
Building a strong foundation in early education is crucial for young learners. The initial steps in their academic journey help shape their problem-solving abilities, critical thinking skills, and confidence. By mastering the core principles early on, children are better prepared for future academic challenges and opportunities.
For many students, the first few lessons may present some challenges, but with the right tools and guidance, these obstacles can be easily overcome. One important aspect is having clear explanations and resources that can assist both learners and educators in navigating the material effectively. This section offers practical solutions and guidance for reinforcing key concepts.
Understanding the basics and providing consistent practice can make a significant difference in student progress. Whether it’s through visual aids, hands-on activities, or additional resources, every step taken towards mastery builds a solid foundation for more complex topics in the future.
Understanding the First Learning Section for Young Learners
The initial lessons in early education focus on building foundational skills that will support more complex learning in the future. These concepts help young students become comfortable with numbers and basic operations. The aim is to foster an environment where children can explore, practice, and master essential ideas that will serve as a base for their academic journey.
Core Topics and Key Concepts
This first section covers essential topics that lay the groundwork for future studies. By breaking down the content into simple, digestible parts, students are able to grasp the concepts gradually. Among these core ideas are the basics of number understanding, simple addition and subtraction, and visual representations of numerical relationships.
Strategies for Mastery
To ensure successful learning, it’s important to focus on consistent practice and reinforcement of key concepts. Visual aids, interactive activities, and real-life applications help students engage with the material in a hands-on way, making it easier to retain and apply the knowledge. Additionally, practicing with similar problems helps students build confidence in their abilities.
| Concept | Focus Area | Learning Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Understanding Numbers | Recognizing and writing numbers | Use of number charts and counting exercises |
| Simple Addition | Combining smaller numbers | Interactive games and visual representations |
| Simple Subtraction | Removing parts from a whole | Story problems and physical counting aids |
Key Concepts of Module 1
The first section of any learning program aims to establish a strong foundation by introducing fundamental principles. This is especially important for young students, as it sets the stage for their future academic success. The core ideas explored in this section focus on numerical relationships, basic operations, and visual methods to understand these concepts effectively.
In this introductory phase, children are encouraged to engage with numbers through activities that emphasize counting, grouping, and simple calculations. These exercises build a clear understanding of how numbers work together, laying the groundwork for more advanced topics later on.
One of the central ideas involves helping students recognize patterns in numbers and operations. By practicing with visual aids and hands-on tools, they begin to see how numbers can be broken down and reassembled in different ways, making abstract concepts more tangible and accessible. Additionally, basic addition and subtraction are introduced in a way that makes learning fun and interactive, helping children relate the concepts to real-world situations.
Importance of Early Math Foundations
Laying a strong foundation in the earliest years of education is crucial for long-term academic success. The skills learned in the early stages not only form the base for more complex subjects but also build a child’s confidence and problem-solving abilities. These initial lessons shape the way students think about and approach numbers and logic throughout their academic careers.
Building Confidence and Understanding
Early exposure to fundamental concepts helps children become comfortable with numbers and calculations, preventing future challenges. By practicing regularly, students gain the confidence needed to tackle more advanced topics later on. Some key benefits include:
- Increased number fluency
- Development of problem-solving strategies
- Stronger conceptual understanding of how numbers relate to each other
Preparing for Future Learning
The concepts learned in the first few years directly impact a child’s ability to grasp more advanced material later. Without a solid understanding of basic principles, students may struggle with more complex ideas. Early learning prepares them by:
- Introducing patterns and relationships in numbers
- Helping students understand the logic behind operations
- Creating a strong foundation for critical thinking and analytical skills
By prioritizing these early lessons, educators can ensure students are equipped to succeed in future academic challenges and develop a love for learning that lasts a lifetime.
Common Challenges in Module 1
As students begin to explore new concepts, they often encounter obstacles that can hinder their progress. These early lessons, while foundational, can present difficulties for young learners. Understanding these common challenges allows educators and parents to provide the right support to help students overcome them and stay on track.
Difficulty with Number Recognition
One of the first challenges is recognizing and writing numbers correctly. Young children are still developing their understanding of numerical symbols, which can lead to confusion or mixing up numbers. This challenge is common but can be addressed with consistent practice and visual aids.
Struggles with Simple Operations
Another hurdle involves performing basic calculations like addition and subtraction. Many students find it difficult to grasp these concepts initially, often due to a lack of concrete understanding of how numbers relate to each other. Engaging activities and interactive exercises can make these operations easier to understand.
| Challenge | Possible Causes | Suggested Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Number Recognition | Limited exposure to numbers or difficulty visualizing symbols | Use number charts, counting games, and visual aids |
| Basic Operations | Difficulty understanding the relationship between numbers | Incorporate hands-on tools like counters and manipulatives |
| Pattern Recognition | Lack of familiarity with number sequences | Use rhythm-based activities and visual pattern exercises |
Identifying and addressing these common struggles early on helps create a positive learning experience and ensures that students build the necessary skills to succeed in future lessons.
How to Approach Word Problems
Word problems are an essential part of early learning, as they encourage students to apply their understanding of numbers and operations to real-world scenarios. However, these problems can often seem overwhelming, especially for young learners who are still developing their problem-solving skills. The key to tackling word problems is to break them down step by step, making the process more manageable and less intimidating.
One effective strategy is to read the problem carefully and identify the important information. Students should highlight key numbers and words that indicate operations such as “more,” “less,” or “altogether.” After identifying the relevant details, the next step is to translate the words into a mathematical expression or equation.
It is also helpful to visualize the problem using drawings or physical objects. This makes abstract concepts more tangible and allows students to physically manipulate numbers, which aids in comprehension. Finally, students should check their solution to ensure it makes sense in the context of the problem.
Tips for Effective Problem Solving
Effective problem-solving is a skill that can be developed over time with practice and the right strategies. For young learners, it’s essential to approach challenges methodically, breaking them down into smaller, more manageable parts. By teaching students a variety of approaches, they can learn to tackle problems confidently and efficiently.
Key Strategies for Success
To guide students in solving problems, the following tips can be particularly helpful:
- Read the problem carefully: Understanding all the details is the first step in finding a solution.
- Identify important numbers and keywords: These will help direct the approach, such as “add,” “subtract,” or “altogether.”
- Draw or visualize the problem: Use pictures or physical objects to make abstract concepts more concrete.
- Break the problem into smaller steps: Simplifying the process helps avoid feeling overwhelmed.
- Check the answer: Verify if the solution makes sense by reviewing the work and considering the context.
Practical Tips to Encourage Problem Solving
Creating a supportive environment for problem-solving can also make a big difference. Encourage students to work through problems slowly and not rush to find the answer. It’s equally important to foster a mindset where mistakes are viewed as learning opportunities rather than failures. Practicing regularly and applying these strategies will enhance a child’s problem-solving skills over time.
Exploring Number Bonds and Their Usage
Number bonds are a powerful tool in early learning, helping students understand how numbers relate to each other and how they can be combined or separated. This concept focuses on breaking numbers into smaller, more manageable parts, which builds a deeper understanding of addition and subtraction. By exploring these relationships, students gain confidence in working with numbers and develop stronger problem-solving abilities.
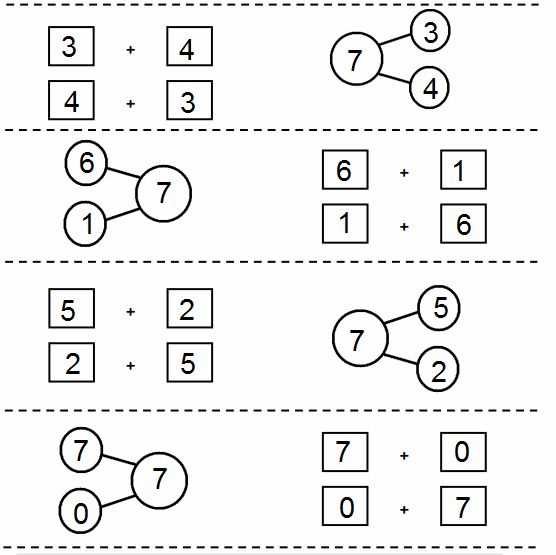
Understanding the Concept of Number Bonds
Number bonds illustrate the connection between a whole and its parts. For example, if the whole number is 5, the number bond shows how it can be split into two parts, such as 2 and 3. This simple but effective tool helps children see that numbers are flexible and can be broken down or combined in various ways. It also emphasizes the idea that addition and subtraction are related, helping children see them as opposite operations.
Practical Applications of Number Bonds
Number bonds can be applied in many real-life situations and learning activities. By using visual aids like number bond diagrams or manipulatives, students can practice creating different combinations of numbers. This method is particularly useful for:
- Building addition and subtraction fluency: Helps students quickly recall number facts and understand how numbers interact.
- Enhancing problem-solving skills: By breaking numbers into parts, children learn to approach more complex problems systematically.
- Fostering mental math abilities: Encourages students to think flexibly and solve problems in their head without relying on written methods.
By mastering number bonds, students can develop a more intuitive understanding of how numbers work, making it easier to tackle more advanced mathematical concepts in the future.
Strategies for Teaching Addition and Subtraction
Teaching addition and subtraction to young learners requires a thoughtful approach that incorporates various techniques to engage students and build a strong understanding of these basic operations. By providing hands-on activities, visual aids, and interactive exercises, teachers can create an environment where students feel confident in their ability to solve problems and think critically about numbers.
Practical Approaches for Instruction
Here are some effective strategies for teaching these foundational concepts:
- Use Visual Aids: Incorporating number lines, pictures, or counters allows students to see the process of adding and subtracting in a tangible way.
- Start with Concrete Materials: Using manipulatives, like blocks or beads, helps students physically experience the actions of adding or removing items before moving to abstract calculations.
- Relate to Real-Life Situations: Giving examples from everyday life, like sharing items or counting objects, makes the concepts more relevant and understandable.
- Practice with Number Sentences: Encourage students to write out addition and subtraction sentences to reinforce their understanding of the relationship between numbers.
Encouraging Mental Math and Flexibility
One important aspect of mastering these operations is helping students become fluent in mental calculations. To do this, consider the following techniques:
- Use Number Bonds: Break down numbers into smaller parts to simplify addition and subtraction.
- Teach Counting Strategies: Encourage students to count forward for addition and backward for subtraction, using skip counting or counting by ones.
- Introduce Doubles: Helping students recognize doubles (e.g., 2 + 2, 3 + 3) makes it easier to solve more complex problems.
By combining these strategies, students will develop both the skills and confidence needed to tackle addition and subtraction problems effectively.
Using Visual Aids for Better Understanding
Visual aids are essential tools that help students grasp abstract concepts by turning them into tangible and easily understandable representations. By incorporating pictures, diagrams, and hands-on materials into lessons, educators can cater to various learning styles and make complex ideas more accessible. Visuals not only enhance comprehension but also engage students, making learning more interactive and enjoyable.
One of the key advantages of using visual aids is that they provide students with a concrete way to see relationships between numbers and operations. For instance, a number line or chart can demonstrate how numbers increase or decrease, making the process of addition or subtraction easier to understand. By visually representing information, students can focus on the logic behind mathematical processes without getting overwhelmed by abstract symbols.
Types of Visual Aids
There are several types of visuals that can be used to reinforce concepts and support learning:
- Number Lines: A simple yet powerful tool for teaching counting, addition, and subtraction, number lines help students visualize the movement between numbers.
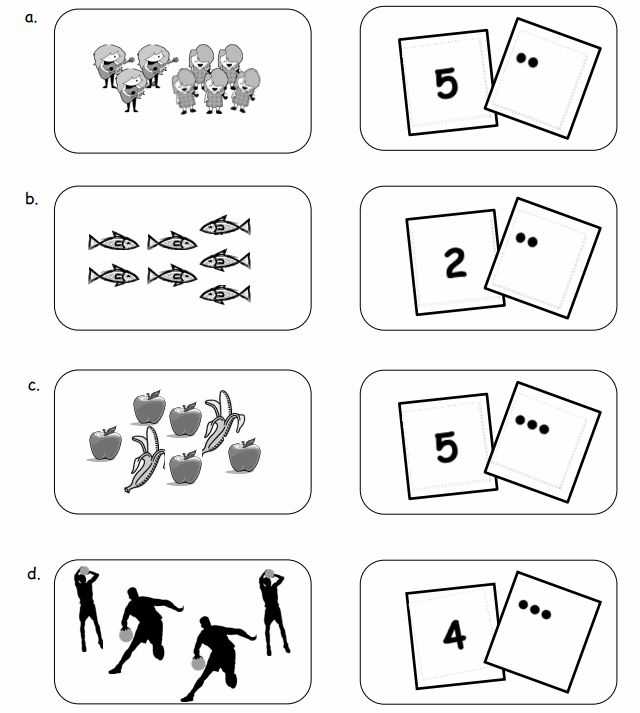
- Pictures and Diagrams: Illustrating word problems or showing sets of objects helps children relate mathematical concepts to real-world situations.
- Manipulatives: Physical objects like blocks, beads, or counters allow students to physically interact with numbers and operations.
- Charts and Graphs: Visualizing data in a chart or graph format enables students to better understand patterns and relationships between numbers.
Benefits of Visual Learning
Incorporating visual aids into lessons helps students build a deeper understanding of the material. Visual learning:
- Improves Retention: Students are more likely to remember concepts when they can associate them with visual images.
- Supports Different Learning Styles: Visual learners can absorb information more easily through diagrams and pictures.
- Promotes Problem-Solving Skills: By using visuals, students can work through problems step by step, making abstract concepts more concrete and less intimidating.
By integrating visual aids into instruction, teachers can create a more inclusive and effective learning environment that supports diverse learners and fosters better understanding of foundational concepts.
Interactive Activities to Reinforce Learning
Engaging students with interactive activities is an effective way to solidify their understanding of key concepts. By allowing children to actively participate in their learning process, they can develop a deeper grasp of material and enhance their problem-solving skills. These hands-on experiences create opportunities for students to explore and practice concepts in a fun and meaningful way.
Hands-On Activities for Reinforcement
Interactive exercises encourage active participation, which fosters better retention and comprehension. Some effective activities include:
- Counting Games: Use objects like blocks, coins, or beads to help students practice counting forward and backward. This hands-on activity strengthens their ability to work with numbers.
- Number Matching: Have students match written numbers with corresponding groups of objects, reinforcing their understanding of numerical values and quantity.
- Board Games: Simple games that involve moving along a number line or solving small addition/subtraction problems can help children learn while having fun.
- Interactive Digital Tools: Online apps or websites that provide practice exercises allow children to engage with numbers in a dynamic, interactive way.
Group Activities to Enhance Collaboration
Collaborative activities help students learn from each other, while practicing important social and communication skills. Some group-based activities include:
- Team Problem Solving: Present problems to groups and allow students to discuss and solve them together. This promotes teamwork and different approaches to finding solutions.
- Group Number Stories: Have students create stories involving numbers and operations, encouraging them to express their thinking while reinforcing their learning through storytelling.
By incorporating these interactive methods into lessons, students will be more engaged and motivated to explore new concepts, reinforcing their learning in an enjoyable and effective manner.
How to Check Student Progress
Assessing student progress is a critical aspect of the learning process, as it helps educators understand how well students are grasping the concepts and identify areas that may need additional support. Regular evaluation allows teachers to adjust their teaching strategies, offer targeted interventions, and ensure that every student is progressing at an appropriate pace.
Methods for Tracking Progress
There are several ways to monitor student progress effectively. Some common methods include:
- Formative Assessments: Regular quizzes, worksheets, or oral questions during class provide immediate feedback on student understanding. These assessments allow teachers to identify learning gaps early and make necessary adjustments.
- Observations: Teachers can track student progress by observing their participation in class activities and discussions. This approach helps gauge engagement, comprehension, and the ability to apply concepts in real-time.
- Interactive Tools: Online platforms and apps that offer practice problems and instant feedback can provide ongoing assessment of student performance, making it easy to track improvements over time.
- Peer and Self-Assessment: Encouraging students to assess their own work or review each other’s can provide valuable insights into their understanding and promote self-reflection.
Using Data to Drive Instruction
After gathering data on student performance, it is essential to use this information effectively. Teachers should:
- Analyze Patterns: Look for trends in common mistakes or areas where many students are struggling. This will highlight where additional practice or different teaching methods may be needed.
- Personalize Support: Use assessment results to provide individualized support to students who are falling behind. Offering additional practice or one-on-one attention can help them catch up.
- Adjust Teaching Methods: Based on student performance, adjust lesson plans to focus on areas that require more attention, ensuring that the learning pace is appropriate for all students.
By regularly checking student progress and using this data to inform teaching strategies, educators can ensure that every student is supported on their learning journey and stays on track toward mastering important skills.
Creating a Positive Learning Environment
Fostering a supportive and engaging classroom environment is essential for students’ success. When children feel comfortable and confident, they are more likely to actively participate and embrace challenges. A positive atmosphere encourages exploration, risk-taking, and growth, allowing students to feel empowered in their learning journey.
Building Confidence and Encouragement
Creating an environment where students feel safe to ask questions and make mistakes is crucial for their development. Some strategies to build confidence include:
- Celebrate Progress: Acknowledge even small improvements to help students see their growth and stay motivated. Positive reinforcement builds self-esteem and encourages continued effort.
- Encourage Effort Over Perfection: Emphasize the importance of trying and learning from mistakes. This shift in focus helps reduce anxiety and fosters a growth mindset.
- Foster Peer Support: Create opportunities for students to collaborate, allowing them to learn from each other. Peer encouragement can boost confidence and create a sense of community.
Creating an Engaging Classroom Culture
A vibrant and interactive classroom culture can make learning more enjoyable and effective. Teachers can establish this by:
- Incorporating Hands-On Activities: Engaging students with interactive tools, visual aids, and games can make the learning process feel more dynamic and fun.
- Using Positive Language: Use language that reinforces effort, perseverance, and curiosity. Words of encouragement create a nurturing environment where students feel valued and capable.
- Providing Clear Expectations: Clearly communicate what is expected from students while maintaining flexibility to accommodate different learning styles. Knowing what is expected helps students focus and stay on track.
By focusing on creating an environment that prioritizes encouragement, engagement, and support, educators can inspire students to build the confidence and skills necessary for long-term success.
Supporting Struggling Students in Module 1
It is essential to provide targeted support to students who may be facing challenges in their learning journey. When students struggle with new concepts, they may feel discouraged, but with the right strategies and encouragement, they can overcome difficulties and succeed. Offering personalized assistance and using effective teaching methods can help these learners build the confidence they need to progress.
Key Strategies for Support
To ensure that struggling students receive the help they need, teachers can implement several strategies tailored to their individual needs:
- One-on-One Attention: Spend additional time with students who need extra help, providing individualized guidance to address specific challenges they may face.
- Break Down Concepts: Simplify complex ideas by breaking them into smaller, more manageable steps. This approach allows students to understand the material in a less overwhelming way.
- Provide Visual Aids: Use pictures, charts, and manipulatives to reinforce concepts and offer visual representations that make abstract ideas more concrete.
- Use Repetition: Regularly review concepts to reinforce learning and help struggling students retain important information. Practice is key to mastery.
- Encourage Peer Support: Pair students with peers who can help explain concepts in a different way. Collaboration fosters a sense of community and provides alternative explanations that may resonate with the student.
Tracking Progress and Adjusting Support
It’s important to continuously monitor the progress of students who are struggling and adjust support as needed. Regular assessments can help identify areas where students need further help. Teachers can use this data to make informed decisions and modify their approach to ensure the student’s continued success.
| Strategy | Benefit |
|---|---|
| One-on-One Attention | Provides personalized support tailored to the student’s needs. |
| Breaking Down Concepts | Makes difficult ideas more digestible and easier to understand. |
| Repetition and Practice | Helps solidify understanding and improves retention of material. |
| Visual Aids | Offers a visual reference to support abstract concepts and aid comprehension. |
By providing targeted support, using a variety of teaching strategies, and regularly evaluating student progress, teachers can help students who are struggling to catch up and succeed in their learning goals.
Ways to Make Learning Fun and Engaging
Creating an enjoyable and interactive learning environment is essential for keeping students motivated and engaged. When the material is presented in a way that sparks curiosity and excitement, students are more likely to retain information and actively participate in the learning process. There are many effective strategies that can make learning enjoyable, encouraging students to explore new concepts with enthusiasm.
Interactive Learning Methods
Hands-on activities, games, and creative exercises can transform the learning experience, turning it into a fun and interactive journey. Here are a few techniques that can make lessons more engaging:
- Incorporating Games: Using educational games helps students practice skills while having fun. Whether it’s through card games, board games, or online interactive tools, these activities promote active participation.
- Group Work: Collaborative learning encourages students to work together, exchange ideas, and solve problems as a team. It can make learning feel less like a task and more like a shared adventure.
- Storytelling: Presenting new topics through stories or narratives can capture students’ attention and make abstract concepts easier to understand.
- Hands-on Activities: Using physical objects like blocks, manipulatives, or art supplies helps bring concepts to life and enhances tactile learning.
Incorporating Technology
Technology can be a powerful tool for making lessons more engaging. Digital resources offer interactive activities, video tutorials, and virtual learning environments that can capture students’ interest. Some methods include:
- Interactive Apps: Educational apps and games allow students to practice skills in a fun and engaging way, while also offering instant feedback.
- Educational Videos: Short, informative videos with animations and graphics can help students understand complex ideas in an entertaining format.
- Virtual Field Trips: Online tools and virtual tours give students the chance to explore places and concepts beyond the classroom, making learning feel like an exciting journey.
Making Learning Relevant
Connecting lessons to real-world experiences can increase student engagement by showing how what they learn applies outside of the classroom. Here are some strategies to bring lessons to life:
- Relating Lessons to Interests: Aligning learning material with students’ personal interests helps them see the relevance and makes the content feel more meaningful.
- Incorporating Real-World Examples: Using practical examples and scenarios helps students connect abstract concepts to everyday life.
By integrating these fun and engaging techniques into lessons, teachers can create a dynamic learning atmosphere that fosters curiosity, creativity, and a love for learning.
Using Online Resources to Supplement Learning
In today’s digital age, the internet offers a wealth of resources that can greatly enhance the learning experience. Online platforms provide interactive tools, videos, practice exercises, and much more, making it easier for students to explore topics at their own pace. By incorporating these digital resources into their studies, students can gain a deeper understanding of concepts and reinforce what they have learned in the classroom.
Types of Online Resources
There are various online platforms designed to support and supplement learning in a way that is both engaging and informative. Here are some examples:
- Interactive Websites: Many websites offer interactive exercises and games that make learning more enjoyable. These activities allow students to practice skills and receive instant feedback, helping them track their progress.
- Educational Videos: Websites like YouTube and specialized platforms like Khan Academy provide video tutorials that break down complex ideas in a visual and engaging manner. These resources are especially helpful for visual learners.
- Practice Apps: Mobile applications designed for educational purposes can offer a variety of practice problems, quizzes, and challenges. These apps often come with different levels to match the student’s progress.
- Virtual Tutors: Some online platforms offer virtual tutoring services, where students can work one-on-one with instructors, ask questions, and receive personalized support.
Benefits of Using Digital Tools
Integrating online tools into learning provides several benefits for both students and educators. Some of the key advantages include:
- Self-Paced Learning: Online resources allow students to explore topics at their own speed. This helps them focus on areas where they need more practice, while also advancing when they feel ready.
- Instant Feedback: Many online platforms provide immediate responses to students’ actions, offering valuable insights into their performance and highlighting areas for improvement.
- Increased Engagement: The interactive nature of digital tools helps maintain student interest and motivation, especially for those who might find traditional lessons less engaging.
By utilizing online resources, students can strengthen their understanding of key concepts, reinforce their learning, and gain access to a wider range of materials and tools that traditional methods may not offer. These resources not only supplement the classroom experience but also foster a more personalized approach to learning.
How Parents Can Help with Homework
Parents play a crucial role in their child’s education, especially when it comes to supporting homework and reinforcing concepts learned in the classroom. While it’s important for children to develop independence in completing assignments, parents can offer guidance and encouragement that fosters a positive learning experience. By providing the right environment and using effective strategies, parents can help their children succeed and build confidence in their abilities.
Creating a Supportive Homework Environment
Establishing the right atmosphere for completing homework can significantly impact a child’s productivity and focus. Here are some tips for creating an ideal setting:
- Designate a Quiet Space: Set up a quiet, well-lit area for homework to minimize distractions and allow your child to focus on the task at hand.
- Provide Necessary Tools: Ensure that all required materials, such as pencils, erasers, paper, and a calculator (if needed), are readily available.
- Set a Routine: Establish a regular homework time each day so that your child knows when to focus on assignments, helping them to stay organized and develop good habits.
Ways Parents Can Assist with Assignments
While it’s essential for children to complete their own work, parents can offer support by using the following approaches:
- Encourage Problem-Solving: Instead of providing answers, help your child break down the problem into manageable steps. Ask guiding questions that encourage them to think critically and work through challenges on their own.
- Be Available for Clarification: Be present to clarify instructions or provide additional explanations if your child doesn’t understand the task. Sometimes a simple explanation can make a big difference in their ability to complete the work.
- Offer Positive Reinforcement: Acknowledge your child’s effort and progress, even if the assignment is difficult. Positive reinforcement can boost their confidence and motivate them to keep trying.
By taking these simple steps, parents can foster an environment that promotes learning and allows their children to approach homework with a positive attitude. Supporting your child through assignments not only strengthens their academic skills but also builds a strong foundation for lifelong learning.
Mastering Core Skills for Future Success
Building a solid foundation in essential skills at an early age is critical for long-term academic and personal success. These core abilities not only help children navigate their current educational journey but also equip them with the tools they need for future challenges. By focusing on fundamental concepts and fostering a deep understanding, children are better prepared to excel in more complex subjects and develop problem-solving strategies that will serve them throughout their lives.
One of the most effective ways to ensure success is by emphasizing the mastery of key skills in areas such as number sense, logical thinking, and basic operations. These skills are often the building blocks of more advanced learning and provide the structure for understanding more intricate concepts later on. Moreover, these core competencies encourage confidence, resilience, and a love for learning, setting the stage for continued achievement in various fields.
In addition to academic skills, it’s important to cultivate social-emotional competencies such as persistence, adaptability, and the ability to work well with others. These traits are just as important as intellectual abilities when it comes to preparing for future success in school and beyond. By supporting a well-rounded development of both cognitive and interpersonal skills, children are more likely to thrive in diverse environments and contribute positively to their communities.