytically and engage with differing opinions effectively.
Understanding Elasticity and Market Equilibrium
Elasticity and market equilibrium are fundamental concepts that describe how markets function and how goods and services are exchanged. Elasticity refers to the responsiveness of the quantity demanded or supplied to changes in price or income. Market equilibrium, on the other hand, is the point where the quantity demanded equals the quantity supplied, ensuring that markets are balanced.
Understanding these concepts helps to predict how changes in price or external factors like taxes or subsidies can influence market behavior. Elasticity allows us to measure the degree to which consumers and producers will react to changes, while market equilibrium shows the outcome of these reactions when demand and supply meet.
Elasticity: Key Types and Their Impact
There are various types of elasticity that offer insights into how sensitive a market is to changes in price and income:
- Price Elasticity of Demand (PED): Measures how much the quantity demanded of a good changes in response to a change in price. A high elasticity means that consumers are sensitive to price changes, while a low elasticity suggests that price changes have little effect on demand.
- Price Elasticity of Supply (PES): Examines how much the quantity supplied of a good changes when the price changes. This is crucial for understanding how quickly producers can respond to price changes.
- Income Elasticity of Demand (YED): Indicates how demand for a good changes as consumer income changes. Goods can be normal (demand increases with higher income) or inferior (demand decreases as income rises).
Market Equilibrium: Reaching Balance
Market equilibrium is reached when the quantity demanded by consumers equals the quantity supplied by producers at a particular price point. This equilibrium price ensures that there is no surplus or shortage of goods in the market.
At this point, the forces of supply and demand are balanced, and no further adjustments are needed unless external factors cause a shift. These shifts can occur due to changes in consumer preferences, production costs, or government intervention, influencing both price and quantity in the market.
Insights on Monetary and Fiscal Policies

Monetary and fiscal strategies are crucial tools used by governments and central banks to influence the overall economic environment. These policies aim to stabilize the economy, control inflation, and promote growth. While both are designed to manage economic activity, they differ in their approaches and mechanisms.
Monetary policy involves controlling the supply of money and interest rates to maintain price stability and foster economic growth. Central banks use this policy to regulate inflation, manage unemployment, and stabilize the national currency. It can be expansionary, aimed at stimulating the economy, or contractionary, aimed at controlling inflation by reducing money supply.
Fiscal policy, on the other hand, refers to government decisions on taxation and public spending. By adjusting taxes and expenditure levels, governments can influence demand within the economy. Expansionary fiscal policy typically involves increasing government spending and cutting taxes to boost demand, while contractionary policy focuses on reducing spending and increasing taxes to control inflationary pressures.
Key Tools of Monetary Policy
- Interest Rate Adjustments: Changing interest rates to either encourage borrowing and investment or cool down an overheating economy.
- Open Market Operations: The buying and selling of government securities to influence the money supply.
- Reserve Requirements: Adjusting the amount of reserves banks must hold, impacting their ability to lend.
Key Tools of Fiscal Policy
- Government Spending: Increasing or decreasing public expenditure on infrastructure, welfare, and other sectors to influence economic activity.
- Taxation: Modifying tax rates to either stimulate consumer spending or reduce budget deficits.
Both monetary and fiscal policies are essential in shaping the overall economic framework, but they often require coordination to achieve the best results. Their success largely depends on the economic context and the timely application of measures aimed at addressing specific challenges.
Collaborative Study Techniques for Group Learning
Working together in study groups can significantly enhance understanding and retention of complex material. Group learning fosters diverse perspectives and enables participants to tackle difficult concepts collectively. It encourages active engagement and accountability among members, leading to deeper insights and improved outcomes.
Peer Teaching: One of the most effective techniques is peer teaching, where group members take turns explaining concepts to one another. This method helps solidify understanding and allows individuals to approach the material from different angles. Teaching others also reinforces one’s own knowledge and highlights areas that need further review.
Group Discussions: Regular discussions on specific topics can help members process information more effectively. These discussions encourage critical thinking and allow participants to articulate their thoughts and ideas. Engaging in debate or dialogue with others often uncovers aspects of a subject that might have been overlooked during independent study.
Collaborative Note-Taking: Another powerful approach is to share and compare notes. Each group member may focus on different sections of the material and then come together to consolidate their findings. This ensures that no critical points are missed and enhances the overall depth of the study session.
Problem-Solving Sessions: When working on complex problems, solving them as a group can be extremely beneficial. Collective problem-solving allows participants to learn different methods for approaching challenges and to benefit from the strengths of others in the group. It also provides immediate feedback, which is essential for improving problem-solving skills.
By using these collaborative techniques, study groups can create a supportive environment that encourages learning and personal growth. Working together not only improves individual understanding but also strengthens the group’s overall performance.
Preparing for Multiple-Choice Questions

Multiple-choice questions require a specific approach for effective preparation. These questions test not only recall but also comprehension and the ability to apply concepts to various situations. Understanding how to navigate these questions efficiently can greatly improve performance and reduce stress during assessments.
Understand the Key Concepts: Before attempting multiple-choice questions, it’s essential to thoroughly understand the core principles of the subject. Review textbooks, notes, and other resources to ensure familiarity with the most commonly tested topics. A strong grasp of the material allows you to eliminate incorrect answers more easily.
Practice with Sample Questions: Familiarizing yourself with the format of multiple-choice questions is crucial. Practice with sample questions and past assessments to develop strategies for answering efficiently. This also helps in identifying common patterns in question structure, making it easier to predict the types of questions that may appear.
Elimination Method: One of the most effective strategies for answering multiple-choice questions is the process of elimination. Start by reviewing all answer choices and eliminating those that are clearly incorrect. This increases the chances of selecting the correct option, especially when you are unsure about the answer.
Time Management: Time management is key when answering multiple-choice questions. Allocate a specific amount of time to each question and stick to it. If a question seems particularly difficult, move on to the next one and come back to it later. This prevents wasting time on a single question and ensures that you can answer as many questions as possible.
Read Carefully: It’s easy to rush through questions, but reading each question carefully is essential. Pay attention to key words such as “always,” “never,” “most likely,” or “except,” as these can change the meaning of the question significantly. Misinterpreting the question can lead to choosing an incorrect answer, even if you know the material well.
By following these strategies, you can approach multiple-choice questions with confidence and maximize your chances of success. Preparation and practice are key to mastering this format and achieving better results.